Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms to Classify Postures and Forecast Motions When Using a Dynamic Chair
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Machine Learning Methods
Random Forest and Gradient Decision Tree Algorithms
2.2. Support Vector Machine (SVM) Algorithm
2.3. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
2.4. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
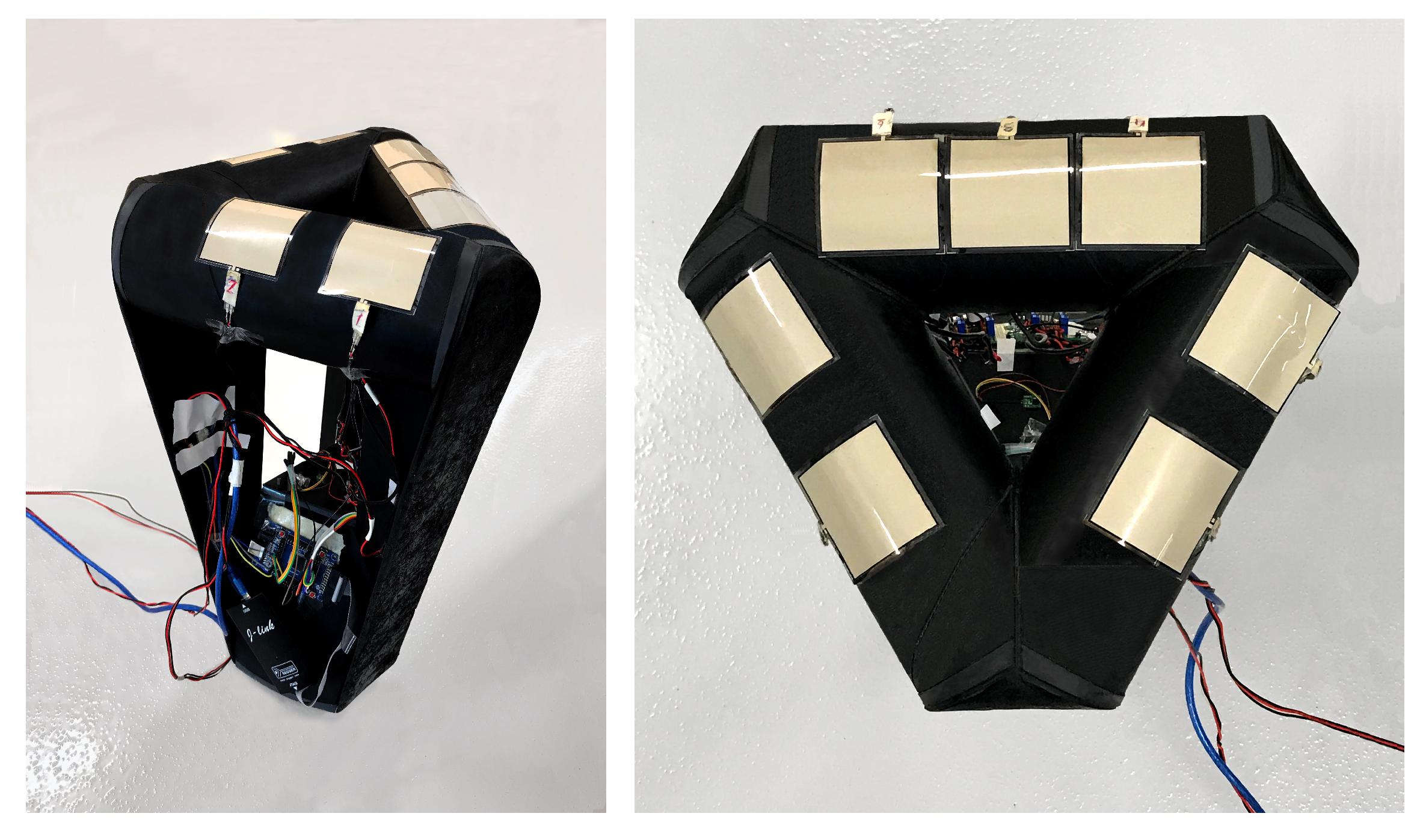
3. Experimental Setup
3.1. Chair Design
- Neutral seat position, body aligned with gravity (labeled as A).
- Forward seat position, body aligned with gravity (labeled as B1).
- Forward seat position, body aligned with gravity and slouched (labeled as B2).
- Left seat position, body aligned with gravity (labeled as C1).
- Left seat position, body not aligned with gravity (labeled as C2).
- Right seat position, body aligned with gravity (labeled as D1).
- Right seat position, body not aligned with gravity (labeled as D2).
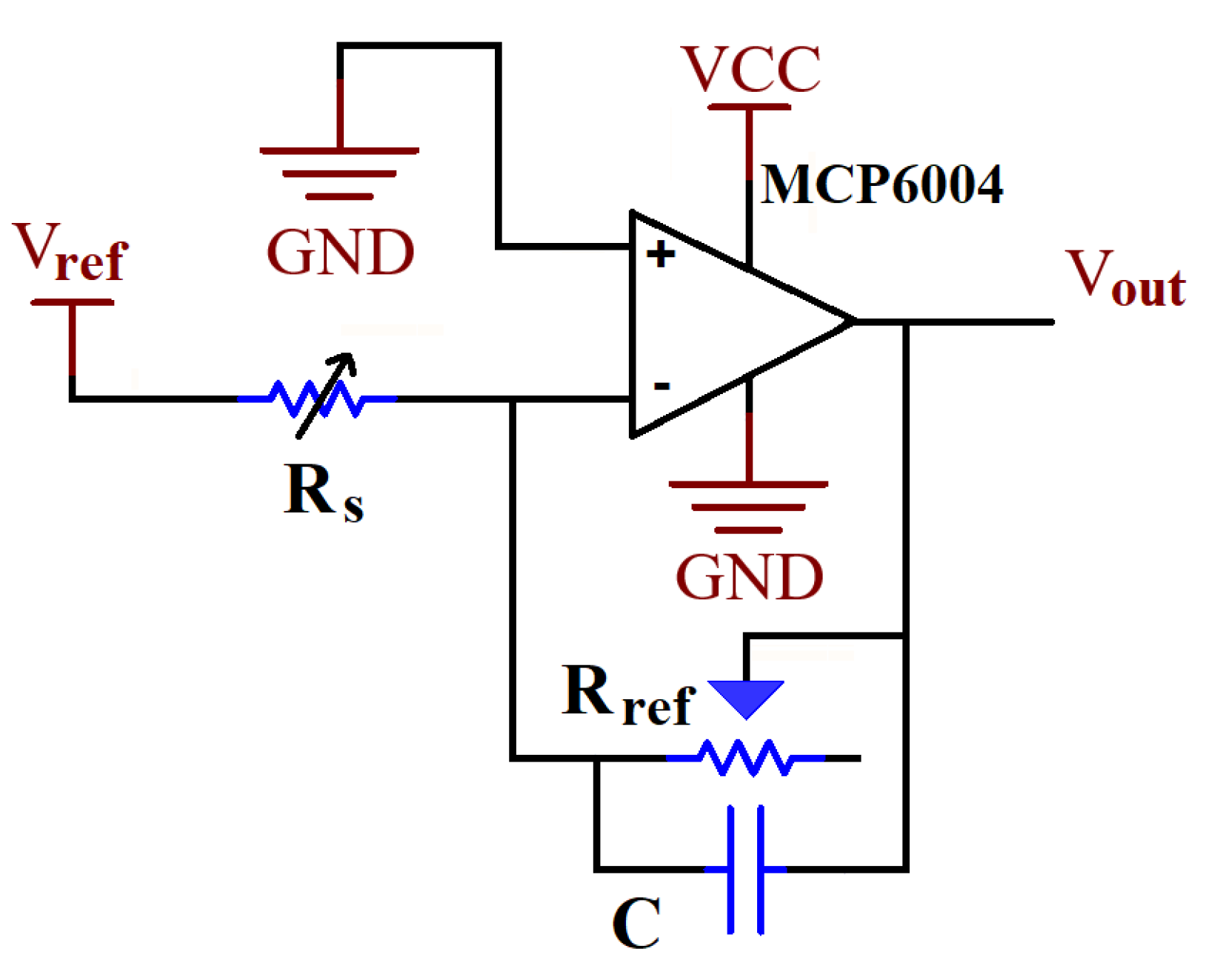
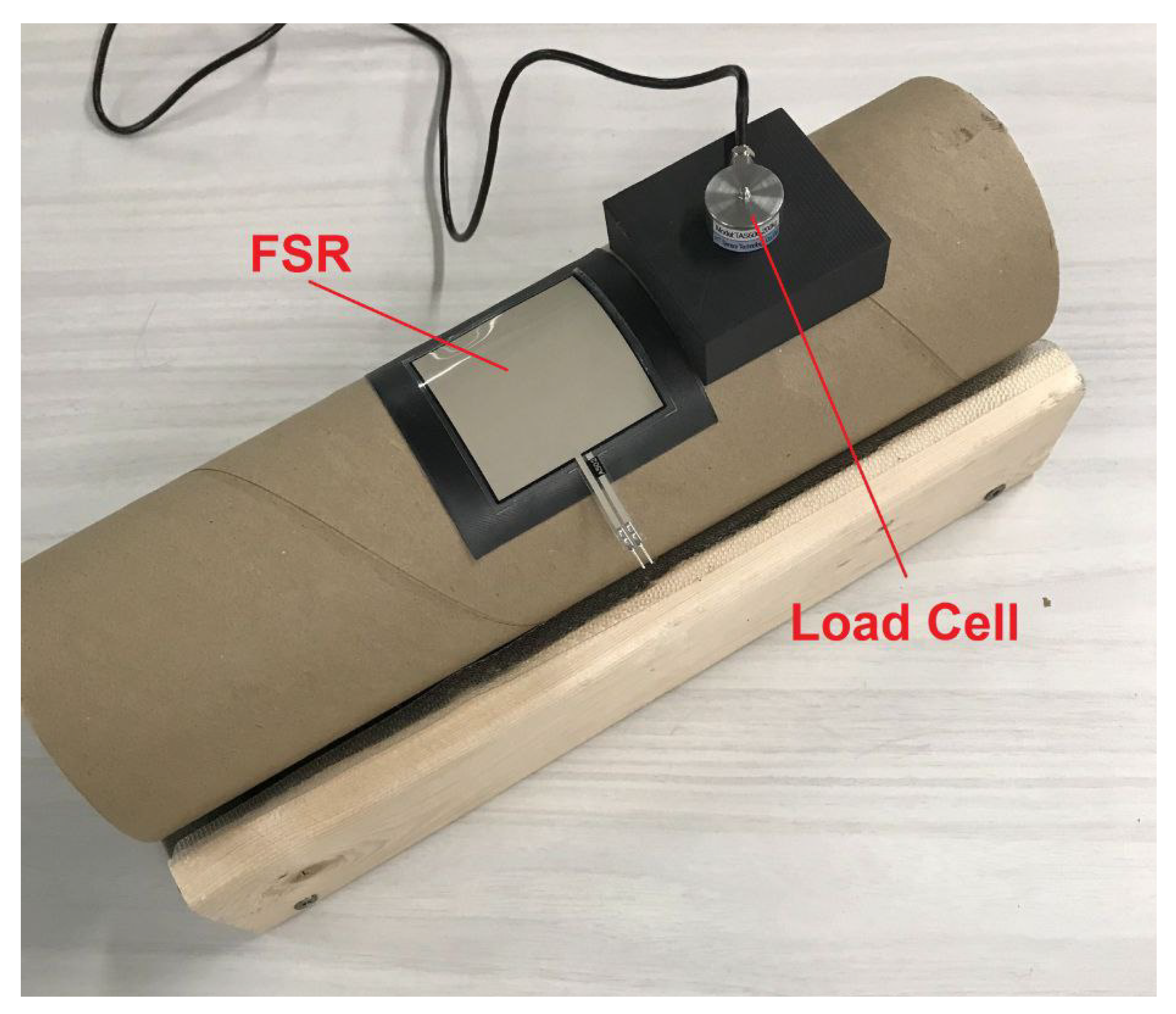
3.2. Data Collection
4. Methods
4.1. Classifiers
4.2. The Forecasting Algorithm
4.2.1. The Architecture of 1D-CNN-LSTM
4.2.2. Feature Extraction for Forecasting
5. Results
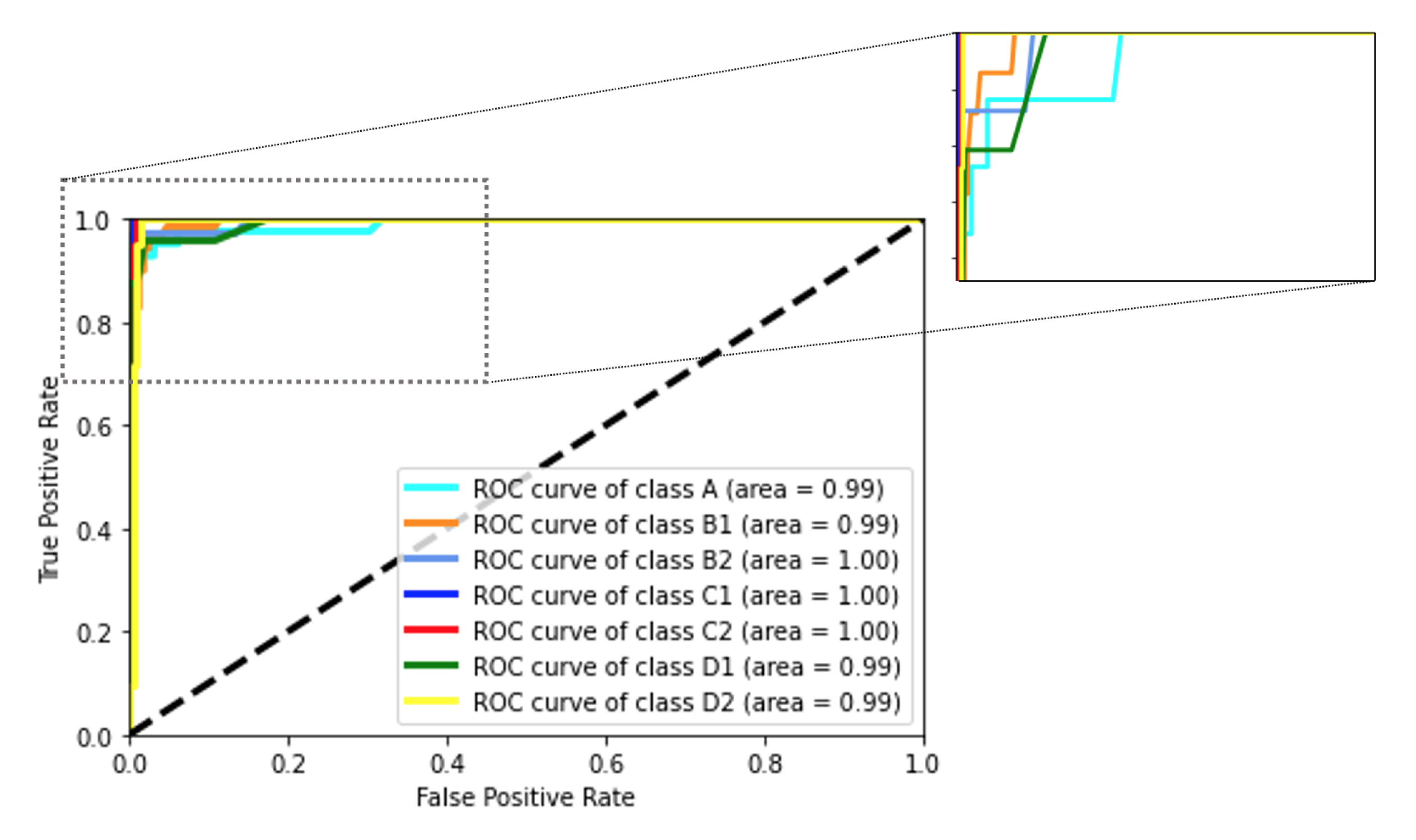
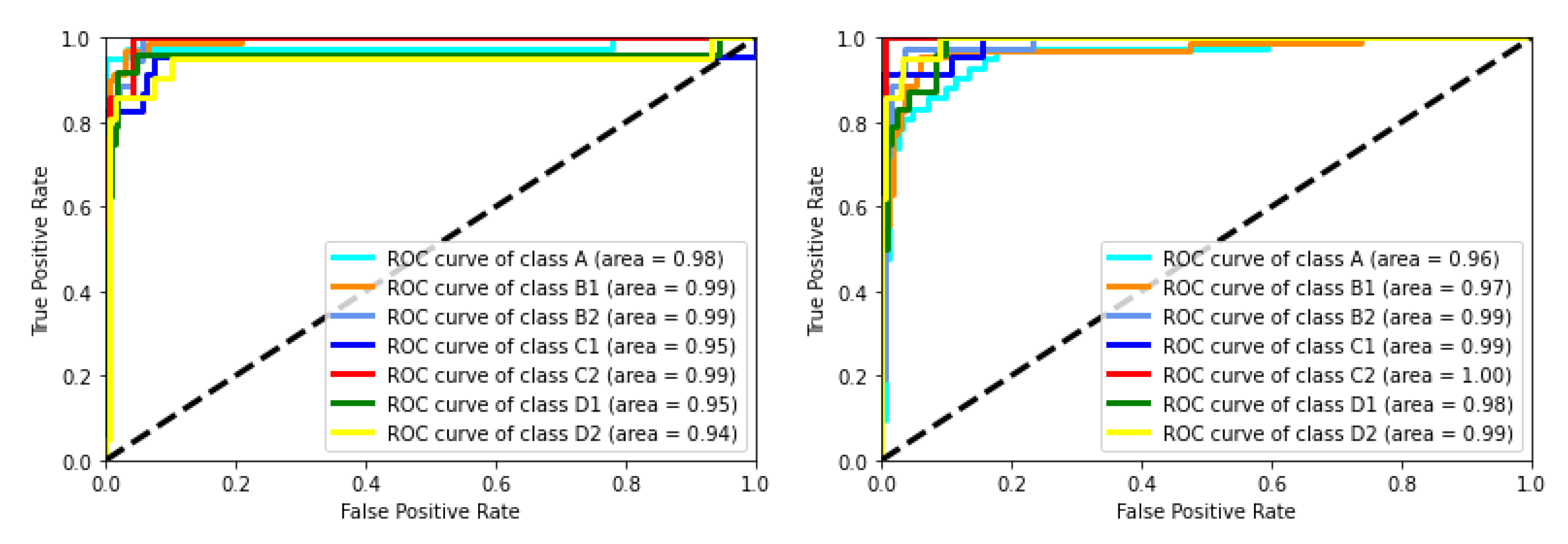
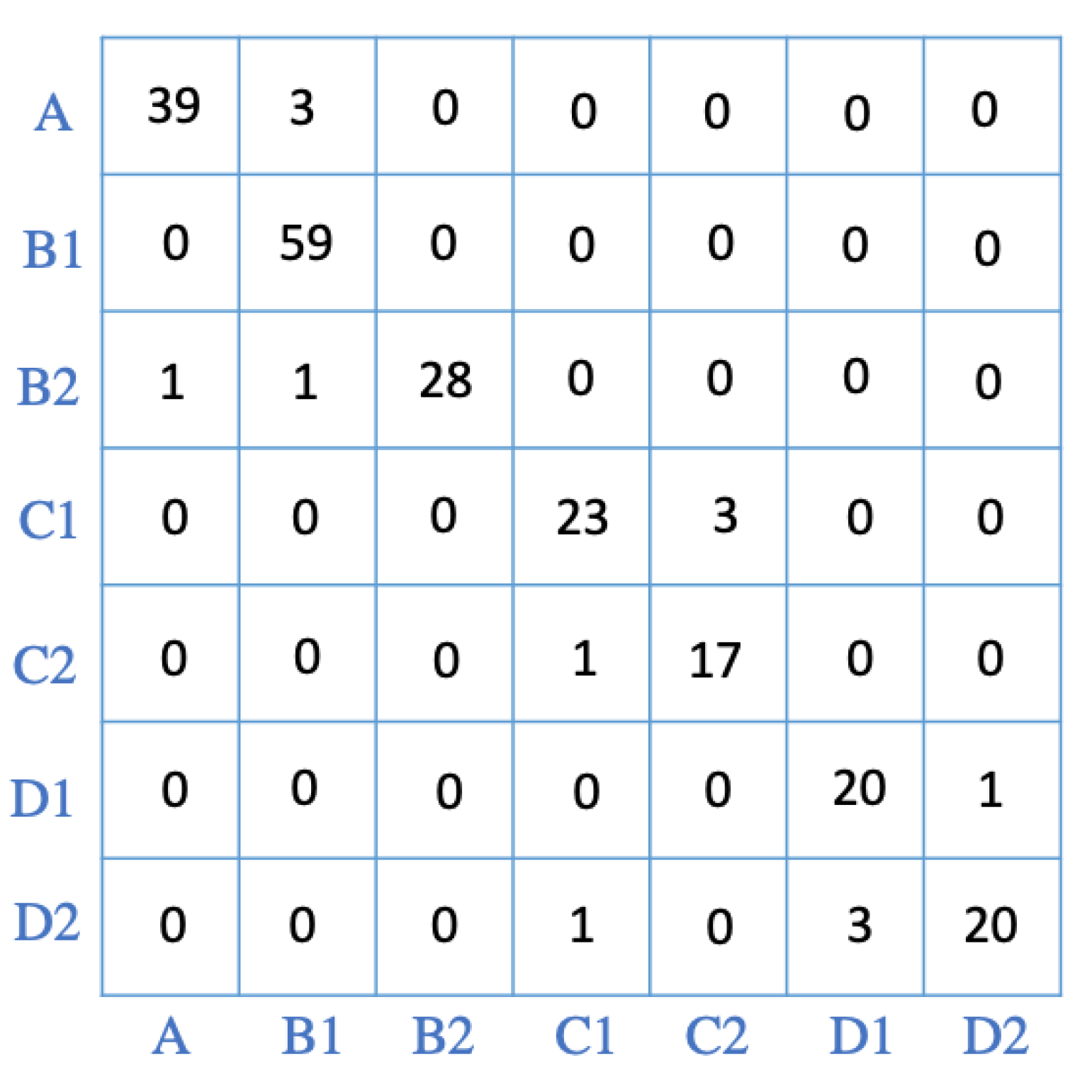
5.1. Classification Results and Evaluation
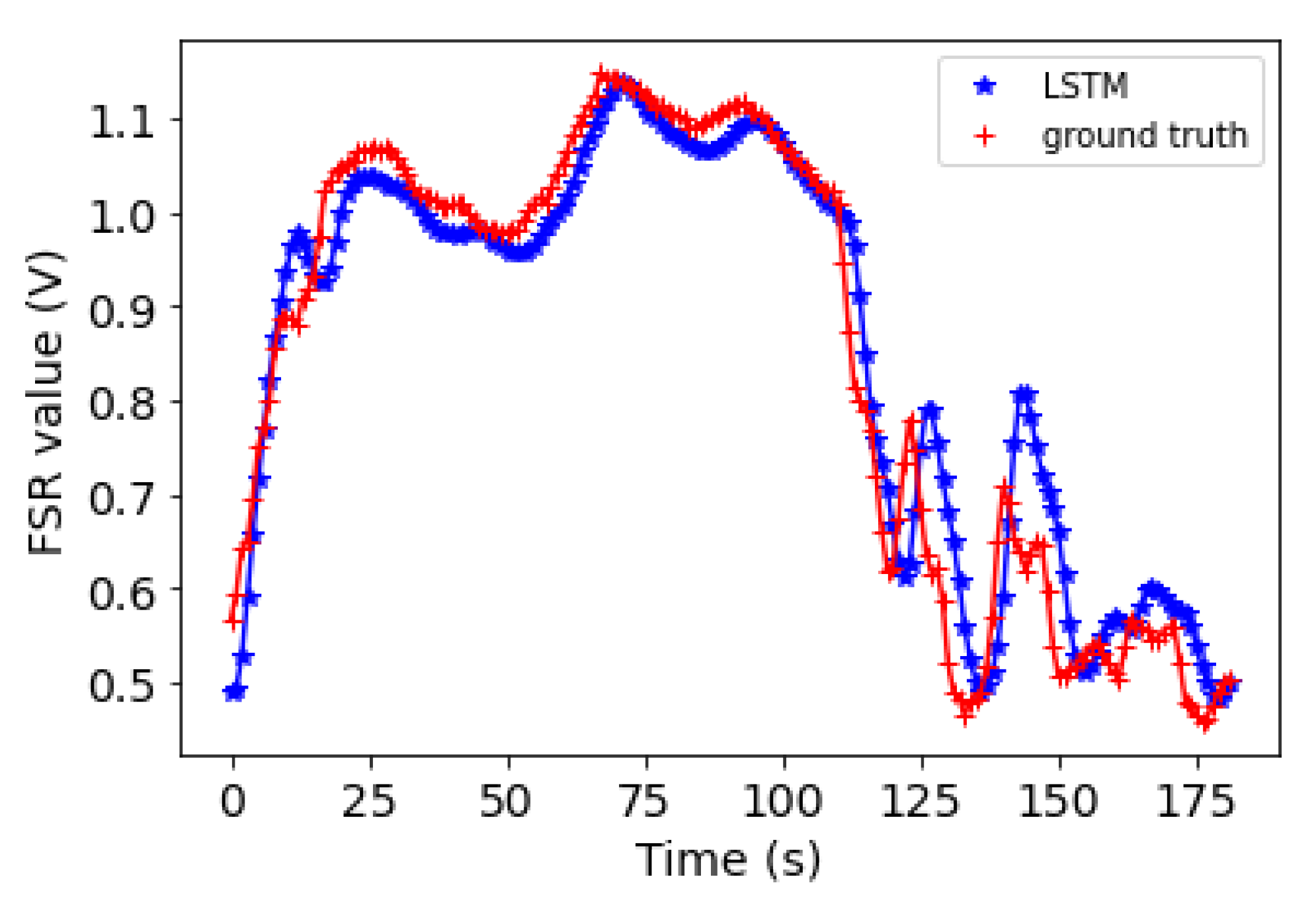
5.2. Forecasting Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Straker, L. Evidence to design ‘just right’work using active workstations is currently limited. Occup. Environ. Med. 2019, 76, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piirtola, M.; Kaprio, J.; Svedberg, P.; Silventoinen, K.; Ropponen, A. Associations of sitting time with leisure-time physical inactivity, education, and body mass index change. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2020, 30, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, D.E.; de Luca, K.; Funabashi, M.; Breen, A.; Wong, A.Y.; Johansson, M.S.; Ferreira, M.L.; Swab, M.; Kawchuk, G.N.; Adams, J.; et al. Association of exposures to seated postures with immediate increases in back pain: A systematic review of studies with objectively measured sitting time. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2020, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rebar, A.L.; Vandelanotte, C.; Van Uffelen, J.; Short, C.; Duncan, M.J. Associations of overall sitting time and sitting time in different contexts with depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms. Ment. Health Phys. Act. 2014, 7, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamatakis, E.; Ekelund, U.; Ding, D.; Hamer, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Lee, I.M. Is the time right for quantitative public health guidelines on sitting? A narrative review of sedentary behaviour research paradigms and findings. Br. J. Sports Med. 2019, 53, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, J.C.; Quon, J.A.; Smith, F.W. Magnetic resonance imaging and stadiometric assessment of the lumbar discs after sitting and chair-care decompression exercise: A pilot study. Spine J. 2010, 10, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, E.; Hünting, W. Ergonomics of posture—Review of various problems of standing and sitting posture. Appl. Ergon. 1977, 8, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triglav, J.; Howe, E.; Cheema, J.; Dube, B.; Fenske, M.J.; Strzalkowski, N.; Bent, L. Physiological and cognitive measures during prolonged sitting: Comparisons between a standard and multi-axial office chair. Appl. Ergon. 2019, 78, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, A.; Hall, J.; Pajazetovic, A.; Gillam, O.; Carpenter, D. Alternative Seat Designs-A Systematic Review of Controlled Trials. Prof. Saf. 2020, 65, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Huang, J.; Fu, S. A survey of e-commerce recommender systems. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management, Chengdu, China, 9–11 June 2007; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sezgin, E.; Özkan, S. A systematic literature review on Health Recommender Systems. In Proceedings of the 2013 E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 21–23 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, J.; Chowdhury, C.; Biswas, S. Review of machine learning and deep learning based recommender systems for health informatics. In Deep Learning Techniques for Biomedical and Health Informatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 101–126. [Google Scholar]
- Dunne, L.E.; Walsh, P.; Smyth, B.; Caulfield, B. Design and evaluation of a wearable optical sensor for monitoring seated spinal posture. In Proceedings of the 2006 10th IEEE International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Montreux, Switzerland, 11–14 October 2006; pp. 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yamato, Y. Experiments of posture estimation on vehicles using wearable acceleration sensors. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Big Data Security on Cloud (Bigdatasecurity), IEEE International Conference on High Performance and Smart Computing (hpsc), and IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data and Security (IDS), Beijing, China, 26–28 May 2012; pp. 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zemp, R.; Tanadini, M.; Plüss, S.; Schnüriger, K.; Singh, N.B.; Taylor, W.R.; Lorenzetti, S. Application of machine learning approaches for classifying sitting posture based on force and acceleration sensors. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5978489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, S.; Kudo, M.; Nakamura, A. Sitting posture diagnosis using a pressure sensor mat. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Identity, Security and Behavior Analysis (ISBA), Sendai, Japan, 26 February–2 March 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.; Xiang, J.; Dong, Y.; Xue, X.; Xiong, H.; Yang, B. Capturing electrocardiogram signals from chairs by multiple capacitively coupled unipolar electrodes. Sensors 2018, 18, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishac, K.; Suzuki, K. Lifechair: A conductive fabric sensor-based smart cushion for actively shaping sitting posture. Sensors 2018, 18, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roh, J.; Park, H.J.; Lee, K.J.; Hyeong, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, B. Sitting posture monitoring system based on a low-cost load cell using machine learning. Sensors 2018, 18, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.M.; Son, Y.; Kim, W.; Jin, B.; Yun, M.H. Classification of children’s sitting postures using machine learning algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bibbo, D.; Carli, M.; Conforto, S.; Battisti, F. A sitting posture monitoring instrument to assess different levels of cognitive engagement. Sensors 2019, 19, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Q.; Tang, X.; Tang, W. A smart chair sitting posture recognition system using flex sensors and FPGA implemented artificial neural network. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 8007–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, J.; Lindvall, C.; Umeton, R. Automated machine learning: Review of the state-of-the-art and opportunities for healthcare. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 104, 101822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdi, A.; Lin, X.; Yang, L.; Yan, F. SEFEE: Lightweight storage error forecasting in large-scale enterprise storage systems. In Proceedings of the SC20: International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–19 November 2020; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.; Kumar, N. A review on machine learning algorithms, tasks and applications. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Eng. Technol. (IJARCET) 2017, 6, 1548–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Shanthamallu, U.S.; Spanias, A.; Tepedelenlioglu, C.; Stanley, M. A brief survey of machine learning methods and their sensor and IoT applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 8th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems & Applications (IISA), Larnaca, Cyprus, 28–30 August 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Qayyum, A.; Qadir, J.; Bilal, M.; Al-Fuqaha, A. Secure and robust machine learning for healthcare: A survey. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 14, 156–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlinet, E.; Géraud, T. A comparative review of component tree computation algorithms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 3885–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Manual on Setting Up, Using, and Understanding Random Forests v3.1; Statistics Department University of California Berkeley: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 1, p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstra, J.; Bengio, Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 281–305. [Google Scholar]
- Knerr, S.; Lé, P.; Dreyfus, G. Single-layer learning revisited: A stepwise procedure for building and training a neural network. In Neurocomputing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern recognition. Mach. Learn. 2006, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, T.; Abe, S. Error correcting output codes vs. fuzzy support vector machines. In Proceedings of the Conference Artificial Neural Networks in Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 26–29 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.W. Time series analysis. In The Oxford Handbook of Quantitative Methods in Psychology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, MS, USA, 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield, C. Time-Series Forecasting; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sezer, O.B.; Gudelek, M.U.; Ozbayoglu, A.M. Financial time series forecasting with deep learning: A systematic literature review: 2005–2019. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 90, 106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lara-Benítez, P.; Carranza-García, M.; Riquelme, J.C. An Experimental Review on Deep Learning Architectures for Time Series Forecasting. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.12057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albawi, S.; Mohammed, T.A.; Al-Zawi, S. Understanding of a convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), Antalya, Turkey, 21–24 May 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Wang, Z.; Kuen, J.; Ma, L.; Shahroudy, A.; Shuai, B.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Cai, J.; et al. Recent advances in convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 77, 354–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiranyaz, S.; Avci, O.; Abdeljaber, O.; Ince, T.; Gabbouj, M.; Inman, D.J. 1D convolutional neural networks and applications: A survey. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 151, 107398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.B.; Cheon, S.; Kim, C.O. A convolutional neural network for fault classification and diagnosis in semiconductor manufacturing processes. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2017, 30, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, C.; Yang, J. Short-term traffic flow prediction based on 1DCNN-LSTM neural network structure. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 35, 2150042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, R.; Suzuki, H.; Kitajima, T.; Kuwahara, A.; Yasuno, T. Wind speed prediction model using LSTM and 1D-CNN. J. Signal Process. 2018, 22, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Formid Official Website. 2019. Available online: https://formid.ca (accessed on 16 December 2021).
- Bradley, A.P. The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recognit. 1997, 30, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holland, P.W.; Welsch, R.E. Robust regression using iteratively reweighted least-squares. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 1977, 6, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietterich, T.G. Approximate statistical tests for comparing supervised classification learning algorithms. Neural Comput. 1998, 10, 1895–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.G.; Siebert, B.R. The use of a Monte Carlo method for evaluating uncertainty and expanded uncertainty. Metrologia 2006, 43, S178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of trees | 10 |
| Number of features selected per node | |
| Minimum samples split | 5 |
| Minimum sample leaf | 1 |
| Maximum depth | None |
| Bootstrap | True |
| Classifier | Accuracy | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.93 |
| GDT | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.87 |
| SVM | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| RF | GDT | SVM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Posture | precision | Recall | precision | Recall | precision | Recall |
| A | 0.97 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.98 |
| B1 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.97 |
| B2 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.86 | 0.95 | 0.97 |
| C1 | 0.95 | 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.78 | 0.96 | 1.00 |
| C2 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 0.90 |
| D1 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 0.85 | 0.92 | 0.84 | 0.88 |
| D2 | 0.95 | 0.86 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 0.85 | 0.81 |
| Weighted Average | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| Sensor | Subject 1 | Subject 2 |
|---|---|---|
| FSR1 | 0.013 | 0.04 |
| FSR2 | 0.019 | 0.056 |
| FSR3 | 0.020 | 0.057 |
| FSR4 | 0.007 | 0.117 |
| FSR5 | 0.031 | 0.059 |
| FSR6 | 0.008 | 0.076 |
| FSR7 | 0.062 | 0.048 |
| x | 0.004 | 0.040 |
| y | 0.017 | 0.026 |
| Average | 0.02 | 0.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farhani, G.; Zhou, Y.; Danielson, P.; Trejos, A.L. Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms to Classify Postures and Forecast Motions When Using a Dynamic Chair. Sensors 2022, 22, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010400
Farhani G, Zhou Y, Danielson P, Trejos AL. Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms to Classify Postures and Forecast Motions When Using a Dynamic Chair. Sensors. 2022; 22(1):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010400
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarhani, Ghazal, Yue Zhou, Patrick Danielson, and Ana Luisa Trejos. 2022. "Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms to Classify Postures and Forecast Motions When Using a Dynamic Chair" Sensors 22, no. 1: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010400
APA StyleFarhani, G., Zhou, Y., Danielson, P., & Trejos, A. L. (2022). Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms to Classify Postures and Forecast Motions When Using a Dynamic Chair. Sensors, 22(1), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010400







