Brain Tumor/Mass Classification Framework Using Magnetic-Resonance-Imaging-Based Isolated and Developed Transfer Deep-Learning Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Dataset
2.2. Isolated and Transfer Learning
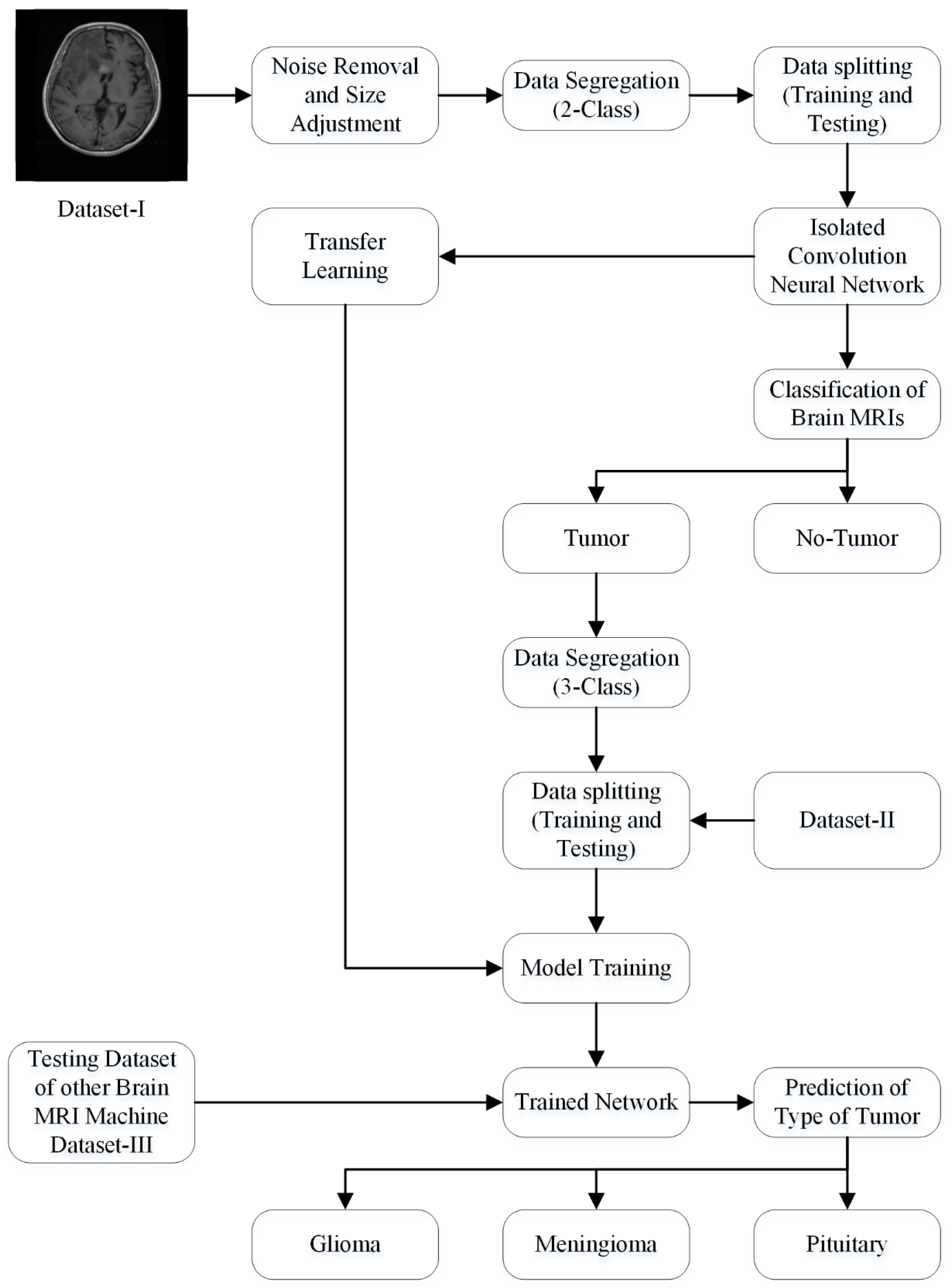
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Magnetic Resonance Images Pre-Processing
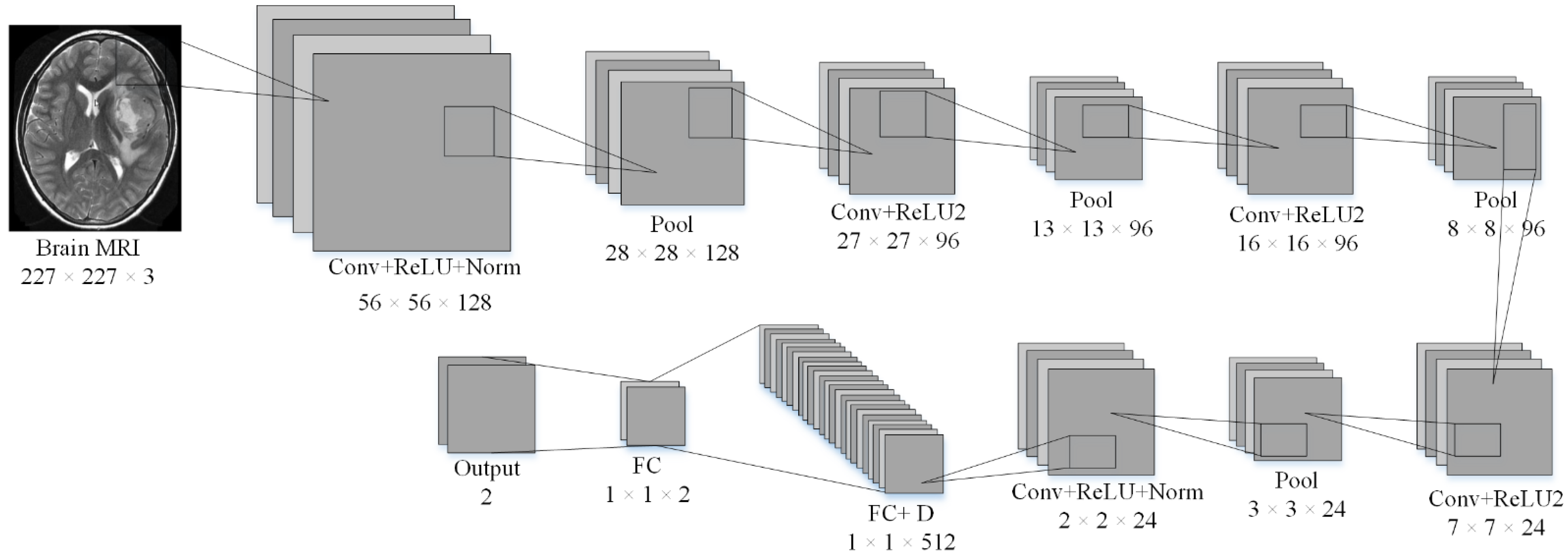
2.3.2. Developed Isolated and Transfer Deep-Learning Models
Isolated Convolutional Neural Network Model
Transfer Learning
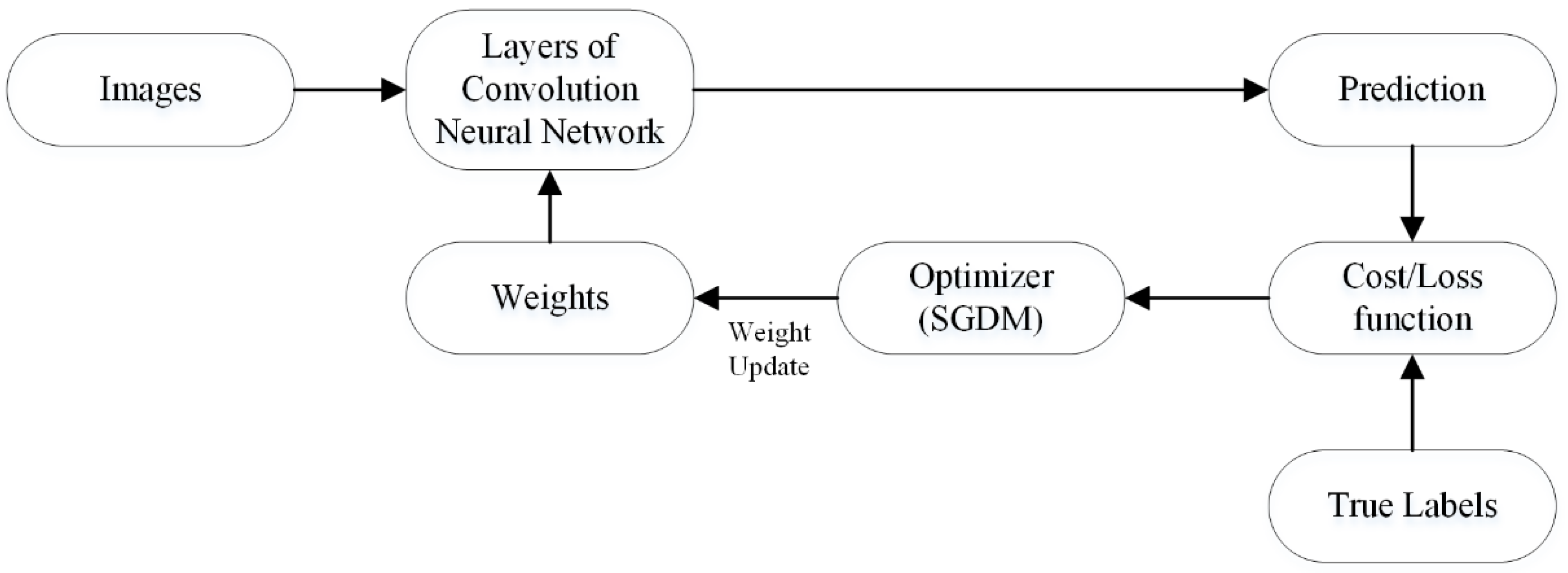
Optimization
2.3.3. Proposed Framework
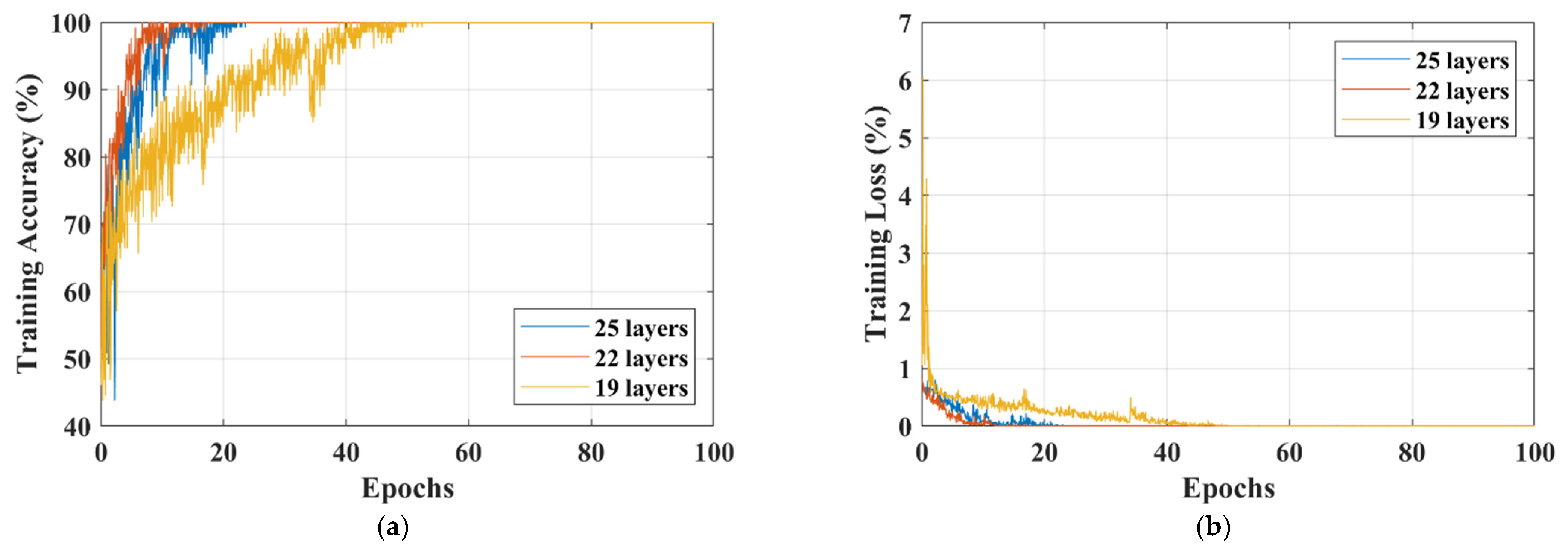
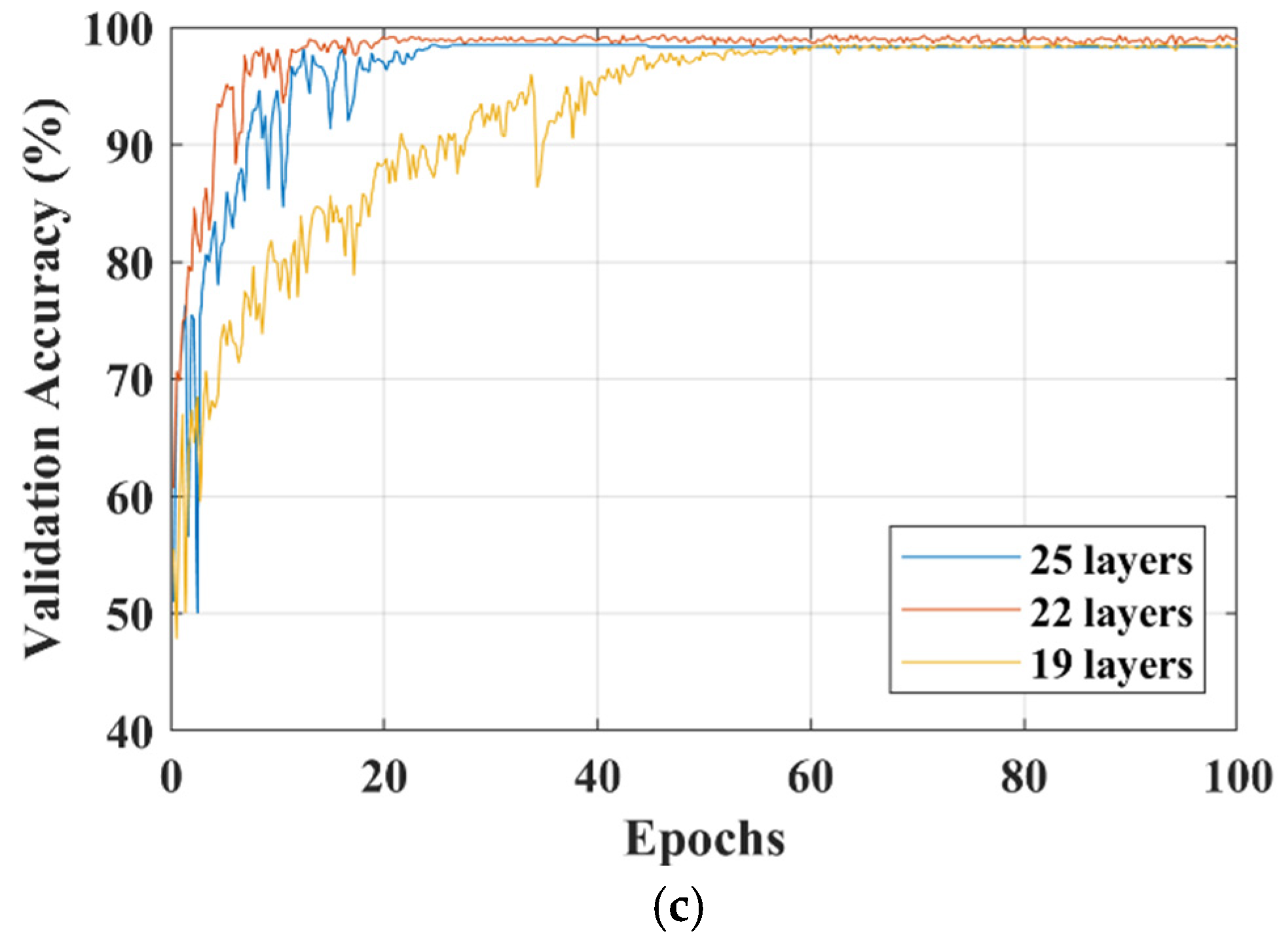
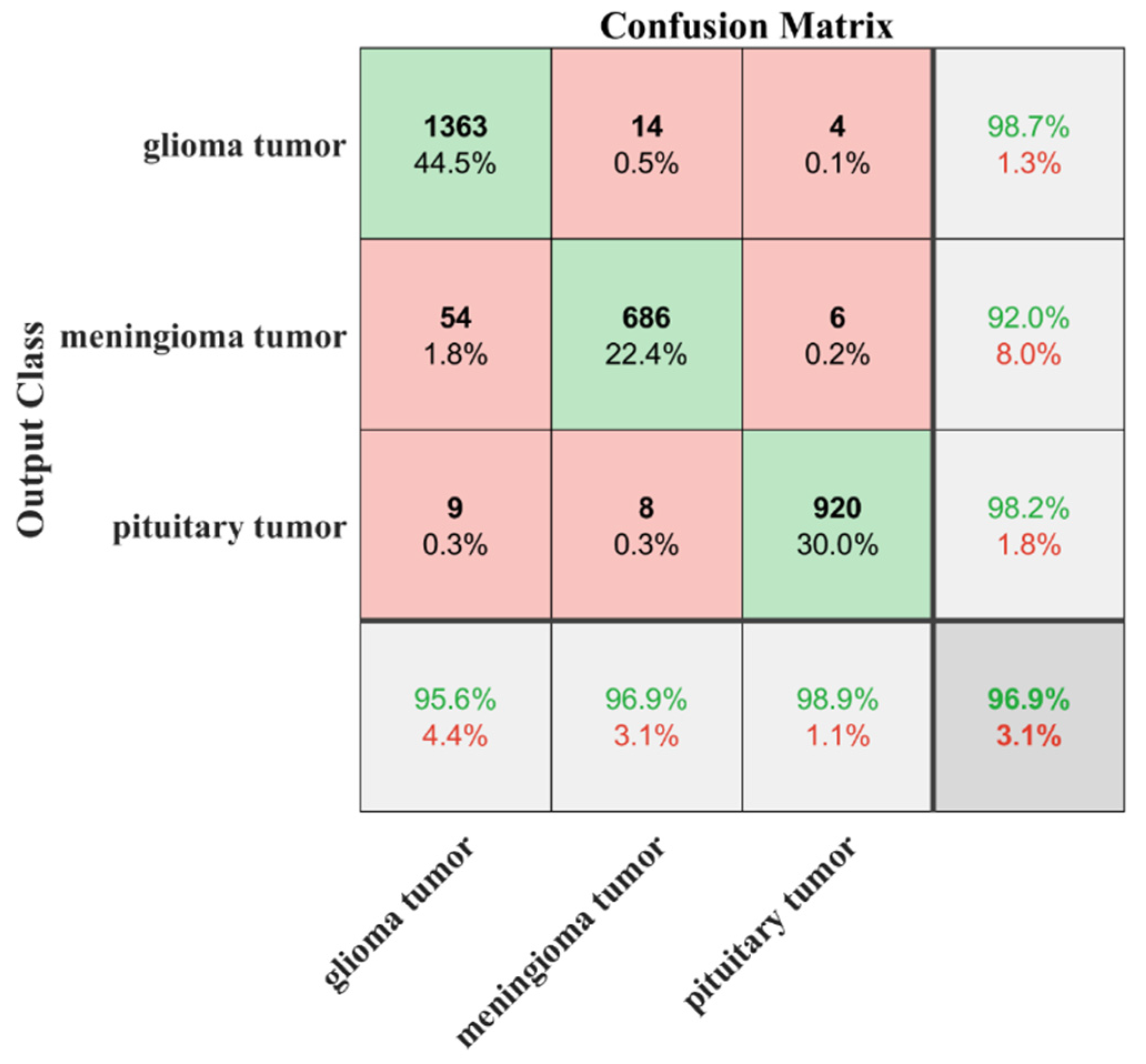
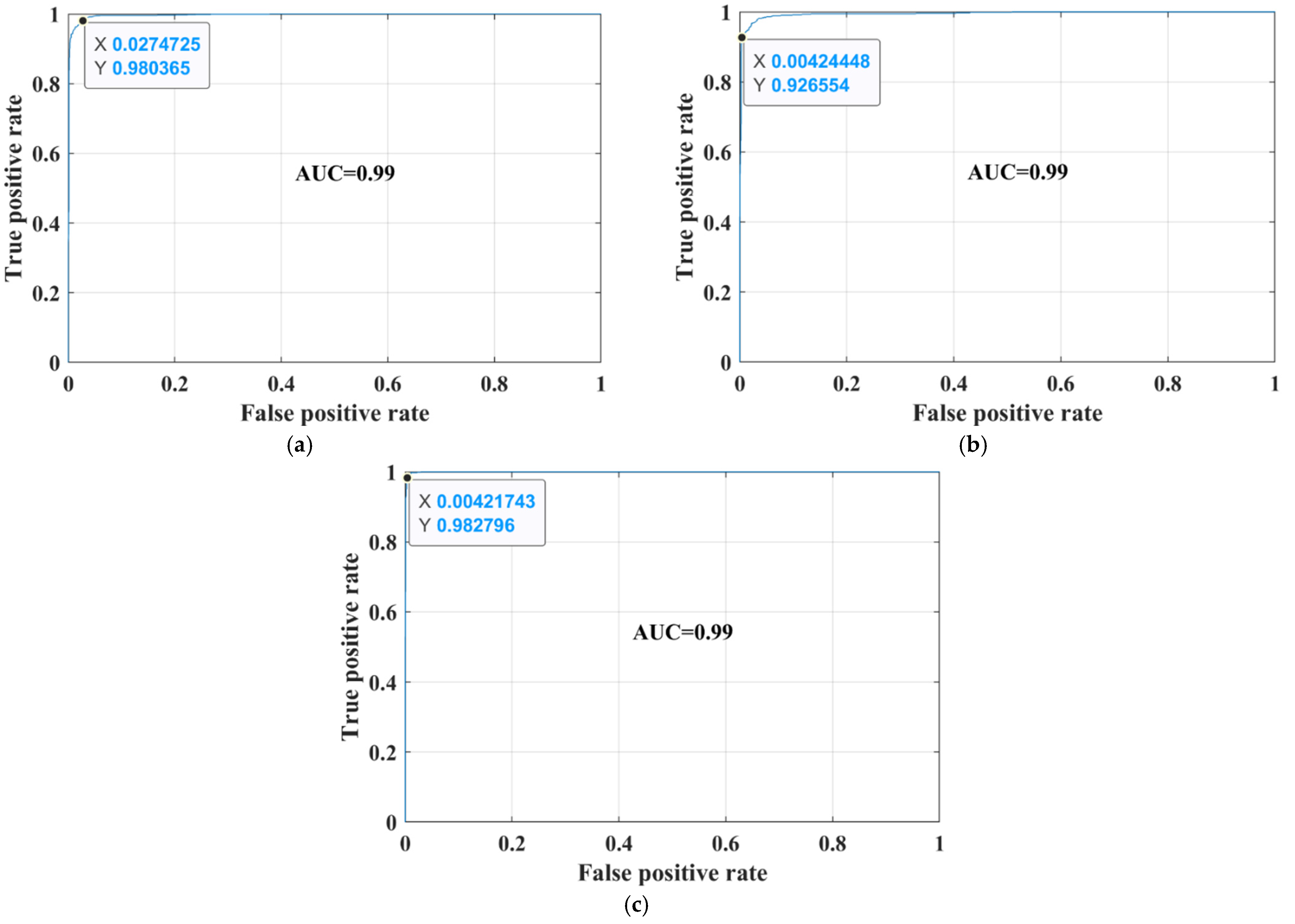
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 world health organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- American Cancer Society. Available online: www.cancer.org/cancer.html (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- Brain Tumor: Diagnosis. Available online: https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/brain-tumor/diagnosis (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- Tandel, G.S.; Biswas, M.; Kakde, O.G.; Tiwari, A.; Suri, H.S.; Turk, M.; Laird, J.R.; Asare, C.K.; Ankrah, A.A.; Khanna, N.N.; et al. A Review on a deep learning perspective in brain cancer classification. Cancers 2019, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viral, S.; Pratiksha, K. Brain Cancer: Implication to disease, therapeutic strategies and tumor targeted drug delivery approaches. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 70–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Iftekharuddin, K.M.; Vossough, A. Efficacy of texture, shape, and intensity feature fusion for posterior-fossa tumor segmentation in MRI. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2011, 15, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deorah, S.; Lynch, C.F.; Sibenaller, Z.A.; Ryken, T.C. Trends in brain cancer incidence and survival in the United States: Surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program, 1973 to 2001. Neurosurg. Focus FOC 2006, 20, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badža, M.M.; Barjaktarović, M.Č. Classification of brain tumors from MRI images using a convolutional neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, S.; Pinto, A.; Alves, V.; Silva, C.A. Brain tumor segmentation using convolutional neural networks in MRI images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1240–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K. Computer-aided diagnosis in medical imaging: Historical review, current status and future potential. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2007, 31, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munir, K.; Elahi, H.; Ayub, A.; Frezza, F.; Rizzi, A. cancer diagnosis using deep learning: A bibliographic review. Cancers 2019, 11, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wadhwa, A.; Bhardwaj, A.; Verma, V.S. A review on brain tumor segmentation of MRI images. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 61, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R. SVM classification an approach on detecting abnormality in brain MRI images. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2013, 3, 1686–1690. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Kaur, K. Classification of abnormalities in brain MRI images using GLCM, PCA and SVM. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2012, 1, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, A.; Munoz, X.; Oliver, A.; Marti, J. Modeling and classifying breast tissue density in mammograms. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR06), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; pp. 1552–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Yang, W.; Huang, M.; Huang, W.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Y.; Feng, Q.; et al. Retrieval of brain tumors by adaptive spatial pooling and fisher vector representation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi, W.; Elhamzi, W.; Charfi, I.; Atri, M. A hybrid feature extraction approach for brain MRI classification based on Bag-of-words. Biomed. Signal. Processing Control 2019, 48, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.; Shakil, S.; Khurshid, K. Role of deep learning in brain tumor detection and classification (2015 to 2020): A review. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 91, 101940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.; Meier, R.; Alves, V.; Reyes, M.; Silva, C.A. Automatic brain tumor grading from MRI data using convolutional neural networks and quality assessment. In Understanding and Interpreting Machine Learning in Medical Image Computing Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 106–114. ISBN 978-3-030-02628-8. [Google Scholar]
- Abiwinanda, N.; Hanif, M.; Hesaputra, S.T.; Handayani, A.; Mengko, T.R. Brain tumor classification using convolutional neural network. In World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 183–189. ISBN 978-981-10-9038-7. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, C. Brain Tumor Dataset. 2017. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/brain_tumor_dataset/1512427 (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- Irmak, E. Multi-Classification of brain tumor MRI images using deep convolutional neural network with fully optimized framework. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 2021, 45, 1015–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, S.; Ameer, P.M. Brain tumor classification using deep CNN features via transfer learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 111, 103345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çinar, A.; Yildirim, M. Detection of tumors on brain MRI images using the hybrid convolutional neural network architecture. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 139, 109684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Ullah, Z.; Gwak, J. MRI-based brain tumor classification using ensemble of deep features and machine learning classifiers. Sensors 2021, 21, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, A. Br35H Brain Tumor Detection 2020 Dataset. 2020. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/ahmedhamada0/brain-tumor-detection/metadata (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- Bhuvaji, S.; Kadam, A.; Bhumkar, P.; Dedge, S.; Kanchan, S. Brain Tumor Classification (MRI) Dataset. 2020. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/sartajbhuvaji/brain-tumor-classification-mri (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- Chollet, F. Deep Learning with Python; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.; Sun, F.; Kong, T.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; Liu, C. A survey on deep transfer learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Rhodes, Greece, 4–7 October 2018; pp. 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, M.W.; Li, G.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, C.; Ahmad, A. Automatic detection of photovoltaic module defects in infrared images with isolated and develop-model transfer deep learning. Sol. Energy 2020, 198, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosebrock, A. Finding Extreme Points in Contours with Open CV. Available online: https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2016/04/11/finding-extreme-points-in-contours-with-opencv/ (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- Sarkar, D.; Bali, R.; Ghosh, T. Hands-On Transfer Learning with Python: Implement. Advanced Deep Learning and Neural Network Models Using TensorFlow and Keras; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.; Naz, S.; Razzak, M.I.; Akram, F.; Imran, M. A Deep learning-based framework for automatic brain tumors classification using transfer learning. Circ. Syst. Signal. Process. 2020, 39, 757–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, H.H.; Salem, N.M.; Al-Atabany, W. Multi-classification of brain tumor images using deep neural network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 69215–69225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlu, H.; Avcı, E. A Novel method for classifying liver and brain tumors using convolutional neural networks, discrete wavelet transform and long short-term memory networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swati, Z.N.K.; Zhao, Q.; Kabir, M.; Ali, F.; Ali, Z.; Ahmed, S.; Lu, J. Brain tumor classification for MR images using transfer learning and fine-tuning. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 75, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajjad, M.; Khan, S.; Muhammad, K.; Wu, W.; Ullah, A.; Baik, S.W. Multi-grade brain tumor classification using deep CNN with extensive data augmentation. J. Comput. Sci. 2019, 30, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Huang, W.; Cao, S.; Yang, R.; Yang, W.; Yun, Z.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q. Correction: Enhanced performance of brain tumor classification via tumor region augmentation and partition. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No Tumor | Glioma Tumor | Meningioma Tumor | Pituitary Tumor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain MRI Images |  | 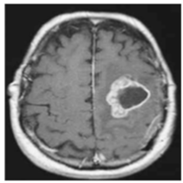 | 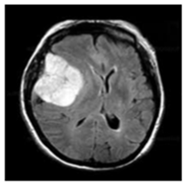 | 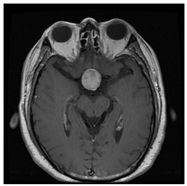 |
| Layer No. | Layer Type | Properties | Learnable |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Image Input | 227 × 227 × 3 images with ‘zerocenter’ normalization | - |
| 2 | Convolutional | 128 6 × 6 convolutions with stride [4 4] and padding [0 0 0 0] | Weights: 6 × 6 × 3 × 128 Bias: 1 × 1 × 128 |
| 3 | ReLU | ReLU | - |
| 4 | Cross Channel Normalization | cross channel normalization with 5 channels per element | - |
| 5 | Max | 2 × 2 max pooling with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] | - |
| 6 | Convolutional | 96 6 × 6 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [2 2 2 2] | Weights: 6 × 6 × 3 × 128 × 96 Bias: 1 × 1 × 96 |
| 7 | ReLU | ReLU | - |
| 8 | Max | 2 × 2 max pooling with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] | - |
| 9 | Convolutional | 96 2 × 2 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [2 2 2 2] | Weights: 2 × 2 × 96 × 96 Bias: 1 × 1 × 96 |
| 10 | ReLU | ReLU | - |
| 11 | Max | 2 × 2 max pooling with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] | - |
| 12 | Convolutional | 24 6 × 6 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [2 2 2 2] | Weights: 6 × 6 × 96 × 24 Bias: 1 × 1 × 24 |
| 13 | ReLU | ReLU | - |
| 14 | Max | 2 × 2 max pooling with stride [2 2] and padding [0 0 0 0] | - |
| 15 | Convolutional | 24 6 × 6 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [2 2 2 2] | Weights: 2 × 2 × 24 × 24 Bias: 1 × 1 × 24 |
| 16 | ReLU | ReLU | - |
| 17 | Batch Normalization | Batch normalization | Offset: 1 × 1 × 24 Scale: 1 × 1 × 24 |
| 18 | Fully | 512 fully connected layer | Weights: 512 × 96 Bias: 512 × 1 |
| 19 | Dropout | 30% dropout | - |
| 20 | Fully | 2 fully connected layer | Weights: 2 × 512 Bias: 2 × 512 |
| 21 | Softmax | - | - |
| 22 | Classification Output | - | - |
| Network | Training Accuracy (%) | Training Loss | Training Time | Validation Accuracy (%) | Validation Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19-layers | 100 | 2.8016 × 10−5 | 15 min 58 s | 98.50 | 0.0850 |
| 22-layers | 100 | 4.8811 × 10−6 | 16 min | 99.33 | 0.0534 |
| 25-layers | 100 | 4.8243 × 10−7 | 15 min 43 s | 98.33 | 0.1412 |
| Network | Training Accuracy (%) | Training Loss | Training Time | Validation Accuracy (%) | Validation Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19-layers | 100 | 1.9454 × 10−4 | 14 min 57 s | 91.27 | 0.4637 |
| 22-layers | 100 | 2.7508 × 10−5 | 14 min 35 s | 92.67 | 0.3208 |
| 25-layers | 100 | 1.6904 × 10−6 | 14 min 22 s | 91.62 | 0.7276 |
| Class | Classified as | TPR (%) | FNR (%) | PPV (%) | FDR (%) | Training Time | Validation Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glioma | Meningioma | Pituitary | |||||||
| Glioma | 157 | 6 | 0 | 96.32 | 3.68 | 95.15 | 4.85 | 13 min 8 s | 95.75% |
| Meningioma | 8 | 151 | 0 | 94.97 | 5.03 | 92.07 | 7.93 | ||
| Pituitary | 0 | 7 | 165 | 95.93 | 4.07 | 100 | 0 | ||
| Study | Type of Dataset | Model | Accuracy (%) | Training Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abiwinanda et al. [21] | Dataset-III | 13-layer CNN | 84.19 | - |
| Irmak. [23] | Dataset-II | 25-layer CNN | 92.66 | - |
| Kang et al. [26] | Dataset-III | Pre-trained CNN models with machine-learning classifiers | 93.72 | - |
| Rehman et al. [34] | Dataset-III | AlexNet GoogleNet VGGNet | 95.86 95.61 95.42 | 43 min 79 min 89 min |
| Proposed | Dataset-II Dataset-III | Developed transfer-learned CNN | 95.75 96.90 | 13 min |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alanazi, M.F.; Ali, M.U.; Hussain, S.J.; Zafar, A.; Mohatram, M.; Irfan, M.; AlRuwaili, R.; Alruwaili, M.; Ali, N.H.; Albarrak, A.M. Brain Tumor/Mass Classification Framework Using Magnetic-Resonance-Imaging-Based Isolated and Developed Transfer Deep-Learning Model. Sensors 2022, 22, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010372
Alanazi MF, Ali MU, Hussain SJ, Zafar A, Mohatram M, Irfan M, AlRuwaili R, Alruwaili M, Ali NH, Albarrak AM. Brain Tumor/Mass Classification Framework Using Magnetic-Resonance-Imaging-Based Isolated and Developed Transfer Deep-Learning Model. Sensors. 2022; 22(1):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010372
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlanazi, Muhannad Faleh, Muhammad Umair Ali, Shaik Javeed Hussain, Amad Zafar, Mohammed Mohatram, Muhammad Irfan, Raed AlRuwaili, Mubarak Alruwaili, Naif H. Ali, and Anas Mohammad Albarrak. 2022. "Brain Tumor/Mass Classification Framework Using Magnetic-Resonance-Imaging-Based Isolated and Developed Transfer Deep-Learning Model" Sensors 22, no. 1: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010372
APA StyleAlanazi, M. F., Ali, M. U., Hussain, S. J., Zafar, A., Mohatram, M., Irfan, M., AlRuwaili, R., Alruwaili, M., Ali, N. H., & Albarrak, A. M. (2022). Brain Tumor/Mass Classification Framework Using Magnetic-Resonance-Imaging-Based Isolated and Developed Transfer Deep-Learning Model. Sensors, 22(1), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010372





