Automatic Pancreatic Cyst Lesion Segmentation on EUS Images Using a Deep-Learning Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Used and Preprocessing
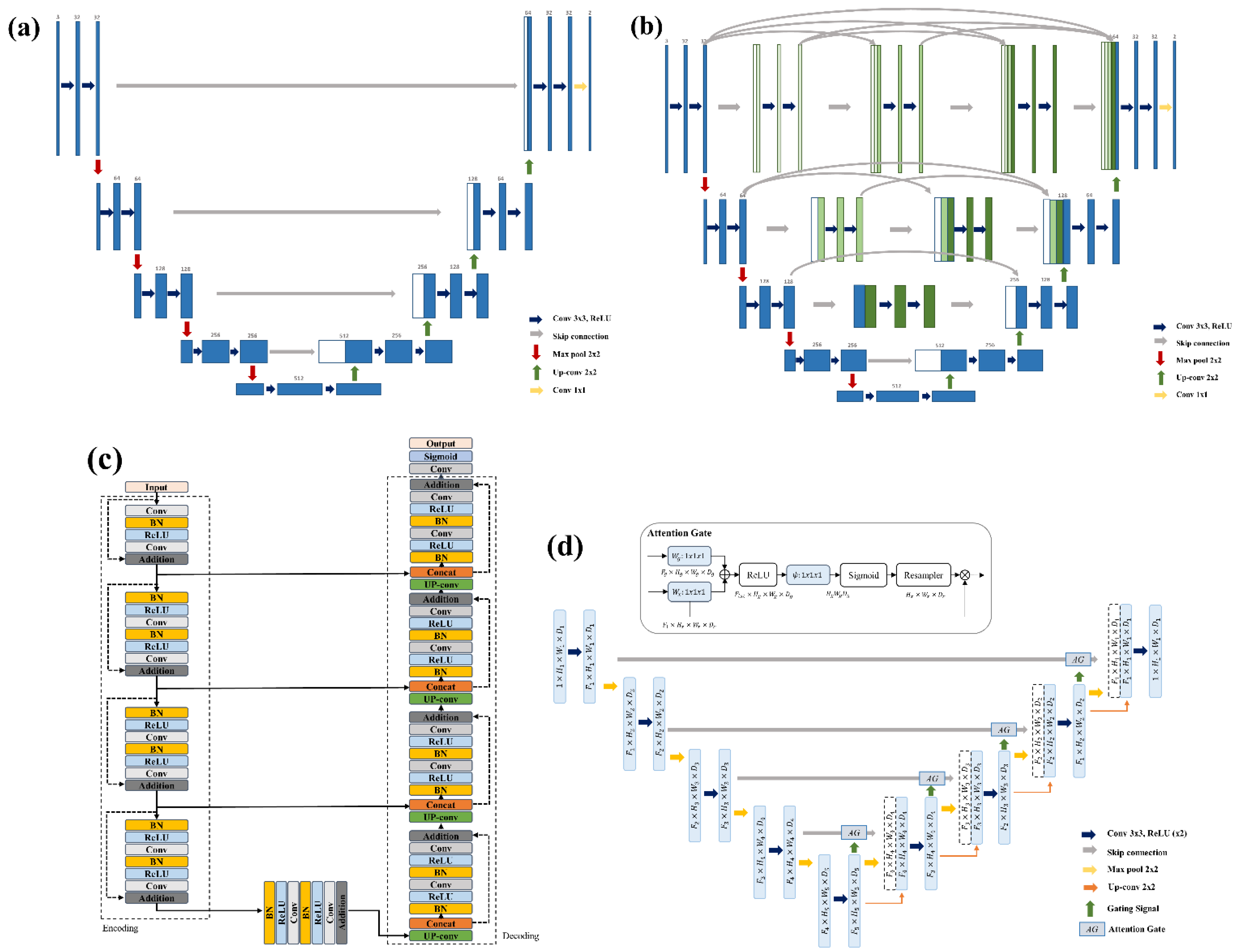
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Segmentation
2.3. Implementation
2.4. Evaluation Metric
3. Results
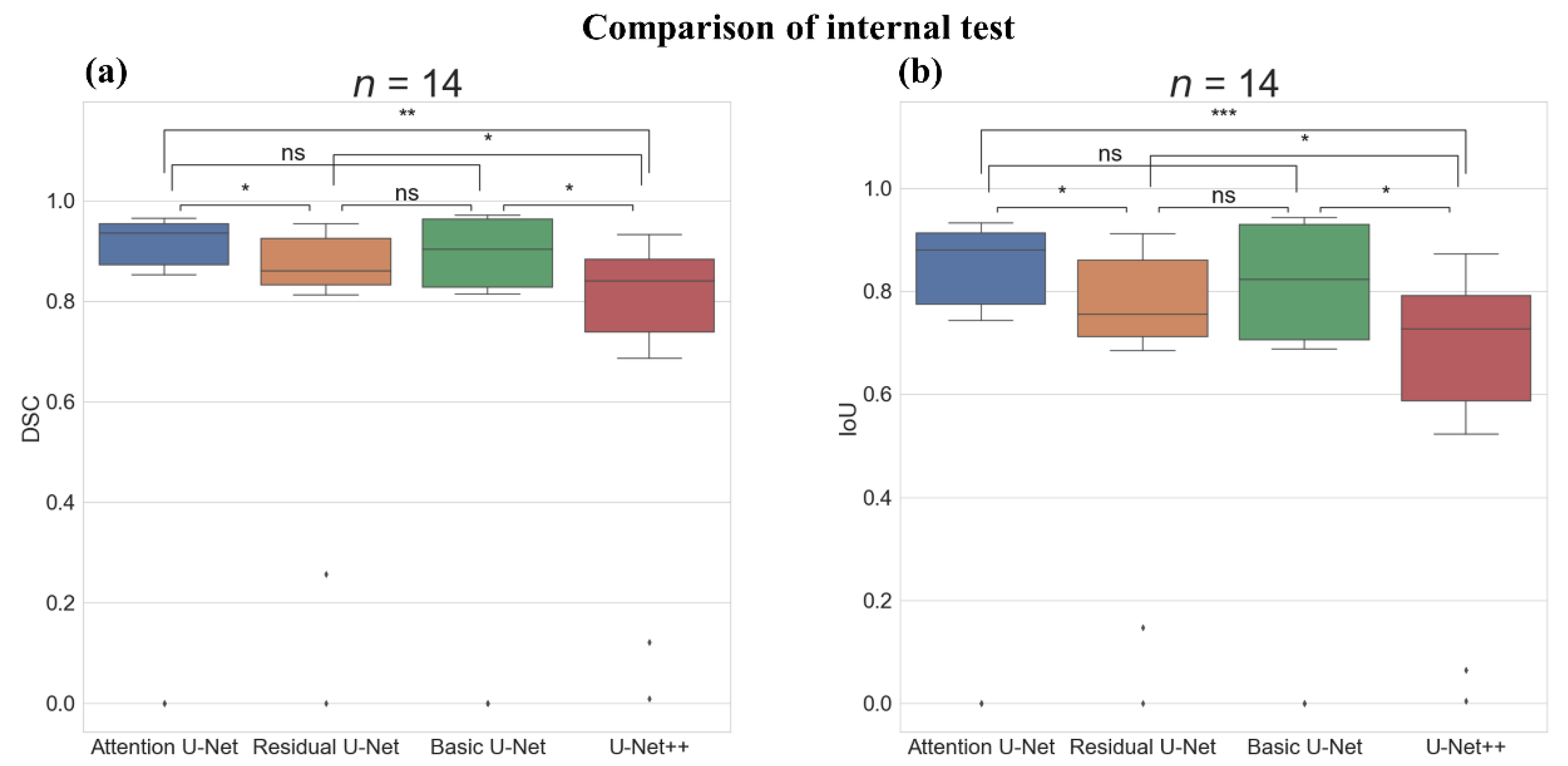
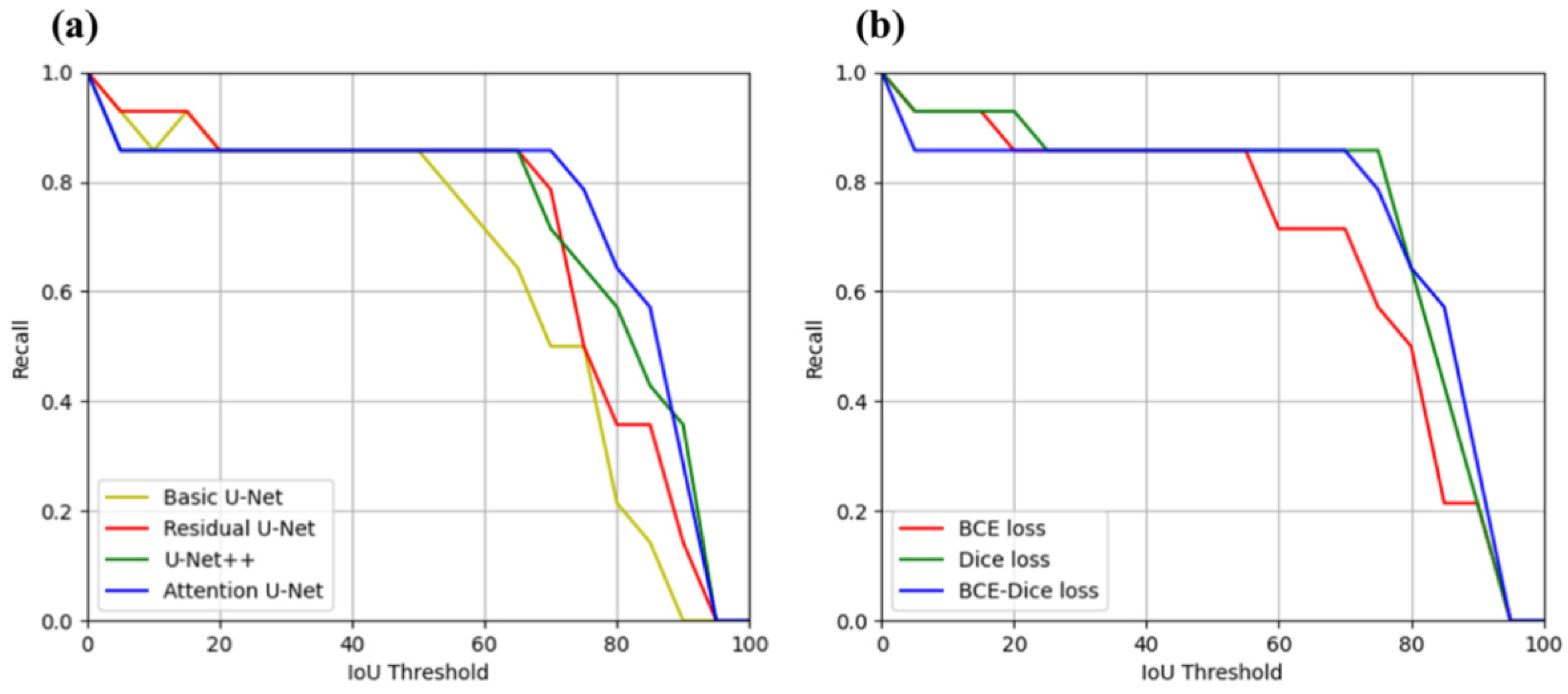
3.1. Internal Test of PCL Segmentation on the EUS Images
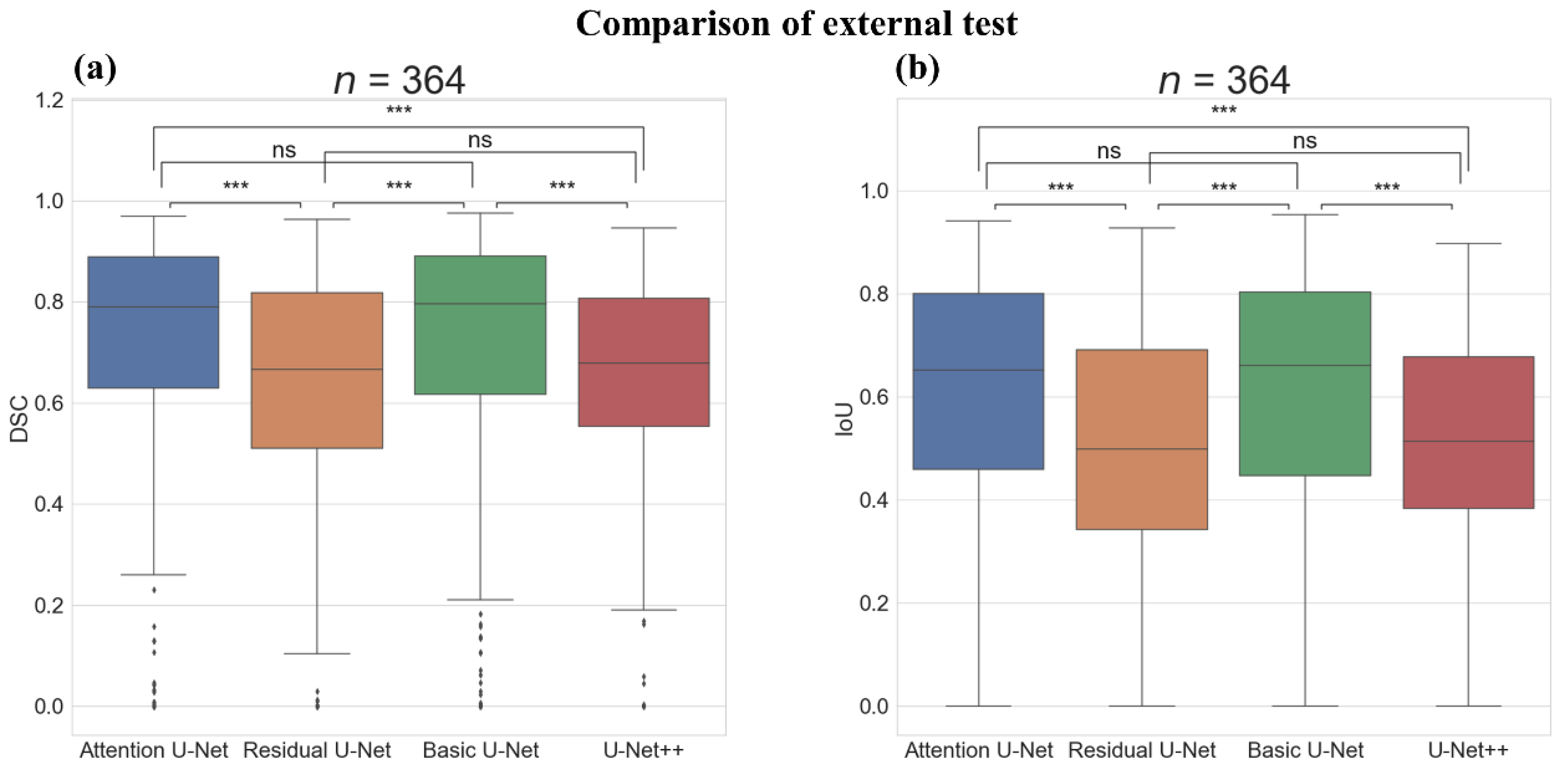
3.2. External Test of PCL Segmentation on the EUS Images
3.3. Cross-Over Study of Dataset
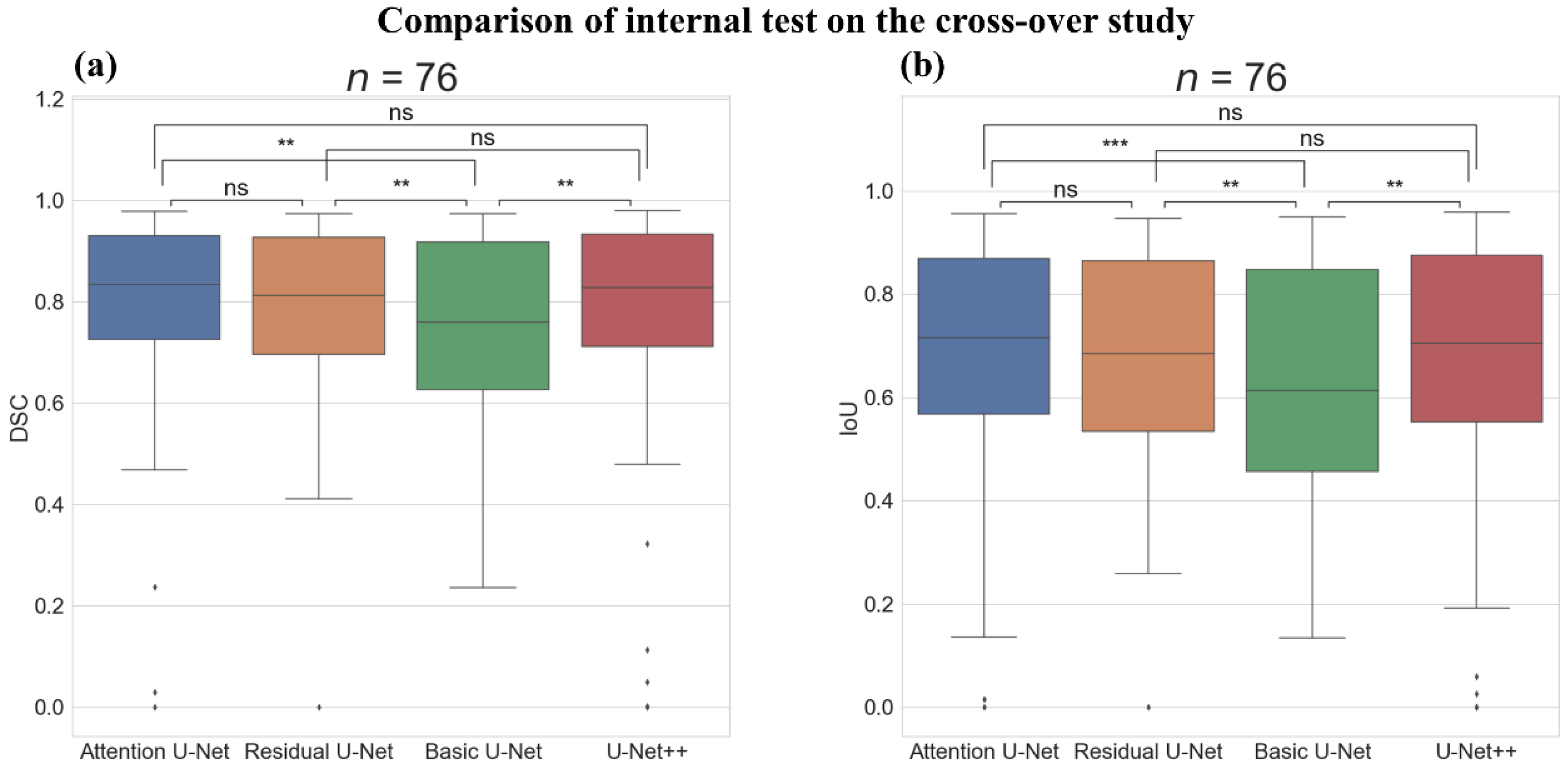
3.3.1. Internal Test on the Cross-Over Study
3.3.2. External Test on the Cross-Over Study
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcea, G.; Ong, S.; Rajesh, A.; Neal, C.; Pollard, C.; Berry, D.; Dennison, A. Cystic lesions of the pancreas: A diagnostic and management dilemma. Pancreatology 2008, 8, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamboni, G.; Hirabayashi, K.; Castelli, P.; Lennon, A.M. Precancerous lesions of the pancreas. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, 299–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Rutherford, M.J.; Bardot, A.; Ferlay, J.; Andersson, T.M.; Myklebust, T.Å.; Tervonen, H.; Thursfield, V.; Ransom, D.; Shack, L. Progress in cancer survival, mortality, and incidence in seven high-income countries 1995–2014 (ICBP SURVMARK-2): A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, R.S.; Scheiman, J.M. EUS and pancreatic cyst fluid analysis: Is the juice worth the aqueeze? J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2011, 2, 199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelvin, Y.M.C.; Park, J.-S.; Seo, D.-W. Role of endosonography in the management of incidental pancreatic cyst lesions. Gastrointest. Interv. 2014, 3, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bhutani, M.S.; Gupta, V.; Guha, S.; Ionuţ Gheonea, D.; Săftoiu, A. Pancreatic cyst fluid analysis—A review. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2011, 20, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Hedenström, P.; Sadik, R. The assessment of endosonographers in training. World J. Clin. Cases 2018, 6, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkan, M.; Cakiroglu, M.; Kocaman, O.; Kurt, M.; Yilmaz, B.; Can, G.; Korkmaz, U.; Dandil, E.; Eksi, Z. Age-based computer-aided diagnosis approach for pancreatic cancer on endoscopic ultrasound images. Endosc. Ultrasound 2016, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Xu, C.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Jin, Z.; Li, Z. Differentiation of pancreatic cancer and chronic pancreatitis using computer-aided diagnosis of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) images: A diagnostic test. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 63820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-M.; Yang, H.; Jin, Z.-D.; Yu, J.-G.; Cai, Z.-Y.; Li, Z.-S. Differential diagnosis of pancreatic cancer from normal tissue with digital imaging processing and pattern recognition based on a support vector machine of EUS images. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 72, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Nguyen, C.C.; Li, F.; Li, B. Digital image analysis of EUS images accurately differentiates pancreatic cancer from chronic pancreatitis and normal tissue. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 67, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguon, L.S.; Seo, K.; Lim, J.-H.; Song, T.-J.; Cho, S.-H.; Park, J.-S.; Park, S. Deep Learning-Based Differentiation between Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm and Serous Cystic Neoplasm in the Pancreas Using Endoscopic Ultrasonography. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, Y.; Iwashita, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Ichikawa, H.; Mita, N.; Uemura, S.; Shimizu, M.; Kuo, Y.-T.; Wang, H.-P.; Hara, T. Automatic Segmentation of Pancreatic Tumors Using Deep Learning on a Video Image of Contrast-Enhanced Endoscopic Ultrasound. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Yao, L.; Ding, X.; Chen, D.; Wu, H.; Lu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, L.; An, P. Deep learning–based pancreas segmentation and station recognition system in EUS: Development and validation of a useful training tool (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonozuka, R.; Itoi, T.; Nagata, N.; Kojima, H.; Sofuni, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ishii, K.; Tanaka, R.; Nagakawa, Y.; Mukai, S. Deep learning analysis for the detection of pancreatic cancer on endosonographic images: A pilot study. J. Hepato Biliary Pancreat. Sci. 2021, 28, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, N.; Paheding, S.; Elkin, C.P.; Devabhaktuni, V. U-net and its variants for medical image segmentation: A review of theory and applications. IEEE Access. 2021, 9, 82031–82057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, London, UK, 20–24 September 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Road extraction by deep residual u-net. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J.U. A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.10165. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hawaii, HI, USA, 21–27 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Sudre, C.H.; Li, W.; Vercauteren, T.; Ourselin, S.; Cardoso, M.J. Generalised dice overlap as a deep learning loss function for highly unbalanced segmentations. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 240–248. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.; Gang, L.; Jun, G. Automated image segmentation using improved PCNN model based on cross-entropy. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Symposium on Intelligent Multimedia, Video and Speech Processing, Hong Kong, China, 20–22 October 2004; pp. 743–746. [Google Scholar]
- Brattain, L.J.; Telfer, B.A.; Dhyani, M.; Grajo, J.R.; Samir, A.E. Machine learning for medical ultrasound: Status, methods, and future opportunities. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Lei, B.; Liu, L.; Li, S.X.; Ni, D.; Wang, T. Deep learning in medical ultrasound analysis: A review. Engineering 2019, 5, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, J.; Brady, P.; Freeman, M.; Gress, F.; Gross, G.; Hassall, E.; Hawes, R.; Jacobsen, N.; Liddle, R.; Ligresti, R. Guidelines for training in electronic ultrasound: Guidelines for clinical application. From the ASGE. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1999, 49, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wani, S.; Hall, M.; Keswani, R.N.; Aslanian, H.R.; Casey, B.; Burbridge, R.; Chak, A.; Chen, A.M.; Cote, G.; Edmundowicz, S.A. Variation in aptitude of trainees in endoscopic ultrasonography, based on cumulative sum analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
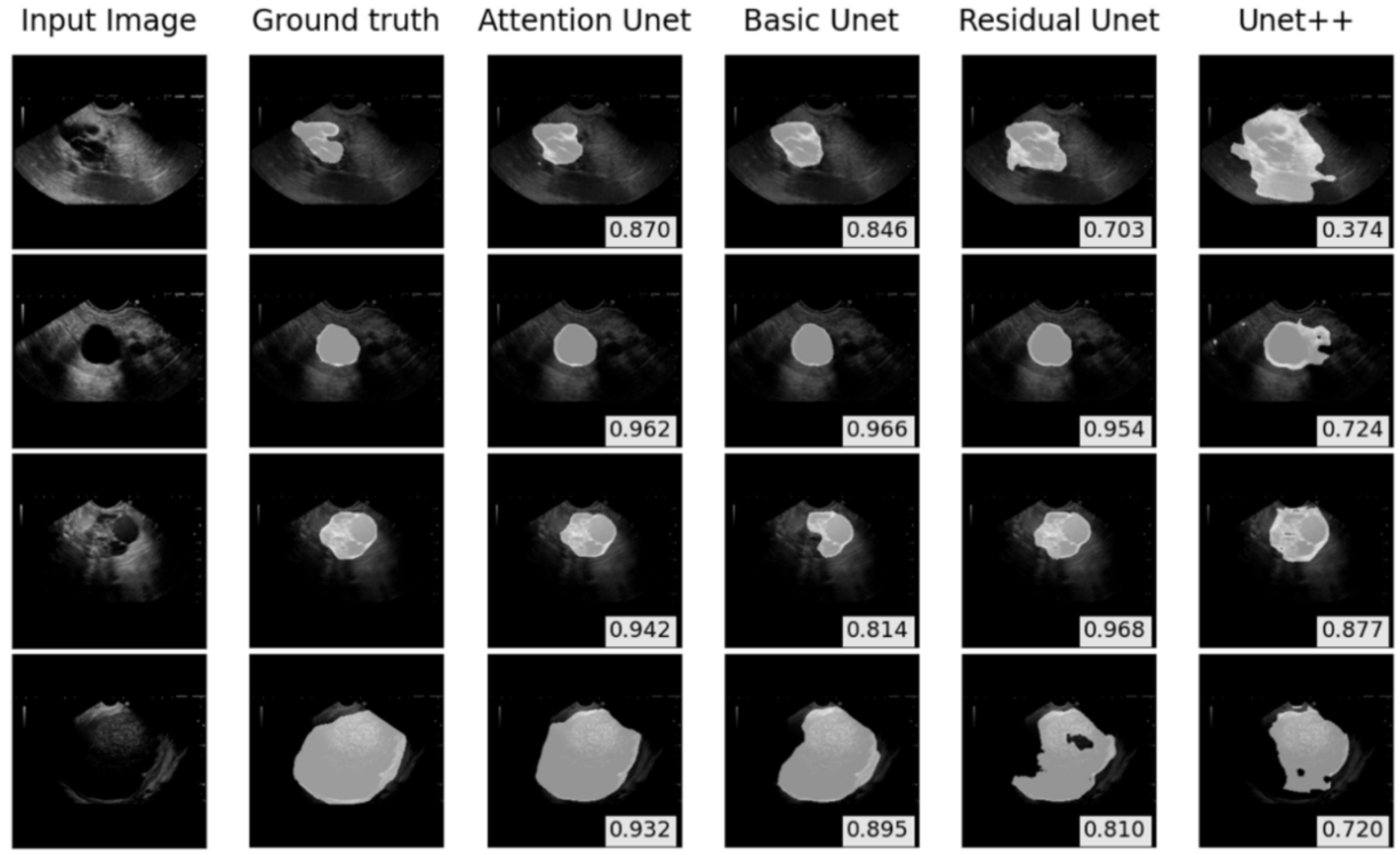




| Patient Characteristics | Dataset A | Dataset B |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Data | ||
| Patients | 52 | 59 |
| Images | 57 | 364 |
| Gender, N(%) | ||
| Male | 20 (38.5) | 36 (61.0) |
| Female | 32 (61.5) | 23 (39.0) |
| Age, N(%) | ||
| 25–44 | 5 (9.6) | 4 (6.8) |
| 45–64 | 18 (34.6) | 17 (28.8) |
| 65 and over | 29 (55.8) | 38 (64.4) |
| Model | Accuracy | Specificity | Sensitivity | DSC | IoU | Recall at IoU > 0.50 | Recall at IoU > 0.70 | Recall at IoU > 0.85 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic U-Net | 0.980 (0.017) | 0.990 (0.013) | 0.774 (0.326) | 0.780 (0.323) | 0.719 (0.307) | 0.857 | 0.714 | 0.429 |
| Residual U-Net | 0.976 (0.014) | 0.984 (0.013) | 0.857 (0.252) | 0.775 (0.272) | 0.691 (0.264) | 0.857 | 0.786 | 0.357 |
| U-Net++ | 0.962 (0.031) | 0.970 (0.024) | 0.799 (0.310) | 0.727 (0.280) | 0.628 (0.262) | 0.857 | 0.500 | 0.143 |
| Attention U-Net | 0.983 (0.012) | 0.991 (0.009) | 0.797 (0.327) | 0.794 (0.326) | 0.741 (0.308) | 0.857 | 0.857 | 0.571 |
| Loss Function | DSC | IoU | Recall at IoU > 0.50 | Recall at IoU > 0.70 | Recall at IoU > 0.85 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCE Loss | 0.770 (0.282) | 0.689 (0.277) | 0.857 | 0.714 | 0.214 |
| Dice Loss | 0.813 (0.268) | 0.744 (0.266) | 0.857 | 0.857 | 0.429 |
| BCE-Dice Loss | 0.794 (0.326) | 0.741 (0.308) | 0.857 | 0.857 | 0.571 |
| Model | Accuracy | Specificity | Sensitivity | DSC | IoU | Recall at IoU > 0.50 | Recall at IoU > 0.70 | Recall at IoU > 0.85 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic U-Net | 0.971 (0.036) | 0.986 (0.018) | 0.759 (0.298) | 0.703 (0.265) | 0.595 (0.263) | 0.687 | 0.437 | 0.168 |
| Residual U-Net | 0.957 (0.041) | 0.970 (0.031) | 0.761 (0.313) | 0.614 (0.260) | 0.488 (0.247) | 0.495 | 0.239 | 0.041 |
| U-Net++ | 0.956 (0.039) | 0.966 (0.030) | 0.817 (0.258) | 0.640 (0.214) | 0.503 (0.208) | 0.514 | 0.190 | 0.005 |
| Attention U-Net | 0.972 (0.037) | 0.989 (0.014) | 0.723 (0.322) | 0.691 (0.283) | 0.587 (0.276) | 0.709 | 0.434 | 0.176 |
| Model | Accuracy | Specificity | Sensitivity | DSC | IoU | Recall at IoU > 0.50 | Recall at IoU > 0.70 | Recall at IoU > 0.85 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic U-Net | 0.872 (0.159) | 0.973 (0.026) | 0.965 (0.033) | 0.749 (0.168) | 0.627 (0.210) | 0.658 | 0.638 | 0.250 |
| Residual U-Net | 0.877 (0.176) | 0.979 (0.023) | 0.972 (0.026) | 0.781 (0.168) | 0.668 (0.202) | 0.829 | 0.474 | 0.276 |
| U-Net++ | 0.811 (0.238) | 0.984 (0.022) | 0.973 (0.028) | 0.768 (0.223) | 0.665 (0.239) | 0.789 | 0.513 | 0.329 |
| Attention U-Net | 0.864 (0.210) | 0.982 (0.024) | 0.973 (0.028) | 0.790 (0.194) | 0.688 (0.217) | 0.829 | 0.539 | 0.316 |
| Model | Accuracy | Specificity | Sensitivity | DSC | IoU | Recall at IoU > 0.50 | Recall at IoU > 0.70 | Recall at IoU > 0.85 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic U-Net | 0.714 (0.287) | 0.983 (0.030) | 0.962 (0.038) | 0.691 (0.271) | 0.583 (0.272) | 0.702 | 0.368 | 0.175 |
| Residual U-Net | 0.719 (0.287) | 0.984 (0.026) | 0.962 (0.038) | 0.687 (0.263) | 0.576 (0.272) | 0.632 | 0.386 | 0.193 |
| U-Net++ | 0.702 (0.300) | 0.979 (0.037) | 0.958 (0.044) | 0.660 (0.299) | 0.565 (0.299) | 0.632 | 0.404 | 0.211 |
| Attention U-Net | 0.726 (0.298) | 0.975 (0.044) | 0.957 (0.048) | 0.671 (0.295) | 0.570 (0.297) | 0.667 | 0.421 | 0.193 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, Y.-T.; Kim, K.-G. Automatic Pancreatic Cyst Lesion Segmentation on EUS Images Using a Deep-Learning Approach. Sensors 2022, 22, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010245
Oh S, Kim Y-J, Park Y-T, Kim K-G. Automatic Pancreatic Cyst Lesion Segmentation on EUS Images Using a Deep-Learning Approach. Sensors. 2022; 22(1):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010245
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Seok, Young-Jae Kim, Young-Taek Park, and Kwang-Gi Kim. 2022. "Automatic Pancreatic Cyst Lesion Segmentation on EUS Images Using a Deep-Learning Approach" Sensors 22, no. 1: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010245
APA StyleOh, S., Kim, Y.-J., Park, Y.-T., & Kim, K.-G. (2022). Automatic Pancreatic Cyst Lesion Segmentation on EUS Images Using a Deep-Learning Approach. Sensors, 22(1), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010245







