Motionless Polarizing Structured Illumination Microscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
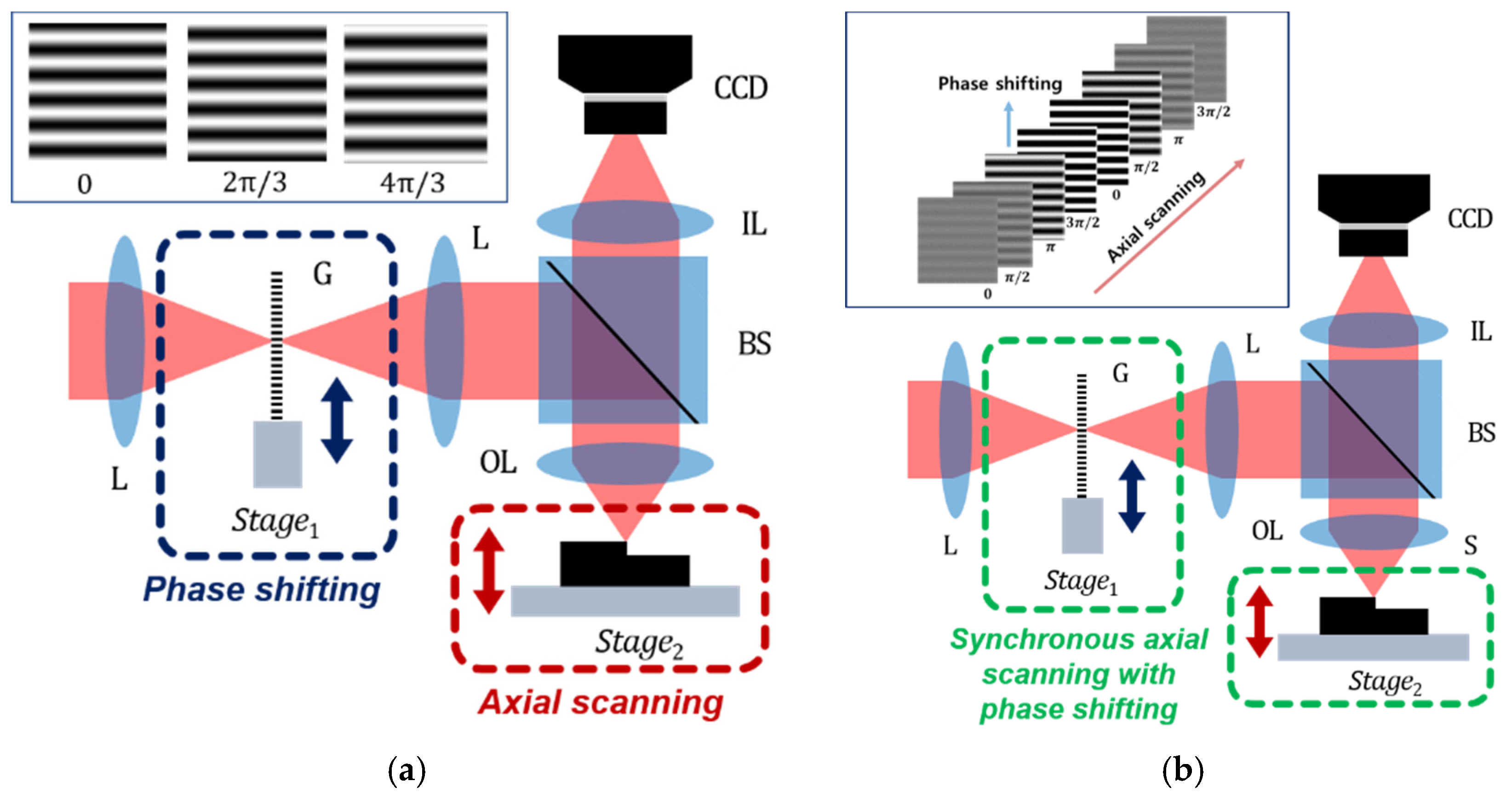
2.1. Principle of Structured Illumination Microscopy (SIM)
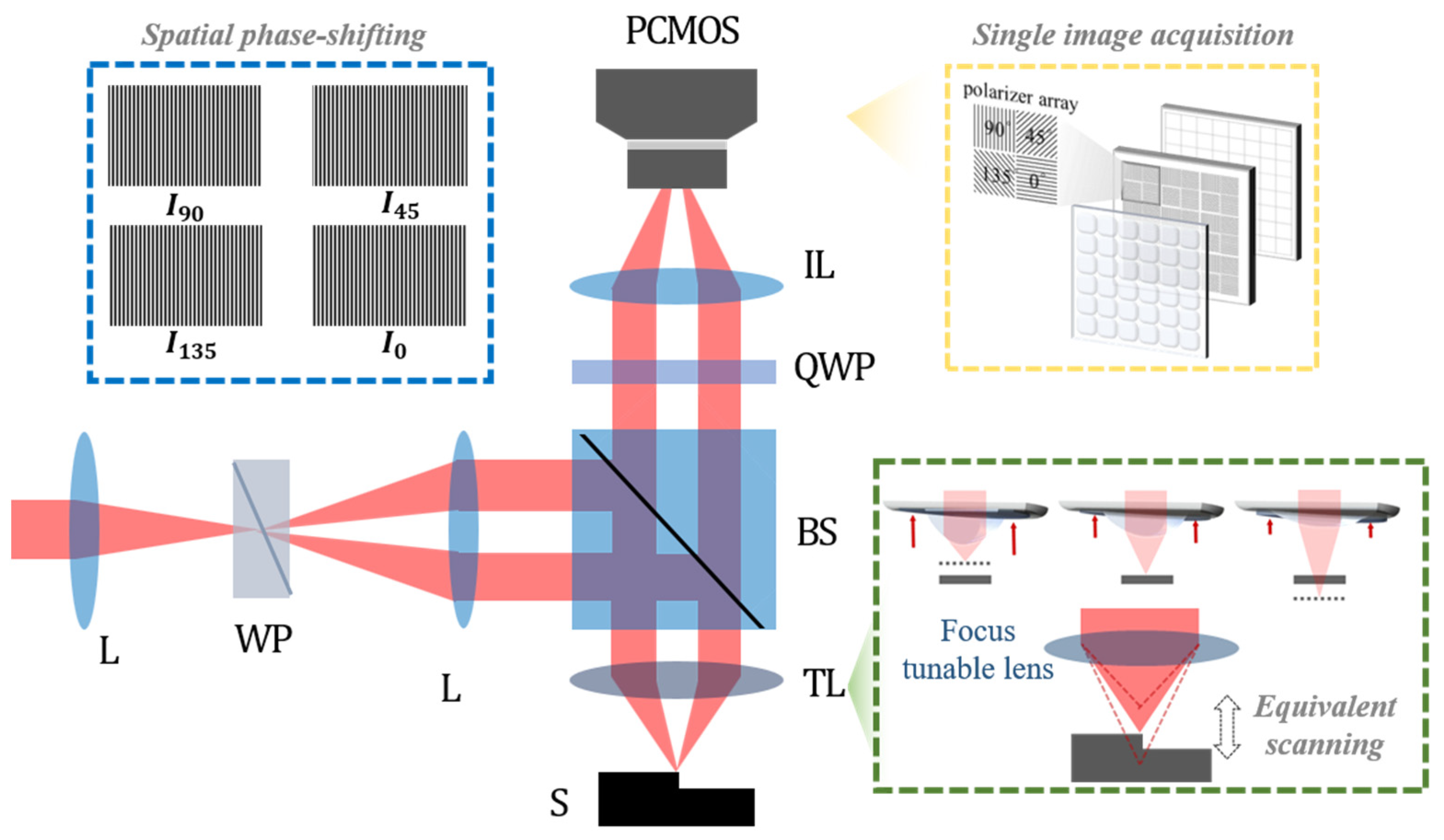
2.2. Principle of Motionless Polarizing Structured Illumination Microscopy (MP-SIM)
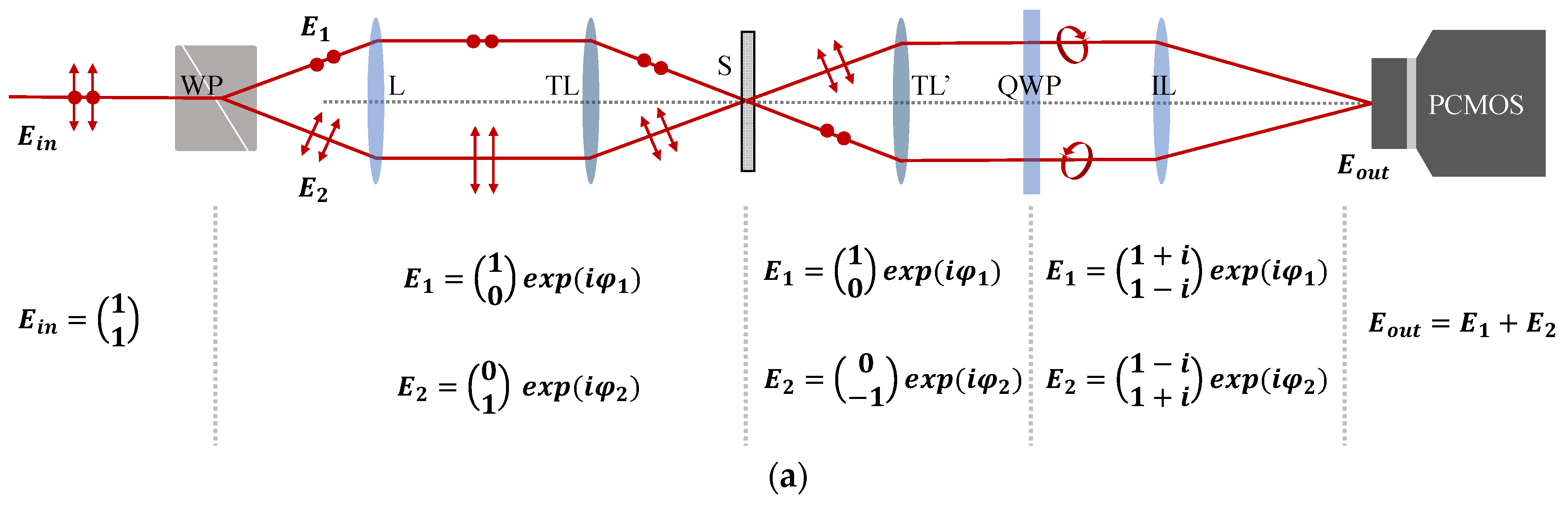
2.2.1. Polarizing Structured Illumination
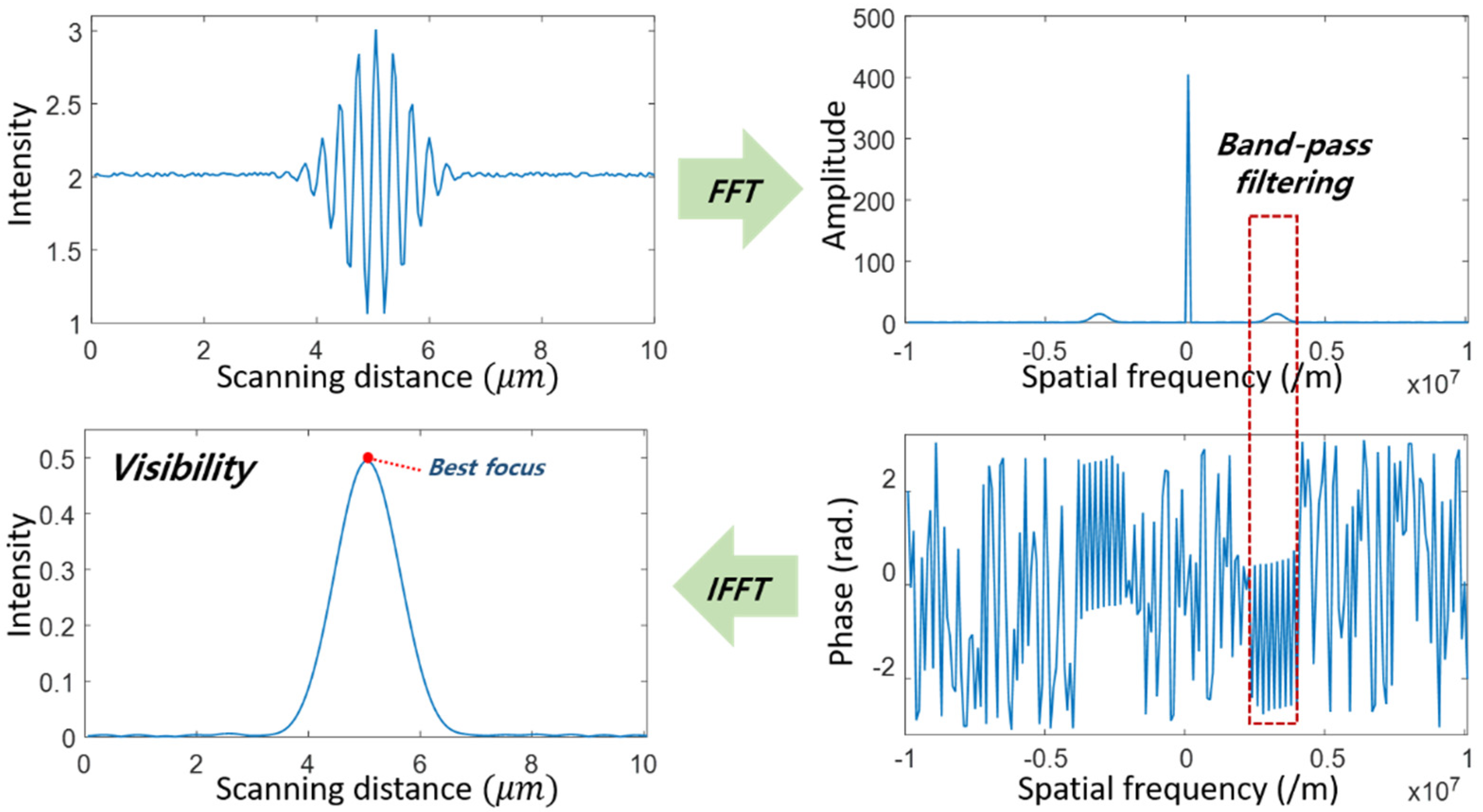
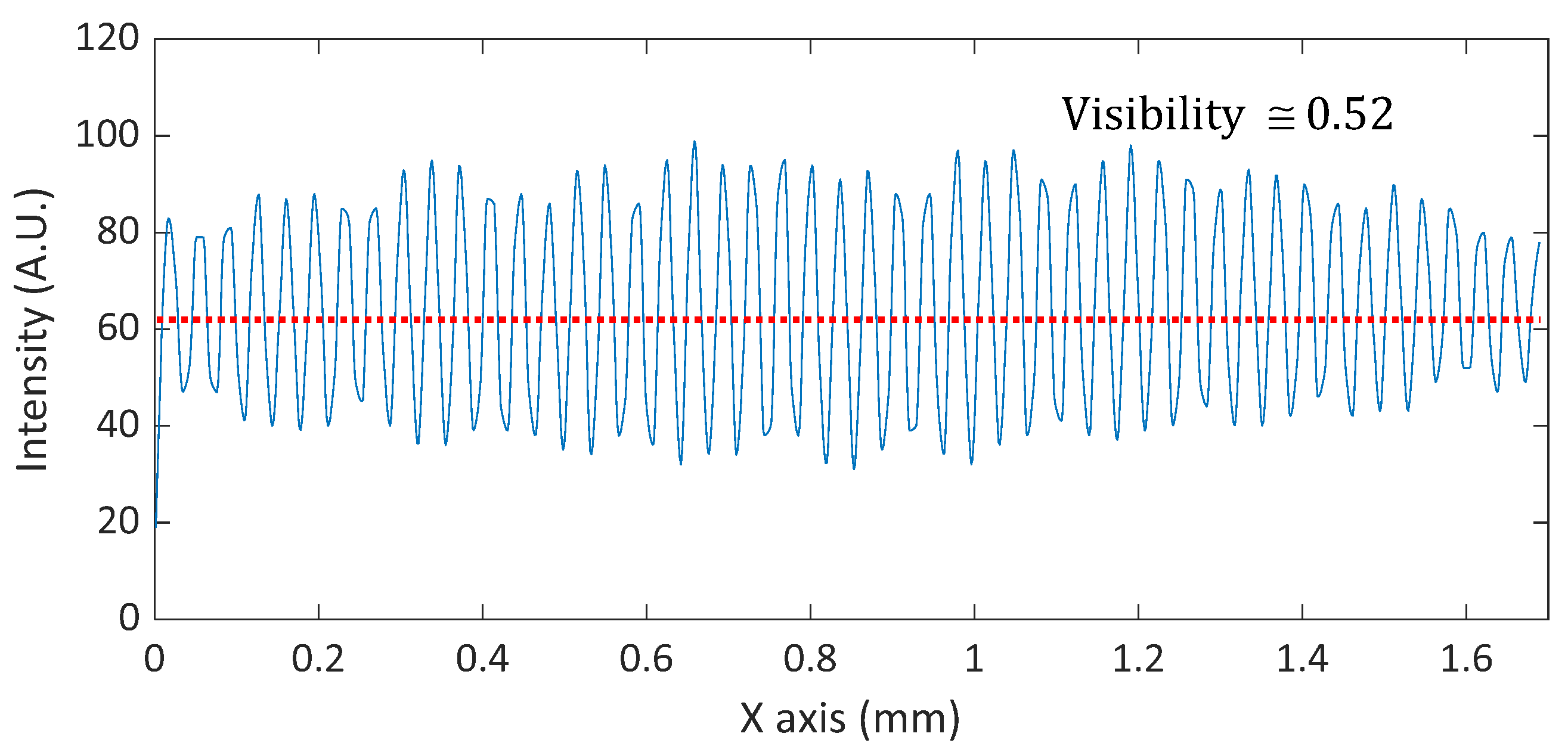
2.2.2. Spatial Phase-Shifting Technique for Calculating the Visibility of the Pattern
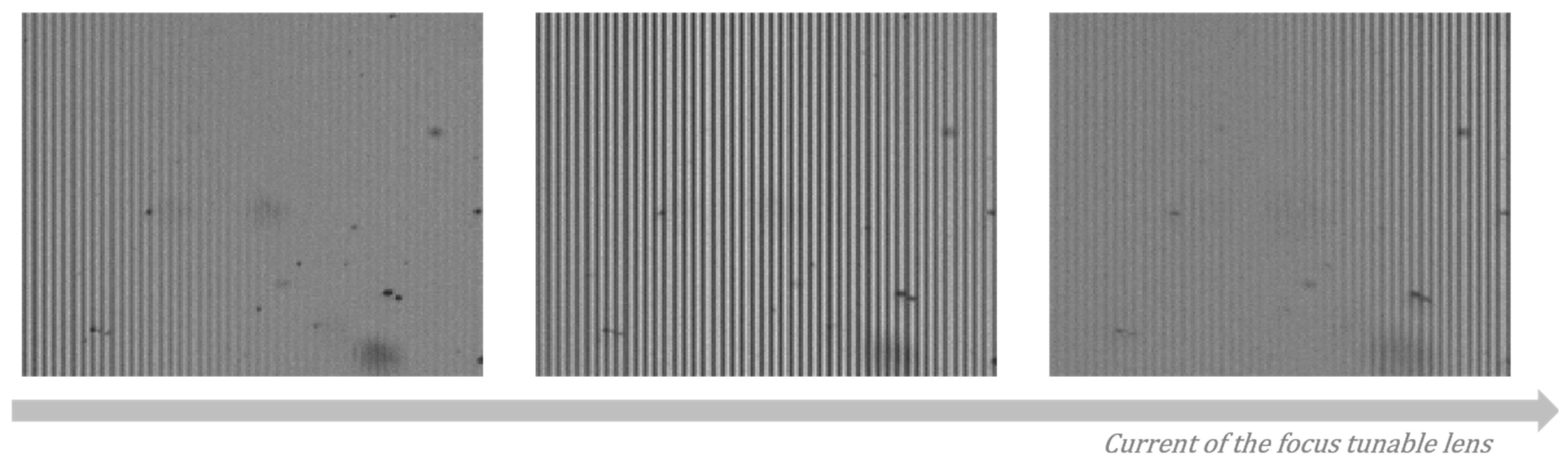
2.2.3. Axial Scanning by a Focus Tunable Lens
3. Results
3.1. Pattern Generation by a Wollaston Prism
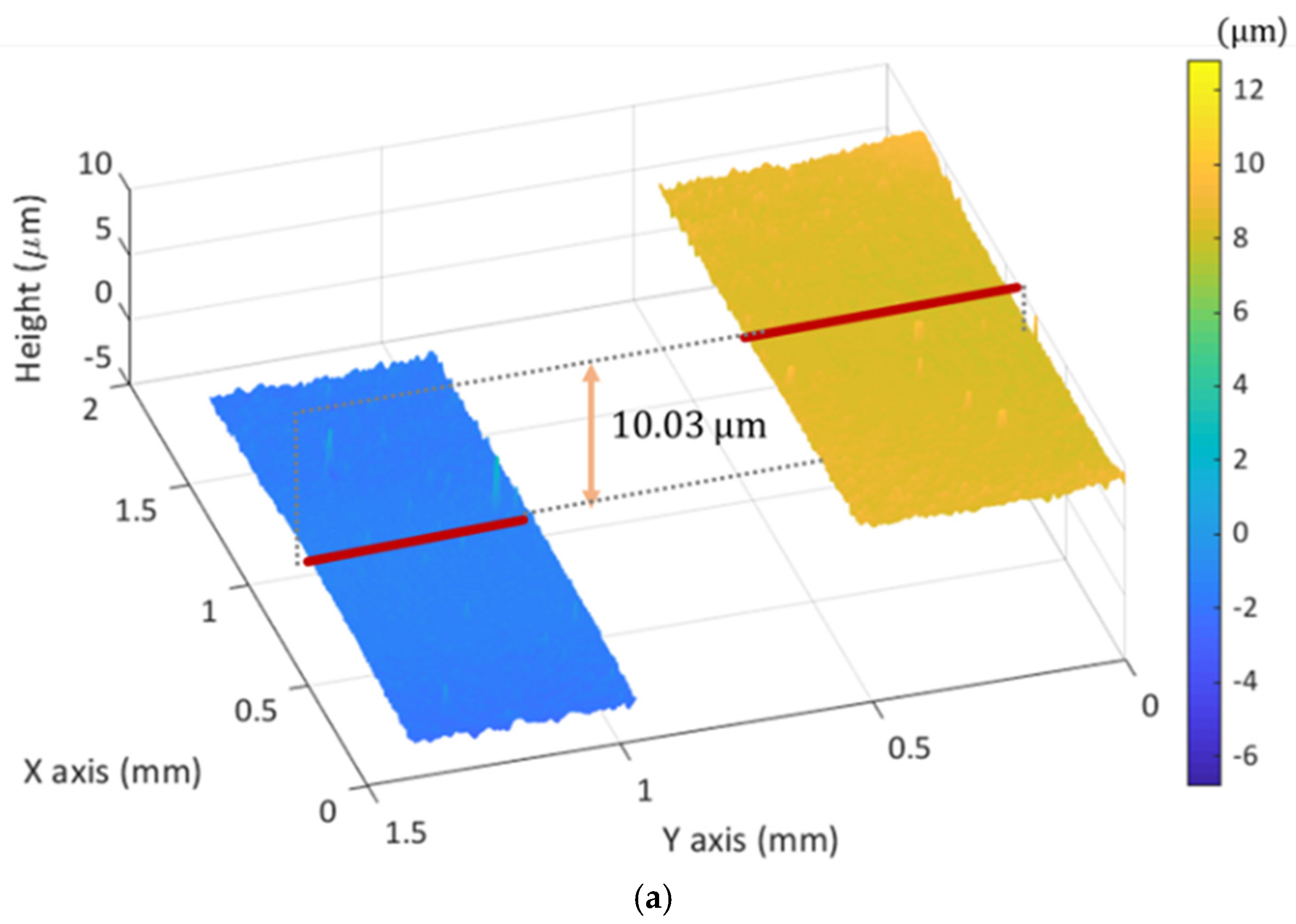
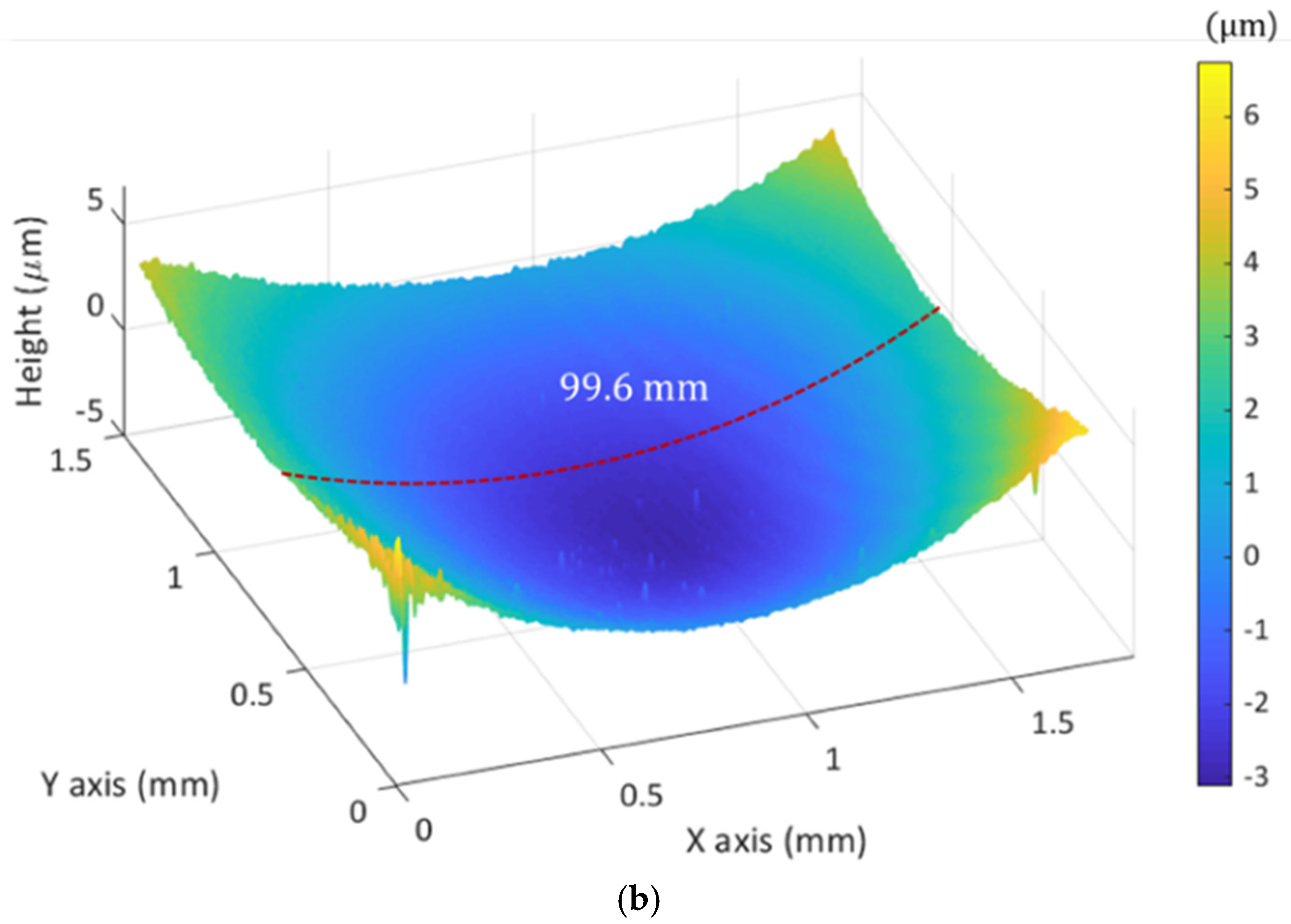
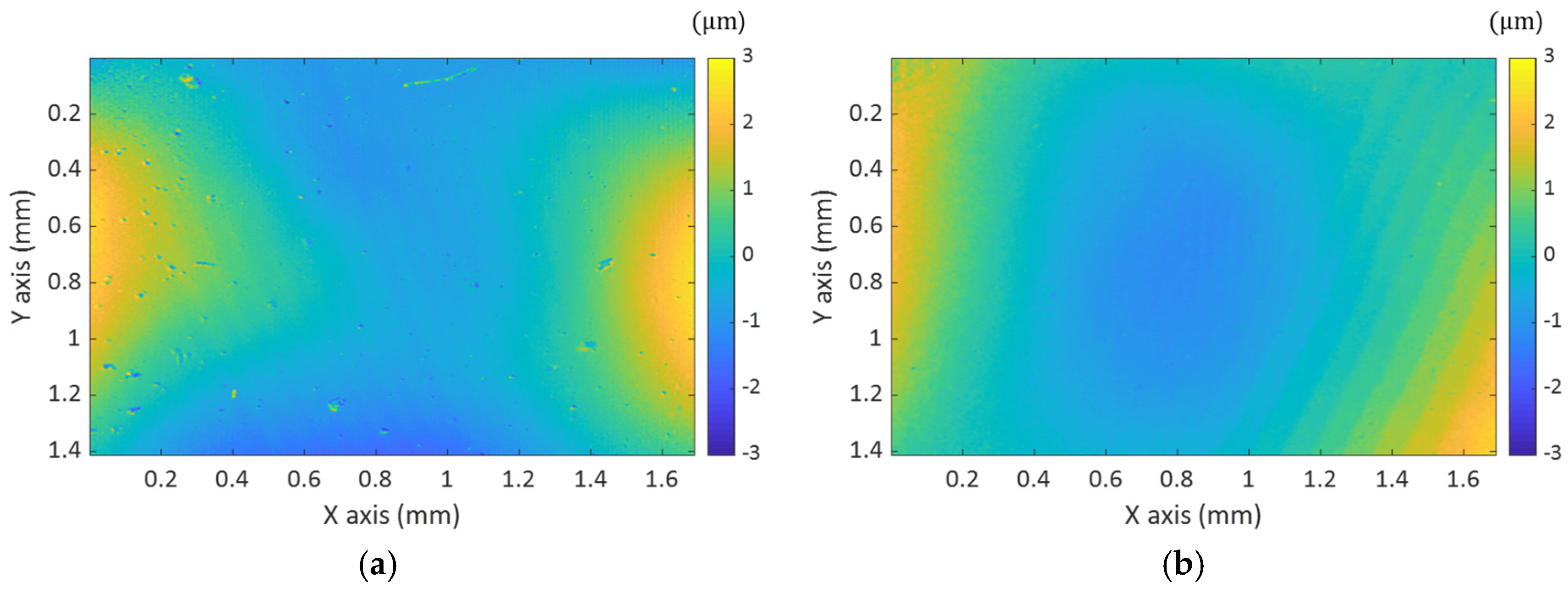
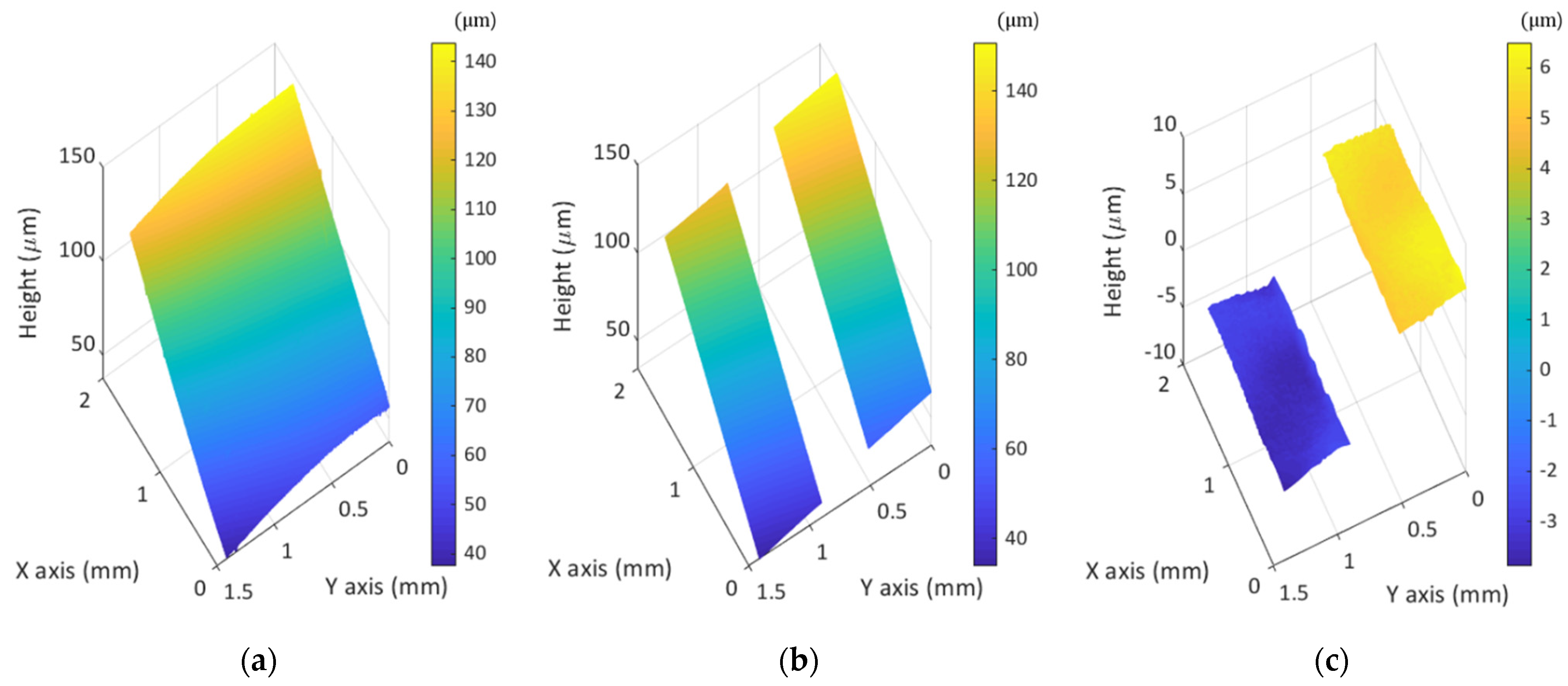
3.2. 3D Surface Profile Measurements by MP-SIM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gustafsson, M.G. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy. J. Microsc. 2000, 198, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shroff, H. Faster, sharper, and deeper: Structured illumination microscopy for biological imaging. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, Ø.I.; Dullo, F.T.; Lahrberg, M.; Tinguely, J.C.; Hellesø, O.G.; Ahluwalia, B.S. Structured illumination microscopy using a photonic chip. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, K.; Park, Y. Super-resolution three-dimensional fluorescence and optical diffraction tomography of live cells using structured illumination generated by a digital micromirror device. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, L.H.; Tian, L.; Waller, L. Structured illumination microscopy with unknown patterns and a statistical prior. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, Q. Surface and thickness measurement of transparent thin-film layers utilizing modulation-based structured-illumination microscopy. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 2944–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, B.; Lin, D.; Yu, H.; Li, S.; Qu, J. Optimized approach for optical sectioning enhancement in multifocal structured illumination microscopy. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 10919–10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.; Han, X.; Wu, J.; Xie, H.; Dai, Q. Improving axial resolution of Bessel beam light-sheet fluorescence microscopy by photobleaching imprinting. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 9464–9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manton, J.D.; Ströhl, F.; Fiolka, R.; Kaminski, C.F.; Rees, E.J. Concepts for structured illumination microscopy with extended axial resolution through mirrored illumination. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 2098–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.; Mehl, J.; Rohrbach, A. Fast TIRF-SIM imaging of dynamic, low-fluorescent biological samples. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 4008–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, M.; Yang, Z.; Kessel, A.; Kranitzky, C.; Faber, C.; Häusler, G. Structured-illumination microscopy on technical surfaces: 3D metrology with nanometer sensitivity. Proc. SPIE 2011, 8082, 80820S. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, B.-J.; Chou, L.-J.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chiang, S.-Y. Isotropic image in structured illumination microscopy patterned with a spatial light modulator. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 14710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neil, M.A.A.; Juškaitis, R.; Wilson, T. Method of obtaining optical sectioning by using structured light in a conventional microscope. Opt. Lett. 1997, 22, 1905–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.M.; Joo, K.-N. Endoscopic precise 3D surface profiler based on continuously scanning structured illumination microscopy. Curr. Opt. Photonics 2018, 2, 172–178. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, K.-N. Fourier domain analysis on continuously scanned structured illumination microscopy. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 057002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintzmann, R.; Huser, T. Super-resolution structured illumination microscopy. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13890–13908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiolka, R.; Markus, B.; Andreas, S. Structured illumination in total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy using a spatial light modulator. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 1629–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.H.; Chen, N.G.; Sheppard, C.J.R. Study on potential of structured illumination microscopy utilizing digital micromirror device for endoscopy purpose. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Symposium on Biophotonics, Nanophotonics and Metamaterials, Hangzhou, China, 16–18 October 2006; pp. 218–221. [Google Scholar]
- Schwider, J.; Falkenstoerfer, O.R.; Schreiber, H.; Zoeller, A.; Streibl, N. New compensating four-phase algorithm for phase-shift interferometry. Opt. Eng. 1993, 32, 1883–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, M.; Millerd, J.; Brock, N.; Morris, M.N.; Hayes, J.; Wyant, J. Analysis of a micropolarizer array-based simultaneous phase-shifting interferometer. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 6861–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Tu, X.; Zhang, J.; Spires, O.; Brock, N.; Pau, S.; Liang, R. Snapshot multi-wavelength interference microscope. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 18279–18291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tian, X.; Xu, P.; Liang, J.; Wu, H.; Spires, O.; Liang, R. Compact snapshot multiwavelength interferometer. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 4463–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Tang, Y.; Feng, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, S. Accurate surface profilometry using differential optical sectioning microscopy with structured illumination. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 11721–11733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Tang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Feng, J.; He, Y.; Hu, S. Fast surface profilometry utilizing structured illumination microscopy based on the time-domain phase-shift technique. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 8180–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, C.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Lei, Z. Deep learning based one-shot optically-sectioned structured illumination microscopy for surface measurement. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 4010–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Han, C.; Feng, J.; Tang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Hu, S. Film Thickness-Profile Measurement Using Iterative Peak Separation Structured Illumination Microscopy. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Ryu, I.; Kim, D.; Kauh, S.K. High-speed Three-dimensional Surface Profile Measurement with the HiLo Optical Imaging Technique. Curr. Opt. Photonics 2018, 2, 568–575. [Google Scholar]
- de Groot, P.; Deck, L. Three-dimensional imaging by sub-Nyquist sampling of white-light interferograms. Opt. Lett. 1993, 18, 1462–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, P.; de Lega, X.C. Signal modeling for low-coherence height-scanning interference microscopy. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 4821–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.W.; Joo, K.-N. Single-shot imaging of two-wavelength spatial phase-shifting interferometry. Sensors 2019, 19, 5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, Y.; Li, C.; Wan, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, C.; Zhang, H. Improved computer-generated moiré profilometry with flat image calibration. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wu, S.; Song, Z. An accurate calibration means for the phase measuring deflectometry system. Sensors 2019, 19, 5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motarou, C.C.; Gaylord, T.K. Analysis and design of modified Wollaston prisms. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 6604–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadaglić, D.; Wilson, T. Image formation in structured illumination wide-field fluorescence microscopy. Micron 2008, 39, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
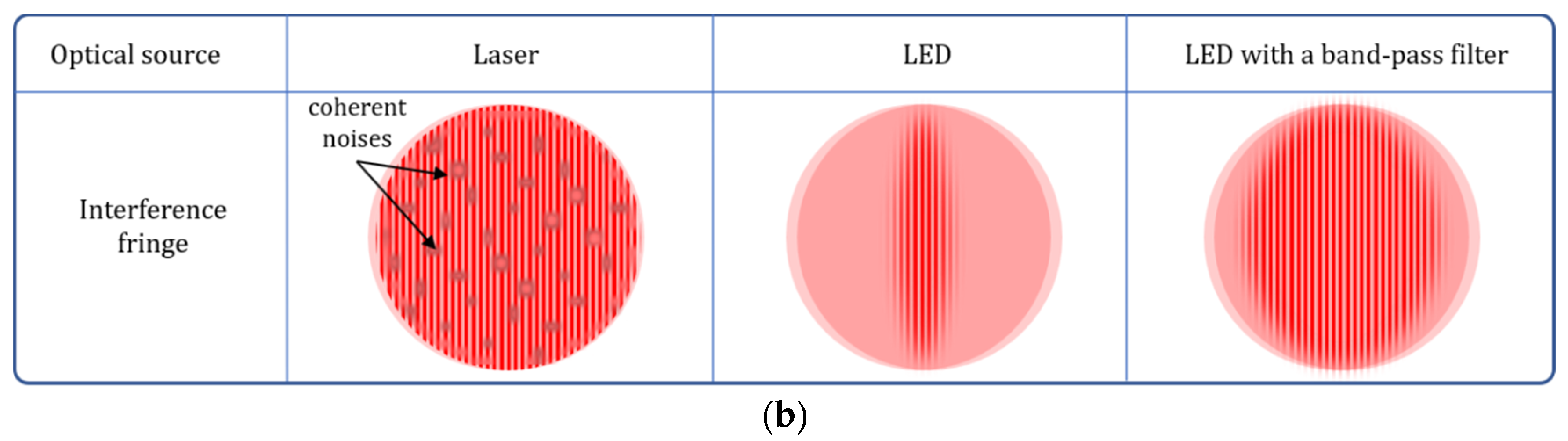




| Typical SIM | CSSIM | MP-SIM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visibility calculation | Temporal phase-shifting | Fourier method (post-processing) | Spatial phase-shifting |
| Image acquisition | Three serial images | Synchronized single image | Four simultaneous images |
| Illumination pattern | Non-polarizing illumination pattern by grid, DMD, or SLM | Polarizing illumination pattern by a Wollaston prism | |
| Axial resolution | Dependent on the numerical aperture of the objective | ||
| Lateral resolution | Dependent on the numerical aperture of the objective | ||
| Measurement speed * | fps of the camera × 3 | fps of the camera | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.M.; Joo, K.-N. Motionless Polarizing Structured Illumination Microscopy. Sensors 2021, 21, 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082837
Park HM, Joo K-N. Motionless Polarizing Structured Illumination Microscopy. Sensors. 2021; 21(8):2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082837
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hyo Mi, and Ki-Nam Joo. 2021. "Motionless Polarizing Structured Illumination Microscopy" Sensors 21, no. 8: 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082837
APA StylePark, H. M., & Joo, K.-N. (2021). Motionless Polarizing Structured Illumination Microscopy. Sensors, 21(8), 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082837






