Electrical and Electromagnetic Geophysical Prospecting for the Monitoring of Rock Glaciers in the Dolomites, Northeast Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
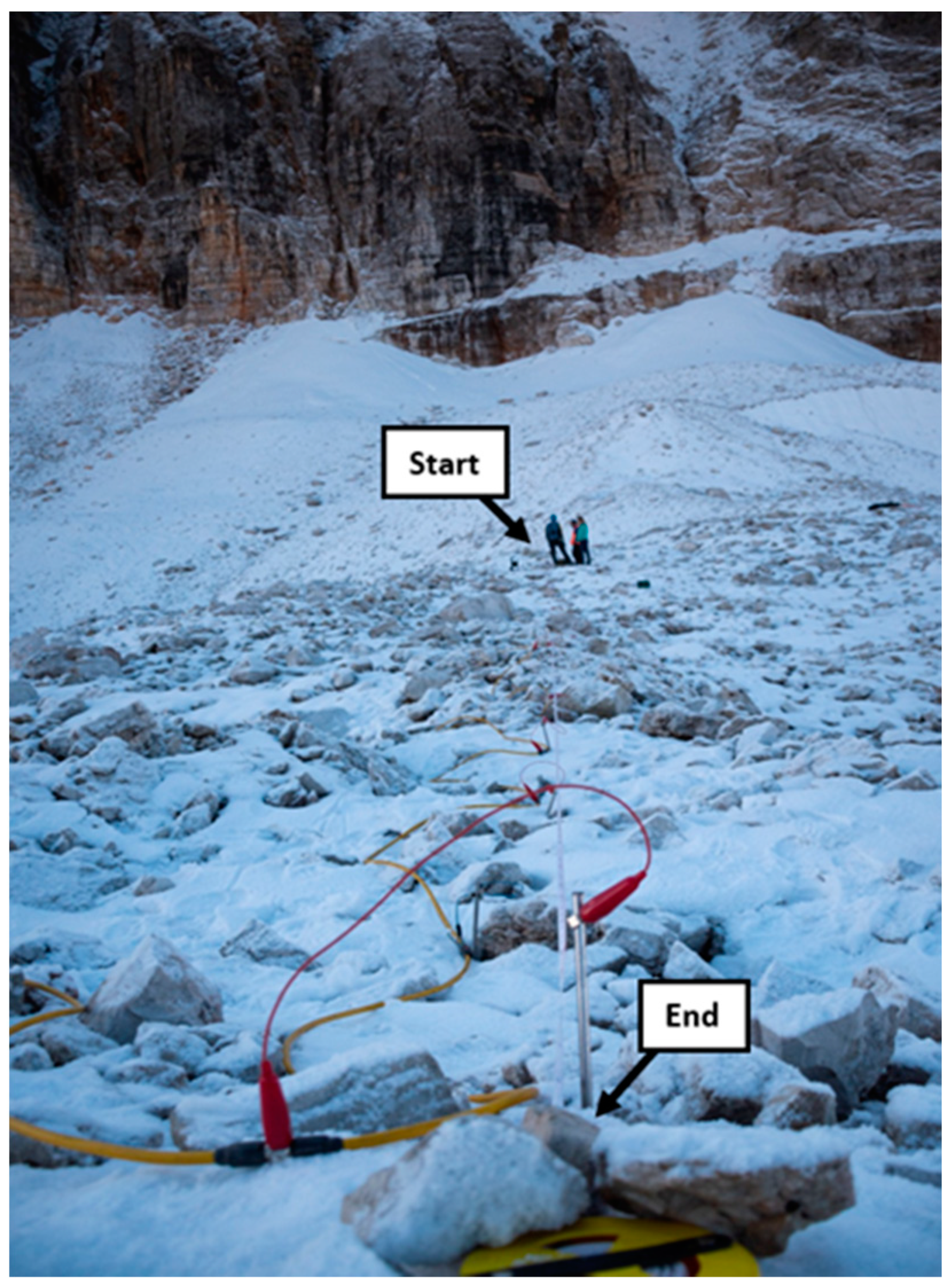
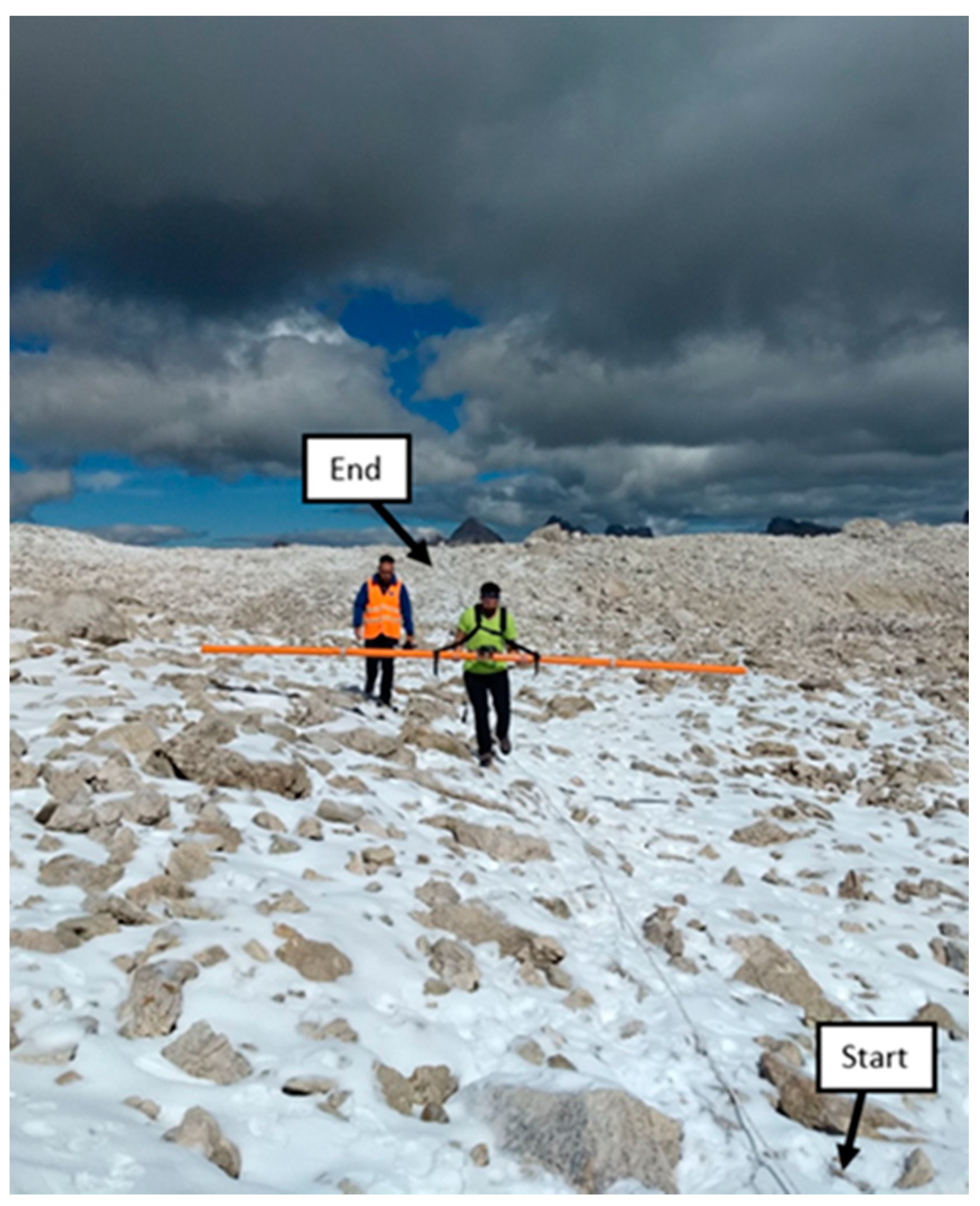
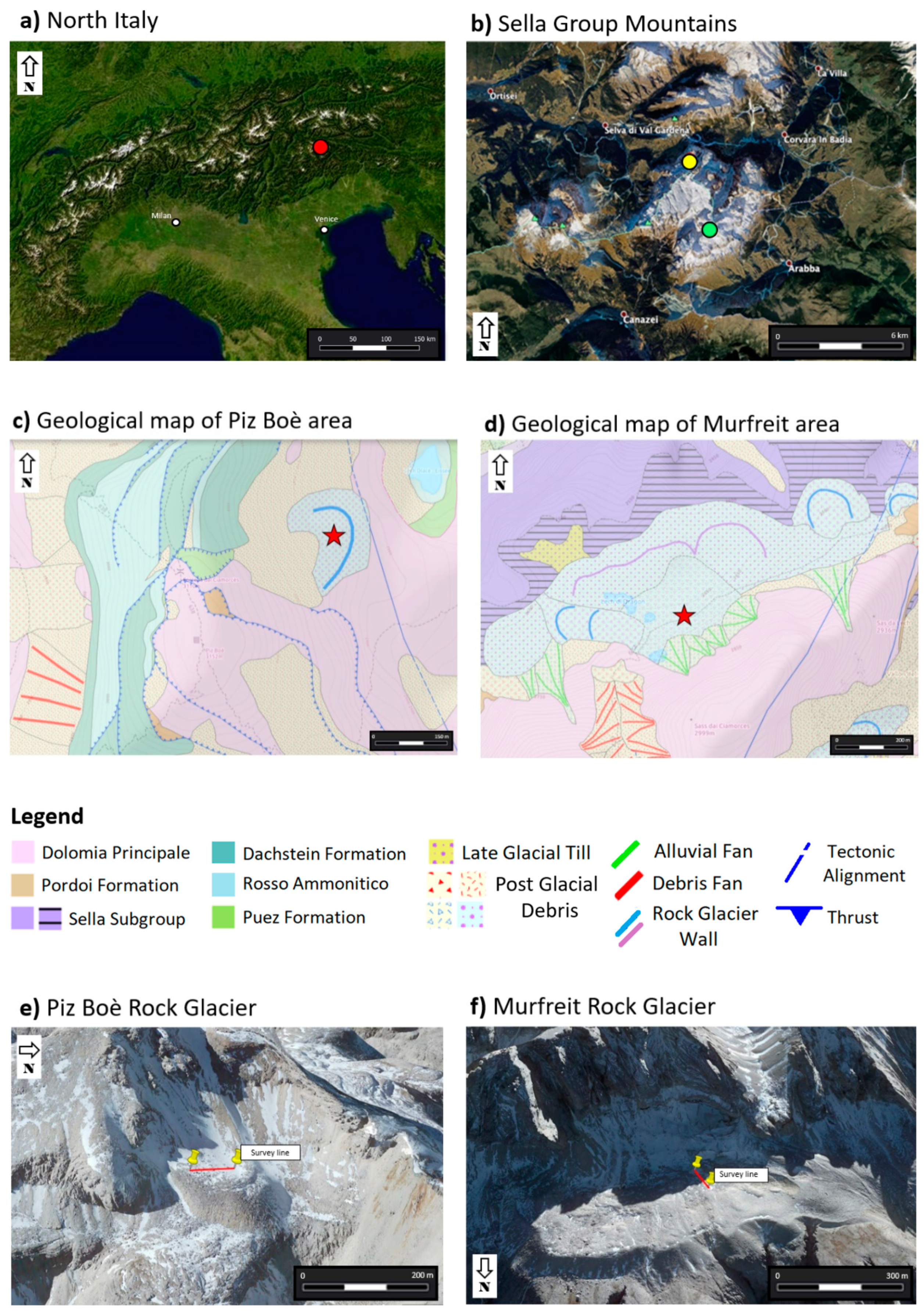
2. Site Description
3. Methods
3.1. Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT)
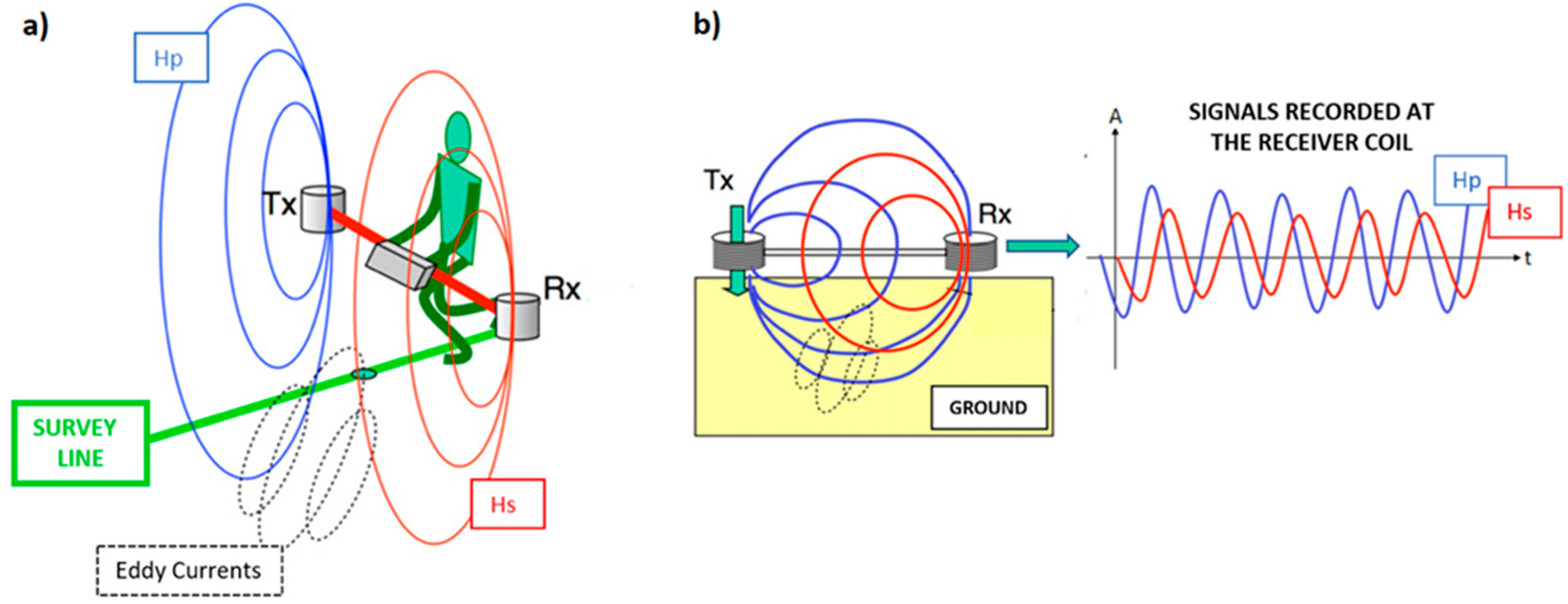
3.2. Frequency Domain Electro-Magnetometry (FDEM)
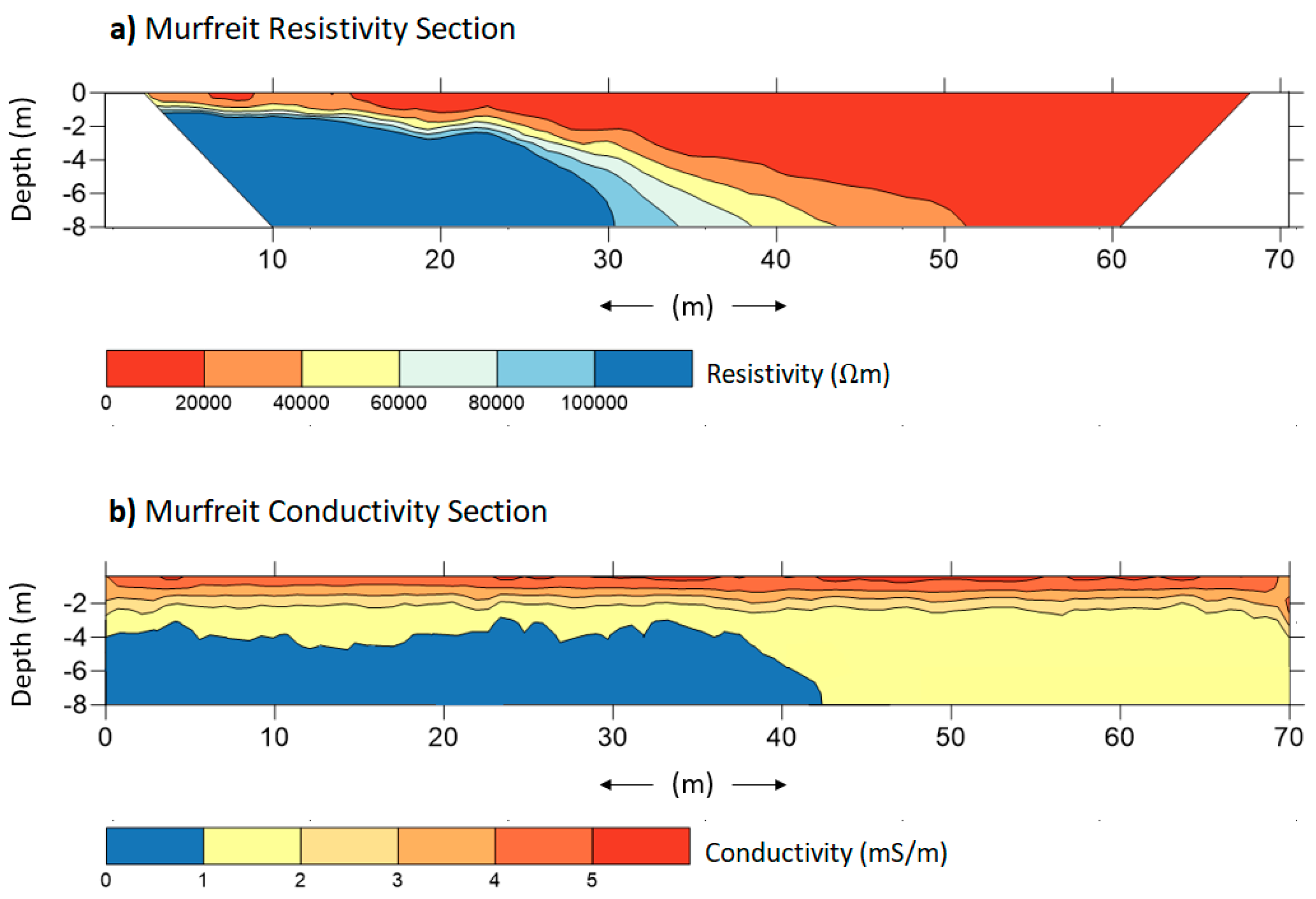
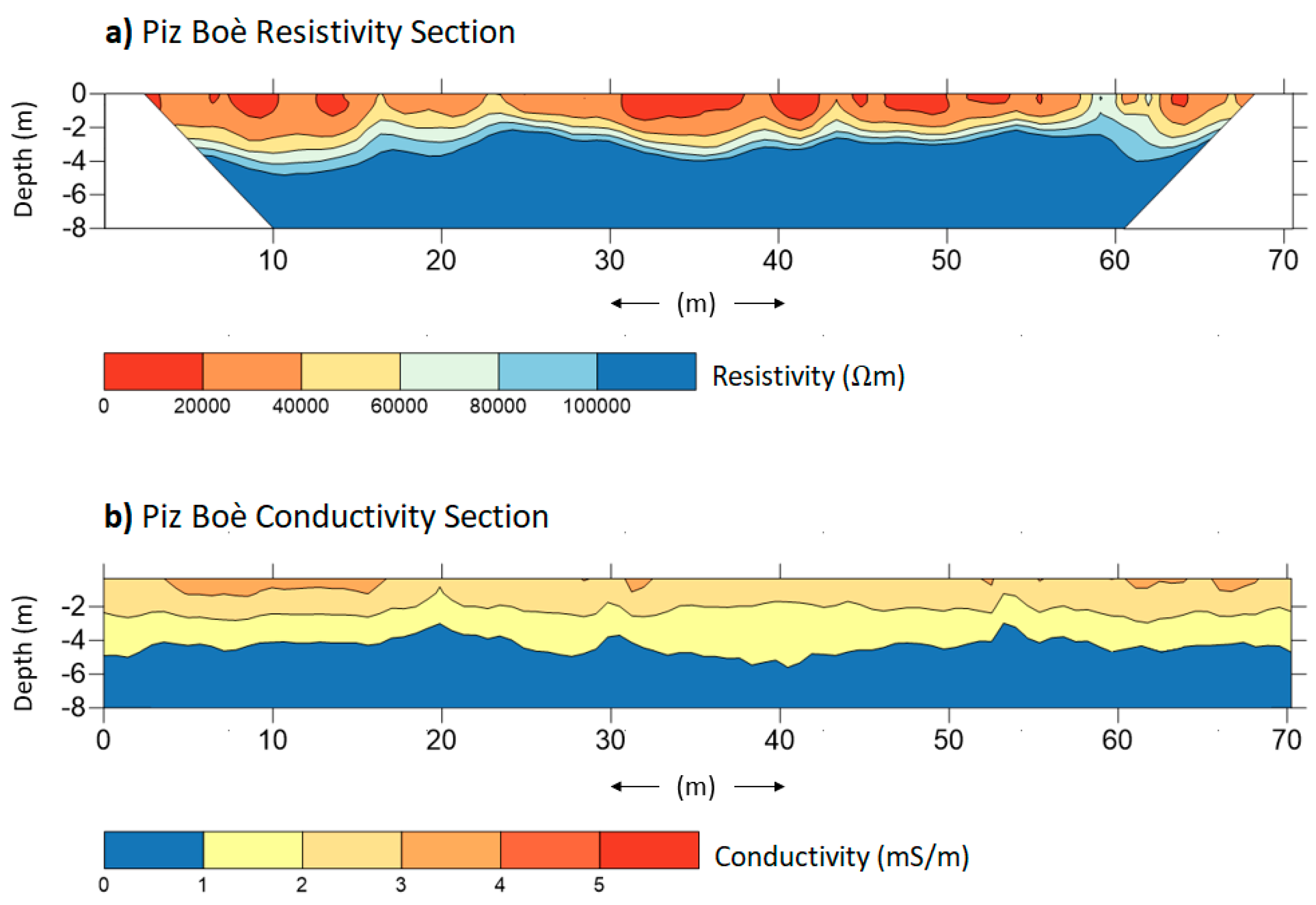
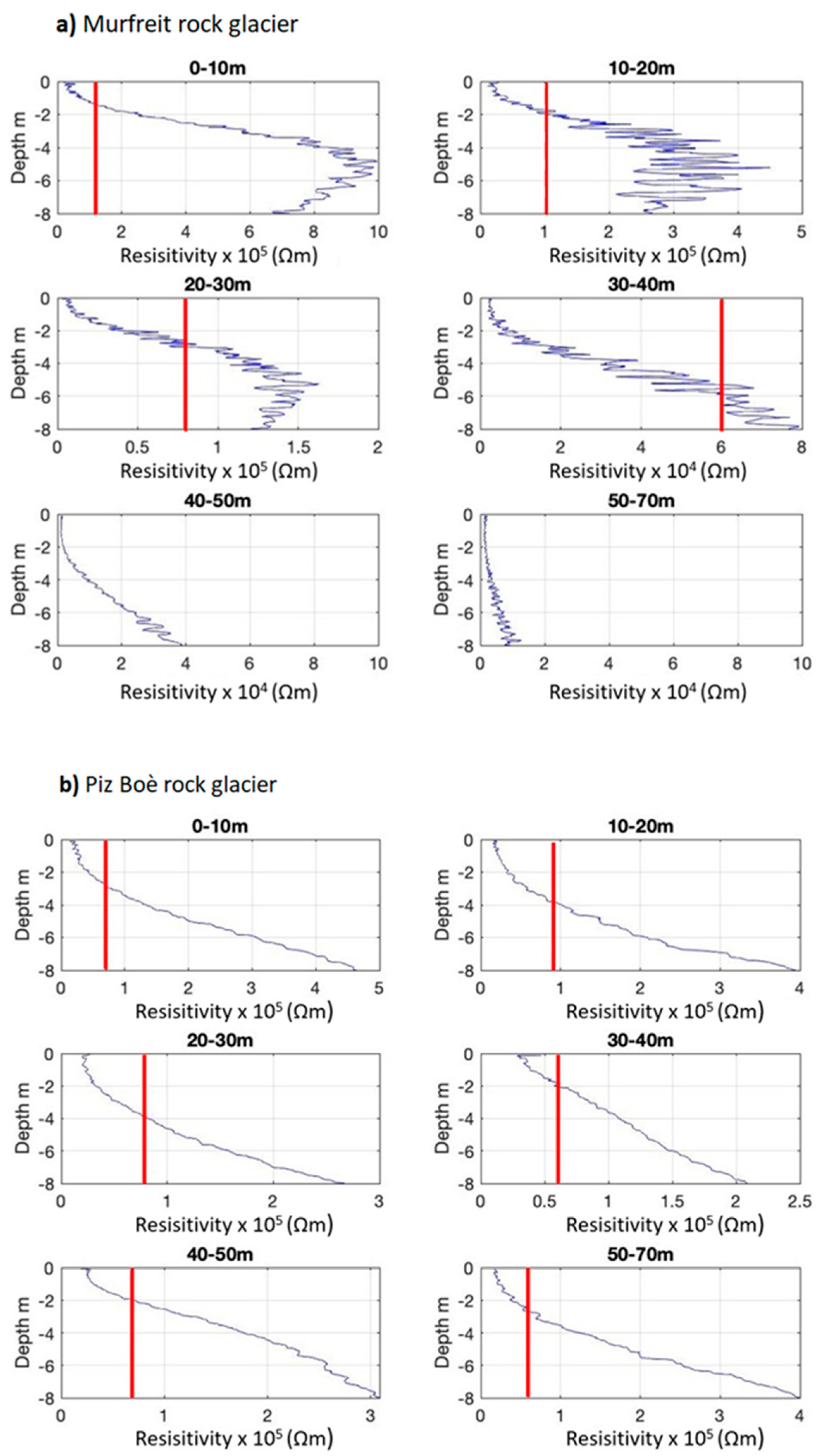
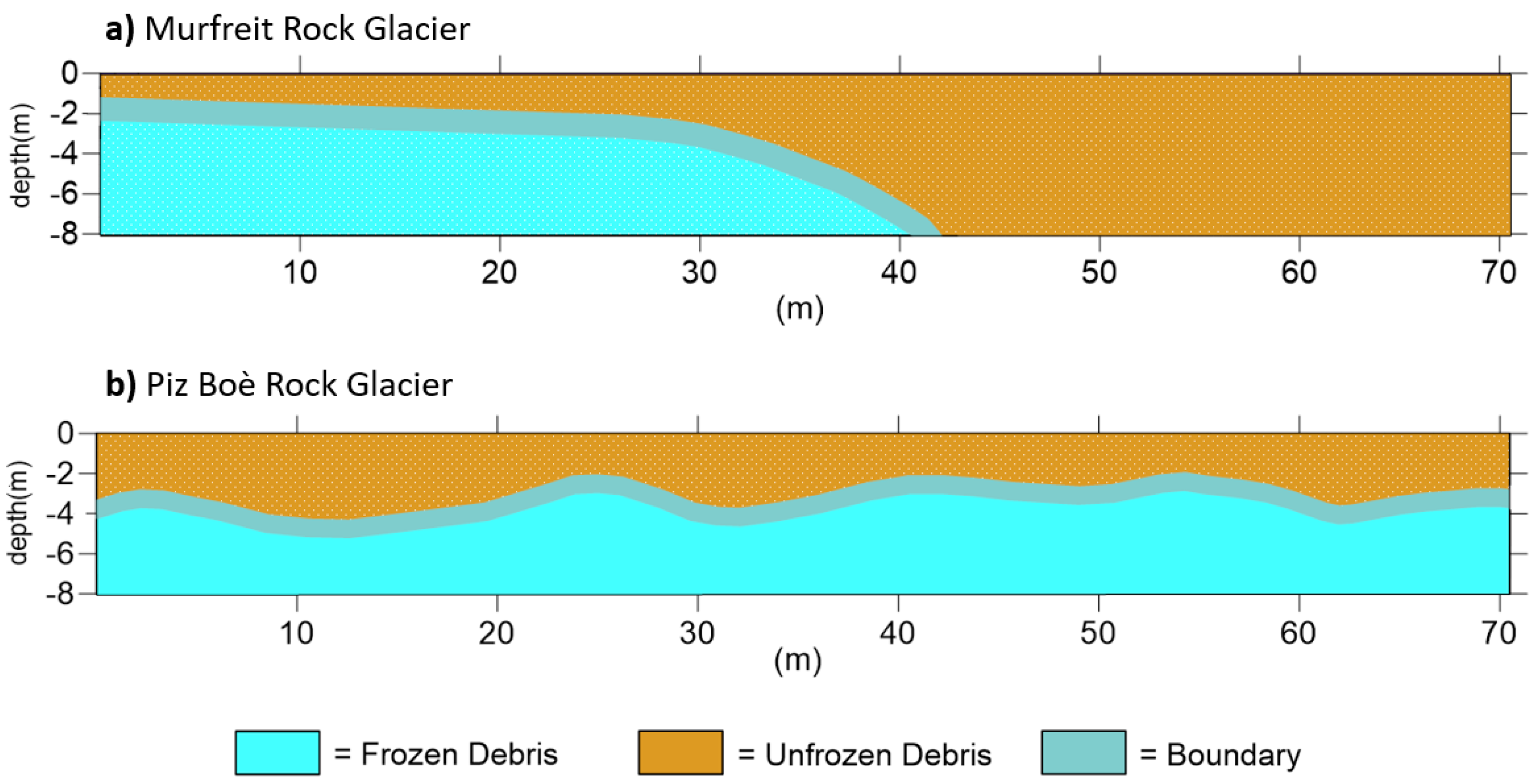
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janke, J.R.; Regmi, N.R.; Giardino, J.R.; Vitek, J.D. Rock Glaciers. In Treatise on Geomorphology; Elsevier Inc., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 238–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterkamp, T.E.; Burn, C.R. Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences; North, G.R., Pyle, J.A., Zhan, F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Barsch, D. Nature and importance of mass wasting by rock glaciers in alpine permafrost environments. Earth Surf. Process. 1977, 2, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsch, D.; Fierz, H.; Haeberli, W. Shallow core drilling and bore-hole measurements in the permafrost of an active rock glacier near the Grubengletscher, Wallis, Swiss Alps. Arct. Alp. Res. 1979, 11, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsch, D. Rock glaciers: Indicators for the Present and Former Geoecology. In High Mountain Environments; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996; p. 331. [Google Scholar]
- Haeberli, W. Modern research perspectives relating to permafrost creep and rock glaciers: A discussion. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2000, 11, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeberli, W.; Frauenfelder, R.; Hoelzle, M.; Maisch, M. On rates and acceleration trends of global glacier mass changes. Geogr. Ann. Ser. A-Phys. Geogr. 1999, 81A, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PermaNET. Permafrost Long-Term Monitoring Network. Synthesis Report; Interpraevent Journal Series 1, Report 3; International Research Society INTERPRAEVENT: Klagenfurt, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vonder Mühll, D. Drilling in alpine permafrost. Norsk Geografisk Tidsskrift 1996, 50, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenson, L.; Hoelzle, M.; Springman, S. Borehole deformation measurements and internal structure of some rock glaciers in Switzerland. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2002, 13, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapozza, C.; Baron, L.; Lambiel, C. Borehole logging in alpine periglacial talus slopes (Valais, Swiss Alps). Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2015, 26, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PERMOS. Permafrost in Switzerland 2014/2015 to 2017/2018. In Swiss Permafrost Bulletin; Noetzli, J., Pellet, C., Staub, B., Eds.; Cryospheric Commission of the Swiss Academy of Sciences (SCNAT): Zurich, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Boaga, J.; Phillips, M.; Noetzli, J.; Haberkorn, A.; Kenner, R.; Bast, A. A Comparison of Frequency Domain Electro-Magnetometry, Electrical Resistivity Tomography and Borehole Temperatures to Assess the Presence of Ice in a Rock Glacier. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaksen, K.; Odegard, R.S.; Eiken, T.; Sollid, J.L. Composition, flow and development of two tongue-shaped rock glaciers in the permafrost of Svalbard. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2000, 11, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, C.; Kneisel, C. Application of capacitively-coupled and DC electrical resistivity imaging for mountain permafrost studies. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2006, 17, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krautblatter, M.; Hauck, C. Electrical resistivity tomography monitoring of permafrost in solid rock walls. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, F02S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbich, C.; Marescot, L.; Hauck, C.; Loke, M.H.; Mäusbacher, R. Applicability of electrical resistivity tomography monitoring to coarse blocky and ice-rich permafrost landforms. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2009, 20, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Daengeli, S.; Hauck, C.; Hoelzle, M. A spatial and temporal analysis of different periglacial materials by using geoelectrical, seismic and borehole temperature data at murtel-corvatsch, upper engadin, swiss alps. Geogr. Helv. 2013, 68, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthling, I.; Etzelmüller, B.; Isaksen, K.; Sollid, J.L. The rock glaciers on Prins Karls Forland (II): GPR soundings and the development of internal structures. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2000, 11, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, C.; Vonder Muhll, D.; Maurer, H. Using DC resistivity tomography to detect and characterize mountain permafrost. Geophys. Prospect. 2003, 51, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, C.; Vonder Muhll, D. Inversion and interpretation of 2-dimensional geoelectrical measurements for detecting permafrost in mountainous regions. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2003, 14, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draebing, D. Application of refraction seismic in alpine permafrost studies: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 155, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthling, I.; Etzelmüller, B.; Wale, M.; Sollid, J.L. Use of Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) soundings for investigating internal structures in rock glaciers. Examples from Prins Karls Forland, Svalbard. Z. Fur Geomorphol. Suppl. 2003, 132, 103–121. [Google Scholar]
- Farbrot, H.; Isaksen, K.; Eiken, T.; Kääb, A.; Sollid, J.L. Composition and internal structures of a rock glacier on the strand flat of western Spitsbergen, Svalbard. Norsk Geografisk Tidsskrift 2005, 59, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Sharkhuu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Kadota, T.; Ohata, T. Ground thermal and moisture conditions at the southern boundary of discontinuous permafrost, Mongolia. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2005, 16, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbich, C.; Hauck, C.; Hoelzle, M.; Scherler, M.; Schudel, L.; Völksch, I. Monitoring mountain permafrost evolution using electrical resistivity tomography: A 7-year study of seasonal, annual, and long-term variations at Schilthorn, Swiss Alps. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, F01S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneisel, C.; Hauck, C.; Fortier, R.; Moorman, B. Advances in geophysical methods for permafrost investigations. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2008, 19, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krautblatter, M.; Verleysdonk, S.; Flores-Orozco, A.; Kemna, A. Temperature-calibrated imaging of seasonal changes in permafrost rock walls by quantitative electrical resistivity tomography (Zugspitze, German/Austrian Alps). J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, F02003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, C.; Böttcher, M.; Mauer, H. A new model for estimating subsurface ice content based on combined electrical and seismic data sets. Cryosphere 2011, 5, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, H.; Krainer, K.; Brückl, E.; Ullrich, C. Internal structure, ice content and dynamics of Ölgrube and kaiserberg rock glaciers (Ötztal Alps, Austria) determined from geophysical surveys. Austrian J. Earth Sci. 2012, 105, 12–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mollaret, C.; Hilbich, C.; Pellet, C.; Flores-Orozco, A.; Delaloye, R.; Hauck, C. Mountain permafrost degradation documented through a network of permanent electrical resistivity tomography sites. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 2557–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneisel, C.; Beylich, A.A.; Sæmundsson, T. Reconnaissance surveys of contemporary permafrost environments in central Iceland using geoelectrical methods: Implications for permafrost degradation and sediment fluxes. Geogr. Ann. 2007, 89, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeberli, W.; Kaab, A.; Muhll, D.V.; Teysseire, P. Prevention of outburst floods from periglacial lakes at Grubengletscher, Valais, Swiss Alps. J. Glaciol. 2001, 47, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaloye, R.; Lambiel, C.; Gärtner-Roer, I. Overview of rock glacier kinematics research in the Swiss Alps: Seasonal rhythm, interannual variations and trends over several decades. Geograph. Helv. 2010, 65, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaksen, K.; Ødegård, R.S.; Etzelmüller, B.; Hilbich, C.; Hauck, C.; Farbrot, H. Degrading mountain permafrost in southern Norway: Spatial and temporal variability of mean ground temperatures, 1999–2009. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2011, 22, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckli, L.; Brenning, A.; Gruber, S.; Noetzli, J. Permafrost distribution in the European Alps: Calculation and evaluation of an index map and summary statistics. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krainer, K.; Bressan, D.; Dietre, B.; Haas, J.N.; Hajdas, I.; Lang, K.; Tonidandel, D. A 10,300-year-old permafrost core from the active rock glacier Lazaun, southern Ötztal Alps (South Tyrol, northern Italy). Quat. Res. 2015, 83, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenner, R.; Phillips, M.; Beutel, J.; Hiller, M.; Limpach, P.; Pointner, E. Factors controlling velocity variations at Short-term, seasonal and multiyear time Scales, ritigraben Rock Glacier, western Swiss Alps. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2017, 28, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenner, R.; Phillips, M.; Hauck, C.; Hilbich, C.; Mulsow, C.; Bühler, Y. New insights on permafrost genesis and conservation in talus slopes based on observations at Flüelapass, Eastern Switzerland. Geomorphology 2017, 290, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roer, I.; Kääb, A.; Dikau, R. Rock glacier acceleration in the Turtmann valley (Swiss Alps): Probable controls. Norsk Geografisk Tidsskrift 2005, 59, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, F.; Hergarten, S. Rock glacier dynamics: Stick-slip motion coupled to hydrology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krainer, K.; Mussner, L.; Behm, M.; Haussman, H. Multi-disciplinary investigation of an active rock glacier in the Sella Group (Dolomites; Northern Italy). Austrian J. Earth Sci. 2012, 105, 48–62. [Google Scholar]
- Arenson, L.; Jakob, M. Periglacial geohazard risks and ground temperature increases. Eng. Geal. Soc. Territory. 2014, 1, 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Bodin, X.; Krysiecki, J.M.; Schoeneich, P.; Le Roux, O.; Lorier, L.; Echelard, T. The 2006 collapse of the Bérard Rock Glacier (Southern French Alps). Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2017, 28, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kääb, A.; Haeberli, W.; Teysseire, P. Entwicklung und Sanierung eines Thermokarstsees am Gruben-Blockgletscher (Wallis). Forschungsberichte Geographisches Institut Universität Freiburg 1996, 8, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Haeberli, W. Glaciers and Permafrost-Investigating glacier–permafrost relationships in high-mountain areas: Historical background, selected examples and research needs. In Cryospheric Systems; Harris, C., Murton, J.B., Eds.; Geological Society: London, UK, 2005; pp. 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Bommer, C.; Phillips, M.; Arenson, L.U. Practical recommendations for planning, constructing and maintaining infrastructure in mountain permafrost. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2010, 21, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvillard, P.A.; Ravanel, L.; Marcer, M.; Schoeneich, P. Recent evolution of damage to infrastructure on permafrost in the French Alps. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2019, 19, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PERMOS. Permafrost in Switzerland: 2002/2003 and 2003/2004. In Swiss Permafrost Bulletin; Cryospheric Commission of the Swiss Academy of Sciences (SCNAT): Zurich, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hauck, C.; Kneisel, C. Applied Geophysics in Periglacial Environments; Cambridge University Press, Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dafflon, B.; Hubbard, S.S.; Ulrich, C.; Peterson, J.E. Electrical conductivity imaging of active layer and permafrost in an Arctic ecosystem, through advanced inversion of electromagnetic induction data. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, vzj2012.0161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PermaNET. Permafrost in the Veneto Region: Distribution, analysis of potential environmental effects permanent project. In Alpine Space Programme Report, Regione del Veneto; PermaNET: Venezia, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Binley, A. Tools and Techniques: Electrical Methods. In Treatise on Geophysics, 2nd ed.; Schubert, G., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2015; Volume 11, pp. 233–259. [Google Scholar]
- Binley, A.; Kemna, A. DC resistivity and induced polarization methods. In Hydrogeophysics; Rubin, Y., Hubbard, S.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, G.; Bruno, V.; Villa, A.; Fusi, N.; Binley, A. A saline trace test monitored via time-lapse surface electrical resistivity tomography. J. Appl. Geophys. 2006, 59, 244–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchy, G.; Saneiyan, S.; Boyd, J.; McLachlan, P.; Binley, A. ResIPy, an intuitive open-source software for complex geoelectrical inversion/modeling. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 137, 104423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koestel, J.; Kemna, A.; Javaux, M.; Binley, A.; Vereecken, H. Quantitative imaging of solute transport in an unsaturated and undisturbed soil monolith with 3-D ERT and TDR. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwakanyamale, K.; Slater, L.; Binley, A.; Ntarlagiannis, D. Lithologic imaging using complex conductivity: Lessons learned from the Hanford 300 Area. Geophysics 2012, 77, E397–E409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaga, J. The use of FDEM in Hydrogeophysics. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 139, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, P.; Blanchy, G.; Binley, A. EMagPy: Open-source standalone software for processing, forward modeling and inversion of electromagnetic induction data. Comput. Geosci. 2021, 146, 104561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollaret, C.; Wagner, F.M.; Hilbich, C.; Scapozza, C.; Hauck, C. Petrophysical joint inversion applied to alpine permafrost field sites to image subsurface ice, water, air and rock contents. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L. Past, Present, and Future Trends in Soil Electrical Conductivity Measurements Using Geophysical Methods. Handb. Agric. Geophys. 2008, 17–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock, M.D.; McDonnell, J.J. A New Tool for Hillslope Hydrologists: Spatially Distributed Groundwater Level and Soilwater Content Measured Using Electromagnetic Induction. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 1965–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafilis, J.; Lesch, S.M. Mapping Clay Content Variation Using Electromagnetic Induction Techniques. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 203–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaga, J.; Ghinassi, M.; D’Alpaos, A.; Deidda, G.P.; Rodriguez, G.; Cassiani, G. Geophysical investigations unravel the vestiges of ancient meandering channels and their dynamics in tidal landscapes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pedrera-Parrilla, A.; Vanderlinden, K.; Taguas, E.V.; Gómez, J.A.; Triantafilis, J. Potential to Map Depth-Specific Soil Organic Matter Content across an Olive Grove Using Quasi-2d and Quasi-3d Inversion of DUALEM-21 Data. CATENA 2017, 152, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaga, J.; Viezzoli, A.; Cassiani, G.; Deidda, G.P.; Tosi, L.; Silvestri, S. Resolving the thickness of peat deposits with contact-less electromagnetic methods: A case study in the Venice coastland. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, P.; McNeill, D. Electromagnetic probing of permafrost. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Permafrost, Yakutsk, Siberia, 12–20 July 1973; pp. 517–526. [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli, A.N.; French, R.B. Electro-magnetic induction methods for mapping permafrost along northern pipeline corridors. Geophys. Subsea Permafr. 1982, 283–295. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, K.; Wada, K.; Fukuda, M. Permafrost Mapping by Transient Electromagnetic Method. Permafrost Periglac. Process. 2000, 11, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, C.; Guglielmin, M.; Isaksen, K.; Vonder Mühll, D. Applicability of frequency-domain and time-domain electromagnetic methods for mountain permafrost studies. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2001, 12, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minsley, B.J.; Smith, B.D.; Hammack, R.; Sams, J.I.; Veloski, G. Calibration and filtering strategies for frequency domain electromagnetic data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 80, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, F.C.M.; Fischer, T.; Valenta, J. Study of Errors in Conductivity Meters Using the Low Induction Number Approximation and How to Overcome Them. In Proceedings of the Near Surface Geoscience-22nd European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Byrd, R.H.; Lu, P.; Nocedal, J.; Zhu, C. A Limited Memory Algorithm for Bound Constrained Optimization. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1995, 16, 1190–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, F.X.; Sarris, A.; Thiesson, J.; Tabbagh, A. Mapping of quadrature magnetic susceptibility/magnetic viscosity of soils by using multi-frequency EMI. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 120, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press, Ed.; Oxford University: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, J.E. Bedrock detection beneath river terrace deposits using three-dimensional electrical resistivity tomography. Geomorphology 2012, 177–178, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussner, L. Die Geologie der Sella-Nordseite (Dolomiten Südtirol) unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Blockgletscher. Master’s Thesis, University of Innsbruck, Innsbruck, Austria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Panissod, C.; Dabas, A.; Jolivet, A.; Tabbagh, A. A novel mobile multipole system (MUCEP) for shallow (0–3m) geoelectrical investigation: The “Vol-de-canards” array. Geophys. Prospect. 1997, 45, 983–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olhoeft, G.R. Electrical properties of permafrost. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Permafrost, Edmonton, Canada, National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 10–13 July 1978; pp. 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kneisel, C.; Hauck, C. Multi-method geophysical investigation of an isolated permafrost occurrence. Z. Für Geomorphol. Suppl. 2003, 132, 145–159. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, F.M.; Mollaret, C.; Günther, T.; Kemna, A.; Hauck, C. Quantitative imaging of water, ice, and air in permafrost systems through petrophysical joint inversion of seismic refraction and electrical resistivity data. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 219, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, C.; Günther, T.; Wagner, F.M. pyGIMLi: An open-source library for modelling and inversion in geophysics. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 109, 06–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Instrument | MAE Digital Georesistivimeter |
| Power Supply | 60 A–12 V External battery |
| Configuration | Dipole–Dipole skip 0 |
| Current Injection Time | 250 ms |
| Stack Max | 6 |
| V Min | 0.001 V |
| V Max | 800 V |
| Electrodes Number | 48 |
| Spacing | 1.5 m |
| Array Length | 70.5 m |
| Instrument Probe | Coil Spacing | Frequency | Nominal Exploration Depth (HCP–VCP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.48 m | 10 kHz | 2.2 m–1.1 m |
| 2 | 2.82 m | 10 kHz | 4.2 m–2.1 m |
| 3 | 4.49 m | 10 kHz | 6.7 m–3.3 m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavoni, M.; Sirch, F.; Boaga, J. Electrical and Electromagnetic Geophysical Prospecting for the Monitoring of Rock Glaciers in the Dolomites, Northeast Italy. Sensors 2021, 21, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041294
Pavoni M, Sirch F, Boaga J. Electrical and Electromagnetic Geophysical Prospecting for the Monitoring of Rock Glaciers in the Dolomites, Northeast Italy. Sensors. 2021; 21(4):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041294
Chicago/Turabian StylePavoni, Mirko, Fabio Sirch, and Jacopo Boaga. 2021. "Electrical and Electromagnetic Geophysical Prospecting for the Monitoring of Rock Glaciers in the Dolomites, Northeast Italy" Sensors 21, no. 4: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041294
APA StylePavoni, M., Sirch, F., & Boaga, J. (2021). Electrical and Electromagnetic Geophysical Prospecting for the Monitoring of Rock Glaciers in the Dolomites, Northeast Italy. Sensors, 21(4), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041294








