An X-Band CMOS Digital Phased Array Radar from Hardware to Software
Abstract
:1. Introduction
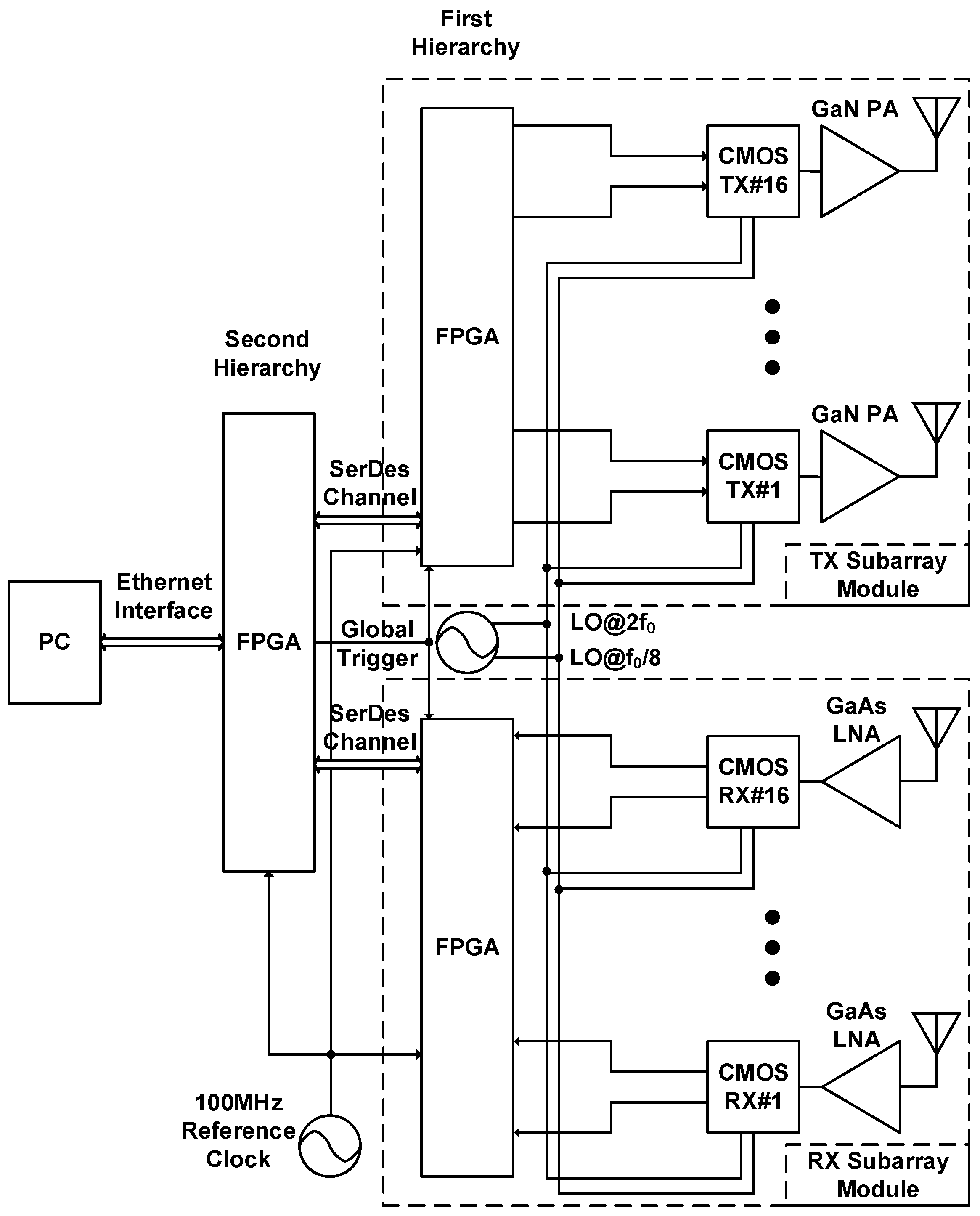
2. System Architecture of the Proposed Radar
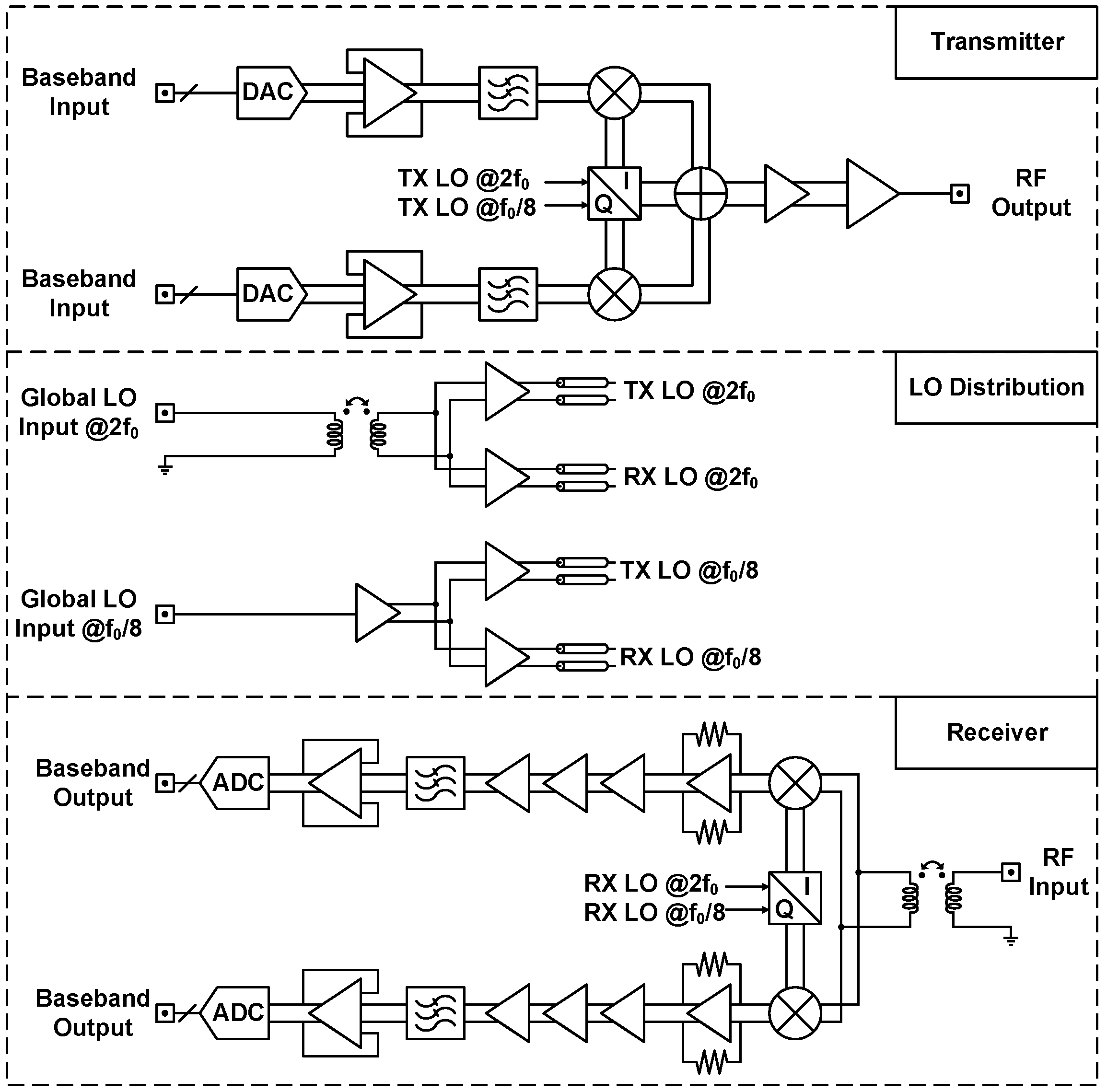
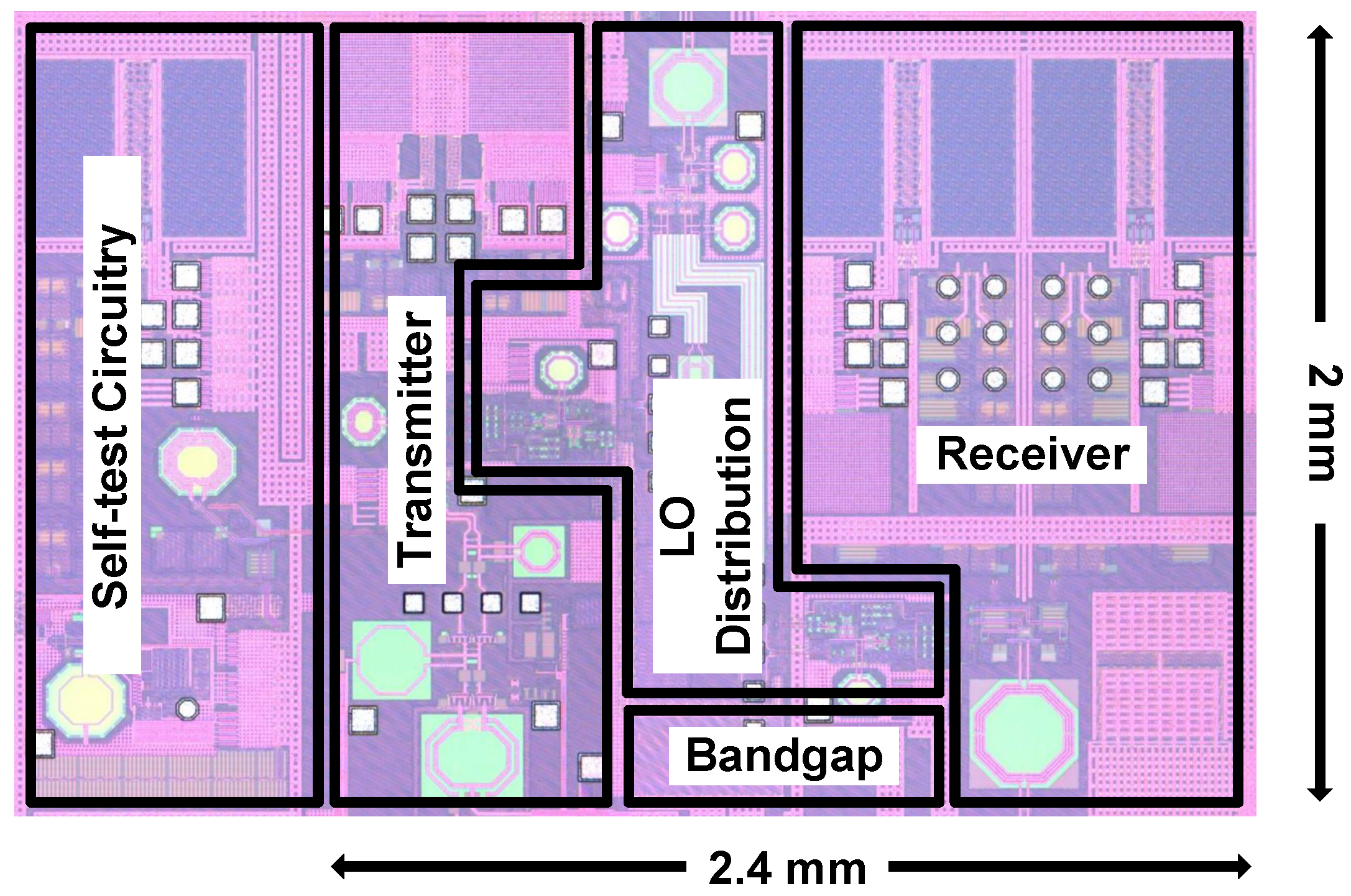
3. Circuit Implementation of X-Band Transceiver
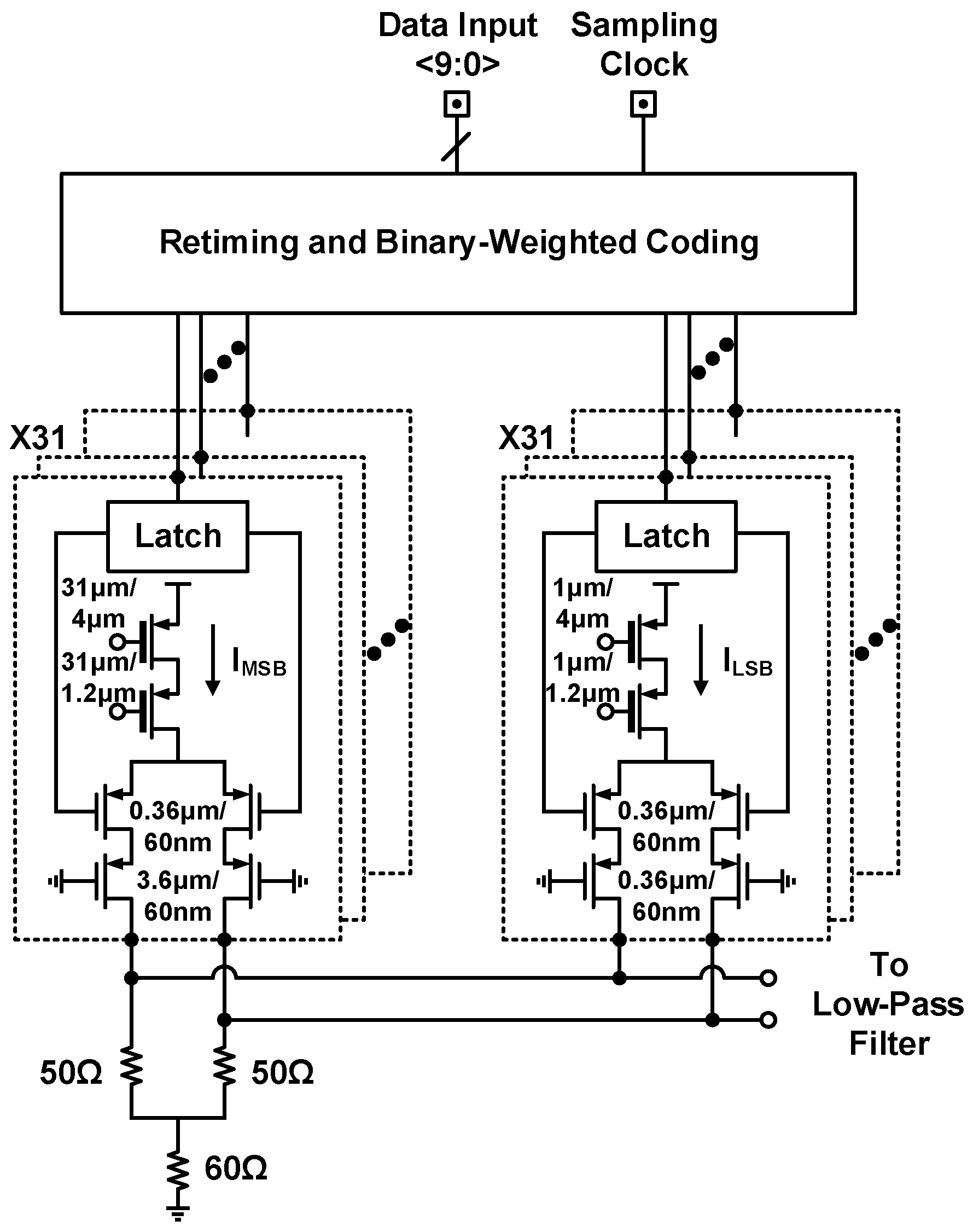
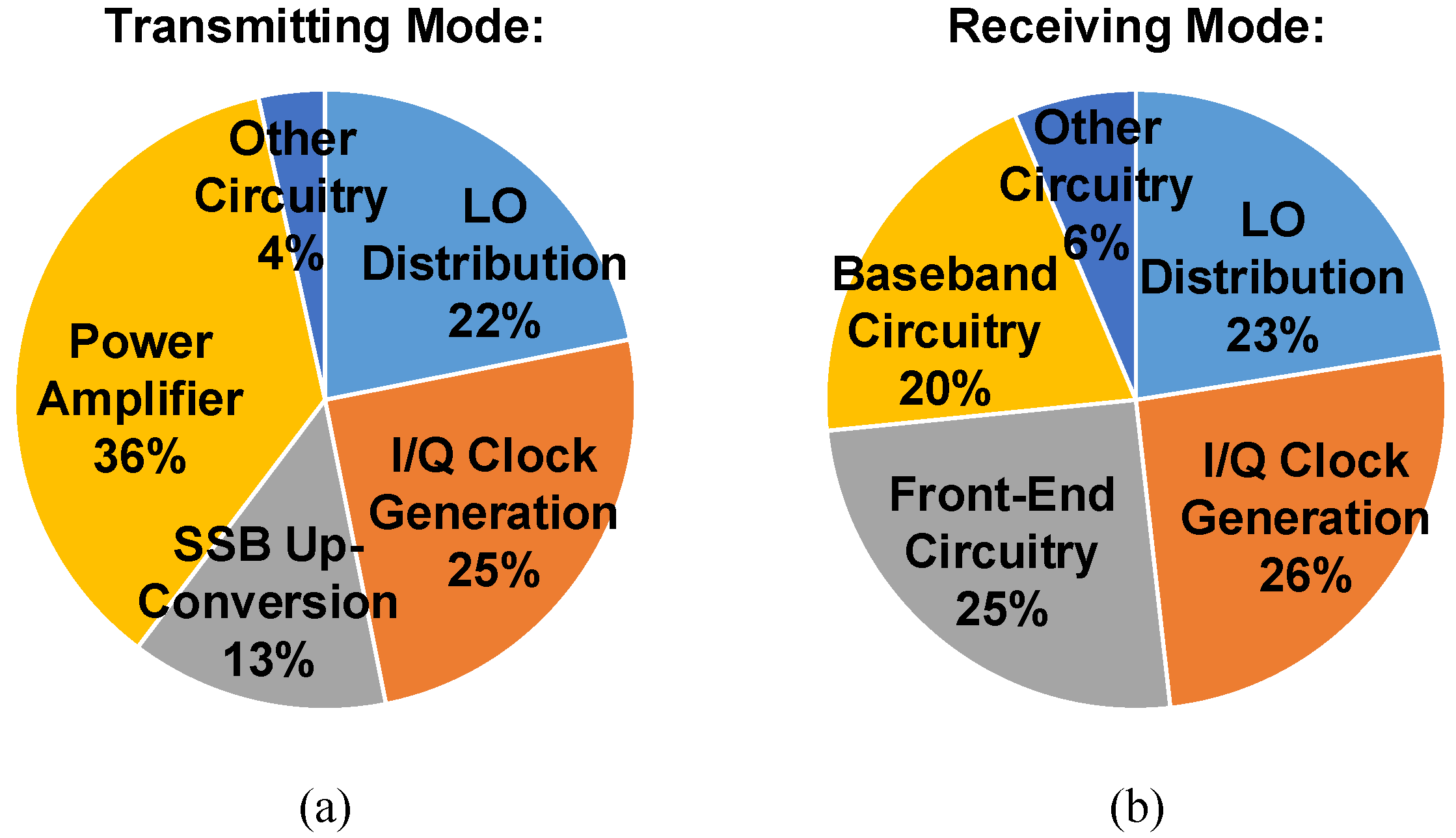
3.1. Transmitter Design
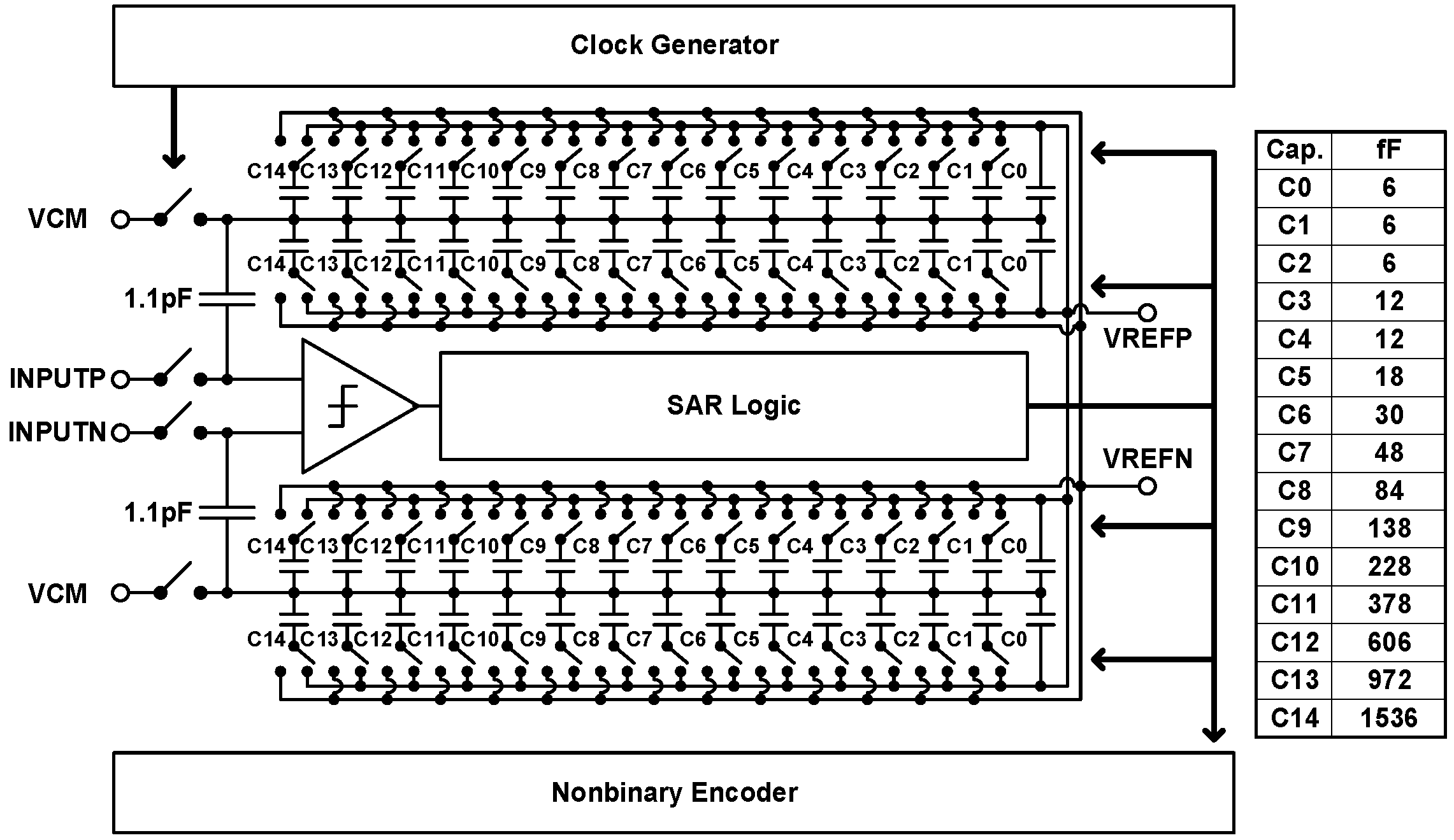
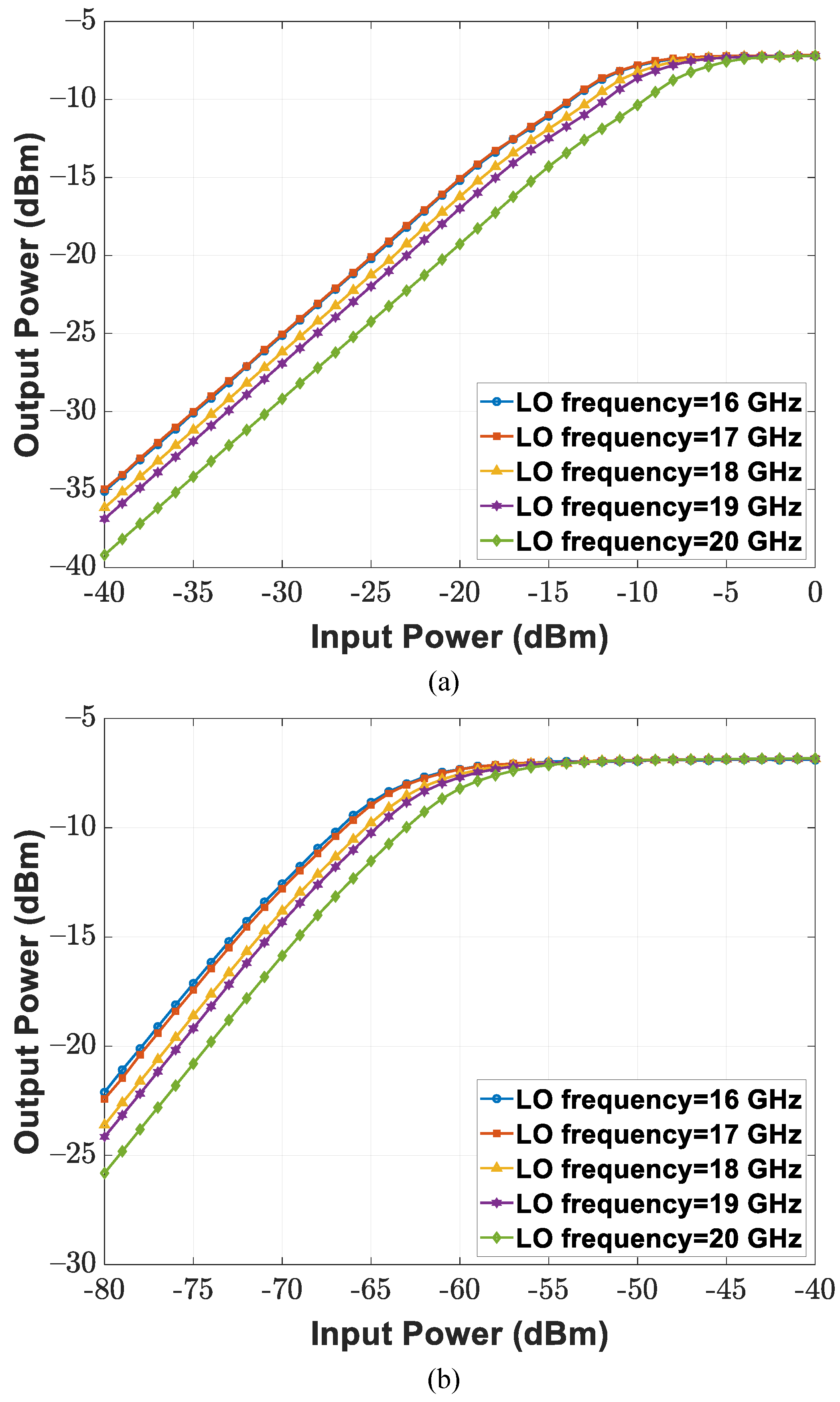
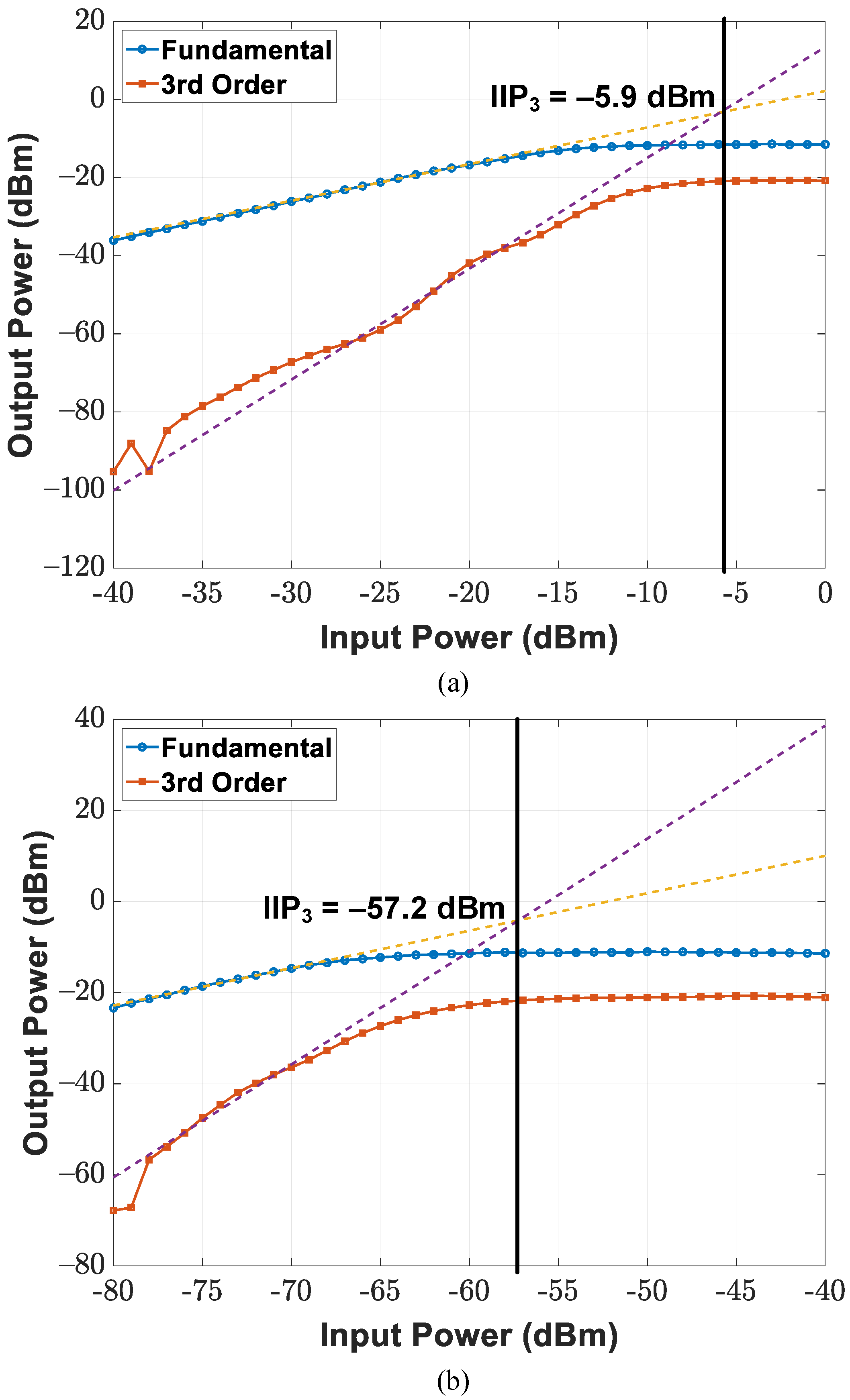
3.2. Receiver Design
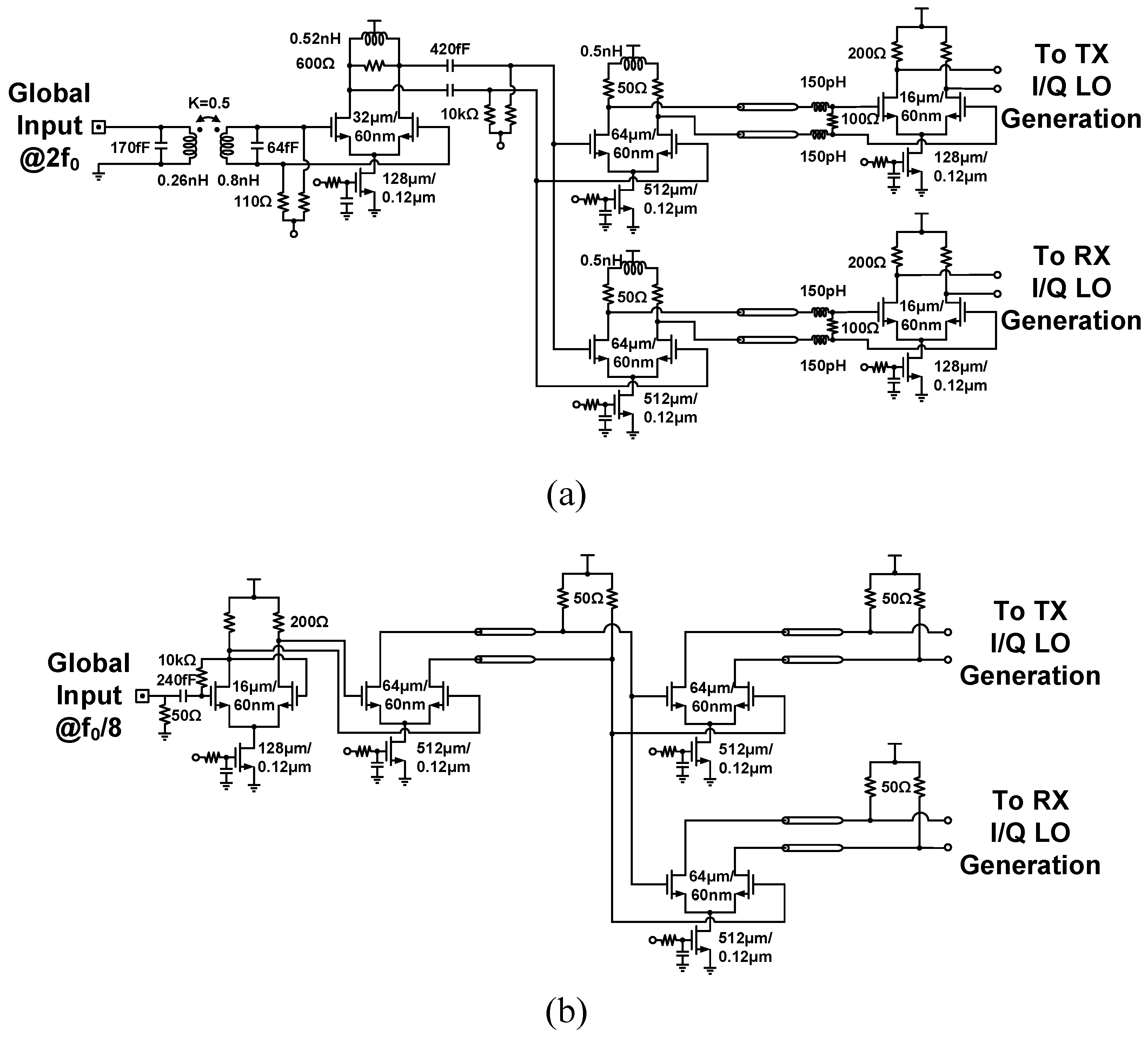
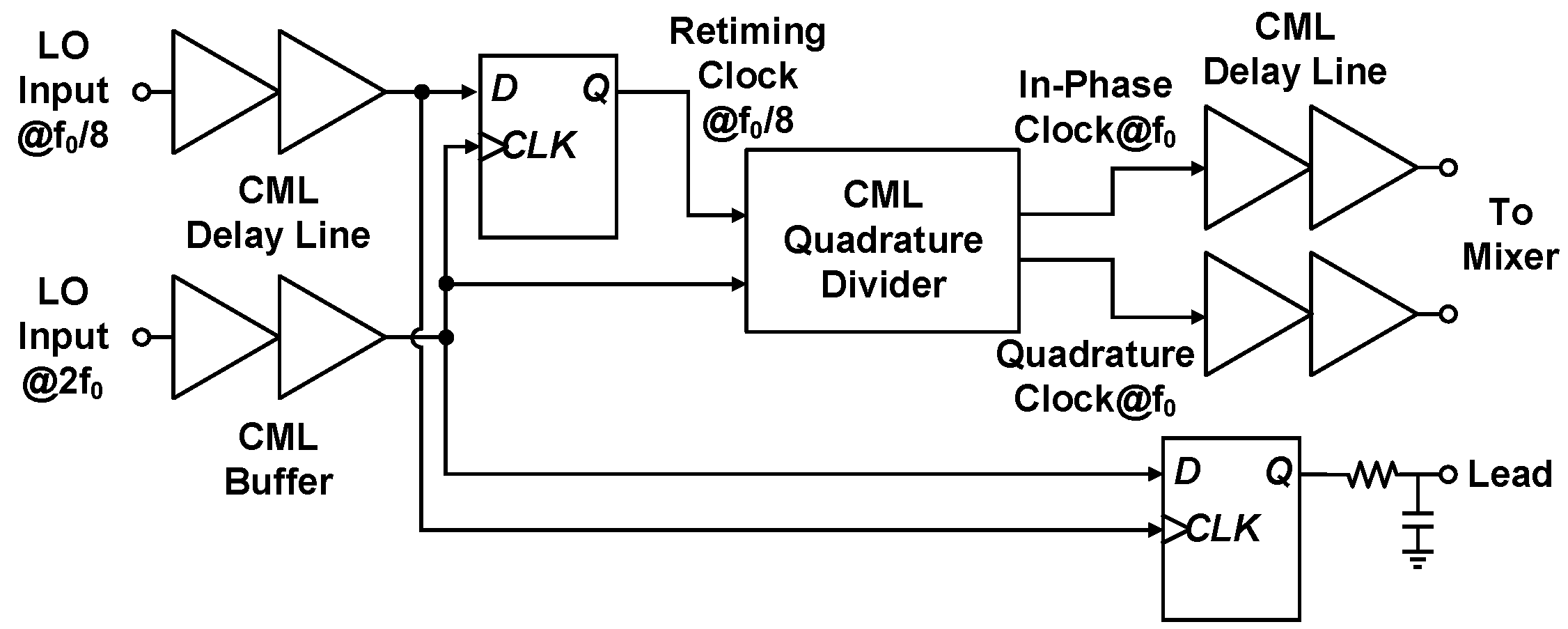
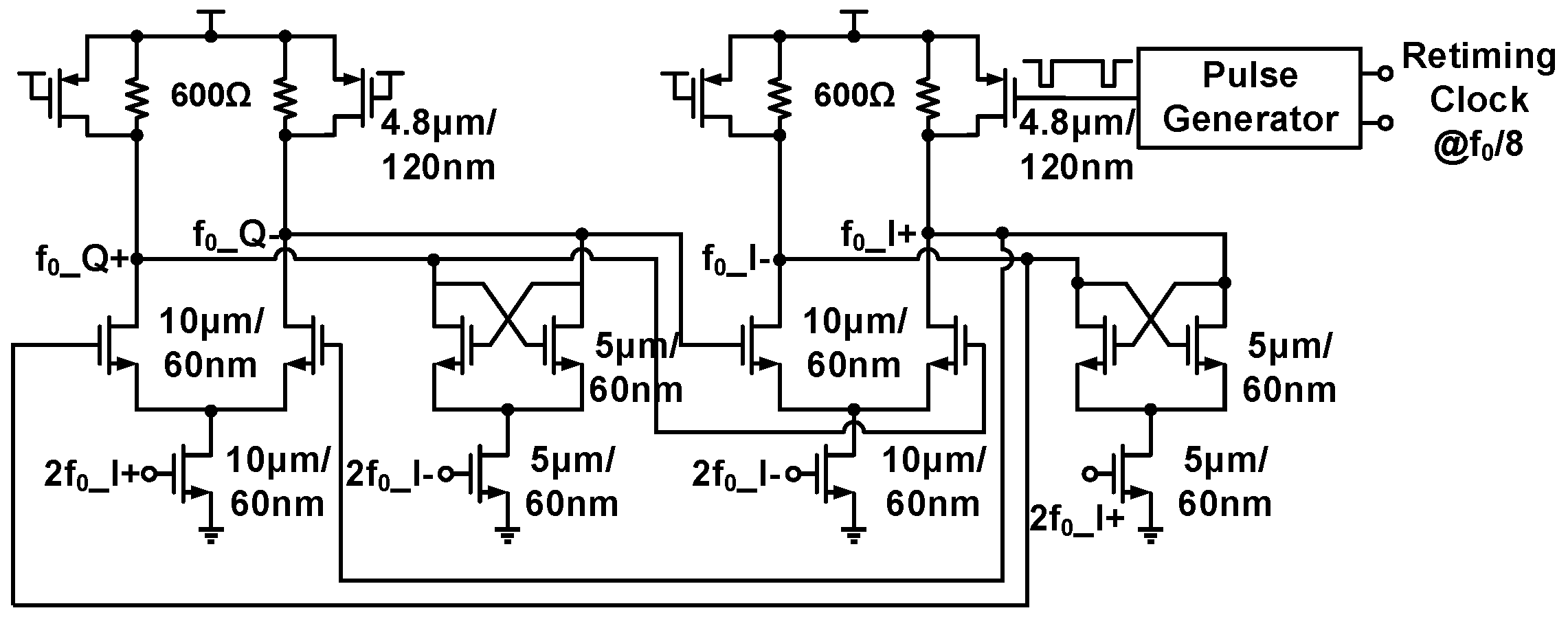
3.3. LO Distribution and Quadrature Clock Generation
4. System Integration of the Proposed Radar
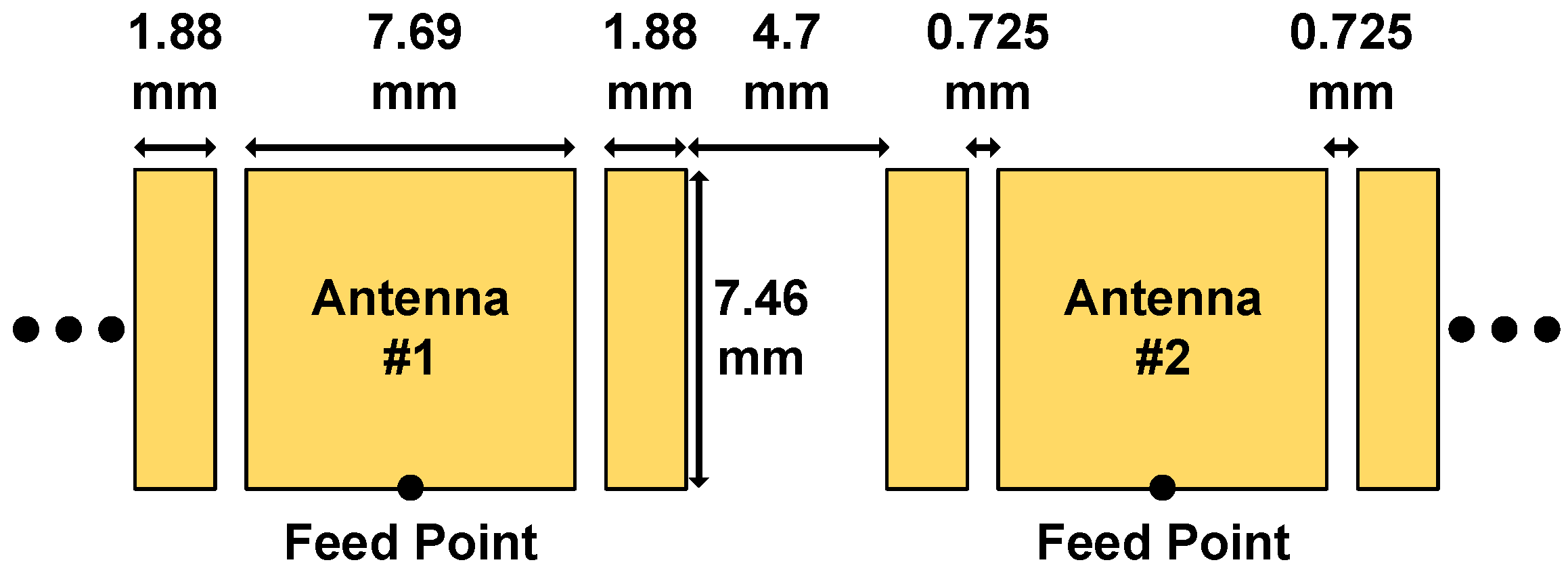
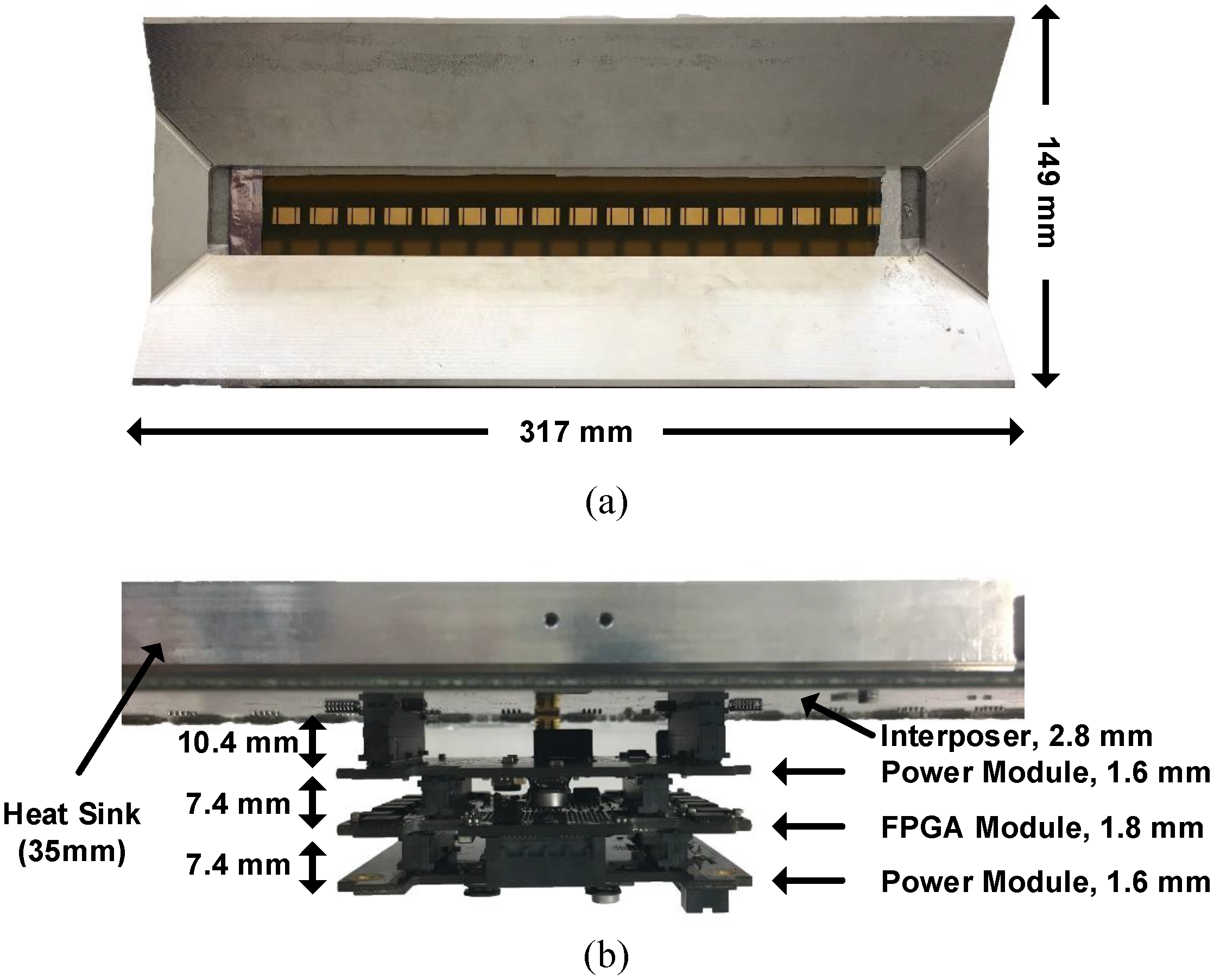
4.1. Array Element Packaging
4.2. Assembly of 1 × 16 Subarray Module
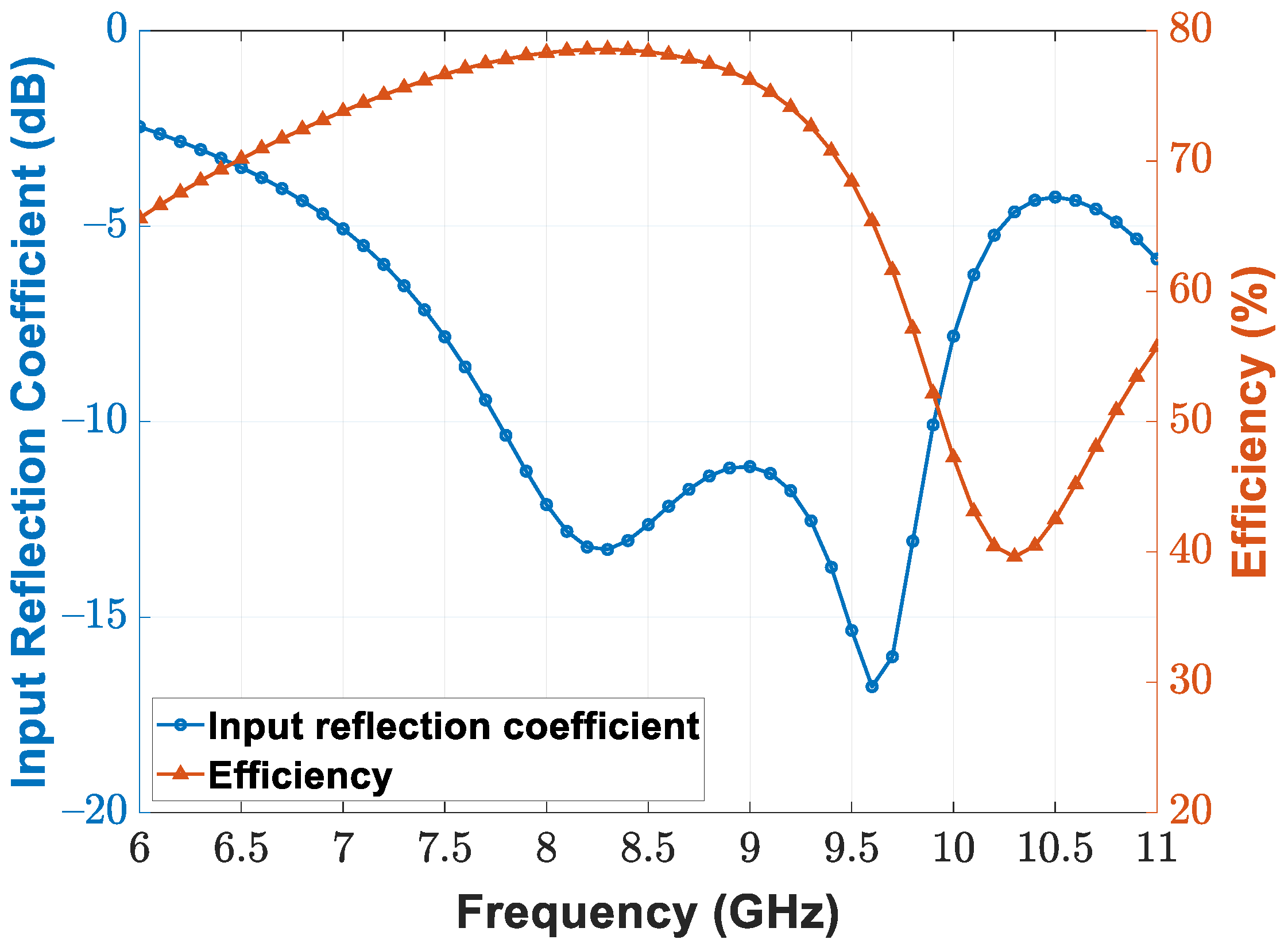
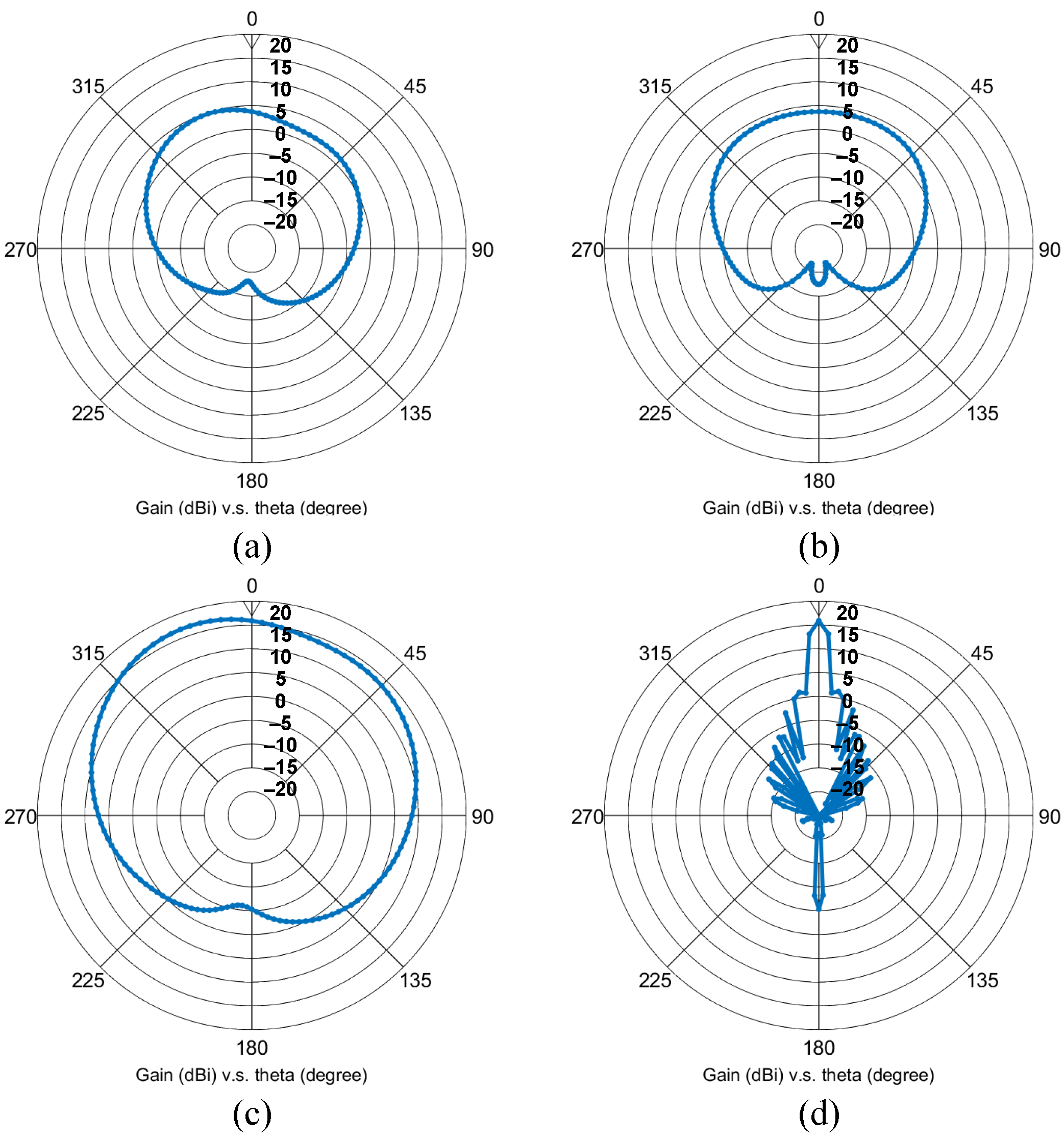
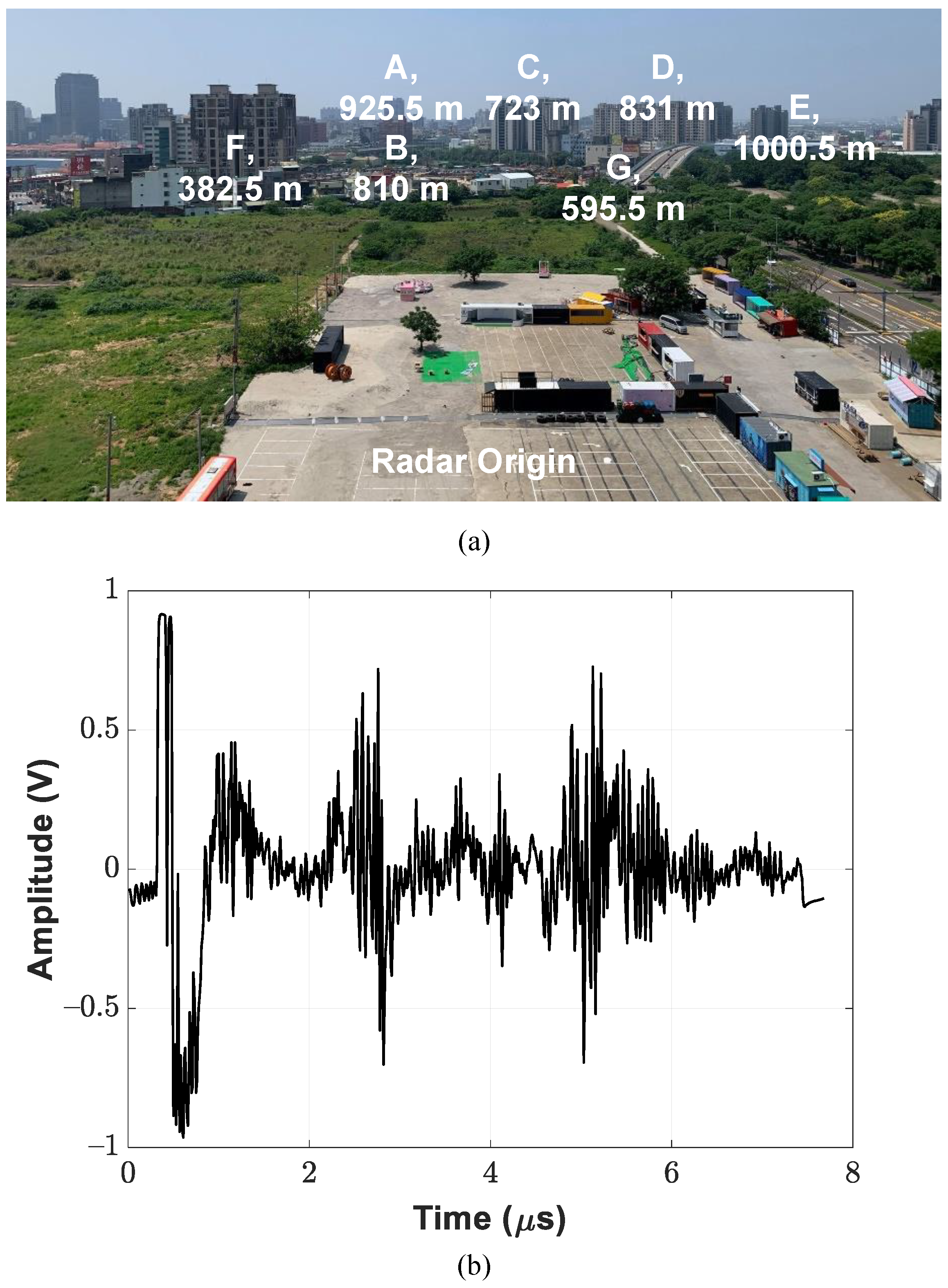
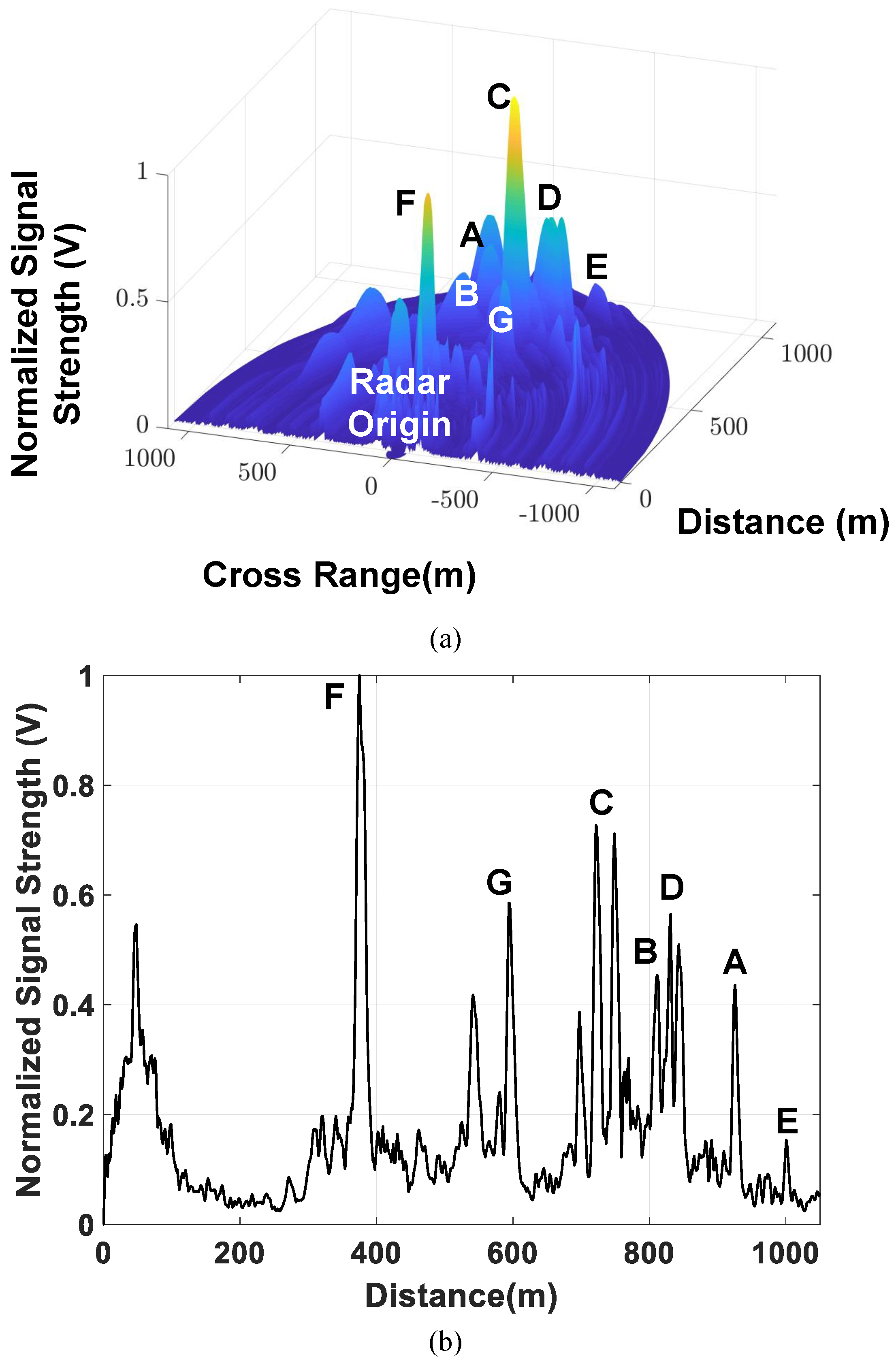
5. Experimental Results
5.1. CMOS Transceiver
5.2. Radar Demonstrator with 1 × 16 Subarray Modules
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herd, J.S.; Conway, M.D. The Evolution to Modern Phased Array Architectures. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talisa, S.H.; O’Haver, K.W.; Comberiate, T.M.; Sharp, M.D.; Somerlock, O.F. Benefits of Digital Phased Array Radars. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, N.; Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. Digital Beamforming on Receive: Techniques and Optimization Strategies for High-Resolution Wide-Swath SAR Imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2009, 45, 564–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huber, S.; Younis, M.; Patyuchenko, A.; Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. Spaceborne Reflector SAR Systems with Digital Beamforming. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 3473–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayaratna, S.; Madanayake, A.; Wijenayake, C.; Bruton, L.T. Digital VLSI Architectures for Beam-Enhanced RF Aperture Arrays. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 1996–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babur, G.; Manokhin, G.O.; Geltser, A.A.; Shibelgut, A.A. Low-Cost Digital Beamforming on Receive in Phased Array Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulipati, S.K.; Ariyarathna, V.; Madanayake, A.; Wijesekara, R.T.; Edussooriya, C.U.S.; Bruton, L.T. A 16-Element 2.4-GHz Multibeam Array Receiver Using 2-D Spatially Bandpass Digital Filters. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 55, 3029–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y. A Novel MIMO-SAR System Based on Simultaneous Digital Beam Forming of Both Transceiver and Receiver. Sensors 2020, 20, 6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, C.; Yeary, M.; Thompson, D.; Lake, J.; Mitchell, A. Digital Phased Arrays: Challenges and Opportunities. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglielli, A.; Townley, A.; LaCaille, G.; Milovanović, V.; Lu, P.; Trotskovsky, K.; Niknejad, A.M. Design of Energy- and Cost-Efficient Massive MIMO Arrays. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 586–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.V.; Nam, H.; Choe, Y.J.; Lee, B.H.; Park, J.D. An X-band Bi-Directional Transmit/Receive Module for a Phased Array System in 65-nm CMOS. Sensors 2018, 18, 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, J.K.; Noh, C.K.; Lee, J.S.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, T.H.; Jung, H.N.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, C.S.; Kim, Y.J. RF Transceiver for the Multi-Mode Radar Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, L.; Chen, B.; Liu, S.; Zheng, Y. A Ku-band 260 mW FMCW synthetic aperture radar TRX with 1.48 GHz BW in 65 nm CMOS for micro-UAVs. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 31 January–4 February 2016; pp. 240–242. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lou, L.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, K.; Qiu, L.; Zheng, Y. A 260-mW Ku-band FMCW transceiver for synthetic aperture radar sensor with 1.48-GHz bandwidth in 65-nm CMOS technology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 4385–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.; Tang, K.; Chen, B.; Guo, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zheng, Y. A 253 mW/channel 4TX/4RX pulsed chirping phased-array radar TRX in 65 nm CMOS for X-band synthetic-aperture radar imaging. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2018; pp. 160–162. [Google Scholar]
- Sayginer, M.; Rebeiz, G.M. An eight-element 2–16-GHz programmable phased array receiver with one, two, or four simultaneous beams in SiGe BiCMOS. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 4585–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.H.; Chou, H.C.; Peng, C.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Su, B.; Chu, T.S. A single-port duplex RF front-end for X-band single-antenna FMCW radar in 65 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2017; pp. 318–320. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, H.C.; Kao, Y.H.; Peng, C.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Chu, T.S. An X-Band Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave Radar Sensor System With a Single-Antenna Interface for Ranging Applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, N.; Jackson, R.W. Active Antenna Module for Low-Cost Electronically Scanned Phased Arrays. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2008, 56, 2286–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhu, B.; Tousi, Y.; Hallin, J.; Sahl, S.; Reynolds, S.K.; Renström, Ö.; Valdes-Garcia, A. A 28-GHz 32-element TRX phased-array IC with concurrent dual-polarized operation and orthogonal phase and gain control for 5G communications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 3373–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.K.; Chun, J.H.; Kwon, Y.S. A 3-D X-band T/R Module Package With an Anodized Aluminum Multilayer Substrate for Phased Array Radar Applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2010, 33, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, W.; Fulton, C. Digital Array Radar panel development. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology, Waltham, MA, USA, 12–15 October 2010; pp. 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, J.A.; Díaz, J.; Aboserwal, N.; Salazar, J.L.; Jeon, L.; Sim, S.; Chun, J. Ultra-compact universal polarization X-band unit cell for high-performance active phased array radar. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology (PAST), Waltham, MA, USA, 18–21 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Urzaiz, F.I.; de Quevedo, Á.D.; Ayuso, A.M.; Machado, Á.G.; Menoyo, J.G.; López, A.A. Design, implementation and first experimental results of an X-band ubiquitous radar system. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 23–27 April 2018; pp. 1150–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Iijima, K.; Okada, Y.; Kumamoto, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Ikeuchi, H.; Sawahara, Y.; Shinonaga, M. Compact Superconducting Sub-array Module for X-band Phased Array Antenna. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 23–27 April 2018; pp. 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, T.; Fulton, C.; Yeary, M.; Saunders, A.; Thompson, D.; Murmann, B.; Guo, A. IMPACT—A common building block to enable next generation radar arrays. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2–6 May 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, T.; Fulton, C.; Yeary, M.; Saunders, A.; Thompson, D.; Murmann, B.; Guo, A. Measured performance of the IMPACT common module—A building block for next generation phase arrays. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology (PAST), Waltham, MA, USA, 18–21 October 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, T.; Livadaru, M.; Jensen, D. IMPACT common module and S-band planar array beamforming measurements. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 23–27 April 2018; pp. 588–592. [Google Scholar]
- Ganis, A.; Navarro, E.M.; Schoenlinner, B.; Prechtel, U.; Meusling, A.; Heller, C.; Ziegler, V. A portable 3-D imaging FMCW MIMO radar demonstrator with a 24 × 24 antenna array for medium-range applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, L.A. The Role of FPGAs in the Push to Modern and Ubiquitous Arrays. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, K.C.; Lee, L.; Chu, T.S.; Huang, Y.H. A Two-Stage Reconstruction Processor for Human Detection in Compressive Sensing CMOS Radar. Sensors 2018, 18, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, H.; Guo, S.; Zhao, P.; Gong, M.; Shen, C. Design and Implementation of a Real-Time Multi-Beam Sonar System Based on FPGA and DSP. Sensors 2021, 21, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.M.; Ke, C.Y.; Wang, C.C.; Tang, Y.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Li, C.T.; Wang, Y.J. An X-band Scalable 4 × 4 Digital Phased Array Module using RF SoC and Antenna-in-Package. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, MA, USA, 22–26 April 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Qorvo. TGA2598-SM. 2019. Available online: https://www.qorvo.com/products/p/TGA2598-SM (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Qorvo. TGA2512-SM. 2019. Available online: https://www.qorvo.com/products/p/TGA2512-1-SM (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Analog Devices. ADF5355 Evaluation Board. 2019. Available online: https://www.analog.com/en/design-center/evaluation-hardware-and-software/evaluation-boards-kits/eval-adf5355.html (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Wang, H.; Sideris, C.; Hajimiri, A. A CMOS Broadband Power Amplifier With a Transformer-Based High-Order Output Matching Network. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 2709–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, C.; Molnar, A.C. A Passive Mixer-First Receiver With Digitally Controlled and Widely Tunable RF Interface. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 2696–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayoun, A.; Razavi, B. A low-power CMOS receiver for 5 GHz WLAN. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.S.; del Mar Hershenson, M.; Boyd, S.P.; Lee, T.H. Bandwidth extension in CMOS with optimized on-chip inductors. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2000, 35, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, M.; Hildebrandt, J.; Ziroff, A.; Zwick, T. Self-Calibration of a 3-D-Digital Beamforming Radar System for Automotive Applications With Installation Behind Automotive Covers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 2994–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Deng, X.D.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Xiong, Y.Z. A fully integrated X-band phased-array transceiver in 0.13-μm SiGe BiCMOS technology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| TMTT2018 [18] | ISSCC2018 [15] | TMTT2017 [14] | TMTT2016 [16] | TMTT2016 [42] | This Work | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency Band | 9.8–10.2 GHz | 9.5–10.5 GHz | 14.26–15.74 GHz | 2–16 GHz | 9–11 GHz | 8–10 GHz |
| Technology | 65 nm CMOS | 65 nm CMOS | 65 nm CMOS | 0.13 m SiGe BiCMOS | 0.13 m SiGe BiCMOS | 65 nm CMOS |
| Die Size | 1.9 × 2 mm | 2 × 3.9 mm | 1.4 × 2.9 mm | 2.5 × 5 mm | 3 × 5.2 mm | 2 × 2.4 mm |
| SoC Integration | 1TX + 1RX | 4TX + 4RX | 1TX + 1RX | 8RX | 1TX + 1RX | 1TX + 1RX |
| TX Output Power | 10.5 dBm | 14.7 dBm | 13.3 dBm | - | 29.2 dBm | 17.96 dBm |
| TX Spurious Level | - | - | - | - | - | −30.35 dBc |
| RX Conversion Gain | 5–72 dB | Front-end: 15.3–28.6 dB Baseband: 0–60 dB | Front-end: 23.5 dB Baseband: 3–58 dB | 6–11 dB | 25 dB | 3.8–57.2 dB |
| RX Noise Figure | 16.5–18 dB | 5.7–6.5 dB | 5.6–6.3 dB | 11.5–12.3 dB | 3 dB | 13.9–14.6 dB |
| RX Front-End Input P | 2 dBm at 5 dB Gain −27 dBm at 32 dB Gain | −37 dBm | −33 dBm | −14 dBm | −18 dBm | −14 dBm |
| RX Front-End IIP | 7 dBm at 5 dB Gain | - | - | - | - | −5.9 dBm |
| RX Baseband Bandwidth | 2 MHz | 60–280 MHz | 0.68–9.8 MHz | - | - | 20 or 40 MHz |
| Power Consumption | 147 mW | 179 mW per TX 74 mW per RX | 259.4 mW | 250 mW per RX | 4.128 W per TX 352 mW per RX | 1.45 W per TX 1.41 W per RX |
| Number of Elements in the Demonstrator | - | 4TX + 4RX | - | 8RX | 1TX + 1RX | 16TX + 16RX |
| Beamforming Scheme | - | TX: RF Phase-Shifting, RX: Digital Beamforming | - | RF Phase-Shifting, Digital Beamforming | RF Phase-Shifting | Digital Beamforming |
| Modulation Type | Triangular Chirp | Pulsed Chirp | Sawtooth Chirp | - | - | Pulsed Chirp |
| Modulation Bandwidth | 400 MHz (4%) | 1 GHz (10%) | 1.48 GHz (9.9%) | - | - | Programmable, 20 MHz for Pulsed Radar |
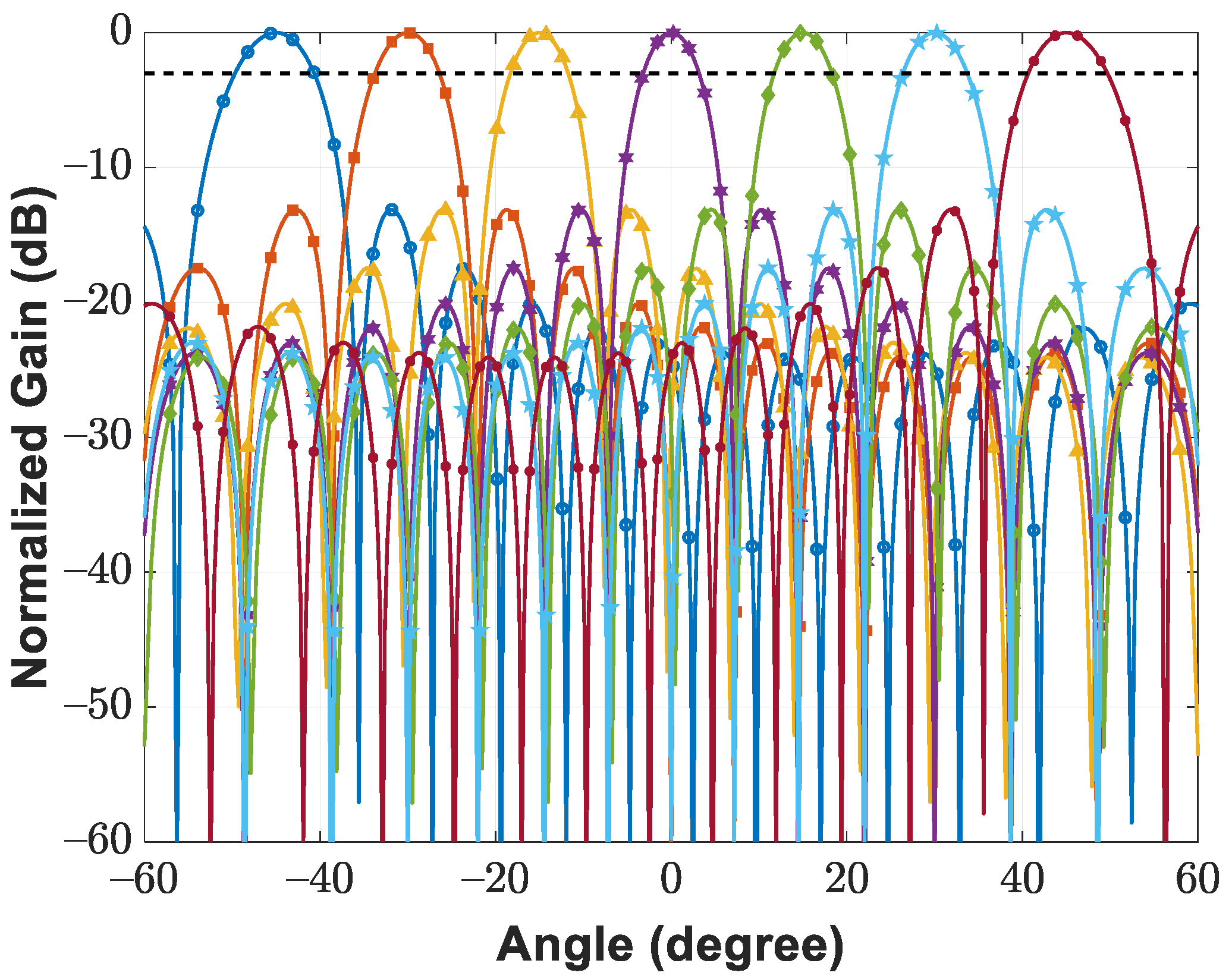
| Multibeamforming Capability | - | Yes (4 beams) | - | Yes (1, 2, or 4 beams) | - | Yes (16 beams) |
| Beam Steering Range | - | - | - | - | E-plane: | |
| Peak Sidelobe Ratio (PSLR) | - | −12.9 dB w/o tapering | −12.7 dB w/o tapering | - | - | −13.1 dB w/o tapering −25.6 dB w/i tapering |
| Radar Imaging Latency | - | off-line | - | - | - | 150 ms per pulsed radar image |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.-M.; Chou, H.-C.; Ke, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Li, C.-T.; Chang, L.-H.; Su, B.; Chu, T.-S.; Wang, Y.-J. An X-Band CMOS Digital Phased Array Radar from Hardware to Software. Sensors 2021, 21, 7382. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217382
Wu Y-M, Chou H-C, Ke C-Y, Wang C-C, Li C-T, Chang L-H, Su B, Chu T-S, Wang Y-J. An X-Band CMOS Digital Phased Array Radar from Hardware to Software. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7382. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217382
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yue-Ming, Hao-Chung Chou, Cheng-Yung Ke, Chien-Cheng Wang, Chien-Te Li, Li-Han Chang, Borching Su, Ta-Shun Chu, and Yu-Jiu Wang. 2021. "An X-Band CMOS Digital Phased Array Radar from Hardware to Software" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7382. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217382
APA StyleWu, Y.-M., Chou, H.-C., Ke, C.-Y., Wang, C.-C., Li, C.-T., Chang, L.-H., Su, B., Chu, T.-S., & Wang, Y.-J. (2021). An X-Band CMOS Digital Phased Array Radar from Hardware to Software. Sensors, 21(21), 7382. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217382






