COVID-19 Case Recognition from Chest CT Images by Deep Learning, Entropy-Controlled Firefly Optimization, and Parallel Feature Fusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A hybrid contrast enhancement technique is proposed by sequentially employing linear filters.
- Transfer learning is performed by fine tuning the parameters of two deep CNN models.
- Features are extracted from both models and an entropy-controlled Firefly optimization algorithm is implemented for optimal features’ selection.
- Selected optimal features are fused using a parallel positive correlation approach.
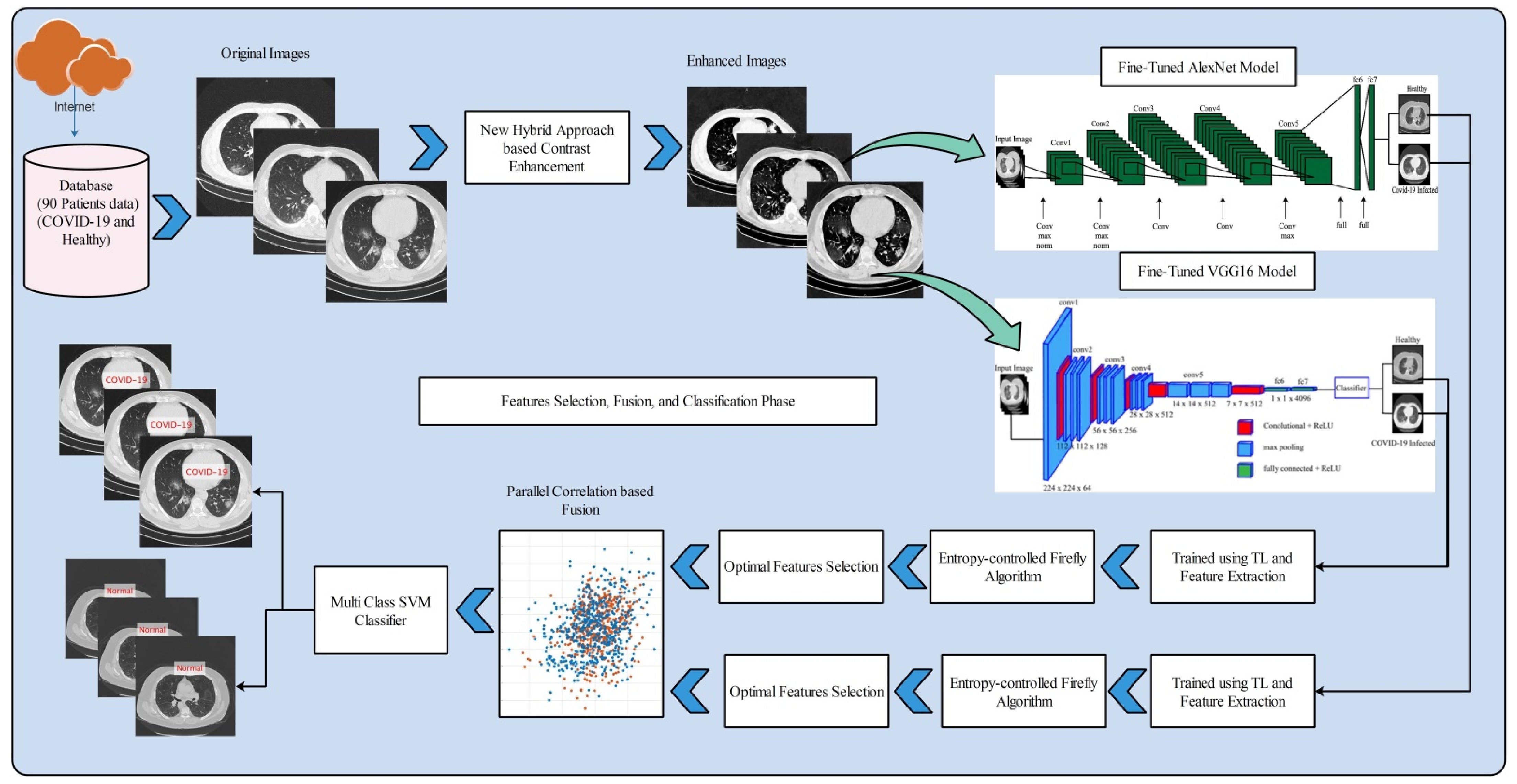
2. Methodology
2.1. Dataset Preparation
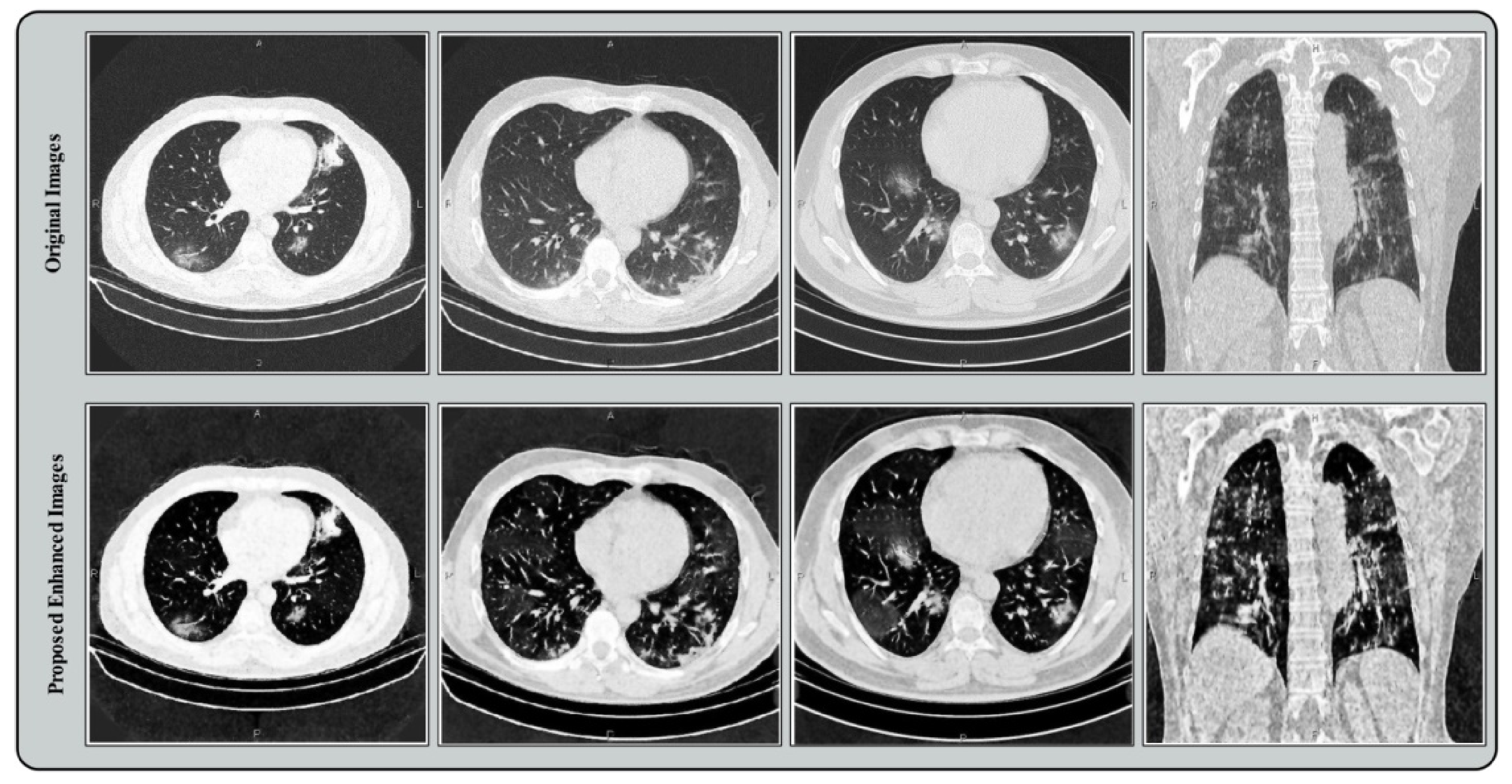
2.2. Contrast Enhancement
2.3. Modified AlexNet Deep Learning Model
2.4. Modified VGG16 Deep Learning Model
2.5. Feature Selection
| Algorithm 1. FA-Based Feature Optimization. |
| Start Step 1: Step 2:, where Step 3: Step 4: Define Absorption Coefficient - - - - - Vary attractiveness with distance via - Move firefly towards using - Evaluate new solutions and update brightness - - - - Find the latest best Firefly - Entropy-based activation is applied - Best Optimal Features are Selected - - Processing results and visualization End |
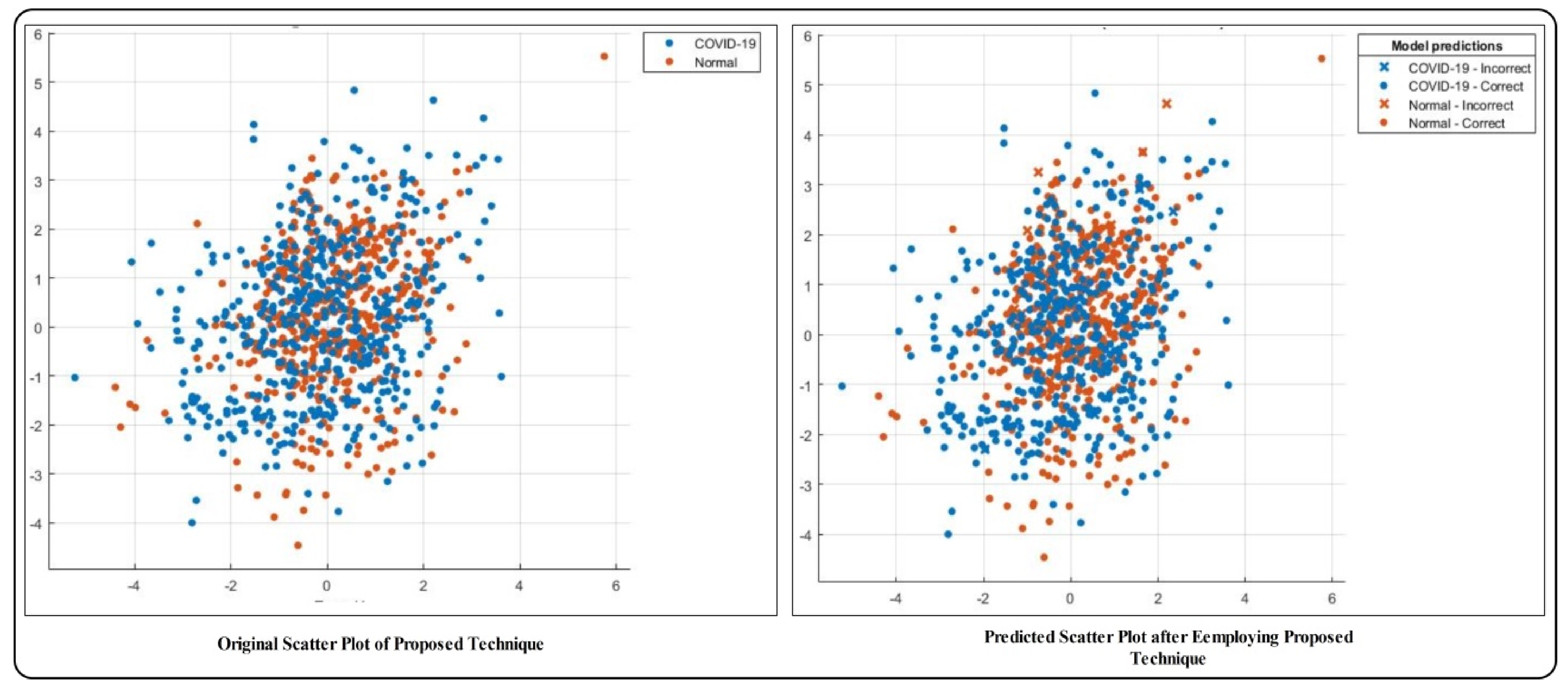
2.6. Feature Fusion and Classification
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Results
| Classifier | Evaluation Measures | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (%) | Precision (%) | F1-Score (%) | AUC | Accuracy (%) | FNR (%) | Time (Seconds) | |
| MC-SVM | 98.0 | 98.05 | 98.02 | 0.99 | 98.0 | 2.0 | 12.416 |
| DT | 94.4 | 94.4 | 94.40 | 0.94 | 94.4 | 5.6 | 13.522 |
| LDA | 94.2 | 94.5 | 94.35 | 0.94 | 94.2 | 5.8 | 20.968 |
| KNB | 94.8 | 94.95 | 94.87 | 0.95 | 94.8 | 5.2 | 42.861 |
| QSVM | 97.6 | 97.65 | 97.62 | 0.99 | 97.6 | 2.4 | 15.202 |
| F-KNN | 96.9 | 95.45 | 96.17 | 0.97 | 96.9 | 3.1 | 12.115 |
| Cosine KNN | 96.5 | 96.5 | 96.50 | 0.99 | 96.5 | 3.5 | 12.334 |
| EBT | 96.3 | 96.35 | 96.32 | 0.97 | 96.3 | 3.7 | 20.253 |
3.2. Analysis and Comparison
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoecklin, S.B.; Rolland, P.; Silue, Y.; Mailles, A.; Campese, C.; Simondon, A.; Mechain, M.; Meurice, L.; Nguyen, M.; Bassi, C.; et al. First cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in France: Surveillance, investigations and control measures, January 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K.S.M.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Wong, J.Y.; et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girdhar, A.; Kapur, H.; Kumar, V.; Kaur, M.; Singh, D.; Damasevicius, R. Effect of COVID-19 outbreak on urban health and environment. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 14, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakijkosol, O.; Jaroenram, W.; Owens, L.; Elliman, J. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) detection for Australian Cherax reovirus from redclaw crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus). Aquaculture 2020, 530, 735881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, D.; Kaur, M.; Damaševičius, R. Overview of current state of research on the application of artificial intelligence techniques for COVID-19. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyasseri, Z.A.A.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Abu Doush, I.; Awadallah, M.A.; Abasi, A.K.; Makhadmeh, S.N.; Alomari, O.A.; Abdulkareem, K.H.; Adam, A.; Damasevicius, R.; et al. Review on COVID-19 diagnosis models based on machine learning and deep learning approaches. Expert Syst. 2021, e12759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-H.; Nayak, D.R.; Guttery, D.S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.-D. COVID-19 classification by CCSHNet with deep fusion using transfer learning and discriminant correlation analysis. Inf. Fusion 2020, 68, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, T.; Attique, M.; Gul, S.; Shahzad, A.; Altaf, M.; Naqvi, S.S.R.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R. A novel framework for rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 on computed tomography scans. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2021, 24, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, N.; Sultan Zia, M.; Meraj, T.; Rauf, H.T.; Damaševičius, R.; El-Sherbeeny, A.M.; El-Meligym, M.A. A Self-Activated CNN Approach for Multi-Class Chest-Related COVID-19 Detection. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, A.; Hafsa, N.E.; Ali, M.A.; Alhumam, A.; Alsalman, S. An Ensemble of Global and Local-Attention Based Convolu-tional Neural Networks for COVID-19 Diagnosis on Chest X-ray Images. Symmetry 2021, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, S.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Dey, N.; Rajinikanth, V.; Gandhi, T.K. Deep transfer learning-based automated detection of COVID-19 from lung CT scan slices. Appl. Intell. 2020, 51, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, A.A.; Kanafi, A.R.; Acharya, U.R.; Khadem, N.; Mohammadi, A. Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansana, D.; Kumar, R.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Hemanth, D.J.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A.; Castillo, O. Early diagnosis of COVID-19-affected patients based on X-ray and computed tomography images using deep learning algorithm. Soft Comput. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, N.; Rajinikanth, V.; Fong, S.J.; Kaiser, M.S.; Mahmud, M. Social Group Optimization–Assisted Kapur’s Entropy and Morphological Segmentation for Automated Detection of COVID-19 Infection from Computed Tomography Images. Cogn. Comput. 2020, 12, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunraj, H.; Wang, L.; Wong, A. COVIDNet-CT: A Tailored Deep Convolutional Neural Network Design for Detection of COVID-19 Cases from Chest CT Images. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 608525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loey, M.; Smarandache, F.; Khalifa, N.E.M. Within the Lack of Chest COVID-19 X-ray Dataset: A Novel Detection Model Based on GAN and Deep Transfer Learning. Symmetry 2020, 12, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rauf, H.T.; Lali, M.I.U.; Khan, M.A.; Kadry, S.; Alolaiyan, H.; Razaq, A.; Irfan, R. Time series forecasting of COVID-19 transmission in Asia Pacific countries using deep neural networks. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.; Siłka, J.; Połap, D.; Woźniak, M.; Damaševičius, R. Real-time neural network based predictor for cov19 virus spread. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, F.; Korkmaz, D. COVIDiagnosis-Net: Deep Bayes-SqueezeNet based Diagnostic of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) from X-ray Images. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 140, 109761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Hussain, N.; Majid, A.; Alhaisoni, M.; Bukhari, S.A.C.; Kadry, S.; Nam, Y.; Zhang, Y.-D. Classification of pos-itive COVID-19 CT scans using deep learning. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 66, 2923–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketu, S.; Mishra, P.K. Enhanced Gaussian process regression-based forecasting model for COVID-19 outbreak and signifi-cance of IoT for its detection. Appl. Intell. 2020, 51, 1492–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Chandna, H.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Upadhyay, N.; Utkarsh, K. IoT-Q-Band: A low cost internet of things based wearable band to detect and track absconding COVID-19 quarantine subjects. EAI Endorsed Trans. Internet Things 2020, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismael, A.M.; Şengür, A. Deep learning approaches for COVID-19 detection based on chest X-ray images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 164, 114054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Gupta, M.; Taneja, S.; Hemanth, D.J. Deep learning based detection and analysis of COVID-19 on chest X-ray images. Appl. Intell. 2020, 51, 1690–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kumar, V.; Yadav, V.; Singh, D.; Kumar, N.; Das, N.N. Metaheuristic-based Deep COVID-19 Screening Model from Chest X-Ray Images. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8829829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zheng, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Zhao, H.; Zha, Y.; et al. Deep learning Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) with CT images. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Kadry, S.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Akram, T.; Sharif, M.; Rehman, A.; Saba, T. Prediction of COVID-19—Pneumonia based on Selected Deep Features and One Class Kernel Extreme Learning Machine. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2020, 90, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Kumar, V.; Kaur, M. Densely connected convolutional networks-based COVID-19 screening model. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 3044–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, N.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Rajinikanth, V.; Pugalenthi, R.; Raja, N.S.M. Customized VGG19 architecture for pneumonia detection in chest X-rays. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 143, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Gianchandani, N.; Singh, D.; Kumar, V.; Kaur, M. Classification of the COVID-19 infected patients using DenseNet201 based deep transfer learning. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 39, 5682–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.; Chung, H.; Kang, W.S.; Kim, K.W.; Shin, Y.; Kang, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, N.Y.; Jung, H.; et al. COVID-19 pneumonia diagnosis using a simple 2d deep learning framework with a single chest ct image: Model development and validation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e19569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Gao, Y.; Niu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Xiao, X.; Wang, M.; Fang, E.F.; Menpes-Smith, W.; Xia, J.; et al. Weakly Supervised Deep Learning for COVID-19 Infection Detection and Classification from CT Images. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 118869–118883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Su, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zeng, L.-L.; Feng, Z.; Shen, H.; Rong, P.; Xu, X.; Qin, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Dual-branch combination network (DCN): Towards accurate diagnosis and lesion segmentation of COVID-19 using CT images. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 67, 101836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Sun, Z.Y.; Qi, L.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Fang, Y.; Xing, Z.; et al. A deep learning approach to characterize 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia in chest CT images. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6517–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horry, M.J.; Chakraborty, S.; Paul, M.; Ulhaq, A.; Pradhan, B.; Saha, M.; Shukla, N. COVID-19 detection through transfer learning using multimodal imaging data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 149808–149824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, T.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, E.A.; Baloglu, U.B.; Yildirim, O.; Acharya, U.R. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Z.; Islam, M.; Asraf, A. A combined deep CNN-LSTM network for the detection of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) using X-ray images. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 20, 100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulodimos, A.; Protopapadakis, E.; Katsamenis, I.; Doulamis, A.; Doulamis, N. A Few-Shot U-Net Deep Learning Model for COVID-19 Infected Area Segmentation in CT Images. Sensors 2021, 21, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.A.; Ahsan, M.; Based, A.; Haider, J.; Kowalski, M. COVID-19 Detection from Chest X-Ray Images Using Feature Fusion and Deep Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafeldeen, A.; Elsharkawy, M.; Alghamdi, N.S.; Soliman, A.; El-Baz, A. Precise Segmentation of COVID-19 Infected Lung from CT Images Based on Adaptive First-Order Appearance Model with Morphological/Anatomical Constraints. Sensors 2021, 21, 5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Shafique, A.; Khalid, S.; Driss, M.; Rubaiee, S. Future Forecasting of COVID-19: A Supervised Learning Approach. Sensors 2021, 21, 3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.I.; Raza, M.; Anjum, A.; Saba, T.; Shad, S.A. Skin lesion segmentation and classification: A unified framework of deep neural network features fusion and selection. Expert Syst. 2019, e12497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Khan, M.A.; Alhaisoni, M.; Wang, S.-H.; Naqvi, S.R.; Rehman, A.; Saba, T. A sustainable deep learning frame-work for object recognition using multi-layers deep features fusion and selection. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzammil, S.; Maqsood, S.; Haider, S.; Damaševičius, R. CSID: A Novel Multimodal Image Fusion Algorithm for Enhanced Clinical Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Sarfraz, M.S.; Alhaisoni, M.; Albesher, A.A.; Wang, S.; Ashraf, I. StomachNet: Optimal Deep Learning Fea-tures Fusion for Stomach Abnormalities Classification. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 197969–197981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlol, A.T.; Elaziz, M.A.; Jamal, A.T.; Damaševičius, R.; Hassan, O.F. A Novel Method for Detection of Tuberculosis in Chest Radiographs Using Artificial Ecosystem-Based Optimisation of Deep Neural Network Features. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Khalil, T.; Nasreen, S. A survey of feature selection and feature extraction techniques in machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2014 Science and Information Conference, London, UK, 27–29 August 2014; pp. 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-S. Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Stochastic Algorithms, Sapporo, Japan, 26–28 October 2009; pp. 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, H.; Zhang, S.; Hapeshi, K. A Review of Nature-Inspired Algorithms. J. Bionic Eng. 2010, 7, S232–S237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Khan, M.A.; Song, O.-Y.; Nazir, M. Medical Imaging Fusion Techniques: A Survey Benchmark Analysis, Open Challenges and Recommendations. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2020, 10, 2523–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, R.; Almazroi, A.; Rauf, H.; Damaševičius, R.; Nasr, E.; Abdelgawad, A. Dilated Semantic Segmentation for Breast Ultrasonic Lesion Detection Using Parallel Feature Fusion. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, L.K.; Padinjappurathu, S.G.; Kadry, S.; Damaševičius, R. Detection of diabetic retinopathy using a fusion of textural and ridgelet features of retinal images and sequential minimal optimization classifier. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, I.; Ubeyli, E.D. Multiclass Support Vector Machines for EEG-Signals Classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2007, 11, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitaula, C.; Hossain, M.B. Attention-based VGG-16 model for COVID-19 chest X-ray image classification. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 2850–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, A.; Khan, M.A.; Nam, Y.; Tariq, U.; Roy, S.; Mostafa, R.R.; Sakr, R.H. COVID19 Classification Using CT Images via Ensembles of Deep Learning Models. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 69, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, P. COVID-CT-dataset: A CT scan dataset about COVID-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.13865. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, T.; Wong, P.K.; Ren, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Automatic distinction between COVID-19 and common pneumonia using multi-scale convolutional neural network on chest CT scans. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozsahin, I.; Sekeroglu, B.; Musa, M.S.; Mustapha, M.T.; Ozsahin, D.U. Review on Diagnosis of COVID-19 from Chest CT Images Using Artificial Intelligence. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020, 2020, 9756518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Muhammad, K.; Sharif, M.; Akram, T.; Kadry, S. Intelligent fusion-assisted skin lesion localization and classification for smart healthcare. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attique Khan, M.; Sharif, M.; Akram, T.; Kadry, S.; Hsu, C.H. A two-stream deep neural network-based intelligent system for complex skin cancer types classification. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-H.; Khan, M.A.; Govindaraj, V.; Fernandes, S.L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.-D. Deep Rank-Based Average Pooling Network for Covid-19 Recognition. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 70, 2797–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Muhammad, K.; Sharif, M.; Akram, T.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. Multi-Class Skin Lesion Detection and Classification via Teledermatology. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Sharif, M.; Akram, T. Pixels to Classes: Intelligent Learning Framework for Multiclass Skin Lesion Localization and Classification. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 90, 106956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Classifier | Deep Model Features | Evaluation Measures | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlexNet | VGG16 | Accuracy (%) | Error Rate (%) | Time (Seconds) | |
| MC-SVM | ✓ | 94.4 | 5.6 | 39.366 | |
| ✓ | 92.4 | 7.6 | 42.896 | ||
| DT | ✓ | 88.3 | 11.7 | 43.266 | |
| ✓ | 88.7 | 11.3 | 40.246 | ||
| LDA | ✓ | 90.1 | 9.9 | 53.042 | |
| ✓ | 89.6 | 10.4 | 59.160 | ||
| KNB | ✓ | 91.6 | 8.4 | 86.116 | |
| ✓ | 87.5 | 12.5 | 94.204 | ||
| QSVM | ✓ | 92.3 | 7.7 | 45.125 | |
| ✓ | 93.6 | 6.4 | 49.334 | ||
| F-KNN | ✓ | 90.7 | 9.3 | 36.846 | |
| ✓ | 92.4 | 7.6 | 44.116 | ||
| Cosine KNN | ✓ | 91.1 | 8.9 | 42.200 | |
| ✓ | 92.9 | 7.1 | 51.244 | ||
| EBT | ✓ | 90.0 | 10.0 | 60.116 | |
| ✓ | 92.7 | 7.3 | 69.201 | ||
| Classifier | Optimal Deep Model Features | Evaluation Measures | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlexNet Optimal | VGG16 Optimal | Accuracy (%) | Error Rate (%) | Time (Seconds) | |
| MC-SVM | ✓ | 96.2 | 3.8 | 14.277 | |
| ✓ | 94.2 | 5.8 | 15.004 | ||
| DT | ✓ | 90.1 | 9.9 | 15.167 | |
| ✓ | 91.2 | 8.8 | 17.286 | ||
| LDA | ✓ | 92.4 | 7.6 | 23.004 | |
| ✓ | 91.6 | 8.4 | 24.120 | ||
| KNB | ✓ | 92.7 | 7.3 | 45.115 | |
| ✓ | 90.3 | 9.7 | 47.016 | ||
| QSVM | ✓ | 93.9 | 6.1 | 17.336 | |
| ✓ | 94.8 | 5.2 | 19.224 | ||
| F-KNN | ✓ | 92.6 | 7.4 | 15.296 | |
| ✓ | 93.5 | 6.5 | 16.110 | ||
| Cosine KNN | ✓ | 93.4 | 6.6 | 15.804 | |
| ✓ | 94.9 | 5.1 | 16.299 | ||
| EBT | ✓ | 92.8 | 7.2 | 23.134 | |
| ✓ | 94.1 | 5.9 | 23.896 | ||
| Method | Accuracy (%) | Error Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| AlexNet + Contrast Enhancement Step | 94.4 | 5.6 |
| AlexNet without Contrast Step | 91.7 | 8.3 |
| VGG16 + Contrast Enhancement Step | 92.4 | 7.6 |
| VGG16 without Contrast Step | 90.3 | 9.7 |
| AlexNet + Contrast Step + Optimal Step | 96.2 | 3.8 |
| VGG16 + Contrast Step + Optimal Step | 94.2 | 5.8 |
| Proposed Method | 98.0 | 2.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.A.; Alhaisoni, M.; Tariq, U.; Hussain, N.; Majid, A.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R. COVID-19 Case Recognition from Chest CT Images by Deep Learning, Entropy-Controlled Firefly Optimization, and Parallel Feature Fusion. Sensors 2021, 21, 7286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217286
Khan MA, Alhaisoni M, Tariq U, Hussain N, Majid A, Damaševičius R, Maskeliūnas R. COVID-19 Case Recognition from Chest CT Images by Deep Learning, Entropy-Controlled Firefly Optimization, and Parallel Feature Fusion. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217286
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Muhammad Attique, Majed Alhaisoni, Usman Tariq, Nazar Hussain, Abdul Majid, Robertas Damaševičius, and Rytis Maskeliūnas. 2021. "COVID-19 Case Recognition from Chest CT Images by Deep Learning, Entropy-Controlled Firefly Optimization, and Parallel Feature Fusion" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217286
APA StyleKhan, M. A., Alhaisoni, M., Tariq, U., Hussain, N., Majid, A., Damaševičius, R., & Maskeliūnas, R. (2021). COVID-19 Case Recognition from Chest CT Images by Deep Learning, Entropy-Controlled Firefly Optimization, and Parallel Feature Fusion. Sensors, 21(21), 7286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217286






