An Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Retrieval Method and Characteristics Analysis of Landscape Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology and Dependence on Experimental Conditions
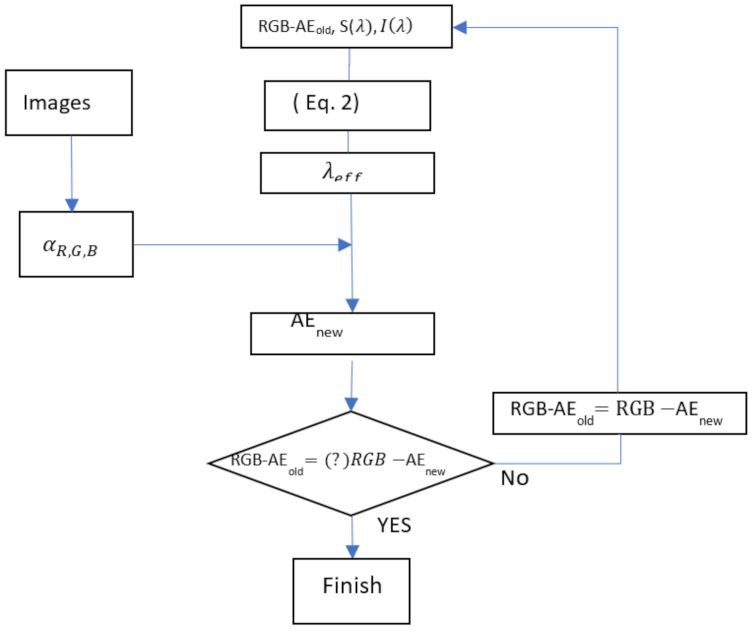
2.1. Theory and Definition of Effective Wavelengths
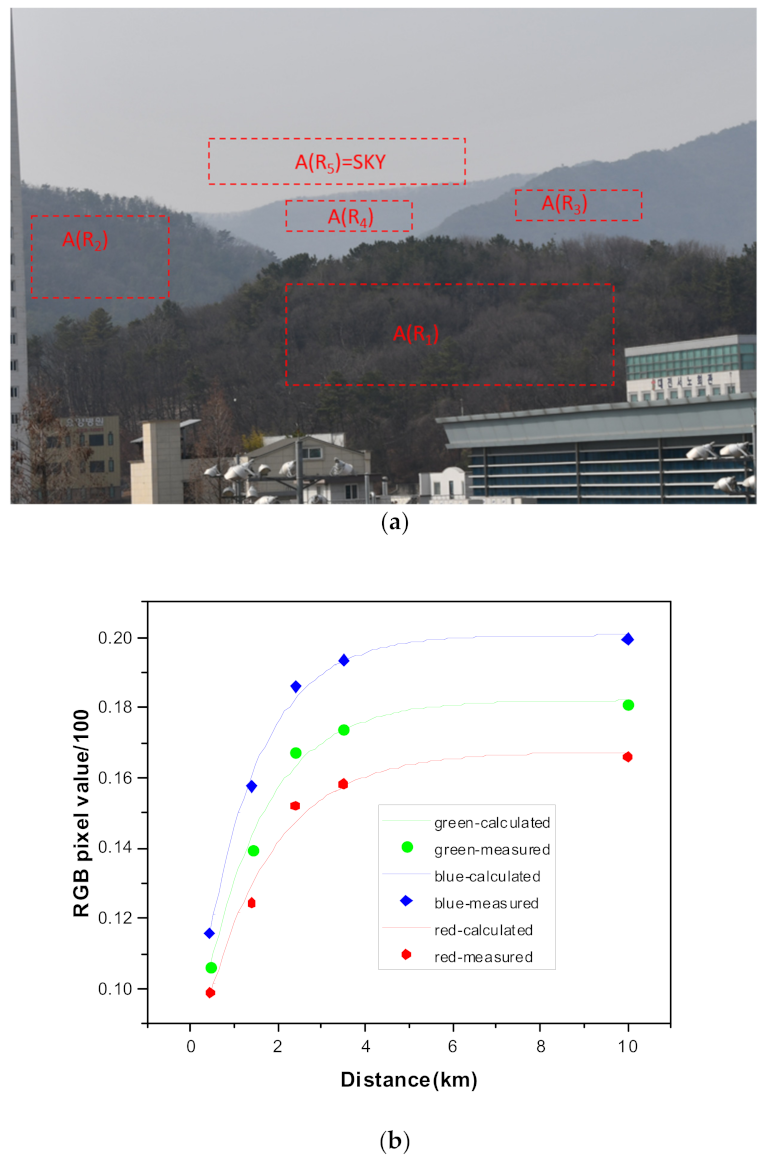
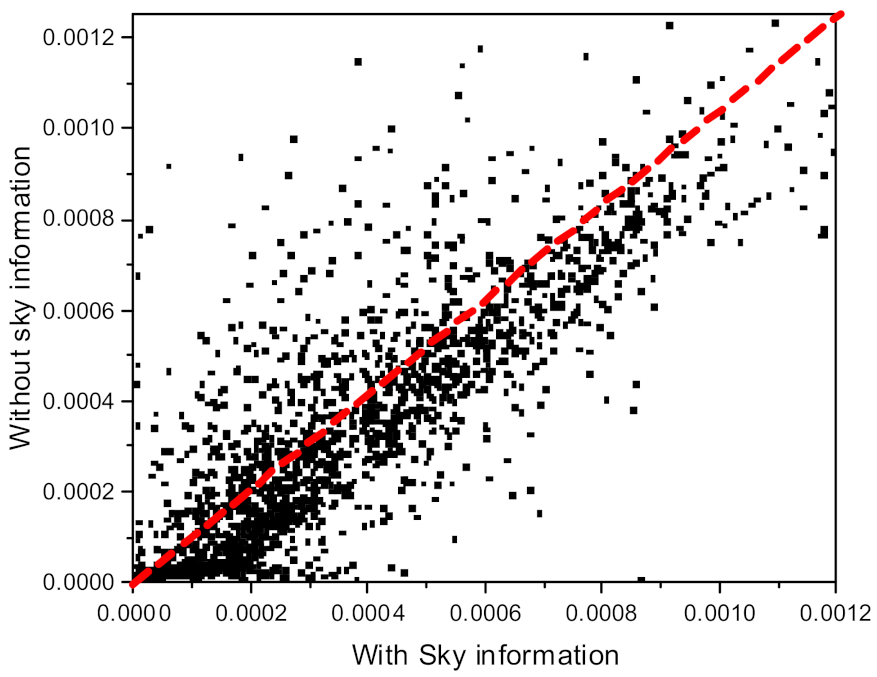
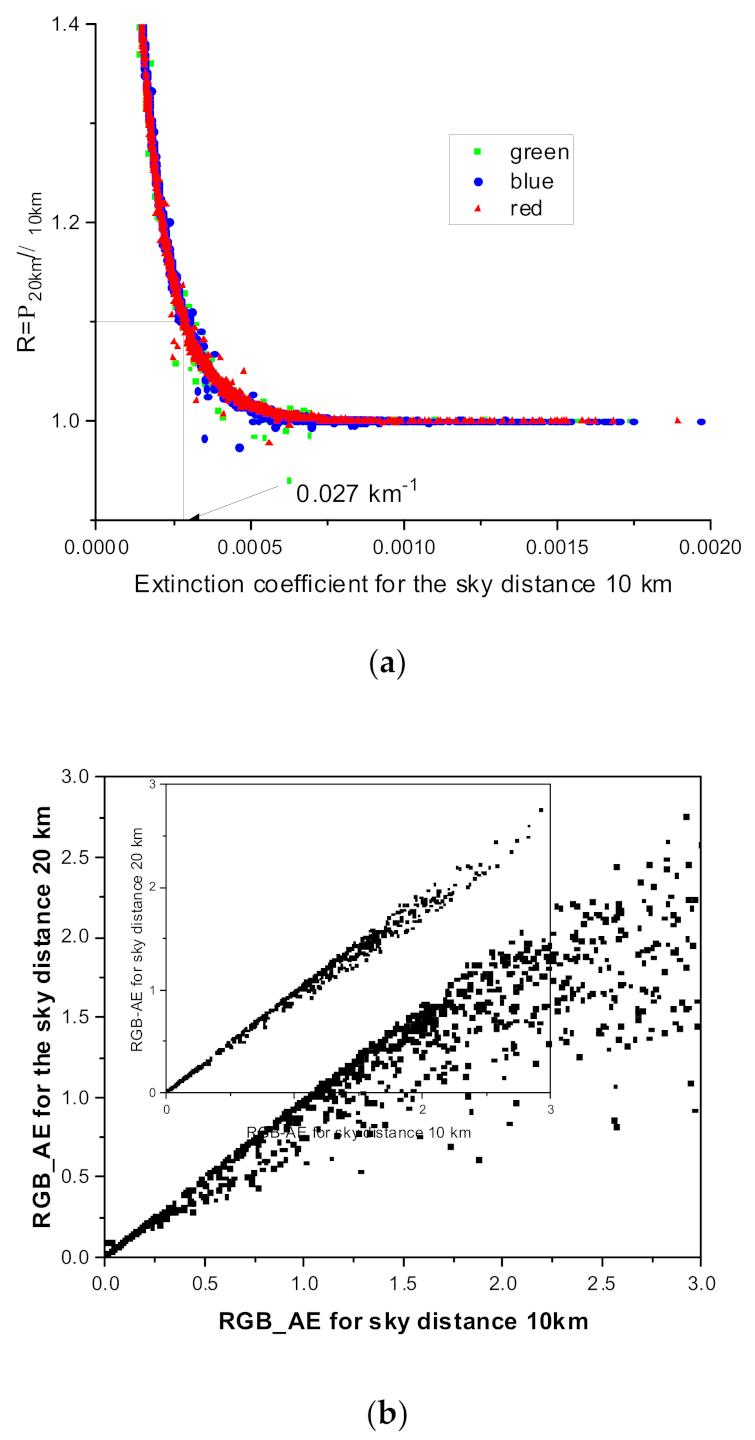
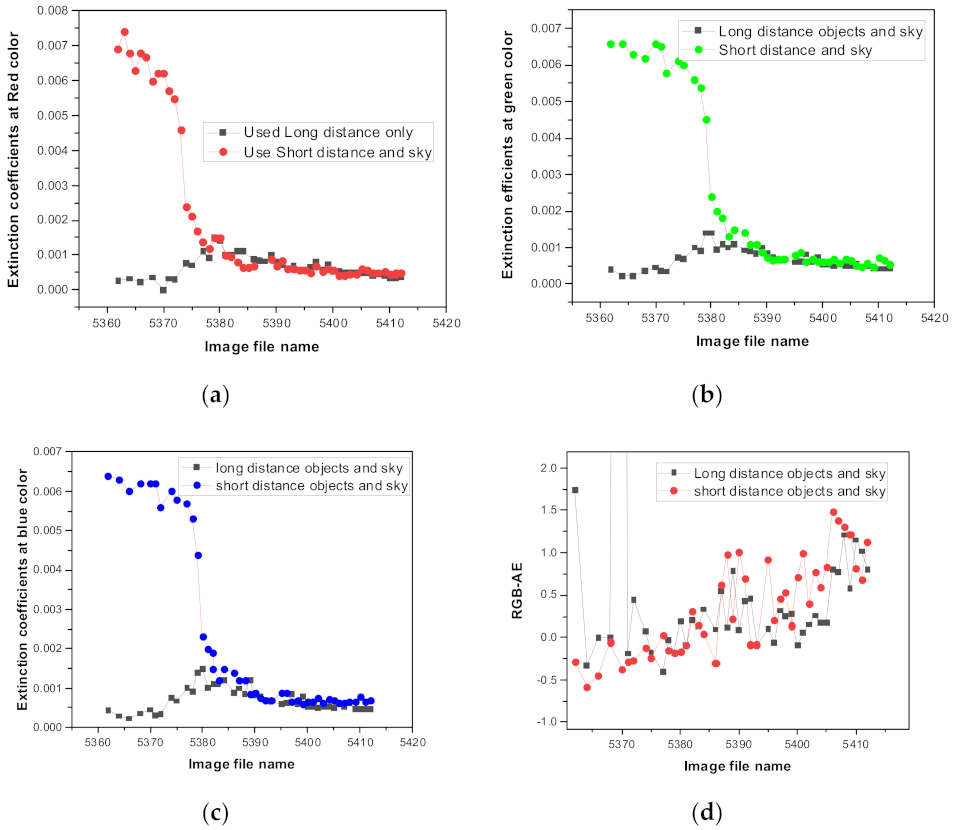
2.2. Dependence of Assumed-Sky Distances
2.3. Dependence of Object-Distances
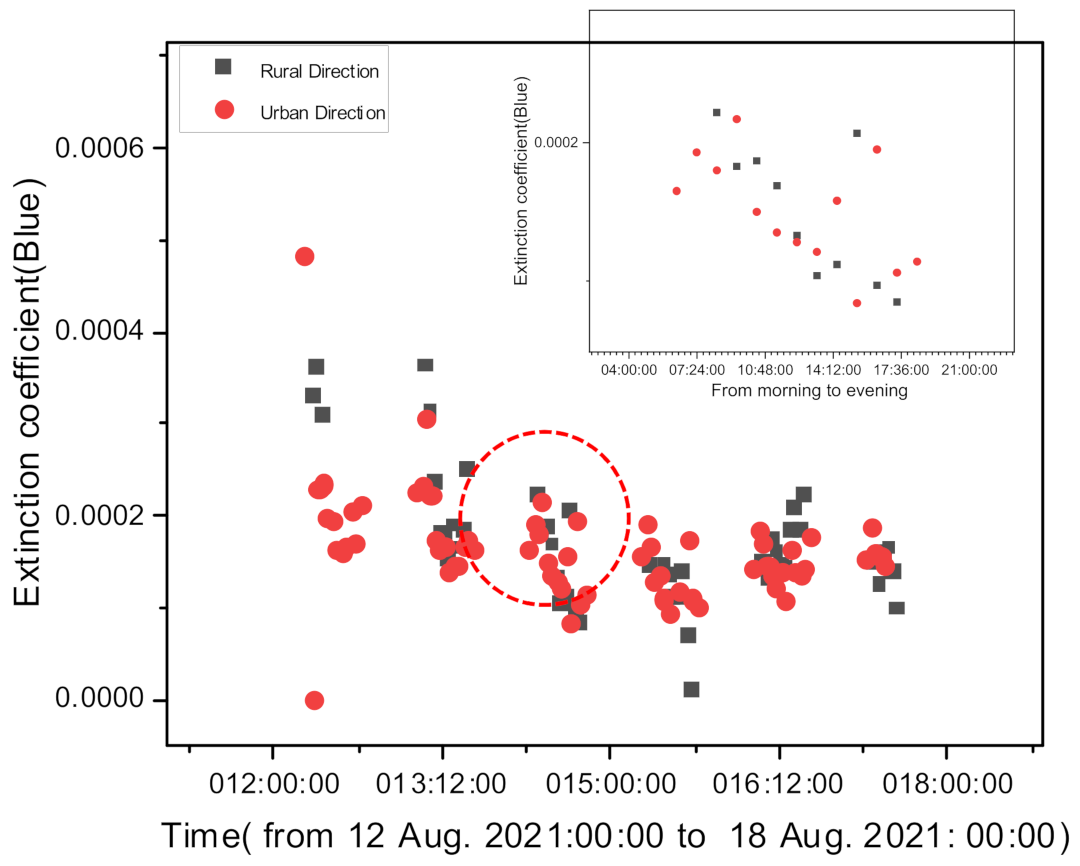
2.4. Dependence of Objects-Direction
2.5. Dependence of Target-Reflectance and Particle Scattering Efficiency
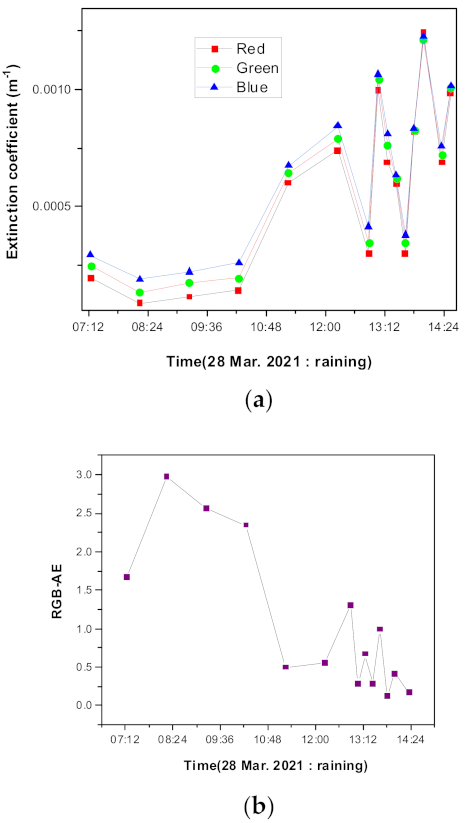
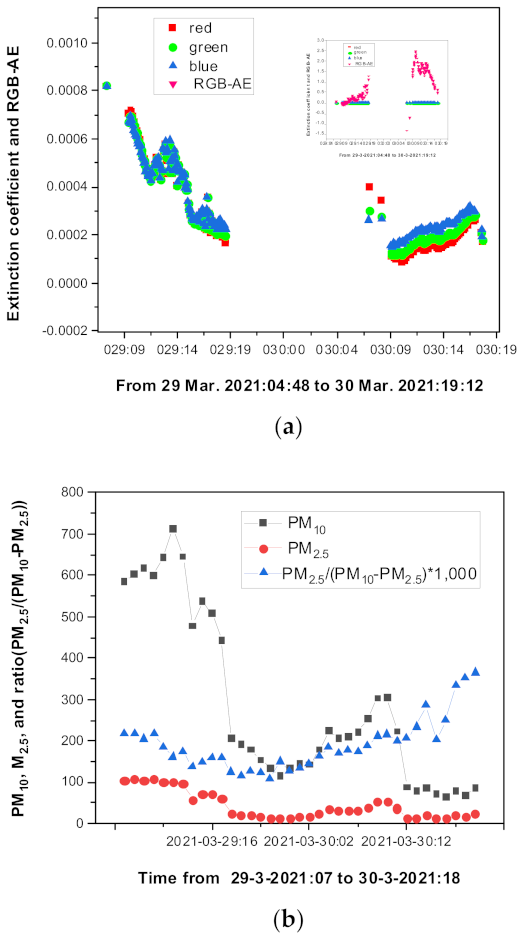
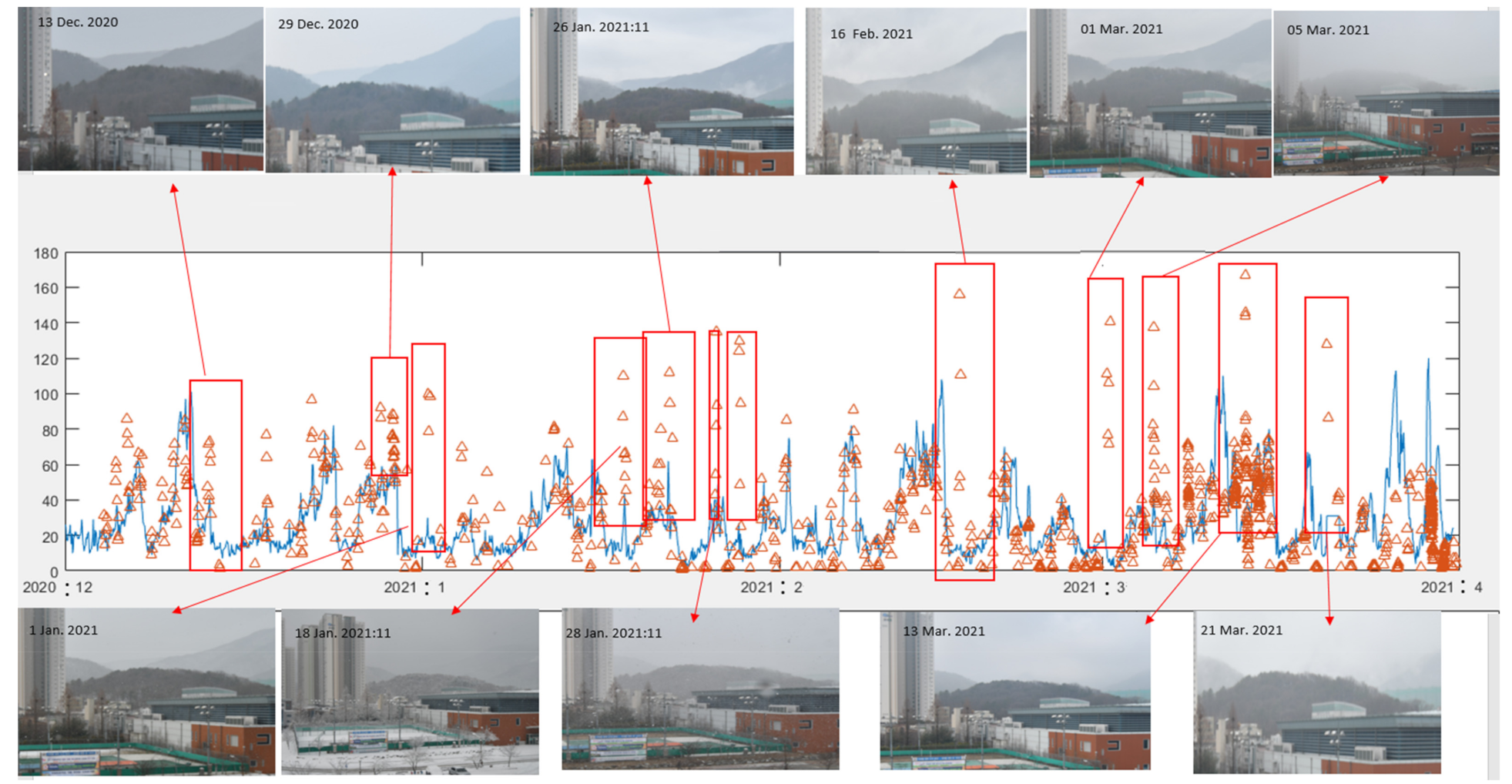
3. Dependence on Weather Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shiraiwa, K.; Ueda, A.; Pozzer, G.; Lammel, C.J.; Kampf, A.; Fushimi, S.; Enami, A.M.; Arangio, J.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, Y.; Fujitani, A.; et al. Aerosol Health Effects from Molecular to Global Scales. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13545–13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, C.; Toro, A.R.; Manzano, C.A.; Canepari, S.; Massimi, L.; Leiva-Guzmán, M.A. Airborne Aerosols and Human Health: Leapfrogging from Mass Concentration to Oxidative Potential. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, M.; Mullins, B.J.; Umhauer, H.; Kasper, G. Performance evaluation of three optical particle counters with an efficient “multimodal” calibration method. J. Aerosol Sci. 2008, 39, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Müller, M.D.; Boybeyi, Z. A new visibility parameterization for warm-fog applications in numerical weather prediction models. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2006, 45, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.J.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhao, L.J.; Lu, C.S.; Lü, J.J.; Yang, J. Summary of a 4-year fog field study in Northern Nanjing, Part 2: Fog Microphysics. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2012, 169, 1137–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.S.; Flecker, B.; Leitgeb, E.; Gebhart, M. Characterization of fog attenuation in terrestrial free space links. Opt. Eng. 2007, 46, 066001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; He, L.; Cai, X.; Ruan, S. A new video-camera-based visiometer system. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2019, 20, e295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, F.; Peng, H.; Tang, J.; Zou, B.; Tang, C. Visibility detection approach to road scene foggy image. Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2016, 10, 4419–4441. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.J.; Chen, Y.Z.; Gao, Y.Y. Real-time visibility distance evaluation based on monocular and dark channel prior. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2015, 10, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Shafin, S.H.; Li, Y.; Hao, H.W. A prototype system for atmospheric visibility estimation based on image analysis and learning. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2014, 11, 4577–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Shi, G.; Uchiyama, A.; Yamazaki, A.; Chen, H.; Goloub, P.; Zhang, X. Inter comparison between aerosol optical properties by a PREDE sky radiometer and CIMEL sun photometer over Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 3199–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, M.; Iwabuch, H.; Murata, I. Estimation of spectral distribution of sky radiance using a commercial digital camera. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmo, F.J.; Cazorla, A.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; López-Álvarez, M.A.; Hernández-Andrés, J.; Romero, J. Retrieval of the optical depth using an all-sky CCD camera. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, H182–H189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Lü, D. Preliminary Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Depth from All-sky Images. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 27, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsultan, S.; Wong, C.J.; Lim, H.S.; MatJafri, M.Z.; Abdullah, K.; Hashim, S.A.; Salleh, N.M. Remote Sensing of PM10 Concentration Measurement by Internet Protocol Camera. ISPRS Proceedings XXXVI. Available online: https://www.isprs.org/proceedings/xxxvi/part7/PDF/242.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2006).
- Ballestrín, J.; Monterreal, R.; Carra, M.E.; Fernandez-Reche, J.; Polo, J.; Enrique, R.; Rodríguez, J.; Casanova, M.; Barbero, F.J.; Alonso-Montesinos, J.; et al. Solar extinction measurement system based on digital cameras. Application to solar tower plants. Renew. Energy 2018, 125, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, N.; Newsam, S. Using visibility cameras to estimate atmospheric light extinction. In 2011 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV); IEEE: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2011; pp. 577–584. [Google Scholar]
- Carretero-Peña, S.; Blázquez, L.C.; Pinilla-Gil, E. Estimation of PM10 levels and sources in air quality networks by digital analysis of smartphone camera images taken from samples deposited on filters. Sensors 2019, 19, 4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazantzidis, A.; Tzoumanikas, P.; Nikitidou, E.; Salamalikis, V.; Wilbert, S.; Prahl, C. Application of simple all-sky imagers for the estimation of aerosol optical depth. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1850, 140012. [Google Scholar]
- Stamnes, K.; Tsay, S.-C.; Laszlo, I. DISORT, a General-Purpose Fortran Program for Discrete-Ordinate-Method Radiative Transfer in Scattering and Emitting Layered Media: Documentation of Methodology. DISORT Report v 1.1.; NASA Report: USA. 2000. Available online: https://fdocuments.in/document/disort-a-general-purpose-fortran-program-for-discrete-vijaypapersrt-modelsdisort.html (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Sun, K.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, T. High resolution aerosol optical depth retrieval using gaofen-1 WFV camera data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.H.; Chen, A.J.; Liu, G.R. An image-based retrieval algorithm of aerosol characteristics and surface reflectance for satellite images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 3477–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, F.; Schläpfer, D.; Nieke, J.; Itten, I.K. Sensor Performance Requirements for the Retrieval of Atmospheric Aerosols by Airborne Optical Remote Sensing. Sensors 2008, 8, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, K.; Wang, K.; Shi, P.; Wang, Y. Quantification of atmospheric visibility with dual digital cameras during daytime and nighttime. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hautiere, N.; Labayrade, R.; Aubert, D. Detection of visibility conditions through use of onboard cameras. In IEEE Proceedings. Intelligent Vehicles Symposium; IEEE: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2005; pp. 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Hautiére, N.; Babari, R.; Dumont, É.; Brémond, R.; Paparoditis, N. Estimating Meteorological Visibility Using Cameras: A Probabilistic Model-Driven Approach. In Computer Vision—ACCV 2010. ACCV 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol 6495; Kimmel, R., Klette, R., Sugimoto, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Babari, R.; Hautière, N.; Dumont, É.; Paparoditis, N.; Misener, J. Visibility monitoring using conventional roadside cameras—Emerging applications. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2012, 22, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narasimhan, S.G.; Nayar, S.K. Vision and the atmosphere. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 48, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, D. Aerosol-extinction retrieval method at three effective RGB wavelengths using a commercial digital camera. Korean J. Opt. Photonics 2020, 31, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.: Weinheim, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D. Real-time measurement of fog aerosol extinction coefficients at the three RGB wavelengths using general landscape images. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Remote Sensing 2021 Virtual Conference, Seoul, Korea, 26–28 May 2021; pp. 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge, R.G. Mist—The transition from haze to log. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1969, 6, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of visibility and particulate matter (PM) in an urban area of Northeast China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2013, 4, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Kwak, K.-H. Using visibility to estimate PM2.5 concentration trends in Seoul and Chuncheon from 1982 to 2014. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 34, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunjobi, K.O.; He, Z.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, Y.J. Aerosol optical depth during episodes of Asian dust storms and biomass burning at Kwangju, South Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, A.; El-Askary, H.; Dogan, A.U. Aerosols size distribution characteristics and role of precipitation during dust storm formation over Saudi Arabia. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 2523–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, Q.; Hao, Z.; Yan, Y.; Tao, B.; Chung, C.; Kim, S. Aerosol optical properties around the East China seas based on AERONET measurements. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.-G.; Hong, J.; Hong, J.; Sung, S.; Yoon, E.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H. Impact of meteorological conditions on the PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations in Seoul. J. Clim. Chang. Res. 2020, 11, 521–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, M.; Gu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, X. Spatial and temporal variability of the PM2.5/PM10 ratio in Wuhan, Central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.; Noh, Y. An Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Retrieval Method and Characteristics Analysis of Landscape Images. Sensors 2021, 21, 7282. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217282
Kim D, Noh Y. An Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Retrieval Method and Characteristics Analysis of Landscape Images. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7282. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217282
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dukhyeon, and Youngmin Noh. 2021. "An Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Retrieval Method and Characteristics Analysis of Landscape Images" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7282. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217282
APA StyleKim, D., & Noh, Y. (2021). An Aerosol Extinction Coefficient Retrieval Method and Characteristics Analysis of Landscape Images. Sensors, 21(21), 7282. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217282




