Comparison of Mathematical Methods for Compensating a Current Signal under Current Transformers Saturation Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
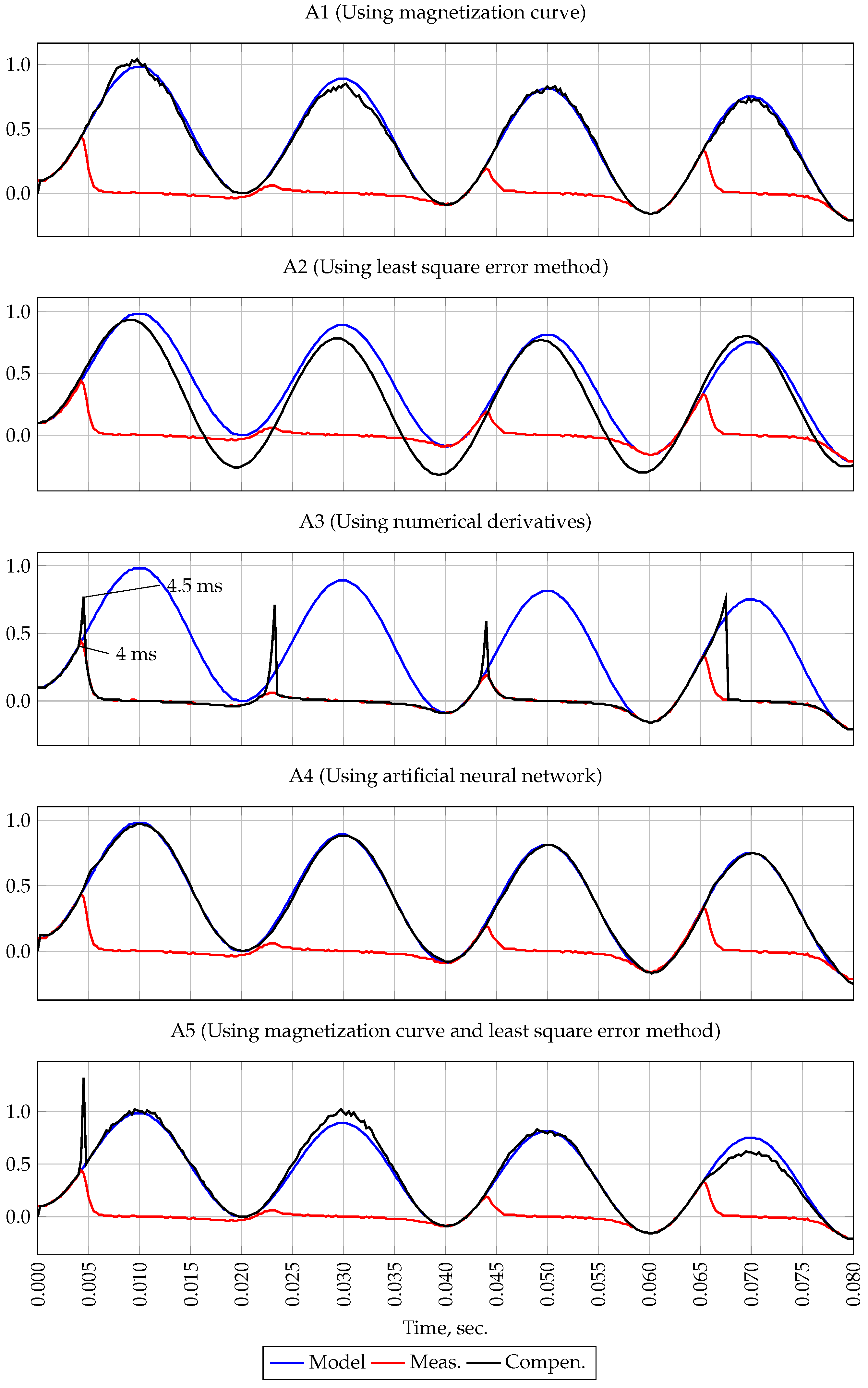
2.1. Current Filtration Using Magnetization Curve
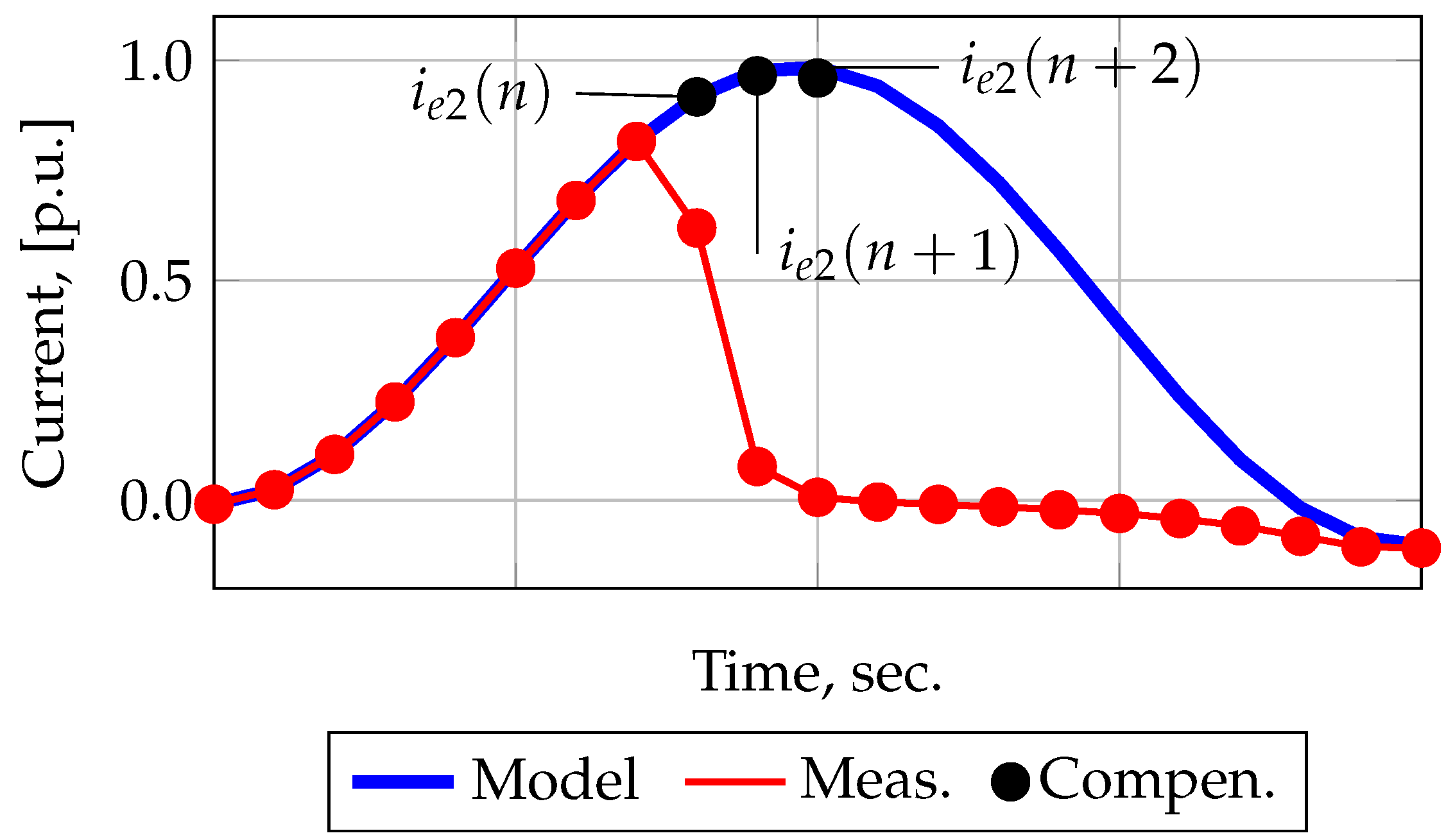
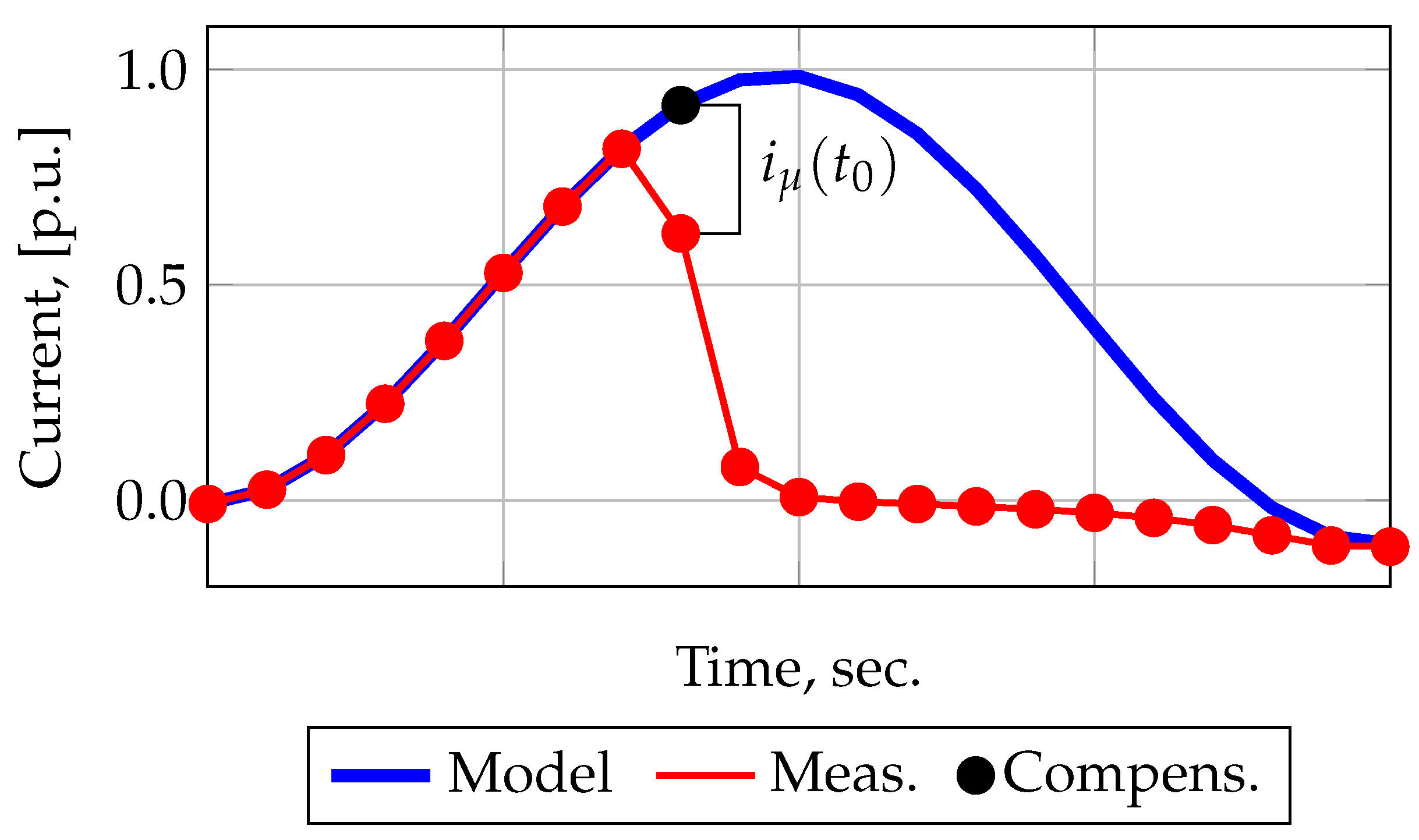
2.2. Filtering Current Using Forecasting Methods
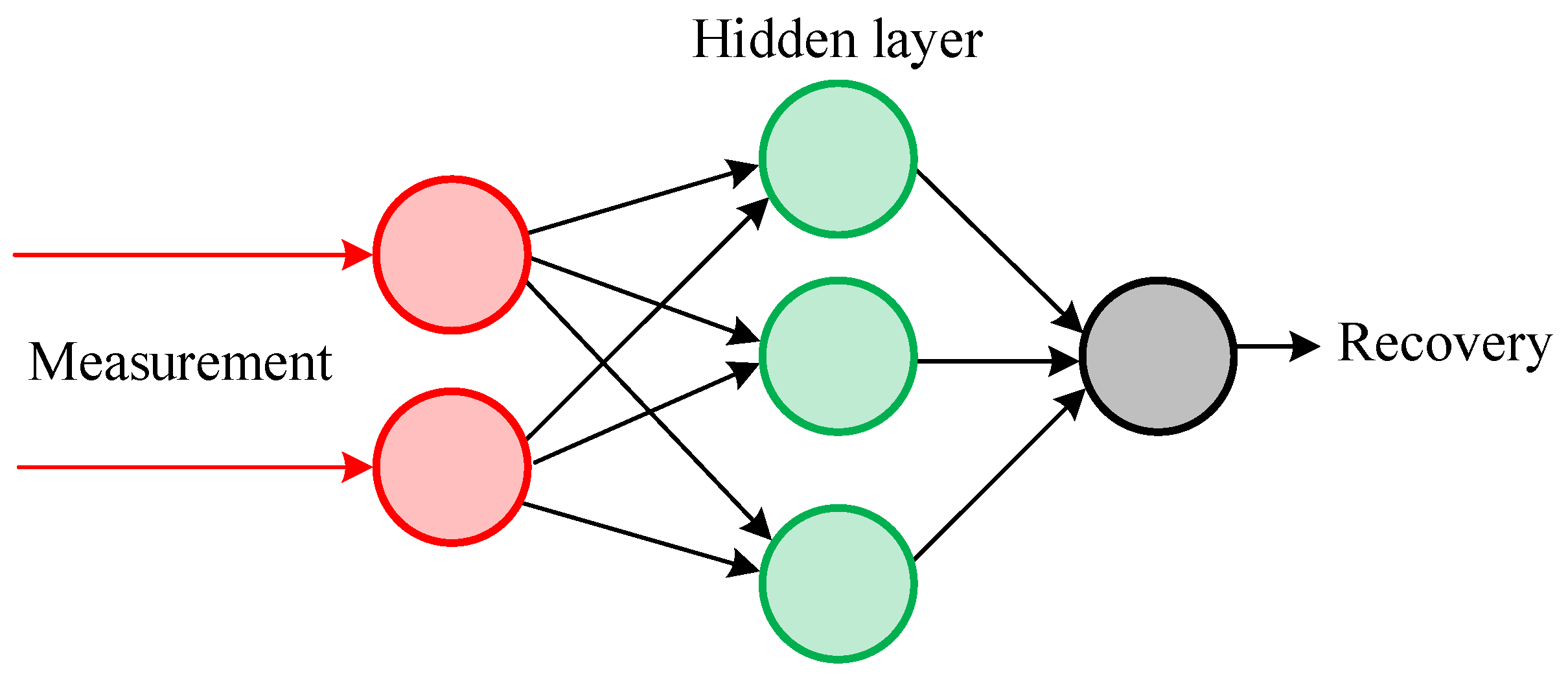
2.3. Filtering Current Using Neural Networks
- There is no need to use CT parameters in the methods;
- Independence from US length;
- Methods are capable of filtering the current with high accuracy in different network modes and degrees of secondary current distortion.
2.4. Filtering Current Using Combined Methods
3. Testing Current Filtering Methods
3.1. Description of CT under Test
3.2. Results
3.3. Calculation of Methods Errors
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunt, R. Impact of CT Errors on Protective Relays—Case Studies and Analyses. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, F.D.C.F.; Mota, W.S. Current Transformer Model. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2007, 22, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC Central Office. IEC61869-2-2012. Instrument Transformers. Part 2: Additional Requirements for Current Transformers, 1st ed.; IEC Central Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Dashti, H.; Sanaye-Pasand, M.; Davarpanah, M. Current transformer saturation detectors for busbar differential protection. In Proceedings of the 2007 42nd International Universities Power Engineering Conference, Brighton, UK, 4–6 September 2007; pp. 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Song, Q.; Zhang, D.; Pan, F.; Wang, L. A hybrid method for current transformer saturation detection and compensation in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2017 4th International Conference on Systems and Informatics (ICSAI), Hangzhou, China, 11–13 November 2017; pp. 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlender, J.; Iżykowski, J.; Solak, K. Compensation of the current transformer saturation effects for transmission line fault location with impedance-differential relay. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 182, 106223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Crossley, P.; Li, K. A Current Transformer Saturation Detection Algorithm for Use in Current Differential Protection. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Electrical and Control Engineering, Wuhan, China, 25–27 June 2010; pp. 3142–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahari, S.; Hasani, T.; Sevedi, H. A New Stabilizing Method of Differential Protection Against Current Transformer Saturation Using Current Derivatives. In Proceedings of the 2020 14th International Conference on Protection and Automation of Power Systems (IPAPS), Tehran, Iran, 31 December–1 January 2019; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behi, D.; Allahbakhshi, M.; Bagheri, A.; Tajdinian, M. A new statistical-based algorithm for CT saturation detection utilizing residual-based similarity index. In Proceedings of the 2017 Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Tehran, Iran, 2–4 May 2017; pp. 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Haifeng, L.; Hui, J.; Jianchun, P.; Chun, H. A Scheme for Detection and Assessment of Current Transformer Saturation. In Proceedings of the 2017 9th International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA), Changsha, China, 14–15 January 2017; pp. 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Kang, S.; Park, J.; Johns, A.; Aggarwal, R. Development and hardware implementation of a compensating algorithm for the secondary current of current transformers. IEEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. Inst. Eng. Technol. (IET) 1996, 143, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Park, J.; Kang, S.; Johns, A.; Aggarwal, R. An algorithm for compensating secondary currents of current transformers. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1997, 12, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locci, N.; Muscas, C. A digital compensation method for improving current transformer accuracy. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2000, 15, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locci, N.; Muscas, C. Hysteresis and eddy currents compensation in current transformers. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2001, 16, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Vu, K.; Hu, Y. An efficient compensation algorithm for current transformer saturation effects. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2004, 19, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macieira, G.; Coelho, A. Evaluation of numerical time overcurrent relay performance for current transformer saturation compensation methods. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 149, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghjoo, F.; Pak, M.H. Compensation of CT Distorted Secondary Current Waveform in Online Conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2016, 31, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiszniewski, A.; Rebizant, W.; Schiel, L. Correction of Current Transformer Transient Performance. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2008, 23, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erenturk, K. ANFIS-Based Compensation Algorithm for Current-Transformer Saturation Effects. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2009, 24, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, J.; Yu, D.; Kojovic, L. Simplified artificial neural network structure with the current transformer saturation detector provides a good estimate of primary currents. In Proceedings of the 2000 Power Engineering Society Summer Meeting (Cat. No.00CH37134), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–20 July 2000; Volume 3, pp. 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorashadi-Zadeh, H.; Sanaye-Pasand, M. An ANN based algorithm for correction of saturated CT secondary current. In Proceedings of the 39th International Universities Power Engineering Conference, 2004. UPEC 2004, Bristol, UK, 6–8 September 2004; Volume 1, pp. 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorashadi-Zadeh, H.; Sanaye-Pasand, M. Correction of Saturated Current Transformers Secondary Current Using ANNs. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2006, 21, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Izykowski, J.; Lukowicz, M.; Rosolowskiz, E. Application of ANN methods for instrument transformer correction in transmission line protection. In Proceedings of the 2001 Seventh International Conference on Developments in Power System Protection (IEE), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 9–12 April 2001; pp. 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, D.; Cummins, J.; Wang, Z.; Yoon, H.J.; Kojovic, L.; Stone, D. Neural network for current transformer saturation correction. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Transmission and Distribution Conference (Cat. No. 99CH36333), New Orleans, LA, USA, 11–16 April 1999; Volume 1, pp. 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Cummins, J.; Wang, Z.; Yoon, H.J.; Kojovic, L. Correction of current transformer distorted secondary currents due to saturation using artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2001, 16, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.Y.; Buse, J.; Wu, Q.H.; Jiang, L. Fast compensation of current transformer saturation. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference Europe (ISGT Europe), Gothenburg, Sweden, 11–13 October 2010; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Buse, J.; Wu, Q.; Guo, C. Current transformer saturation compensation based on a partial nonlinear model. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2013, 97, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.C.; Lim, U.J.; Kang, S.H.; Crossley, P. Compensation of the distortion in the secondary current caused by saturation and remanence in a CT. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2004, 19, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Lim, U.; Kang, S. Compensating algorithm suitable for use with measurement-type current transformers for protection. IEE Proc.-Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2005, 152, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, E.; Vakilian, M.; Sanaye-Pasand, M. Current-Transformer Saturation Compensation for Transformer Differential Relays. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2015, 30, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.C.; Kang, S.H.; Crossley, P. An algorithm for detecting CT saturation using the secondary current third-difference function. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Bologna Power Tech Conference Proceedings, Bologna, Italy, 23–26 June 2003; Volume 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olgac, A.; Karlik, B. Performance Analysis of Various Activation Functions in Generalized MLP Architectures of Neural Networks. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Expert Syst. 2011, 1, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zaplata, F.; Kasal, M. Using the Goertzel algorithm as a filter. In Proceedings of the 2014 24th International Conference Radioelektronika, Bratislava, Slovakia, 15–16 April 2014; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


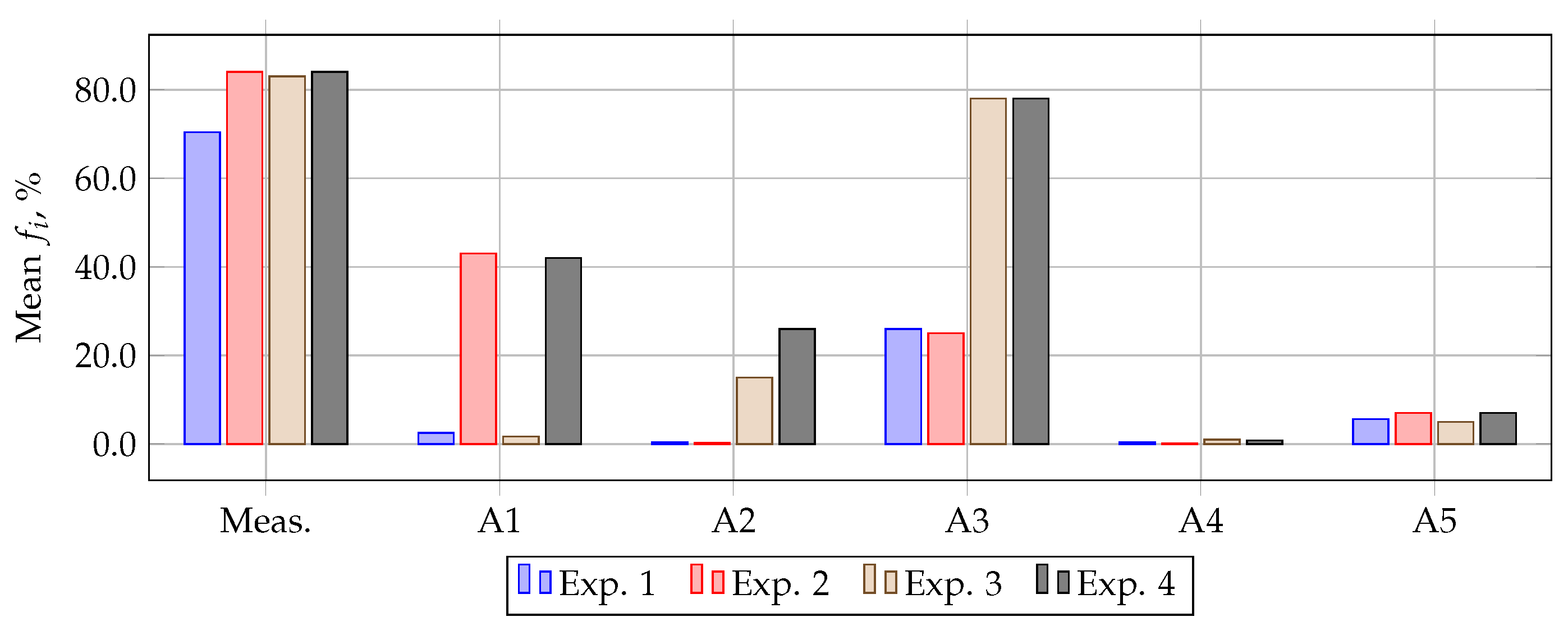
| Method and Reference | Computational Experiment 1 | Computational Experiment 2 | Computational Experiment 3 | Computational Experiment 4 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| , % | , % | , % | , % | , % | , % | , % | , % | |||||||||
| Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | |
| A1 [11,12] | 6.5 | 4 | 7 | 4.2 | 43 | 42 | 44 | 43 | 7.2 | 3.4 | 8 | 5 | 49 | 43 | 52 | 44 |
| A2 [15,16,17] | 4 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1.2 | 3 | 2 | 18 | 10 | 38 | 32 | 23 | 12 | 65 | 59 |
| A3 [18] * | 79 | 37 | 90 | 58 | 79 | 36.6 | 90 | 58 | 91 | 75 | 100 | 98 | 91 | 75 | 100 | 98 |
| A4 [19,20,21,22,23,24,25] | 1.2 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 3 | 2 | 1.44 | 1 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 1 | 0.3 | 3 | 2 |
| A5 [28,29,30] | 6.2 | 3.6 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 5 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 9 | 5 | 13 | 8.6 | 27 | 11 |
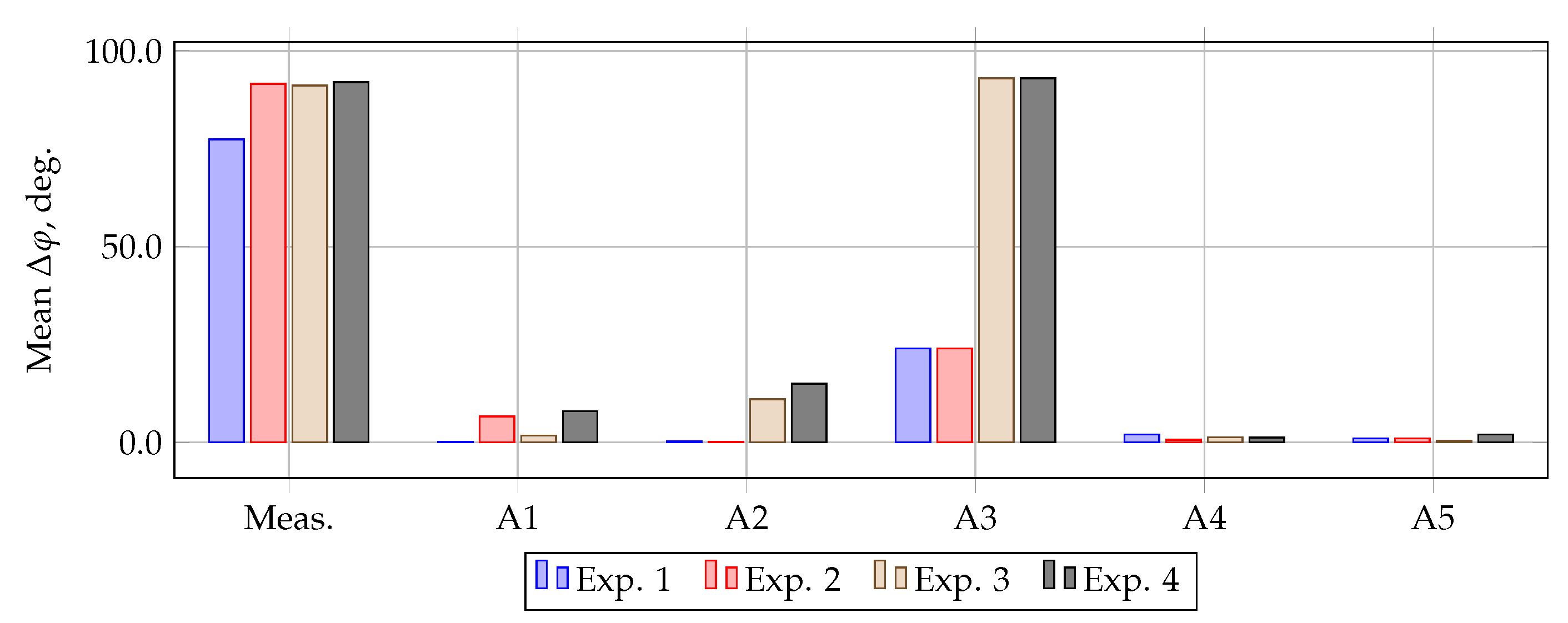
| Method and Reference | Computational Experiment 1 | Computational Experiment 22 | Computational Experiment 3 | Computational Experiment 4 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| , % | , ° | , % | , ° | , % | , ° | , % | , ° | |||||||||
| Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | Max | Avg. | |
| A1 [11,12] | 3.7 | 2.5 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 45 | 43 | 12 | 6.6 | 4.3 | 1.7 | 3 | 1.7 | 43 | 42 | 14 | 8 |
| A2 [15,16,17] | 1 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.16 | 27 | 15 | 19 | 11 | 48 | 26 | 27 | 15 |
| A3 [18] | 37 | 26 | 30 | 24 | 37 | 25 | 30 | 24 | 84 | 78 | 109 | 93 | 84 | 78 | 110 | 93 |
| A4 [19,20,21,22,23,24,25] | 2 | 0.4 | 3.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.2 | 1 | 0.7 | 2 | 1 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 2 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 1.2 |
| A5 [28,29,30] | 7.6 | 5.6 | 2 | 1 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 6.5 | 5 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 10 | 7 | 8 | 2 |
| Method and Reference | Approach | Advantages and Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| A1 [11,12] | Based on the use of the magnetization curve | (+) High stability with respect to white noise, the ability to filter a signal regardless of US. (−) High sensitivity to initial flux density. |
| A2 [15,16,17] | Based on the use of US samples |
(+) No dependence on CT parameters and high stability with respect to the initial flux density. (−) High sensitivity relative to white noise, US referenced. |
| A3 [18] | ||
| A4 [19,20,21,22,23,24,25] | Based on the use of neural networks | (+) High accuracy in the presence of both initial flux density and white noise, there is no dependence on US and CT parameters. (−) To take into account all the factors affecting the occurrence of saturation, a large amount of memory of the microprocessor device is required. It is also necessary to solve a number of problems related to the accuracy of the current saturation mode recognition by the neural network. |
| A5 [28,29,30] | Based on the use of the magnetization curve and ICT samples | (+) Stability with respect to the initial magnetic induction and white noise. (−) Dependence on the parameters of the CT magnetic circuit and the number of measured signal in the IPT samples. The accuracy of the method depends on the forecasting methods used. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Odinaev, I.; Gulakhmadov, A.; Murzin, P.; Tavlintsev, A.; Semenenko, S.; Kokorin, E.; Safaraliev, M.; Chen, X. Comparison of Mathematical Methods for Compensating a Current Signal under Current Transformers Saturation Conditions. Sensors 2021, 21, 7273. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217273
Odinaev I, Gulakhmadov A, Murzin P, Tavlintsev A, Semenenko S, Kokorin E, Safaraliev M, Chen X. Comparison of Mathematical Methods for Compensating a Current Signal under Current Transformers Saturation Conditions. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7273. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217273
Chicago/Turabian StyleOdinaev, Ismoil, Aminjon Gulakhmadov, Pavel Murzin, Alexander Tavlintsev, Sergey Semenenko, Evgenii Kokorin, Murodbek Safaraliev, and Xi Chen. 2021. "Comparison of Mathematical Methods for Compensating a Current Signal under Current Transformers Saturation Conditions" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7273. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217273
APA StyleOdinaev, I., Gulakhmadov, A., Murzin, P., Tavlintsev, A., Semenenko, S., Kokorin, E., Safaraliev, M., & Chen, X. (2021). Comparison of Mathematical Methods for Compensating a Current Signal under Current Transformers Saturation Conditions. Sensors, 21(21), 7273. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217273









