Synchronized Data Collection for Human Group Recognition †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We identified the synchronized data collection problem in the human group recognition.
- We proposed a trajectory interpolation algorithm to solve different start time and frequency problem in the human group recognition. A reasonable error function is designed to optimize the interpolation.
- We utilize message passing to estimate and minimize the deviation of clocks between devices.
- Extensive evaluations are carried out and the results show that the proposed algorithms outperform the existing approaches.
2. Related Work
3. System Model
4. Aligned Trajectory Interpolation
| Algorithm 1: Start time determination |
 |
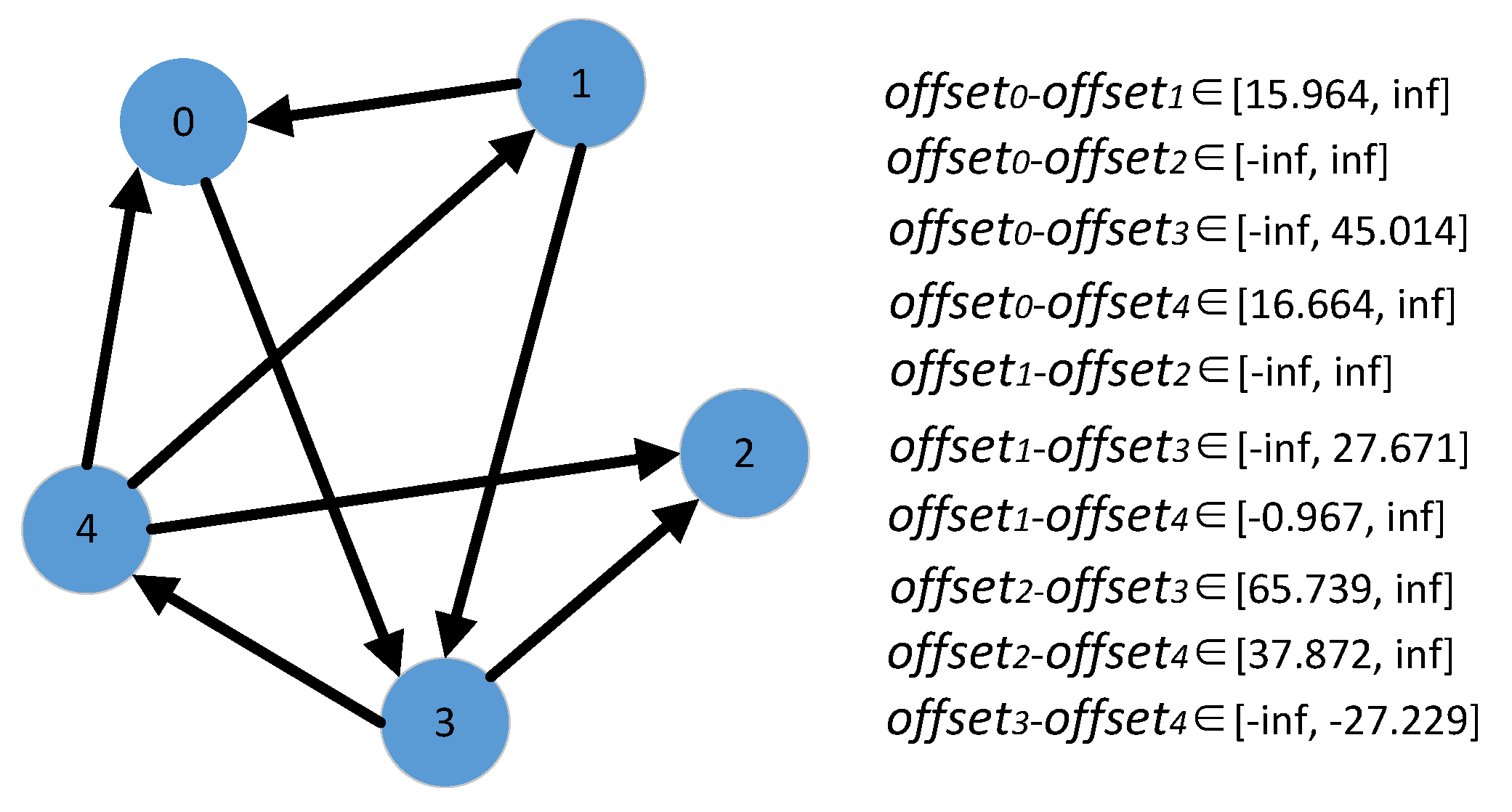
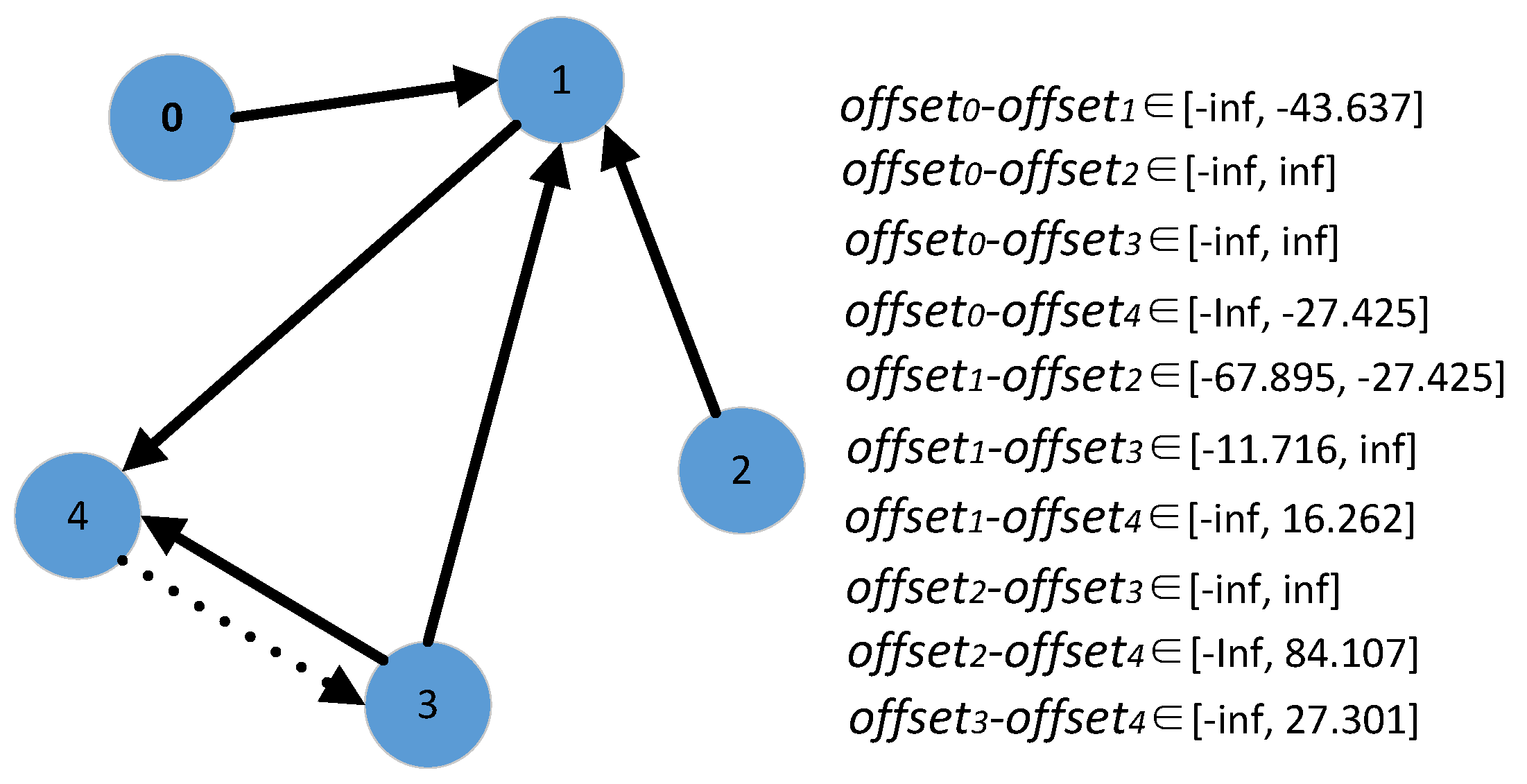
5. Time Deviation Estimation and Elimination
5.1. Time Deviation Estimation Based on Message Passing
5.2. Improvement on the Estimation of Time Deviation
| Algorithm 2: Additional Message Passing Determination |
 |
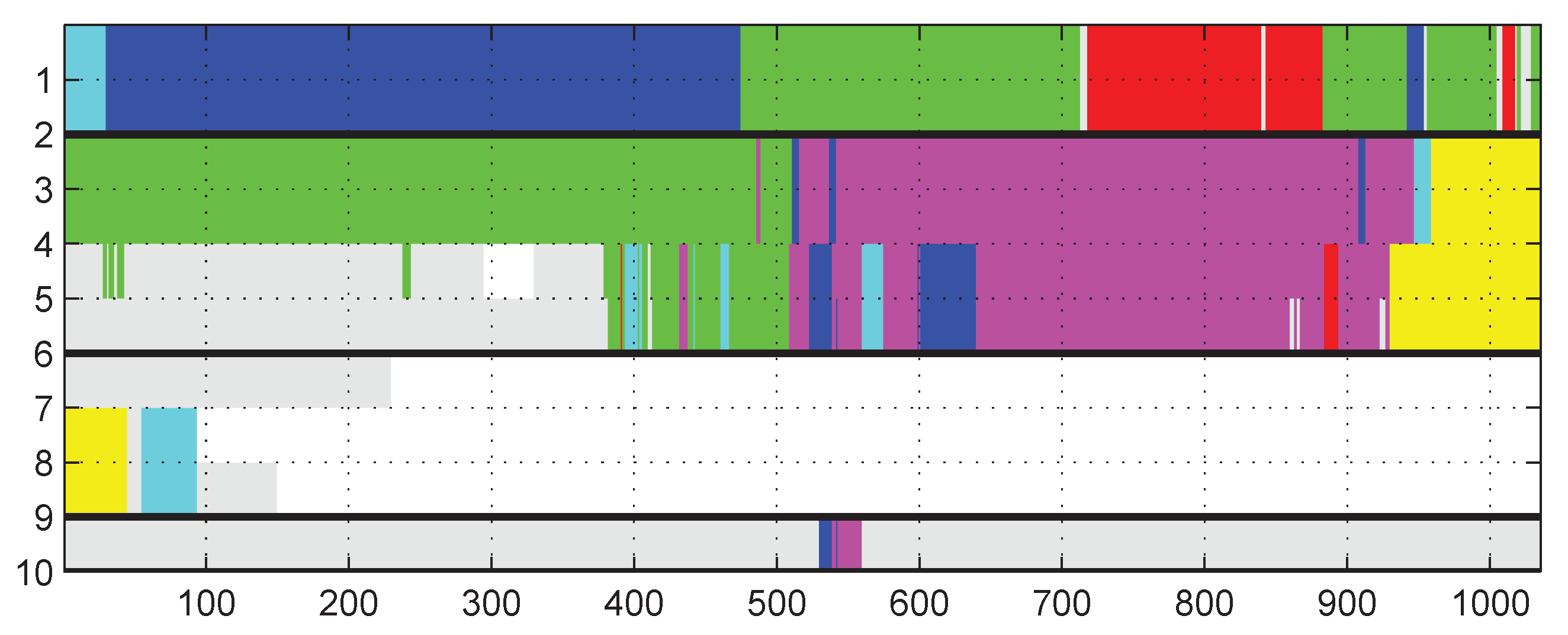
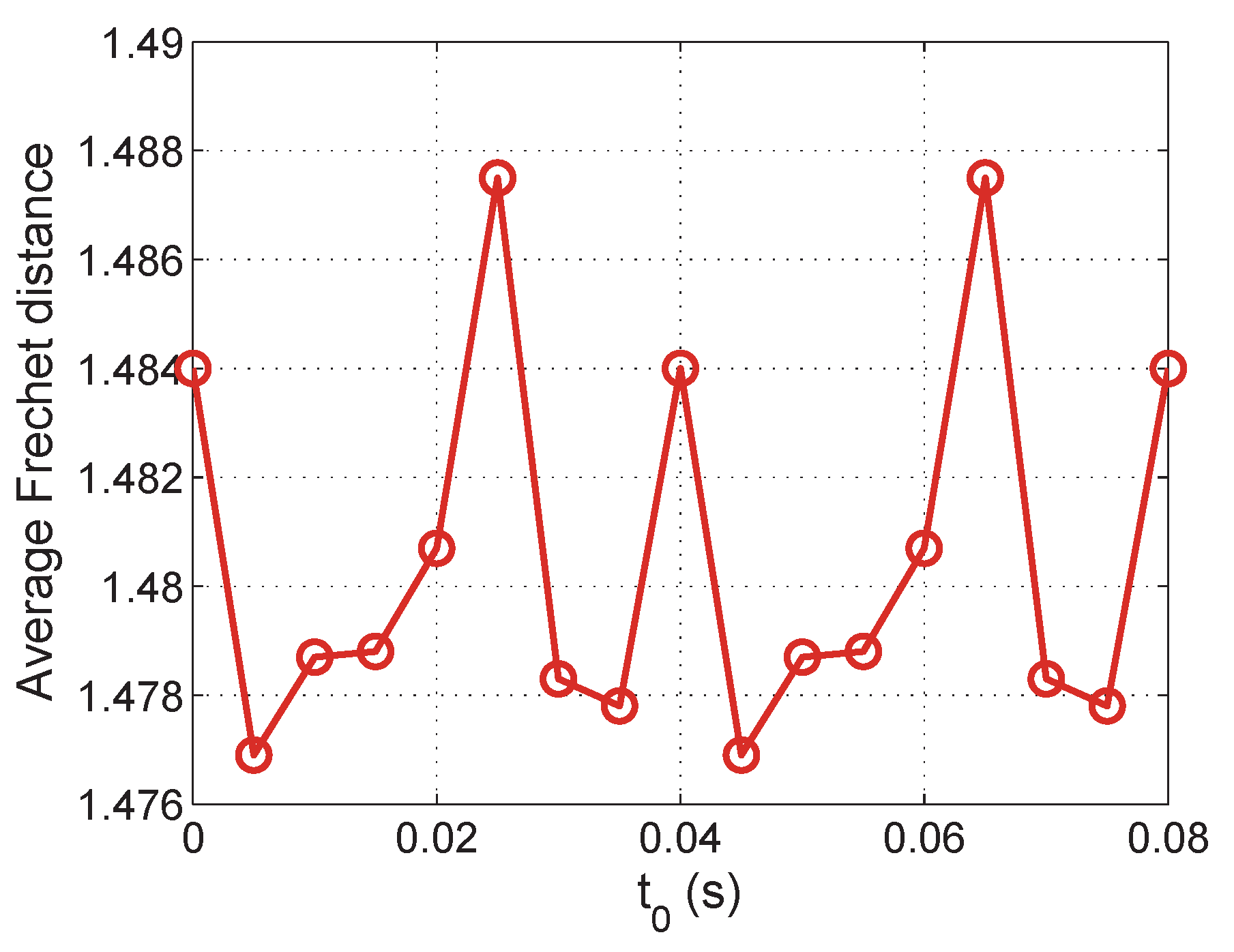
6. Evaluation Results
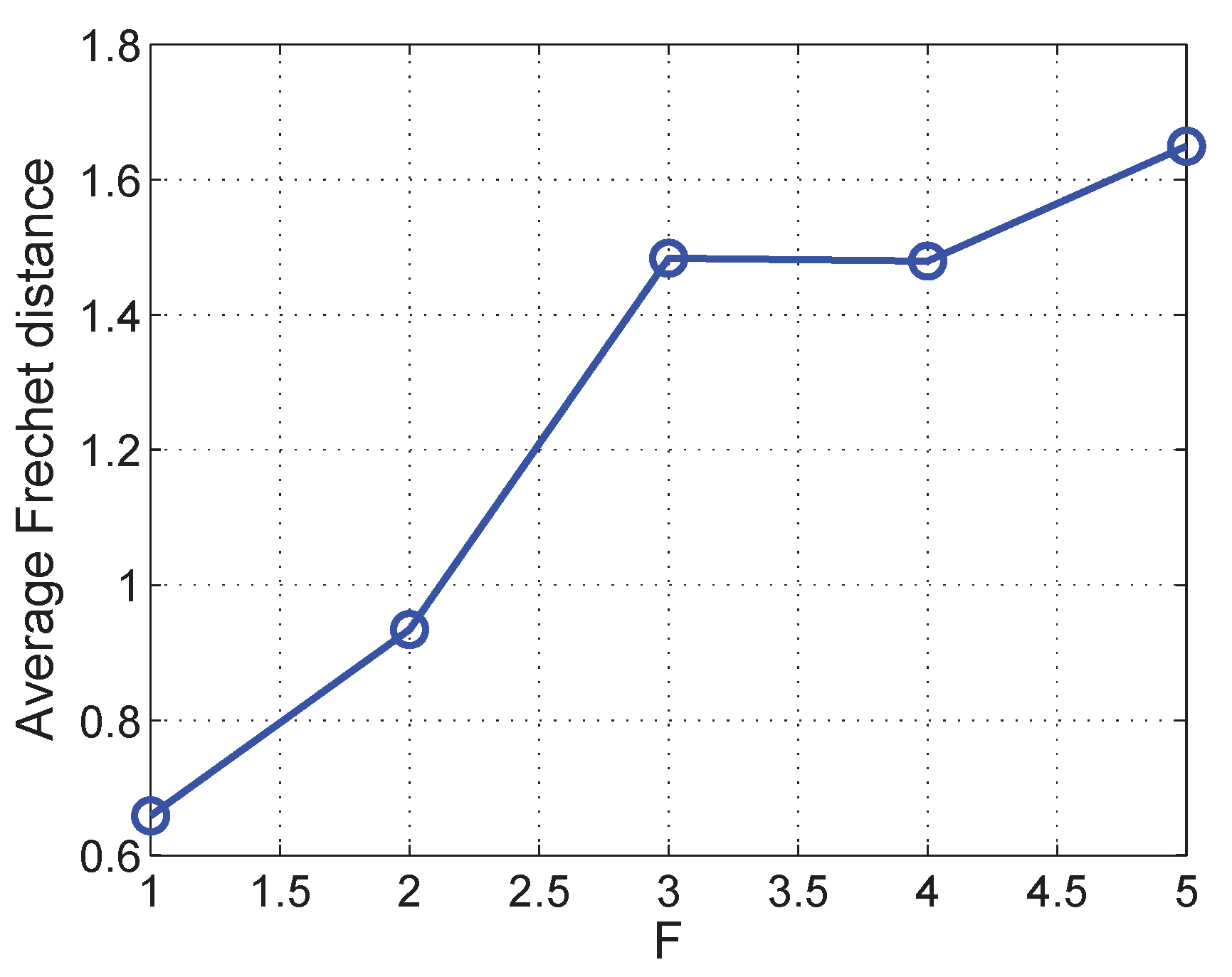
6.1. Evaluation of Aligned Trajectory Interpolation
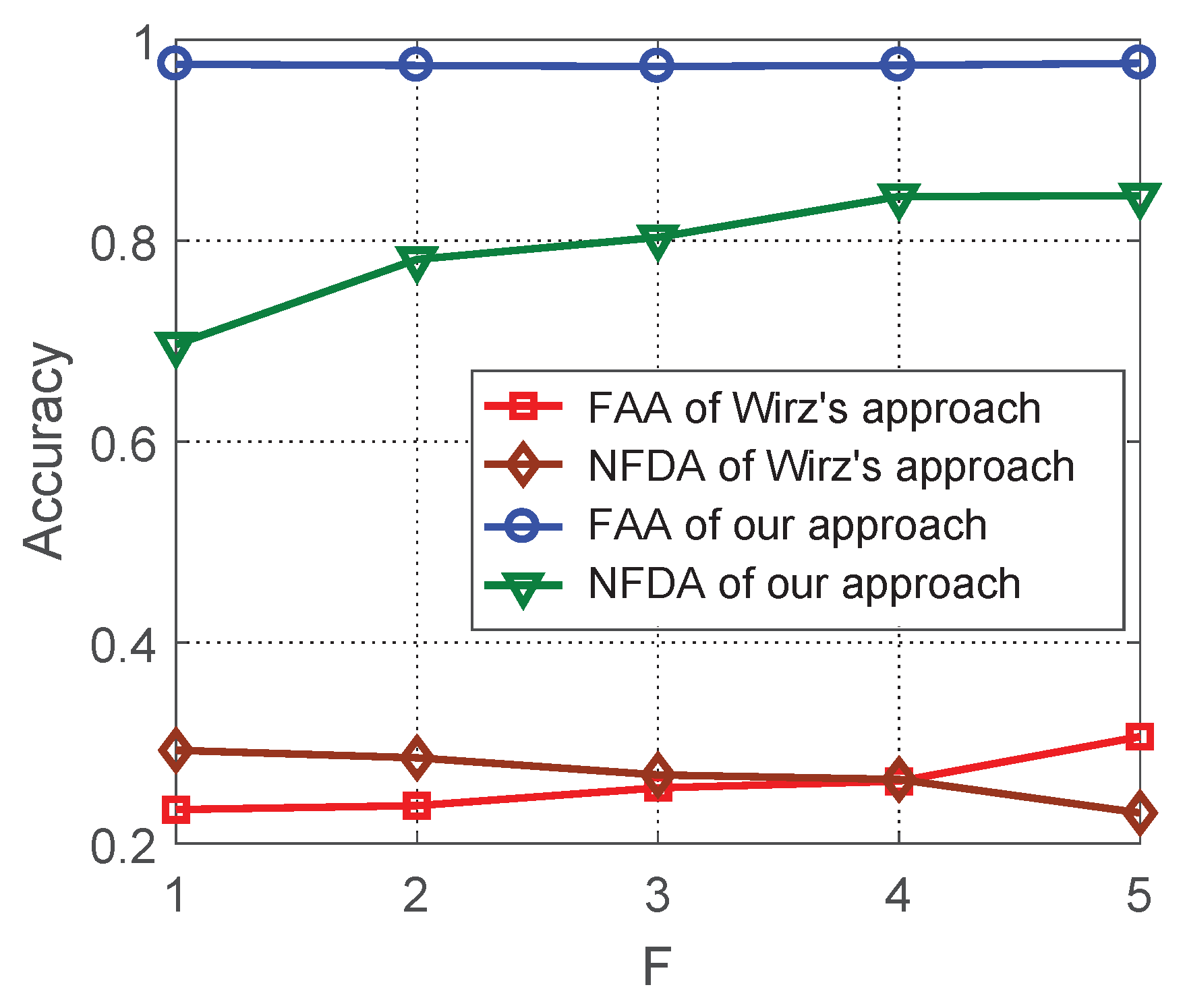
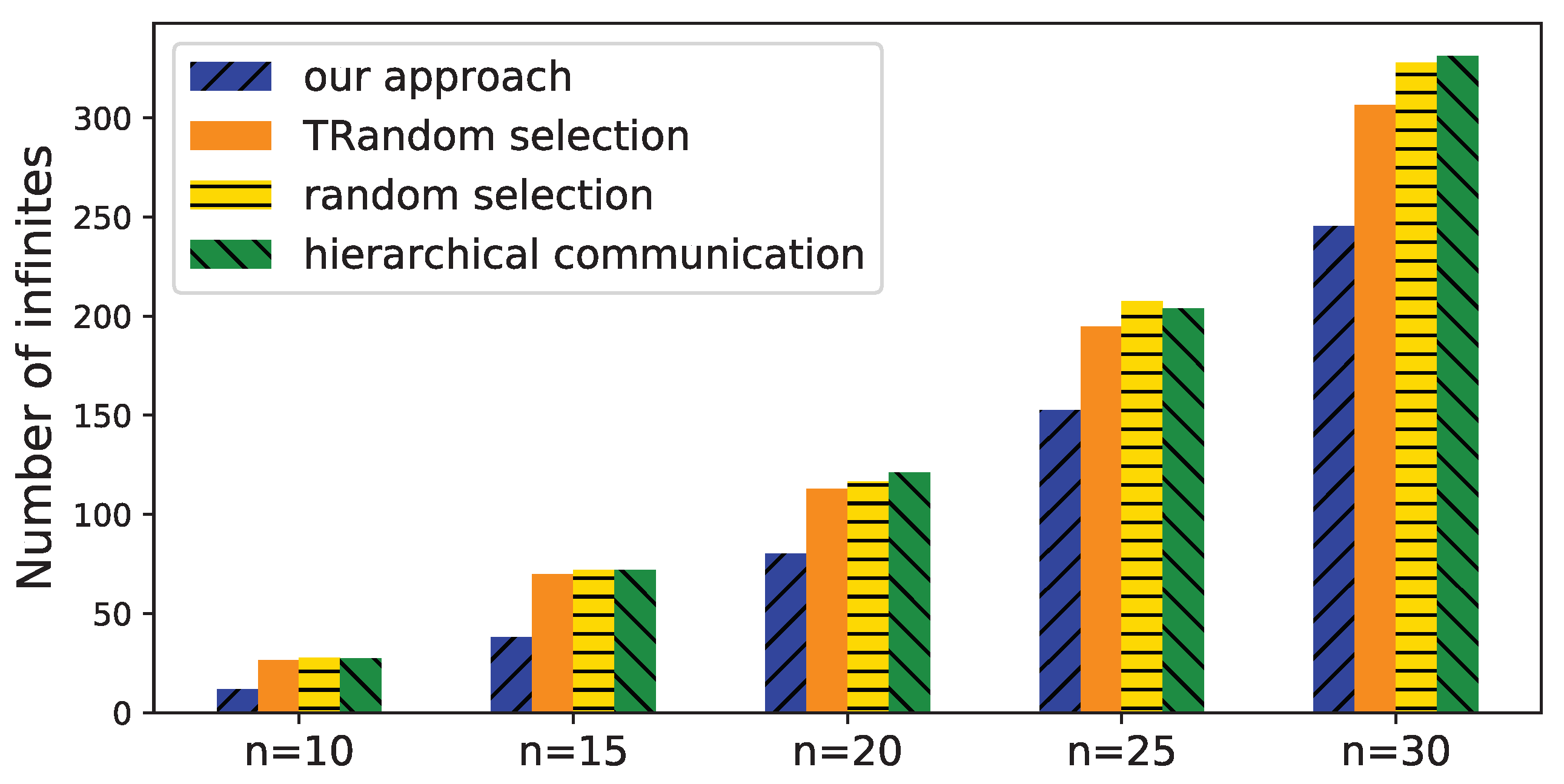
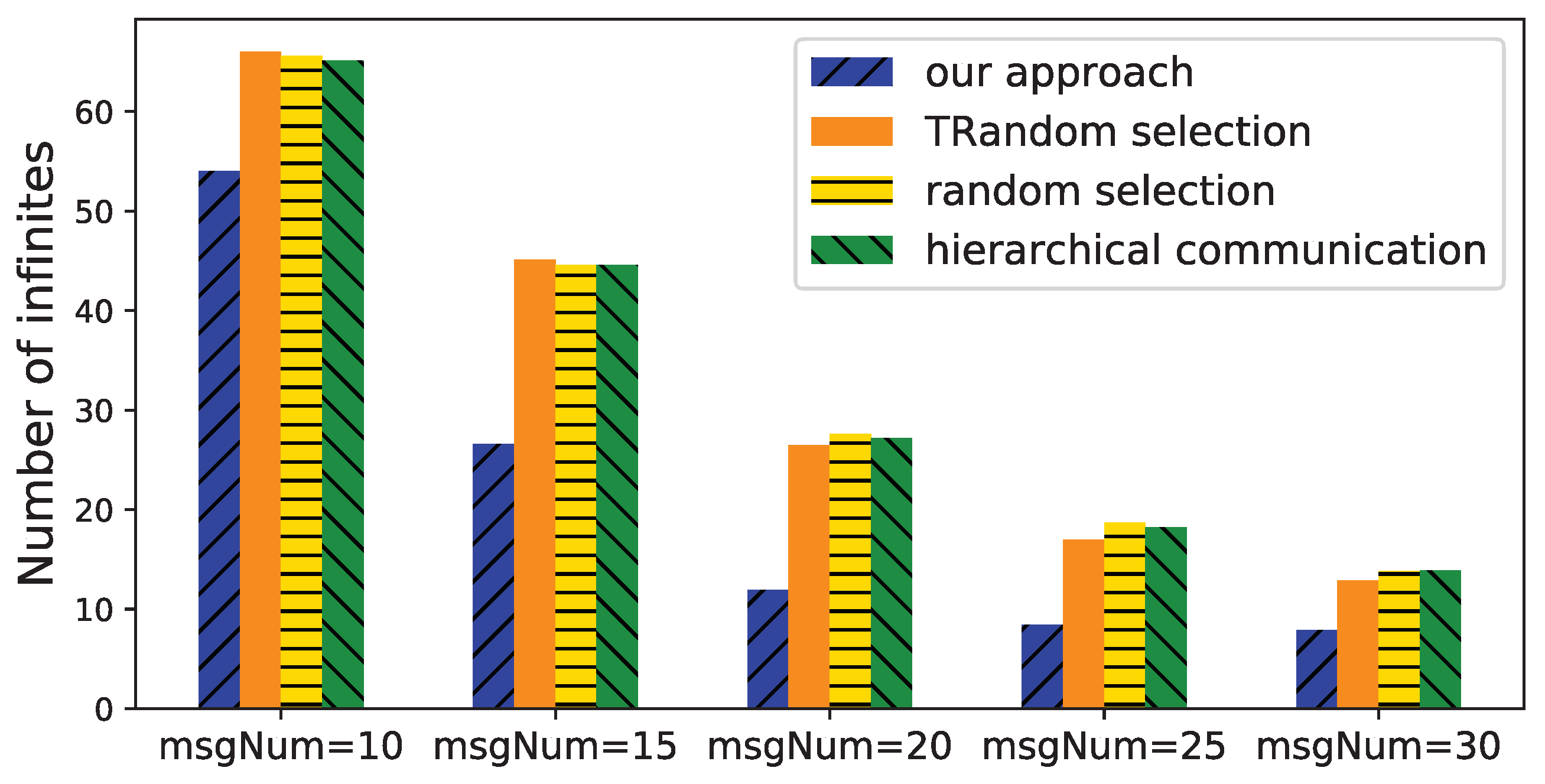
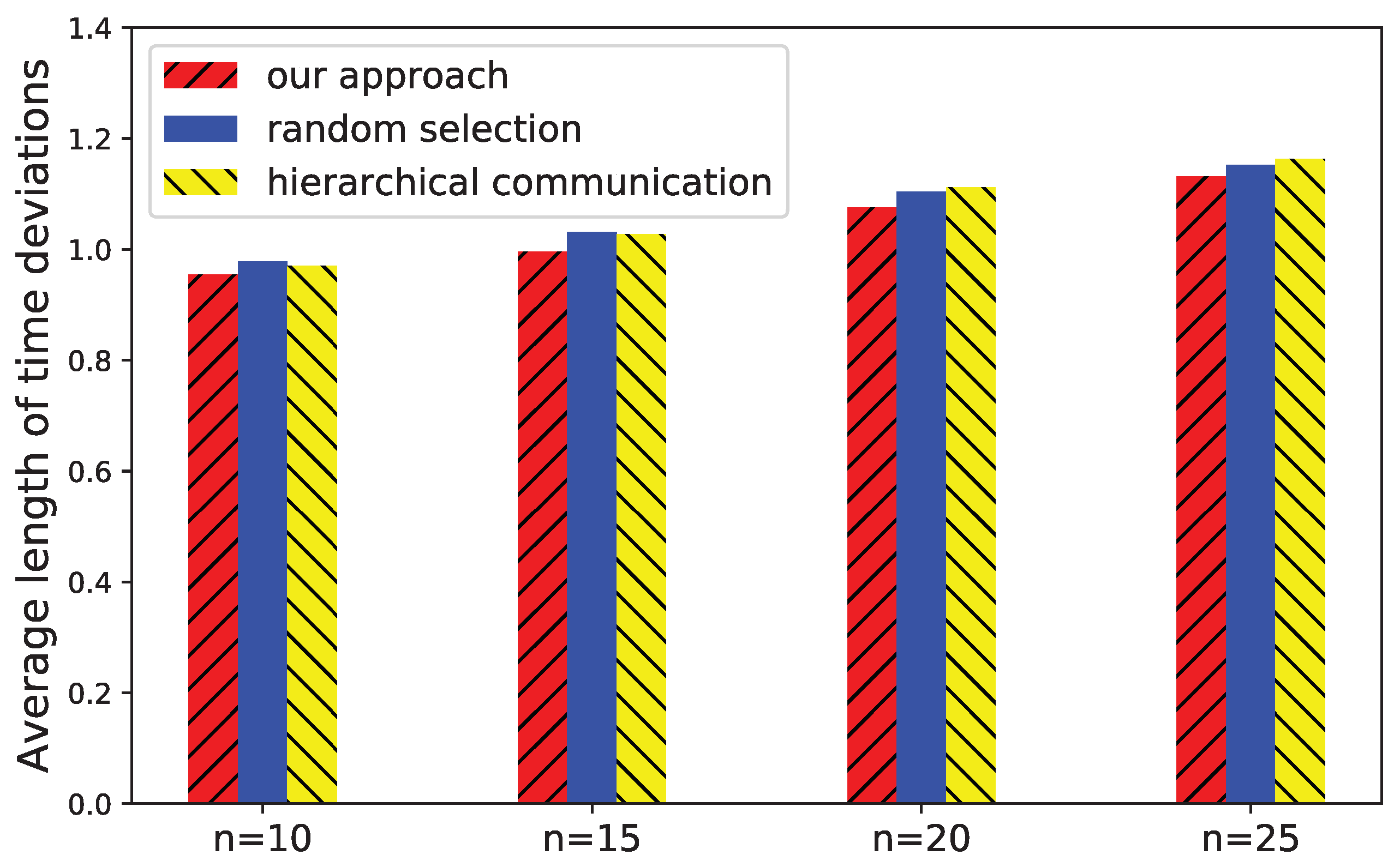
6.2. Evaluation of Time Deviation Estimation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sen, R.; Lee, Y.; Jayarajah, K.; Misra, A.; Balan, R.K. GruMon: Fast and accurate group monitoring for heterogeneous urban spaces. In Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems (SenSys), Memphis, TN, USA, 3–6 November 2014; pp. 46–60. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Cao, J.; Liu, X. BaG: Behavior-aware Group Detection in Crowded Urban Spaces Using WiFi Probes. In Proceedings of the World Wide Web Conference (WWW), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feese, S.; Arnrich, B.; Tröster, G.; Burtscher, M.; Meyer, B.; Jonas, K. CoenoFire: Monitoring performance indicators of firefighters in real-world missions using smartphones. In Proceedings of the ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Zurich, Switzerland, 8–12 September 2013; pp. 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Feese, S.; Arnrich, B.; Tröster, G.; Burtscher, M.; Meyer, B.; Jonas, K. Sensing group proximity dynamics of firefighting teams using smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Zurich, Switzerland, 9–12 September 2013; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Mawson, A.R. Understanding mass panic and other collective responses to threat and disaster. Psychiatry Interpers. Biol. Process. 2005, 68, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moussaïd, M.; Perozo, N.; Garnier, S.; Helbing, D.; Theraulaz, G. The walking behaviour of pedestrian social groups and its impact on crowd dynamics. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Lederman, O.; Cao, J.; Berg, F.; Tang, S.; Pentland, A. GINA: Group Gender Identification Using Privacy-Sensitive Audio Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), Singapore, 17–20 November 2018; pp. 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Luo, C.; Chan, M. SocialProbe: Understanding Social Interaction Through Passive WiFi Monitoring. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services (MobiQuitous), Hiroshima, Japan, 28 November–1 December 2016; pp. 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærgaard, M.B.; Wirz, M.; Roggen, D.; Tröster, G. Detecting pedestrian flocks by fusion of multi-modal sensors in mobile phones. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–8 September 2012; pp. 240–249. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Qin, Z.; Song, H. A temporal-spatial method for group detection, locating and tracking. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 4484–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhu, W. The Synchronization of Data Collection for Real-time Group Recognition. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 129, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirz, M.; Schläpfer, P.; Kjærgaard, M.B.; Roggen, D.; Feese, S.; Tröster, G. Towards an online detection of pedestrian flocks in urban canyons by smoothed spatio-temporal clustering of GPS trajectories. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGSPATIAL International Workshop on Location-Based Social Networks, Chicago, IL, USA, 1 November 2011; pp. 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kalnis, P.; Mamoulis, N.; Bakiras, S. On discovering moving clusters in spatio-temporal data. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Advances in Spatial and Temporal Databases (SSTD), Angra dos Reis, Brazil, 22–24 August 2005; pp. 364–381. [Google Scholar]
- Ram, A.; Jalal, S.; Jalal, A.S.; Kumar, M. A density based algorithm for discovering density varied clusters in large spatial databases. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2010, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Frankowski, D.; Ludford, P.; Shekhar, S.; Terveen, L. Discovering personal gazetteers: An interactive clustering approach. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual ACM International Workshop on Geographic Information Systems, Arlington, VA, USA, 12–13 November 2004; pp. 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulos, C.; Hadjiefthymiades, S.; Kolomvatsos, K. Time-optimized user grouping in location based services. Comput. Netw. 2015, 81, 220–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, C.; Kolomvatsos, K.; Hadjiefthymiades, S. Efficient Location Based Services for Groups of Mobile Users. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management, Milan, Italy, 3–6 June 2013; pp. 6–15. [Google Scholar]
- Roggen, D.; Wirz, M.; Tröster, G.; Helbing, D. Recognition of Crowd Behavior from Mobile Sensors with Pattern Analysis and Graph Clustering Methods. Netw. Heterog. Media 2011, 6, 521–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Han, Q. Grace: Recognition of Proximity-Based Intentional Groups Using Collaborative Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 28–30 October 2014; pp. 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Cao, J.; Liu, X.; Tang, S. SNOW: Detecting Shopping Groups Using WiFi. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 3908–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærgaard, M.B.; Wirz, M.; Roggen, D.; Tröster, G. Mobile sensing of pedestrian flocks in indoor environments using wifi signals. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), Austin, TX, USA, 23–27 March 2012; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kjærgaard, M.B.; Blunck, H.; Wüstenberg, M.; Gr, K.; Wirz, M.; Roggen, D.; Tröster, G. Time-lag method for detecting following and leadership behavior of pedestrians from mobile sensing data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), San Diego, CA, USA, 18–22 March 2013; pp. 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Min, C.; Hwang, C.; Lee, J.; Hwang, I.; Ju, Y.; Yoo, C.; Moon, M.; Lee, U.; Song, J. SocioPhone: Everyday face-to-face interaction monitoring platform using multi-phone sensor fusion. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services (MobiSys), Taipei, Taiwan, 25–28 June 2013; pp. 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Gu, Y. A Recognition Approach for Groups with Interactions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications, Tianjin, China, 20–22 June 2018; pp. 846–852. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, D.; Wirz, M.; Roggen, D.; Tröster, G.; Beigl, M. Group affiliation detection using model divergence for wearable devices. In Proceedings of the ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–17 September 2014; pp. 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, N.; Zhao, Y.; Han, Q.; Zhu, W.; Wu, H. Identification of Partitions in a Homogeneous Activity Group Using Mobile Devices. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2016, 2016, 3545327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cristian, F. Probabilistic clock synchronization. Distrib. Comput. 1989, 3, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusella, R.; Zatti, S. The accuracy of the clock synchronization achieved by TEMPO in Berkeley UNIX 4.3BSD. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 1987, 7, 260–261. [Google Scholar]
- Veríssimo, P.; Rodrigues, L.; Casimiro, A. CesiumSpray: A Precise and Accurate Global Time Service for Large-scale Systems. Real-Time Syst. 1997, 12, 243–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeriwal, S.; Kumar, R.; Srivastava, M.B. Timing-sync Protocol for Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 5–7 November 2003; pp. 138–149. [Google Scholar]
- Lenzen, C.; Sommer, P.; Wattenhofer, R. PulseSync: An Efficient and Scalable Clock Synchronization Protocol. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2015, 23, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, Y.; Liu, S.; Yin, Z.; Naik, A.V.; Prabhakar, B.; Rosunblum, M.; Vahdat, A. Exploiting a natural network effect for scalable, fine-grained clock synchronization. In Proceedings of the 15th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI), Renton, WA, USA, 9–11 April 2018; pp. 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Li, D. A Nonlinear Model for Time Synchronization. In Proceedings of the 2019 Workshop on Synchronization and Timing Services, San Jose, CA, USA, 25–28 March 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- del Aguila Pla, P.; Pellaco, L.; Dwivedi, S.; Händel, P.; Jaldén, J. Clock synchronization over networks—Identifiability of the sawtooth model. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.08208v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuksel, C.; Schaefer, S.; Keyser, J. Parameterization and applications of Catmull–Rom curves. Computer-Aided Des. 2011, 43, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fidge, C.J. Timestamps in Message-Passing Systems That Preserve the Partial Ordering. Aust. Comput. Sci. Commun. 1988, 10, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tarjan, R. Depth-first search and linear graph algorithms. SIAM J. Comput. 1972, 1, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brscic, D.; Kanda, T.; Ikeda, T.; Miyashita, T. Person tracking in large public spaces using 3-D range sensors. IEEE Trans. Human-Mach. Syst. 2013, 43, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, H.; Godau, M. Computing the Fréchet distance between two polygonal curves. Int. J. Comput. Geom. Appl. 1995, 5, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toohey, K.; Duckham, M. Trajectory similarity measures. Sigspat. Spec. 2015, 7, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number of Messages | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (InfNum, AveLength) | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 |
| Exp.1 | (8, 1.015) | (9, 1.113) | (8, 1.028) | (0, 1.346) | (0, 0.965) | (0, 0.935) | (0, 0.781) | (0, 0.636) |
| Exp.2 | (12, inf) | (5, 0.607) | (7, 0.616) | (3, 0.965) | (3, 1.314) | (0, 1.036) | (0, 0.941) | (0, 0.705) |
| Exp.3 | (15, inf) | (3, 1.979) | (7, 0.621) | (3, 1.273) | (1, 1.417) | (0, 0.649) | (0, 1.087) | (0, 0.657) |
| Exp.4 | (12, inf) | (10, inf) | (2, 0.944) | (0, 1.531) | (0, 1.414) | (1, 0.925) | (0, 0.93) | (0, 0.489) |
| Exp.5 | (12, 1.342) | (9, 0.795) | (4, 1.317) | (4, 1.231) | (2, 0.594) | (0, 1.281) | (0, 0.74) | (0, 0.495) |
| Average | (11.8, inf) | (7.2, inf) | (5.6, 0.905) | (2.2, 1.269) | (1.4, 1.141) | (0.2, 0.965) | (0, 0.896) | (0, 0.596) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, W.; Xu, L.; Tang, Y.; Xie, R. Synchronized Data Collection for Human Group Recognition. Sensors 2021, 21, 7094. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217094
Zhu W, Xu L, Tang Y, Xie R. Synchronized Data Collection for Human Group Recognition. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7094. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217094
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Weiping, Lin Xu, Yijie Tang, and Rong Xie. 2021. "Synchronized Data Collection for Human Group Recognition" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7094. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217094
APA StyleZhu, W., Xu, L., Tang, Y., & Xie, R. (2021). Synchronized Data Collection for Human Group Recognition. Sensors, 21(21), 7094. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217094






