Improvement of Reliability Determination Performance of Real Time Kinematic Solutions Using Height Trajectory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. LAMBDA Method and Ratio Test
- Z is composed of all integer values.
- The inverse of Z exists.
- The inverse of Z likewise consists of all integer values.
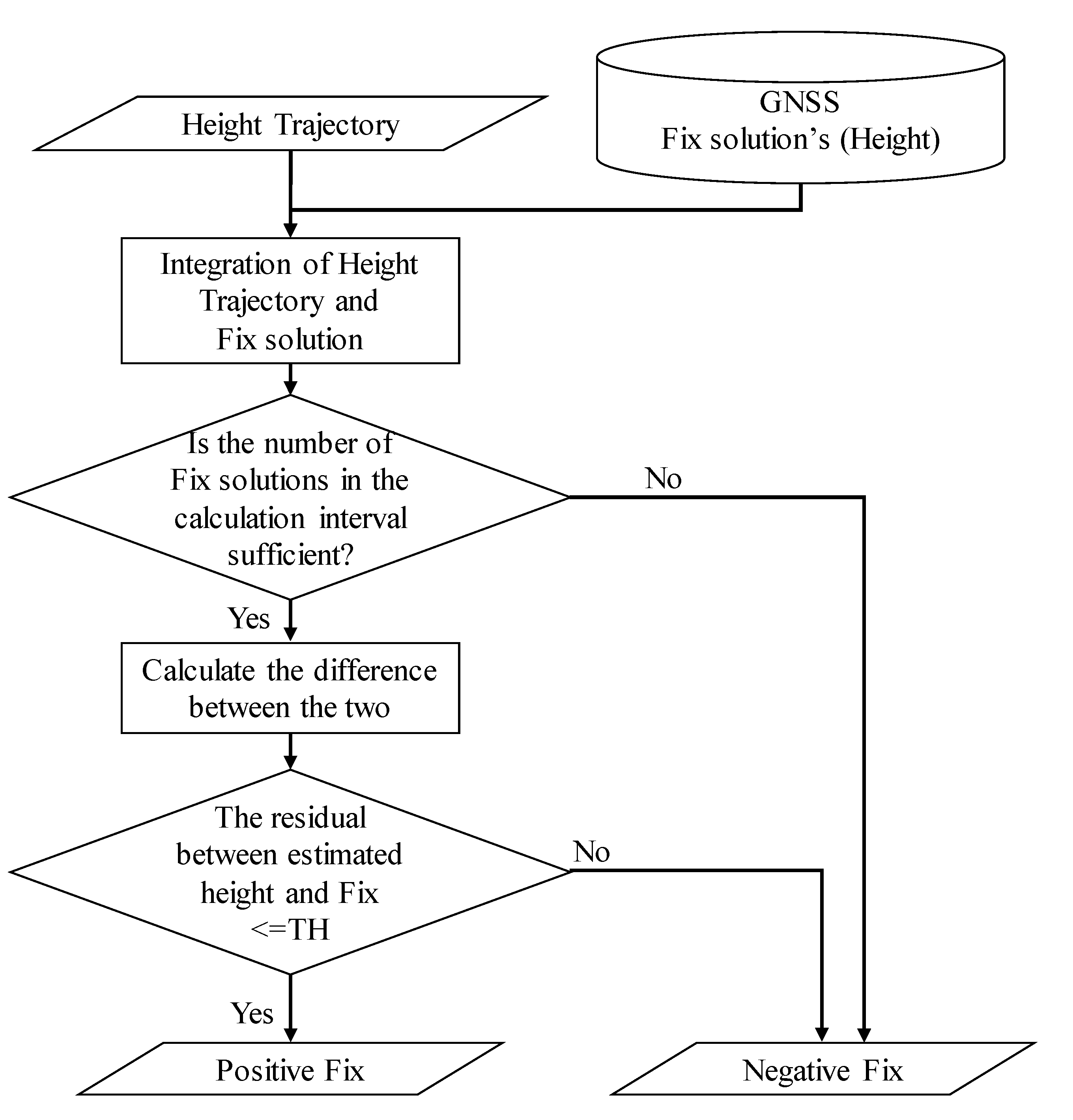
3. Proposed Method
3.1. A method for Determining the Reliability of Fix Solutions Using Height Trajectories
3.2. Estimation of Height Trajectory
3.3. Fix Solution Verification
- Estimate the acceleration error without determining the fix solution.
- Determine the fix solution using the estimated acceleration error.
- Update the time.
- Estimate the acceleration error using the judged fix solution.
- Repeat these steps.
4. Evaluation Test
4.1. Summary of Evaluation Test Conditions
4.2. Test in Urban Area (Route A)
4.3. Test in Dense Urban Area (Route B)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takasu, T.; Yasuda, A. Development of the low cost RTK-GPS receiver with an open source program package RTKLIB. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on GPS/GNSS, Jeju, Korea, 4–6 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Dubbelman, G. An Experimental study on relative and absolute pose graph fusion for vehicle localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 11–14 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, E.; Mohammadiha, N. A statistical GPS error model for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Changshu, Suzhou, China, 26–30 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, B.C.; Fassbender, D.; Wuensche, H.J. Precise object-relative positioning for car-like robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1–4 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Cai, B.; Wang, J. Track-constrained GNSS/Odometer-based train localization using a particle filter. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Gotenburg, Sweden, 19–22 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.; Gu, Y.; Kamijo, S. Vehicle positioning with the integration of scene understanding and 3D map in urban environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 11–14 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ghallabi, F.; Ghayath, E.; Mitte, M.; Nashashibi, F. LIDAR-Based road signs detection For Vehicle Localization in an HD Map. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Paris, France, 9–12 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aldibaja, M.; Yanase, A.; Kim, T.H.; Kuramoto, A.; Yoneda, K.; Suganuma, N. Accurate elevation maps based graph-slam framework for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Paris, France, 9–12 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Puricer, P.; Kl, P.; Seidl, L.; Vejražka, F. GNSS software receiver—A versatile platform for navigation systems signals processing. In Proceedings of the 47th International Synposium ELMAR-2005, Zadar, Croatia, 8–10 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Prades, F.C.; Avilés, C.; Estove, L.; Arribas, J.; Closas, P. Design patterns for GNSS software receivers. In Proceedings of the 5th ESA Workshop on Satellite Navigation Technologies and European Workshop on GNSS Signals and Signal Processing (NAVITEC), Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 8–10 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Frei, E. Rapid static positioning based of the first ambiguity resolution approach “FARA”: Theory and first results. Manuscr. Geod. 1990, 15, 325–356. [Google Scholar]
- Hatch, R. Instantaneous Ambiguity Resolution. In Kinematic Systems in Geodesy, Surveying, and Remote Sensing; Schwarz, K.P., Lachapelle, G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 299–308. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: A method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J. Geod. 1996, 70, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, Y. Reliability of partial ambiguity fixing with multiple GNSS constellations. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Verhagen, S.; Wu, J. A data driven partial ambiguity resolution: Two step success rate criterion, and its simulation demonstration. Adv. Space Res. 2016, 58, 2435–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meguro, J.; Kojima, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Teramoto, E. Positioning technique based on vehicle trajectory using GPS raw data and low-cost IMU. Int. J. Automot. Eng. 2012, 3, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kikuchi, R.; Kubo, N. Reliability Estimation for RTK-GNSS/IMU/Vehicle Speed Sensors in Urban Environment. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on GNSS (IS-GNSS), Kyoto, Japan, 16–19 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.W.; Park, C.G. Enhanced pedestrian navigation based on course angle error estimation using cascaded Kalman filters. Sensors 2018, 18, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, G.; Einicke, G.A.; Malos, J.T.; Dovis, F. Performance analysis of constrained loosely coupled GPS/INS integration solutions. Sensors 2012, 12, 15983–16007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qifen, L.; Lun, A.; Junpeng, A.; Hsu, L.T.; Kamijo, S.; Gu, Y. Tightly coupled RTK/MIMU using single frequency BDS/GPS/QZSS receiver for automatic driving vehicle. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Monterey, CA, USA, 23–26 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rabbou, M.A.; El-Rabbany, A. Tightly coupled integration of GPS precise point positioning and MEMS-based inertial systems. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Rabiee, R.; Yan, Y.; Tay, W.P. A particle filter for vehicle tracking with lane level accuracy under GNSS-denied environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Yokohama, Japan, 16–19 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Falco, G.; Pini, M.; Marucco, G. Loose and tight GNSS/INS integrations: Comparison of performance assessed in real urban scenarios. Sensors 2017, 17, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, B. A robust vehicle localization approach based on GNSS/IMU DMI/LiDAR sensor fusion for autonomous vehicles. Sensors 2017, 17, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, N.; Zhang, Y.; Hatta, D. Integration of GNSS-PPP and IMU/SPEED sensors in urban areas. In Proceedings of the IEEE the Institute of Navigation (ION), Reston, VA, USA, 28–31 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, J.S.; Gerhmann, A.; Thevenon, P.; Brocard, P.; Afia, A.B.; Julien, O. Use of a fisheye camera for GNSS NLOS exclusion and characterization in urban environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE institute of Navigation (ION), Savannah, GA, USA, 11–14 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Wada, Y.; Hsu, L.T.; Kamijo, S. SLAM with 3Dimensional-GNSS. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Savannah, GR, USA, 11–16 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Low-cost, high-precision, single-frequency GPS–BDS RTK positioning. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Odolinski, R.; Odijk, D. Instantaneous BeiDou+GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles. J. Geod. 2013, 88, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Odijk, D. Combined BDS, Galileo, QZSS and GPS single-frequency RTK. GPS Solut. 2014, 19, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Niu, X.; Gao, Z. Tightly-Coupled integration of Multi-GNSS single-frequency RTK and MEMS-IMU for enhanced positioning performance. Sensors 2017, 17, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meguro, J.; Murata, T.; Takiguchi, J.; Amano, Y.; Hashizume, T. GPS multipath mitigation for urban area using omnidirectional infrared camera. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2009, 10, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.T. GNSS multipath detection using a machine learning approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Yokohama, Japan, 16–19 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Meguro, J.; Arakawa, T.; Mizutani, S.; Takanose, A. Low-cost lane-level positioning in urban area using optimized long time series GNSS and IMU data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Least-squares estimation of the integer GPS ambiguities. Invited Lecture, Section IV Theory and Methodology. In Proceedings of the IAG General Meeting, Beijing, China, 6–13 August 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.W.; Yang, X.; Zhou, T. MLAMBDA: A modified LAMBDA method for integer least-squares estimation. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Verhagen, S. On GNSS ambiguity acceptance tests. In Proceedings of the IGNSS Symposium, Sydney, Australia, 4–6 December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Verhagen, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. The ratio test for future GNSS ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Verhagen, S.; Wu, J. An efficient implementation of fixed failure-rateRatio test for GNSS ambiguity resolution. Sensors 2016, 16, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
















| Proposal Method | High Reliability | Low Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| Status Name | Positive Fix | Negative Fix |
| Equipment | Manufacturer | Model |
|---|---|---|
| GNSS Antennas | Aero | AT1645-540T |
| GNSS receiver | U-blox | F9P |
| IMU | Tamagawa | AU7684 |
| Speed | Toyota Sienta | CAN |
| Reference | Applanix | POSLV220 |
| Error Max (m) | Error Mean (m) | Error SD (m) | Error RMS (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fix | 2D | 78.5 | 0.07 | 2.08 | 4.16 |
| Height | 186.6 | 0.64 | 6.77 | 6.79 | |
| Positive Fix | 2D | 5.58 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.17 |
| Height | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| Number | Conventional Fix | Proposal Positive Fix | Proposal Negative Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| Error < 0.3 m | 6372 | 6369 | 3 |
| Error > 0.3 m | 134 | 4 | 131 |
| Error Max (m) | Error Mean (m) | Error SD (m) | Error RMS (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fix | 2D | 390.7 | 0.37 | 7.38 | 14.8 |
| Height | 808.7 | 0.85 | 13.9 | 13.9 | |
| Positive Fix | 2D | 1.07 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.22 |
| Height | 0.73 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.13 |
| Number | Conventional Fix | Proposal Positive Fix | Proposal Negative Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| Error < 0.3 m | 6577 | 5370 | 1207 |
| Error > 0.3 m | 619 | 14 | 605 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takanose, A.; Atsumi, Y.; Takikawa, K.; Meguro, J. Improvement of Reliability Determination Performance of Real Time Kinematic Solutions Using Height Trajectory. Sensors 2021, 21, 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020657
Takanose A, Atsumi Y, Takikawa K, Meguro J. Improvement of Reliability Determination Performance of Real Time Kinematic Solutions Using Height Trajectory. Sensors. 2021; 21(2):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020657
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakanose, Aoki, Yoshiki Atsumi, Kanamu Takikawa, and Junichi Meguro. 2021. "Improvement of Reliability Determination Performance of Real Time Kinematic Solutions Using Height Trajectory" Sensors 21, no. 2: 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020657
APA StyleTakanose, A., Atsumi, Y., Takikawa, K., & Meguro, J. (2021). Improvement of Reliability Determination Performance of Real Time Kinematic Solutions Using Height Trajectory. Sensors, 21(2), 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020657




