Artificial Intelligence for Pigment Classification Task in the Short-Wave Infrared Range
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Short-Wave Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging (SWIR)
2.2. Visible Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging (VIS-RIS)
2.3. Single Point X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)
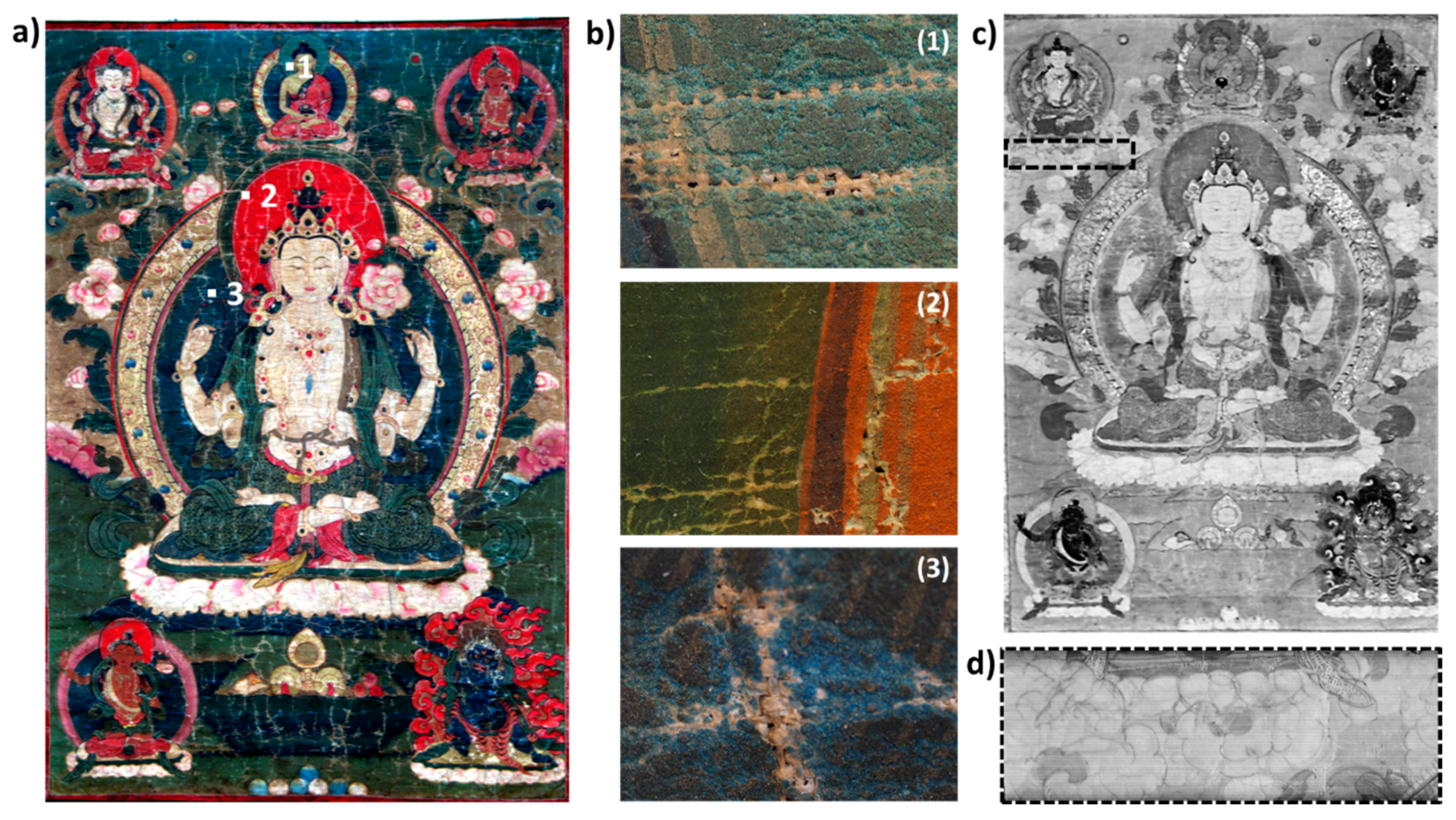
2.4. Samples
2.5. DNN Model
2.5.1. Overall DNN Workflow
2.5.2. DNN Input Dataset
2.5.3. DNN Architecture
2.6. Spectral Angle Mapping Algorithm (SAM)
3. Results
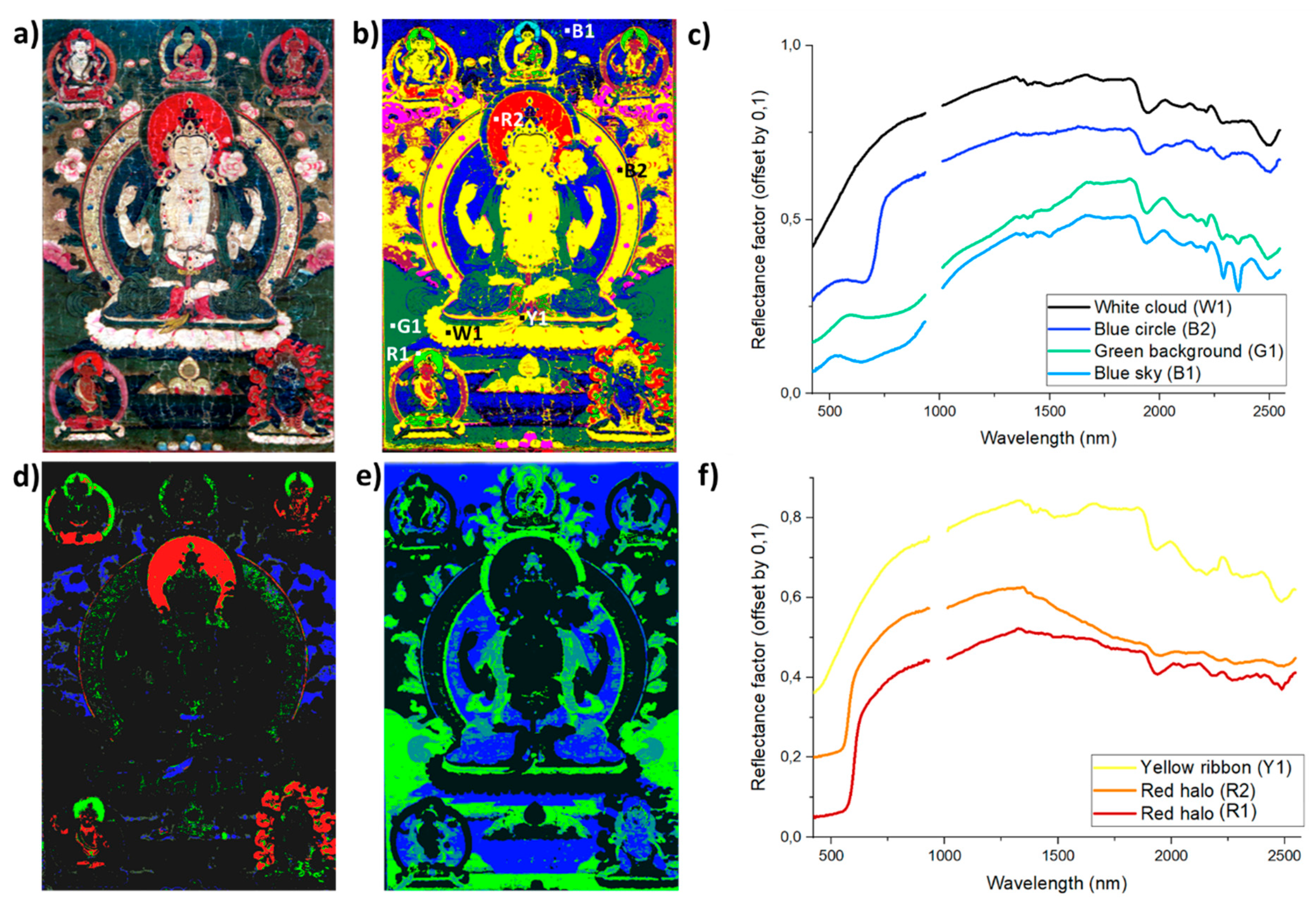
3.1. Comparison of DNN versus SAM for Pigment Classification and Mapping Tasks
3.2. The Use of Deep NN for Classification Task in Historical Tangkas
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walter, P.; de Viguerie, L. Materials science challenges in paintings. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alfeld, M.; de Viguerie, L. Recent developments in spectroscopic imaging techniques for historical paintings—A review. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2017, 136, 81–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picollo, M.; Cucci, C.; Casini, A.; Stefani, L. Hyper-Spectral Imaging Technique in the Cultural Heritage Field: New Possible Scenarios. Sensors 2020, 20, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucci, C.; Casini, A. Hyperspectral imaging for artworks investigation, in Data Handling in Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 32, pp. 583–604. [Google Scholar]
- Delaney, J.K.; Thoury, M.; Zeibel, J.G.; Ricciardi, P.; Morales, K.M.; Dooley, K.A. Visible and infrared imaging spectroscopy of paintings and improved reflectography. Herit. Sci. 2016, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabrieli, F.; Dooley, K.A.; Facini, M.; Delaney, J.K. Near-UV to mid-IR reflectance imaging spectroscopy of paintings on the macroscale. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cucci, C.; Delaney, J.K.; Picollo, M. Reflectance hyperspectral imaging for investigation of works of art: Old master paintings and illuminated manuscripts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 2070–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Li, G.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lei, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, L. Shortwave infrared imaging spectroscopy for analysis of ancient paintings. Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 71, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagnini, M.; Miliani, C.; Cartechini, L.; Rocchi, P.; Brunetti, B.G.; Sgamellotti, A. FT-NIR spectroscopy for non-invasive identification of natural polymers and resins in easel paintings. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 395, 2107–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Viguerie, L.; Pladevall, N.O.; Lotz, H.; Freni, V.; Fauquet, N.; Mestre, M.; Walter, P.; Verdaguer, M. Mapping pigments and binders in 15th century Gothic works of art using a combination of visible and near infrared hyperspectral imaging. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, K.A.; Lomax, S.; Zeibel, J.G.; Miliani, C.; Ricciardi, P.; Hoenigswald, A.; Loew, M.; Delaney, J.K. Mapping of egg yolk and animal skin glue paint binders in Early Renaissance paintings using near infrared reflectance imaging spectroscopy. Analyst 2013, 138, 4838–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokobza, L. Near infrared spectroscopy. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 1998, 6, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, M.A.; Morisawa, Y.; Futami, Y.; Ozaki, Y. Advances in molecular structure and interaction studies using near-infrared spectroscopy. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9707–9744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, B.; Masarczyk, W.; Głomb, P.; Mendys, A. Automatic pigment identification from hyperspectral data. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.J.; Duan, P.Q.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, L.F. An automatic hyperspectral scanning system for the technical investigations of Chinese scroll paintings. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, S.R.; Burnstock, A.; Michelin, A. A Preliminary Study on the Differentiation of Linseed and Poppy Oil Using Principal Component Analysis Methods Applied to Fiber Optics Reflectance Spectroscopy and Diffuse Reflectance Imaging Spectroscopy. Sensors 2020, 20, 7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Meng, D.; Hou, M.; Tian, S.; Huang, C.; Mao, J. Nonlinear Mixing Characteristics of Reflectance Spectra of Typical Mineral Pigments. Minerals 2021, 11, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Hao, Y.; Liu, X.; Hou, M.; Zhao, X. Study on the Spectral Mixing Model for Mineral Pigments Based on Derivative of Ratio Spectroscopy-Take Vermilion and Stone Yellow for Example. International Archives of the Photogrammetry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Rohani, N.; Pouyet, E.; Walton, M.; Cossairt, O.; Katsaggelos, A.K. Nonlinear unmixing of hyperspectral datasets for the study of painted works of art. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 11076–11080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohani, N.; Pouyet, E.; Walton, M.; Cossairt, O.; Katsaggelos, A.K. Pigment Unmixing of Hyperspectral Images of Paintings Using Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kleynhans, T.; Patterson, C.M.S.; Dooley, K.A.; Messinger, D.W.; Delaney, J.K. An alternative approach to mapping pigments in paintings with hyperspectral reflectance image cubes using artificial intelligence. Herit. Sci. 2020, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, K.; Tsumura, N.; Berns, R. Estimating Pigment Concentrations from Spectral Images Using an Encoder-Decoder Neural Network. J. Imaging Sci. Technol. 2020, 64, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gilles, B. Les Peintures du Bouddhisme Tibétain, French ed.; RMN: Paris, France, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.; Jackson, J. Tibetan Thangka Painting: Methods and Materials; Natl Book Network: Lanham, MD, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi, P.; Pallipurath, A. 21 The Five Colours of Art: Non-Invasive Analysis of Pigments in Tibetan Prints and Manuscripts. In Tibetan Printing: Comparison, Continuities, and Change; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 485–500. [Google Scholar]
- Brocchieri, J.; de Viguerie, L.; Sabbarese, C.; Boyer, M. Combination of noninvasive imaging techniques to characterize pigments in Buddhist thangka paintings. Xray Spectrom. 2021, 50, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, V.A.; Papillon, E.; Cotte, M.; Walter, P.; Susini, J.A. A multiplatform code for the analysis of energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectra. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2007, 62, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobbs, J.H. Kubelka—Munk theory and the prediction of reflectance. Rev. Prog. Color. Relat. Top. 1985, 15, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullback, S.; Leibler, R.A. On information and sufficiency. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Available online: https://github.com/fchollet/keras (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Bergstra, J.; Breuleux, O.; Bastien, F.; Lamblin, P.; Pascanu, R.; Desjardins, G.; Turian, J.; Bengio, Y. Theano: A CPU and GPU math expression compiler. In Proceedings of the Python for Scientific Computing Conference (SciPy), Austin, TX, USA, 28–30 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- De Carvalho, O.A.; Meneses, P.R. Spectral correlation mapper (SCM): An improvement on the spectral angle mapper (SAM). In Summaries of the 9th JPL Airborne Earth Science Workshop; JPL Publication: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2000; Volume 9, pp. 00–18. [Google Scholar]
- Spectral Python (SPy). Available online: http://www.spectralpython.net (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Ricciardi, P.; Pallipurath, A.; Rose, K. ‘It’s not easy being green’: A spectroscopic study of green pigments used in illuminated manuscripts. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 3819–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pouyet, E.; Miteva, T.; Rohani, N.; de Viguerie, L. Artificial Intelligence for Pigment Classification Task in the Short-Wave Infrared Range. Sensors 2021, 21, 6150. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186150
Pouyet E, Miteva T, Rohani N, de Viguerie L. Artificial Intelligence for Pigment Classification Task in the Short-Wave Infrared Range. Sensors. 2021; 21(18):6150. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186150
Chicago/Turabian StylePouyet, Emeline, Tsveta Miteva, Neda Rohani, and Laurence de Viguerie. 2021. "Artificial Intelligence for Pigment Classification Task in the Short-Wave Infrared Range" Sensors 21, no. 18: 6150. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186150
APA StylePouyet, E., Miteva, T., Rohani, N., & de Viguerie, L. (2021). Artificial Intelligence for Pigment Classification Task in the Short-Wave Infrared Range. Sensors, 21(18), 6150. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186150






