Distributed Fibre Optic Sensing (DFOS) for Deformation Assessment of Composite Collectors and Pipelines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
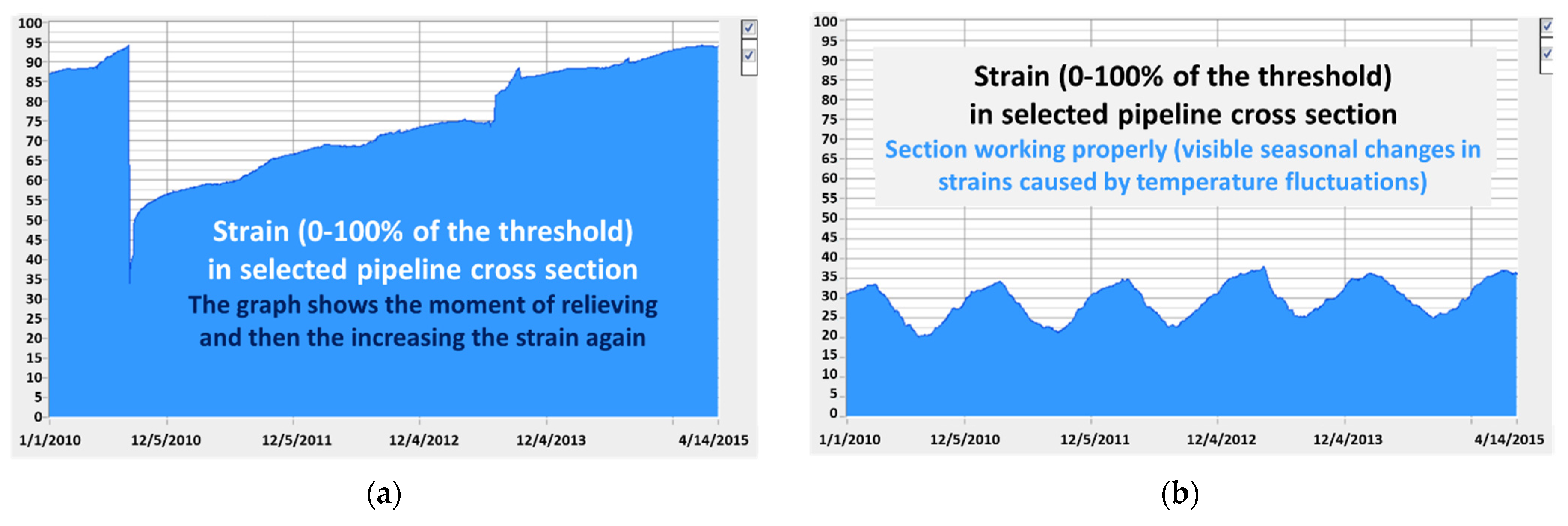
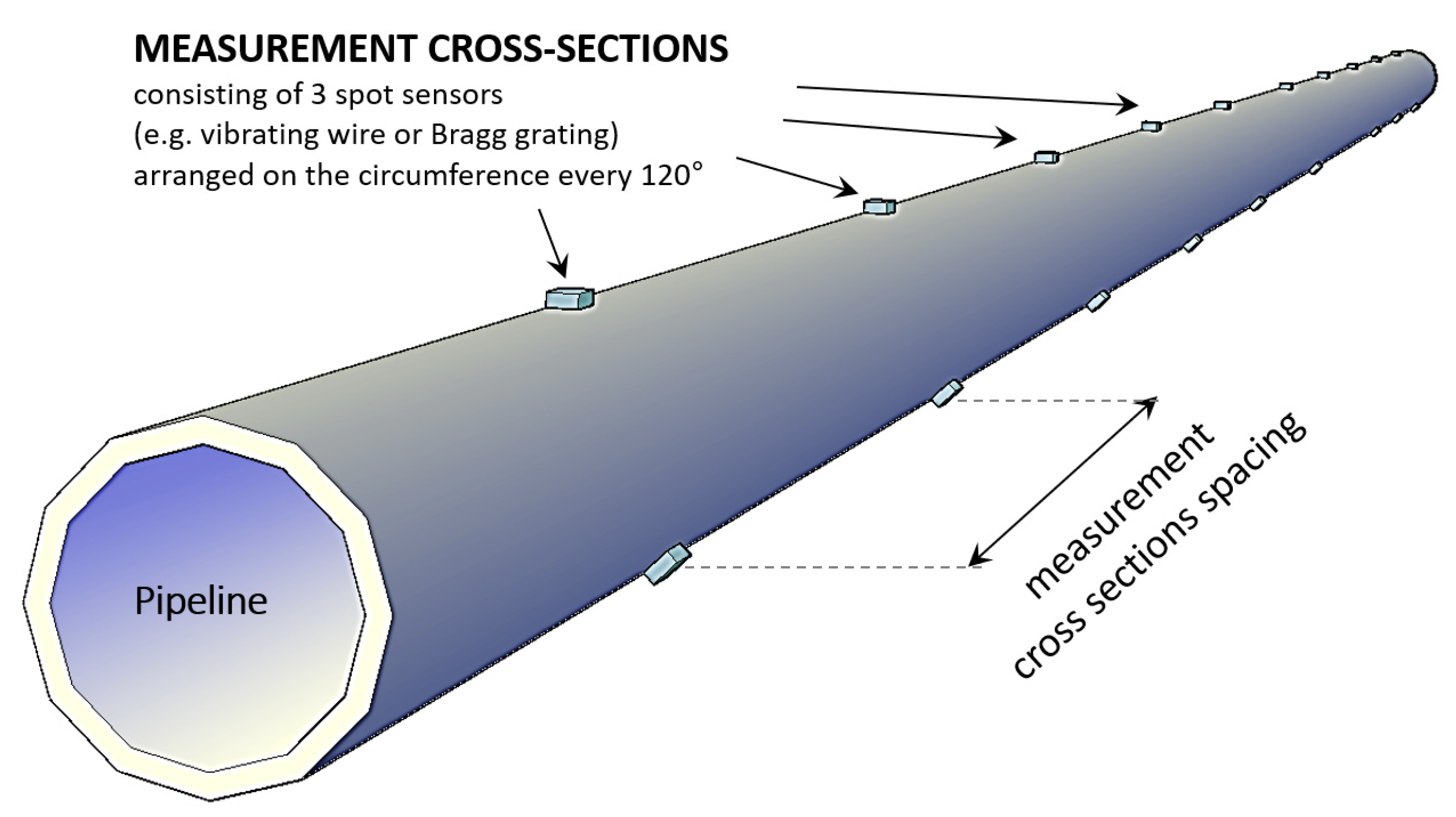
2. Structural Health Monitoring of the Pipelines
3. Distributed Fibre Optic Sensing
3.1. Operation Rules
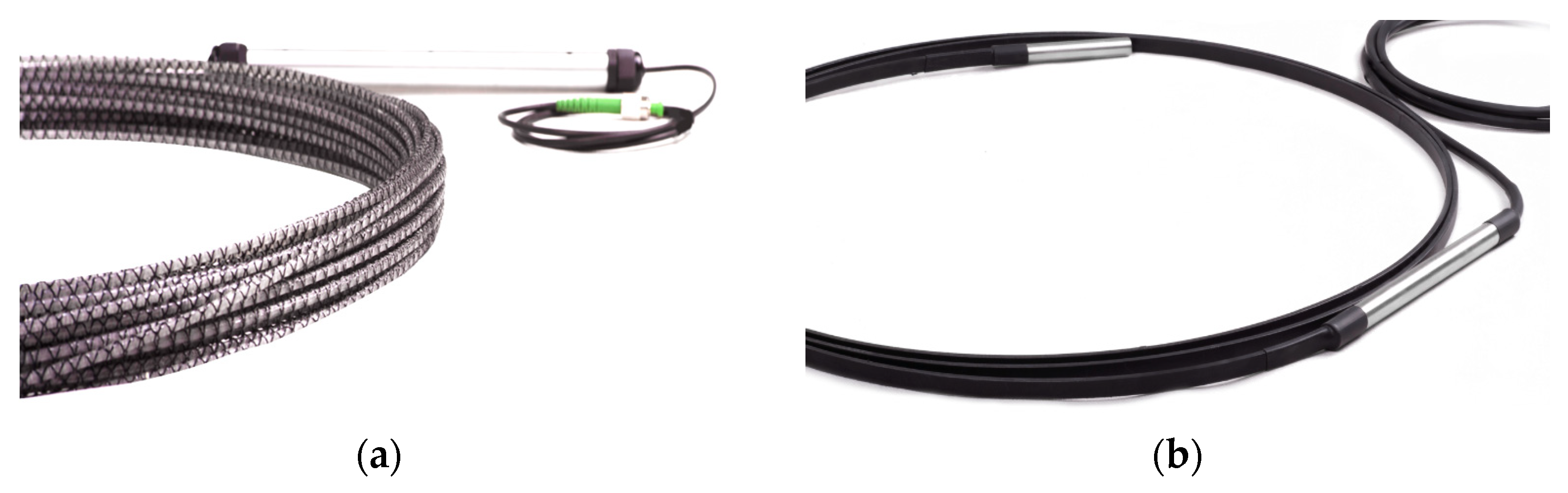
3.2. Optical Fibres for Strain Measurements
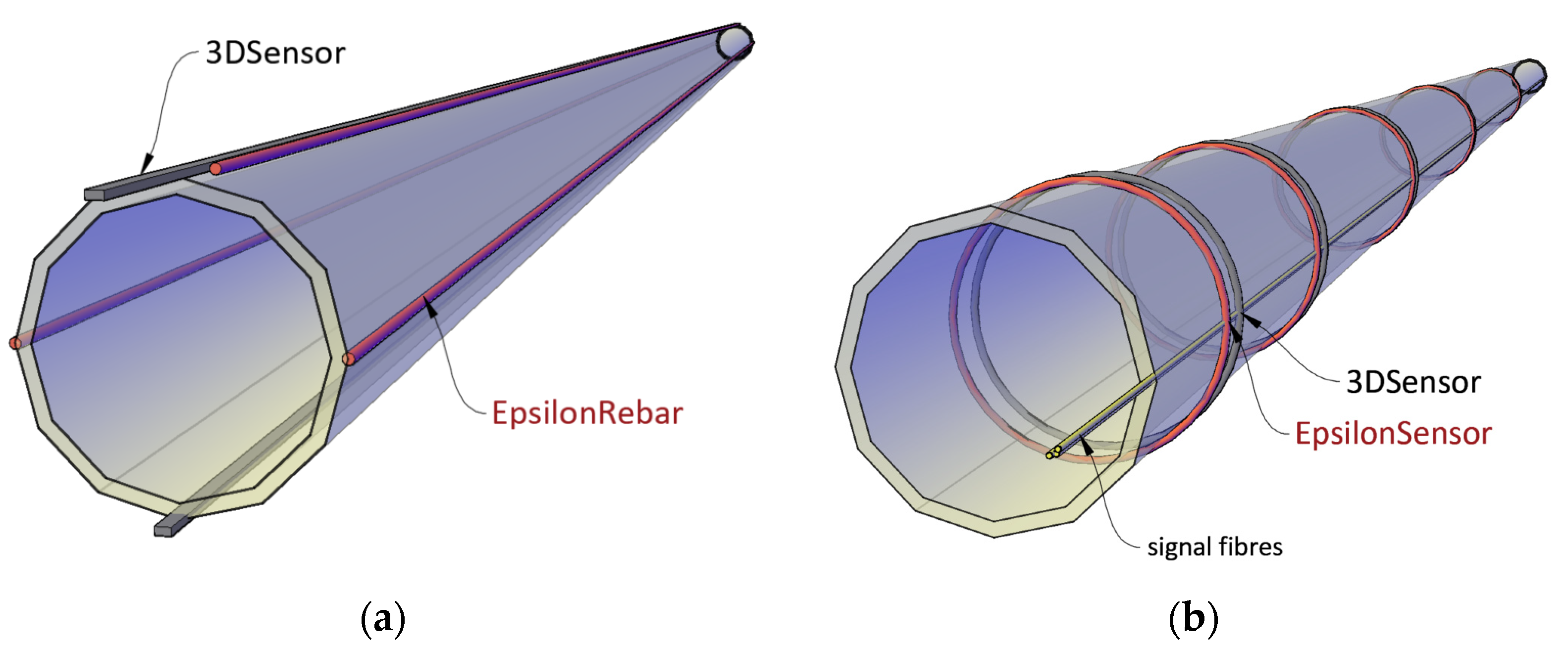
3.3. Fibre Optic Sensors for Geotechnics and Civil Engineering Applications
4. Laboratory Research
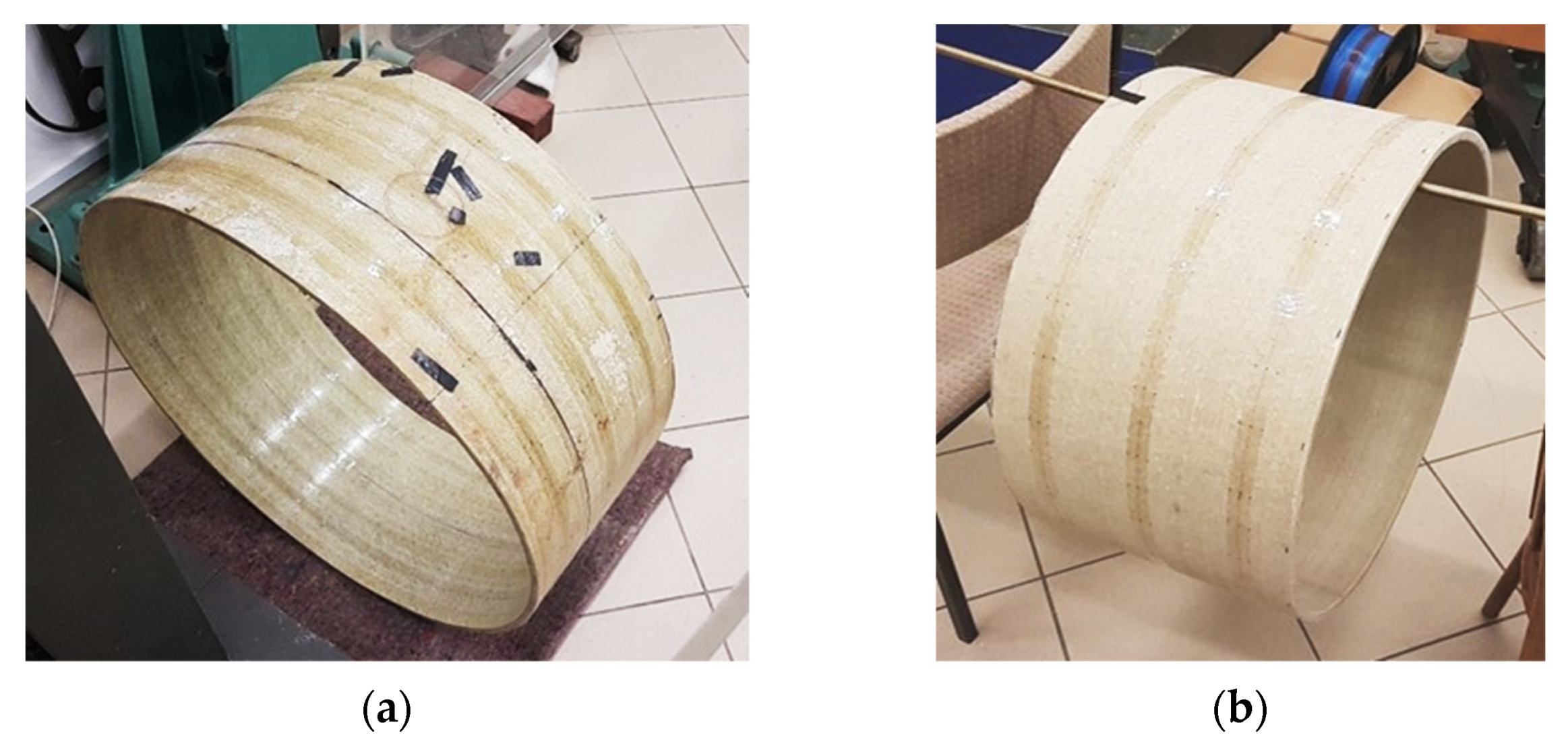
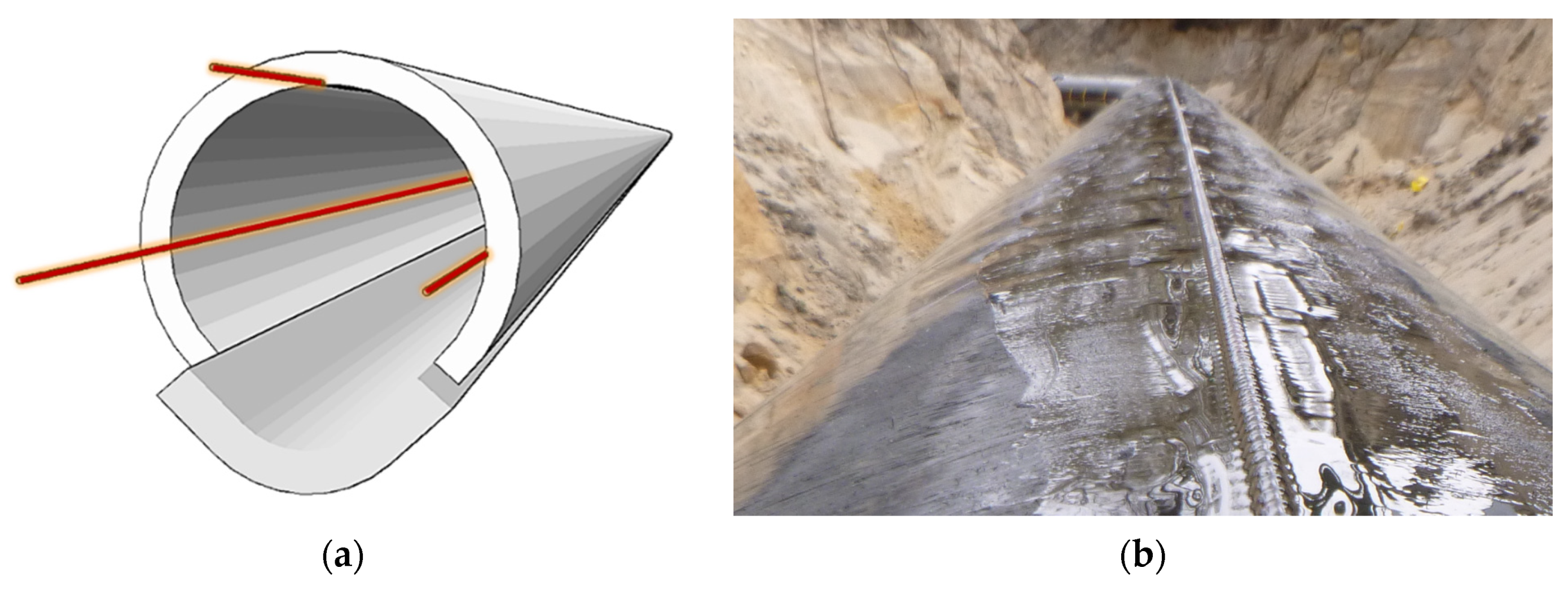
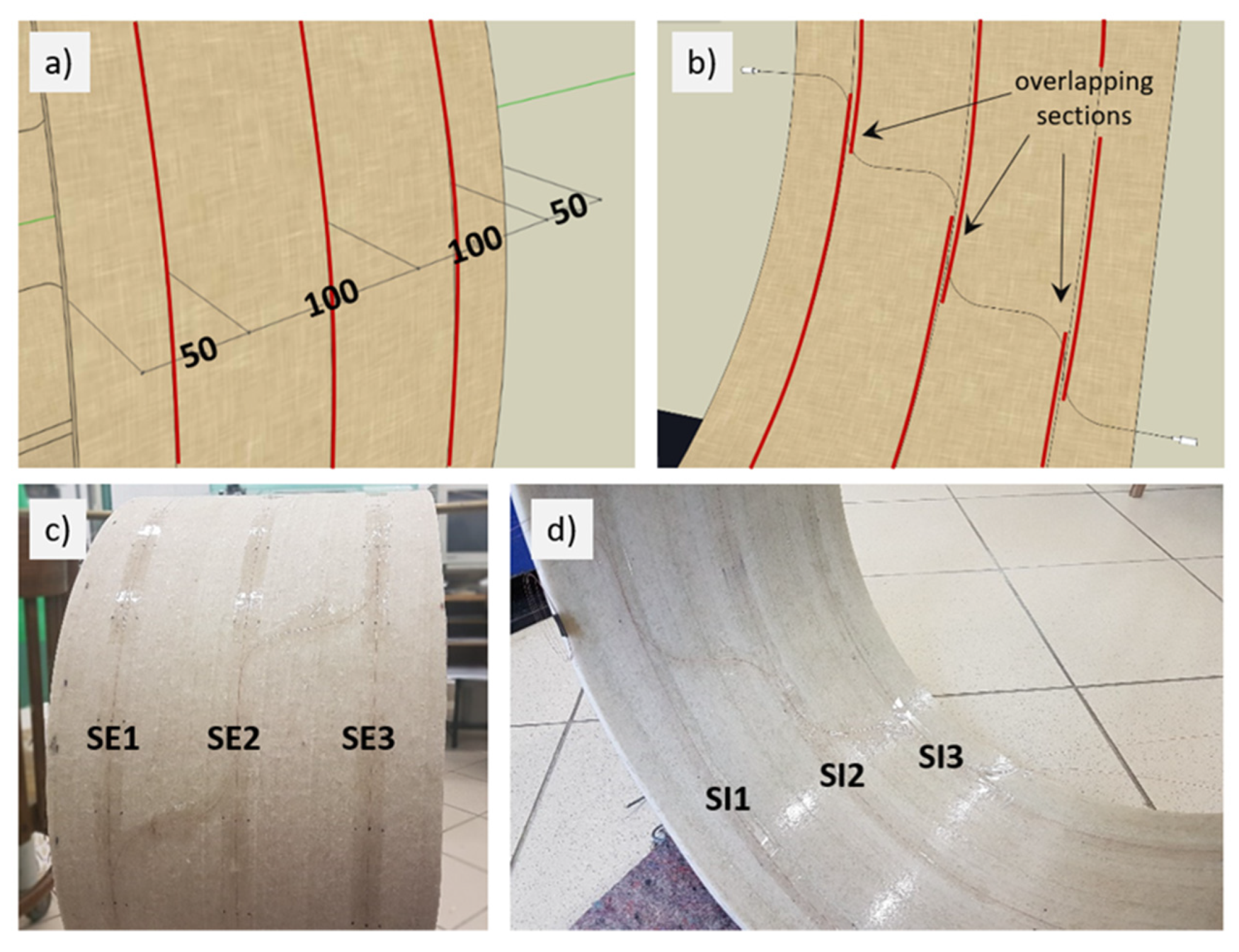
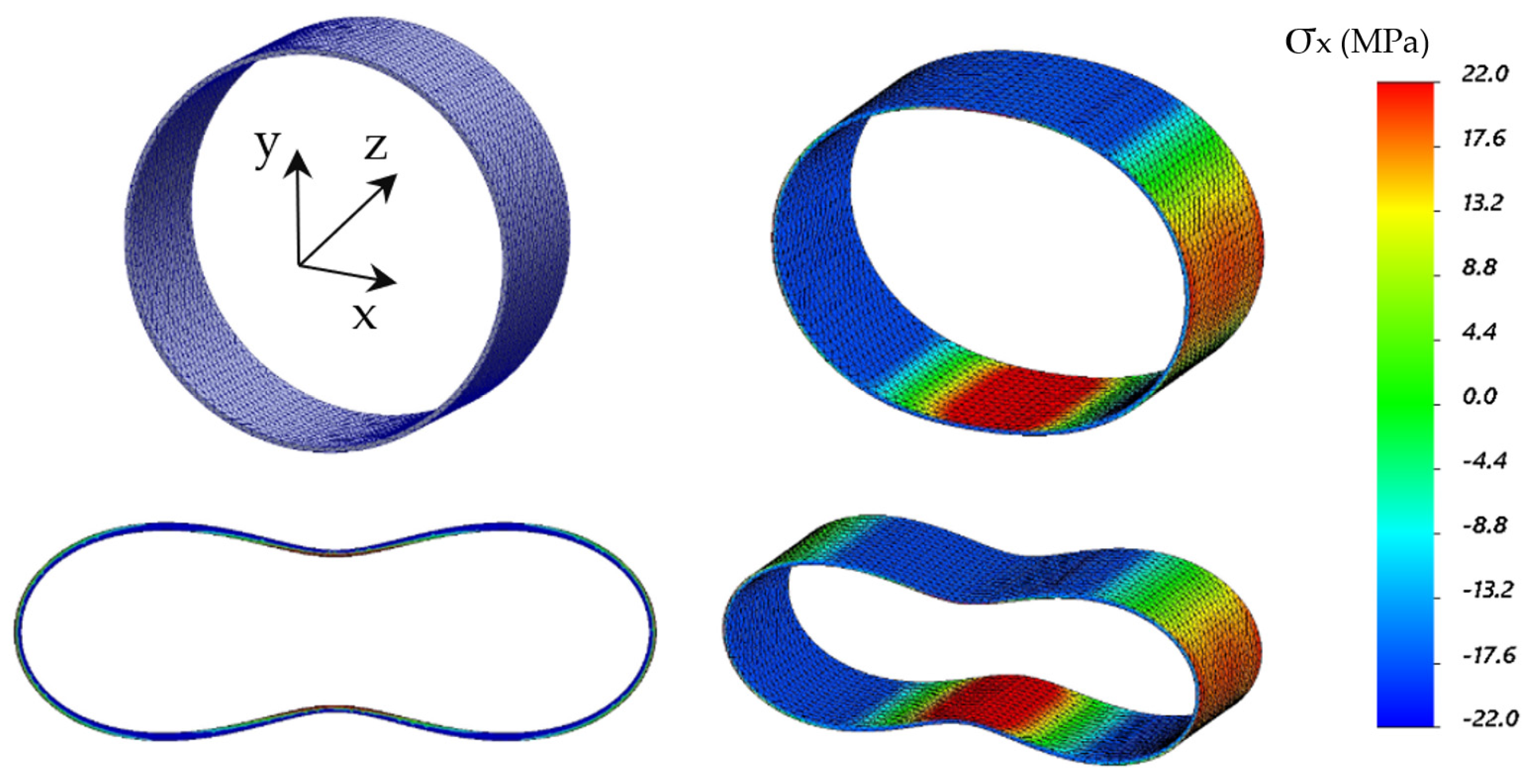
4.1. Description of the Specimens
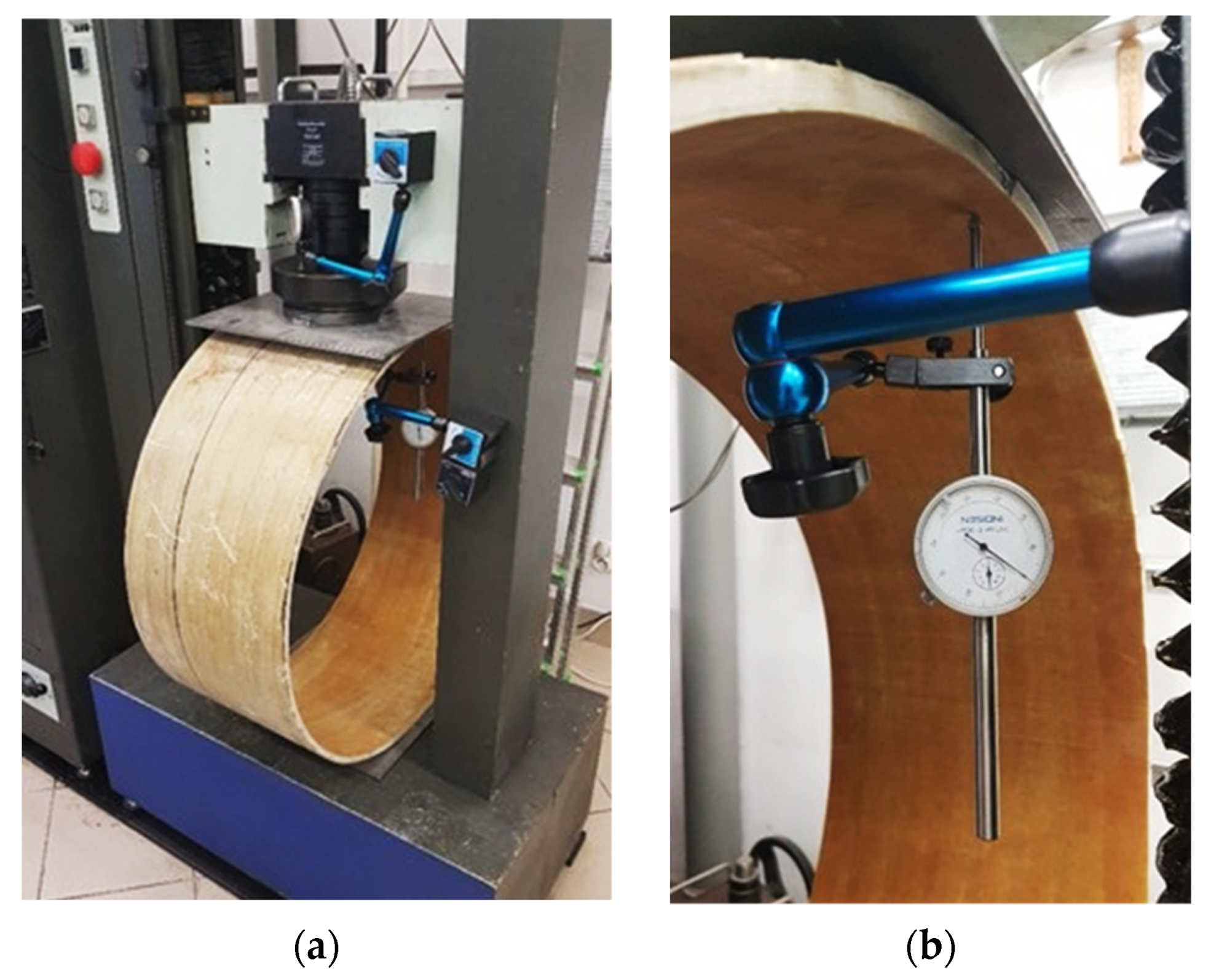
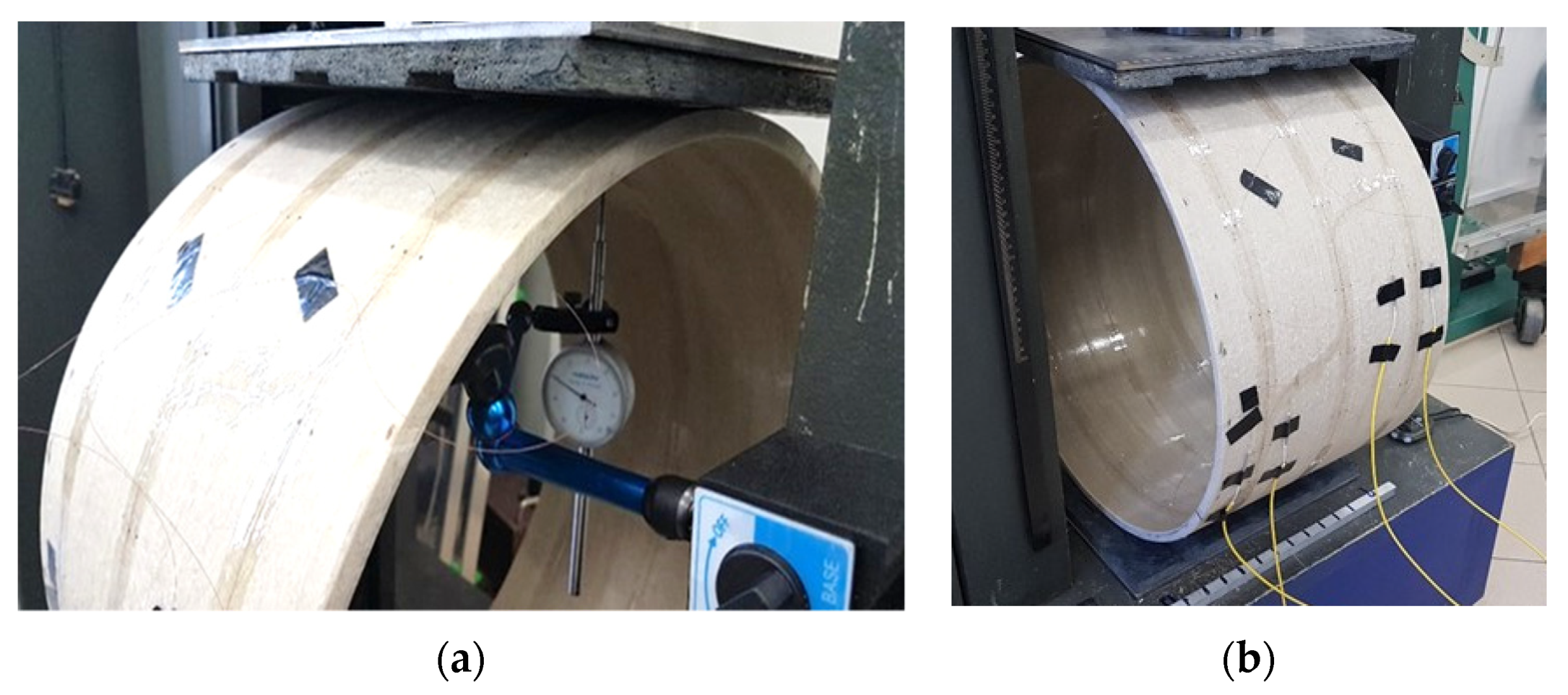
4.2. Measurement Station and Course of the Study
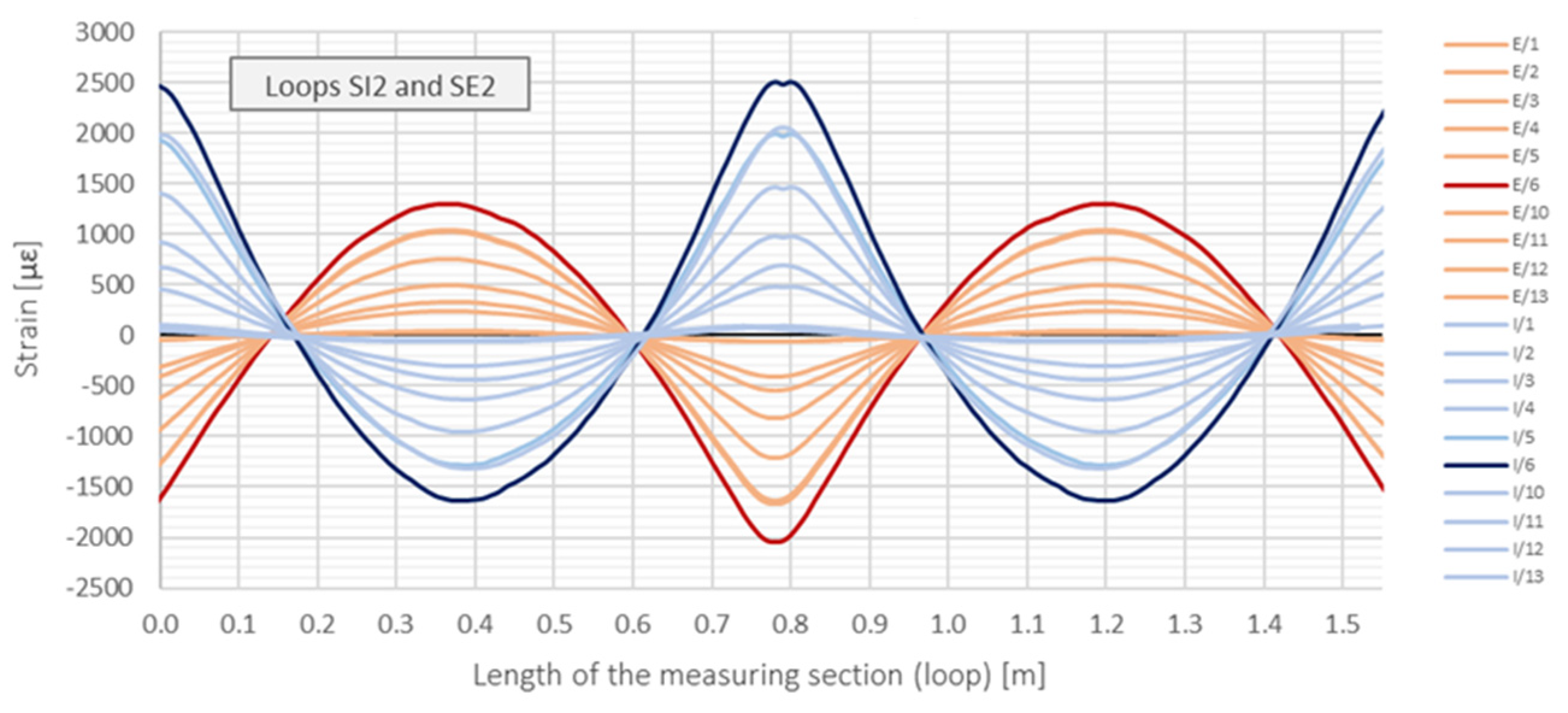
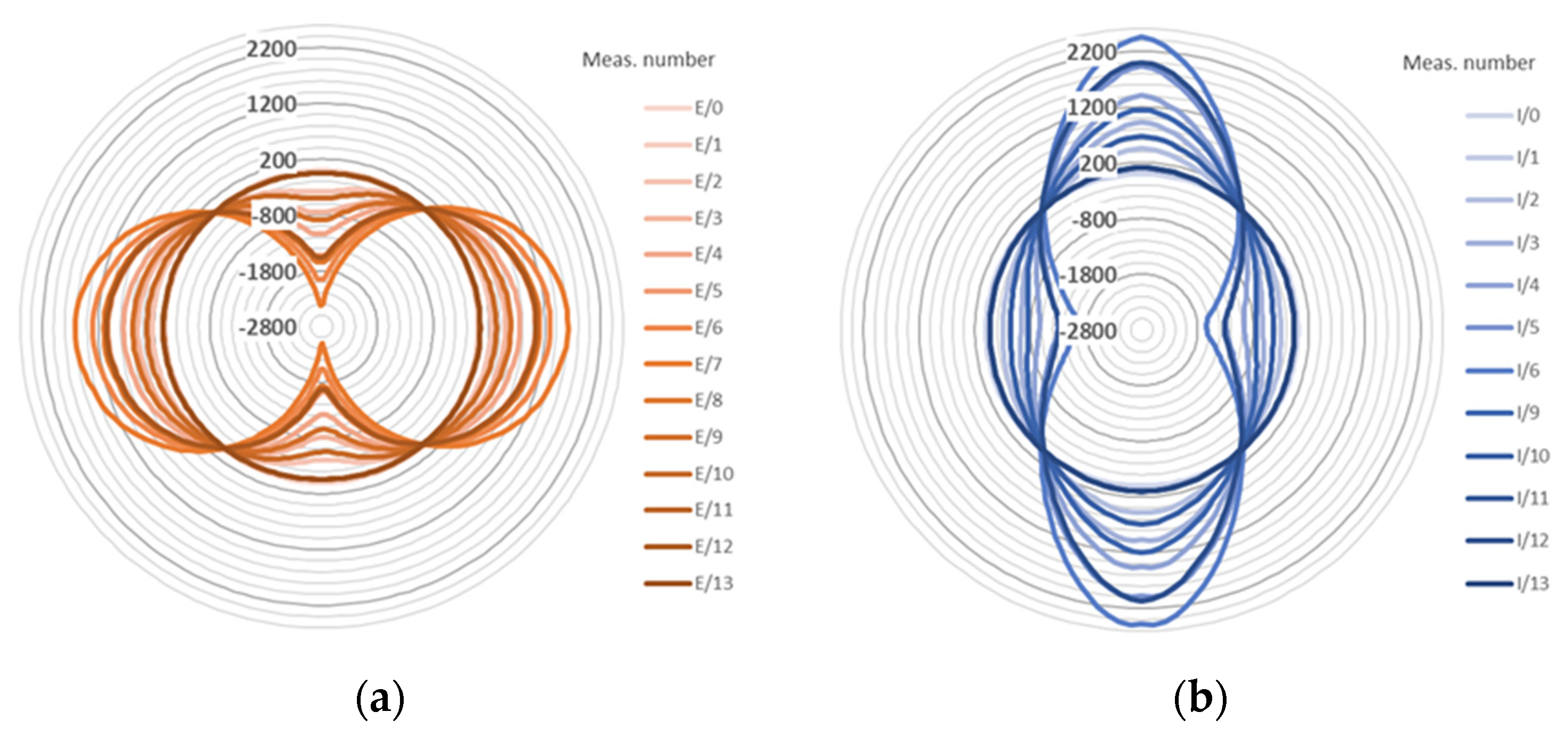
4.3. Example Measurement Results
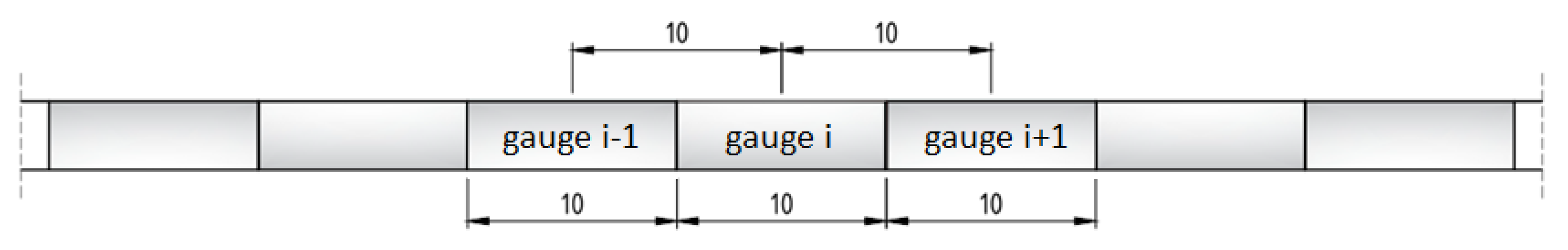
4.3.1. Strains Distributions
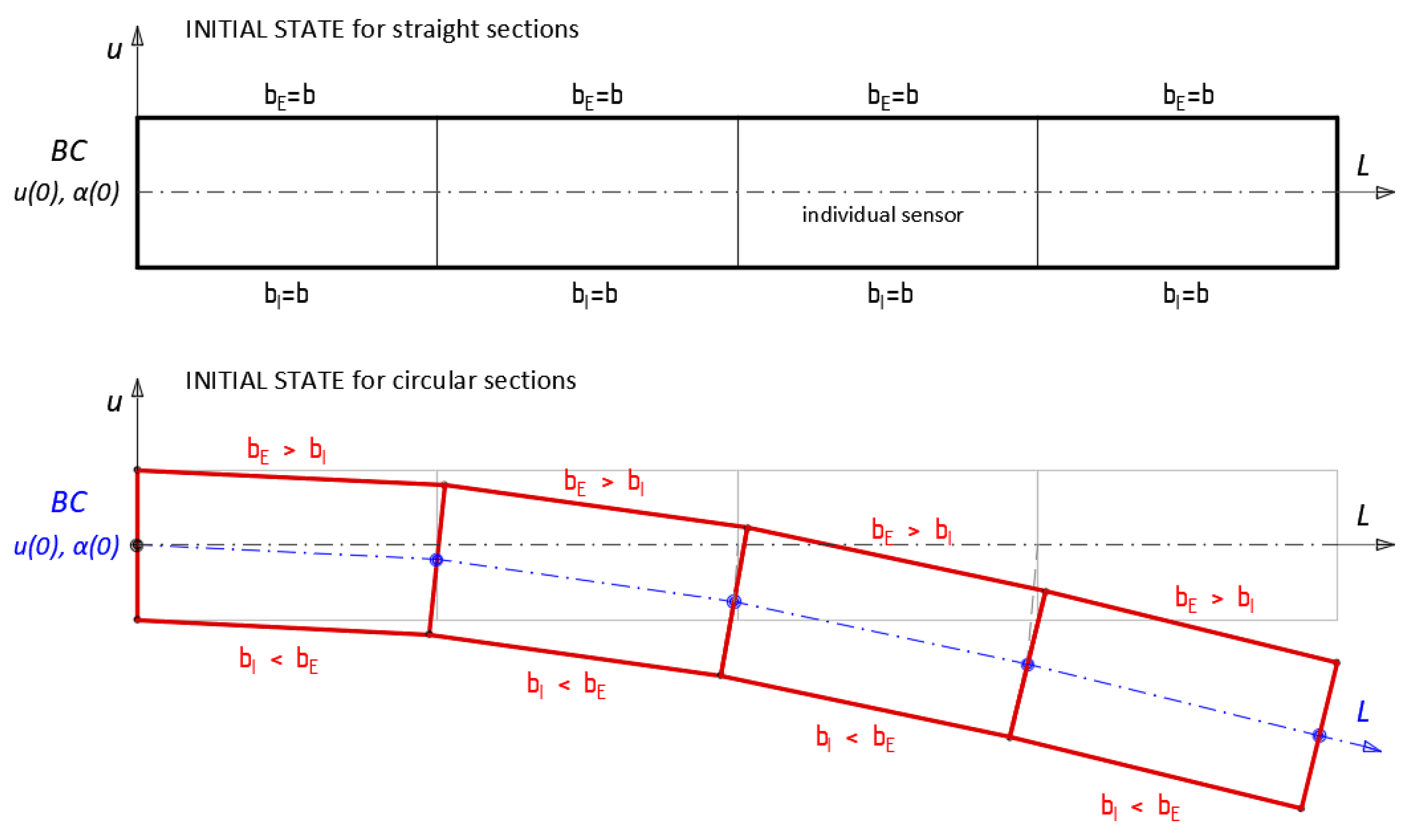
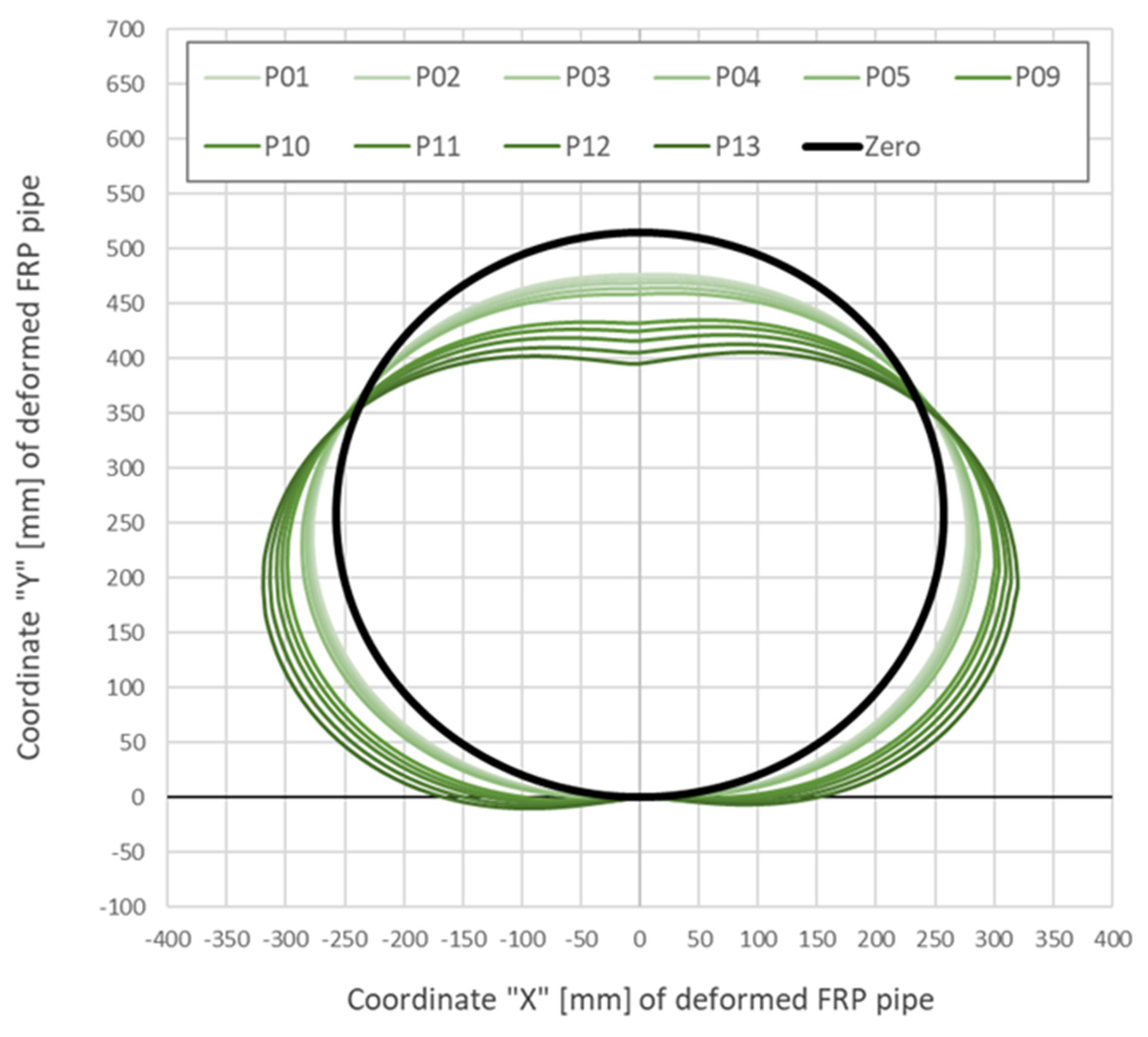
4.3.2. Displacement Analysis
- —curvature;
- —radius of curvature;
- —displacement.
- uv—displacement profile (mm) over measuring length;
- εI—strain profile [με] over internal measuring length;
- εE—strain profile [με] over external measuring length;
- t—wall thickness [mm] (distance between optical fibres);
- b—spatial resolution [mm] (base length of individual sensors over length);
- bc—boundary conditions (e.g., initial displacement and rotation angle or displacements in two known locations).
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The novelty of presented measurement approach lies in the possibility of parallel calculations of displacements (changes in shape) with satisfying accuracy directly based on measured strain profiles.
- (2)
- (3)
- Data were compared with independent reference technique and numerical simulations, obtaining very good compliance. Mean error level was less than 0.2 mm. Thus, the efficiency of the proposed method for DFOS data post-processing was confirmed.
- (4)
- Application of distributed fibre optic sensors allows to obtain comprehensive knowledge about the deformation state of the collectors and pipelines. This knowledge includes not only structural strains, but also displacements and could be successfully used for assessment of structural condition.
- (5)
- Because of the extremely low diameter of optical fibres only in their primary coatings, compared to the size of composite structural members, such fibres can be integrated inside the composite laminates during their production process [42]. This will allow for creating smart structures able for auto-diagnosis [34].
- (6)
- Due to the very low costs of fibre optic sensors and their advantages over conventional spot techniques, it is recommended to equip safety-critical pipelines with this type of measurement solution. Measurements could be performed during construction, repair works and further operation of the collectors modernised with GFRP panels.
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kishk, M.; Al-Hajj, A.; Pollock, R.; Bakis, N.; Aouad, G.F.; Bakis, N. Whole-life costing in construction—A state of the art review. In The RICS Research Paper Series; Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors: London, UK, 31 December 2003; Volume 4, Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/11511/80048 (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Bai, J. Advanced Fibre-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Composites for Structural Applications; Woodhead Publishing Series in Civil and Structural Engineering 46; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013; ISBN 9780857098641. [Google Scholar]
- Mufti, A.A.; Neale, K.W. State-of-the-Art of FRP and SHM Applications in Bridge Structures in Canada. Compos. Res. J. 2008, 2, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Vedernikov, A.; Safonov, A.; Tucci, F.; Carlone, P.; Akhatov, I. Pultruded materials and structures: A review. J. Compos. Mater. 2020, 54, 4081–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasy Chan, Y.W.; Zhou, Z. Advances of FRP-based smart components and structures. Pac. Sci. Rev. 2014, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uddin, N. Developments in Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Composites for Civil Engineering; Woodhead Publishing Series in Civil and Structural Engineering 45; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013; ISBN 9780857098955. [Google Scholar]
- Rubino, F.; Nisticò, A.; Tucci, F.; Carlone, P. Marine Application of Fiber Reinforced Composites: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajak, D.K.; Pagar, D.D.; Menezes, P.L.; Linul, E. Fiber-reinforced polymer composites: Manufacturing, properties, and applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glišić, B.; Inaudi, D. Fibre Optic Methods for Structural Health Monitoring; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 1–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Measures, R.M. Structural Monitoring with Fiber Optic Technology; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; ISBN 9780080518046. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghiu, C.; Labossiére, P.; Proulx, J. Fiber Optic Sensors for Strain Measurement of CFRP-strengthened RC Beams. Struct. Health Monit. 2005, 4, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanzadeh, M.; Aminossadati, S.M.; Kizil, M.S.; Rakić, A.D. Recent developments in fibre optic shape sensing. Measurement 2018, 128, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piccolo, A.; Delepine-Lesoille, S.; Bumbieler, F.; Zghondi, J.; Lecieux, Y.; Leduc, D.; Teixeria, P.; Gay, O. Tunnel monitoring: Performances of several innovative shape sensing systems. In Proceedings of the TINCE 2018—Technological Innovations in Nuclear Civil Engineering, Paris, France, 29–31 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.P.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. Distributed temperature and strain discrimination with stimulated brillouin scattering and rayleigh backscatter in an optical fiber. Sensors 2013, 13, 1836–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Higuera, J.M.; Cobo, L.R.; Incera, A.Q.; Cobo, A. Fiber optic sensors in structural health monitoring. J. Light. Technol. 2011, 29, 587–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiec, D. Distributed fibre-optic temperature and strain measurement with extremely high spatial resolution. Photonik Int. 2012, 1, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Karbhari, V.M. Rehabilitation of Pipelines Using Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Composites; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 9780857096920. [Google Scholar]
- Raïffa, H.; Schlaifer, R. Applied Statistical Decision Theory; Studies in Managerial Economics; Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1961; ISBN 9780875840178. [Google Scholar]
- Gerbrandt, J.L.; Westman, C.N. When a pipe breaks: Monitoring an emergency spill in the oil sands and documenting its erasure of indigenous interests in land. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2020, 7, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novosad, L. Geomonitoring—Specialista na Bezdrátový Monitorovací Systém—Loadsensing. Contact by: https://www.geomonitoring.cz/.
- Inaudi, D.; Glisic, B. Long-range pipeline monitoring by distributed fiber optic sensing. J. Press. Vessel Technol. Trans. ASME 2010, 132, 0117011–0117019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galíndez, C.; López-Higuera, J.M. Brillouin Distributed Fiber Sensors: An Overview and Applications. J. Sens. 2012, 2012, 204121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monsberger, C.M.; Lienhart, W. Distributed fiber optic shape sensing along shotcrete tunnel linings: Methodology, field applications, and monitoring results. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 11, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NERVE Composite DFOS Sensors. Available online: http://nerve-sensors.com (accessed on 2 August 2021).
- Tucci, F.; Rubino, F.; Carlone, P. Strain and temperature measurement in pultrusion processes by fiber Bragg grating sensors. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oromiehie, E.; Prusty, B.G.; Compston, P.; Rajan, G. Characterization of process-induced defects in automated fiber placement manufacturing of composites using fiber Bragg grating sensors. Struct. Health Monit. 2018, 17, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Chen, L. Recent Progress in Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors. Sensors 2012, 12, 8601–8639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glisic, B.; Yao, Y. Fiber optic method for health assessment of pipelines subjected to earthquake-induced ground movement. Struct. Health Monit. 2012, 11, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienko, R.; Bednarski, L.; Kanty, P.; Howiacki, T. Application of Distributed Optical Fibre Sensor for Strain and Temperature Monitoring within Continuous Flight Auger Columns. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 221, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarski, Ł.; Sieńko, R.; Grygierk, M.; Howiacki, T. New Distributed Fibre Optic 3D Sensor with Thermal Self-Compensation System: Design, Research and Field Proof Application inside Geotechnical Structure. Sensors 2021, 21, 5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, M.; Rajan, G.; Semenova, Y.; Farrell, G. Overview of fiber optic sensor technologies for strain/temperature sensing applications in composite materials. Sensors 2016, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghoshal, A.; Ayers, J.; Gurvich, M.; Urban, M.; Bordick, N. Corrigendum to “Experimental investigations in embedded sensing of composite components in aerospace vehicles” [J Compos Part B 71C (15 March 2015) 52–62]. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 81, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwowski, T.; Rajchel, M.; Sienko, R.; Bednarski, L. Smart Monitoring of the FRP Composite Bridge with Distributed Fibre Optic Sensors. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Fibre-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Composites in Civil Engineering (CICE 2018), Paris, France, 17–19 July 2018; pp. 918–925. [Google Scholar]
- Kulpa, M.; Howiacki, T.; Wiater, A.; Siwowski, T.; Sieńko, R. Strain and displacement measurement based on distributed fibre optic sensing (DFOS) system integrated with FRP composite sandwich panel. Measurement 2021, 175, 109099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieńko, R.; Bednarski, Ł.; Howiacki, T.; Zuziak, K.; Labocha, S. Possibilities of composite distributed fibre optic 3DSensor on the example of footing pulled out from the ground: A case study. In Civil Structural Health Monitoring, Proceedings of the CSHM-8 Workshop, Naples, Italy, 29–31 March 2021; Rainieri, C., Fabbrocino, G., Caterino, N., Ceroni, F., Notarangelo, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- SHM System. Available online: http://www.shmsystem.pl (accessed on 2 August 2021).
- Walczak, R. GRP pipes produced in the winding technology applied in excavation-free renovation of pressure and gravitational pipelines. Inżynieria Bezwykopowa 2008, 2, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Popielski, P.; Kodura, A.; Smoliński, B. Analysis of the technical condition of the sewage collector with the use of numerical simulation. Czas. Tech. 2017, 3, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Sante, R. Fibre optic sensors for structural health monitoring of aircraft composite structures: Recent advances and applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 18666–18713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrias, A.; Casas, J.R.; Villalba, S. A review of distributed optical fiber sensors for civil engineering applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schilder, C.; Schukar, M.; Steffen, M.; Krebber, K. Structural health monitoring by distributed fibre optic sensors applied on the surface of composite structures. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace, Singapore, 13–15 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Sim, L.M. Damage detection and assessment in fibre-reinforced composite structures with embedded fibre optic sensors-review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2002, 11, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| No. of Load Step | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Force [kN] | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
| DFOS displ. [mm] | 0.00 | 2.17 | 5.06 | 8.31 | 10.67 | 15.22 | 17.65 |
| Ref. displ. [mm] | 0.00 | 2.70 | 5.44 | 8.17 | 11.06 | 14.95 | 17.21 |
| FEM displ. [mm] | 0.00 | 2.21 | 5.02 | 7.99 | 10.90 | 14.30 | 17.70 |
| Diff. (REF—DFOS) [mm] | 0.00 | 0.38 | −0.14 | 0.39 | −0.27 | −0.44 | 0.38 |
| Diff. (FEM—DFOS) [mm] | 0.00 | −0.04 | −0.32 | 0.23 | −0.92 | 0.05 | −0.04 |
| Mean error (REF—FDOS) [mm] | 0.08 | ||||||
| Stdv. (REF—DFOS) [mm] | 0.37 | ||||||
| Mean error (FEM—FDOS) [mm] | −0.16 | ||||||
| Stdv. (FEM—DFOS) [mm] | 0.38 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bednarz, B.; Popielski, P.; Sieńko, R.; Howiacki, T.; Bednarski, Ł. Distributed Fibre Optic Sensing (DFOS) for Deformation Assessment of Composite Collectors and Pipelines. Sensors 2021, 21, 5904. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21175904
Bednarz B, Popielski P, Sieńko R, Howiacki T, Bednarski Ł. Distributed Fibre Optic Sensing (DFOS) for Deformation Assessment of Composite Collectors and Pipelines. Sensors. 2021; 21(17):5904. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21175904
Chicago/Turabian StyleBednarz, Bartosz, Paweł Popielski, Rafał Sieńko, Tomasz Howiacki, and Łukasz Bednarski. 2021. "Distributed Fibre Optic Sensing (DFOS) for Deformation Assessment of Composite Collectors and Pipelines" Sensors 21, no. 17: 5904. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21175904
APA StyleBednarz, B., Popielski, P., Sieńko, R., Howiacki, T., & Bednarski, Ł. (2021). Distributed Fibre Optic Sensing (DFOS) for Deformation Assessment of Composite Collectors and Pipelines. Sensors, 21(17), 5904. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21175904






