Deployment, Calibration, and Cross-Validation of Low-Cost Electrochemical Sensors for Carbon Monoxide, Nitrogen Oxides, and Ozone for an Epidemiological Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Context
2.2. Low-Cost Monitor Deployment
2.3. Low-Cost Monitor and Sensor Descriptions
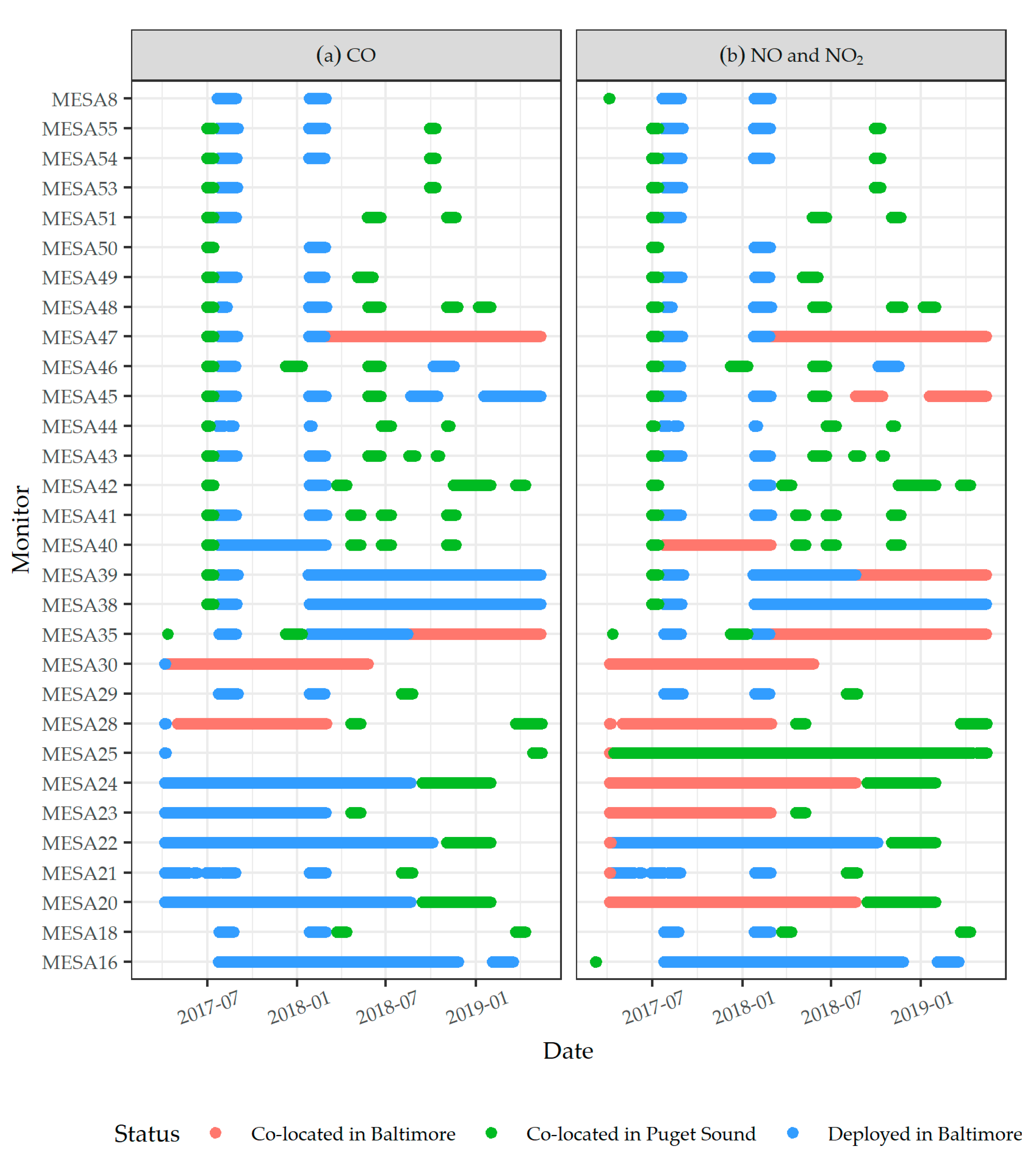
2.4. Co-Location of LCMs with Air Quality System Monitors
2.5. Sensor Quality Assurance and Data Exclusion Criteria
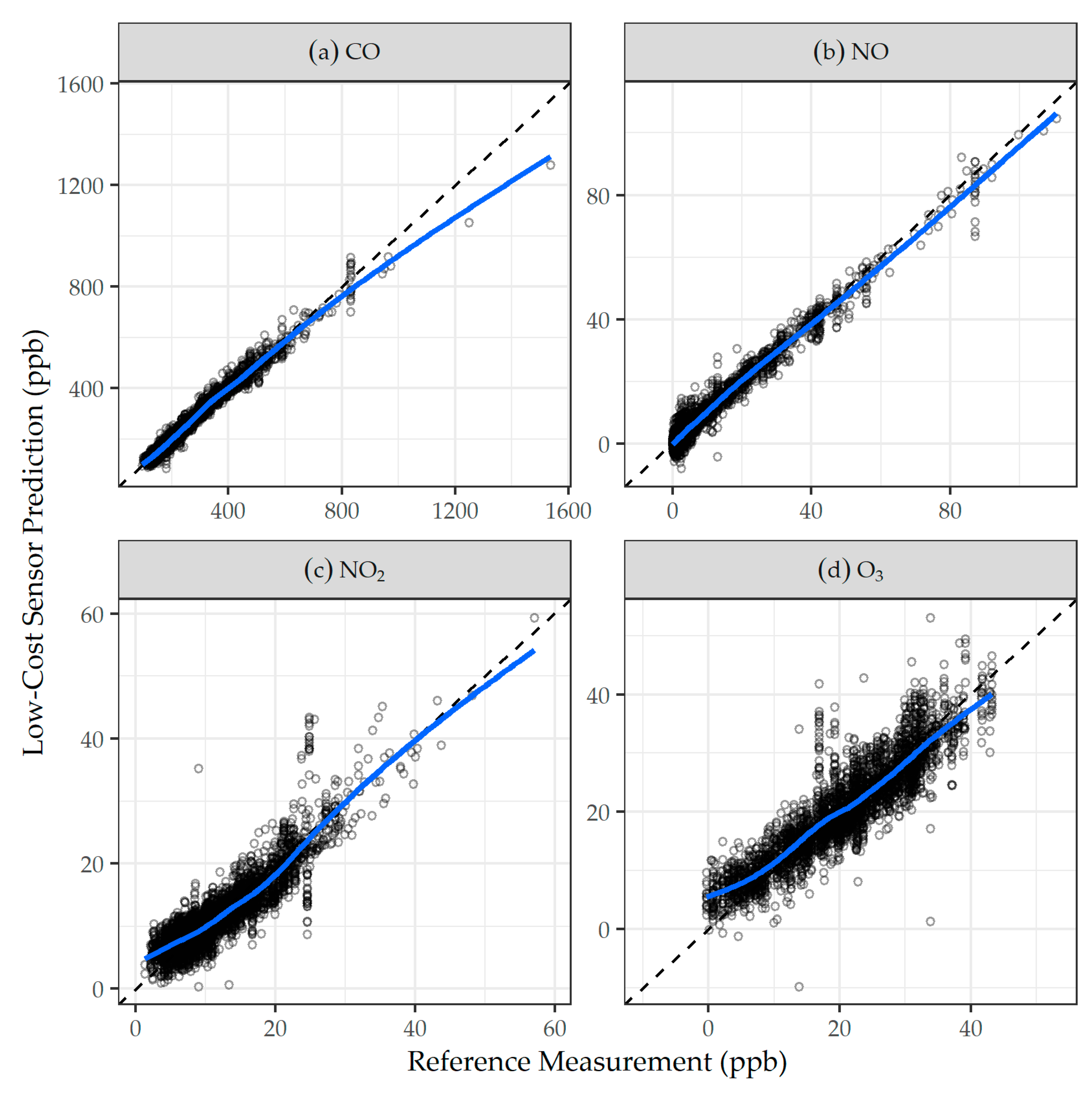
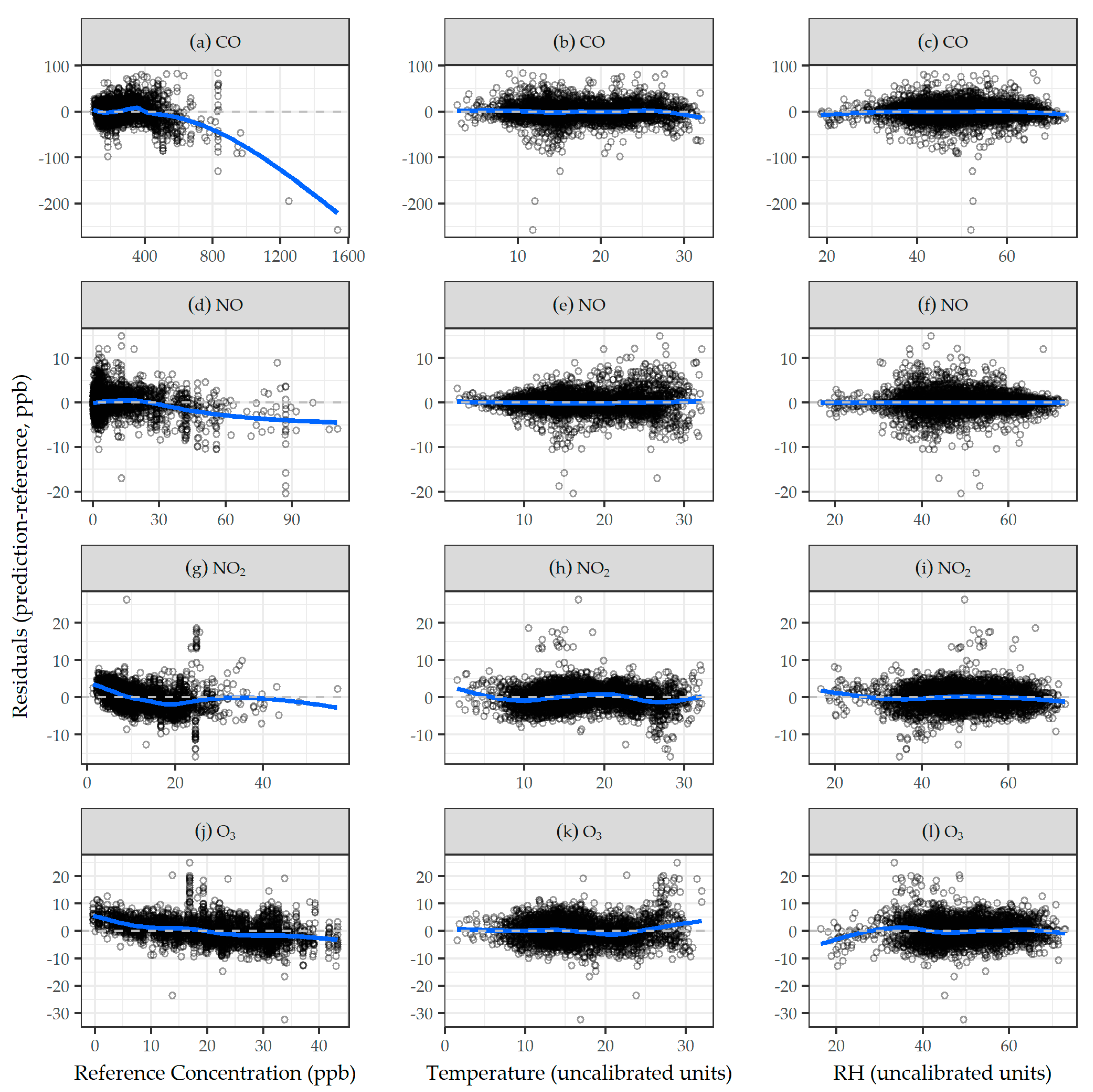
2.6. Calibration Models
2.7. Cross Validation and Model Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Site Descriptive Characteristics and LCM Co-Location
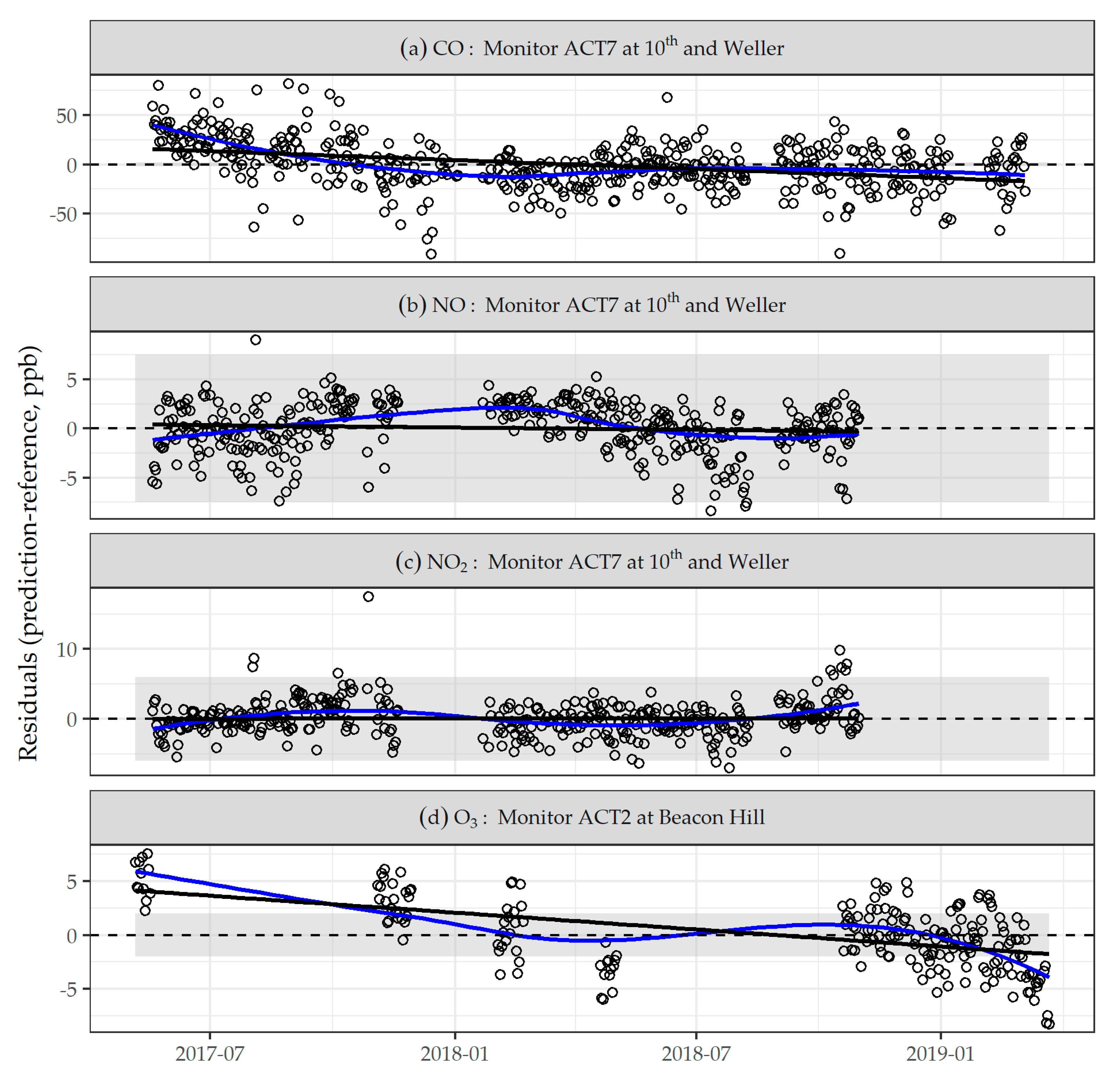
3.2. Evaluation of Calibration Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Background
Appendix A.2. Methods
- Consider all pairwise comparisons for sensors that were ever co-located, and create a matrix for both WE and Aux that records these pairwise average differences.
- Fill in missing data using a weighting scheme based on the time of co-location and relying on multiple degrees of separation.
- After several iterations, the sensor differences relative to a single reference sensor are obtained, which can be used to adjust the sensor signal (mV).
Appendix A.3. Results and Discussion
| Fit in Puget Sound | Evaluated in Baltimore | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # Co-Location Sites | # Monitor Days Co-Location | CV-RMSE (ppb) | CV-R2 | # Co-Location Sites | # Monitor Days Co-location | CV-RMSE (ppb) | CV-R2 | |
| CO | 1 | 494 | 19 | 0.97 | 2 | 498 | 56 | 0.51 |
| NO | 1 | 520 | 5 | 0.89 | 4 | 1604 | 8 | 0.45 |
| NO2 | 1 | 507 | 6 | 0.22 | 4 | 2029 | 6 | 0.20 |
| CO | NO | NO2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Terms | CV-RMSE (ppb) | CV-R2 | CV-RMSE (ppb) | CV-R2 | CV-RMSE (ppb) | CV-R2 |
| B2 | Pre-adjusted WE, pre-adjusted Aux | 51 | 0.53 | 7 | 0.61 | 5 | 0.33 |
| B3 | Model B2 with temperature and RH | 39 | 0.73 | 7 | 0.58 | 5 | 0.40 |
| B4 | Model B3 with WE–temperature and WE–RH interactions | 36 | 0.76 | 7 | 0.62 | 5 | 0.36 |
| B5 | Model B3 with WE– and Aux–temperature and WE– and Aux–RH interactions | 37 | 0.75 | 7 | 0.64 | 5 | 0.29 |
| B6 | Model B2 with WE–temperature spline and WE–RH spline interactions | 41 | 0.70 | 7 | 0.63 | 5 | 0.41 |
| B7 | Model B4 with WE–Aux interaction | 37 | 0.74 | 7 | 0.62 | 5 | 0.45 |
| B8 | Model B4 with WE spline | 38 | 0.74 | 7 | 0.61 | 5 | 0.36 |
References
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; AlMazroa, M.A.; Amann, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Andrews, K.G.; et al. A Comparative Risk Assessment of Burden of Disease and Injury Attributable to 67 Risk Factors and Risk Factor Clusters in 21 Regions, 1990–2010: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human Health Effects of Air Pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.; Saffell, J. Amperometric Gas Sensors as a Low Cost Emerging Technology Platform for Air Quality Monitoring Applications: A Review. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1553–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsev, A.; Schade, S.; Craglia, M.; Gerboles, M.; Spinelle, L.; Signorini, M. Next Generation Air Quality Platform: Openness and Interoperability for the Internet of Things. Sensors 2016, 16, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Morawska, L.; Martani, C.; Biskos, G.; Neophytou, M.; Di Sabatino, S.; Bell, M.; Norford, L.; Britter, R. The Rise of Low-Cost Sensing for Managing Air Pollution in Cities. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.C.; Lee, J.D.; Edwards, P.M.; Shaw, M.D.; Evans, M.J.; Moller, S.J.; Smith, K.R.; Buckley, J.W.; Ellis, M.; Gillot, S.R.; et al. Evaluating the Performance of Low Cost Chemical Sensors for Air Pollution Research. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 189, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedrahita, R.; Xiang, Y.; Masson, N.; Ortega, J.; Collier, A.; Jiang, Y.; Li, K.; Dick, R.P.; Lv, Q.; Hannigan, M.; et al. The next Generation of Low-Cost Personal Air Quality Sensors for Quantitative Exposure Monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3325–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigliautile, I.; Marseglia, G.; Pisello, A.L. Investigation of CO2 Variation and Mapping Through Wearable Sensing Techniques for Measuring Pedestrians’ Exposure in Urban Areas. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, E.G.; Watkins, T.H.; Solomon, P.A.; Thoma, E.D.; Williams, R.W.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Shelow, D.; Hindin, D.A.; Kilaru, V.J.; Preuss, P.W. The Changing Paradigm of Air Pollution Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11369–11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromar, K.R.; Duncan, B.N.; Bartonova, A.; Benedict, K.; Brauer, M.; Habre, R.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Haynes, J.A.; Khan, S.; Kilaru, V.; et al. Air Pollution Monitoring for Health Research and Patient Care. An Official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report. Annals ATS 2019, 16, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Compton, R.G. Amperometric Gas Detection: A Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Mead, M.I.; Popoola, O.A.M.; Stewart, G.B.; Landshoff, P.; Calleja, M.; Hayes, M.; Baldovi, J.J.; McLeod, M.W.; Hodgson, T.F.; Dicks, J.; et al. The Use of Electrochemical Sensors for Monitoring Urban Air Quality in Low-Cost, High-Density Networks. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Villani, M.G.; Aleixandre, M.; Bonavitacola, F. Field Calibration of a Cluster of Low-Cost Available Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring. Part A: Ozone and Nitrogen Dioxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 215, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, I.; Bright, V.B.; McLeod, M.W.; Mead, M.I.; Popoola, O.A.M.; Stewart, G.B.; Jones, R.L. Source Attribution of Air Pollution by Spatial Scale Separation Using High Spatial Density Networks of Low Cost Air Quality Sensors. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 113, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, J.; Tahir, A.; Kazmi, H.; Khan, Z.; Javed, R.; Masood, U. View: Implementing Low Cost Air Quality Monitoring Solution for Urban Areas. Environ. Syst. Res. 2012, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Kresin, F.; Bregt, A.K.; Kooistra, L.; Pareschi, E.; van Putten, E.; Volten, H.; Wesseling, J. Citizen Sensing for Improved Urban Environmental Monitoring. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Hagler, G.; Williams, R.; Sharpe, R.; Brown, R.; Garver, D.; Judge, R.; Caudill, M.; Rickard, J.; Davis, M.; et al. Community Air Sensor Network (CAIRSENSE) Project: Evaluation of Low-Costsensor Performance in a Suburban Environment in the Southeastern UnitedStates. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5281–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moltchanov, S.; Levy, I.; Etzion, Y.; Lerner, U.; Broday, D.M.; Fishbain, B. On the Feasibility of Measuring Urban Air Pollution by Wireless Distributed Sensor Networks. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Shaw, M.D.; Lewis, A.C.; Carpenter, L.J.; Batchellier, T. Electrochemical Ozone Sensors: A Miniaturised Alternative for Ozone Measurements in Laboratory Experiments and Air-Quality Monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorte, S.; Arunachalam, S.; Naess, B.; Seppanen, C.; Rodrigues, V.; Valencia, A.; Borrego, C.; Monteiro, A. Assessment of Source Contribution to Air Quality in an Urban Area Close to a Harbor: Case-Study in Porto, Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wong, K.; Wei, P.; Ye, S.; Huang, H.; Yang, F.; Westerdahl, D.; Louie, P.; Luk, C.; Ning, Z. Development and Application of a Next Generation Air Sensor Network for the Hong Kong Marathon 2015 Air Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2016, 16, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerrett, M.; Donaire-Gonzalez, D.; Popoola, O.; Jones, R.; Cohen, R.C.; Almanza, E.; de Nazelle, A.; Mead, I.; Carrasco-Turigas, G.; Cole-Hunter, T.; et al. Validating Novel Air Pollution Sensors to Improve Exposure Estimates for Epidemiological Analyses and Citizen Science. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, L.; Thai, P.K.; Liu, X.; Asumadu-Sakyi, A.; Ayoko, G.; Bartonova, A.; Bedini, A.; Chai, F.; Christensen, B.; Dunbabin, M.; et al. Applications of Low-Cost Sensing Technologies for Air Quality Monitoring and Exposure Assessment: How Far Have They Gone? Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, A.; Edwards, P. Validate Personal Air-Pollution Sensors. Nature 2016, 535, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, E.S.; Williams, L.R.; Lewis, D.K.; Magoon, G.R.; Onasch, T.B.; Kaminsky, M.L.; Worsnop, D.R.; Jayne, J.T. Use of Electrochemical Sensors for Measurement of Air Pollution: Correcting Interference Response and Validating Measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3575–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, D.H.; Isaacman-VanWertz, G.; Franklin, J.P.; Wallace, L.M.M.; Kocar, B.D.; Heald, C.L.; Kroll, J.H. Calibration and Assessment of Electrochemical Air Quality Sensors by Co-Location with Regulatory-Grade Instruments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Katlenburg-Lindau 2018, 11, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, N.; Piedrahita, R.; Hannigan, M. Quantification Method for Electrolytic Sensors in Long-Term Monitoring of Ambient Air Quality. Sensors 2015, 15, 27283–27302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, O.A.M.; Stewart, G.B.; Mead, M.I.; Jones, R.L. Development of a Baseline-Temperature Correction Methodology for Electrochemical Sensors and Its Implications for Long-Term Stability. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Villani, M.G.; Aleixandre, M.; Bonavitacola, F. Field Calibration of a Cluster of Low-Cost Commercially Available Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring. Part B: NO, CO and CO2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvall, R.M.; Clements, A.L.; Hagler, G.; Kamal, A.; Kilaru, V.; Goodman, L.; Frederick, S.; Johnson Barkjohn, K.K.; VonWald, I.; Greene, D.; et al. Performance Testing Protocols, Metrics, and Target Values for Ozone Air Sensors: Use in Ambient, Outdoor, Fixed Site, Non-Regulatory and Informational Monitoring Applications; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2021.
- Casey, J.G.; Collier-Oxandale, A.; Hannigan, M. Performance of Artificial Neural Networks and Linear Models to Quantify 4 Trace Gas Species in an Oil and Gas Production Region with Low-Cost Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, J.G.; Hannigan, M.P. Testing the Performance of Field Calibration Techniques for Low-Cost Gas Sensors in New Deployment Locations: Across a County Line and across Colorado. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6351–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Mei, H.; Liu, D.; Zeng, N.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y. Calibrations of Low-Cost Air Pollution Monitoring Sensors for CO, NO2, O3, and SO2. Sensors 2021, 21, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malings, C.; Tanzer, R.; Hauryliuk, A.; Kumar, S.P.N.; Zimmerman, N.; Kara, L.B.; Presto, A.A. R. Subramanian Development of a General Calibration Model and Long-Term Performance Evaluation of Low-Cost Sensors for Air Pollutant Gas Monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 903–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalović, D.B.; Davidović, M.D.; Jovanović, M.; Bartonova, A.; Ristovski, Z.; Jovašević-Stojanović, M. In Search of an Optimal In-Field Calibration Method of Low-Cost Gas Sensors for Ambient Air Pollutants: Comparison of Linear, Multilinear and Artificial Neural Network Approaches. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 640–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, N.; Presto, A.A.; Kumar, S.P.N.; Gu, J.; Hauryliuk, A.; Robinson, E.S.; Robinson, A.L. R. Subramanian A Machine Learning Calibration Model Using Random Forests to Improve Sensor Performance for Lower-Cost Air Quality Monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maag, B.; Zhou, Z.; Thiele, L. A Survey on Sensor Calibration in Air Pollution Monitoring Deployments. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 4857–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACT-AP Air Pollution, the Aging Brain and Alzheimer’s Disease | Environmental & Occupational Health Sciences. Available online: https://deohs.washington.edu/air-pollution-aging-brain-and-alzheimers-disease (accessed on 8 November 2019).
- MESA MESA Air Study | Environmental & Occupational Health Sciences. Available online: https://deohs.washington.edu/mesaair/mesa-air-study (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- Chou, J. Hazardous Gas Monitors: A Practical Guide to Selection, Operation and Applications; McGraw-Hill Professional Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0-07-135876-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zusman, M.; Schumacher, C.S.; Gassett, A.J.; Spalt, E.W.; Austin, E.; Larson, T.V.; Carvlin, G.; Seto, E.; Kaufman, J.D.; Sheppard, L. Calibration of Low-Cost Particulate Matter Sensors: Model Development for a Multi-City Epidemiological Study. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphasense Ltd. CO-B4 Carbon Monoxide Sensor. Available online: http://www.alphasense.com/WEB1213/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/CO-B4.pdf (accessed on 8 November 2019).
- Alphasense Ltd. NO-B4 Nitric Oxide Sensor. Available online: http://www.alphasense.com/WEB1213/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/NO-B4.pdf (accessed on 8 November 2019).
- Alphasense Ltd. NO2-B43F Nitrogen Dioxide Sensor. Available online: http://www.alphasense.com/WEB1213/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/NO2-B43F.pdf (accessed on 8 November 2019).
- Alphasense Ltd. OX-B431 Oxidising Gas Sensor. Available online: http://www.alphasense.com/WEB1213/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/OX-B431.pdf (accessed on 8 November 2019).
- Hossain, M.; Saffell, J.; Baron, R. Differentiating NO 2 and O 3 at Low Cost Air Quality Amperometric Gas Sensors. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA List of Designated Reference and Equivalent Methods. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2019-08/documents/designated_reference_and-equivalent_methods.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- EPA Air Quality System (AQS). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/aqs (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- PSCAA Puget Sound Clean Air Agency, WA | Official Website. Available online: https://pscleanair.gov/ (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Alphasense Ltd. Alphasense 4-Electrode Individual Sensor Board (ISB); User Manual 085-2217. 2019. Available online: http://www.apollounion.com/en/p-Alphasense-4-electrode-Individual-Sensor-Board-486.html (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- PSCAA. 2019 Air Quality Data Summary; Puget Sound Clean Air Agency. 2020. Available online: https://pscleanair.gov/DocumentCenter/View/4164/Air-Quality-Data-Summary-2019 (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Castell, N.; Dauge, F.R.; Schneider, P.; Vogt, M.; Lerner, U.; Fishbain, B.; Broday, D.; Bartonova, A. Can Commercial Low-Cost Sensor Platforms Contribute to Air Quality Monitoring and Exposure Estimates? Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; Aleixandre, M.; Gerboles, M.; European Commission; Joint Research Centre; Institute for Environment and Sustainability. Protocol of Evaluation and Calibration of Low-Cost Gas Sensors for the Monitoring of Air Pollution; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2013; ISBN 978-92-79-32691-2. [Google Scholar]
| Model | Analyte(s) | Sensor Noise (ppb) 1 | Range (ppm) 2 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO-B4 | CO | 4 | 1000 | [42] |
| NO-B4 | NO | 15 | 20 | [43] |
| NO2-B43F | NO2 | 12 | 20 | [44] |
| OX-B431 | O3, NO2 | 4 | 20 | [45] |
| Agency Site | Site Type | # LCMs Ever Co-Located | Co-Location Monitor-Days (Weeks) | CO (ppb) Mean ± SD 1 | NO (ppb) Mean ± SD 1 | NO2 (ppb) Mean ± SD 1 | O3 (ppb) Mean ± SD 1 | Avg Temp (°C) Mean ± SD 2 | Avg RH (%) Mean ± SD 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beacon Hill | Suburban | 54 | 204,498 (99) | 223 ± 89 | 6 ± 10 | 11 ± 5 | 20 ± 9 | 11 ± 4 | 76 ± 12 |
| 10th and Weller | Urban | 1 3 | 525 (89) | 422 ± 131 | 27 ± 18 | 20 ± 7 | --- 4 | 13 ± 5 | 72 ± 11 |
| Gas | Terms | Model Number | CV-RMSE (ppb) | CV-R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | Manufacturer’s sensor-specific slope and intercept 1 | 0 | 150 | 0.49 |
| WE, Aux, and sensor ID | 1 | 29 | 0.94 | |
| WE, Aux, sensor ID, temperature, RH, and WE–temperature and WE–RH interactions | 3 | 18 | 0.97 | |
| NO | Manufacturer’s sensor-specific slope and intercept 1 | 0 | 36 | 0.41 |
| WE, Aux, and sensor ID | 1 | 2 | 0.97 | |
| WE, Aux, Sensor ID, and temperature and RH splines 2 with WE interactions | 4 | 2 | 0.97 | |
| NO2 | Manufacturer’s sensor-specific slope and intercept 1 | 0 | 24 | 0.08 |
| WE, Aux, and sensor ID | 1 | 5 | 0.35 | |
| WE, Aux, Sensor ID, temperature and RH splines 2 with WE interactions, and [CO]CO-B4 3 | 4 | 3 | 0.79 | |
| O3 | Manufacturer’s sensor-specific slope and intercept 1 | 0 | 41 | 0.04 |
| WE, Aux, and sensor ID | 1 | 5 | 0.66 | |
| WE, Aux, Sensor ID, temperature and RH splines 2 with WE interactions, and [NO2]NO2-B43F 4 | 4 | 4 | 0.81 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuidema, C.; Schumacher, C.S.; Austin, E.; Carvlin, G.; Larson, T.V.; Spalt, E.W.; Zusman, M.; Gassett, A.J.; Seto, E.; Kaufman, J.D.; et al. Deployment, Calibration, and Cross-Validation of Low-Cost Electrochemical Sensors for Carbon Monoxide, Nitrogen Oxides, and Ozone for an Epidemiological Study. Sensors 2021, 21, 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124214
Zuidema C, Schumacher CS, Austin E, Carvlin G, Larson TV, Spalt EW, Zusman M, Gassett AJ, Seto E, Kaufman JD, et al. Deployment, Calibration, and Cross-Validation of Low-Cost Electrochemical Sensors for Carbon Monoxide, Nitrogen Oxides, and Ozone for an Epidemiological Study. Sensors. 2021; 21(12):4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124214
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuidema, Christopher, Cooper S. Schumacher, Elena Austin, Graeme Carvlin, Timothy V. Larson, Elizabeth W. Spalt, Marina Zusman, Amanda J. Gassett, Edmund Seto, Joel D. Kaufman, and et al. 2021. "Deployment, Calibration, and Cross-Validation of Low-Cost Electrochemical Sensors for Carbon Monoxide, Nitrogen Oxides, and Ozone for an Epidemiological Study" Sensors 21, no. 12: 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124214
APA StyleZuidema, C., Schumacher, C. S., Austin, E., Carvlin, G., Larson, T. V., Spalt, E. W., Zusman, M., Gassett, A. J., Seto, E., Kaufman, J. D., & Sheppard, L. (2021). Deployment, Calibration, and Cross-Validation of Low-Cost Electrochemical Sensors for Carbon Monoxide, Nitrogen Oxides, and Ozone for an Epidemiological Study. Sensors, 21(12), 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124214






