A New Approach for Estimating Dissolved Oxygen Based on a High-Accuracy Surface Modeling Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
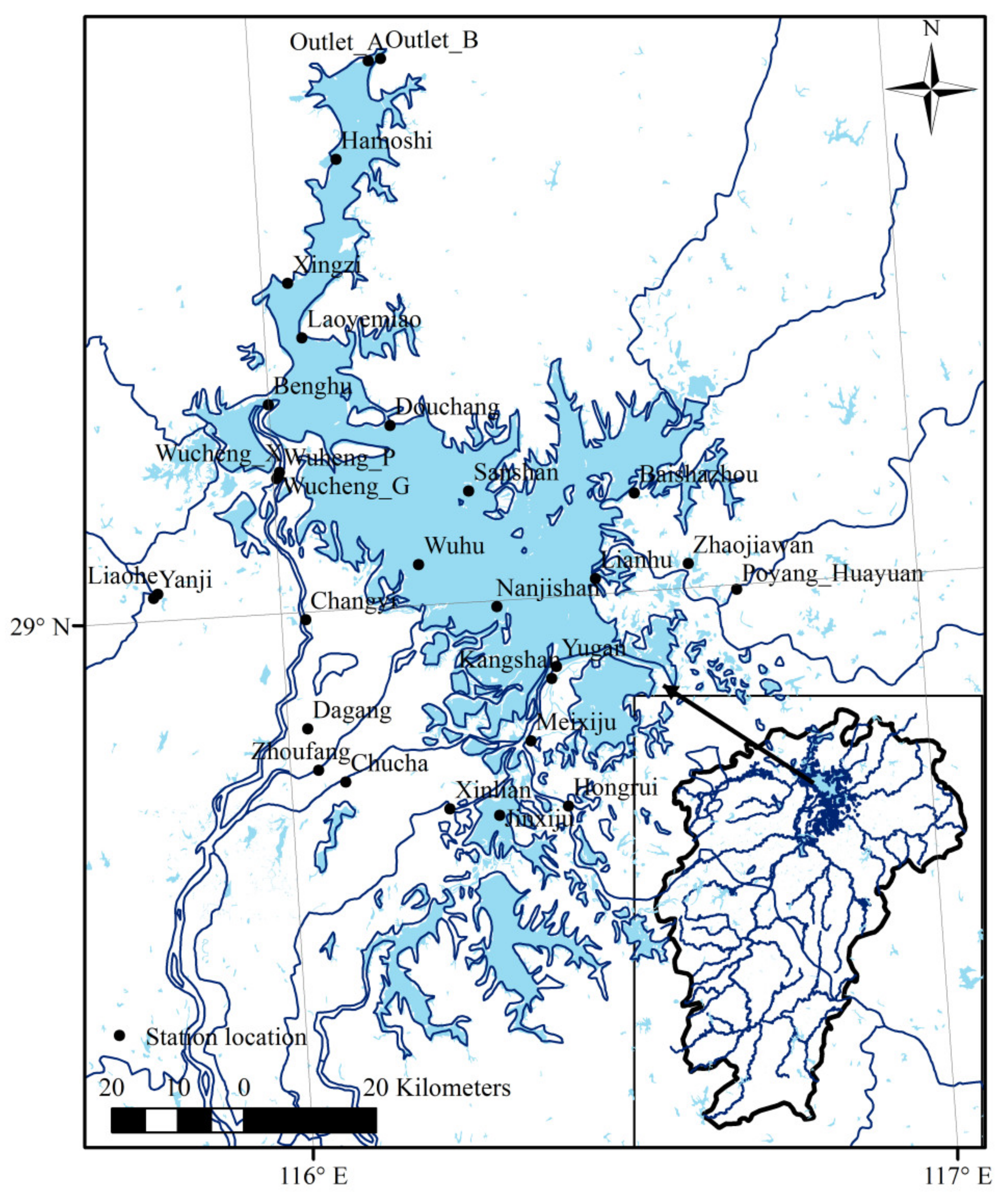
2. Study Area and Data
3. Methods
3.1. HASM
3.2. HASM_MOD
3.3. Support Vector Machine
3.4. Cokriging Method
3.5. Performance Assessment of the Methods
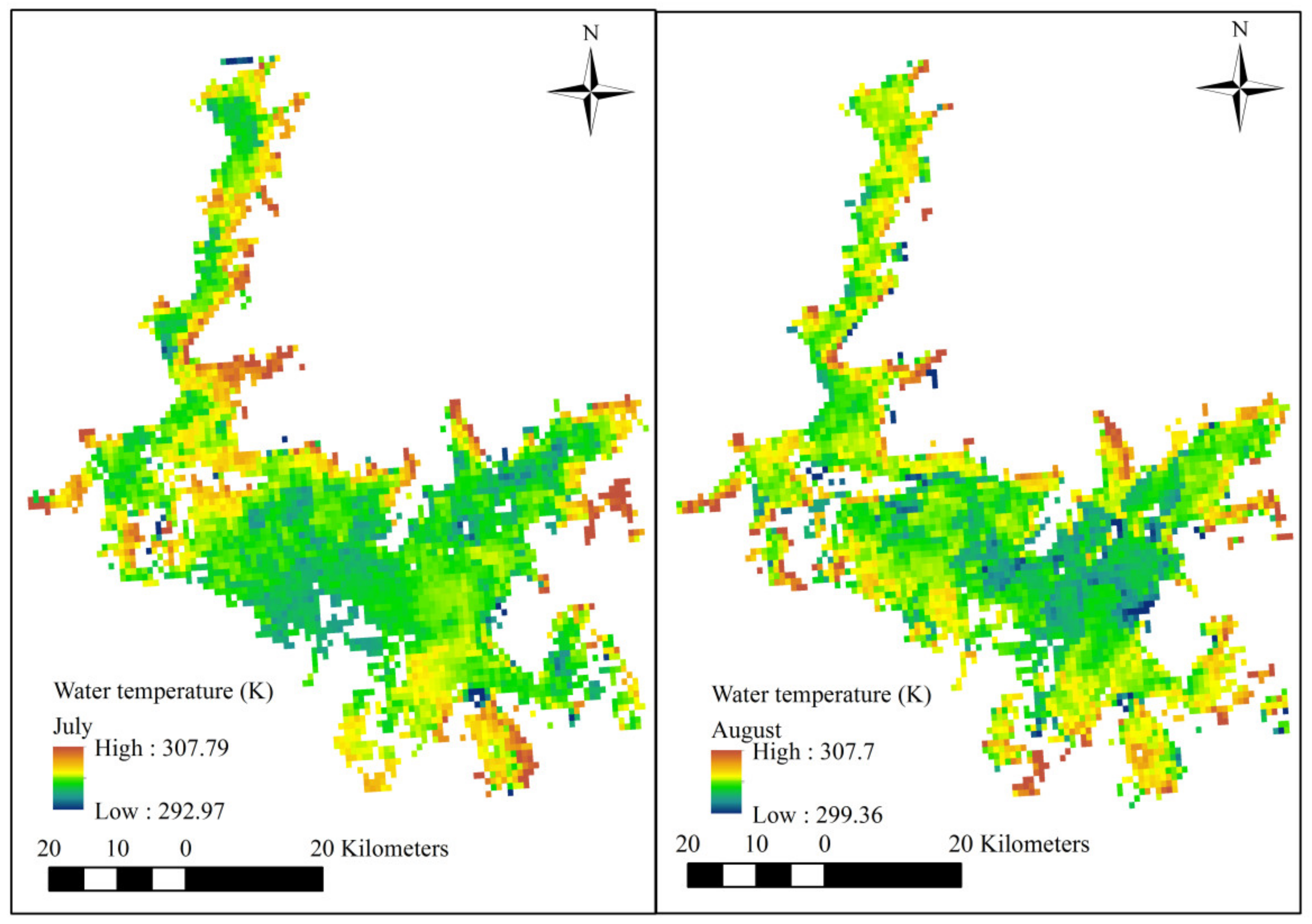
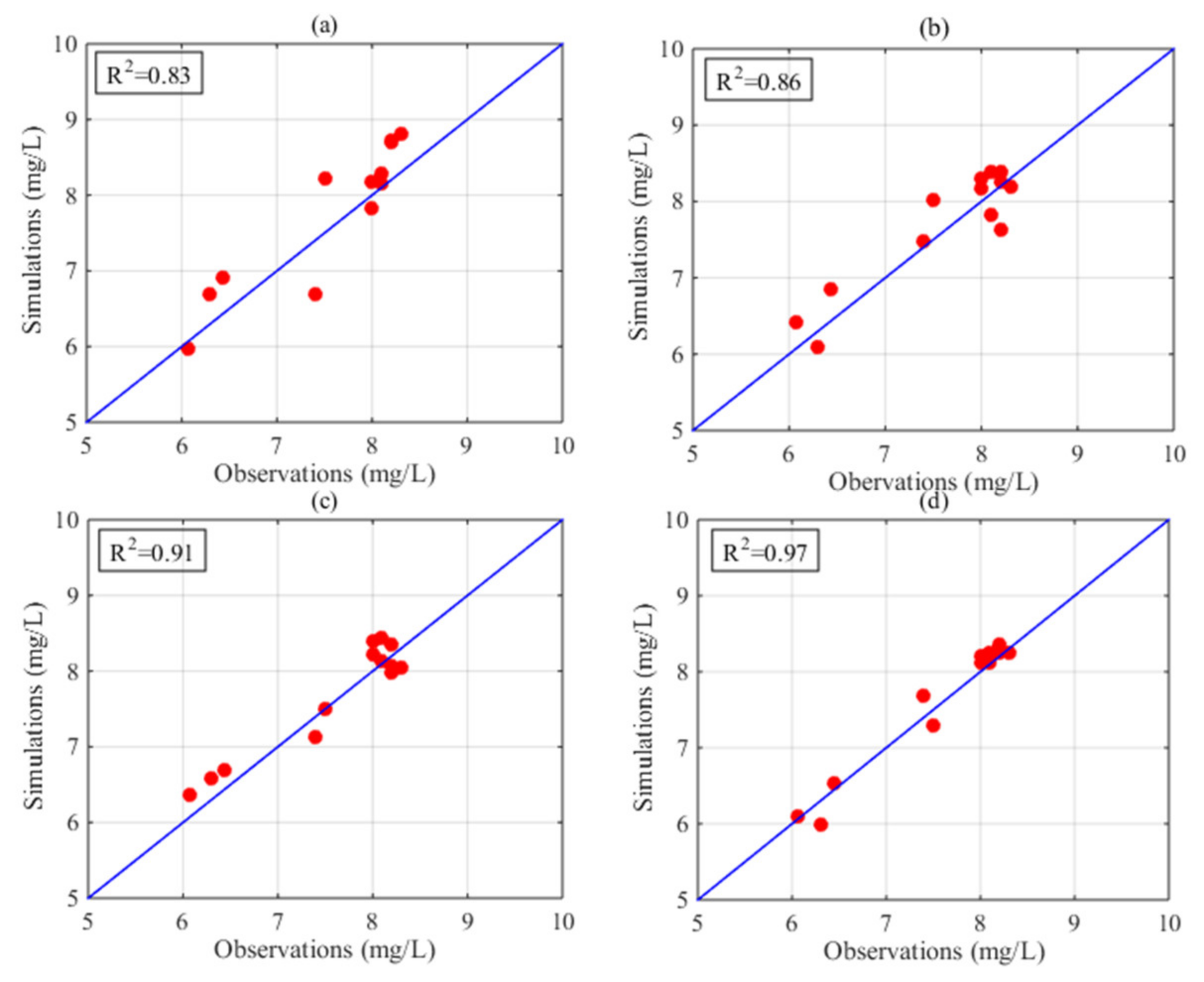
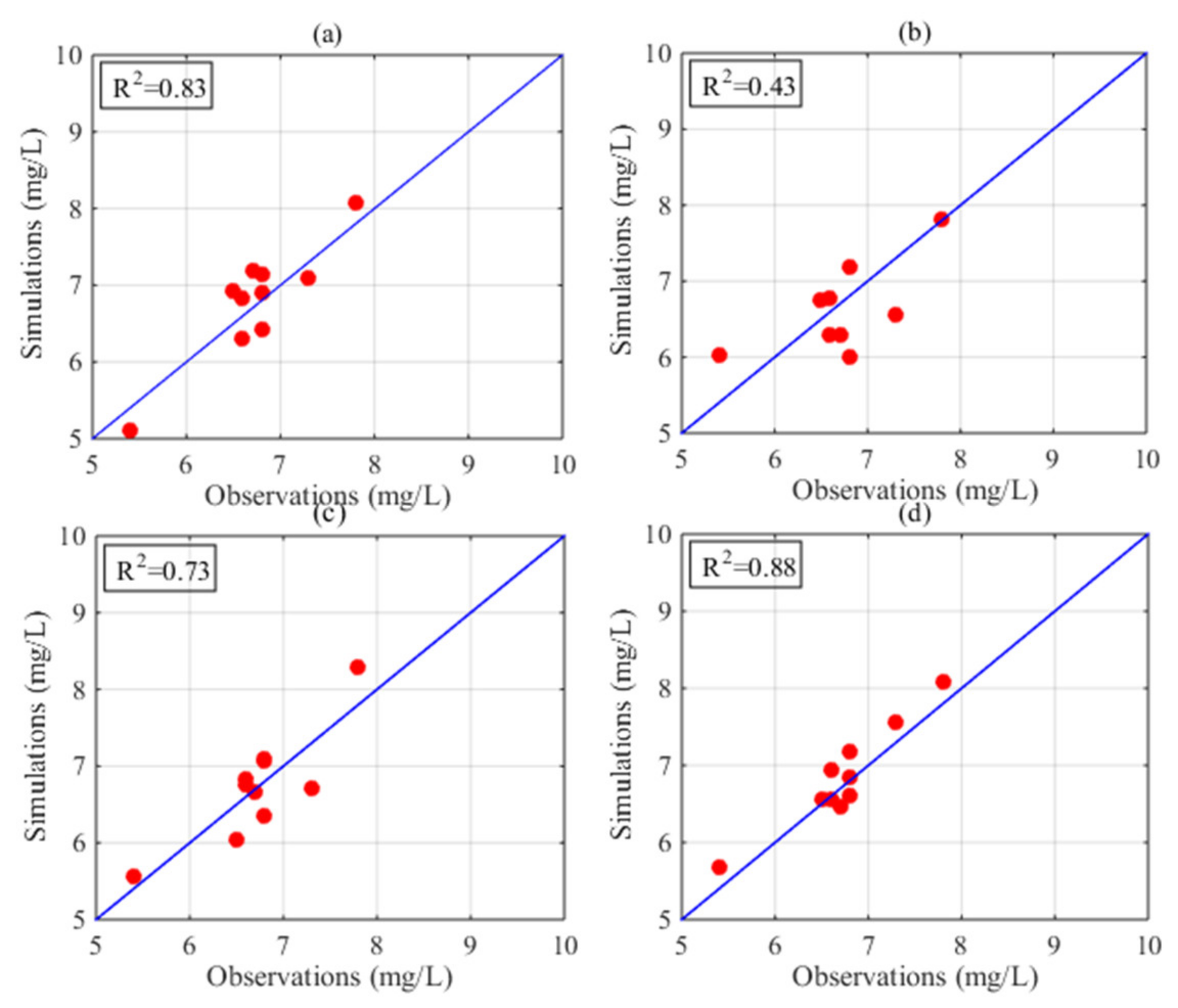
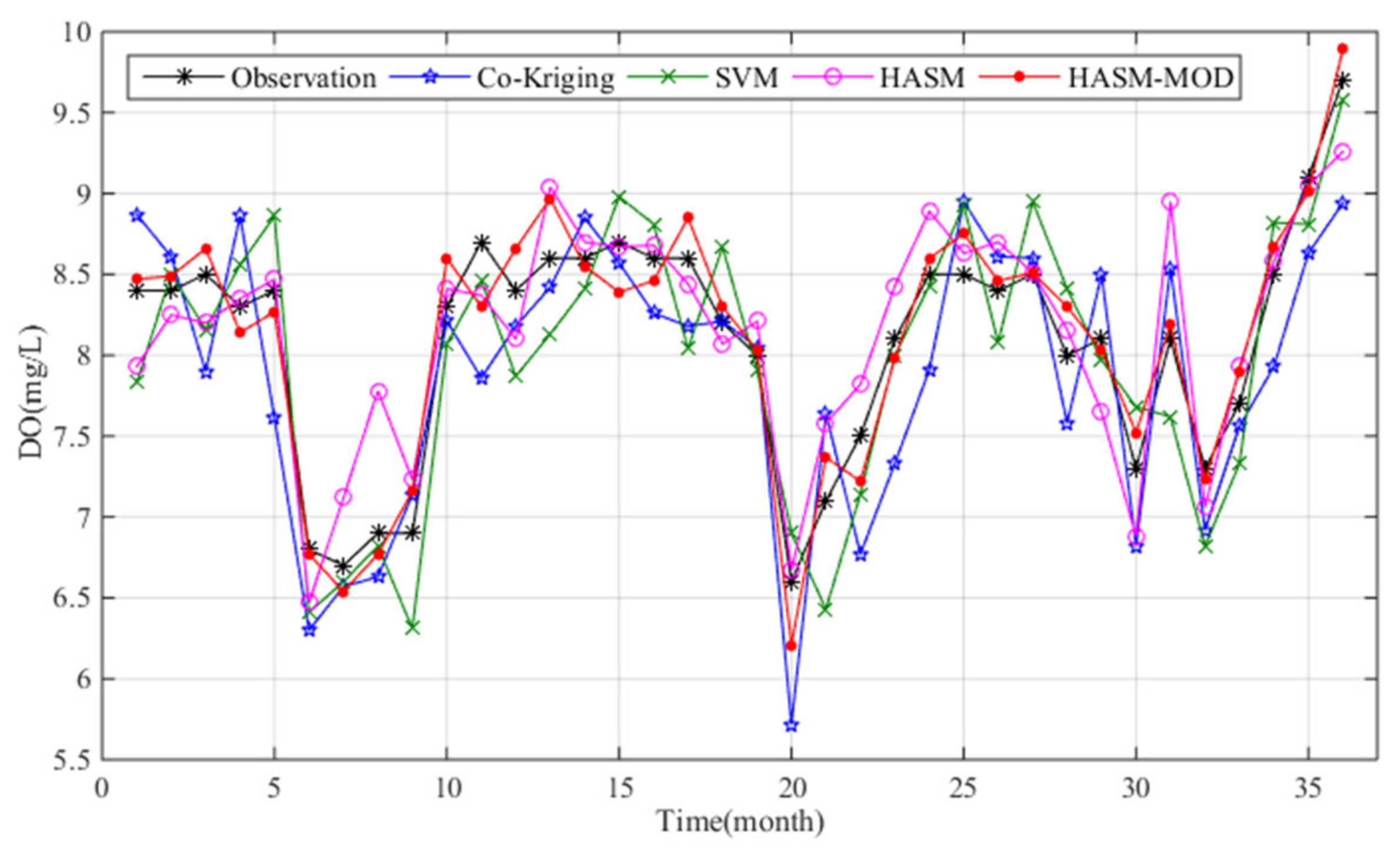
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Middelburg, J.; Levin, L.A. Coastal hypoxia and sediment biogeochemistry. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 1273–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayram, A.; Uzlu, E.; Kankal, M.; Dede, T. Modeling stream dissolved oxygen concentration using teaching-learning based optimization algorithm. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 6565–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, K.L.; Doubleday, Z.A.; Gillanders, B.M. Prolonged exposure to low oxygen improves hypoxia tolerance in a freshwater fish. Conserv. Physiol. 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, D.T.; Richardson, L.B. Effect of Oxygen Reduction Rate and Constant Low Dissolved Oxygen Concentrations on Two Estuarine Fish. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1980, 109, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, D.L. Dissolved oxygen and fish behavior. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1987, 18, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidtko, S.; Stramma, L.; Visbeck, M. Decline in global oceanic oxygen content during the past five decades. Nature 2017, 542, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitburg, D.; Levin, L.A.; Oschlies, A.L.; Gregoire, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Conley, D.J.; Garcon, V.; Gilbert, D.; Gutierrez, D.; Gutierrez, D.; et al. Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science 2018, 359, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. A comprehensive review on water quality parameters estimation using remote sensing techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Jia, P.; Qi, C.; Ding, F. A review of surface water quality models. Sci. World J. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikhina, T.; Khovanova, N.A. Handling limited datasets with neural networks in medical applications: A small-data approach. Artif. Intell. Med. 2017, 75, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siljic, T.A.; Antanasijevic, D.; Ristic, M.; Peric-Grujic, A.; Pocajt, V. A linear and non-linear polynomial neural network modeling of dissolved oxygen content in surface water: Inter-and extrapolation performance with inputs’ significance analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, A.; James, D.E.; Hayes, D.F. Estimation of water quality profiles in deep lakes based on easily measurable constituents at the water surface using artificial neural networks coupled with stationary wavelet transform. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Chakrabarty, M.; Rakshit, N.; Bhowmich, R.A. Environmental factors as indicators of dissolved oxygen concentration and aooplankton abundance: Deep learning versus traditional regression approach. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 100, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, E.K.; Kipkorir, E.C.; Kosgei, J.R. Dissolved oxygen modelling using artificial neural network: A case of River Nzoia, Lake Victoria Basin, Kenya. J. Water Secur. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.; Lye, M.L.; Khan, A.A.; Paterson, R. The influence of air temperature on temperature and the concentration of dissolved oxygen in Newfound land rivers. Can. Water Resour. J. 2013, 36, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stajkowski, S.; Zeynoddin, M.; Farghaly, H.; Gharabaghi, B.; Bonakdari, H. A methodology for forecasting dissolved oxygen in urban streams. Water 2020, 12, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koko, S.; Irvine, K.N.; Jindal, R.; Thongdara, R. Spatial and temporal variations of dissolved oxygen in Chaam municipality wastewater treatment ponds using GIS kriging interpolation. J. Water Manage. Model. 2017, 1, 427–437. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, R.; Oliver, M.A. Geostatistics for Environmental Scientists: Statistics in Practice; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hooshmand, A.; Delghandi, M.; Izadi, A.; Aali, K.A. Application of kriging and cokriging in spatial estimation of groundwater quality parameters. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 3402–3408. [Google Scholar]
- Rankovic, V.; Radulovic, J.; Radojevic, I.; Ostojic, A.; Comic, L. Neural network modeling of dissolved oxygen in the Gruza reservoir, Serbia. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Yan, J.; Gao, C.; Yang, S. Prediction of water quality time series data based on least dquares support vector machine. Proc. Eng. 2012, 31, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarmizi, A.; Ahmed, A.N.; EL-Shafi, A. Dissolved oxygen prediction using support vector machine in Terengganu River. Midele East J. Sci. Res. 2014, 21, 2182–2188. [Google Scholar]
- Emamgholizadeh, S.; Kashi, H.; Marofpoor, I.; Zalaghi, E. Prediction of water quality parameters of Karoon River (Iran) by artificial intelligence-based models. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heddam, S.; Kisi, O. Modelling daily dissolved oxygen concentration using least square support vector machine, multivariate adaptive regression splines and M5 model tree. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najah, A.; El-Shafie, A.; Karim, O.; Jaafar, O.; El-Shafir, A.H. An application of different artificial intelligences techniques for water quality prediction. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2011, 22, 5298–5308. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tan, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J. Deep learning in environmental remote sensing: Achievements and challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Montzka, C.; Chai, L.; Liu, S.; Ge, Y.; Liu, J.; Lu, Z.; He, X.; Zheng, J. Inter-comparison of several soil moisture downscaling methods over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.X. Surface Modeling: High Accuracy and High Speed Methods; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Du, Z.P.; Song, Y.J.; Chen, C.F.; Yue, T.X. Surface modelling of soil pH. Geoderma 2009, 150, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Yue, T.X. A method of DEM construction and related error analysis. Comput. Geosci. 2010, 36, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Yue, T.X. A modification of HASM for interpolating precipitation in China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 116, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.X.; Du, Z.P.; Lu, M.; Fan, Z.M.; Wang, C.L.; Tian, Y.Z.; Xu, B. Surface modeling of ecosystem responses to climatic change in Poyang Lake Baisn of China. Ecol. Model. 2015, 306, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yue, T.X.; Jiao, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.P.; Bao, Z.Y. Fusion of simulated and observational temperature data in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region based on high-accuracy surface modeling. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S.E. Surface Modeling: High Accuracy and High Speed Methods. CRC Press, published February (2011), 711p., hardbound, price 129.95$. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Tian, L.; Gan, W. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using MODIS observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.B.; Yan, D.H.; Wang, H. Responses of lakeshore wetlands landscape to water levels changes in Poyang lake. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2015, 34, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Son, S.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, B.; Park, Y.G.; Nam, J.H.; Ryu, J. Application of satelliate remote sensing in monitoring dissolved oxygen variabilities: A case study for coastal waters in Korea. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Wang, X.-Y.; Li, W.-S.; Wei, Y.-G.; An, D. Research of dissolved oxygen prediction in recirculating aquaculture systems based on deep belief network. Aquacult. Eng. 2020, 90, 102085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heddam, S. Generalized regression neural network (GRNN) based approach for modeling hourly dissolved oxygen concentration in the upper Klamath River, Oregon, USA. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najah, A.; El-Shafie, A.; Karim, O.A.; El-Shafie, A.F. Performance of ANFIS versus MLP-NN dissolved oxygen prediction models in water quality monitoring. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 1658–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.J.; Fang, H.Y.; Qin, G.X.; Tan, X.Q.; Huang, Z.W.; Zeng, F.T.; Du, H.W.; Li, S.P. Concentration estimation of dissolved oxygen in Pearl River Basin using input variable selection and machine learning techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.G.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, D.W.; Lin, L.S. Quantitative retrieval of chlorophyll a concentration based on Landsat-8 OLI in the Lakes. Jiangxi Sci. 2016, 34, 441–456. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, T.; Wells, N.; Charnock, H. The sea surface thermal boundary layer and its relevance to the measurement of sea surface temperature by airborne and spaceborne radiometers. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1984, 5, 19–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, C.E.; Faux, R.N.; McIntosh, B.A.; Poage, N.J.; Norton, D.J. Airborne thermal remote sensing for water temperature assessment in rivers and streams. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretaux, J.F.; Merchant, C.J.; Duguay, C.; Simis, S.; Calmettes, B.; Berge-Nguyen, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Carrea, L.; Liu, X.; et al. ESA Lakes Climate Change Initiative (Lake_cci): Lake Products, Version 1.0; Centre for Environmental Data Analysis. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.5285/3c324bb4ee394d0d876fe2e1db217378 (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- Henderson, D.W. Differential Geometry; Prentice-Hall Inc.: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Somasundaram, D. Differential Geometry; Alpha Science International Ltd: Harrow, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liseikin, V.D. A Computational Differential Geometry Approach to Grid Generation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Toponogov, V.A. Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces; Birkhaeuser Boston: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zand, T.; Siahkoohi, H.R.; Malcolm, A.; Gholami, A.; Richardson, A. Concensus optimization of total variation-based reverse time migration. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 24, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osher, S.; Burger, M.; Goldfarb, D.; Xu, J.; Yin, W. An iterative regularization method for total variation-based image restoration. Multiscale Model. Simul. 2005, 4, 460–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Silva, H.; Gómez-Treviño, E. Bregman iterative algorithms for 2D geosounding inversion. Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng. 2015, 23, 1085–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindermann, S.; Raik, K. A simplified L-curve method as error estimator. Electron. Trans. Numer. Anal. 2020, 53, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, R.; Shaharuddin, S.; Chang, C.K.; Zakaria, N.A.; Ghani, A.A.; Chan, N.W. Predition of water quality index in constructed wetlands using support vector machine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 6208–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keerthi, S.S.; Lin, C.J. Asymptotic behaviors of support vector machines with Gaussian kernel. Neural Comput. 2001, 15, 1667–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattermann, F.; Krysanova, V.; Wechsung, F.; Wattenbach, M. Runoff simulation on the macroscale with the ecohydrological model SWIM in the Elbe catchment-validation and uncertainty analysis. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, J.P. Review of Surface Modeling. In Surface modelling by computer: Proceedings of a Conference jointly sponsored by the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors and the Institution of Civil Engineers, London, UK, 6 October 1976; ICE: London, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Y.; Suganthan, P.N.; Amaratunga, G. Ensemble deep learning for regreesion and time series forecasting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Ensemble Learning (CIEL), Orlando, FL, USA, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]



| Month | July | August | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error | MAE | RMSE | R2 | MAE | RMSE | R2 |
| Cokriging | 0.39 | 0.45 | 0.93 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.96 |
| SVM | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.96 | 0.41 | 0.47 | 0.83 |
| HASM | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.98 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.97 |
| HASM_MOD | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.99 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.97 |
| Station | Outlet A | Sanshan | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error | MAE | RMSE | R2 | MAE | RMSE | R2 |
| Cokriging | 0.41 | 0.47 | 0.72 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.88 |
| SVM | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.82 | 0.31 | 0.36 | 0.86 |
| HASM | 0.27 | 0.37 | 0.78 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.77 |
| HASM_MOD | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.93 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.93 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, N.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, M. A New Approach for Estimating Dissolved Oxygen Based on a High-Accuracy Surface Modeling Method. Sensors 2021, 21, 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21123954
Zhao N, Fan Z, Zhao M. A New Approach for Estimating Dissolved Oxygen Based on a High-Accuracy Surface Modeling Method. Sensors. 2021; 21(12):3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21123954
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Na, Zemeng Fan, and Miaomiao Zhao. 2021. "A New Approach for Estimating Dissolved Oxygen Based on a High-Accuracy Surface Modeling Method" Sensors 21, no. 12: 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21123954
APA StyleZhao, N., Fan, Z., & Zhao, M. (2021). A New Approach for Estimating Dissolved Oxygen Based on a High-Accuracy Surface Modeling Method. Sensors, 21(12), 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21123954







