Multi-Odor Discrimination by Rat Sniffing for Potential Monitoring of Lung Cancer and Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Odors
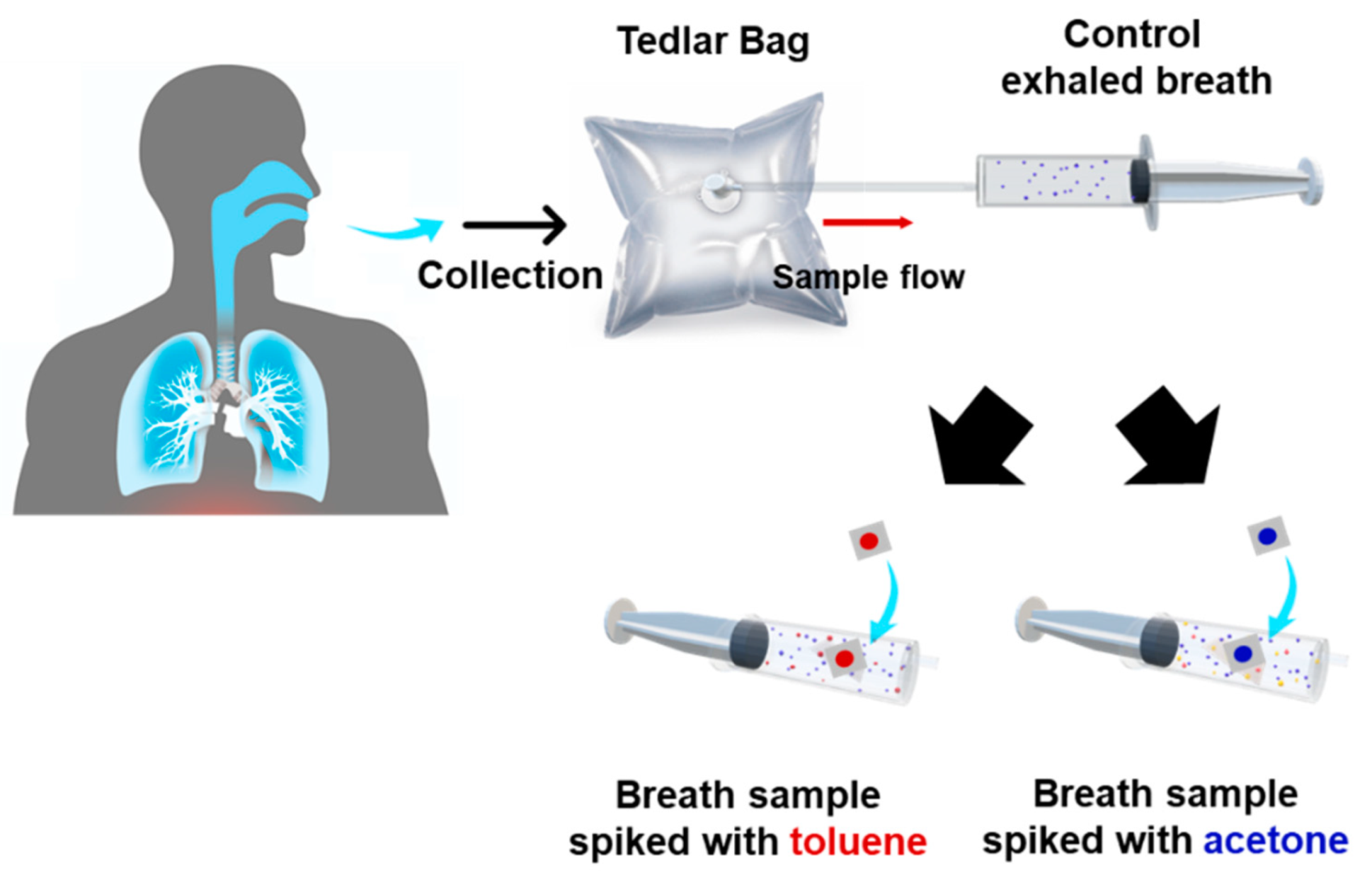
2.2. Spiked Breath Sampling
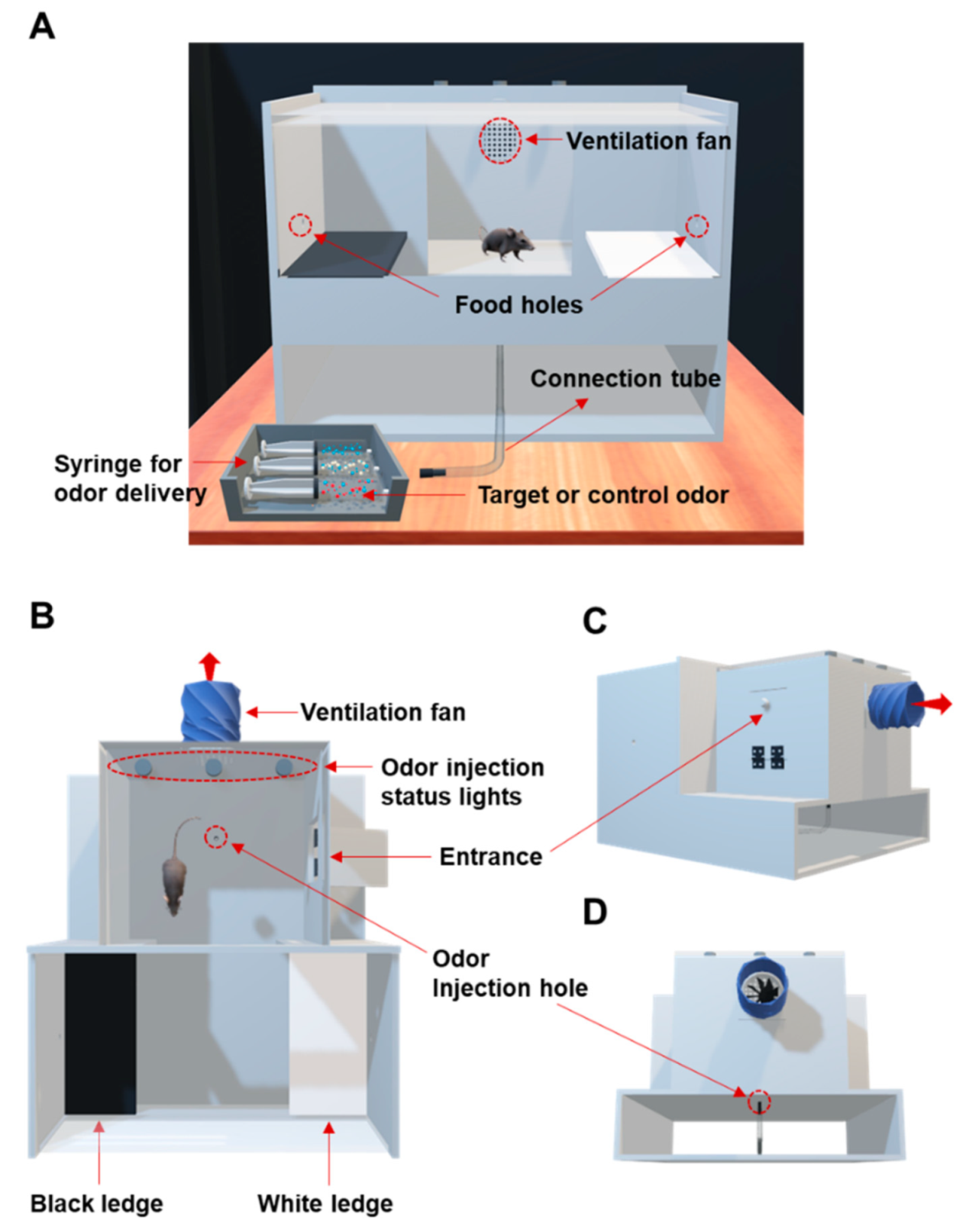
2.3. Multi-Odor Discrimination Device
2.4. Performance Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
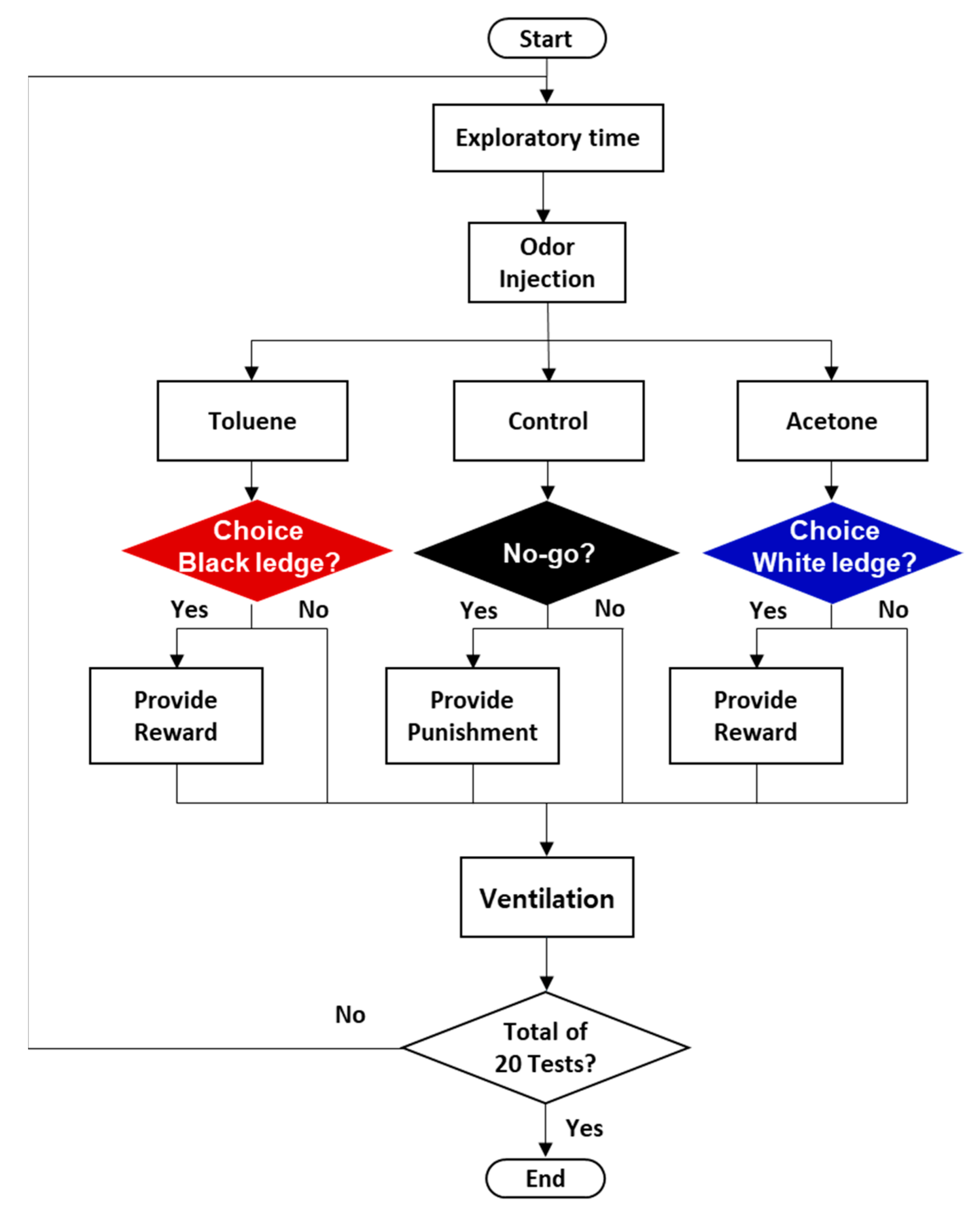
3.1. Multi-Odor Discrimination Device Based on the Combined 2-Choice/No-Go Paradigm
3.2. Animal Training for Multi-Odor Discrimination
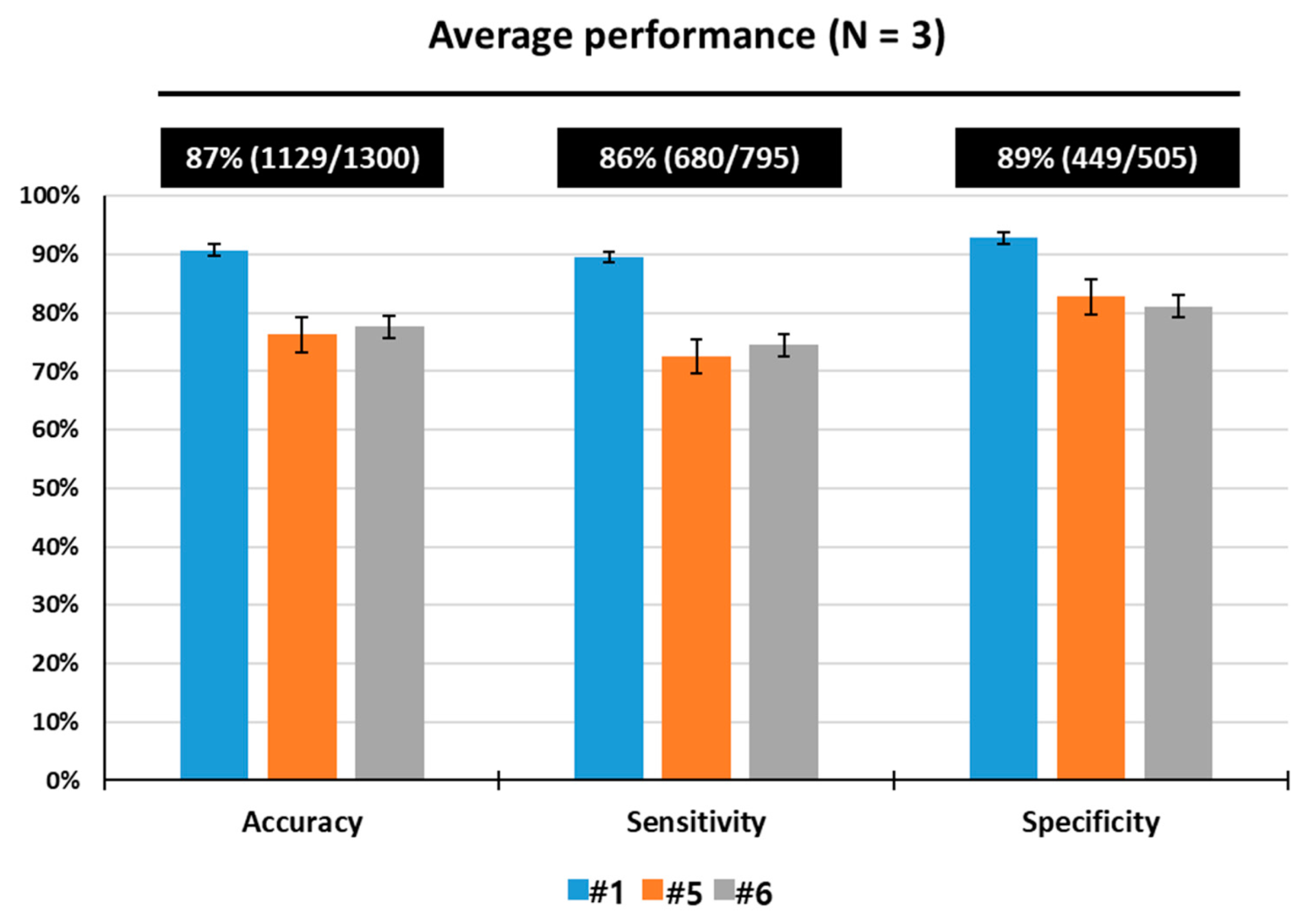
3.3. Measurement of Multi-Odor Detection Performance
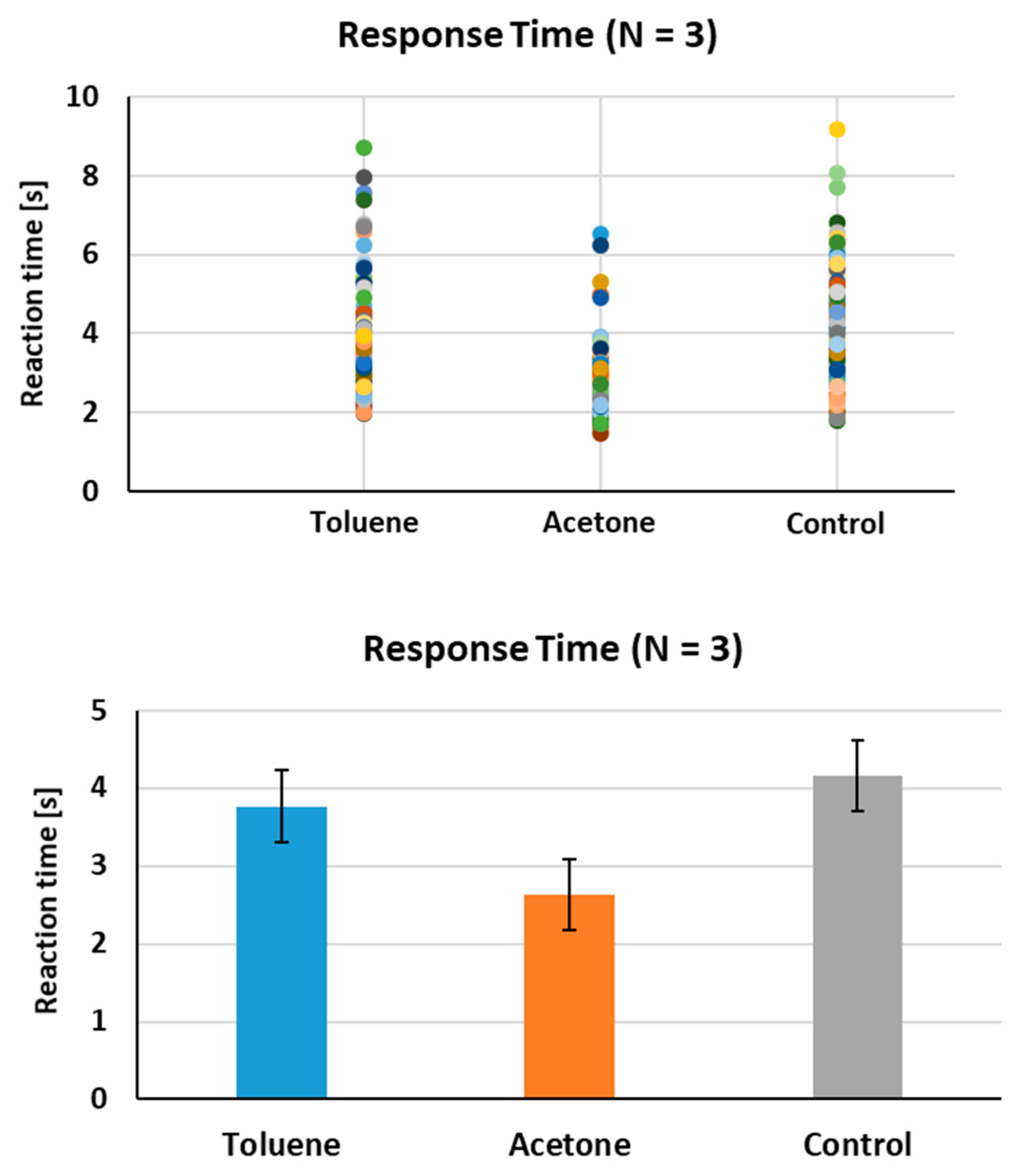
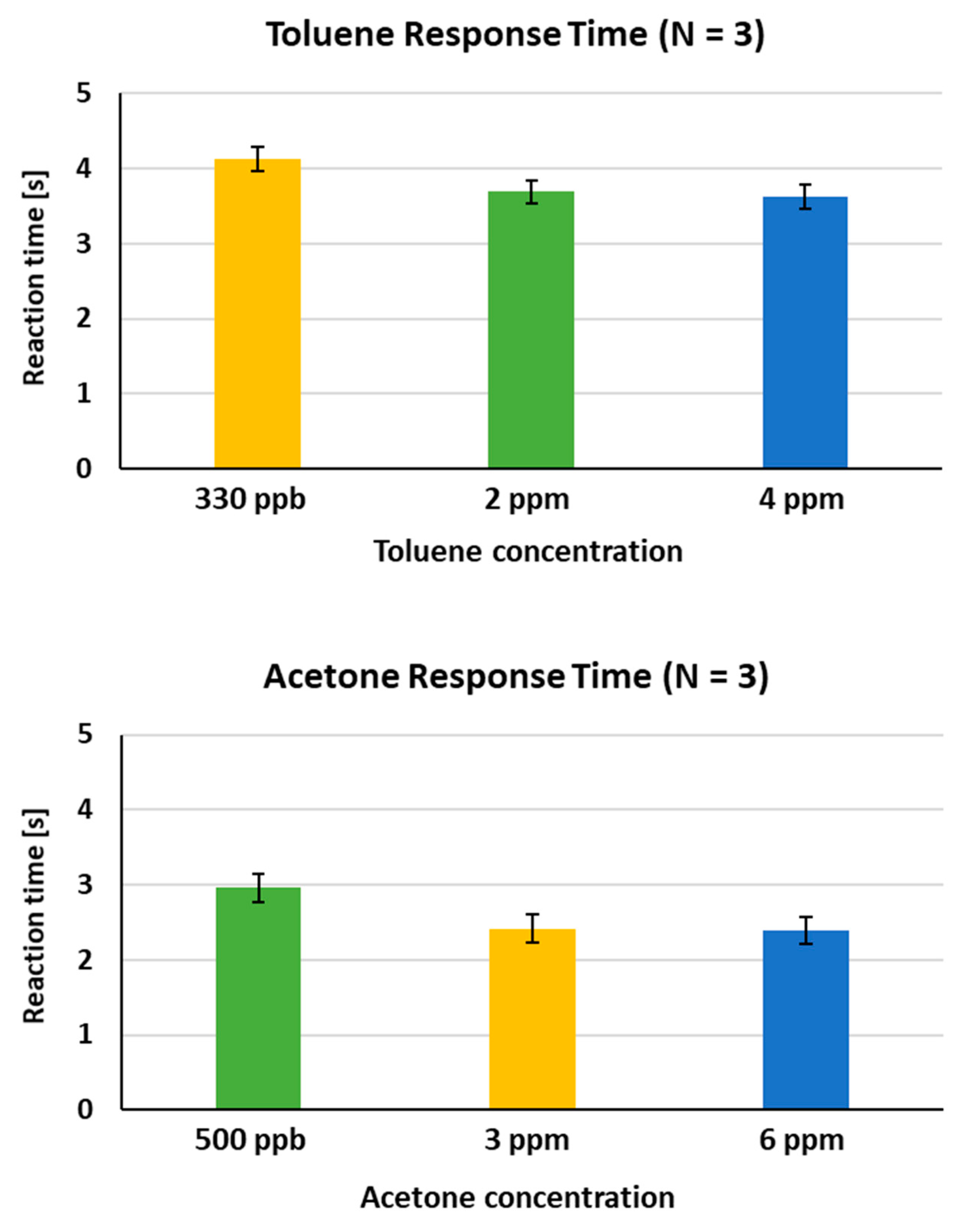
3.4. Response Time
3.5. Quantitative Analysis
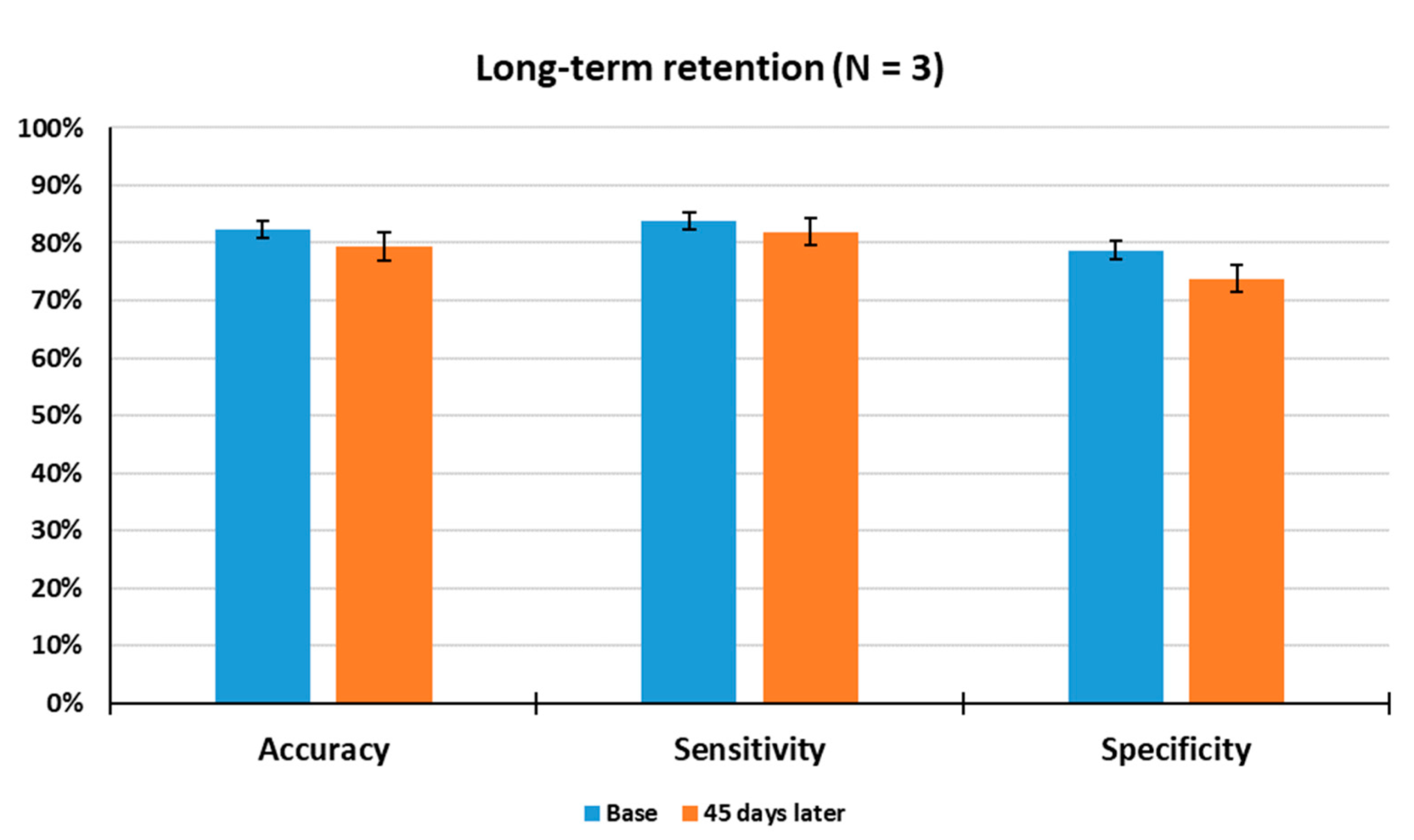
3.6. Measurement of Long-Term Retention
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Approval
References
- Oh, Y.; Lee, Y.; Heath, J.; Kim, M. Applications of animal biosensors: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 637–645. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, T.L.; Browne, C.M.; Schoon, A.; Cox, C.; Poling, A. Animal olfactory detection of human diseases: Guidelines and systematic review. J. Vet. Behav. 2017, 20, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah, C.; Beebe, S.C.; Howell, T.J.; Bennett, P.C. Using scent detection dogs in conservation settings: A review of scientific literature regarding their selection. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Angle, C.; Waggoner, L.P.; Ferrando, A.; Haney, P.; Passler, T. Canine detection of the volatilome: A review of implications for pathogen and disease detection. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dam, A.; Schoon, A.; Wierda, S.F.; Heeringa, E.; Aalders, C.G. The use of crime scene detection dogs to locate semen stains on different types of fabric. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 302, 109907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarowski, L.; Waggoner, L.P.; Krichbaum, S.; Singletary, M.; Haney, P.; Rogers, B.; Angle, C. Selecting dogs for explosives detection: Behavioral characteristics. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jezierski, T.; Adamkiewicz, E.; Walczak, M.; Sobczyńska, M.; Gorecka-Bruzda, A.; Ensminger, J.; Papet, E. Efficacy of drug detection by fully-trained police dogs varies by breed, training level, type of drug and search environment. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 237, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menchetti, L.; Guelfi, G.; Speranza, R.; Carotenuto, P.; Moscati, L.; Diverio, S. Benefits of dietary supplements on the physical fitness of German Shepherd dogs during a drug detection training course. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poling, A.; Weetjens, B.J.; Cox, C.; Beyene, N.W.; Bach, H.; Sully, A. Using trained pouched rats to detect land mines: Another victory for operant conditioning. J. Appl. Behavior Anal. 2011, 44, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, A.; Durgin, A.; Poling, A.; Weetjens, B.J.; Cox, C.; Tewelde, T.; Gilbert, T. Mine detection rats: Effects of repeated extinction on detection accuracy. J. Conv. Weapons Destr. 2015, 16, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Cornua, J.N.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; Ondet, V.; Girardet, C.; Cussenot, O. Olfactory detection of prostate cancer by dogs sniffing urine: A step forward in early diagnosis. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, H.; Kohnoe, S.; Yamazato, T.; Satoh, Y.; Morizono, G.; Shikata, K.; Morita, M.; Watanabe, A.; Morita, M.; Kakeji, Y.; et al. Colorectal cancer screening with odour material by canine scent detection. Gut 2011, 60, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooney, N.J.; Guest, C.M.; Swanson, L.C.M.; Morant, S.V. How effective are trained dogs at alerting their owners to changes in blood glycaemic levels? Variations in performance of glycaemia alert dogs. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.; Morant, S.; Kane, S.; Pesterfield, C.; Guest, C.; Rooney, N.J. An owner-independent investigation of diabetes alert dog performance. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weetjens, B.J.; Mgode, G.F.; Machang’u, R.S.; Kazwala, R.; Mfinanga, G.; Lwilla, F.; Cox, C.; Jubitana, M.; Kanyagha, H.; Mtandu, R.; et al. African pouched rats for the detection of pulmonary tuberculosis in sputum samples. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2009, 13, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mgode, G.F.; Weetjens, B.J.; Nawrath, T.; Lazar, D.; Cox, C.; Jubitana, M.; Mahoney, A.; Kuipers, D.; Machang’u, R.S.; Weiner, J.; et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis volatiles for diagnosis of tuberculosis by Cricetomys rats. Tuberculosis 2012, 92, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bjanes, D.A.; Moritz, C.T. Automated center-out rodent behavioral trainer (ACRoBaT), an automated device for training rats to perform a modified center out task. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 346, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wei, J.; Rizak, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Ma, Y. An odor detection system based on automatically trained mice by relative go no-go olfactory operant conditioning. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaczkes, T.J.; Kumar, P. Very rapid multi-odour discrimination learning in the ant Lasius niger. Insect. Soc. 2020, 67, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliff, R.; Voskuilen, C.; Teodorescu, A. Modeling 2-alternative forced-choice tasks: Accounting for both magnitude and difference effects. Cogn. Psychol. 2018, 103, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, P.; Ratcliff, R.; Perea, M. A model of the go/no-go task. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2007, 136, 389–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aston-Jones, G.; Rajkowski, J.; Kubiak, P.; Alexinsky, T. Locus coeruleus neurons in monkey are selectively activated by attended cues in a vigilance task. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 4467–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, G.; Tisch, U.; Adams, O.; Hakim, M.; Shehada, N.; Broza, Y.Y.; Billan, S.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Haick, H. Diagnosing lung cancer in exhaled breath using gold nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righettoni, M.; Tricoli, A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Si:WO(3) Sensors for highly selective detection of acetone for easy diagnosis of diabetes by breath analysis. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3581–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Dai, W.; Liu, M.; Long, Y.; Wang, C.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Peng, X.; et al. VOC biomarkers identification and predictive model construction for lung cancer based on exhaled breath analysis: Research protocol for an exploratory study. Br. Med. J. 2019, 9, 028448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotnick, B.; Hanford, L.; Hodos, W. Can rats acquire an olfactory learning set? J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process 2000, 26, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotnick, B. Animal cognition and the rat olfactory system. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2001, 5, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millman, D.J.; Murthy, V.N. Rapid learning of odor–value association in the olfactory striatum. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 4335–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, F.; Elsayed, G.F.; Cao, R.; Pnevmatikakis, E.; Latham, P.E.; Cunningham, J.P.; Churchland, A.K. Excitatory and inhibitory subnetworks are equally selective during decision-making and emerge simultaneously during learning. Neuron 2020, 105, 165–179.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotnick, B.M.; Kufera, A.; Silberberg, A.M. Olfactory learning and odor memory in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 1991, 50, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Range, F.; Huber, L. Dogs’ attention towards humans depends on their relationship, not only on social familiarity. Anim. Cogn. 2013, 16, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, L.; Baxter, G.; Murray, P. You are not my handler! Impact of changing handlers on dogs’ behaviours and detection performance. Animals 2018, 8, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwema, C.L.; Fang, H.; Kurtz, D.B.; Youngentob, S.L.; Schwob, J.E. Odorant receptor expression patterns are restored in lesionrecovered rat olfactory epithelium. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Presence of Target Odor | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | ||
| Animal tests | Positive | a | b |
| Negative | c | d | |
| Detection Performance | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number 1 | Number 5 | Number 6 | |
| Mean Accuracy (MA ± standard error S.E.) | 91.0% ± 0.2 | 82.3% ± 0.5 | 83.7% ± 0.4 |
| Mean Sensitivity (MS ± standard error S.E.) | 89.6% ± 0.2 | 80.7% ± 0.5 | 86.3% ± 0.5 |
| Mean Specificity (MS ± standard error S.E.) | 93.2% ± 0.3 | 85.6% ± 0.7 | 81.5% ± 0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, Y.; Kwon, O.; Min, S.-S.; Shin, Y.-B.; Oh, M.-K.; Kim, M. Multi-Odor Discrimination by Rat Sniffing for Potential Monitoring of Lung Cancer and Diabetes. Sensors 2021, 21, 3696. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113696
Oh Y, Kwon O, Min S-S, Shin Y-B, Oh M-K, Kim M. Multi-Odor Discrimination by Rat Sniffing for Potential Monitoring of Lung Cancer and Diabetes. Sensors. 2021; 21(11):3696. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113696
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Yunkwang, Ohseok Kwon, Sun-Seek Min, Yong-Beom Shin, Min-Kyu Oh, and Moonil Kim. 2021. "Multi-Odor Discrimination by Rat Sniffing for Potential Monitoring of Lung Cancer and Diabetes" Sensors 21, no. 11: 3696. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113696
APA StyleOh, Y., Kwon, O., Min, S.-S., Shin, Y.-B., Oh, M.-K., & Kim, M. (2021). Multi-Odor Discrimination by Rat Sniffing for Potential Monitoring of Lung Cancer and Diabetes. Sensors, 21(11), 3696. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113696








