Synchronization of Acoustic Signals for Steganographic Transmission
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Embedding and Extraction Algorithm
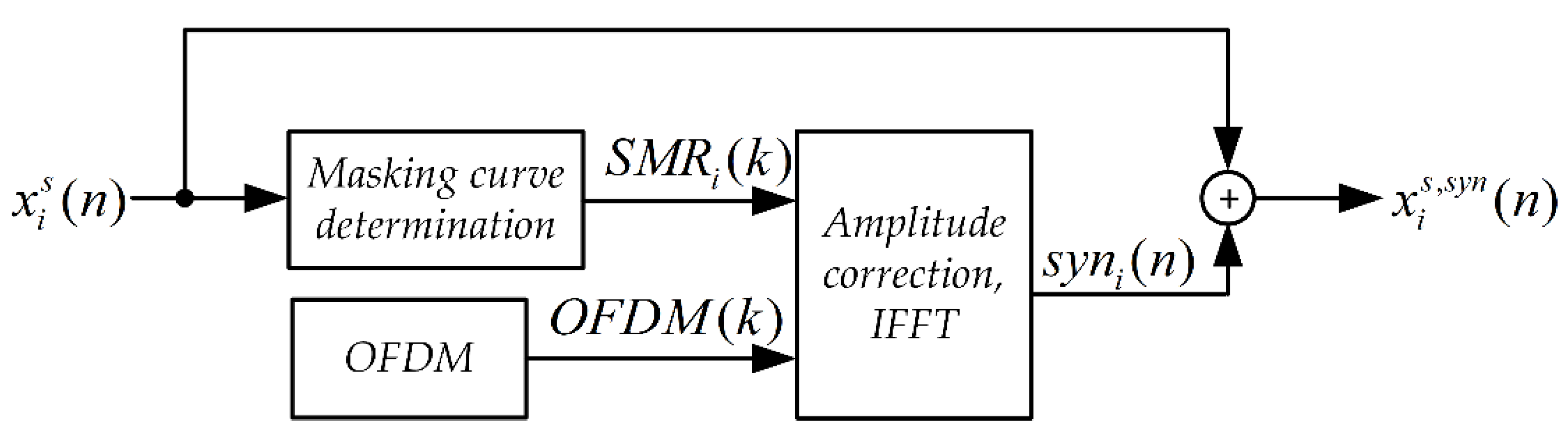
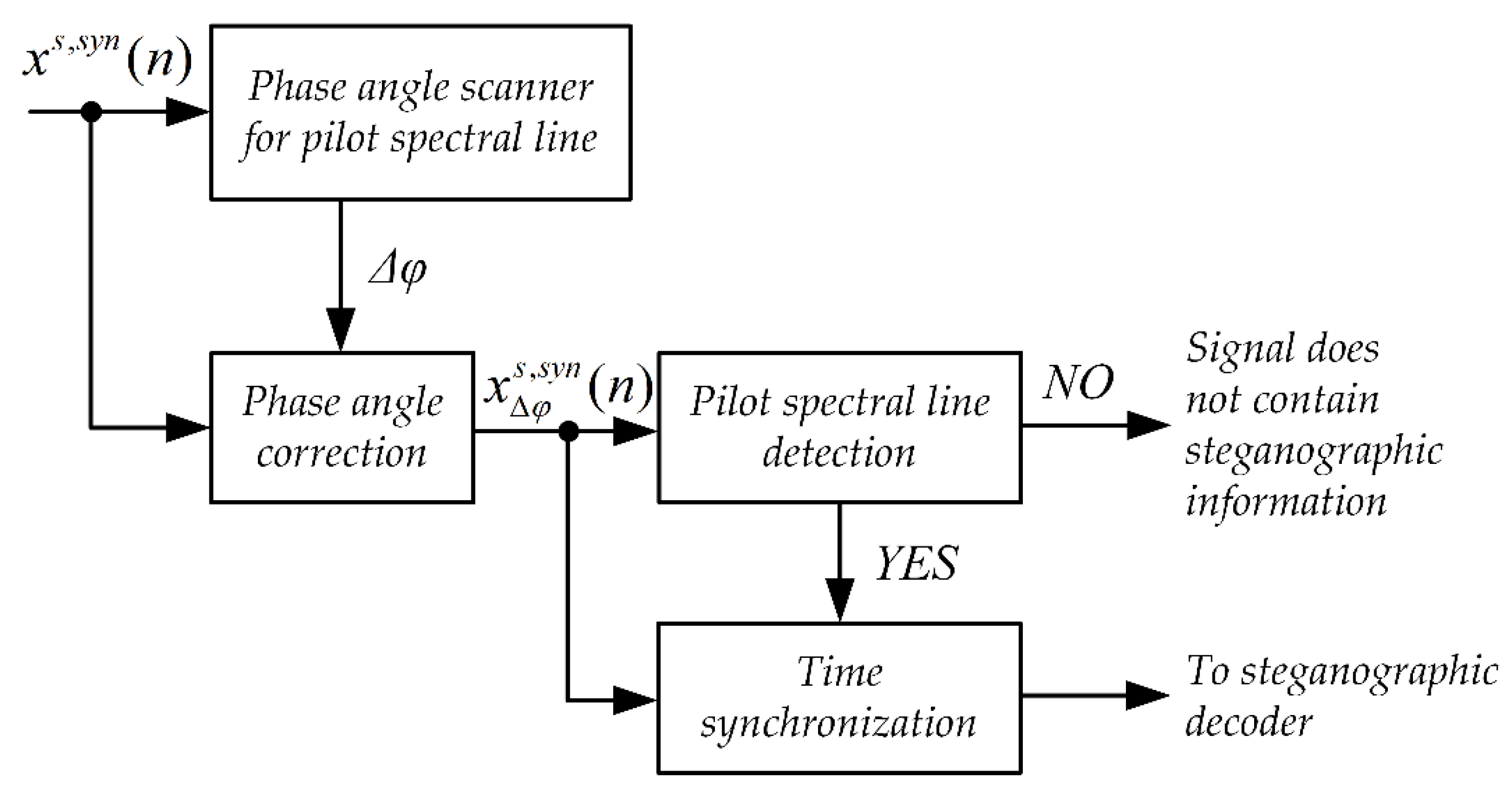
4. Technique Development and Implementation
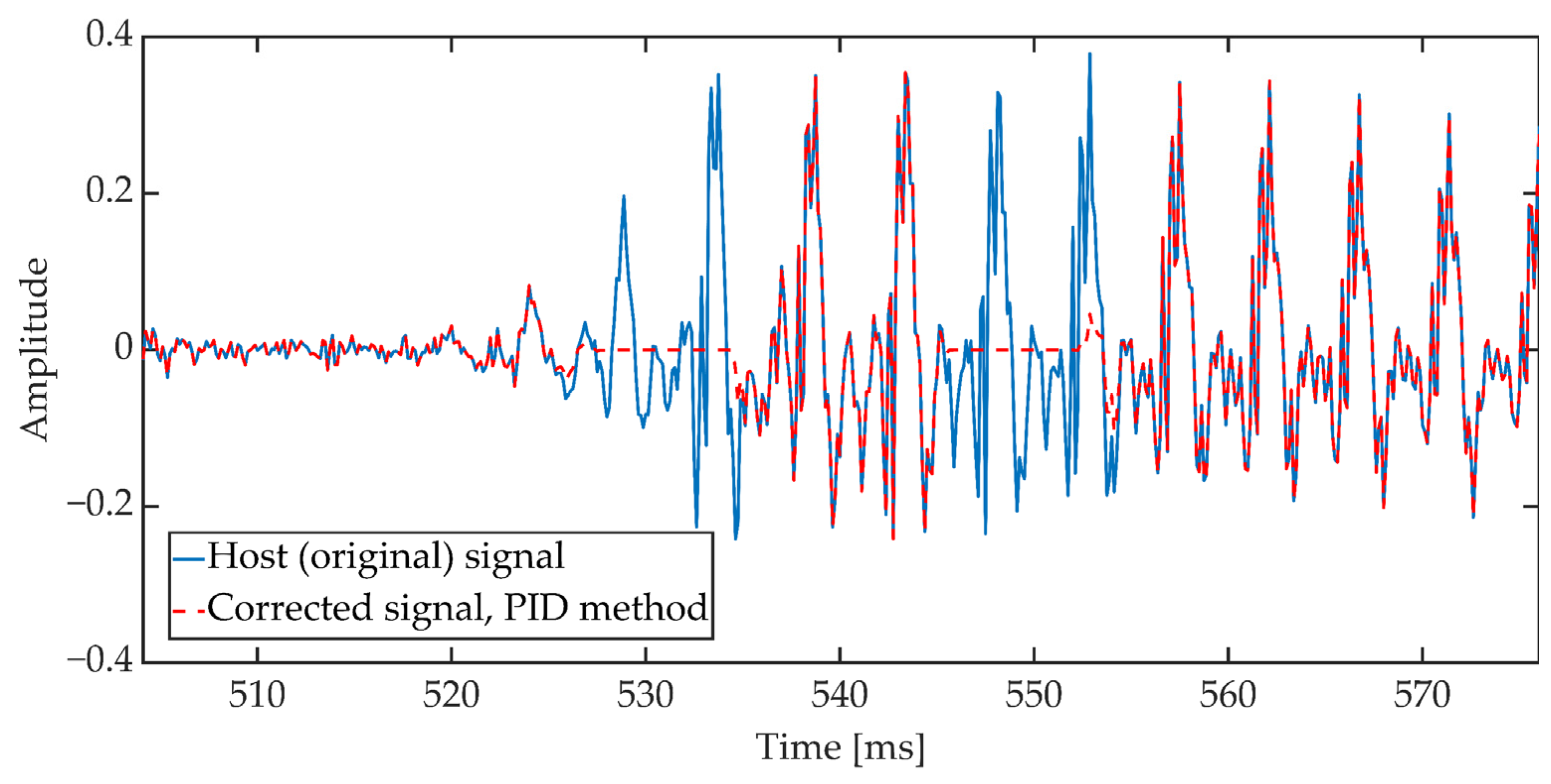
4.1. Monotonic Phase Correction
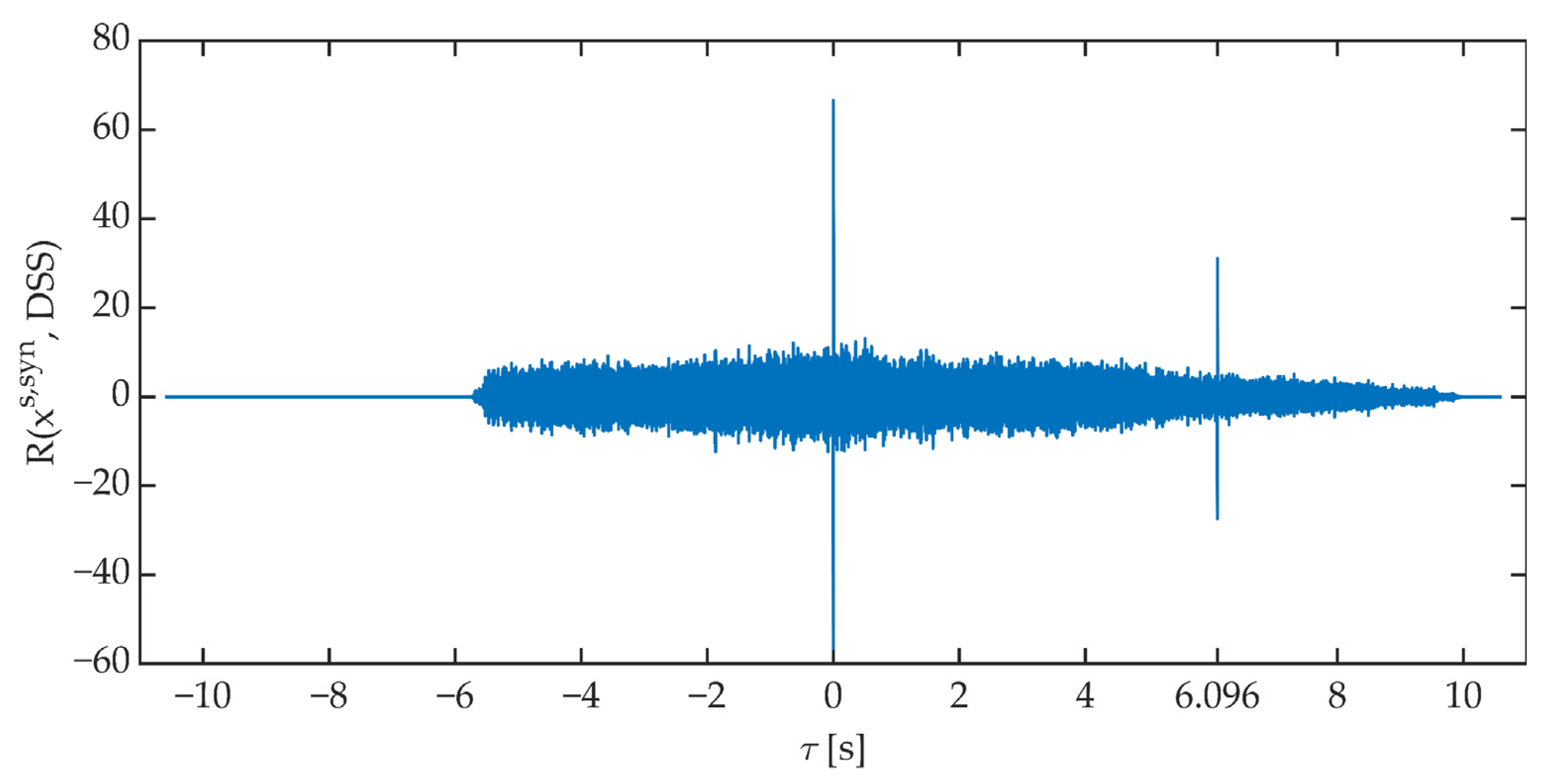
4.2. Direct Spread Spectrum
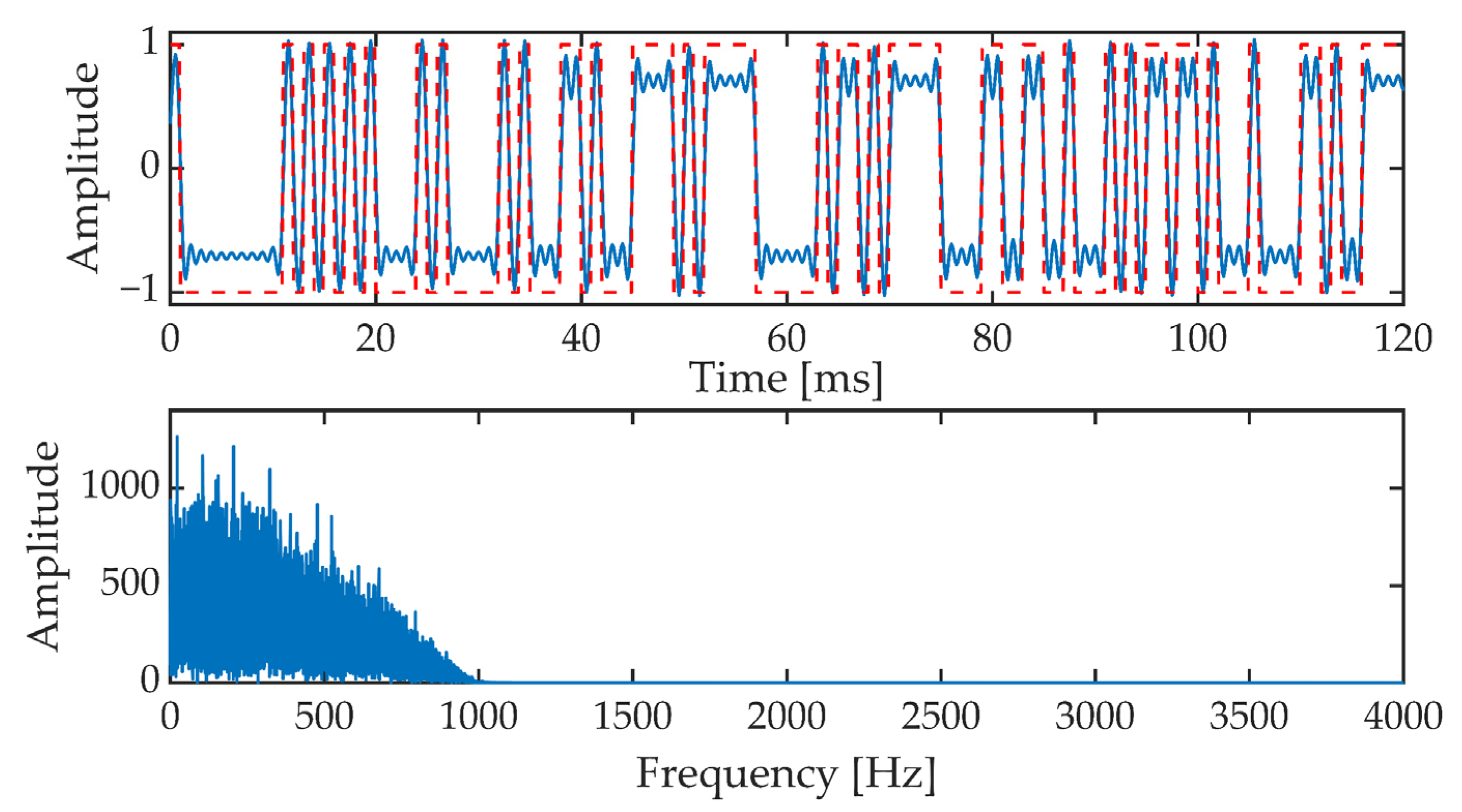
4.3. Pattern Insertion Detection
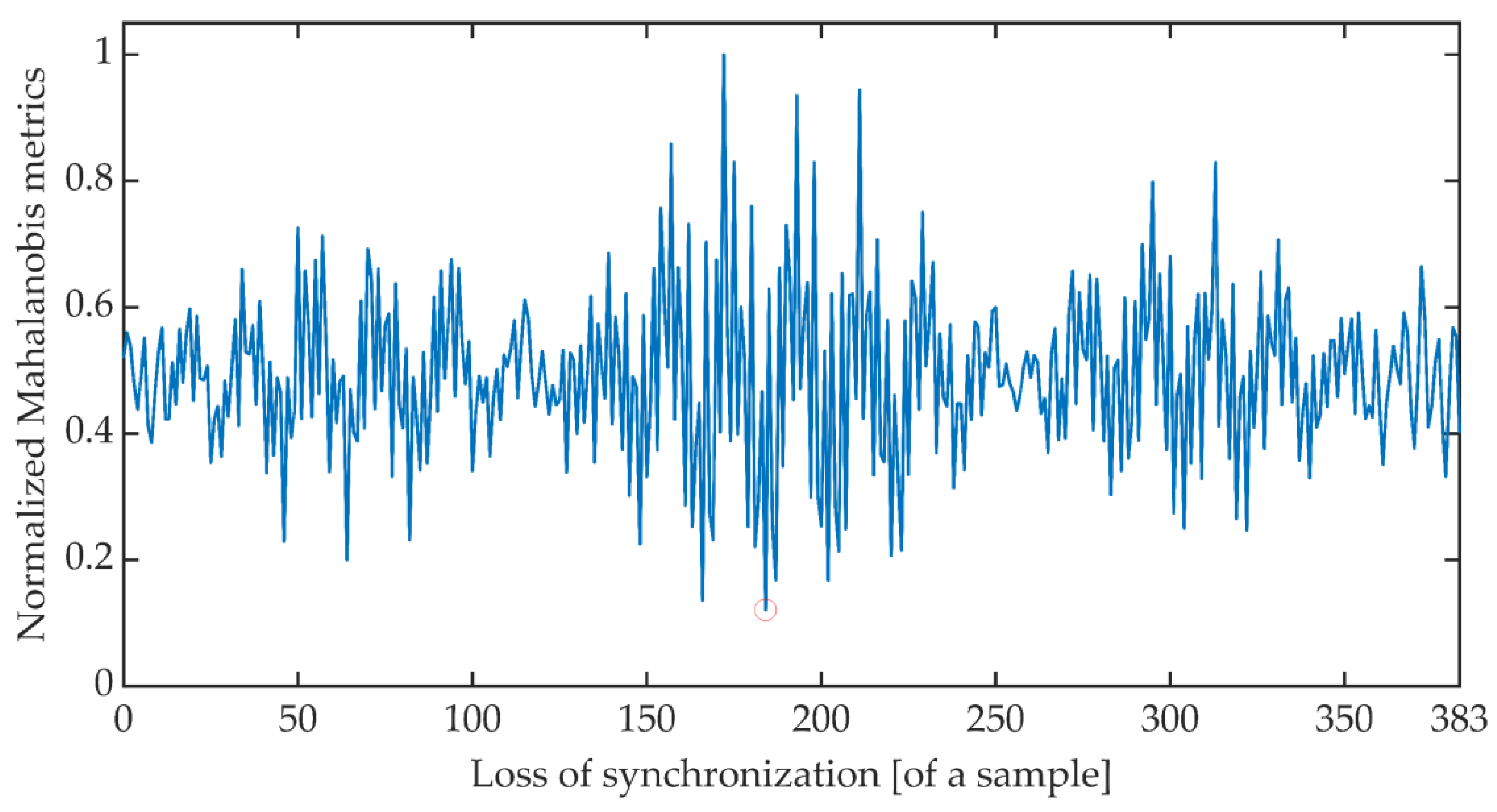
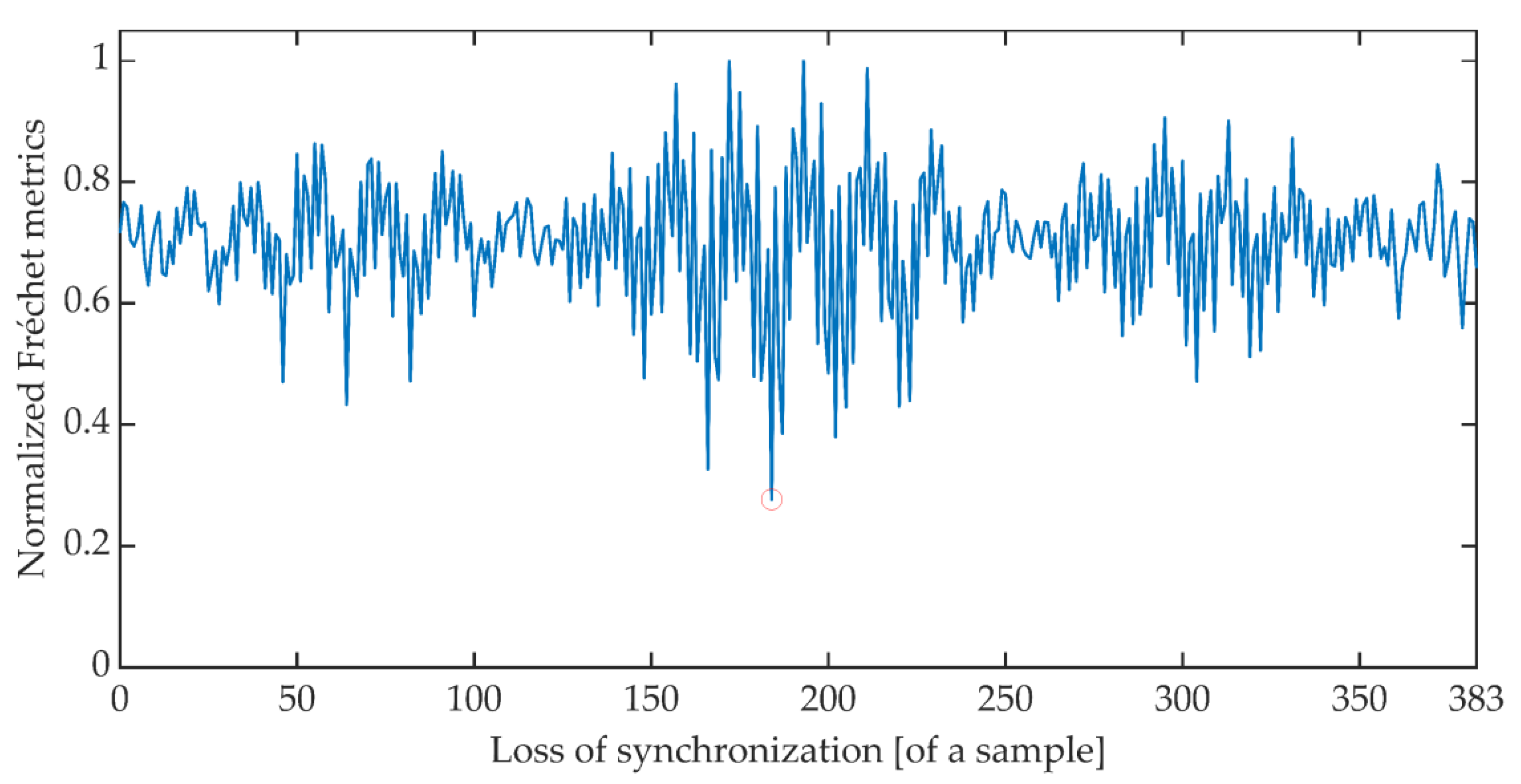
4.4. Minimal Error Synchronization
- where:
- n specifies the length (in the number of bits) of the code vector, ,
- m—integer, m ≥ 3,
- k—specifies the length (in the number of bits) of the information vector,
- t—is the corrective ability of the code.
- Model with PCMA codec;
- Model with iLBC codec variant 15.2 kbit/s.
- n = 127, k = 50, t = 13;
- n = 127, k = 15, t = 27.
5. Results
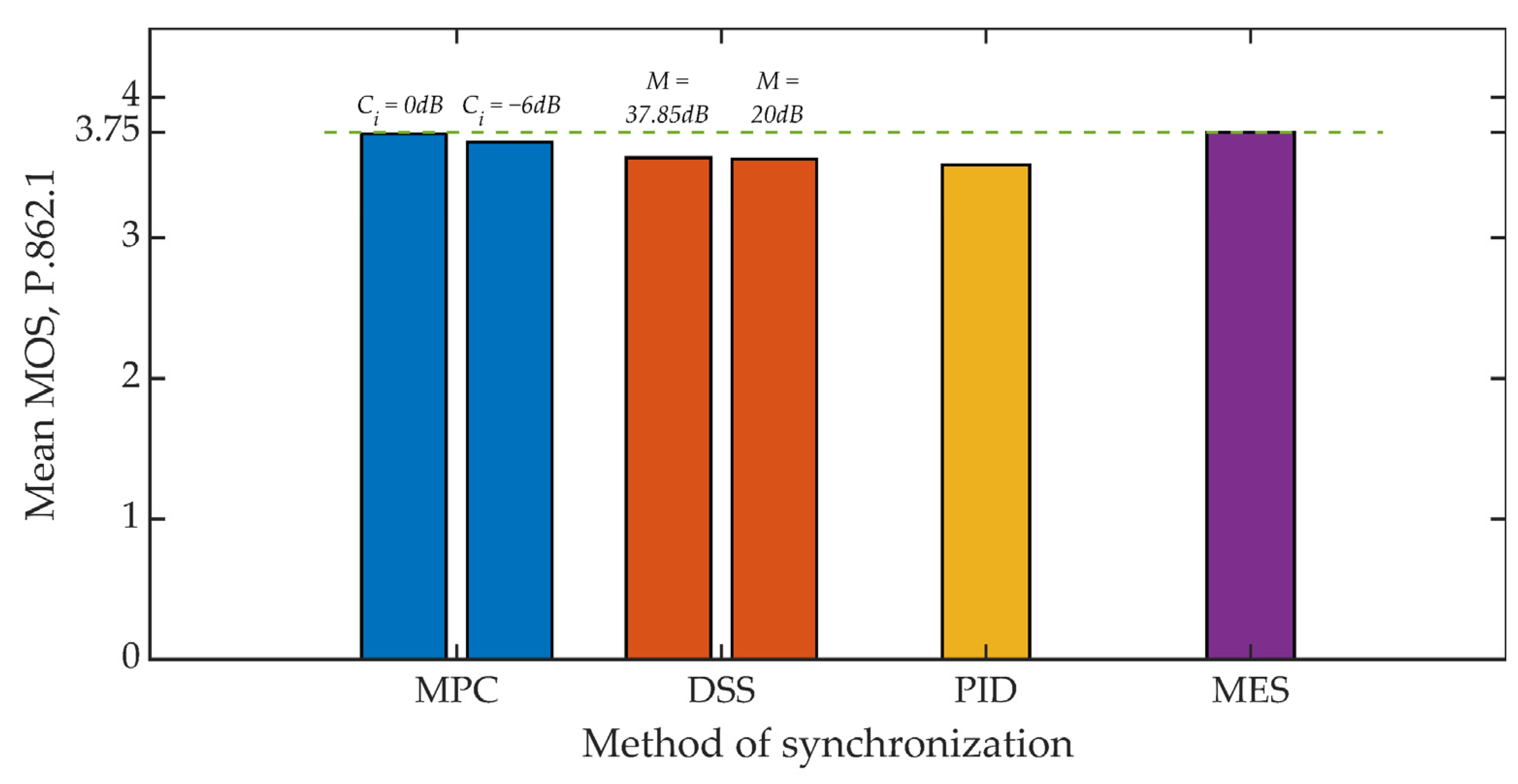
5.1. Signal Quality Assessment
- “raw” data (PESQ raw score or PESQ score);
- PESQ LQ (Listening Quality);
- P.862.1 (MOS—LQO, Mean Opinion Score Listening Quality Objective);
- P.862.2 (PESQ—WB).
5.2. Hidden Transmission Effectiveness Assessment
5.2.1. Steganographic Transmission on the VHF Radio Link
- Analogue Fixed Frequency (AFF) with F3E;
- Digital Fixed Frequency (DFF) with F1D, CVSD 16 kbit/s and encryption;
- Fast Frequency Hopping (FFH) with F1D and CVSD 16 kbit/s and encryption.
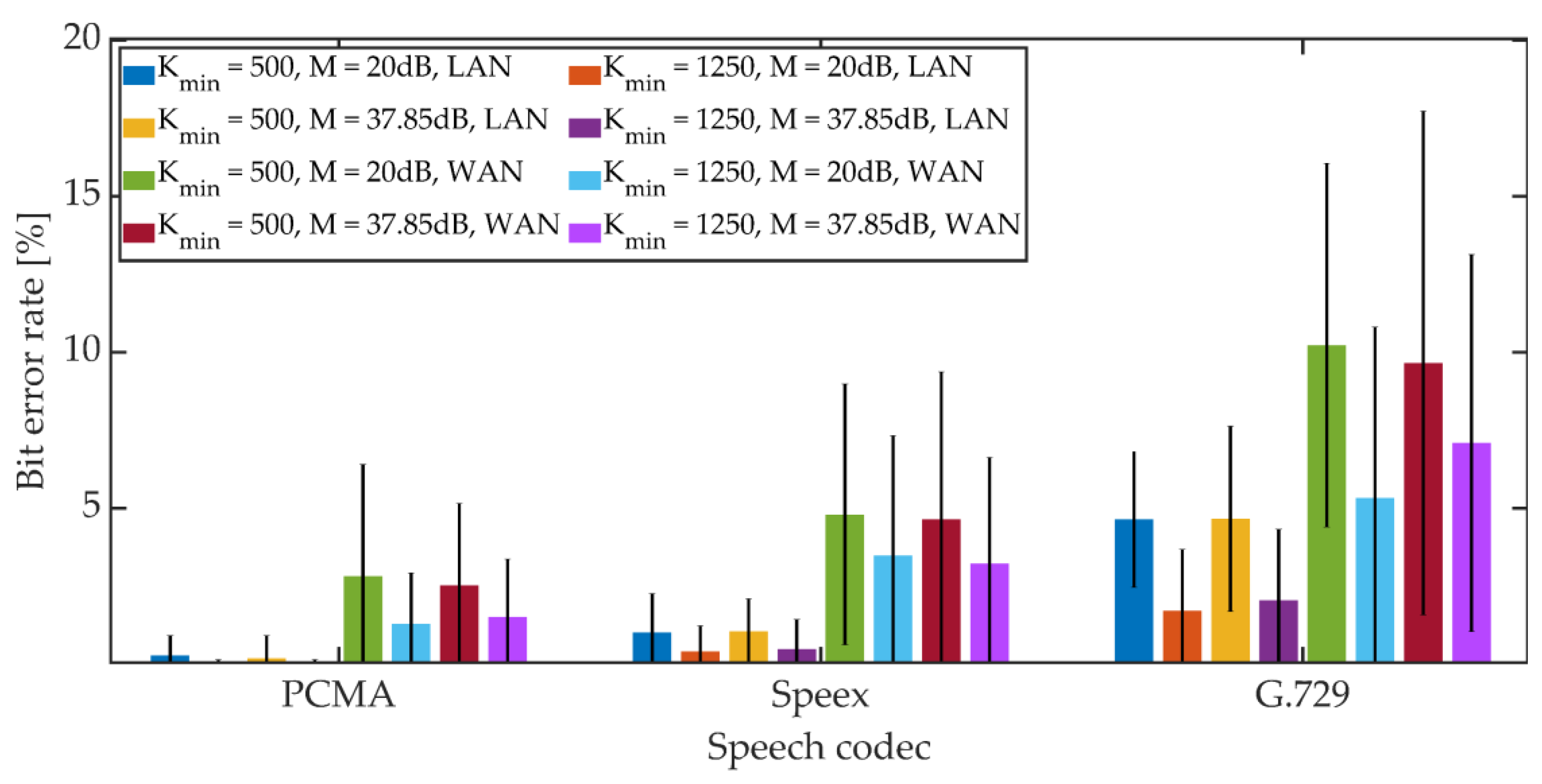
5.2.2. Steganographic Transmission in VoIP Channel
- PCMA, 64 kbit/s;
- Speex, 24.6 kbit/s;
- G.729, 8 kbit/s.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cox, J.; Miller, M.L.; Bloom, J.A.; Fridrich, J.; Kalker, T. Digital Watermarking and Steganography, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pfitzmann, B. Information hiding terminology. In Information Hiding; Anderson, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; Volume 1174, pp. 347–350. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S. Communication Systems, 3rd ed.; John and Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Djebbar, F.; Ayad, B.; Meraim, K.A.; Hamam, H. Comparative study of digital audio steganography techniques. EURASIP J. Audio Speech Music Process. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiser, B.; Mertz, F.; Vary, P. Steganographic packet loss concealment for wireless VoIP. In Proceedings of the ITG Conference on Voice Communication, Aachen, Germany, 8–10 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.-J.; Gao, W.; Yang, W. LPC parameters substitution for speech information hiding. J. China Univ. Posts Telecommun. 2009, 16, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y. Universal steganography model for low bit-rate speech codec. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2015, 9, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Lee, W. An assessment of VoIP covert channel threats. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Security and Privacy in Communications Networks and the Workshops, Nice, France, 17–21 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Liang, Y. Perceptually transparent information hiding in G.729 bitstream. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, Harbin, China, 15–17 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Zhou, K.; Huang, Y.; Feng, D.; Liu, J. A covert communication model based on least significant bits steganography in voice over IP. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference for Young Computer Scientists, Hunan, China, 18–21 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Xiao, B.; Huang, Y. Implementation of covert communication based on steganography. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, Harbin, China, 15–17 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Yang, Z. Simple and effective speech steganography in G.723.1 low-rate codes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Communications & Signal Processing, Nanjing, China, 13–15 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xie, C.; Xie, Y. Covert communication method based on GSM for low-bit-rate speech. Chin. J. Circuits Syst. 2008, 13, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, J.; Tian, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.A. An efficient VoIP steganography based on random binary matrix. In Proceedings of the International Conference on P2P, Parallel, Grid, Cloud and Internet Computing, Kraków, Poland, 4–6 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Bocko, M.F.; Ignjatovic, Z. Robustness analysis of a digital audio steganographic method based on phase manipulation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 31 August–4 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, R.; Malik, H.; Khokhar, A. Data-hiding in audio using frequency-selective phase alteration. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–21 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nutzinger, M.; Wurzer, J. A novel phase coding technique for steganography in auditive media. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security, Vienna, Austria, 22–26 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Manunggal, T.T.; Arifianto, D. Data protection using interaural quantified-phase steganography on stereo audio signals. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Conference, Singapore, 22–25 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alsabhany, A.A.; Ridzuan, F.; Azni, A.H. The adaptive multi-level phase coding method in audio steganography. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 129291–129306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymarski, P.; Markiewicz, R. Time and sampling frequency offset correction in audio watermarking. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 16–18 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowski, Z.; Stasiewicz, K.; Wojtun, J. Using drift correction modulation for steganographic radio transmission. In Proceedings of the Sensor Signal Processing for Defence (SSPD 2012), London, UK, 25–27 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, N.M.; Unoki, M.; Minh, N.N. Robust and reliable audio watermarking based on phase coding. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, South Brisbane, Australia, 19–24 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wodecki, K.; Piotrowski, Z.; Wojtuń, J. Acoustic steganographic transmission algorithm using signal coherent averaging. In Proceedings of the Military Communications and Information Systems Conference, Gdansk, Poland, 8–9 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Skopin, D.E.; El-Emary, I.M.M.; Rasras, R.J.; Diab, R.S. Advanced algorithms in audio steganography for hiding human speech signal. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Computer Control, Shenyang, China, 27–29 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, D.; Ghoshal, N. Secured data transmission through audio signal. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems, Gwalior, India, 15–17 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dymarski, P.; Markiewicz, R. Robust audio watermarks in frequency domain. J. Telecommun. Inf. Technol. 2014, 2, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowski, Z.; Wojtuń, J. Comparison of selected steganography algorithms. In Proceedings of the Signal Processing: Algorithms, Architectures, Arrangements, and Applications, Poznań, Poland, 22–24 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dymarski, P.; Markiewicz, R. Steganografia akustyczna w tle sygnału mowy. Przegląd Telekomunikacyjny Wiadomości Telekomunikacyjne 2017, 8, 665–669. [Google Scholar]
- Delforouzi, A.; Pooyan, M. Adaptive digital audio steganography based on integer wavelet transform. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 26–28 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shivaram, H.; Acharya, D.U.; Adige, R.; Deepthi, S.; Jyothi, U.K. Audio steganography in discrete wavelet transform domain. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2015, 10, 37544–37549. [Google Scholar]
- Carrion, P.; de Oliveira, H.M.; Campe, R.M. A Low-Throughput Wavelet-Based Steganography Audio Scheme; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.T.; Chen, S.H.; Hsu, L.Y. Incorporation of perceptually energy-compensated QIM into DWT-DCT based blind audio watermarking. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, Kitakyushu, Japan, 27–29 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Santosa, R.A.; Bao, P. Audio-to-image wavelet transform based audio steganography. In Proceedings of the International Symposium ELMAR, Zadar, Croatia, 8–10 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Shen, R.; Yu, F.; Lu, Z. Data hiding in audio based on audio-to-image wavelet transform and vector quantization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, Athens, Greece, 18–20 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Coronel, S.L.; Acevedo-Mosqueda, M.A.; Mosqueda, M.E.A. Steganography in audio files by Hermite Transform. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2014, 8, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraeian, S.M.E.; Akhaee, M.A.; Sankur, B.; Marvasti, F. Robust multiplicative watermarking technique with maximum likelihood detector. In Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference, Lausanne, Switzerland, 25–29 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gazor, S.; Zhang, W. Speech probability distribution. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2003, 10, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, F. A new detection scheme for echo hiding. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Information Theory and Information Security, Beijing, China, 17–19 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemzadeh, H.; Kayvanrad, M.H. Toward a robust and secure echo steganography method based on parameters hopping. In Proceedings of the Signal Processing and Intelligent Systems Conference, Tehran, Iran, 16–17 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tabara, B.; Wojtun, J.; Piotrowski, Z. Data hiding method in speech using echo embedding and voicing correction. In Proceedings of the Signal Processing Symposium, Jachranka, Poland, 12–14 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nugraha, R.M. Implementation of direct sequence spread spectrum steganography on audio data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics, Bandung, Indonesia, 17–19 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kohls, K.S.; Holz, T.; Kolossa, D.; Pöpper, C. SkypeLine: Robust hidden data transmission for VoIP. In Proceedings of the Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Xi’an, China, 30 May–3 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, A.A.; Chandran, C.S.; Kamal, S.; Supriya, M. Spread spectrum based encrypted audio steganographic system with improved security. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Circuits, Controls, and Communications, Bangalore, India, 15–16 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, I.J.; Doërr, G.; Furon, T. Watermarking is not cryptography. In Digital Watermarking; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Markiewicz, R. Znakowanie Wodne Sygnałów Fonicznych w Dziedzinie Częstotliwości. Ph.D. Thesis, Politechnika Warszawska, Warszawa, Poland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Information Technology—Coding of Moving Pictures and Associated Audio for Digital Storage Media at up to About 1.5 Mbit/s—Part 3: Audio; IEC 11172-3:1993; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M. Writing on dirty paper. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1983, 29, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, Z. Precise psychoacoustic correction method based on calculation of JND level. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2009, 116, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, Z. Drift correction modulation scheme for digital audio watermarking. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Information Networking and Security, Nanjing, China, 4–6 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowski, Z. Drift correction modulation scheme for digital signal processing. Math. Comput. Model. J. 2013, 57, 2260–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L. Distance Metric Learning: A Comprehensive Survey; Department of Computer Science and Engineering Michigan State University: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- De Maesschalck, R.; Jouan-Rimbaud, D.; Massart, D.L. The Mahalanobis distance. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2000, 50, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, P.; Joseph, E.; Lillo, R.E. The Mahalanobis distance for functional data with applications to classification. Technometrics 2015, 52, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiter, T.; Mannila, H. Computing Discrete Fréchet Distance; Christian Doppler Labor für Expertensyteme Technische Universität Wien: Vienna, Austria, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wylie, T.; Zhu, B. Following a curve with the discrete Fréchet distance. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2014, 556, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izydorczyk, J. Matlab i Podstawy Telkomunikacji; Helion: Gliwice, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, R.C. Spread Spectrum Systems: With Commercial Applications, 3rd ed.; John and Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiner, R.; Schafer, R.W. Digital Processing of Speech Signals; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- ITU-T. Recommendation G.1010. End-User Multimedia QoS Categories; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- ITU-T. Recommendation I.432. B-ISDN User-Network Interface—Physical Layer Specification; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert, G.; Sapanel, J.C. ATM: The Broadband Telecommunications Solution; The Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- ITU-T. Recommendation P.862. Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality (PESQ): An Objective Method for End-to-End Speech Quality Assessment of Narrow-Band Telephone Networks and Speech Codecs; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Voice Quality Testing and Performance Assessment. Available online: https://www.opalesystems.com/multidsla-audio-voice-quality-testing/ (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Łubkowski, P.; Mazewski, T. Ocena wpływu szyfrowania na jakość usługi VoIP w sieci heterogenicznej. Przegląd Telekomunikacyjny i Wiadomości Telekomunikacyjne 2019, 7, 529–532. [Google Scholar]
- ITU-T. Recommendation P.862.3. Application Guide for Objective Quality Measurement Based on Recommendations P.862, P.862.1 and P.862.2; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- ITU-T. Recommendation P.501. Test Signals for Use in Telephonometry; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ITU-T. Recommendation P.862.1. Mapping Function for Transforming P.862 Raw Result Scores to MOS-LQO; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- ITU-T. Recommendation P.800. Methods for Objective and Subjective Assessment of Quality; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Malden Electronics. Speech Quality Assessment. Background Information for DSLA and MultiDSLA User with PESQv2.2; Malden Electronics: Epsom, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- ITU-R. Recommendation BS.1116-3. Methods for the Subjective Assessment of Small Impairments in Audio Systems; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ITU-T. Recommendation P.50—Appendix I. Test Signals; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hersent, O.; Petit, J.-P.; Gurle, D. Beyond VoIP Protocols; John and Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- PJSIP. Available online: https://www.pjsip.org/ (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Chadov, T.A.; Erokhin, S.D.; Tikhonyuk, A.I. Machine learning approach on synchronization for FEC enabled channels. In Proceedings of the Systems of Signal Synchronization, Generating and Processing in Telecommunications (SYNCHROINFO), IEEE Xplore, Minsk, Belarus, 4–5 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, G.; Pu, B.; Ju, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Research on high precision algorithm of network time synchronization based on machine self-learning. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP), IEEE Xplore, Wanzhou, China, 9–11 November 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







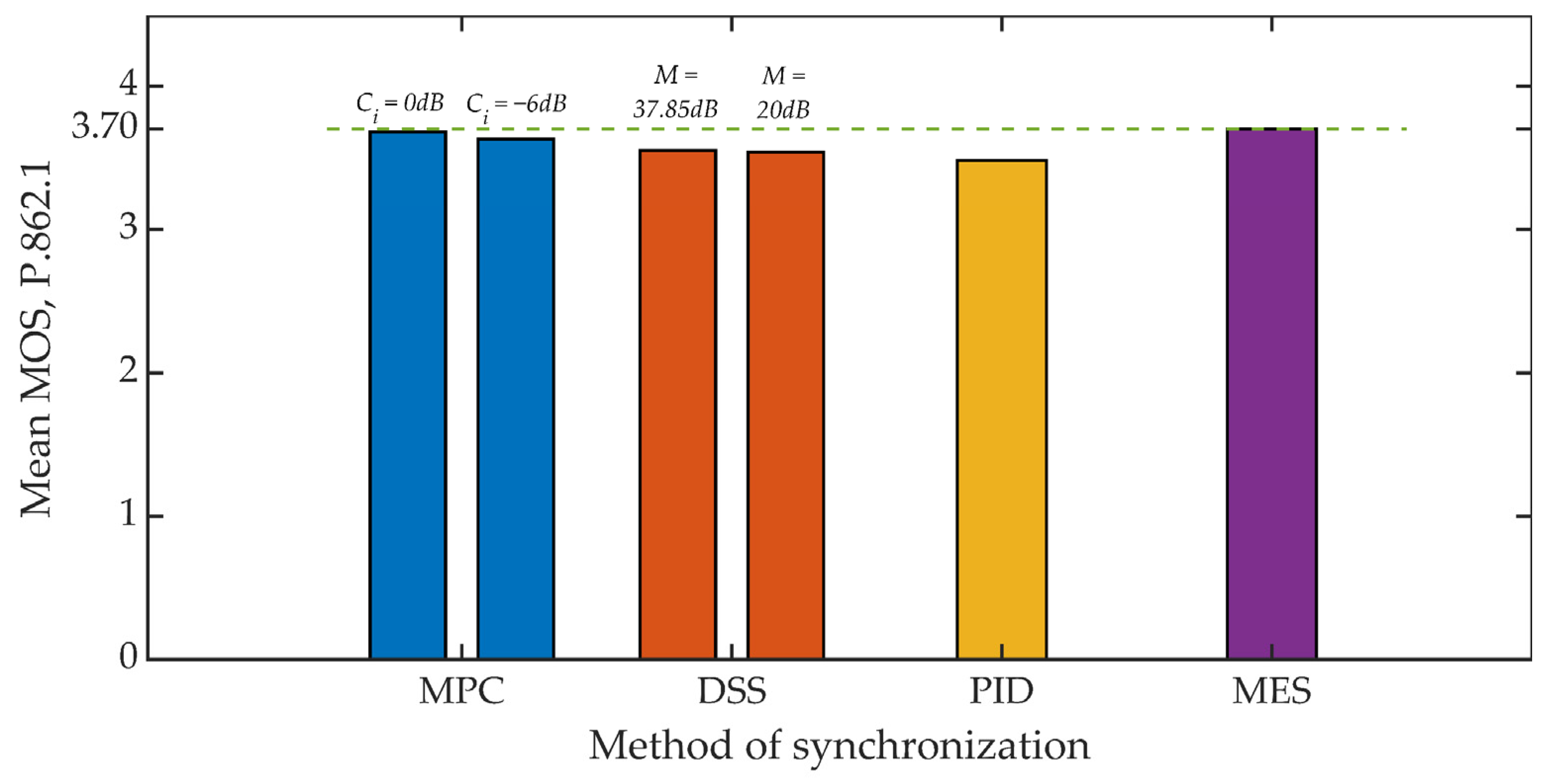

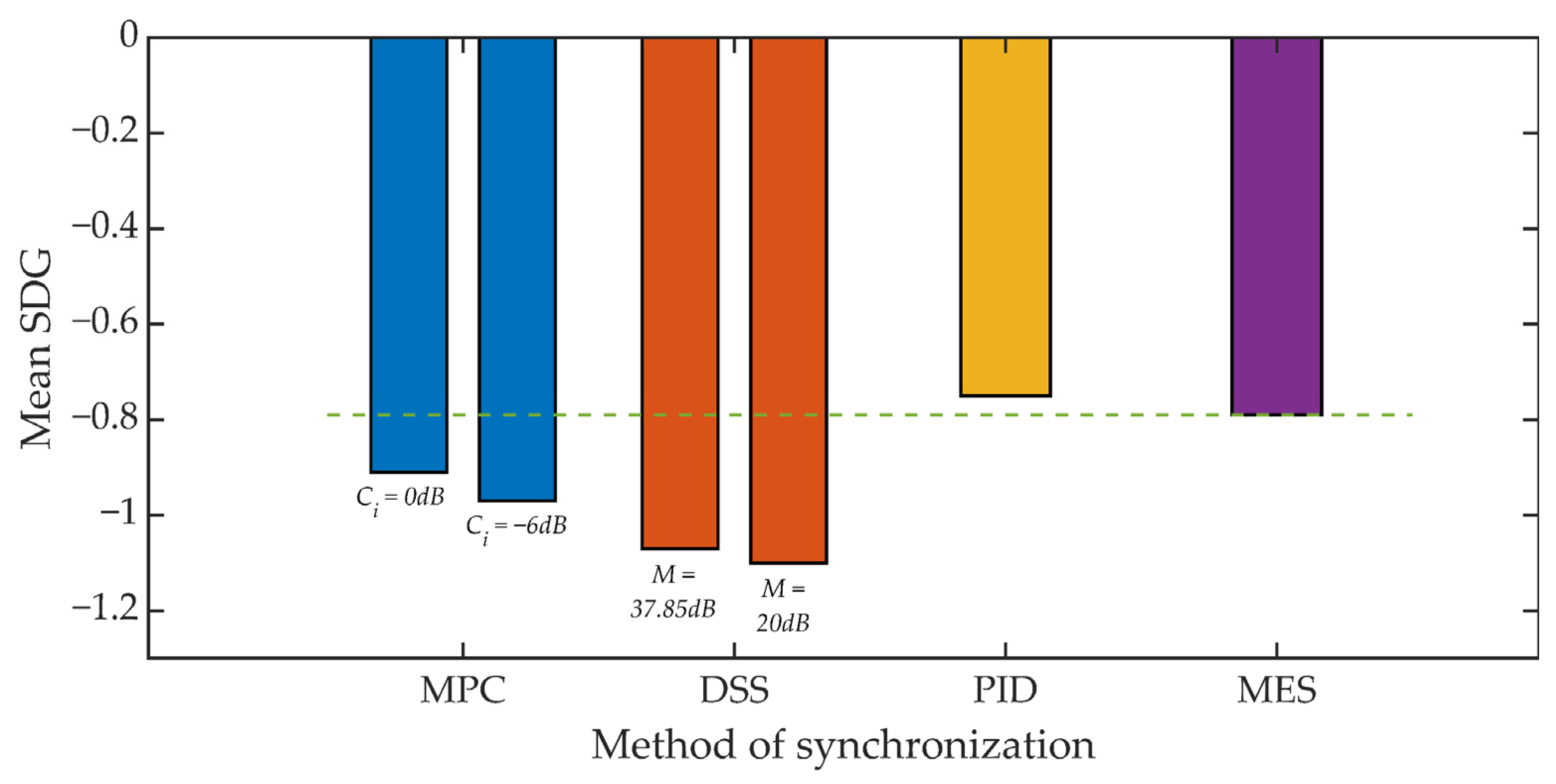

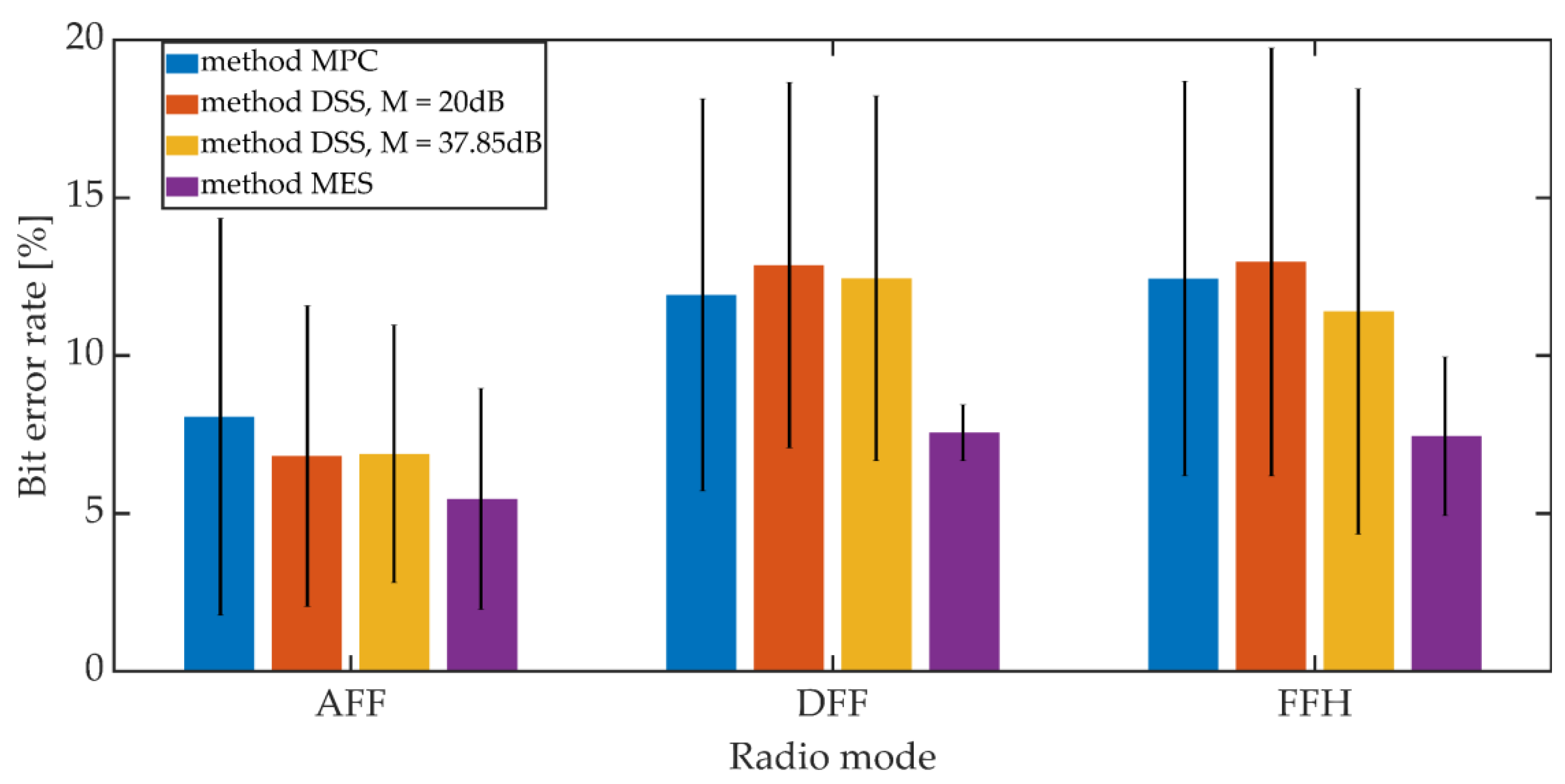

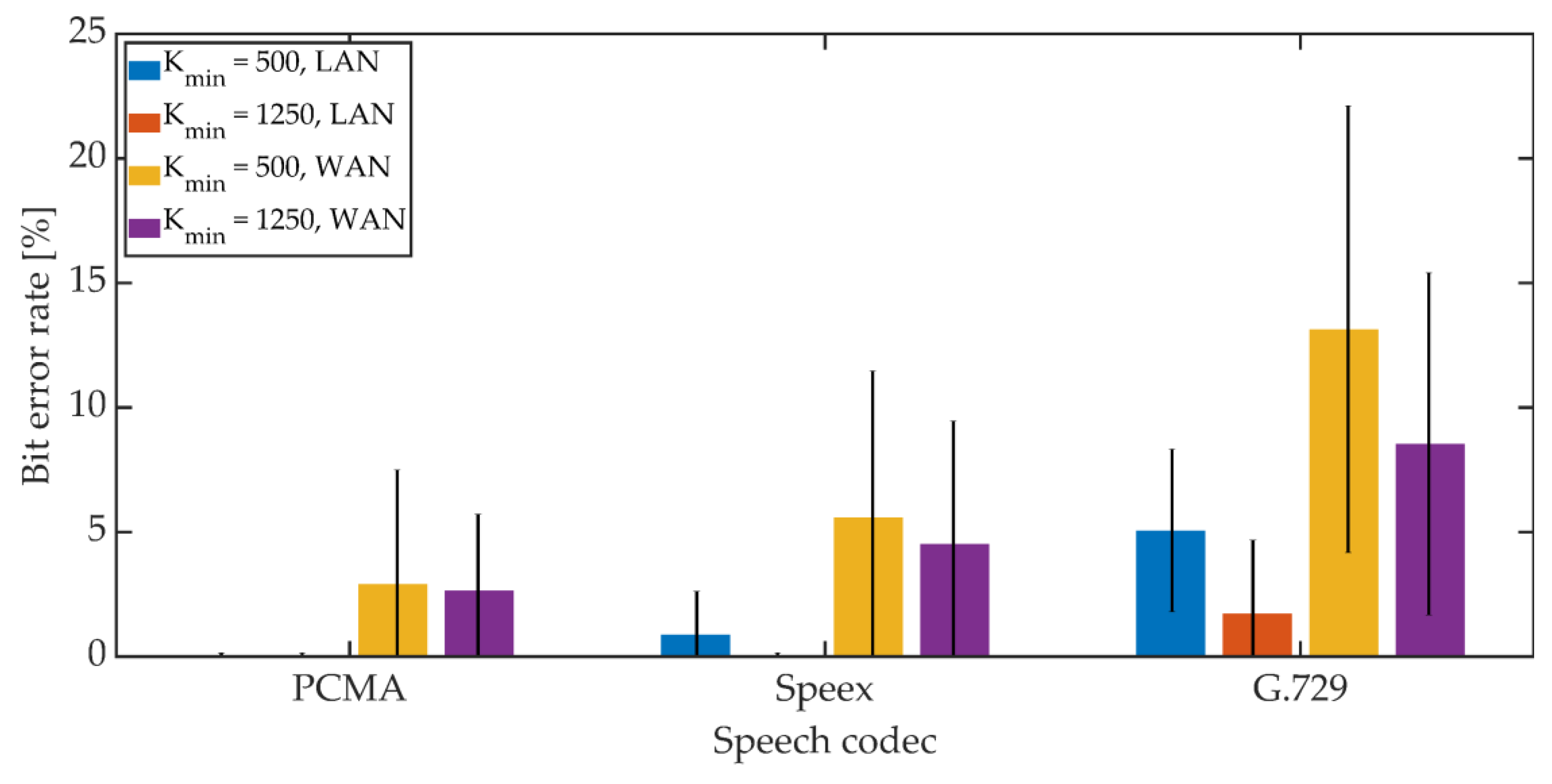

| Length of Observation Window d | PCMA | iLBC |
|---|---|---|
| 31 | 7 | 6 |
| 63 | 7 | 8 |
| 127 | 7 | 10 |
| 255 | 10 | 15 |
| n | k | t | R [bit/s] | T [s] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31 | 6 | 7 | 4.03 | 1.488 |
| 63 | 18 | 10 | 5.95 | 3.024 |
| 63 | 16 | 11 | 5.29 | 3.024 |
| 63 | 10 | 13 | 3.31 | 3.024 |
| 63 | 7 | 15 | 2.31 | 3.024 |
| 127 | 57 | 11 | 9.35 | 6.096 |
| 127 | 50 | 13 | 8.20 | 6.096 |
| 127 | 43 | 14 | 7.05 | 6.096 |
| 127 | 36 | 15 | 5.91 | 6.096 |
| 127 | 29 | 21 | 4.76 | 6.096 |
| 127 | 22 | 23 | 3.61 | 6.096 |
| 127 | 15 | 27 | 2.46 | 6.096 |
| 127 | 8 | 31 | 1.31 | 6.096 |
| n | k | t | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 31 | 6 | 7 | 1.06676·10−1 |
| 63 | 18 | 10 | 4.42610·10−3 |
| 63 | 16 | 11 | 5.43770·10−3 |
| 63 | 10 | 13 | 1.55420·10−3 |
| 63 | 7 | 15 | 2.40600·10−3 |
| 127 | 57 | 11 | 2.50000·10−6 |
| 127 | 50 | 13 | 1.10000·10−6 |
| 127 | 43 | 14 | 1.00000·10−6 |
| 127 | 36 | 15 | 1.00000·10−6 |
| 127 | 29 | 21 | 1.00000·10−6 |
| 127 | 22 | 23 | 1.00000·10−6 |
| 127 | 15 | 27 | 1.00000·10−6 |
| 127 | 8 | 31 | 4.00000·10−7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojtuń, J.; Piotrowski, Z. Synchronization of Acoustic Signals for Steganographic Transmission. Sensors 2021, 21, 3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103379
Wojtuń J, Piotrowski Z. Synchronization of Acoustic Signals for Steganographic Transmission. Sensors. 2021; 21(10):3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103379
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojtuń, Jarosław, and Zbigniew Piotrowski. 2021. "Synchronization of Acoustic Signals for Steganographic Transmission" Sensors 21, no. 10: 3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103379
APA StyleWojtuń, J., & Piotrowski, Z. (2021). Synchronization of Acoustic Signals for Steganographic Transmission. Sensors, 21(10), 3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103379







