Evaluation of the Sheet Resistance of Inkjet-Printed Ag-Layers on Flexible, Uncoated Paper Substrates Using Van-der-Pauw’s Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Surface Characteristics of the Used Paper Substrates
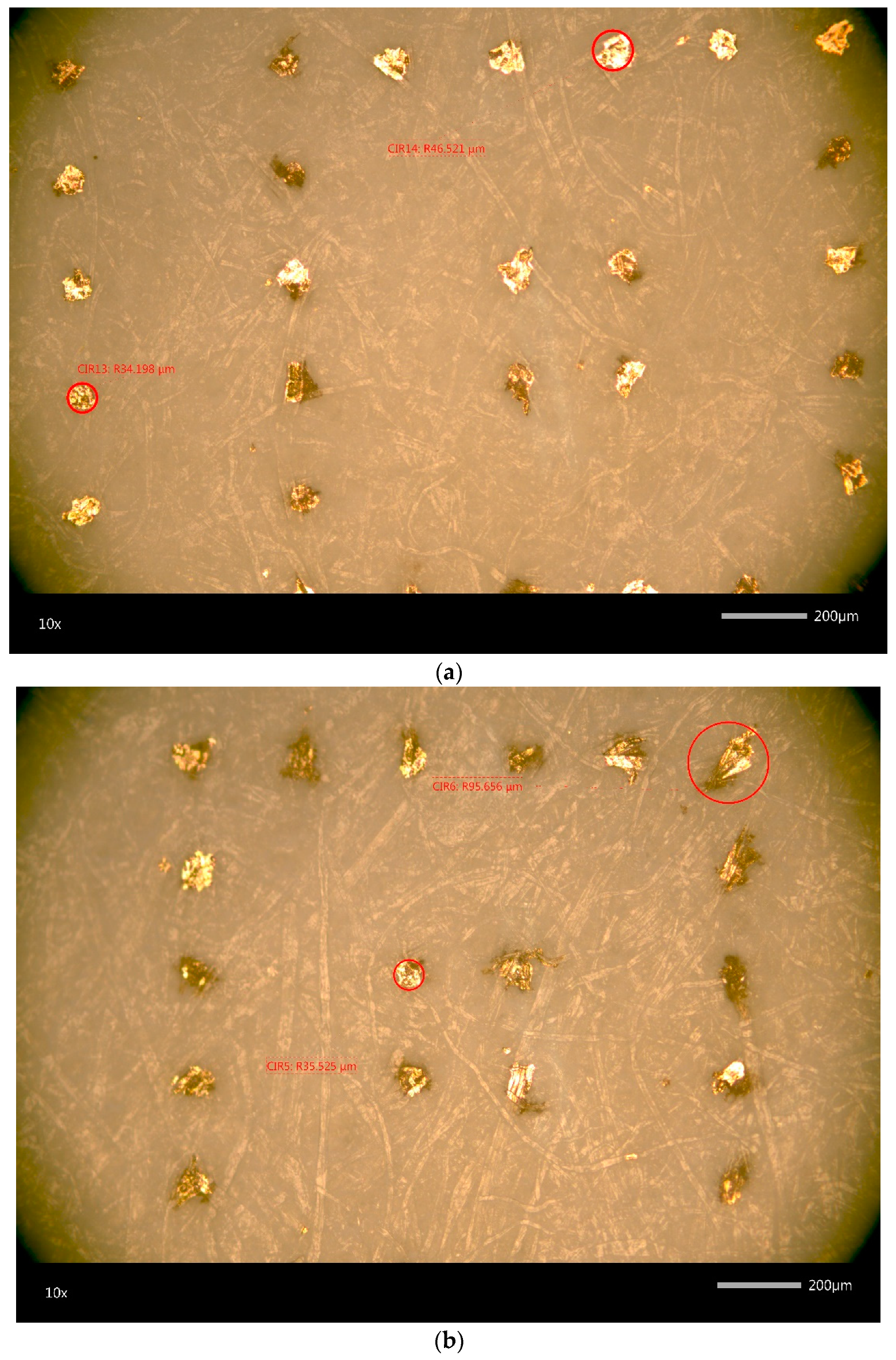
3.1.1. White Light Interferometry
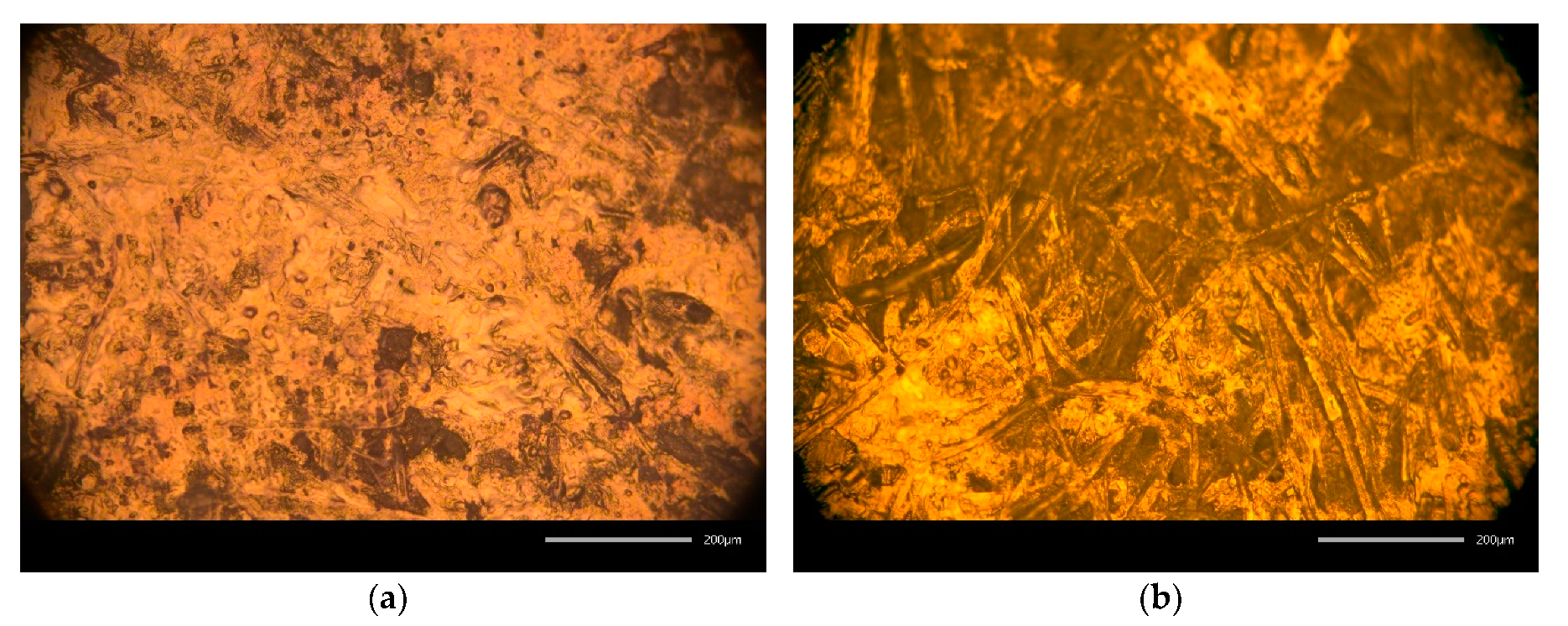
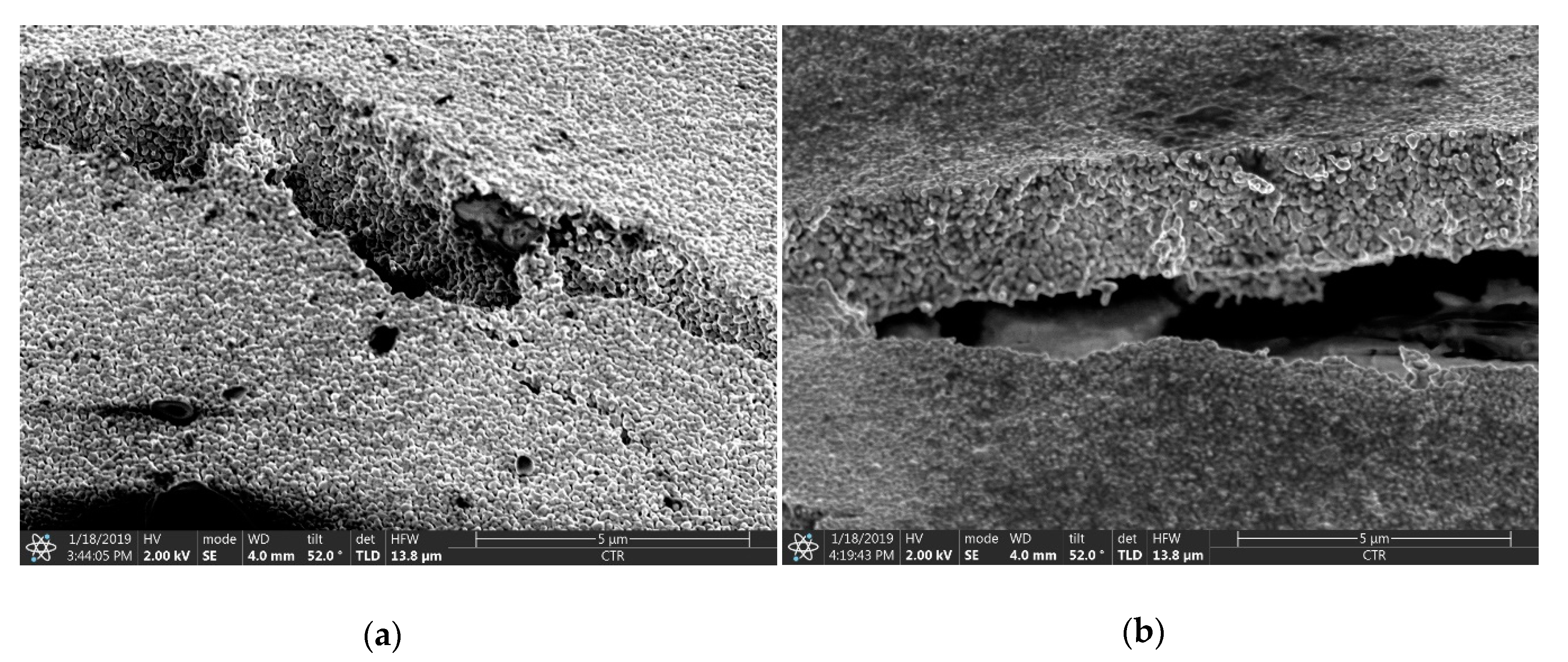
3.1.2. Microscopy and SEM Imaging
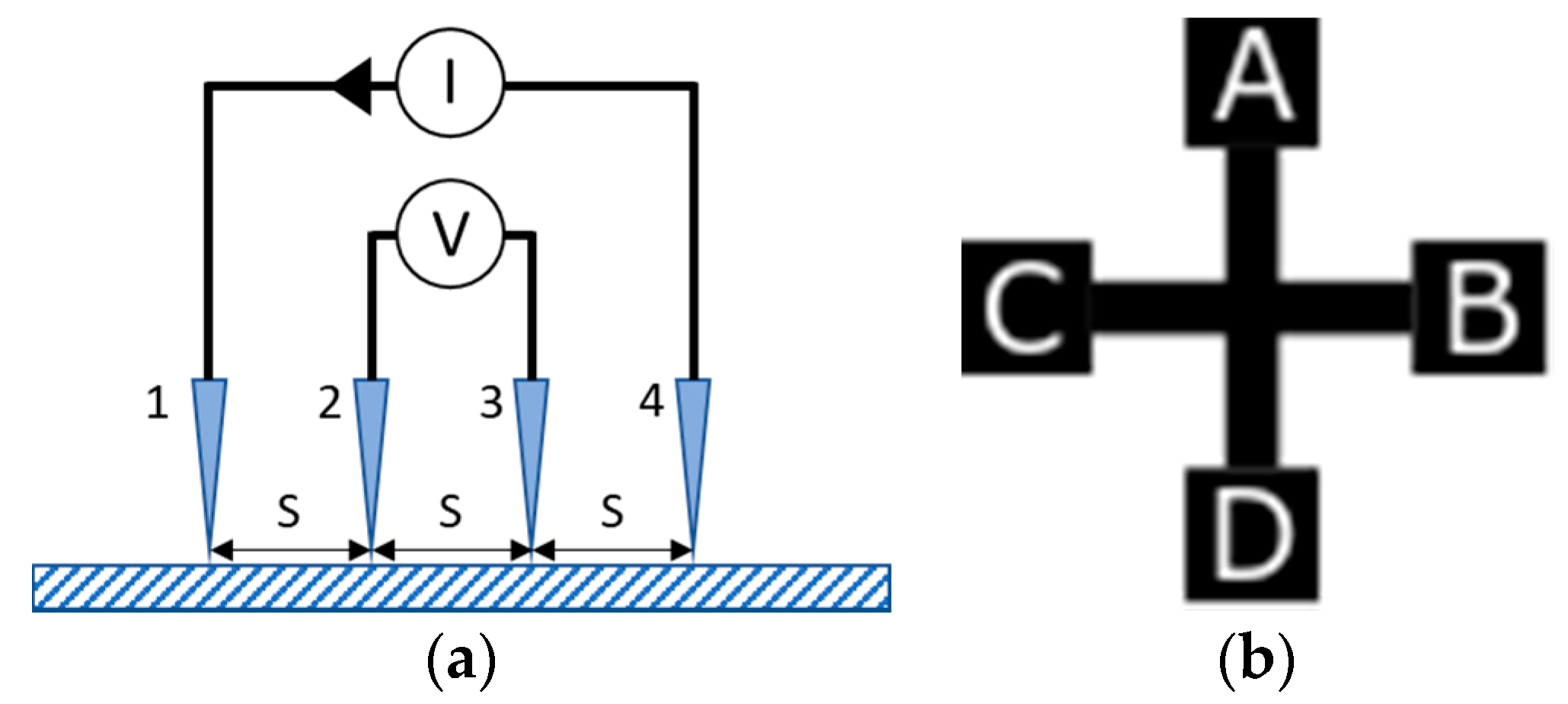
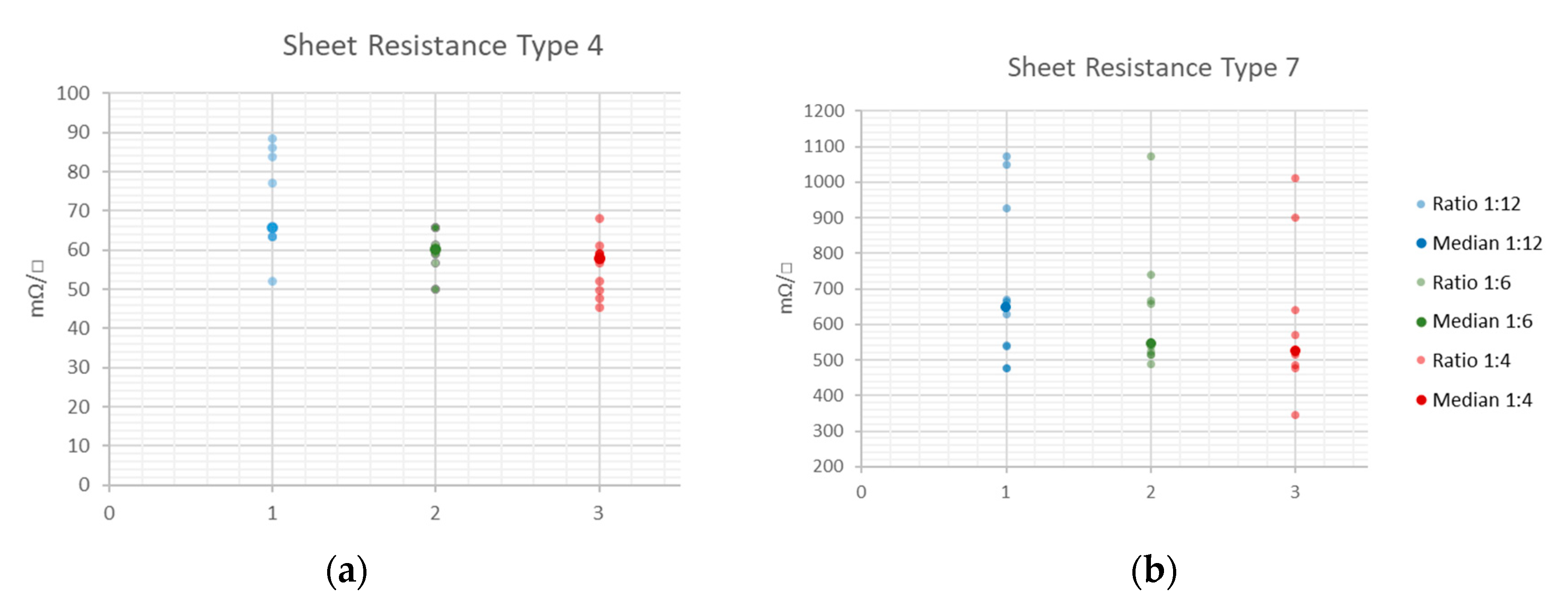
3.2. Sheet Resistance Measurement Using Van-der-Pauw’s Method
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, J.S.; Facchetti, A.F.; Reuss, R. A circuits and systems perspective of organic/printed electronics: Review, challenges, and contemporary and emerging design approaches. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2017, 7, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.G.; Kramer, R. All-printed flexible and stretchable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreenilayam, S.P.; Ahad, I.U.; Nicolosi, V.; Garzon, V.A.; Brabazon, D. Advanced materials of printed wearables for physiological parameter monitoring. Mater. Today 2010, 32, 147–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D. Overview of inkjet-based micromanufacturing. In Inkjet-Based Micromanufacturing; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Das, R. Printing Technologies find their Place in Printed Electronics; IDTechEx: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tobjörk, D.; Österbacka, R. Paper electronics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1935–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; He, Z.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y. Direct desktop printed-circuits-on-paper flexible electronics. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Mäntysalo, M.; Cabezas, A.L.; Feng, Y.; Jonsson, F.; Zheng, L.-R. Electrical performance and reliability evaluation of inkjet-printed Ag interconnections on paper substrates. Mater. Lett. 2012, 88, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihalainen, P.; Määttänen, A.; Järnström, J.; Tobjörk, D.; Österbacka, R.; Peltonen, J. Influence of surface properties of coated papers on printed electronics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 6025–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Romaguera, V.; Wünscher, S.; Turki, B.M.; Abbel, R.; Barbosa, S.; Tate, D.J.; Oyeka, D.; Batchelor, J.C.; Parker, E.A.; Schubert, U.S.; et al. Inkjet printed paper based frequency selective surfaces and skin mounted RFID tags: The interrelation between silver nanoparticle ink, paper substrate and low temperature sintering technique. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.; Joyce, T.; Joyce, M. Printed electronics: A landfill simulation study to assess environmental impacts. J. Solid Waste Technol. Manag. 2017, 43, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, C.; Olkkonen, J.; Passoja, S.; Smolander, M. Paper as active layer in inkjet-printed capacitive humidity sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Ahmad, M.; Punjiya, M.; Sadeqi, A.; Baghini, M.S.; Sonkusale, S. Respiration Monitoring Using a Flexible Paper-Based Capacitive Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE SENSORS, New Delhi, India, 28–31 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Barmpakos, D.; Segkos, A.; Tsamis, C.; Kaltsas, G. A disposable inkjet-printed humidity and temperature sensor fabricated on paper. Multi. Digit. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2018, 2, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraović, M.; Muck, T.; Pivar, M.; Trontelj, J.; Pleteršek, A. Humidity sensors printed on recycled paper and cardboard. Sensors 2014, 14, 13628–13643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgese, M.; Dicandia, F.A.; Costa, F.; Genovesi, S.; Manara, G. An inkjet printed chipless RFID sensor for wireless humidity monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 4699–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, J.; Ukkonen, L.; Björninen, T.; Elsherbeni, A.Z.; Sydänheimo, L. Inkjet-printed humidity sensor for passive UHF RFID systems. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 60, 2768–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xie, L.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, L.-R. Low-cost printed chipless RFID humidity sensor tag for intelligent packaging. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 15, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.-Z.; Wang, L.-F.; Dong, L.; Deng, W.-J.; Huang, Q.-A. Low cost paper-based LC wireless humidity sensors and distance-insensitive readout system. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 4717–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Brahma, S.; Mackay, J.; Cao, C.; Aliakbarian, B. The role of smart packaging system in food supplychain. Concise Rev. Hypotheses Food Sci. 2020, 85, 517–525. [Google Scholar]
- Bollström, R.; Pettersson, F.; Dolietis, P.; Preston, J.; Österbacka, R.; Toivakka, M. Impact of humidity on functionality of on-paper printed electronics. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojic, T.; Stojanovic, G.M.; Miletic, A.; Radovanovic, M.; Al-Salami, H.; Arduini, F. Testing and characterization of different papers as substrate material for printed electronics and application in humidity sensing. Sens. Mater. 2019, 31, 2981–2995. [Google Scholar]
- Bollström, R.; Tobjörk, D.; Dolietis, P.; Salminen, P.J.; Preston, J.; Österbacka, R.; Toivakka, M. Printability of functional inks on multilayer curtain coated paper. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2013, 68, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozutok, Z.; Kinj, O.; Torun, I.; Ozdemir, A.T.; Onses, M.S. One-step deposition of hydrophobic coatings on paperfor printed-electronics applications. Cellulose 2019, 26, 3503–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trnovec, B.; Stanel, M.; Hahn, U.; Hübler, A.C.; Kempa, H.; Sangl, R.; Forster, M. Coated paper for printed electronics. Prof. Papermak. 2009, 1, 104. [Google Scholar]
- Öhlund, T.; Örtegren, J.; Forsberg, S.; Nilsson, H.-E. Paper surfaces for metal nanoparticle inkjet printing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 259, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husband, J.C.; Preston, J.S.; Gate, L.F.; Blair, D.; Creaton, P. Factors affecting the printing strength of kaolin-based paper coatings. TAGA J. 2008, 84, 84–100. [Google Scholar]
- Barras, R.; Cunha, I.; Gaspar, D.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Pereira, L. Printable cellulose-based electroconductive composites for sensing elements in paper electronics. Flex. Print. Electron. 2017, 2, 014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeng, F.; Bras, J.; Gicquel, E.; Krosnicki, G.; Denneulin, A. Inkjet printing of nanocellulose–silver ink onto nanocellulose coated cardboard. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15372–15381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-Y.; Wu, G.-W.; Hsieh, W.-J. Fabrication of micro sensors on a flexible substrate. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 147, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattana, G.; Briand, D. Recent advances in printed sensors on foil. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankoco, M.D.; Tesfay, G.Y.; Benevent, E.; Bendahan, M. Temperature sensor realized by inkjet printing process on flexible substrate. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2016, 205, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikulnig, J.; Hirschl, C.; Rauter, L.; Krivec, M.; Lammer, H.; Riemelmoser, F.; Roshanghias, A. Inkjet printing and characterisation of a resistive temperature sensor on paper substrate. Flex. Print. Electron. 2019, 4, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, D.; Clemens, W.; Breitung, S.; Hecker, K. OE-A roadmap for organic and printed electronics. In Applications of Organic and Printed Electronics; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Anner, G.E. Planar Processing Primer; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ossila. Sheet Resistance: A Guide to Theory. Available online: https://www.ossila.com/pages/sheet-resistance-theory (accessed on 5 March 2020).
- Van der Pauw, L.J. A method of measuring the resistivity and hall coefficient on lamellae of arbitrary shape. Philips Tech. Rev. 1958, 20, 220–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, L.K.; Hrehorova, E.; Joyce, T.W.; Fleming, P.D.; Joyce, M.; Pekarovicova, A.; Bliznyuk, V. Paper substrates and inks for printed electronics. In Pira Ink on Paper Symposium; Smithers Pira: Surrey, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Cook, B.; Le, T.; Cooper, J.; Lee, H.; Lakafosis, V.; Vyas, R.; Moro, R.; Bozzi, M.; Georgiadis, A.; et al. Inkjet-printed antennas, sensors and circuits on paper substrate. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2013, 7, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavčič, U.; Karlovits, I. Invasive plant-based paper as a substrate for electroconductive printing inks. Adv. Print. Media Technol. 2019, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Pammo, A.; Christophliemk, H.; Keskinen, J.; Björkqvist, T.; Siljander, S.; Mäntysalo, M.; Tuukkanen, S. Nanocellulose Films as Substrates for Printed Electronics. In Proceedings of the MARSS 2019—International Conference on Manipulation Automation and Robotics at Small Scales, Helsinki, Finland, 1–5 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Moralez-Rodriguez, M.E.; Fuhr, P.L. Printed conductive transparent films for the fabrication of sensors by aerosol inkjet systems. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 6, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Kazani, I.; De Mey, G.; Hertleer, C.; Banaszczyk, J.; Schwarz, A.; Guxho, G.; Van Langenhove, L. Van Der Pauw method for measuring resistivities of anisotropic layers printed on textile substrates. Text. Res. J. 2011, 81, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieva, E.; Nikolov, G.; Nikolova, B. Sheet Resistance Measurement of Inkjet Printed Layers. In Proceedings of the 42nd International Spring Seminar on Electronics Technology (ISSE), Wrocław, Poland, 15–19 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Enderling, S.; Brown, C.L.; Smith, S.; Dicks, M.H.; Stevenson, J.T.; Ross, A.W.S.; Mitkova, M.; Kozicki, M.N.; Walton, A.J. Suspended Greek Cross Test Structures for Measuring the Sheet Resistance on Non-Standard Cleanroom Materials. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Microelectronic Test Structures, ICMTS 2005, Leuven, Belgium, 4–7 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nanocell, P.V. Product Data Sheet. Available online: http://www.pvnanocell.com/sicrys-i50tm-119.html (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Nilsson, H.-E.; Unander, T.; Sidén, J.; Andersson, H.; Manuilskiy, A.; Hummelgard, M.; Gulliksson, M. System integration of electronics functions in smart packaging applications. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 2, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO—International Organization of Standardization. ISO 25178 Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Areal; International Organization of Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Matula, R.A. Electrical resistivity of copper, gold, palladium, and silver. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1979, 8, 1147–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraden, I. Handbook of Modern Sensors: Physics, Designs, and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Traiwatcharanon, P.; Timsorn, K.; Wongchoosuk, C. Flexible room-temperature resistive humidity sensor based on silver nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 085038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.C.; Phillips, S.T.; Dickey, M.D.; Lu, N.; Suo, Z.; Whitesides, G.M. Foldable printed circuit boards on paper substrates. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeninckx, G.; Berghmans, H.; Overgergh, N.; Smets, G. Crystallization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) induced by inorganic compounds. I. Crystallization behavior from the glassy state in a low-temperature region. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 1974, 12, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Paper Substrate | Grammage in g/m2 | Sa in µm | Sq in µm | Porosity in mL/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 4 | 120 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 50 |
| Type 7 | 87 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 350 |
| Line to Width Ratio | 1:12 | 1:6 | 1:4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | 10 | 10 | 7 |
| Minimum (mΩ/□) | 23.3 | 25.2 | 27.2 |
| Median (mΩ/□) | 25.2 | 26.5 | 27.6 |
| Maximum (mΩ/□) | 27.9 | 28.8 | 28.3 |
| Line to Width Ratio | 1:12 | 1:6 | 1:4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Minimum (mΩ/□) | 52.1 | 49.9 | 45.3 |
| Median (mΩ/□) | 65.7 | 60.1 | 57.8 |
| Maximum (mΩ/□) | 88.4 | 65.7 | 68.0 |
| Line to Width Ratio | 1:12 | 1:6 | 1:4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Minimum (mΩ/□) | 475.9 | 487.2 | 344.5 |
| Median (mΩ/□) | 647.0 | 545.0 | 523.5 |
| Maximum (mΩ/□) | 1071.9 | 1071.9 | 1010.7 |
| Substrate | ρ (1:12) in µΩ∙cm | ρ (1:6) in µΩ∙cm | ρ (1:4) in µΩ∙cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET (t = 2.5 µm) | 6.3 (4 × bulk) | 6.6 (4.2 × bulk) | 6.9 (4.3 × bulk) |
| Type 4 (t = 2 µm) | 13.1 (8.3 × bulk) | 12.0 (7.6 × bulk) | 11.6 (7.3 × bulk) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zikulnig, J.; Roshanghias, A.; Rauter, L.; Hirschl, C. Evaluation of the Sheet Resistance of Inkjet-Printed Ag-Layers on Flexible, Uncoated Paper Substrates Using Van-der-Pauw’s Method. Sensors 2020, 20, 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082398
Zikulnig J, Roshanghias A, Rauter L, Hirschl C. Evaluation of the Sheet Resistance of Inkjet-Printed Ag-Layers on Flexible, Uncoated Paper Substrates Using Van-der-Pauw’s Method. Sensors. 2020; 20(8):2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082398
Chicago/Turabian StyleZikulnig, Johanna, Ali Roshanghias, Lukas Rauter, and Christina Hirschl. 2020. "Evaluation of the Sheet Resistance of Inkjet-Printed Ag-Layers on Flexible, Uncoated Paper Substrates Using Van-der-Pauw’s Method" Sensors 20, no. 8: 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082398
APA StyleZikulnig, J., Roshanghias, A., Rauter, L., & Hirschl, C. (2020). Evaluation of the Sheet Resistance of Inkjet-Printed Ag-Layers on Flexible, Uncoated Paper Substrates Using Van-der-Pauw’s Method. Sensors, 20(8), 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082398






