On the Performance of Variational Mode Decomposition-Based Radio Frequency Fingerprinting of Bluetooth Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Works
1.2. Contributions
- (1)
- The effects of HOS features extracted from the band-limited modes and the reconstructed signal itself on classification accuracy in VMD-based RFF method are evaluated experimentally with BT devices for the first time.
- (2)
- This study is the first report to analyze the lower SNR bounds in which the VMD can be effectively implemented in the classification of BT devices.
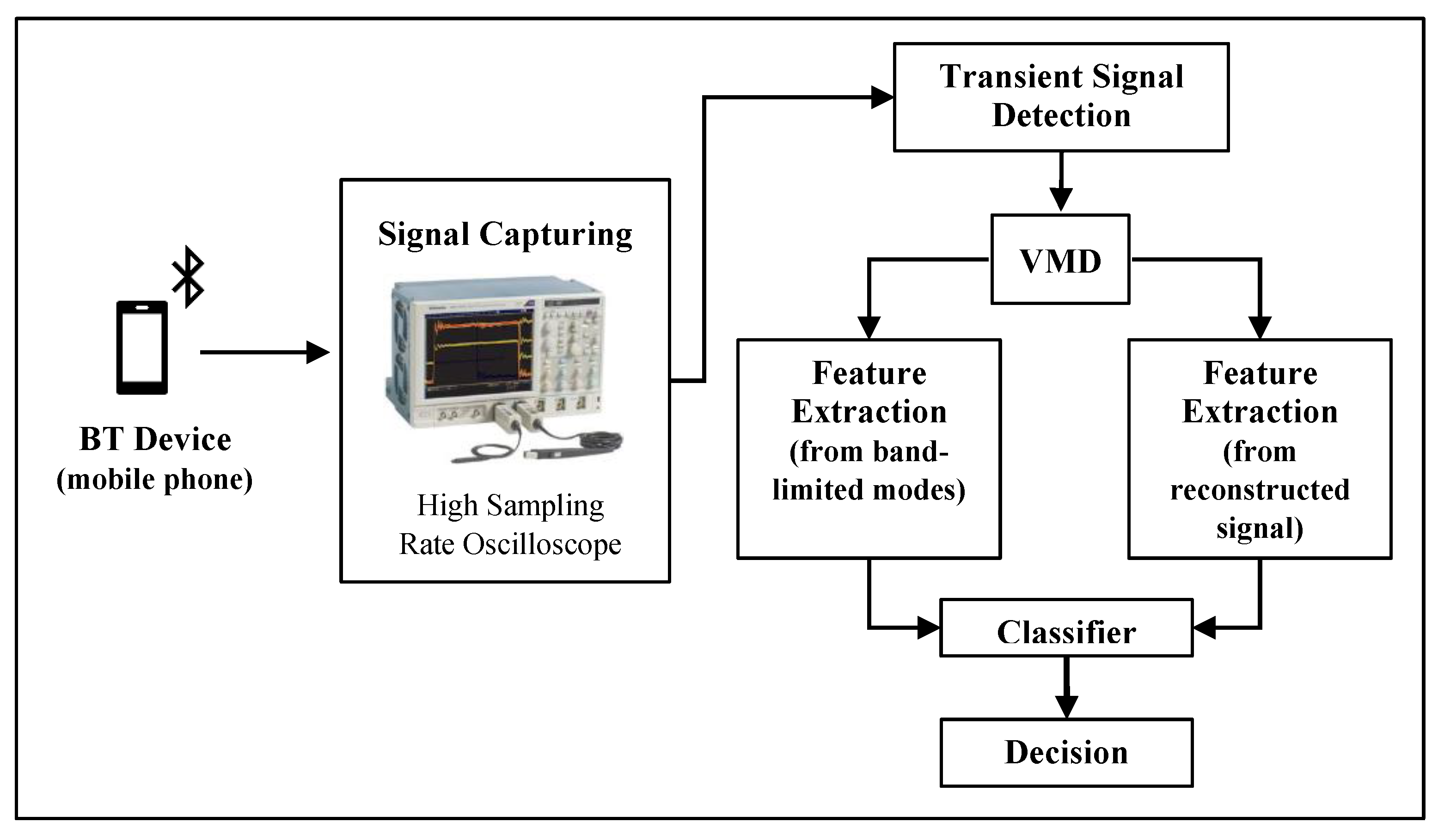
2. Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD)-based Radio Frequency Fingerprinting (RFF)
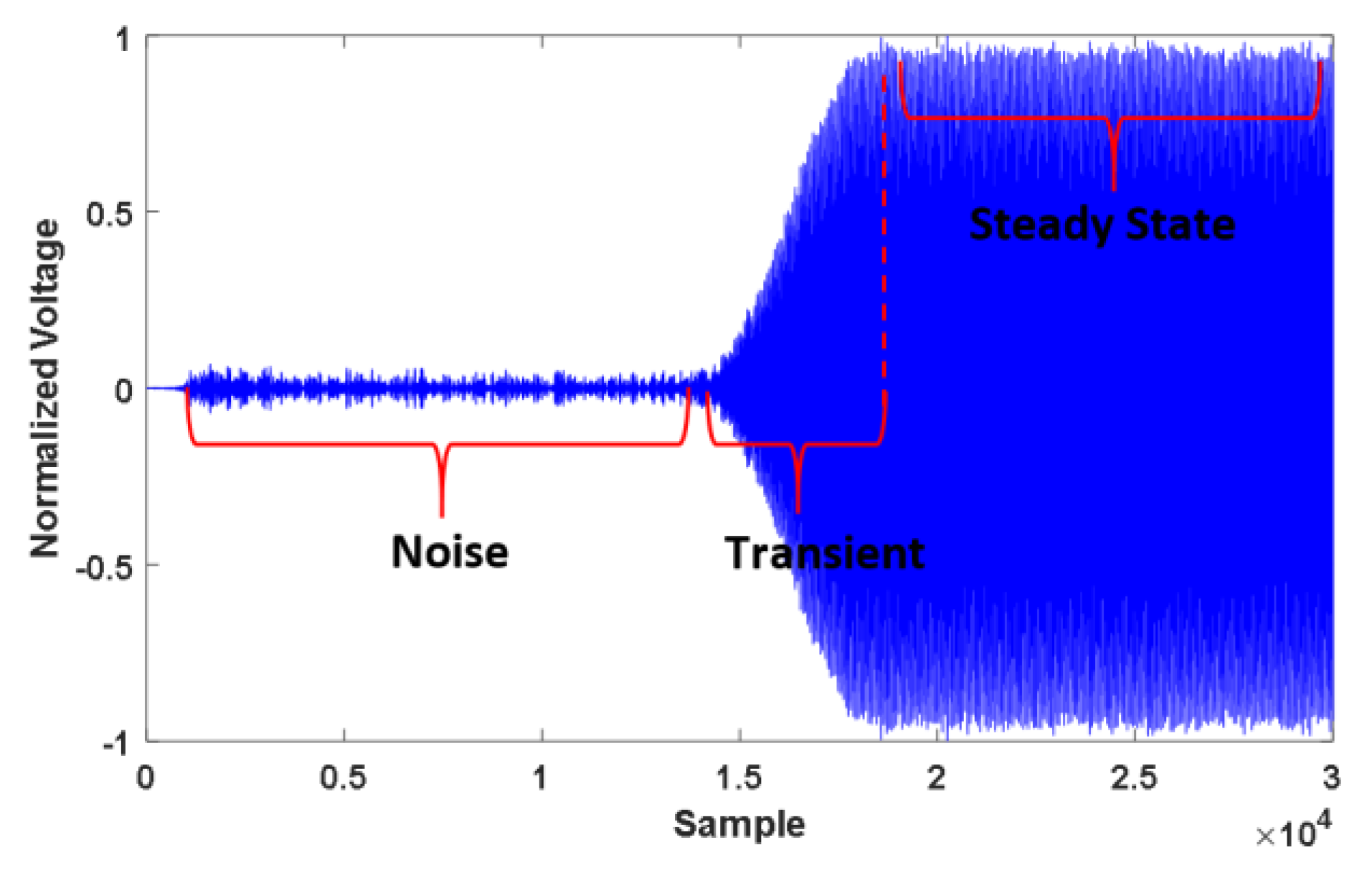
2.1. Data Collection (Signal Capturing) and Transient Detection
2.2. Transient Signal Decomposition
- Computing the corresponding analytic signal for each mode by using the Hilbert transform
- Shifting frequency spectrum of the mode to baseband by using heterodyning
- Estimating the bandwidth of the mode by smoothing the demodulated signal, so-called Wiener filtering.
2.3. Feature Extraction
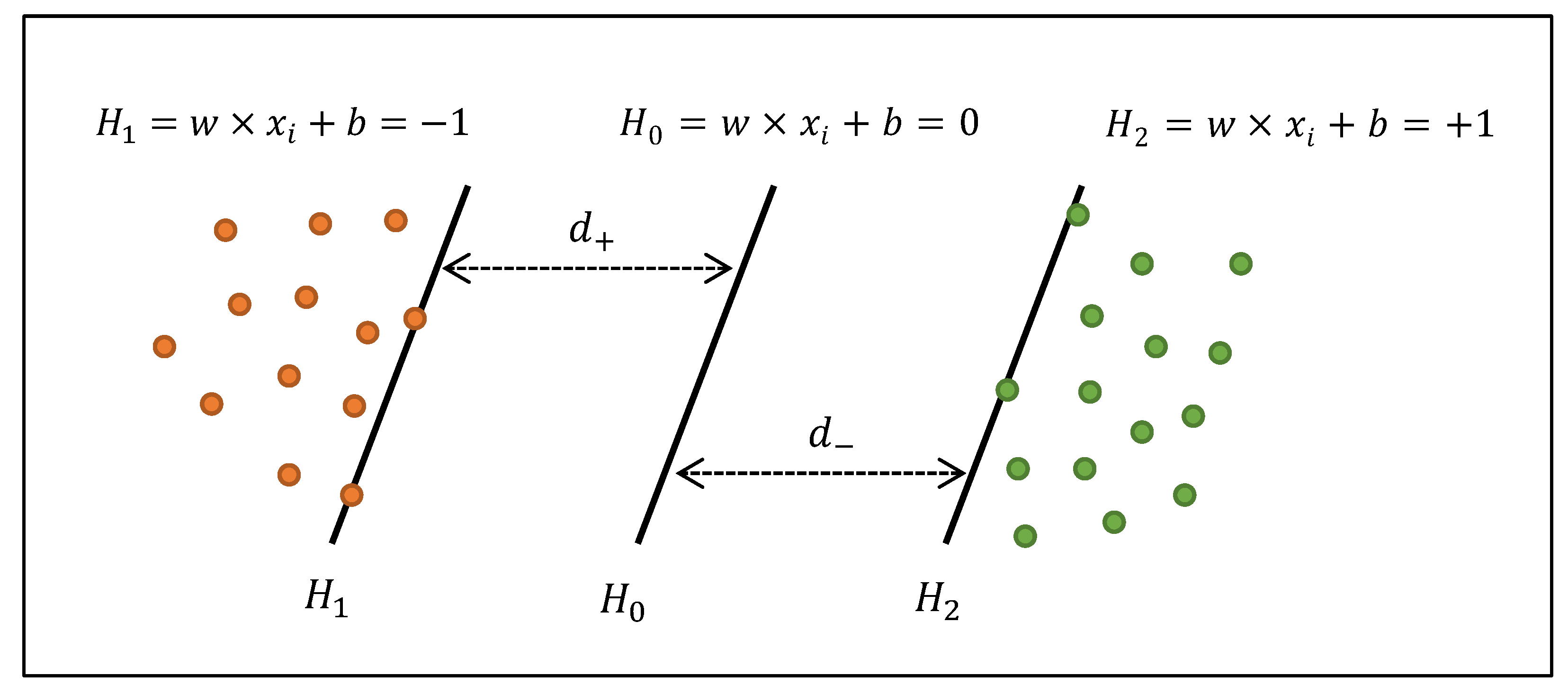
2.4. Classification
2.5. Results
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Youssef, K.; Bouchard, L.; Haigh, K.; Silovsky, J.; Thapa, B.; Vander Valk, C. Machine learning approach to rf transmitter identification. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2018, 2, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Chang, K.-D.; Chao, H.-C. Transaction-pattern-based anomaly detection algorithm for IP multimedia subsystem. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2010, 6, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-S.; Tseng, Y.-C.; Chao, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-M. A neighbor caching mechanism for handoff in IEEE 802.11 wireless networks. J. Supercomput. 2008, 45, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.W.; Temple, M.A.; Mendenhall, M.J. Application of wavelet-based RF fingerprinting to enhance wireless network security. J. Commun. Netw. 2009, 11, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbeau, M.; Hall, J.; Kranakis, E. Detection of rogue devices in bluetooth networks using radio frequency fingerprinting. In Proceedings of the 3rd IASTED International Conference on Communications and Computer Networks (CCN), Lima, Peru, 4–6 October 2006; pp. 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, R.W.; Temple, M.A.; Mendenhall, M.J. Application of wavelet denoising to improve OFDM-based signal detection and classification. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2010, 3, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suski, W.C., II; Temple, M.A.; Mendenhall, M.J.; Mills, R.F. Using spectral fingerprints to improve wireless network security. In Proceedings of the IEEE GLOBECOM 2008–2008 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, New Orleans, LO, USA, 30 November–4 December 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Danev, B.; Capkun, S. Transient-based identification of wireless sensor nodes. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–16 April 2009; pp. 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Köse, M.; Taşcioğlu, S.; Telatar, Z. RF Fingerprinting of IoT devices based on transient energy spectrum. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 18715–18726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, X. Specific emitter identification based on Hilbert–Huang transform-based time–frequency–energy distribution features. IET Commun. 2014, 8, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Uzundurukan, E.; Kara, A. Assessment of features and classifiers for bluetooth RF fingerprinting. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 50524–50535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Peng, Z.; Wei, K.; Shi, P.; Tian, W. Superiorities of variational mode decomposition over empirical mode decomposition particularly in time–frequency feature extraction and wind turbine condition monitoring. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2016, 11, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satija, U.; Trivedi, N.; Biswal, G.; Ramkumar, B. Specific emitter identification based on variational mode decomposition and spectral features in single hop and relaying scenarios. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 14, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Li, M.; Yin, H. Variational mode decomposition denoising combined the detrended fluctuation analysis. Signal Process. 2016, 125, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok, G.; Alp, Y.K.; Altıparmak, F. Radar fingerprint extraction via variational mode decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2017 25th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Antalya, Turkey, 15–18 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Aghnaiya, A.; Ali, A.M.; Kara, A. Variational mode decomposition-based radio frequency fingerprinting of bluetooth devices. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 144054–144058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzundurukan, E.; Ali, A.M.; Dalveren, Y.; Kara, A. Performance analysis of modular RF front end for RF fingerprinting of bluetooth devices. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Uzundurukan, E.; Kara, A. Improvements on transient signal detection for RF fingerprinting. In Proceedings of the 2017 25th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Antalya, Turkey, 15–18 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, F.; Wen, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, L.; Chen, Y.; Song, H. Optimized coherent integration-based radio frequency fingerprinting in Internet of Things. IEEE Intern. Things J. 2018, 5, 3967–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Wen, H.; Wu, J.; Hou, W.; Song, H.; Zhang, T.; Liao, R.; Jiang, Y. Data augmentation for radio frequency fingerprinting via pseudo-random integration. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, S.; Wu, S. Improving support vector machine classifiers by modifying kernel functions. Neural Netw. 1999, 12, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottou, L.; Lin, C.-J. Support Vector Machine Solvers Large Scale Kernel Machines; Mit Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]

| Technique | Ref. | Signal Type | #Device | Feature Extraction | Classifier/Process | SNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelet | [5] | BT | 10 | The amplitude, phase and frequency | Hotelling’s T2 statistics | NA |
| [6] | Wi-Fi | 3 | HOS | MDA with ML | −3 − 10 dB | |
| FT | [7] | Wi-Fi | 3 | PSD | Spectral Correlation Process | −10 − 20 dB |
| [8] | Wi-Fi | 50 | Fisher | EER and ROC | NA | |
| [9] | Wi-Fi | 8 | Spectral, PCA and Amplitude | PNN | 0 − 20 dB | |
| HHT | [10] | GSM | 8 | TFED | SVM | NA |
| [11] | BT | 20 | TFED | Complex Decision Tree, LSVM, LDA | 8 − 23 dB | |
| VMD | [18] | BT | 20 | HOS | LSVM | 5 − 25 dB |
| HOS Features | SNR Ranges | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (−5–0 dB) | Moderate (0–5 dB) | High (5–10 dB) | |
| Band-limited Modes | 70.1% | 91.0% | 97.1% |
| Reconstructed Transient | 67.5% | 87.3% | 96.7% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aghnaiya, A.; Dalveren, Y.; Kara, A. On the Performance of Variational Mode Decomposition-Based Radio Frequency Fingerprinting of Bluetooth Devices. Sensors 2020, 20, 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061704
Aghnaiya A, Dalveren Y, Kara A. On the Performance of Variational Mode Decomposition-Based Radio Frequency Fingerprinting of Bluetooth Devices. Sensors. 2020; 20(6):1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061704
Chicago/Turabian StyleAghnaiya, Alghannai, Yaser Dalveren, and Ali Kara. 2020. "On the Performance of Variational Mode Decomposition-Based Radio Frequency Fingerprinting of Bluetooth Devices" Sensors 20, no. 6: 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061704
APA StyleAghnaiya, A., Dalveren, Y., & Kara, A. (2020). On the Performance of Variational Mode Decomposition-Based Radio Frequency Fingerprinting of Bluetooth Devices. Sensors, 20(6), 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061704





