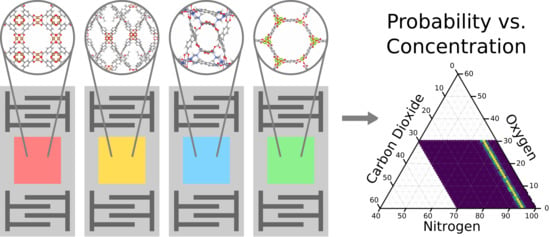
Genetic Algorithm Design of MOF-based Gas Sensor Arrays for CO2-in-Air Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
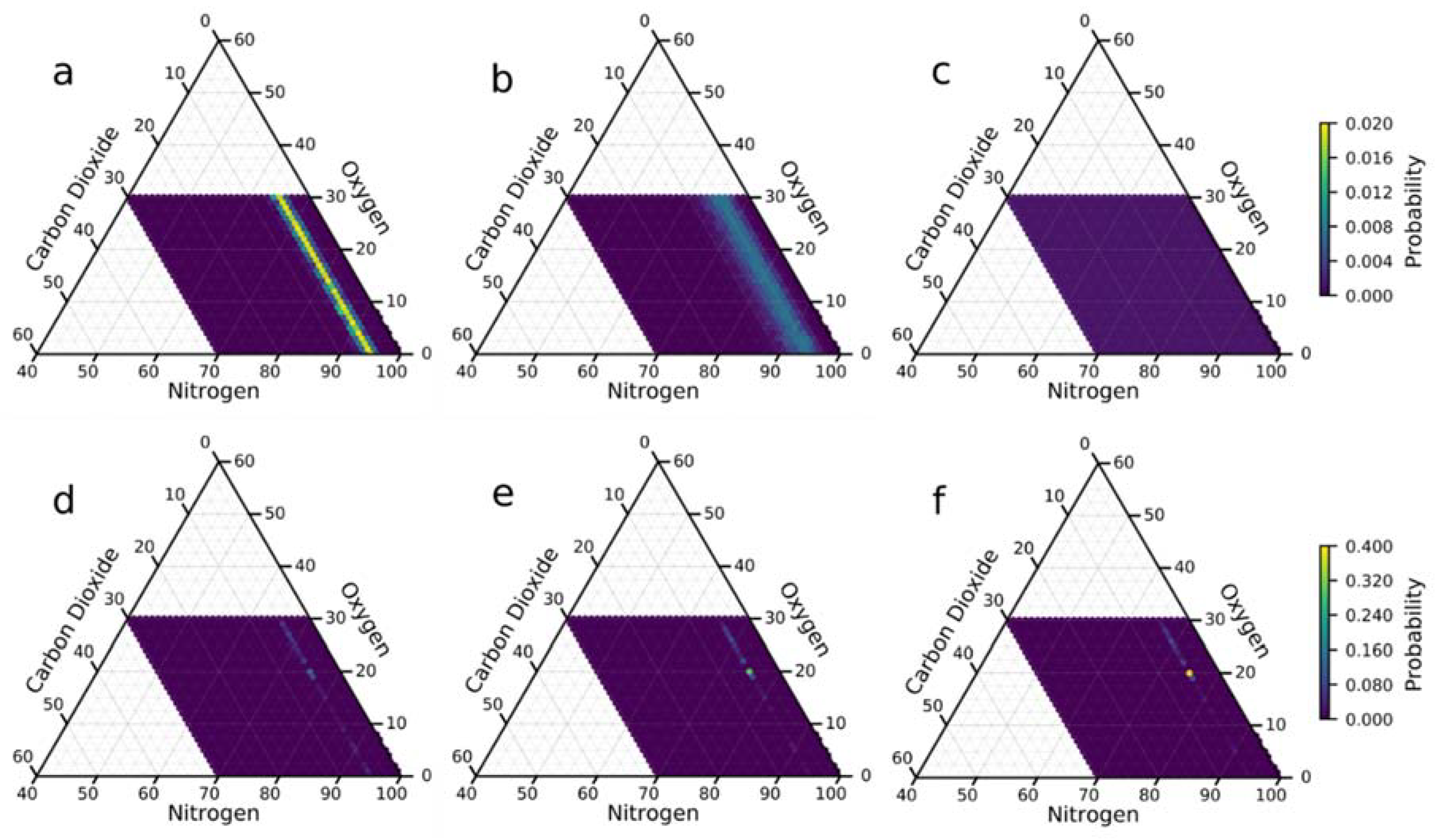
3.1. Complementary Effect of Sensing Elements in a Single Array
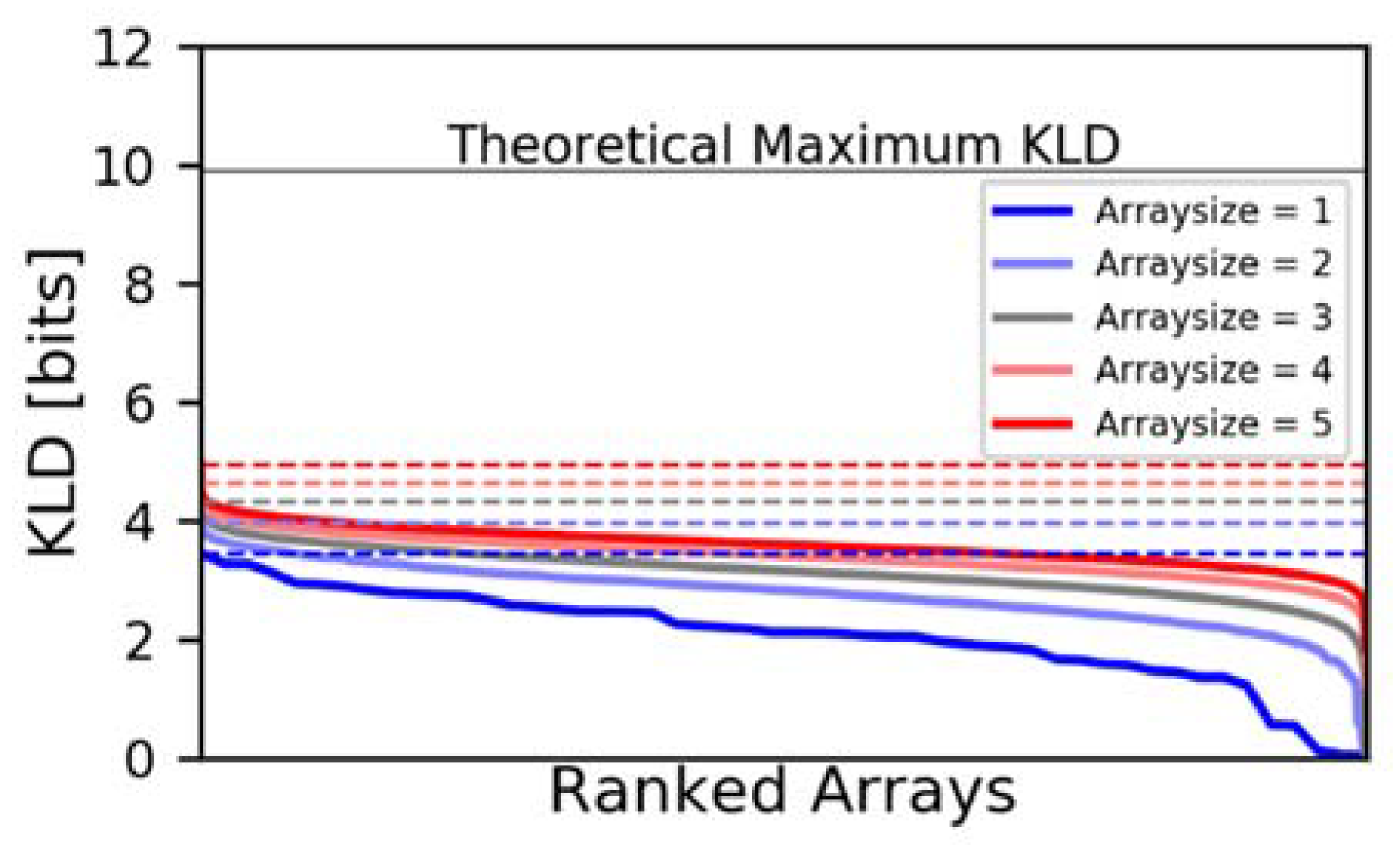
3.2. Brute Force and Genetic Algorithm Results
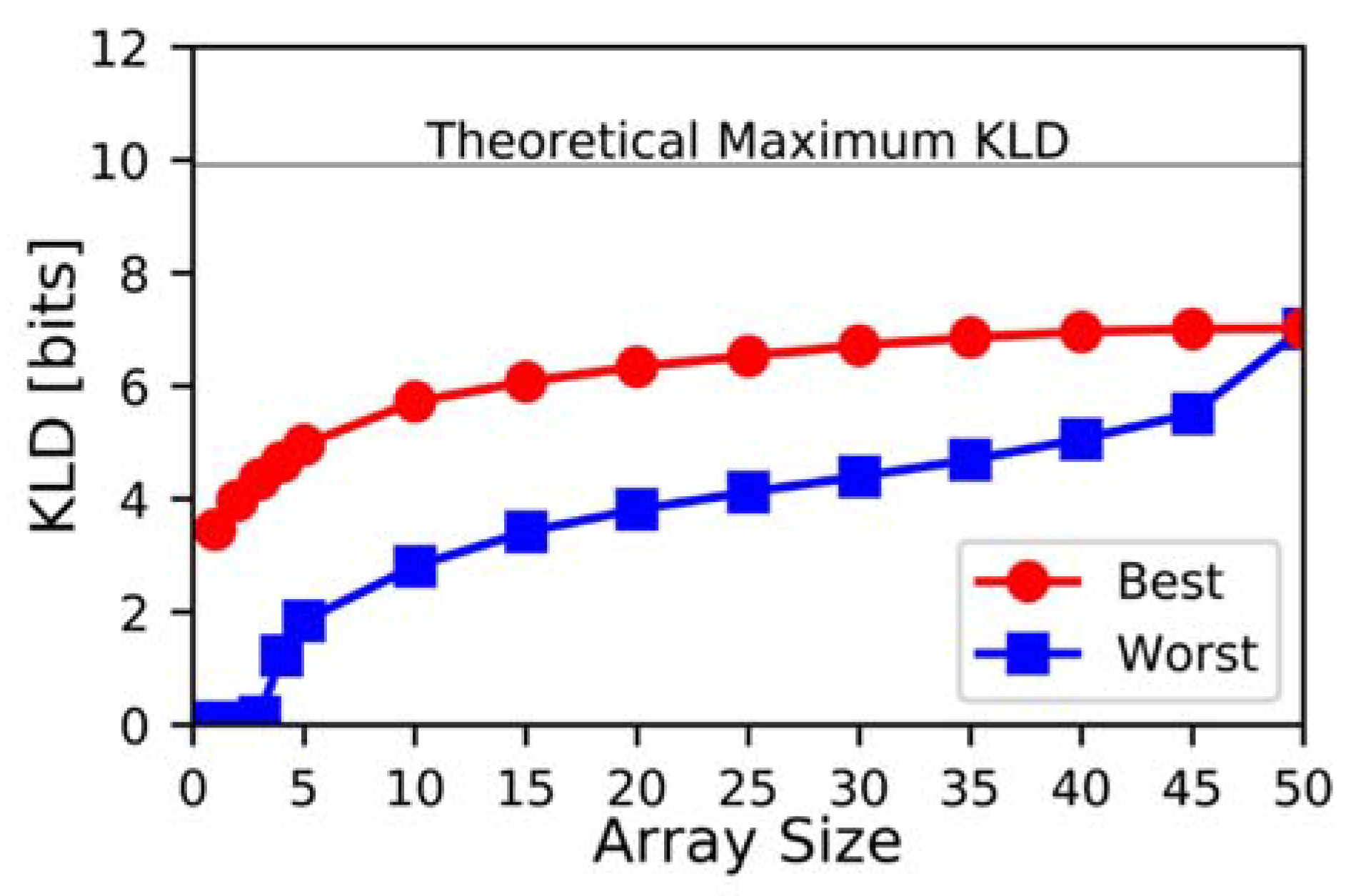
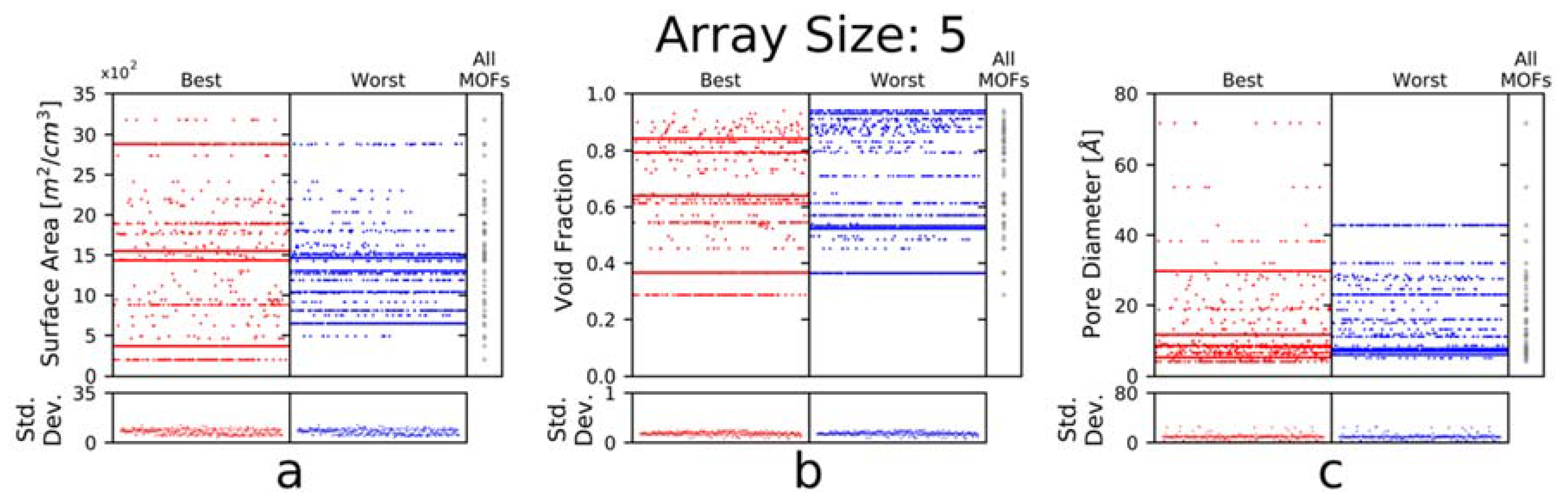
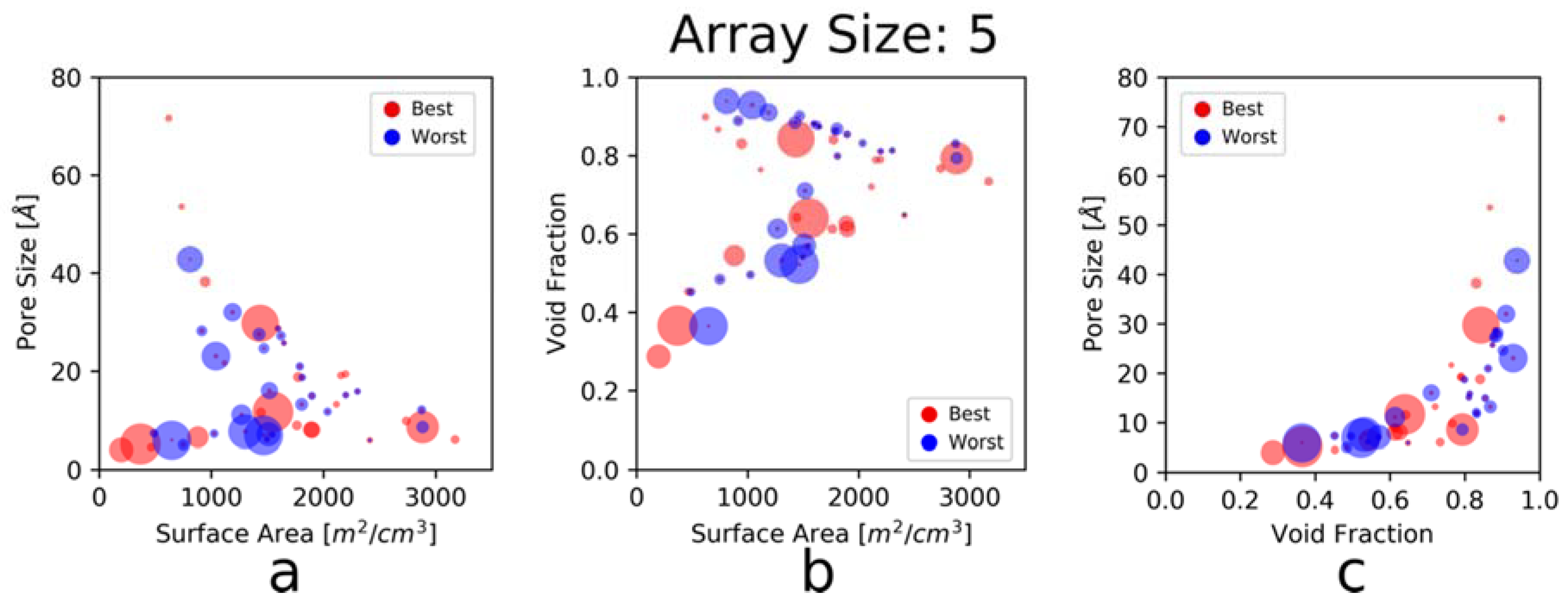
3.3. Maximum KLD vs. Number of Elements in an Array
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagle, H.T.; Gutierrez-Osuna, R.; Schiffman, S.S. The how and why of electronic noses. IEEE Spectr. 1998, 35, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshak, K.; Moore, E.; Lyons, G.M.; Harris, J.; Clifford, S. A review of gas sensors employed in electronic nose applications. Sens. Rev. 2004, 24, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röck, F.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Electronic nose: Current status and future trends. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiguzel, Y.; Kulah, H. Breath sensors for lung cancer diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 65, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.W.; Shin, H.W.; Hines, E.L. An electronic nose system to diagnose illness. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 70, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellini, A.; Blasioli, S.; Biondi, E.; Bertaccini, A.; Braschi, I.; Spinelli, F. Potential applications and limitations of electronic nose devices for plant disease diagnosis. Sensors 2017, 17, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, D. A novel medical e-nose signal analysis system. Sensors 2017, 17, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permentier, K.; Vercammen, S.; Soetaert, S.; Schellemans, C. Carbon dioxide poisoning: A literature review of an often forgotten cause of intoxication in the emergency department. Int. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallari, M.R.; Izquierdo, J.E.E.; Braga, G.S.; Dirani, E.A.T.; Pereira-da-Silva, M.A.; Rodríguez, E.F.G.; Fonseca, F.J. Enhanced Sensitivity of Gas Sensor Based on Poly(3-hexylthiophene) Thin-Film Transistors for Disease Diagnosis and Environment Monitoring. Sensors 2015, 15, 9592–9609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgués, J.; Hernández, V.; Lilienthal, A.J.; Marco, S. Smelling Nano Aerial Vehicle for Gas Source Localization and Mapping. Sensors 2019, 19, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Jiménez, J.; Monroy, J.; Blanco, J.L. The Multi-Chamber Electronic Nose—An Improved Olfaction Sensor for Mobile Robotics. Sensors 2011, 11, 6145–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loutfi, A.; Coradeschi, S.; Karlsson, L.; Broxvall, M. Putting olfaction into action: Using an electronic nose on a multi-sensing mobile robot. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37566), Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004; Volume 1, pp. 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, N.; Miura, N. Environmental gas sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 20, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zosel, J.; Oelßner, W.; Decker, M.; Gerlach, G.; Guth, U. The measurement of dissolved and gaseous carbon dioxide concentration. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 072001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duren, R.M.; Miller, C.E. Measuring the carbon emissions of megacities. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, C.M.; Unger, A.J.A. On Leakage and Seepage from Geologic Carbon Sequestration Sites. Vadose Zone J. 2003, 2, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewicki, J.L.; Oldenburg, C.M.; Dobeck, L.; Spangler, L. Surface CO2 leakage during two shallow subsurface CO2 releases. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanak, K.D.; Bennett, P.C.; Yang, C.; Hovorka, S.D. Process-based approach to CO2 leakage detection by vadose zone gas monitoring at geologic CO2 storage sites. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisont, S.; Chirachariyavej, T.; Peonim, A.V.M.V. A carbon dioxide fatality from dry ice. J. Forensic Sci. 2009, 54, 961–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish, U.; Mendell, M.J.; Shekhar, K.; Hotchi, T.; Sullivan, D.; Streufert, S.; Fisk, W.J. Is CO2 an indoor pollutant? Direct effects of low-to-moderate CO2 concentrations on human decision-making performance. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.K.; Kim, K.-H. The Relative Performance of NDIR-based Sensors in the Near Real-time Analysis of CO2 in Air. Sensors 2007, 7, 1683–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MedlinePlus-Health Information from the National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://medlineplus.gov/ (accessed on 8 October 2019).
- Campbell, M.G.; Dincă, M. Metal–organic frameworks as active materials in electronic sensor devices. Sensors 2017, 17, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, J.A.; Wilmer, C.E. Intelligent selection of metal–organic framework arrays for methane sensing via genetic algorithms. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, J.A.; Wilmer, C.E. Computational design of metal–organic framework arrays for gas sensing: Influence of array size and composition on sensor performance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 6033–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, J.A.; Wilmer, C.E. Optimizing information content in MOF sensor arrays for analyzing methane-air mixtures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 267, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturluson, A.; Sousa, R.; Zhang, Y.; Huynh, M.T.; Laird, C.; York, A.H.P.; Silsby, C.; Chang, C.-H.; Simon, C. Curating metal-organic frameworks to compose robust gas sensor arrays in dilute conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 6546–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, A.D.; Frost, C.G.; Mahon, M.F.; Richardson, C. Post-synthetic modification of tagged metal–organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8482–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, O.K.; Eryazici, I.; Jeong, N.C.; Hauser, B.G.; Wilmer, C.E.; Sarjeant, A.A.; Snurr, R.Q.; Nguyen, S.T.; Yazaydın, A.Ö.; Hupp, J.T. Metal–organic framework materials with ultrahigh surface areas: Is the Sky the limit? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15016–15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreno, L.E.; Leong, K.; Farha, O.K.; Allendorf, M.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Hupp, J.T. Metal–organic framework materials as chemical sensors. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1105–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zheng, H.; Wei, X.; Lin, Z.; Guo, L.; Qiu, B.; Chen, G. Metal–organic framework (MOF): A novel sensing platform for biomolecules. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Kitagawa, S. Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). Chem Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5415–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Q.-G.; Bu, X.; Mao, C.; Zhao, X.; Daemen, L.; Cheng, Y.; Ramirez-Cuesta, A.J.; Feng, P. An ultra-tunable platform for molecular engineering of high-performance crystalline porous materials. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurin, G.; Serre, C.; Cooper, A.; Férey, G. The new age of MOFs and of their porous-related solids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3104–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Düren, T.; Bae, Y.-S.; Snurr, R.Q. Using molecular simulation to characterise metal–organic frameworks for adsorption applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getman, R.B.; Bae, Y.-S.; Wilmer, C.E.; Snurr, R.Q. Review and analysis of molecular simulations of methane, hydrogen, and acetylene storage in metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 703–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitler, T.R.; Allendorf, M.D.; Greathouse, J.A. Grand canonical Monte Carlo simulation of low-pressure methane adsorption in nanoporous framework materials for sensing applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 3492–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Romero, L. Understanding the Role of Sensor Diversity and Redundancy to Encode for Chemical Information in Gas Sensor Arrays. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de Barcelona, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dubbeldam, D.; Calero, S.; Ellis, D.E.; Snurr, R.Q. RASPA: Molecular simulation software for adsorption and diffusion in flexible nanoporous materials. Mol. Simul. 2016, 42, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.G.; Camp, J.; Haranczyk, M.; Sikora, B.J.; Bury, W.; Krungleviciute, V.; Yildirim, T.; Farha, O.K.; Sholl, D.S.; Snurr, R.Q. Computation-ready, experimental metal–organic frameworks: A tool to enable high-throughput screening of nanoporous crystals. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 6185–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmer, C.E.; Kim, K.C.; Snurr, R.Q. An extended charge equilibration method. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 2506–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.G.; Siepmann, J.I. Transferable potentials for phase equilibria. 1. United-atom description of n-alkanes. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 2569–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, D.J.C.; Kay, D.J.C.M. Information Theory, Inference and Learning Algorithms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; ISBN 978-0-521-64298-9. [Google Scholar]
- Rosi, N.L.; Kim, J.; Eddaoudi, M.; Chen, B.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Rod packings and metal–organic frameworks constructed from rod-shaped secondary building units. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1504–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, D.; Maini, L.; Mazzeo, P.P.; Ventura, B. Reversible interconversion between luminescent isomeric metal–organic frameworks of [Cu4I4(DABCO)2] (DABCO=1,4-Diazabicyclo [2.2.2]octane). Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, G.-L.; Kong, X.-J.; Long, L.-S.; Huang, R.-B.; Zheng, L.-S. Effect of lanthanide contraction on crystal structures of lanthanide coordination polymers with 2,5-piperazinedione-1,4-diacetic acid. CrystEngComm 2010, 12, 2691–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, H.; Düren, T.; Snurr, R.Q. Effects of surface area, free volume, and heat of adsorption on hydrogen uptake in metal−organic frameworks. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 9565–9570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhong, C. Molecular Simulation of Carbon Dioxide/Methane/Hydrogen Mixture Adsorption in Metal−Organic Frameworks. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 17776–17783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-R.; Ma, Y.; McCarthy, M.C.; Sculley, J.; Yu, J.; Jeong, H.-K.; Balbuena, P.B.; Zhou, H.-C. Carbon dioxide capture-related gas adsorption and separation in metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1791–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.F.; Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T. Fundamentals of gas permeation through membranes. In Gas Separation Membranes: Polymeric and Inorganic; Ismail, A.F., Chandra Khulbe, K., Matsuura, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 11–35. ISBN 978-3-319-01095-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poloni, R.; Lee, K.; Berger, R.F.; Smit, B.; Neaton, J.B. Understanding trends in CO2 adsorption in metal–organic frameworks with open-metal sites. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.W.; Boilot, P.; Hines, E.L. Enhancing electronic nose performance by sensor selection using a new integer-based genetic algorithm approach. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 106, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.J.; Teich-McGoldrick, S.L.; Meek, S.T.; Greathouse, J.A.; Haranczyk, M.; Allendorf, M.D. Noble Gas Adsorption in Metal–Organic Frameworks Containing Open Metal Sites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 11685–11698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Day, B.A.; Wilmer, C.E. Genetic Algorithm Design of MOF-based Gas Sensor Arrays for CO2-in-Air Sensing. Sensors 2020, 20, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030924
Day BA, Wilmer CE. Genetic Algorithm Design of MOF-based Gas Sensor Arrays for CO2-in-Air Sensing. Sensors. 2020; 20(3):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030924
Chicago/Turabian StyleDay, Brian A., and Christopher E. Wilmer. 2020. "Genetic Algorithm Design of MOF-based Gas Sensor Arrays for CO2-in-Air Sensing" Sensors 20, no. 3: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030924
APA StyleDay, B. A., & Wilmer, C. E. (2020). Genetic Algorithm Design of MOF-based Gas Sensor Arrays for CO2-in-Air Sensing. Sensors, 20(3), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030924