Potentiometric E-Tongue System for Geosmin/Isoborneol Presence Monitoring in Drinkable Water
Abstract
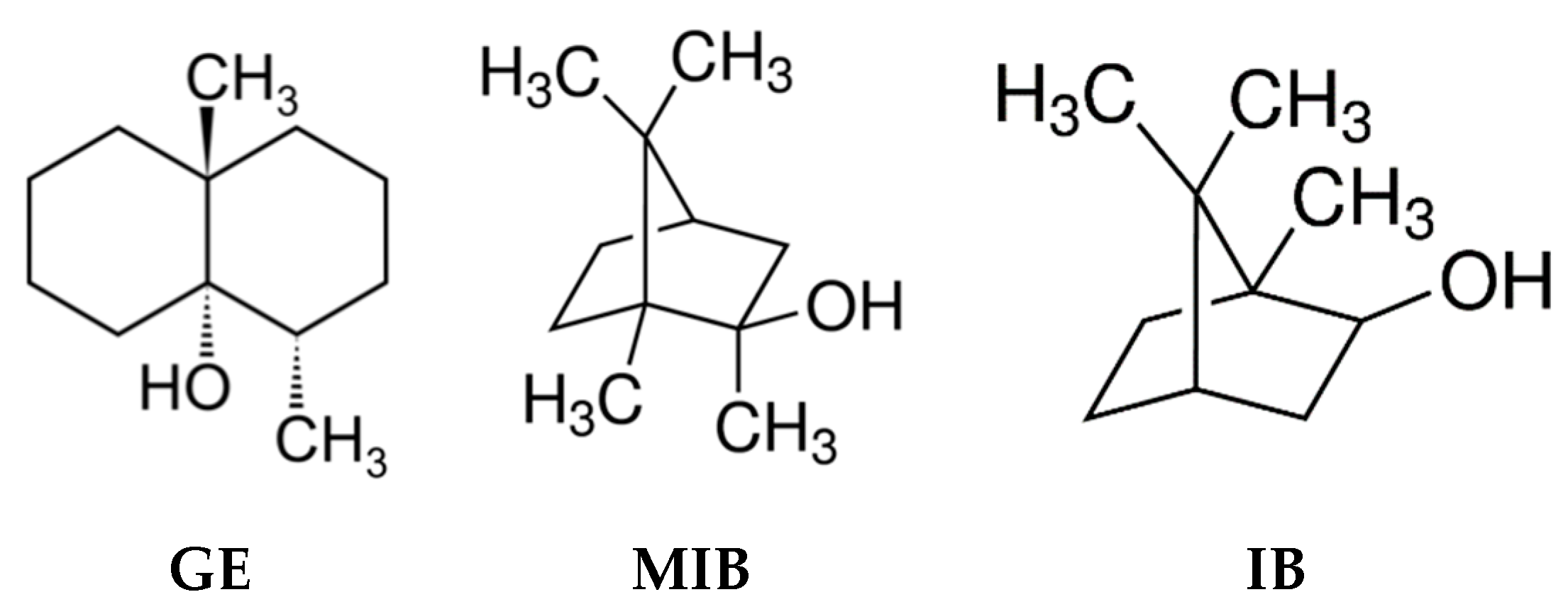
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Sensor System
2.3. Water Samples
2.4. Data Processing
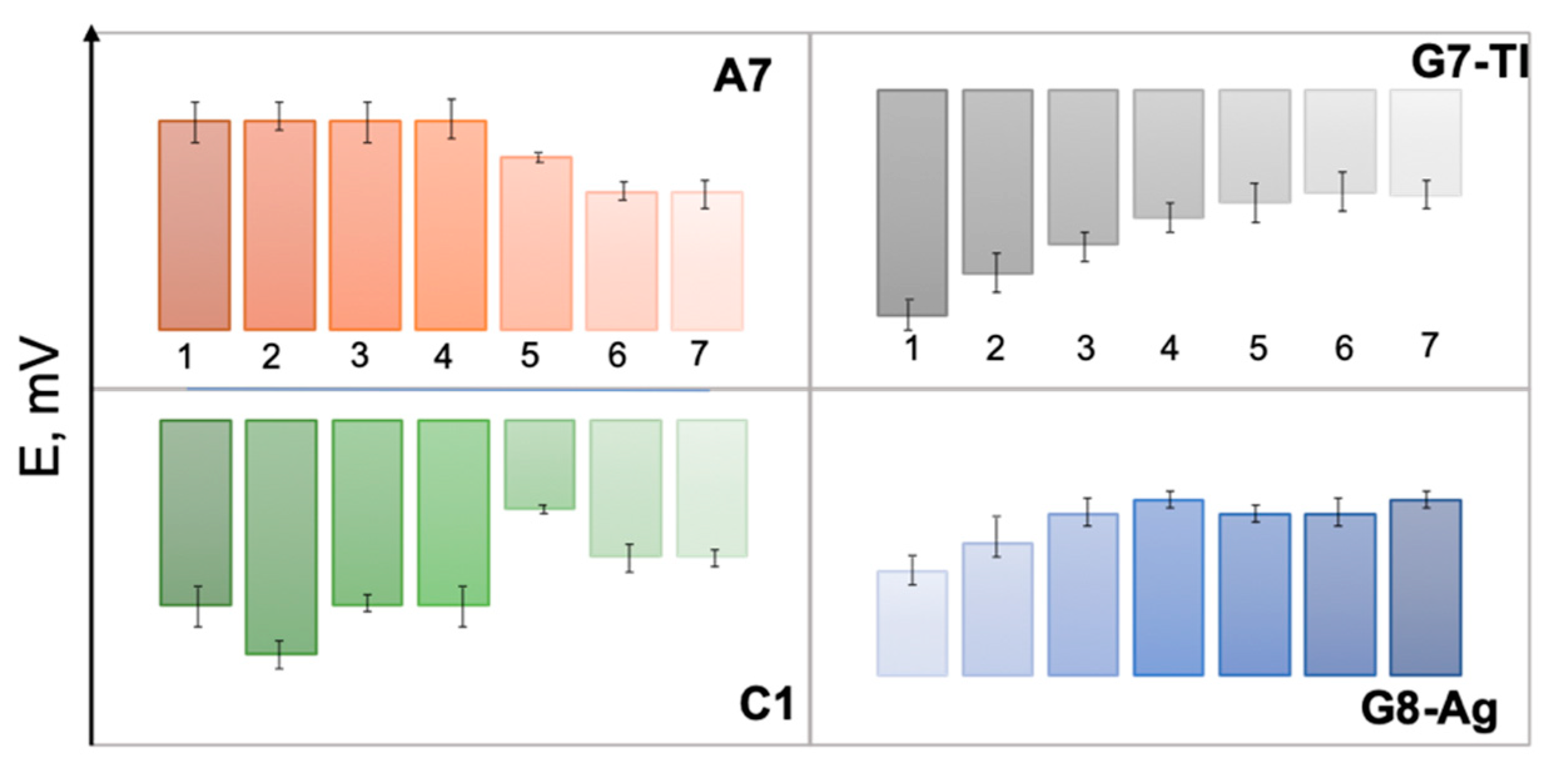
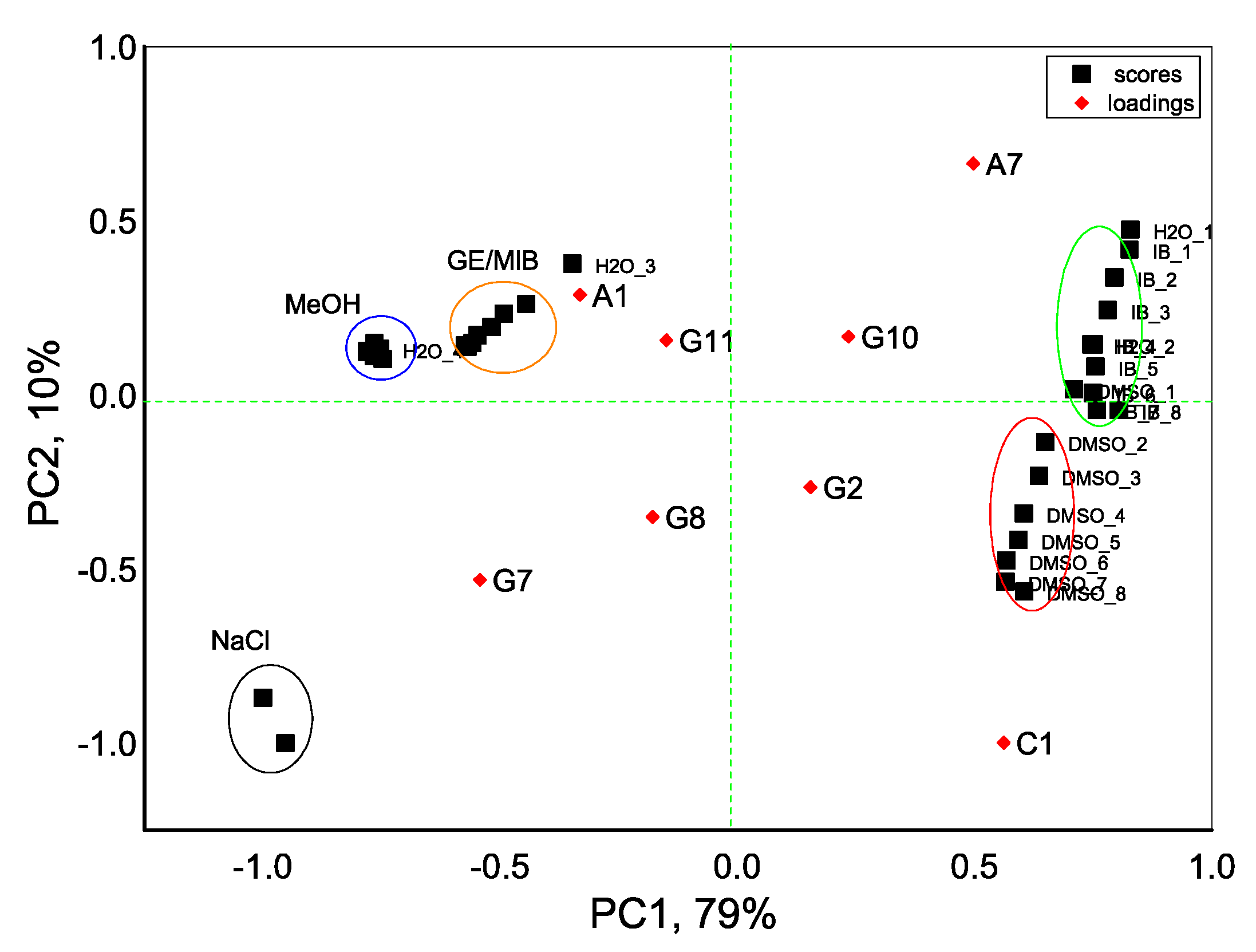
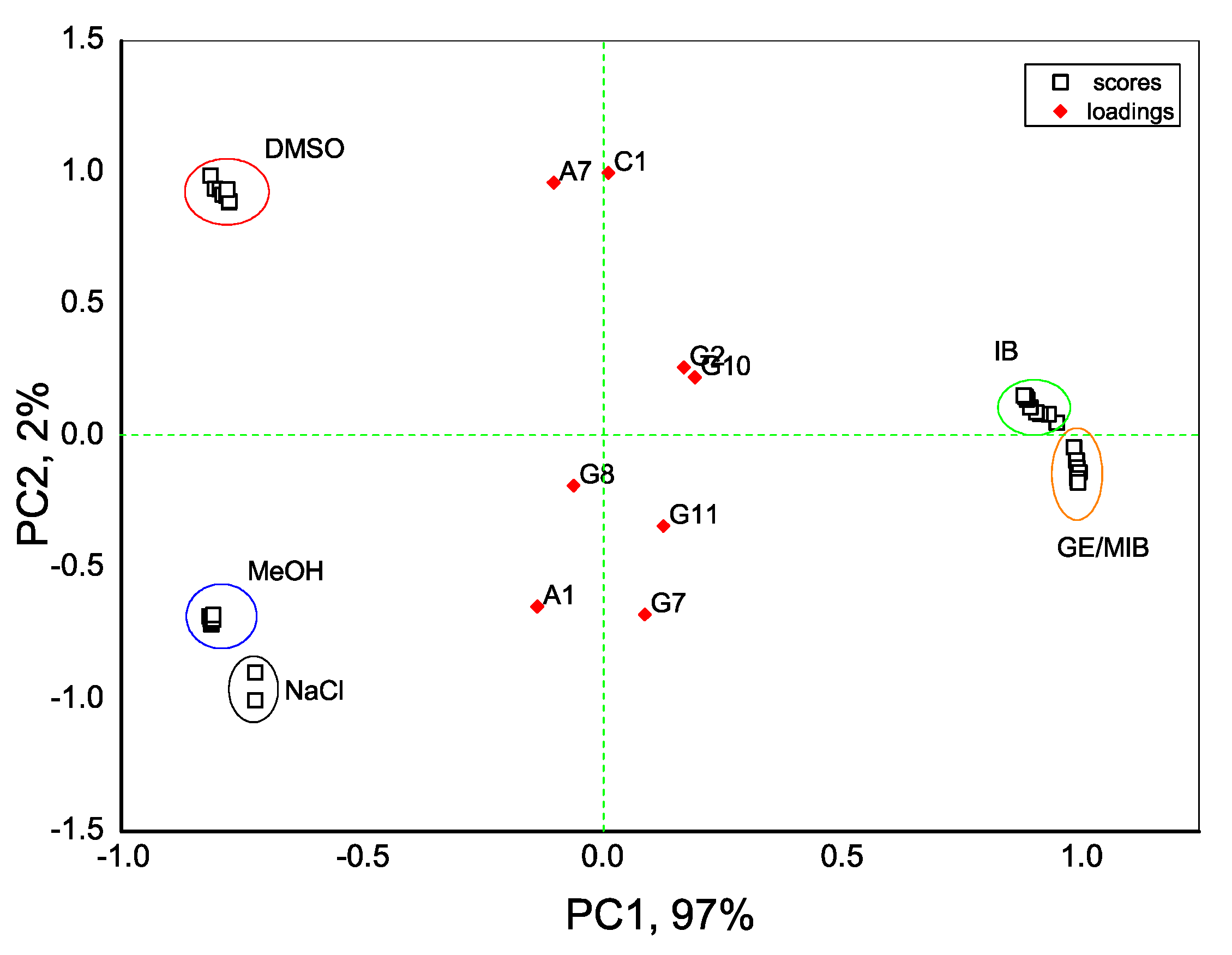
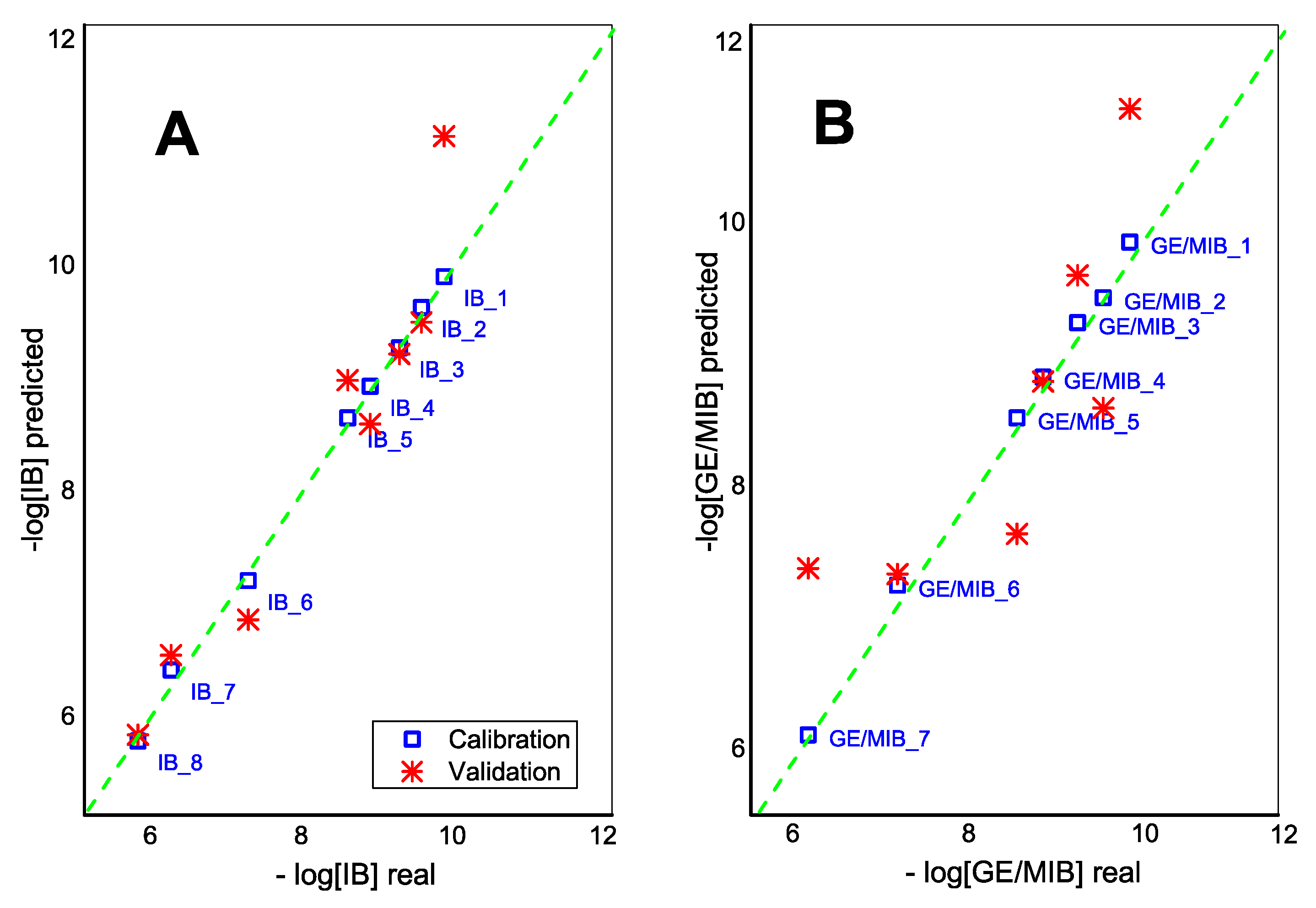
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNESCO. Managing Water Under Uncertainty and Risk; The United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Available online: https://www.unwater.org/publications/managing-water-uncertainty-risk/ (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; 631p, Available online: https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/gdwq4-1st-addendum/en/ (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- The European Parliament and The Council of The European Union. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council Establishing a Framework for the Community Action in the Field of Water Policy (EU Water Framework Directive). 2000. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/policy-documents/directive-2000-60-ec-of (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- Technologies and Techniques for Early Warning Systems to Monitor and Evaluate Drinking Water Quality: State of-the-Art Review; United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- UNEP. Global Drinking Water Quality Index Development and Sensitivity Analysis Report. 2007. Available online: https://www.un.org/waterforlifedecade/pdf/global_drinking_water_quality_index.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- Graham, J.L.; Loftin, K.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Ziegler, A.C. Cyanotoxin Mixtures and Taste-and-Odor Compounds in Cyanobacterial Blooms from the Midwestern United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7361–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, R.; Sorial, G.A. Treatment of taste and odor causing compounds 2-methyl isoborneol and geosmin in drinking water: A critical review. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B.; Ridal, J.; Boyer, G.L. Taste and odor and cyanobacterial toxins: Impairment, prediction, and management in the Great Lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 1779–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, S.W.; Lea, J.M.; Zimba, P.V.; Grimm, C.C. Rapid analysis of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in water using solid phase micro extraction procedures. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2140–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Single-Use Plastics: A Roadmap for Sustainability. 2018. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/25496/singleUsePlastic_sustainability.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- UN Environment. Available online: https://www.unenvironment.org/interactive/beat-plastic-pollution (accessed on 30 December 2019).
- Bristow, R.L.; Young, I.S.; Pemberton, A.; Williams, J.; Maher, S. An extensive review of the extraction techniques and detection methods for the taste and odour compound geosmin (trans-1, 10-dimethyl-trans-9-decalol) in water. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaziur, W.; Salemi, A.; Jochmann, M.A.; Schmid, T.C. Automated determination of picogram-per-liter level of water taste and odor compounds using solid-phase microextraction arrow coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, H.; Lin, Q.; Sun, G. Automated ultratrace determination of musty odiferous compounds from environmental waters by online purge and trap (P&T) gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS). Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2019, 47, 278–291. [Google Scholar]
- Hensarling, T.P.; Waage, S.K. A bromine-based color reaction for the detection of geosmin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 1236–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.Y.; Vercellotti, J.R.; Johnsen, P.B.; Klesius, P.H. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for geosmin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-Y.; Johnsen, P.B.; Klesius, P.H. Development of an ELISA Using Polyclonal Antibodies Specific for 2-Methylisoborneol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plhak, L.C.; Park, E.S. High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibodies for Detection of the Microbial Metabolite, 2-Methylisoborneol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3731–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.S.; McNiven, S.; Lee, K.H.; Saito, T.; Ikebukuro, K.; Karube, I. Increasing the sensitivity of piezoelectric odour sensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 15, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuetz, R.M.; White, M.; Fenner, R.A. Use of an electronic nose to detect tainting compounds in raw and treated potable water. Aqua J. Water Serv. Res. Technol. 1998, 47, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Son, M.; Cho, D.G.; Lim, J.H.; Park, J.; Hong, S.; Ko, H.J.; Park, T.H. Real-time monitoring of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol, representative odor compounds in water pollution using bioelectronic nose with human-like performance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, G.S.; Paterno, L.G.; Fonseca, F.J. Performance of an electronic tongue during monitoring 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin in water samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvova, L.; Kirsanov, D.; Legin, A.; Di Natale, C. Multisensor Systems for Chemical Analysis: Materials and Sensors; Pan Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2013; p. 392, ISBN 978-981441116-5; 978-981441115-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lvova, L.; Di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R. Chemical Sensors for Water Potability Assessment. In Bottled and Packaged Water, The Science of Beverages; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; Volume 4, pp. 177–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchmenko, T.A.; Lvova, L.B. A Perspective on Recent Advances in Piezoelectric Chemical Sensors for Environmental Monitoring and Foodstuffs Analysis. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legin, E.; Zadorozhnaya, O.; Khaydukova, M.; Kirsanov, D.; Rybakin, V.; Zagrebin, A.; Ignatyeva, N.; Ashina, J.; Sarkar, S.; Mukherjee, S.; et al. Rapid Evaluation of Integral Quality and Safety of Surface and Waste Waters by a Multisensor System (Electronic Tongue). Sensors 2019, 19, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facure, M.H.M.; Mercante, L.A.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Correa, D.S. Detection of trace levels of organophosphate pesticides using an electronic tongue based on graphene hybrid nanocomposites. Talanta 2017, 167, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvova, L.; Guanais Gonçalves, C.; Petropoulos, K.; Micheli, L.; Volpe, G.; Kirsanov, D.; Legin, A.; Viaggiu, E.; Congestri, R.; Guzzella, L.; et al. Electronic tongue for microcystins screening in waters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchuk, V.; Lvova, L.; Kirsanov, D.; Guanais Goncalves, C.; Di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R. Extending electronic tongue calibration lifetime through mathematical drift correction: Case study of microcystin toxicity analysis in waters. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.M. (Ed.) Porphyrins and Metallo-Porphyrins; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Levitchev, S.S.; Smimova, A.L.; Khitrova, V.L.; Lvova, L.B.; Bratov, A.V.; Viasov, Y.G. Photocurable carbonate-selective membranes for chemical sensors containing lipophilic additives. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1997, 44, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvova, L.; Pudi, R.; Galloni, P.; Lippolis, V.; Di Natale, C.; Lundstrom, I.; Paolesse, R. Multi-transduction sensing films for Electronic Tongue applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207B, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Feng, M.; Xu, X.; Liu, F.; Ke, F.; Li, W. Co-occurrence of microcystins and taste-and-odor compounds in drinking water source and their removal in a full-scale drinking water treatment plant. Toxins 2018, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchuk, V.; Semenov, V.; Lvova, L.; Legin, A.; Kirsanov, D. Response Standardization for Drift Correction and Multivariate Calibration Transfer in Electronic Tongue studies. In Biomimetic Sensing: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology; Fitzgerald, J.E., Fenniri, H., Eds.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2027, pp. 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

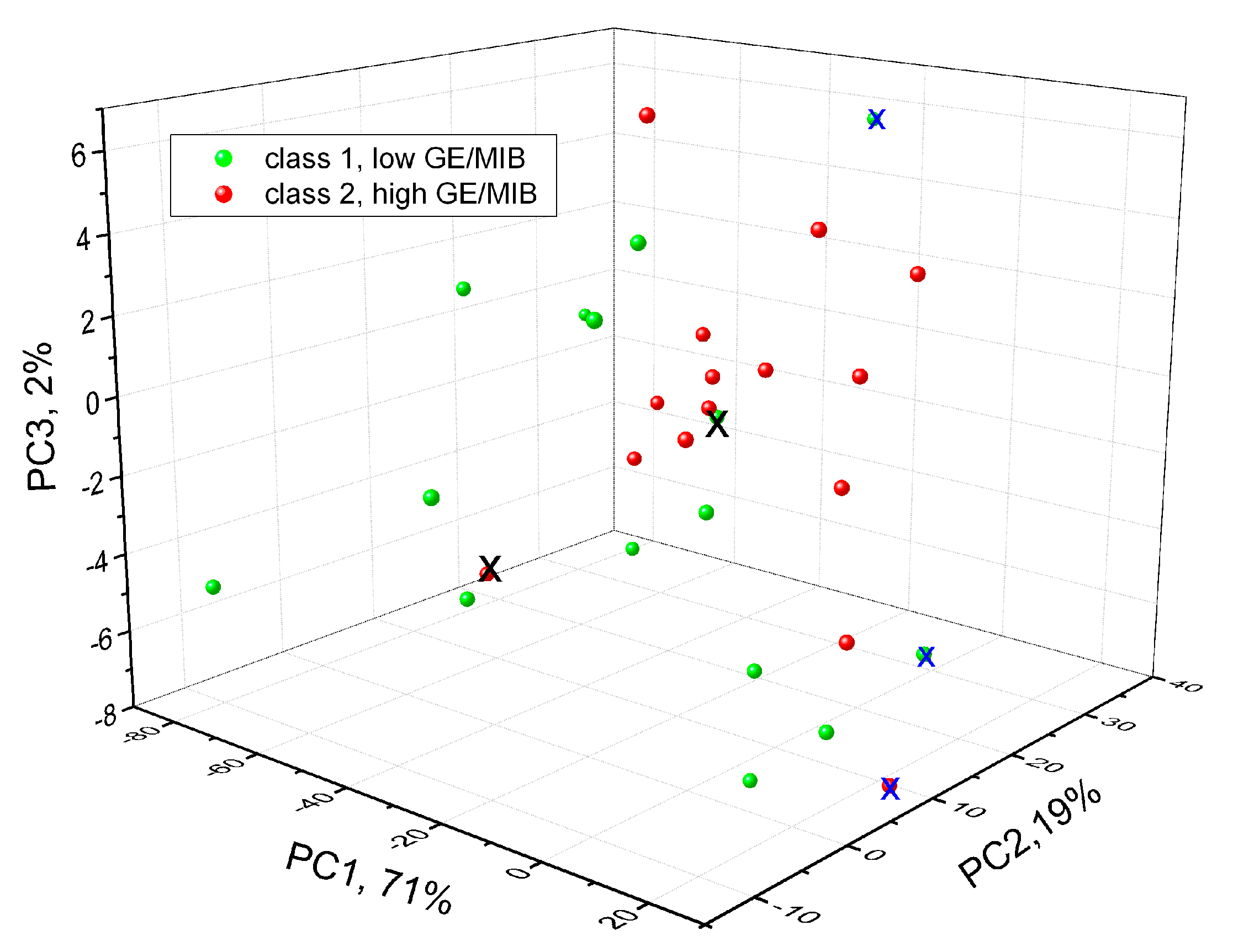
| Expected | Predicted | |
|---|---|---|
| Class 1, Low Content (20–100 ng/ L) | Class 2, High Content (0.25–10 mg/L) | |
| Class 1 | 13 | 1 |
| Class 2 | 1 | 12 |
| Non classified | 2 | 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lvova, L.; Jahatspanian, I.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Correa, D.S.; Oleneva, E.; Legin, A.; Di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R. Potentiometric E-Tongue System for Geosmin/Isoborneol Presence Monitoring in Drinkable Water. Sensors 2020, 20, 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030821
Lvova L, Jahatspanian I, Mattoso LHC, Correa DS, Oleneva E, Legin A, Di Natale C, Paolesse R. Potentiometric E-Tongue System for Geosmin/Isoborneol Presence Monitoring in Drinkable Water. Sensors. 2020; 20(3):821. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030821
Chicago/Turabian StyleLvova, Larisa, Igor Jahatspanian, Luiz H.C. Mattoso, Daniel S. Correa, Ekaterina Oleneva, Andrey Legin, Corrado Di Natale, and Roberto Paolesse. 2020. "Potentiometric E-Tongue System for Geosmin/Isoborneol Presence Monitoring in Drinkable Water" Sensors 20, no. 3: 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030821
APA StyleLvova, L., Jahatspanian, I., Mattoso, L. H. C., Correa, D. S., Oleneva, E., Legin, A., Di Natale, C., & Paolesse, R. (2020). Potentiometric E-Tongue System for Geosmin/Isoborneol Presence Monitoring in Drinkable Water. Sensors, 20(3), 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030821










