Reinforcement Learning-Based Joint User Pairing and Power Allocation in MIMO-NOMA Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
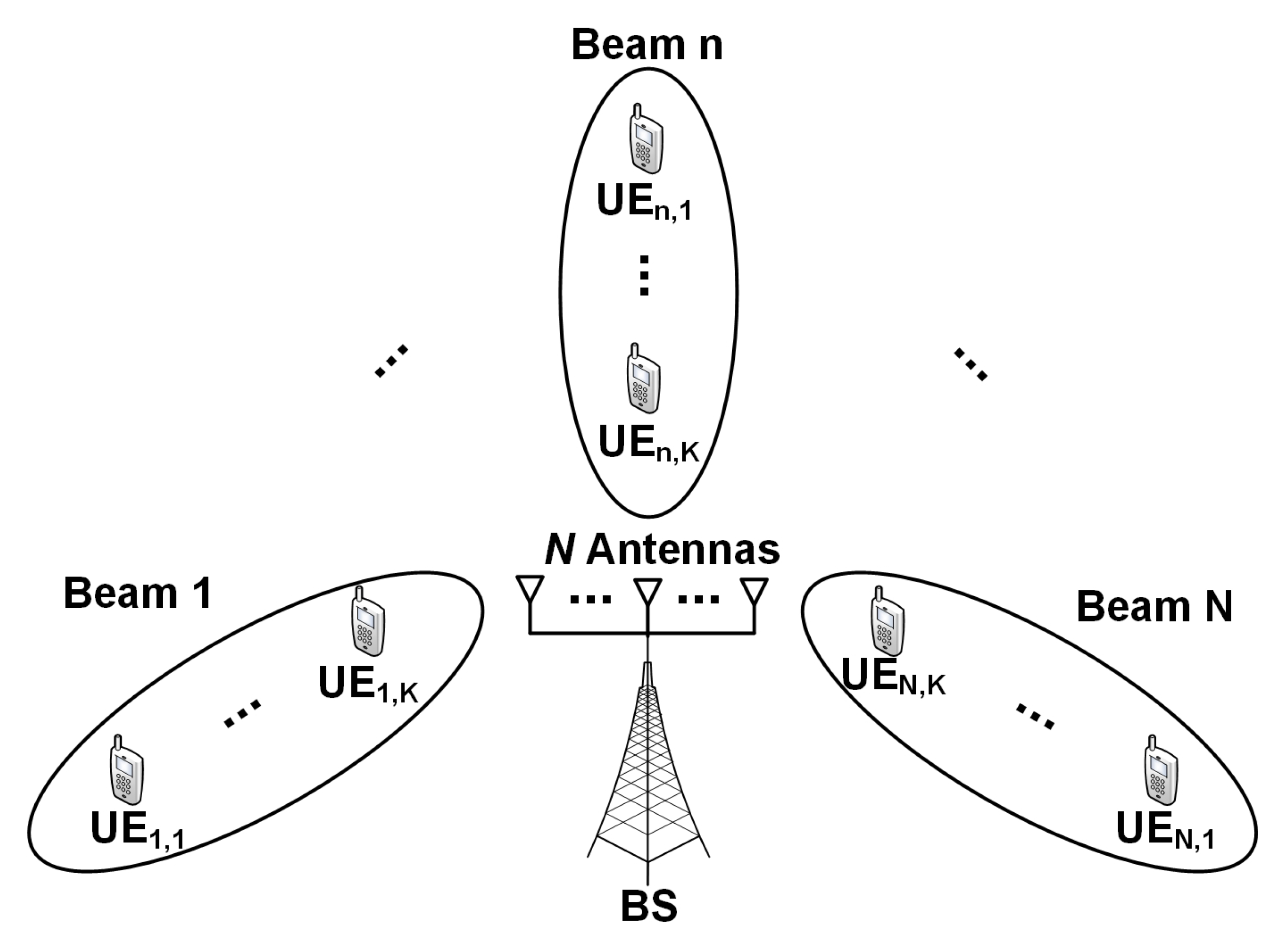
2. System Model
2.1. System Description
2.2. Problem Formulation
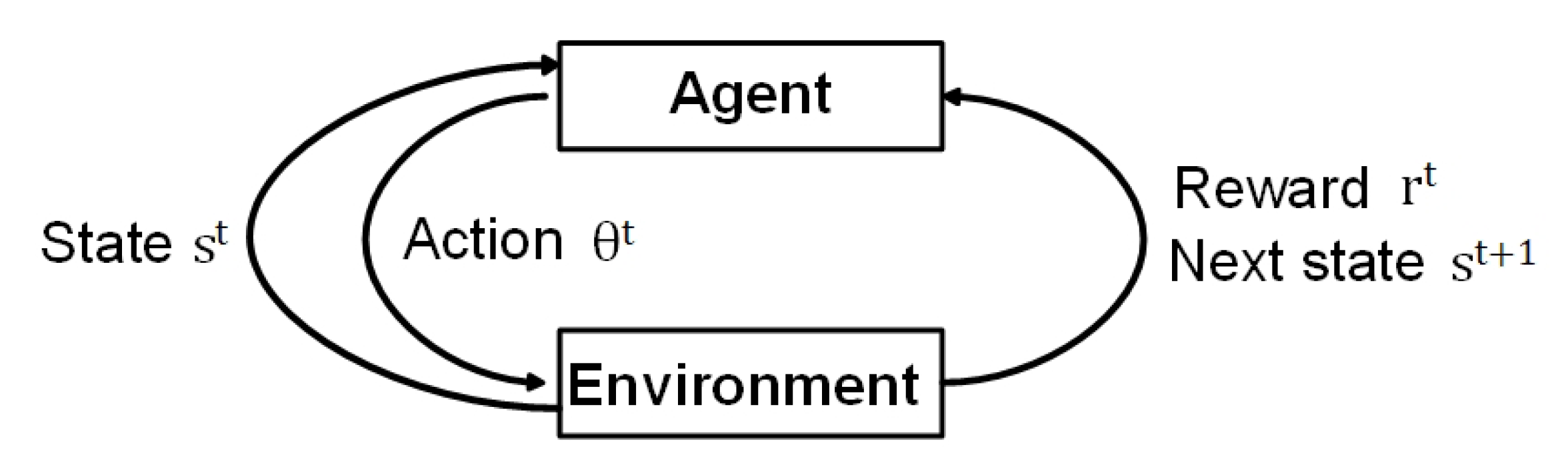
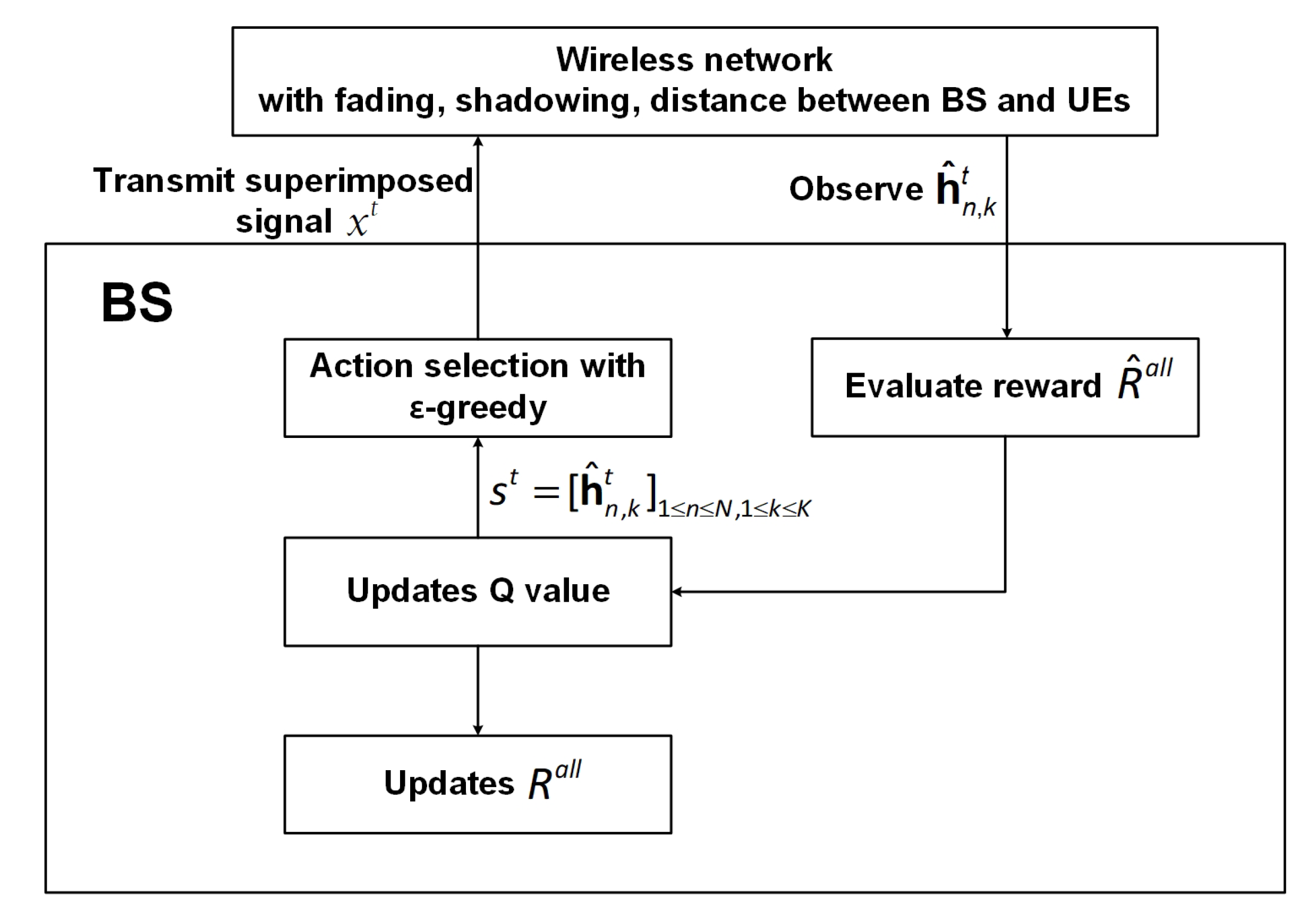
3. Proposed RL-Based Joint User Pairing and Power Allocation
3.1. Design State and Action
3.2. Q-Learning-Based Joint User Pairing and Power Allocation Procedure
| Algorithm 1 Joint user pairing and power allocation with Q-learning |
|
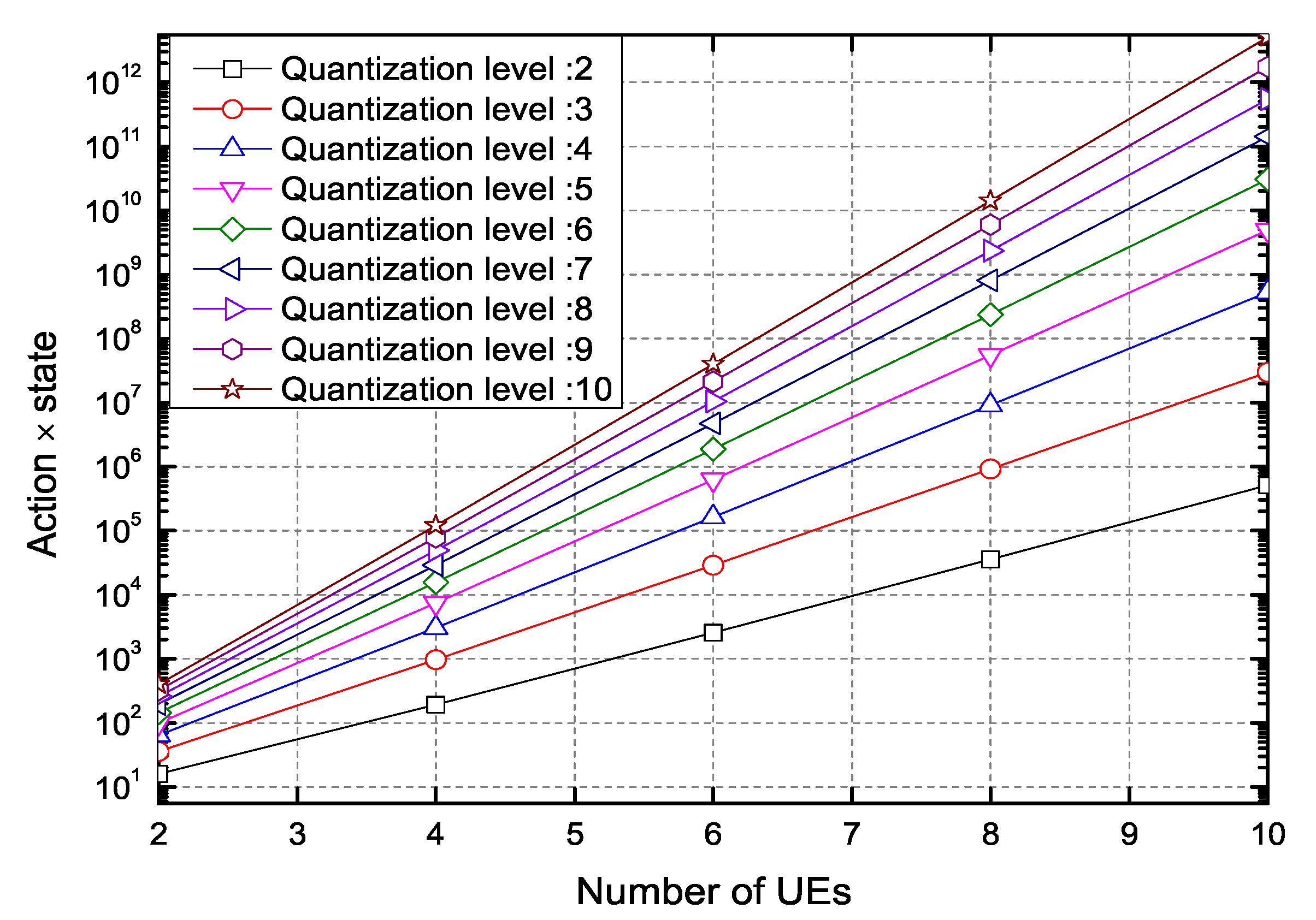
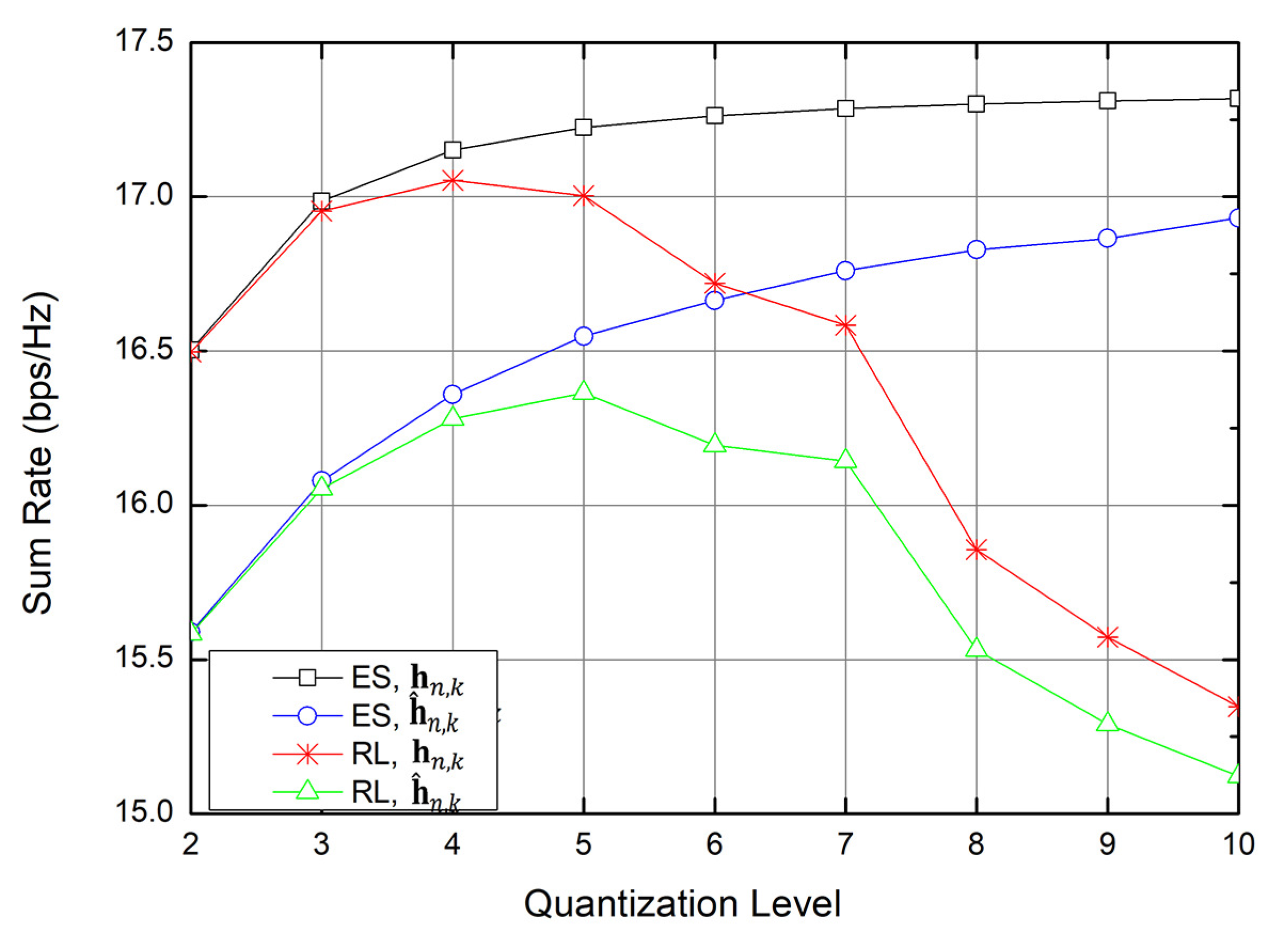
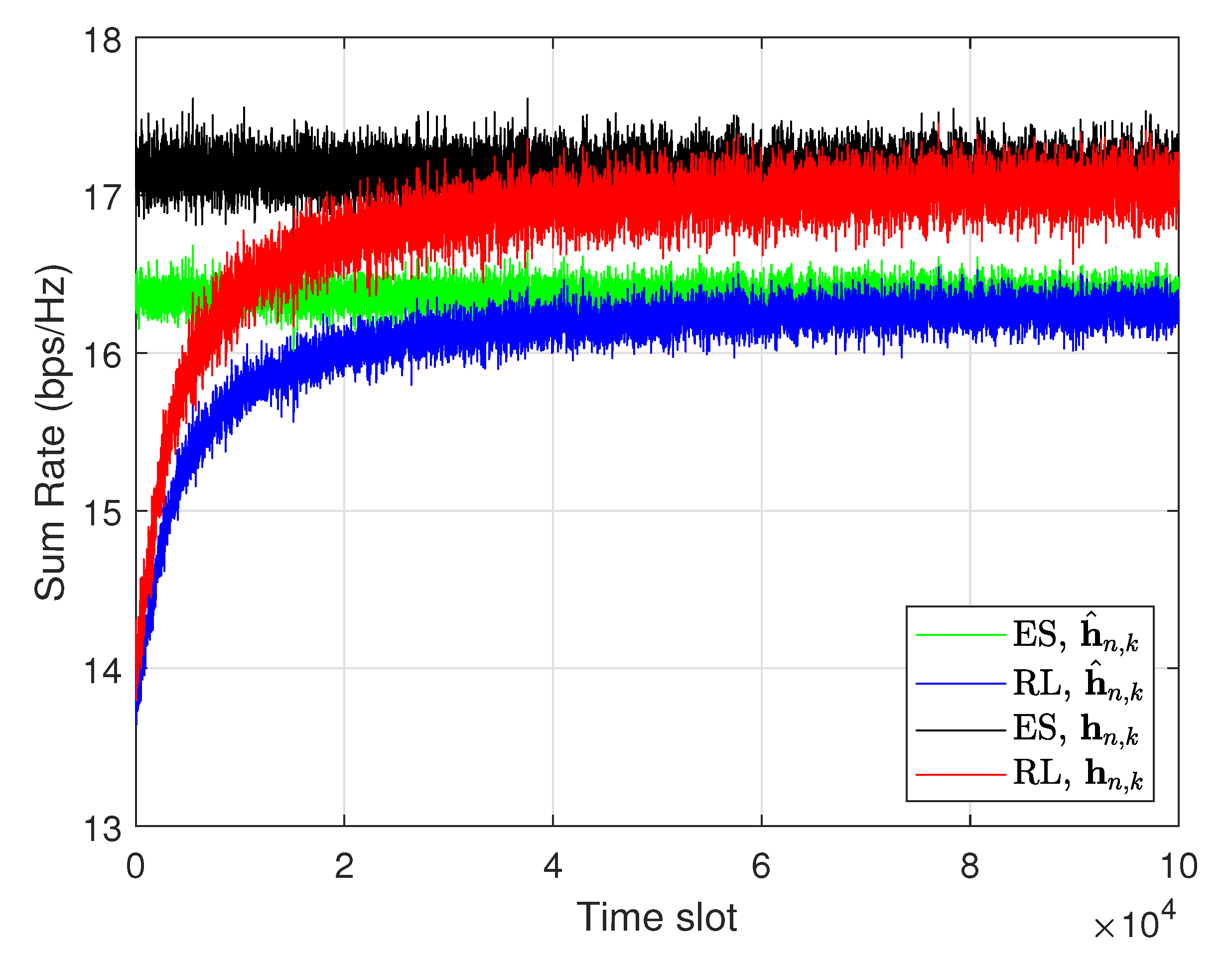
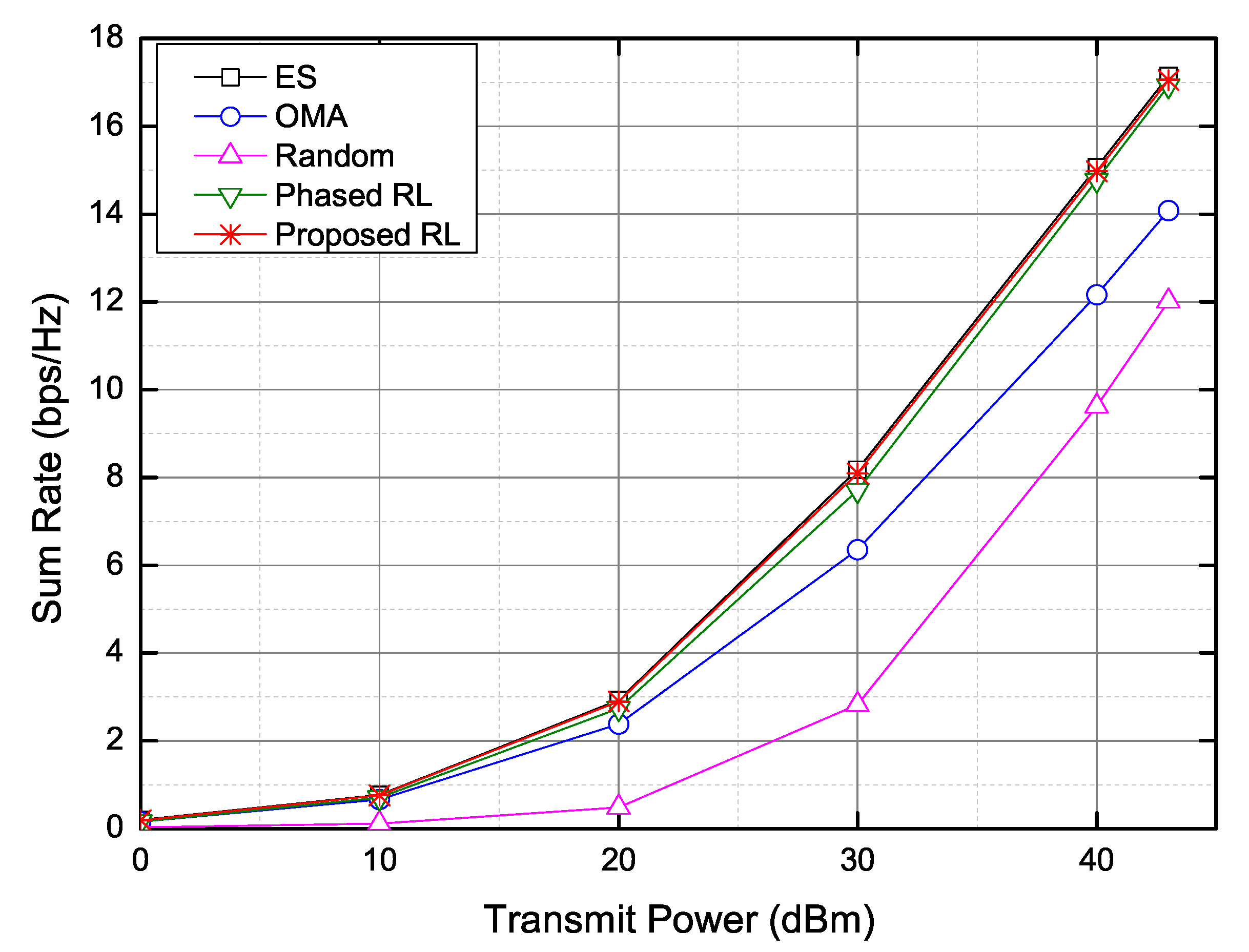
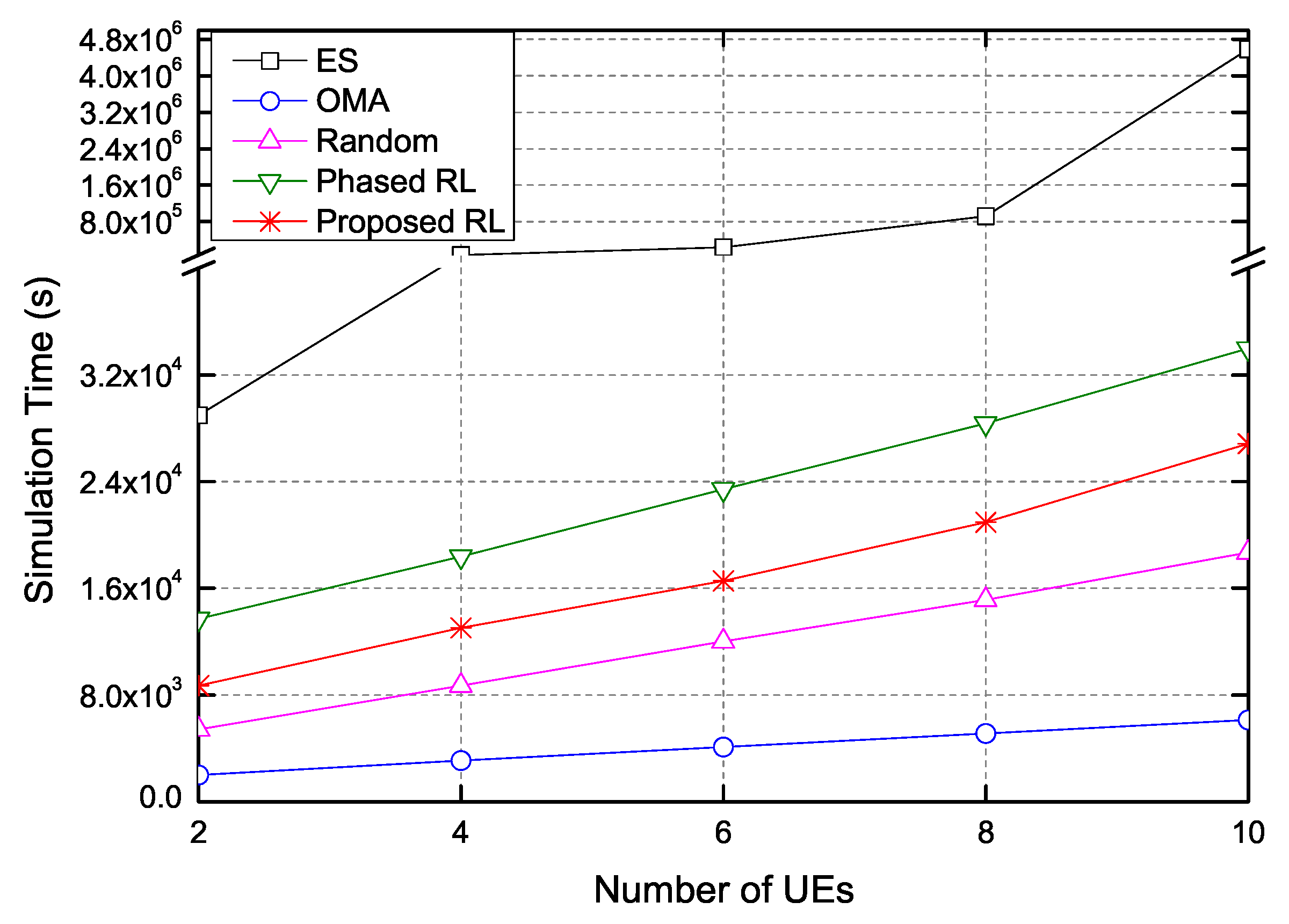
4. Numerical Results
| Algorithm 2 Phased RL-based user pairing and power allocation |
|
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saito, Y.; Kishiyama, Y.; Benjebbour, A.; Nakamura, T.; Li, A.; Higuchi, K. Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) for cellular future radio access. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 77th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Dresden, Germany, 2–5 June 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Wang, B.; Ding, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Hanzo, L. A Survey of Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access for 5G. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2294–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerkovits, T.; Liva, G.; Amat, A.G.I. Improving the decoding threshold of tailbiting spatially coupled LDPC codes by energy shaping. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, P.; Cai, G.; Lau, F.C.M.; Liew, S.C.; Han, G. Outage-limit-approaching channel coding for future wireless communications:Root-protograph low-density parity-check codes. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2019, 14, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Adachi, F.; Poor, H.V. The application of MIMO to non-orthogonal multiple access. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2016, 15, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Hu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, T.; Chen, H. Joint user pairing and power allocation in virtual MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 3697–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gong, F.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Song, P. User pairing and pair scheduling in massive MIMO-NOMA systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Xu, Y.; Hu, R.Q. A NOMA and MU-MIMO supported cellular network with underlaid D2D communications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 83rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Nanjing, China, 15–18 May 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Han, S.; Chin-Lin, I.; Pan, Z. On the ergodic capacity of MIMO NOMA systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2015, 4, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timotheou, S.; Krikidis, I. Fairness for non-orthogonal multiple access in 5G systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, B. User pairing and power allocation for downlink non-orthogonal multiple access. In Proceedings of the IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Washington, DC, USA, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Mähönen, P.; Petrova, M. Proportional fairness-based user pairing and power allocation for non-orthogonal multiple access. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communication (PIMRC), Hong Kong, China, 30 August–2 September 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Patras, P.; Haddadi, H. Deep learning in mobile and wireless networking: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2224–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, N.C.; Hoang, D.T.; Gong, S.; Niyato, D.; Wang, P.; Liang, Y.; Kim, D.I. Applications of deep reinforcement learning in communications and networking: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 3133–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, N.; Lee, W.; Cho, D. Deep learning-aided SCMA. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, K.N.; Vaezi, M.; Shin, W.; Poor, H.V.; Shin, H.; Quek, T.Q.S. Power allocation in cache-aided NOMA systems: Optimization and deep reinforcement learning approaches. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020, 68, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, G.; Huang, H.; Song, Y.; Sari, H. Deep learning for an effective nonorthogonal multiple access scheme. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 8440–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, Y.; Dai, C.; Dai, H.; Poor, H.V. Reinforcement learning-based NOMA power allocation in the presence of smart jamming. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 3377–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, L. Fast reinforcement learning for anti-jamming communications. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.05364. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Lv, T.; Zhang, X. Multi-agent reinforcement learning-based user pairing in multi-carrier NOMA systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Shanghai, China, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, B. Joint power allocation and channel assignment for NOMA with deep reinforcement learning. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2019, 37, 2200–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Gomes, P.H.; Krishnamachari, B. Deep reinforcement learning for dynamic multichannel access in wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Cognit. Commun. Netw. 2018, 4, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennes, R.; De Figueiredo, F.A.; Latré, S. Multi-Agent Deep Learning for Multi-channel Access in Slotted Wireless Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 95032–95045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.I.; Hossain, E. A deep Q-learning methods for downlink power allocation in multi-cell networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.13032. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Kim, I.; Chun, C. Deep learning-based MIMO-NOMA with imperfect SIC decoding. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 14, 3414–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, C.J.; Dayan, P. Technical note: Q-learning. Mach. Learn. 1992, 8, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP. 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Study on New Radio Access Technology Physical Layer Aspects (Release 14); Version 14.2.0; Technical Report (TR) 38.802; 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP): Valbonne, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.; Lei, X.; Karagiannidis, G.K.; Schober, R.; Yuan, J.; Bhargava, V.K. A survey on non-orthogonal multiple access for 5G networks: Research challenges and future trends. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 2181–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| M | Total number of users |
| n | Number of BS antennas |
| k | Number of users in a beam |
| Total power of the BS | |
| Transmit power at the nth beam | |
| Signal transmitted to the kth UE at the nth beam | |
| Superimposed signal at the nth beam | |
| Channel vector to the kth UE at the nth beam | |
| Quantized channel vector to the kth UE at the nth beam | |
| Distance between BS and the kth UE at the nth beam | |
| Precoding vector at the nth beam | |
| SINR of the kth UE at the nth beam | |
| Data rate of the kth UE at the nth beam | |
| Sum rate of MIMO-NOMA systems | |
| Sum rate of MIMO-NOMA systems using quantized channel vector | |
| The user pairing set at the nth beam | |
| Power allocation coefficient to the kth UE at the nth beam | |
| Path loss exponent | |
| Addictive white gaussian noise (AWGN) to the kth UE at the nth beam | |
| L | Number of CSI quantization level |
| Inter-beam interference to the kth UE at the nth beam | |
| Intra-beam interference to the kth UE at the nth beam | |
| s | State of Q-learning |
| Action of Q-learning | |
| r | Reward of Q-learning |
| Learning rate | |
| Discount factor |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Total number of UEs, M | 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 |
| Number of transmit antennas, N | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 |
| Number of UEs in a beam, K | 2 |
| Power allocation coefficient, | 0.2, 0.4 |
| Path loss coefficient, | 3 |
| Learning rate, | 0.9999 |
| Discount factor, | 0.0001 |
| Time slot (1 ms), T | 100,000 |
| Number of iterations, I | 1000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; So, J. Reinforcement Learning-Based Joint User Pairing and Power Allocation in MIMO-NOMA Systems. Sensors 2020, 20, 7094. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20247094
Lee J, So J. Reinforcement Learning-Based Joint User Pairing and Power Allocation in MIMO-NOMA Systems. Sensors. 2020; 20(24):7094. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20247094
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jaehee, and Jaewoo So. 2020. "Reinforcement Learning-Based Joint User Pairing and Power Allocation in MIMO-NOMA Systems" Sensors 20, no. 24: 7094. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20247094
APA StyleLee, J., & So, J. (2020). Reinforcement Learning-Based Joint User Pairing and Power Allocation in MIMO-NOMA Systems. Sensors, 20(24), 7094. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20247094






