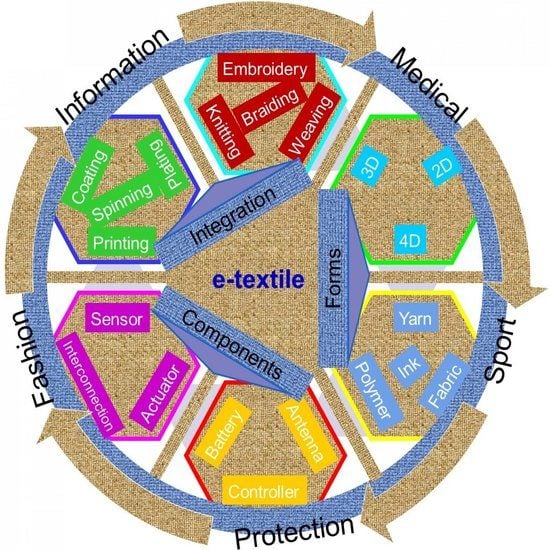
Integration of Conductive Materials with Textile Structures, an Overview
Abstract
1. Introduction
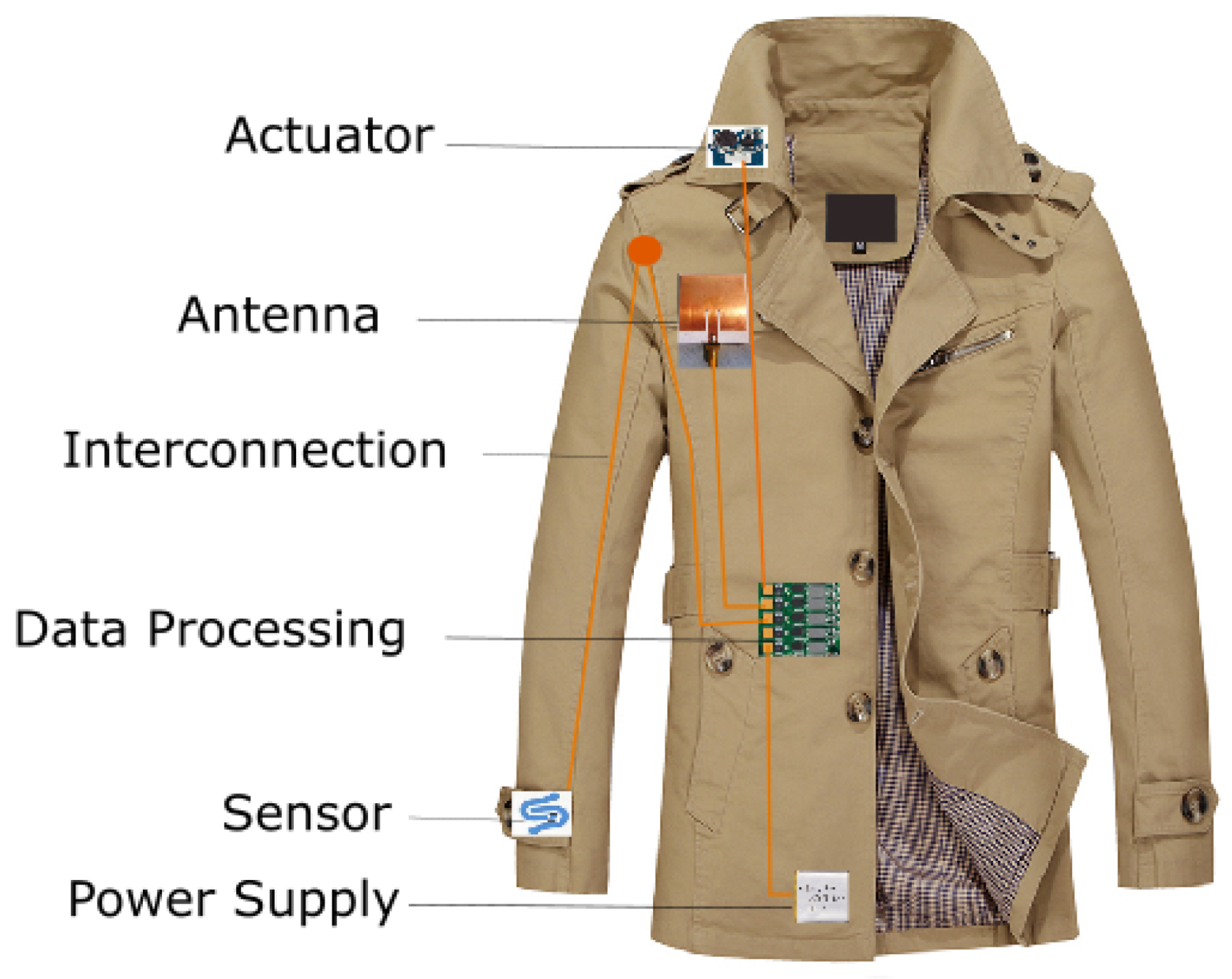
Building Blocks of Smart Textile Systems
2. Search Method
3. Conductive Materials for Textiles
3.1. Conductive Inks
3.2. Carbon-Based Conductive Materials
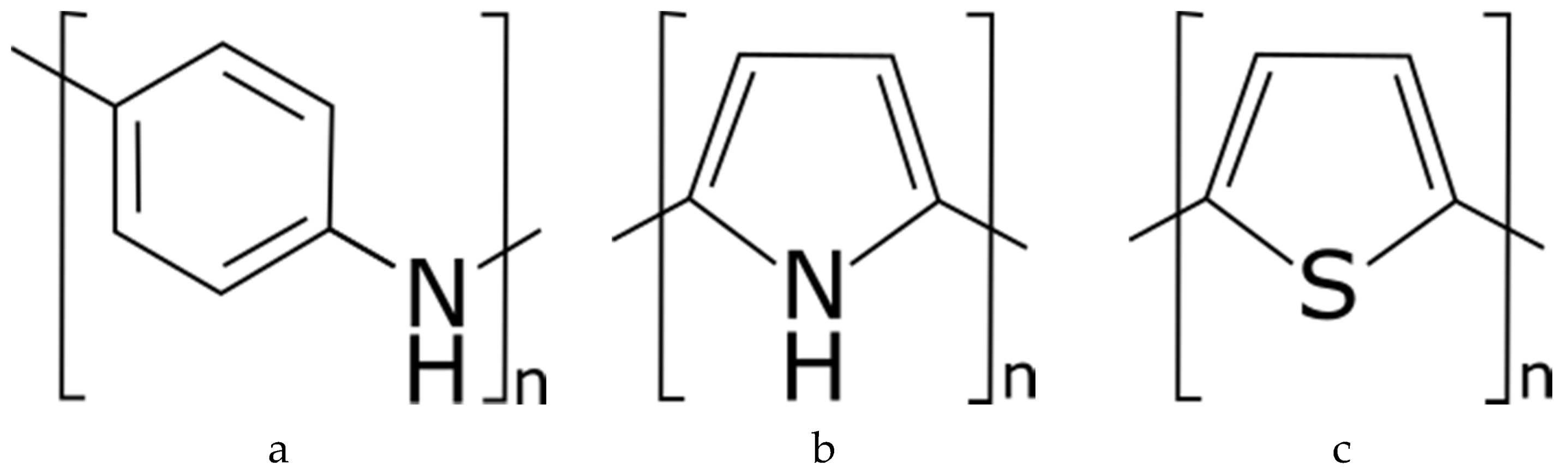
3.3. Intrinsically Conductive Polymers
3.4. Conductive Polymer Composites
4. Integration Techniques of Conductive Materials on/into a Textile Structure
4.1. Integration of Conductive Compounds
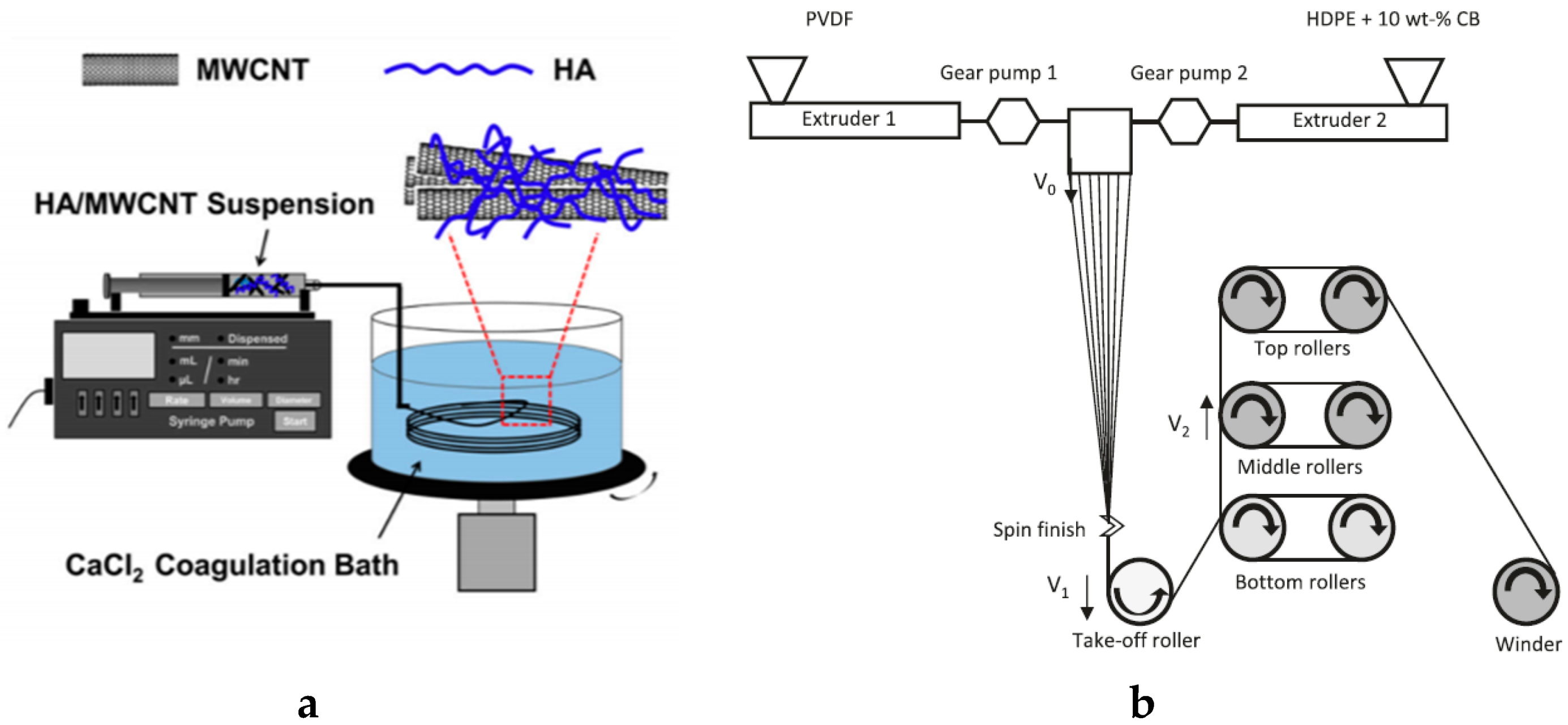
4.1.1. Fiber Spinning
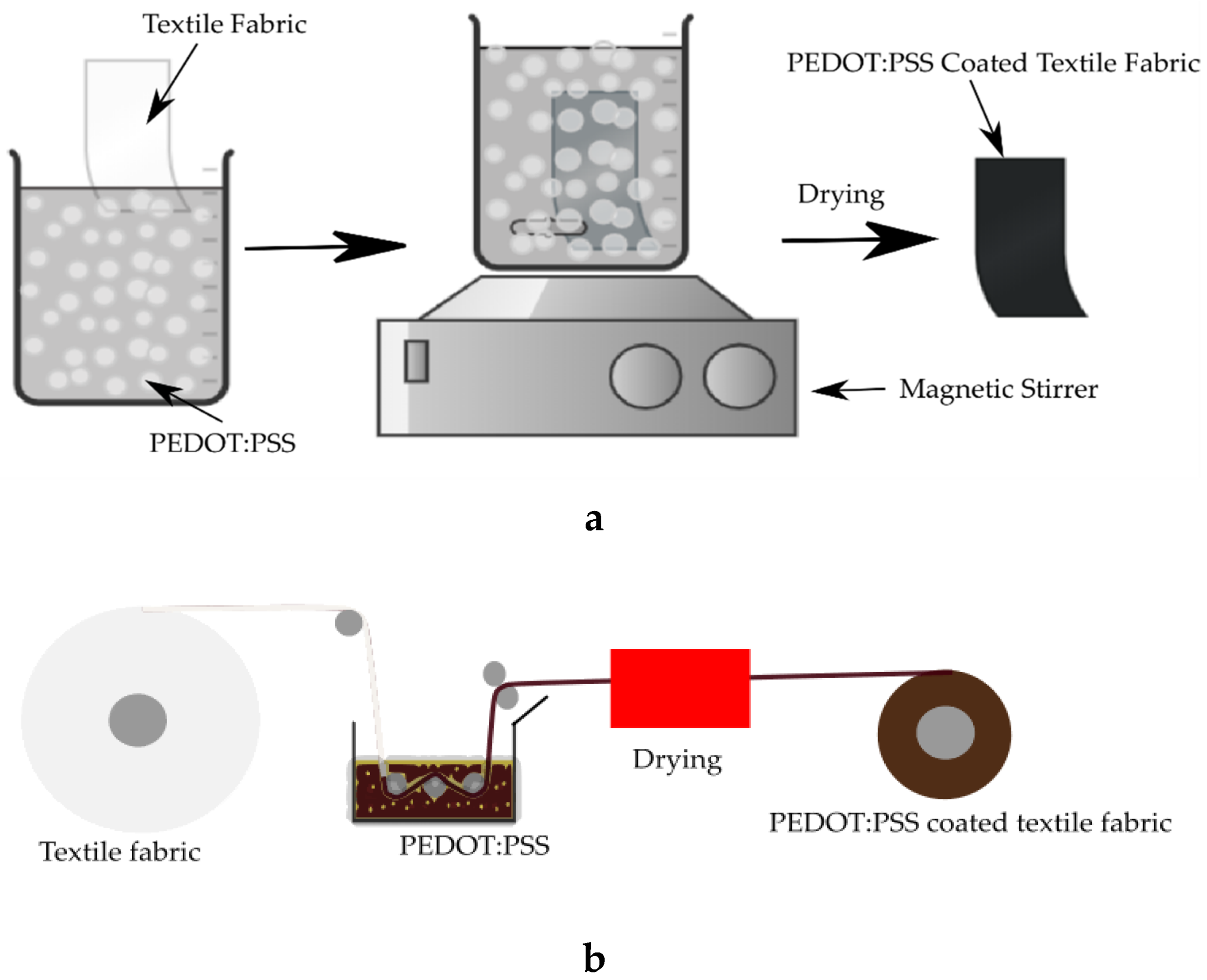
4.1.2. Dip-Coating
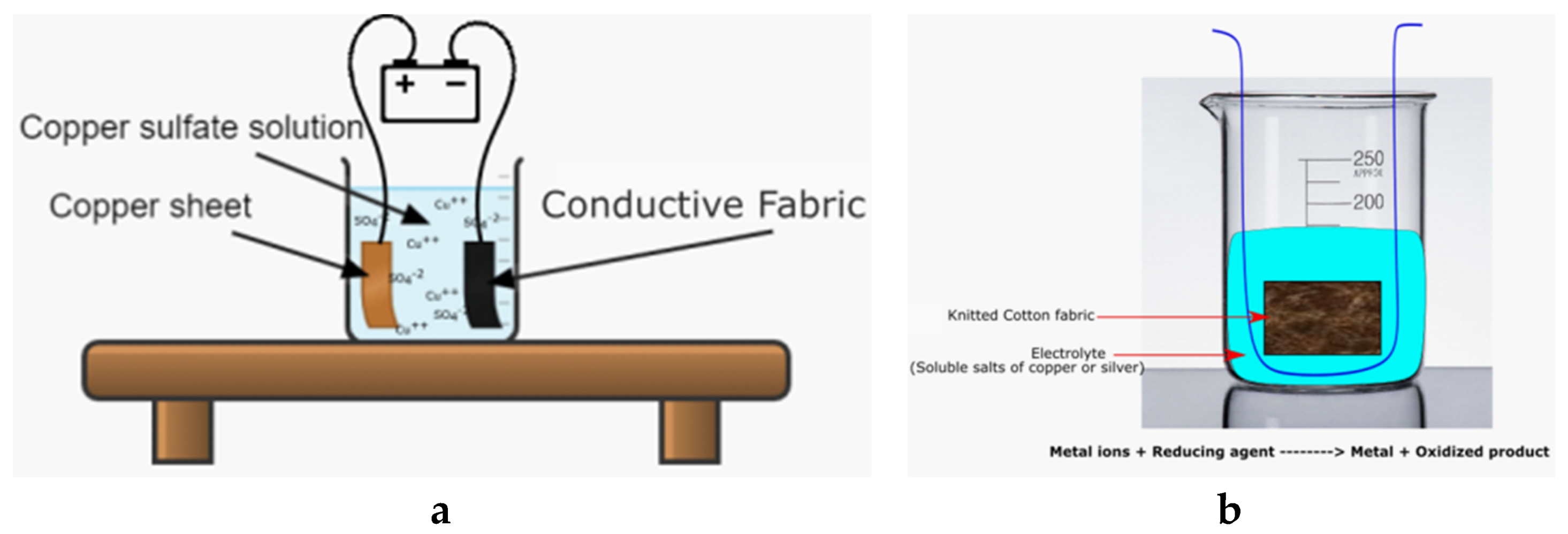
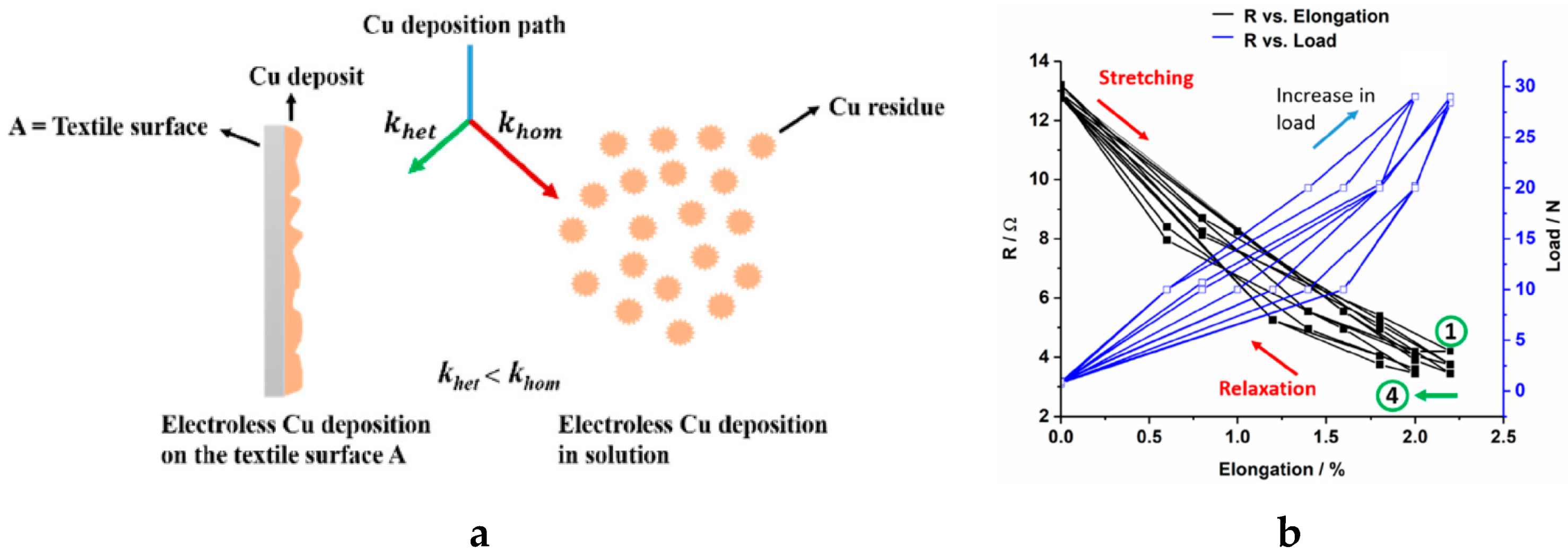
4.1.3. Plating
4.1.4. Screen Printing
4.1.5. Spray-Coating
4.1.6. Transfer Printing
4.1.7. Inkjet Printing
4.2. Integration of Conductive Yarn and Conductive Filament Fiber
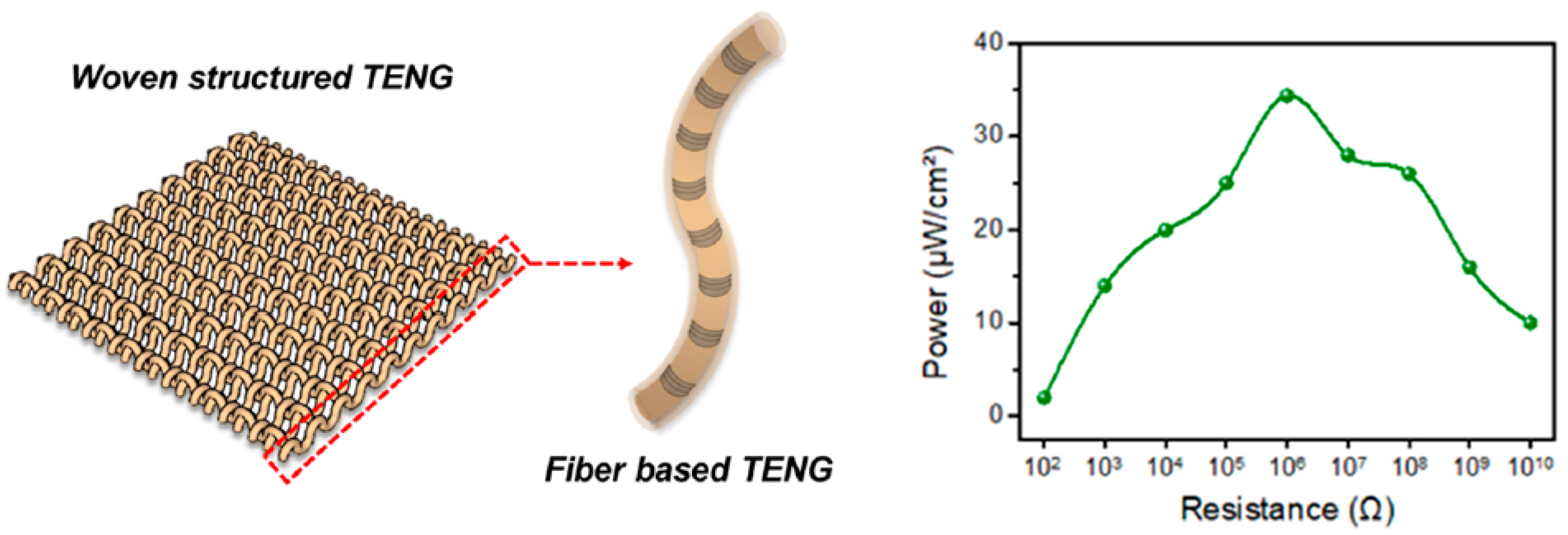
4.2.1. Weaving
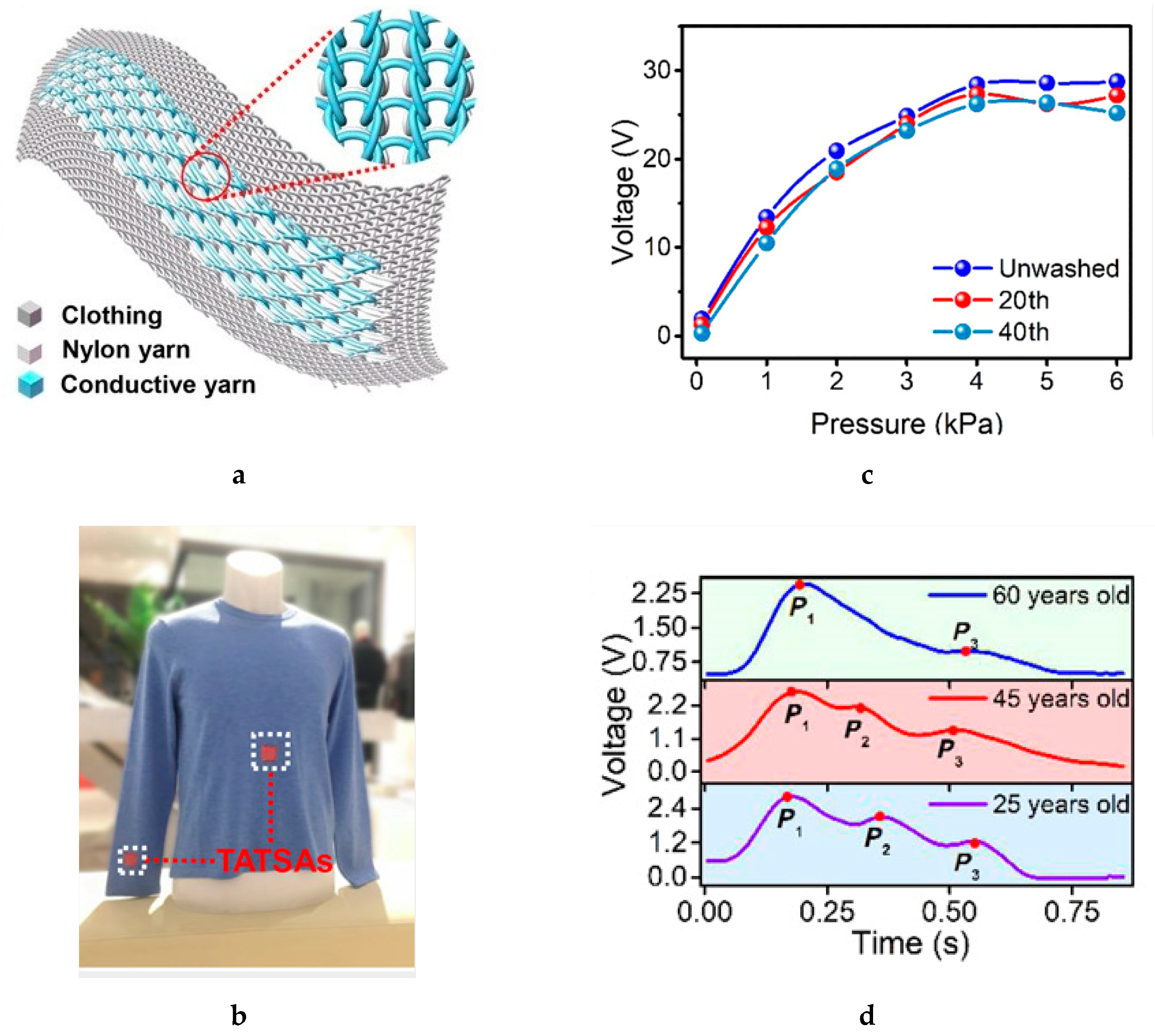
4.2.2. Knitting
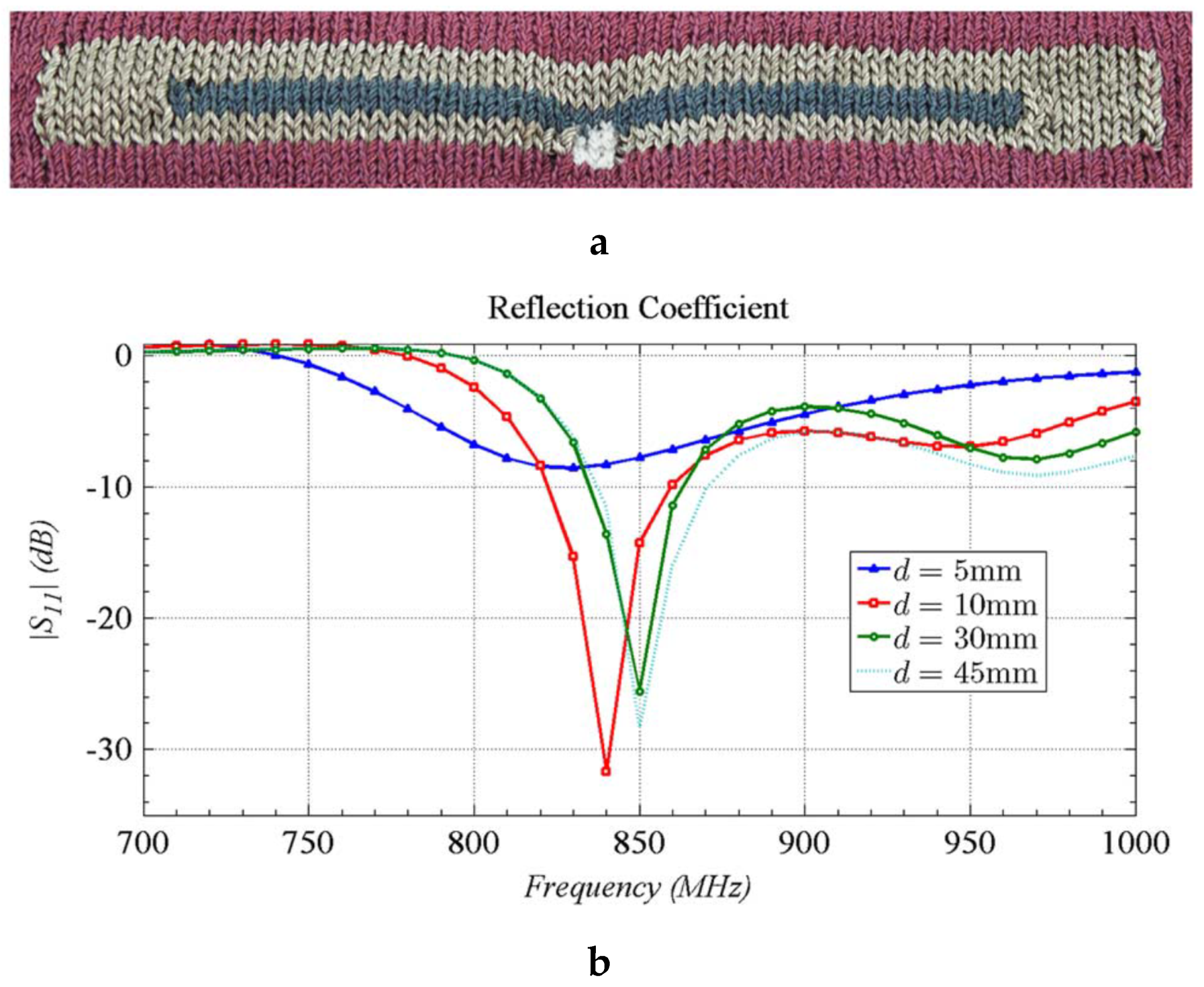
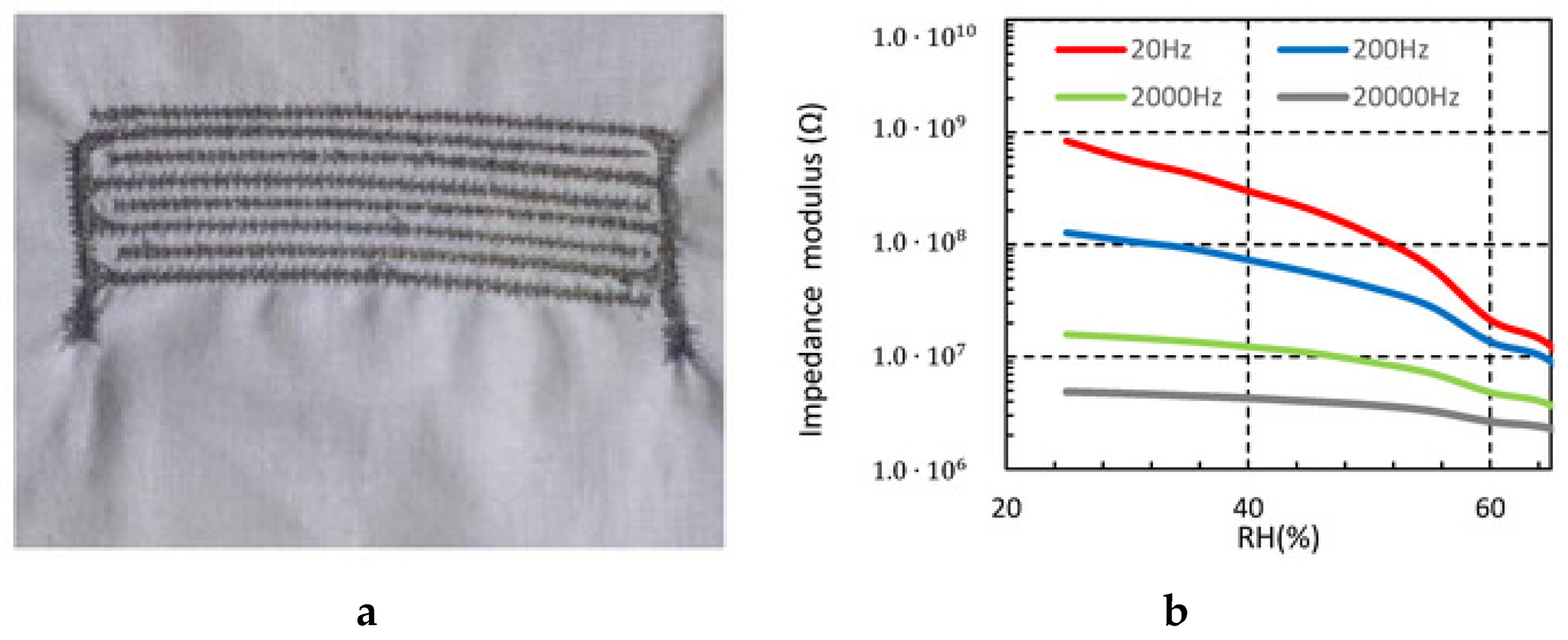
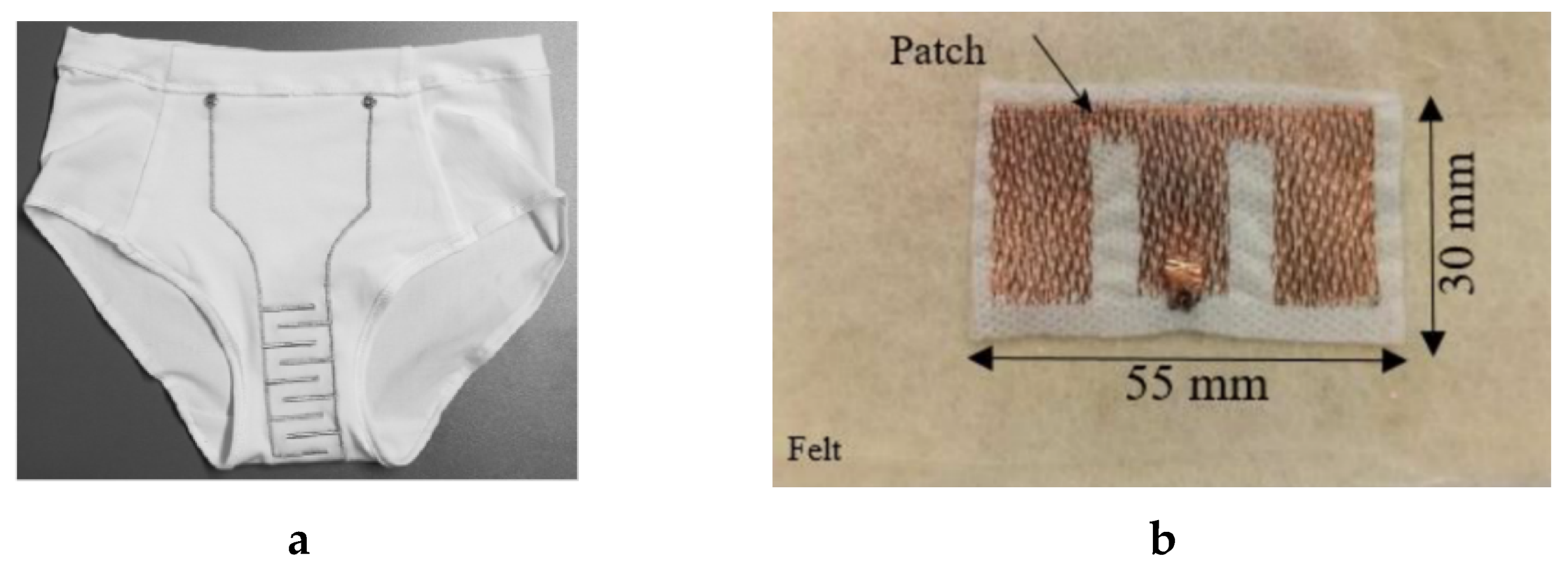
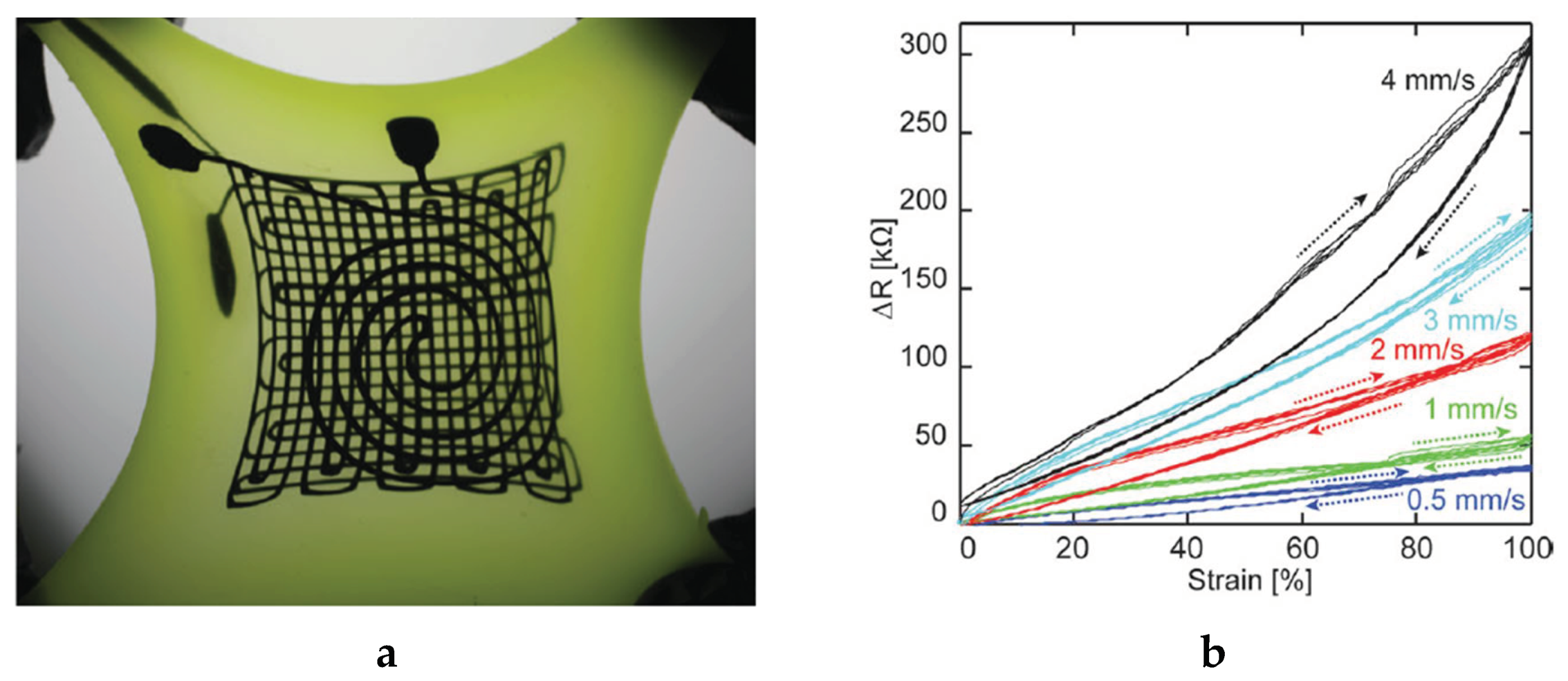
4.2.3. Embroidery
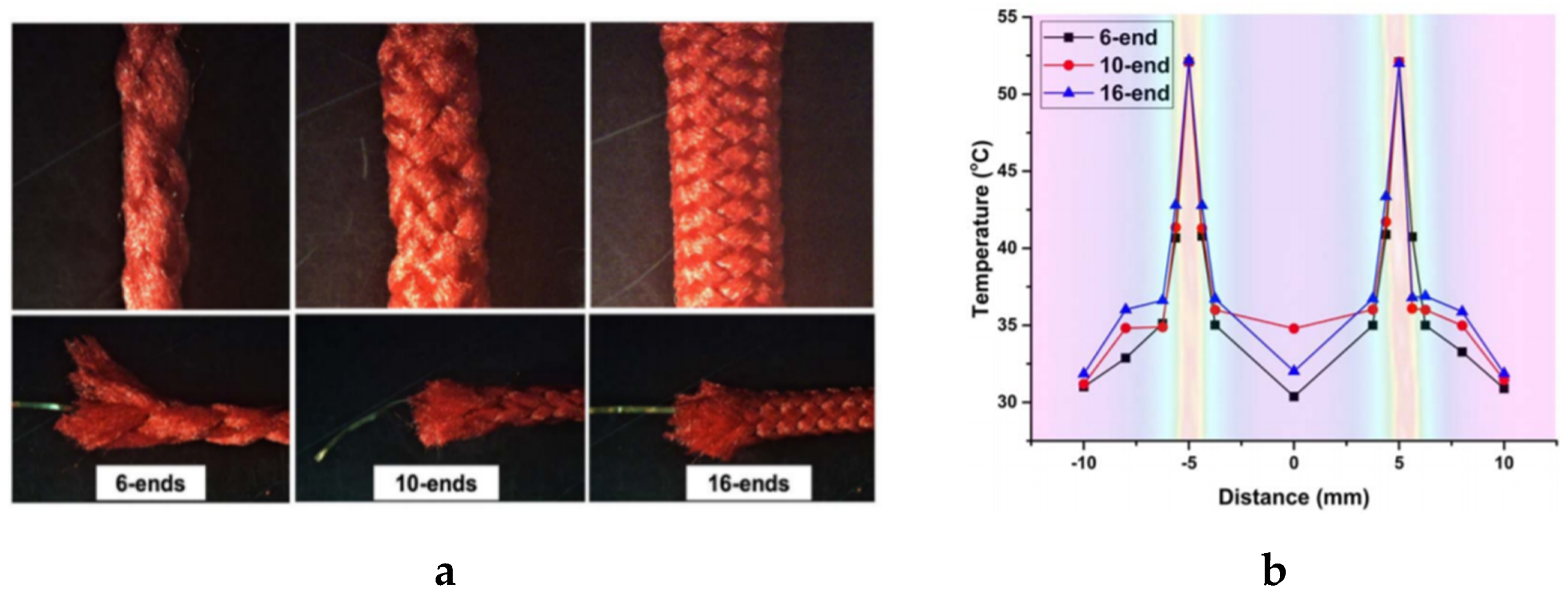
4.2.4. Braiding
4.3. Integration of Conductive Sheets: Laminating
5. Outlook and Future Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tseghai, G.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Van Langenhove, L. The Status of Textile-Based Dry EEG Electrodes. Autex Res. J. 2020. Ahead of Print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CENTEXBEL VKC. Smart Textiles. 2019. Available online: https://www.centexbel.be/en/lexicon/smart-textiles (accessed on 12 February 2019).
- Steele, J.R.; Gho, S.A.; Campbell, T.E.; Richards, C.J.; Beirne, S.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G. The Bionic Bra: Using electromaterials to sense and modify breast support to enhance active living. J. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. Eng. 2018, 5, 205566831877590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable Electronics and Smart Textiles: A Critical Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadi, H.H. Literature over View of Smart Textiles; Boras University: Boras, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, X. Smart Fibres, Fabrics and Clothing, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Seyedin, S.; Razal, J.M.; Innis, P.C.; Jeiranikhameneh, A.; Beirne, S.; Wallace, G.G. Knitted Strain Sensor Textiles of Highly Conductive All-Polymeric Fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 21150–21158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Jug, L.; Meng, E.; Lee, C.; Jug, L.; Meng, E. High strain biocompatible polydimethylsiloxane-based conductive graphene and multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposite strain sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 183511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedin, M.Z.; Razal, J.M.; Innis, P.C.; Wallace, G.G. Strain-responsive polyurethane/PEDOT:PSS elastomeric composite fibers with high electrical conductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2957–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Papadopoulou, E.L.; Athanassiou, A.; Bayer, I.S. Strain-responsive mercerized conductive cotton fabrics based on PEDOT:PSS/grapheme. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Zein, A.; Hupp, C.; Cochrane, C. Development of a Flexible Strain Sensor Based on PEDOT: PSS for Thin Film Structures. Sensors 2017, 17, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, D.; Dess, A.; Saenz-cogollo, J.F.; Barabino, G.; Fraboni, B.; Bonfiglio, A. Fully Textile, PEDOT:PSS Based Electrodes for Wearable ECG Monitoring Systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Cho, G. PU nanoweb-based textile electrode treated with single-walled carbon nanotube/silver nanowire and its application to ECG monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankhili, A.; Tao, X.; Koncar, V.; Coulon, D.; Tarlet, J. Ambulatory Evaluation of ECG Signals Obtained Using Washable Textile-Based Electrodes Made with. Sensors 2019, 19, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achilli, A.; Bonfiglio, A.; Pani, D. Design and characterization of screen-printed textile electrodes for ECG monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 8, 4097–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Stylios, G.K. A hybrid textile electrode for electrocardiogram (ECG) measurement and motion tracking. Materials 2018, 11, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, G.M.; Cao, F.; Torah, R.; Yang, K.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. A smart textile based facial EMG and EOG computer interface. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 14, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, M.O.; Kang, T.; Park, J.; Choi, Y. Knit Band Sensor for Myoelectric Control of Surface EMG-Based Prosthetic Hand. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 8578–8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niijima, A.; Isezaki, T.; Aoki, R.; Watanabe, T. hitoeCap: Wearable EMG Sensor for Monitoring Masticatory Muscles with PEDOT-PSS Textile Electrodes. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Maui, HI, USA, 11–15 September 2017; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Golparvar, A.J.; Yapici, M.K. Electrooculography by Wearable Graphene Textiles. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 8971–8978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-T.; Liao, L.-D.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wang, I.-J.; Lin, B.-S.; Chang, J.-Y. Novel Dry Polymer Foam Electrodes for Long-Term EEG Measurement. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahi, A.; Rai, P.; Oh, S.; Ramasamy, M.; Harbaugh, R.E.; Varadan, V.K. Neural activity based biofeedback therapy for Autism spectrum disorder through wearable wireless textile EEG monitoring system. Nanosens. Biosens. Info-Tech Sens. Syst. 2014, 9060, 90600D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Jian, J.; Tu, T.; Yang, Z.; Ling, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Tian, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Wearable humidity sensor based on porous graphene network for respiration monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 116, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weremczuk, J.; Tarapata, G.; Jachowicz, R. Humidity Sensor Printed on Textile with Use of Ink-Jet Technology. Procedia Eng. 2012, 47, 1366–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.A.B.; Vryonides, P.; Nikolaou, S. Humidity sensor devices using PEDOT:PSS. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–25 July 2015; pp. 1366–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, T.-G.; Park, J.-K.; Yun, G.-H.; Choi, H.H.; Lee, H.-J.; Yook, J.-G. A real-time humidity sensor based on a microwave oscillator with conducting polymer PEDOT:PSS film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslik, J.; Andersson, H.; Forsberg, V.; Engholm, M.; Zhang, R.; Olin, H. PEDOT:PSS temperature sensor ink-jet printed on paper substrate. J. Instrum. 2018, 13, C12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zang, Y.; Huang, D.; Di, C.-A.; Zhu, D. Flexible and self-powered temperature–pressure dual-parameter sensors using microstructure-frame-supported organic thermoelectric materials. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.F.; Lee, K.-F.; Lee, M.-Y. Development of a flexible PDMS capacitive pressure sensor for plantar pressure measurement. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 99, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Nigusse, A.B.; Langenhove, L.V. Development and evaluation of resistive pressure sensors from electro-conductive textile fabric. In Proceedings of the Second International Forum on Textiles for Graduate Students (IFTGS) 2018, Tianjin, China, 30 September 2018; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Macharia, D.K.; Ahmed, S.; Zhu, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Mwasiagi, J.I.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, M. UV/NIR-Light-Triggered Rapid and Reversible Color Switching for Rewritable Smart Fabrics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 13370–13379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesarini, M.; Vasile, F.; Natali, D. Inkjet printed hybrid light sensors based on titanium dioxide and Inkjet printed hybrid light sensors based on titanium dioxide and PEDOT:PSS. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 024005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, A.; Khasim, S.; Ahmed, F.; Dhananjaya, K.N. Fabrication of gas sensor device using poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly (styrenesulfonate)-doped reduced graphene oxide organic thin films for detection of ammonia gas at room temperature. Iran. Polym. J. 2019, 28, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinkeldei, T.; Zysset, C.; Münzenrieder, N.; Tröster, G. An electronic nose on flexible substrates integrated into a smart textile. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 174, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Lin, T.; Hu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Du, Z.; Jin, J.; Zhang, D.; Cui, Z. Double layer printed high performance OLED based on PEDOT:PSS/Ir(bt)2acac:CDBP. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 115112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, G.; Park, J. Improved Intrapixel Thickness Uniformity of Slot-Coated PEDOT:PSS Films for OLEDs via Dilution and Predrying Treatments. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2018, 65, 4506–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yu, J.-L.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Wei, B.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, C.-H.; Yang, Y. Highly efficient red fluorescent organic light-emitting diodes by sorbitol-doped PEDOT:PSS. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 225302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X. Handbook of Smart Textiles, 1st ed.; Springer Science+Business Media: Singapore, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Koncar, V. Smart Textiles and Their Applications; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- van Langenhove, L. Advances in Smart Medical Textiles: Treatments and Health Monitoring; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L. Intelligent Macromolecules for Smart Devices: From Materials Synthesis to Device Applications; Springer: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kirstein, T. Multidisciplinary Know-How for Smart-Textiles Developers, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Ahn, S.; Kim, J.; Jeong, J.; Park, T.H.; Yoon, H.; Hur, J.; Park, J.-J. Textile Speaker Using Polyvinylidene Fluoride/ZnO Nanopillar on Au Textile for Enhancing the Sound Pressure Level. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2018, 10, 1788–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, E.; Luthy, K.; Muth, J.; Mattos, L.S.; Braly, J.; Seyam, A.-F.M.; Ghosh, T.; Dhawan, A.; Natarajan, K. Developing portable acoustic arrays on a large-scale e-textile substrate. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2004, 16, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthy, K.A.; Mattos, L.S.; Braly, J.C.; Grant, E.; Muth, J.F.; Dhawan, A.; Natarajan, K.; Ghosh, T.; Seyam, A. Initial Development of a Portable Acoustic Array on a Large-Scale E-Textile Substrate. MRS Proc. 2002, 736, D3.7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briedis, U.; Valisevskis, A.; Grecka, M. Development of a Smart Garment Prototype with Enuresis Alarm Using an Embroidery-machine-based Technique for the Integration of Electronic Components. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 104, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komolafe, A.O.; Torah, R.N.; Yang, K.; Tudor, J.; Beeby, S.P. Durability of screen printed electrical interconnections on woven textiles. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 65th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), San Diego, CA, USA, 26–29 May 2015; pp. 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Wen, F.; Chen, T. Nano Energy Beyond energy harvesting-multi-functional triboelectric nanosensors on a textile. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, A.; Darabi, S.; Hultmark, S.; Ryan, J.D.; Andersson, B.; Ström, A.; Müller, C. Roll-to-Roll Dyed Conducting Silk Yarns: A Versatile Material for E-Textile Devices. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenBCI. Ultracortex ‘Mark IV’ EEG Headset. 2019. Available online: https://openbci.com/ (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Hertleer, C.; Rogier, H.; Member, S.; Vallozzi, L.; van Langenhove, L. A Textile Antenna for Off-Body Communication Integrated Into Protective Clothing for Firefighters. IEEE Trans. Propag. 2009, 57, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannadhasan, S.; Shagar, A.C. Design and Analysis of U-Shaped Microstrip Patch Antenna. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Information, Communication and Bio-Informatics (AEEICB17) Design, Chennai, India, 27–28 February 2017; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Roshni, S.B.; Jayakrishnan, M.P.; Mohanan, P.; Surendran, K.P. Design and fabrication of an E-shaped wearable textile antenna on PVB-coated hydrophobic polyester fabric. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Fumeaux, C.; Chivers, B.; Shepherd, R. A 5.8-GHz Flexible Microstrip-Fed Slot Antenna Realized in PEDOT:PSS Conductive Polymer. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Fajardo, Puerto Rico, 26 June–1 July 2016; Volume 2015, pp. 1317–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Sun, T.; Fan, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Yang, J.; Jiang, W. Synthesis of freestanding PEDOT:PSS/PVA@Ag NPs nanofiber film for high-performance flexible thermoelectric generator. Polymer 2019, 167, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Arumugam, S.; Tudor, J.; Beeby, S. Screen Printed Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSCs) on Woven Polyester Cotton Fabric for Wearable Energy Harvesting Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 13753–13758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Lim, S.; Sim, J.Y.; Jeon, J.S.; No, K.; Park, S.; Hong, S. Nano Energy Intrinsically stretchable multi-functional fiber with energy harvesting and strain sensing capability. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuri, A.; Colella, S.; Listorti, A.; Rizzo, A.; Mele, C.; Esposito, C. GO/glucose/PEDOT:PSS ternary nanocomposites for fl exible supercapacitors. Compos. Part B 2018, 148, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhou, H.; Li, J. Facile one-step hydrothermal synthesis of PEDOT:PSS/MnO2 nanorod hybrids for high-rate supercapacitor electrode materials. Ionics 2018, 25, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.D.; Smoukov, S.K.; Wang, T. Multidimensional performance optimization of conducting polymer-based supercapacitor electrodes. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2017, 1, 1857–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuramdhani, I.; Malengier, B.; Deferme, W.; de Mey, G.; van Langenhove, L. Charge-Discharge Characteristics of Textile Energy Storage Devices Having Different PEDOT:PSS Ratios and Conductive Yarns Configuration. Polymers 2019, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahariar, H.; Kim, I.; Soewardiman, H.; Jur, J.S. Inkjet Printing of Reactive Silver Ink on Textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6208–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.L.; Saleh, S.M.; Yudin, M.B.M.; Harun, F.K.C.; Sriprachuabwong, C.; Tuantranont, A.; Wicaksono, D.H. Graphene Ink-Coated Cotton Fabric-Based Flexible Electrode for Electrocardiography. In Proceedings of the 2017 5th International Conference on Instrumentation, Communications, Information Technology, and Biomedical Engineering (ICICI-BME), Bandung, Indonesia, 6–7 November 2017; pp. 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangakameshwaran, N.; Santhoskumar, A.U. Cotton Fabric Dipped in Carbon Nano Tube Ink for Smart Textile Applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2014, 63, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.-C.; Ku, H.-J.; Cho, C.-J.; Chen, W.-C.; Lee, W.-Y.; Chen, W.-C.; Rwei, S.-P.; Borsali, R.; Kuo, C.-C. An intrinsically stretchable and ultrasensitive nanofiber-based resistive pressure sensor for wearable electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 5361–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Tian, M.; Qu, L.; Zhu, S.; Han, G. Multifunctional cotton fabrics with graphene/polyurethane coatings with far-infrared emission, electrical conductivity, and ultraviolet-blocking properties. Carbon 2015, 95, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, B.S.; Chen, W.; Doty, C.; Xu, C.; Kotov, N.A. Smart Electronic Yarns and Wearable Fabrics for Human Biomonitoring made by Carbon Nanotube Coating with Polyelectrolytes. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4151–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, R.; Khair, N.; Ahmed, D.M.; Shahariar, H. Fabrication of low cost and scalable carbon-based conductive ink for E-textile applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 19, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugetsu, B.; Sano, E.; Yu, H.; Mori, K.; Tanaka, T. Graphene oxide as dyestuffs for the creation of electrically conductive fabrics. Carbon 2010, 48, 3340–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulan, L.; Zhi, L.; Lan, C.; Sihao, C.; Dayang, W.; Fangyin, D. Reduced Graphene Oxide Coated Silk Fabrics with Conductive Property for Wearable Electronic Textiles Application. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, S.J.P.; Yang, K.; Braveenth, R.; Raagulan, K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.S.; Yang, C.-M.; Jung, M.J.; Chai, K.Y. MWCNT Coated Free-Standing Carbon Fiber Fabric for Enhanced Performance in EMI Shielding with a Higher Absolute EMI SE. Materials 2017, 10, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, C.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Liang, T.; Wei, Z.; Run, M.; Yan, X.; Liu, X. Flexible Graphene Electrodes for Prolonged Dynamic ECG Monitoring. Sensors 2016, 16, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.J.; Mieno, T. Conductive Cotton Textile from Safely Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Qiang, Z.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; You, Z.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Ye, C. Multi-functional and Highly Conductive Textiles with Ultra-high Durability through ‘Green’ Fabrication Process. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 406, 127140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, K.; Tabor, J.; Ghosh, T.K. Electrically Conductive Coatings for Fiber-Based E-Textiles. Fibers 2019, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Chakrabarty, T.; Singh, A.K.; Shahi, V.K. Polymer thin films embedded with metal nanoparticles for electrochemical biosensors applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Chatterjee, A. Polypyrrole Based Electro-Conductive Cotton Yarn. J. Text. Sci. Eng. 2014, 4, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, A.; Pani, D.; Bonfiglio, A. Characterization of Screen-Printed Textile Electrodes Based on Conductive Polymer for ECG Acquisition. In Proceedings of the 2017 Computing in Cardiology Conference, Rennes, France, 24–27 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, K.N.A.; Mohanta, K. Preparation of Highly Conductive Yarns by an Optimized Impregnation Process. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 47, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillón, R.; Pérez, J.J.; Andrade-Caicedo, H. Electrical performance of PEDOT:PSS-based textile electrodes for wearable ECG monitoring: A comparative study. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellomäki, T.; Virkki, J.; Merilampi, S.; Ukkonen, L. Towards Washable Wearable Antennas: A Comparison of Coating Materials for Screen-Printed Textile-Based UHF RFID Tags. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Xu, L.; Yan, D.-X.; Li, Z.-M. Conductive polymer composites with segregated structures. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1908–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Chatterjee, A. Textile/Polypyrrole Composites for Sensory Applications. J. Compos. 2015, 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Nigusse, A.B.; van Langenhove, L. Development of a Flex and Stretchy Conductive Cotton Fabric Via Flat Screen Printing of PEDOT:PSS/PDMS Conductive Polymer Composite. Sensors 2020, 20, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, J.F.; Grohens, Y. Electrical response of Poly(styrene)/carbon black conductive polymer composites (CPC) to methanol, toluene, chloroform and styrene vapors as a function of filler nature and matrix tacticity. Synth. Met. 2005, 154, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadim, M.F.; Imani, A.; Farzi, G. Synthesis of PPy–silver nanocomposites via in situ oxidative polymerization. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2014, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Bac, L.H.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, B.-K.; Kim, J.-C. Synthesis and Characterization of Conducting Polyaniline-Copper Composites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 7728–7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loryuenyong, V.; Khadthiphong, A.; Phinkratok, J.; Watwittayakul, J.; Supawattanakul, W.; Buasri, A. The fabrication of graphene-polypyrrole composite for application with dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 17, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-X.; Liu, H.-H.; Wang, J.-P.; Zhang, X.-X. Thermoelectric behavior of PEDOT:PSS/CNT/graphene composites. J. Polym. Eng. 2018, 38, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafti, A.; Manero, R.B.R.; Borg, A.M.; Althoefer, K.; Howard, M.J. Embroidered Electromyography: A Systematic Design Guide. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 25, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Tennant, A.; Langley, R.J.; Hurley, W.; Dias, T. A knitted textile waveguide. In Proceedings of the 2014 Loughborough Antennas and Propagation Conference (LAPC), Loughborough, UK, 10–11 November 2014; Volume 1, pp. 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkonen, J.; Pouta, E. Flexible Wire-Component for Weaving Electronic Textiles. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 66th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 May–3 June 2016; pp. 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Xu, N.; Kan, Q.; Li, H.; Lu, C.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X. Wet-Spinning Assembly of Continuous, Highly Stable Hyaluronic/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Microfibers. Polymers 2019, 11, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pragya, A.; Singh, H.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, H.; Shankar, P. Designing and investigation of braided-cum-woven structure for wearable heating textile. Eng. Res. Express 2020, 2, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhu, L.; Xue, J.; Hao, L.; Jin, L.; He, Y.; Cheng, B. A Novel Two-Step Method for Fabricating Silver Plating Cotton Fabrics. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baurley, S. Interactive and experiential design in smart textile products and applications. Pres. Ubiquit. Comput. 2004, 8, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.; Choi, H.-J.; Kim, H.; Yeo, S.Y. Properties of Conductive Polyacrylonitrile Fibers Prepared by Using Benzoxazine Modified Carbon Black. Polymers 2020, 12, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, J.C. Electrically Conductive Poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)–Polystyrene Sulfonic Acid/Polyacrylonitrile Composite Fibers Prepared by Wet Spinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzuan, N.A.M.; Sulong, A.B.; Somalu, M.R. Extrusion Process of Polypropylene Composites Reinforced Milled Carbon Fibre for Conductive Polymer Composite Application. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences: 4th Engineering Science and Technology International Conference (ESTIC 2018), Padang, West Sumatra, Indonesia, 28–29 August 2018; Volume 248, p. 01012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerfeldt, M.; Nilsson, E.; Gillgard, P.; Walkenström, P. Textile piezoelectric sensors—Melt spun bi-component poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibres with conductive cores and poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene)-poly(styrene sulfonate) coating as the outer electrode. Fash. Text. 2014, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Tuo, X. Preparation of polypyrrole coated cotton conductive fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankhili, A.; Tao, X.; Cochrane, C.; Coulon, D.; Koncar, V. Washable and Reliable Textile Electrodes Embedded into Underwear Fabric for Electrocardiography (ECG) Monitoring. Materials 2018, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Mengistie, D.A.; Fante, K.A.; van Langenhove, L. Knitted Cotton Fabric Strain Sensor by In-situ Polymerization of Pyrrole. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Intelligent Textiles & Mass Customization, Marrakech, Morocco, 13–15 November 2019; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 827, p. 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
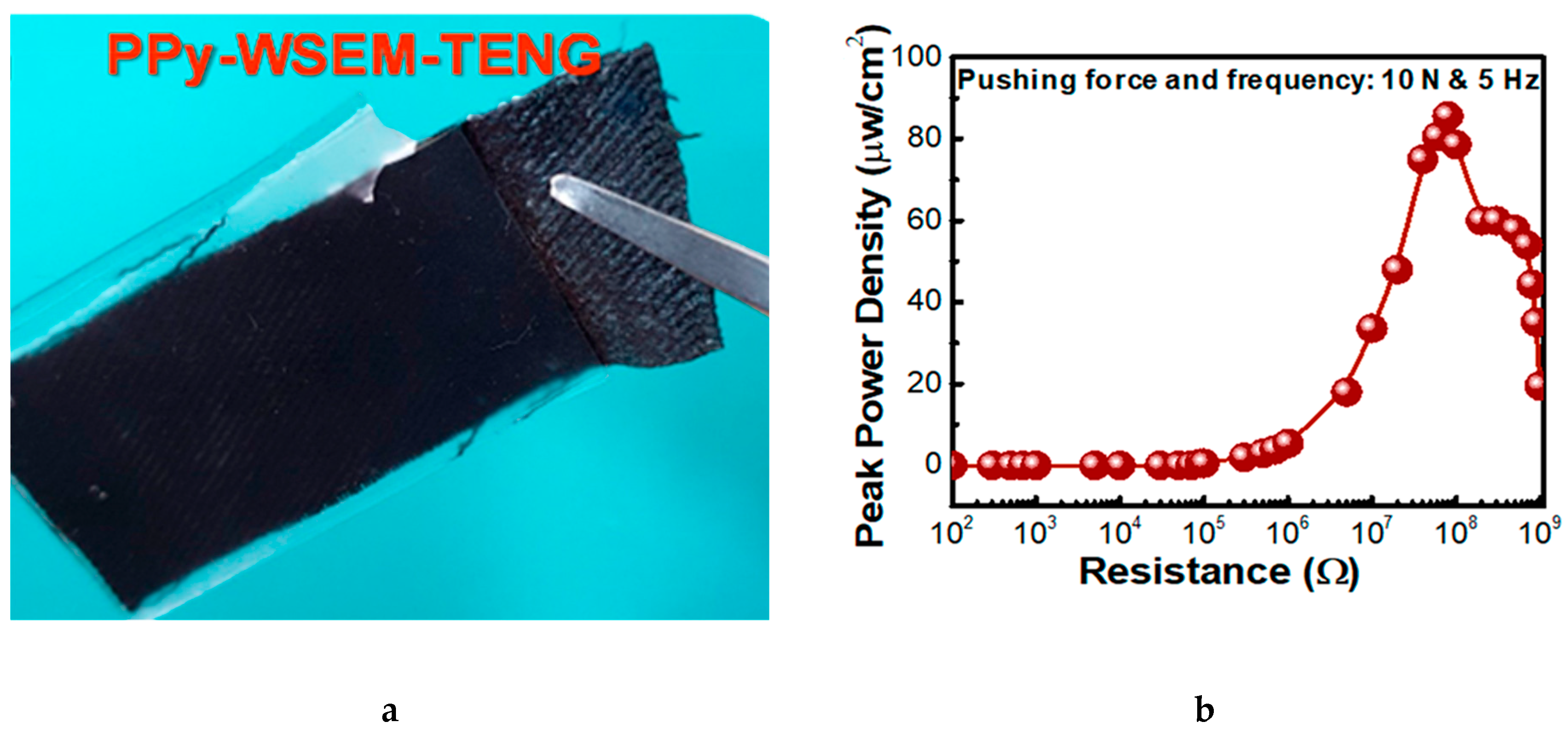
- Mule, A.R.; Dudem, B.; Patnam, H.; Graham, S.A.; Yu, J.S. Wearable Single-Electrode-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator via Conductive Polymer-Coated Textiles for Self-Power Electronics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 16450–16458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maqdasi, Z.; Hajlane, A.; Renbi, A.; Ouarga, A.; Chouhan, S.S.; Joffe, R. Conductive Regenerated Cellulose Fibers by Electroless Plating. Fibers 2019, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardianto, H.; Mey, G.D.; Malengier, B.; Hertleer, C.; Langenhove, V. Characterization of Carbon-Nickel thermocouples integrated in textile fabrics. In Proceedings of the AUTEX2019: 19th World Textile Conference on Textiles at the Crossroads, Ghent, Belgium, 11–15 June 2019; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.M.; Thilagavathi, G. Design and Development of Textile Electrodes for EEG Measurement using Copper Plated Polyester Fabrics. J. Text. Appar. Technol. Manag. 2014, 8, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Xu, R.; Wang, W.; Yu, D. A wearable, anti-bacterial strain sensor prepared by silver plated cotton/spandex blended fabric for human motion monitoring. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 582, 123918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, W.; Wright, T.; Caven, B.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Flexible Textile Strain Sensor Based on Copper-Coated Lyocell Type Cellulose Fabric. Polymers 2019, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willfahrt, A. Screen Printing Technology for Energy Devices. Ph.D. Thesis, Linköping Univeristy, Linköping, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kazani, I. Study of Screen-Printed Electroconductive Textile Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nigusse, A.B.; Malengier, B.; Mengistie, D.A.; Tseghai, G.B.; van Langenhove, L. Development of Washable Silver Printed Textile Electrodes for Long-Term ECG Monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzetuska, E.; Puchalski, M.; Krucińska, I. Chemically Driven Printed Textile Sensors Based on Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes. Sensors 2014, 14, 16816–16828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Nigusse, A.B.; Etana, B.B.; van Langenhove, L. PEDOT:PSS/PDMS-coated cotton fabric for ECG electrode. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Manchester, UK, 16–19 August 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauraya, A.; Whittow, W.G.; Vardaxoglou, J.C.; Li, Y.; Torah, R.; Yang, K.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. Inkjet printed dipole antennas on textiles for wearable communications. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2013, 7, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Arumugam, S.; Krishnan, C.; Charlton, M.D.B.; Beeby, S.P. Encapsulated Textile Organic Solar Cells Fabricated by Spray Coating. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, S.; Li, Y.; Senthilarasu, S.; Torah, R.; Kanibolotsky, A.L.; Inigo, A.R.; Skabara, P.J.; Beeby, S.P. Fully spray-coated organic solar cells on woven polyester cotton fabric for wearable energy harvesting applications. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 5561–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, N.; Abd-Ellah, M.; Goldthorpe, I.A. Transfer printing of silver nanowire conductive ink for e-textile applications. Flex. Print. Electron. 2019, 4, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Kim, B.; Son, Y.K.; Kim, J.E.; Cho, I.-Y. A flexible textile wristwatch using Transfer Printed Textile Circuit technique. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–15 January 2012; pp. 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauraya, A.; Seager, R.; Whittow, W.; Zhang, S.; Vardaxoglou, Y. Embroidered Frequency Selective Surfaces on textiles for wearable applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 Loughborough Antennas & Propagation Conference (LAPC), Loughborough, UK, 11–12 November 2013; pp. 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-naiemy, Y.; Elwi, T.A.; Khaleel, H.R.; Al-rizzo, H. A Systematic Approach for the Design, Fabrication, and Testing of Microstrip Antennas Using Inkjet Printing Technology A Systematic Approach for the Design, Fabrication, and Testing of Microstrip Antennas Using Inkjet Printing Technology. ISRN Commun. Netw. 2012, 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidmar, T.; Topič, M.; Dzik, P.; Krašovec, U.O. Inkjet printing of sol-gel derived tungsten oxide inks. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 125, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Brent, J.R.; Ding, H.; Yang, J.; Lewis, D.J.; O’Brien, P.; Derby, B. Fully printed high performance humidity sensors based on two-dimensional materials. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 5599–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidik, H.; Dupont, D.; Bedek, G. Development of a radiative heat fluxmeter with a textile substrate. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2018, 271, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, D.; Choi, A.Y.; Kim, Y.T. Flexible single-strand fiber-based woven-structured triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered electronics. APL Mater. 2018, 6, 101106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patron, D.; Mongan, W.; Kurzweg, T.P.; Fontecchio, A.; Dion, G.; Anday, E.K.; Dandekar, K.R. On the Use of Knitted Antennas and Inductively Coupled RFID Tags for Wearable Applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2016, 10, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, A.; Hurley, W.; Dias, T. Knitted, textile, high impedance surface with integrated conducting vias. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; He, Q.; Meng, K.; Tan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Machine-knitted washable sensor array textile for precise epidermal physiological signal monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, B.; Fernández-García, R.; Gil, I. E-textile embroidered metamaterial transmission line for signal propagation control. Materials 2018, 11, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Estrada, M.; Moradi, B.; Fernández-Garcia, R.; Gil, I. Impact of manufacturing variability and washing on embroidery textile sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, S.; Chaudhari, S.; Inshaar, A.; Shah, H.; Zou, C.; Harne, R.L.; Kiourti, A. E-Textile Origami Dipole Antennas with Graded Embroidery for Adaptive RF Performance. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 2218–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadzade, B.; Hashmi, R.M.; Simorangkir, R.B.V.B.; Gharaei, R.; Rehman, S.U.; Abbasi, Q.H. Recent Advances in Fabrication Methods for Flexible Antennas in Wearable Devices: State of the Art. Sensors 2019, 19, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The mechanics of the braiding process. In Braiding Technology for Textiles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 177–209.
- Vanveerdeghem, P.; van Torre, P.; Stevens, C.; Knockaert, J.; Rogier, H. Synchronous Wearable Wireless Body Sensor Network Composed of Autonomous Textile Nodes. Sensors 2014, 14, 18583–18610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, S. Method for Preparing Fabric Laminate. U.S. Patent No. 3383263, 14 May 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; McCutcheon, J.W. Tapes and Articles Therefrom. U.S. Patent No. 2016/0333232 A1, 19 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wagih, M.; Weddell, A.S.; Beeby, S. Overcoming the Efficiency Barrier of Textile Antennas: A Transmission Lines Approach. Proceedings 2019, 32, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Mengistie, D.A.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; van Langenhove, L. PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Textiles and Their Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, E.; Rahiminejad, S.; Enoksson, P. Evaluation of 3D printed materials used to print WR10 horn antennas. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 757, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, T.; Williams, J. 3D Printing; Chery Lake Publishing: Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bellacicca, A.; Santaniello, T.; Milani, P. Embedding electronics in 3D printed structures by combining fused filament fabrication and supersonic cluster beam deposition. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 24, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Chen, K.; Dunn, C.K.; Wu, J.; Li, V.C.F.; Qi, H.J. 3D Printing of Highly Stretchable, Shape-Memory, and Self-Healing Elastomer toward Novel 4D Printing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7381–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwala, S.; Goh, G.L.; Yap, Y.L.; Yu, H.; Yeong, W.Y.; Tran, T. Development of bendable strain sensor with embedded microchannels using 3D printing. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2017, 263, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muth, J.T.; Vogt, D.M.; Truby, R.L.; Mengüç, Y.; Kolesky, D.B.; Wood, R.J.; Lewis, J.A. Embedded 3D Printing of Strain Sensors within Highly Stretchable Elastomers. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6307–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayate, A.; Jain, P.K. A Review on 4D Printing Material Composites and Their Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 20474–20484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Nigusse, A.B.; Van Langenhove, L. Integration of Conductive Materials with Textile Structures, an Overview. Sensors 2020, 20, 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236910
Tseghai GB, Malengier B, Fante KA, Nigusse AB, Van Langenhove L. Integration of Conductive Materials with Textile Structures, an Overview. Sensors. 2020; 20(23):6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236910
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseghai, Granch Berhe, Benny Malengier, Kinde Anlay Fante, Abreha Bayrau Nigusse, and Lieva Van Langenhove. 2020. "Integration of Conductive Materials with Textile Structures, an Overview" Sensors 20, no. 23: 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236910
APA StyleTseghai, G. B., Malengier, B., Fante, K. A., Nigusse, A. B., & Van Langenhove, L. (2020). Integration of Conductive Materials with Textile Structures, an Overview. Sensors, 20(23), 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236910