Ionospheric Phase Compensation for InSAR Measurements Based on the Faraday Rotation Inversion Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Ionosphere Effects on Radar Interferometry
2.2. Derivation of the FR Inversion Method
2.2.1. FR Calculation Based on Appleton-Hartree Formula
2.2.2. Estimation of FR Angle from Full-polarimetric SAR Images
2.2.3. Ionospheric Phase Calculation
2.2.4. Accuracy of the FR-TEC Inversion Method
3. Materials and Implementation
3.1. Datasets and Study Area
3.2. Experiment Implementation
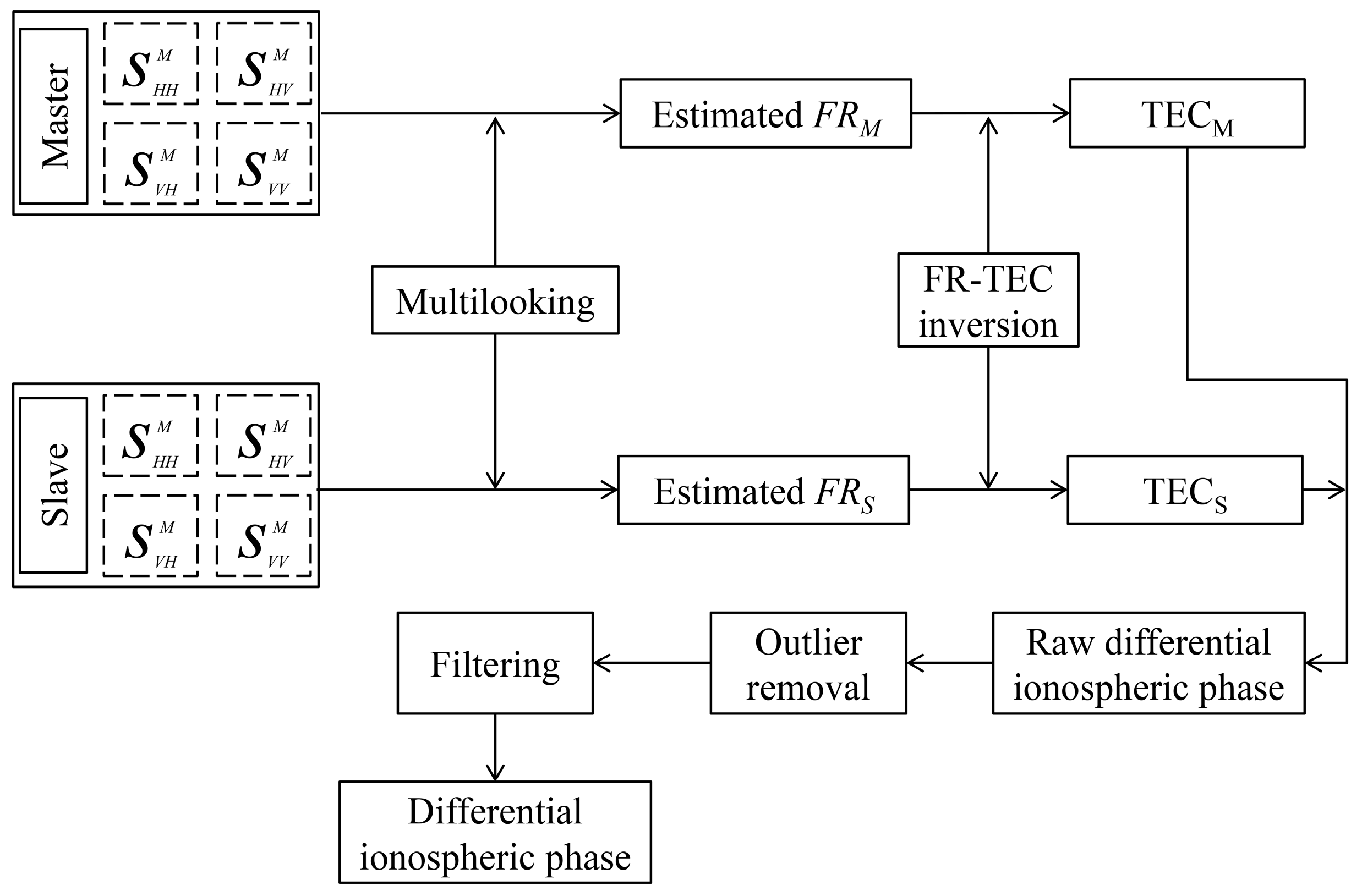
3.2.1. Data Processing for the FR Inversion Method
3.2.2. Ionospheric Phase Compensation for SAR Interferograms
4. Experimental Results
4.1. FR Estimation
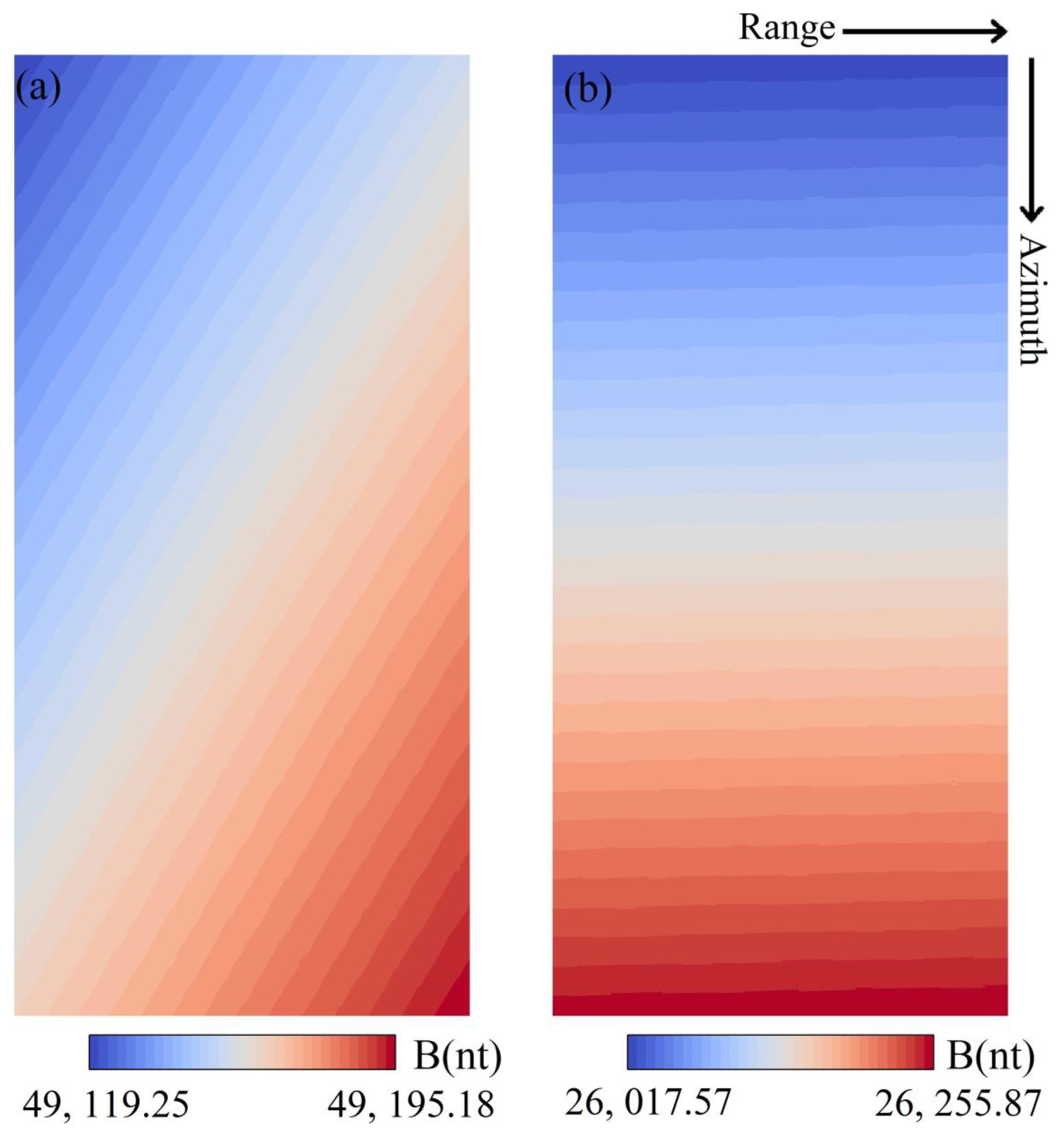
4.2. Magnetic Field Calculation
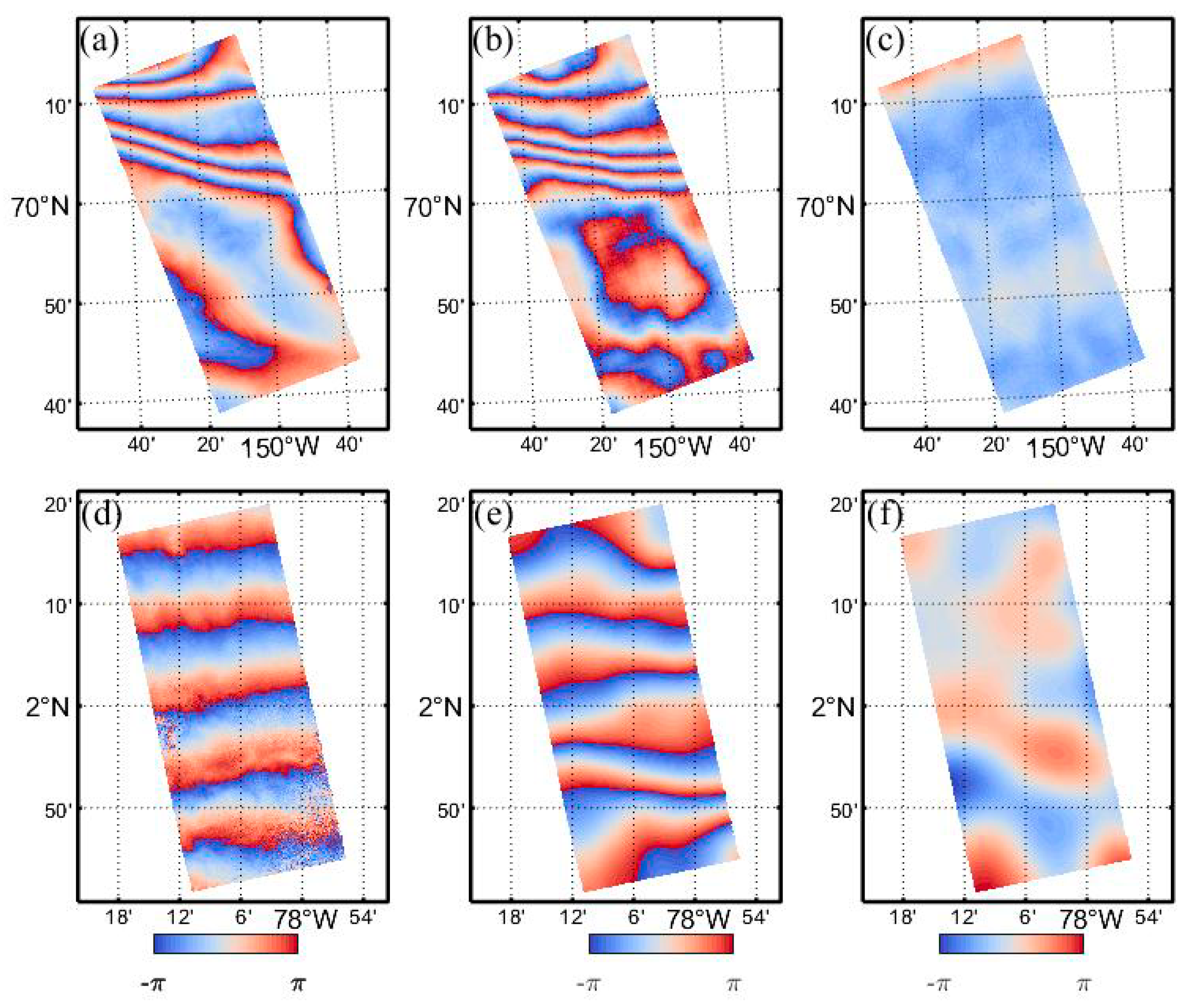
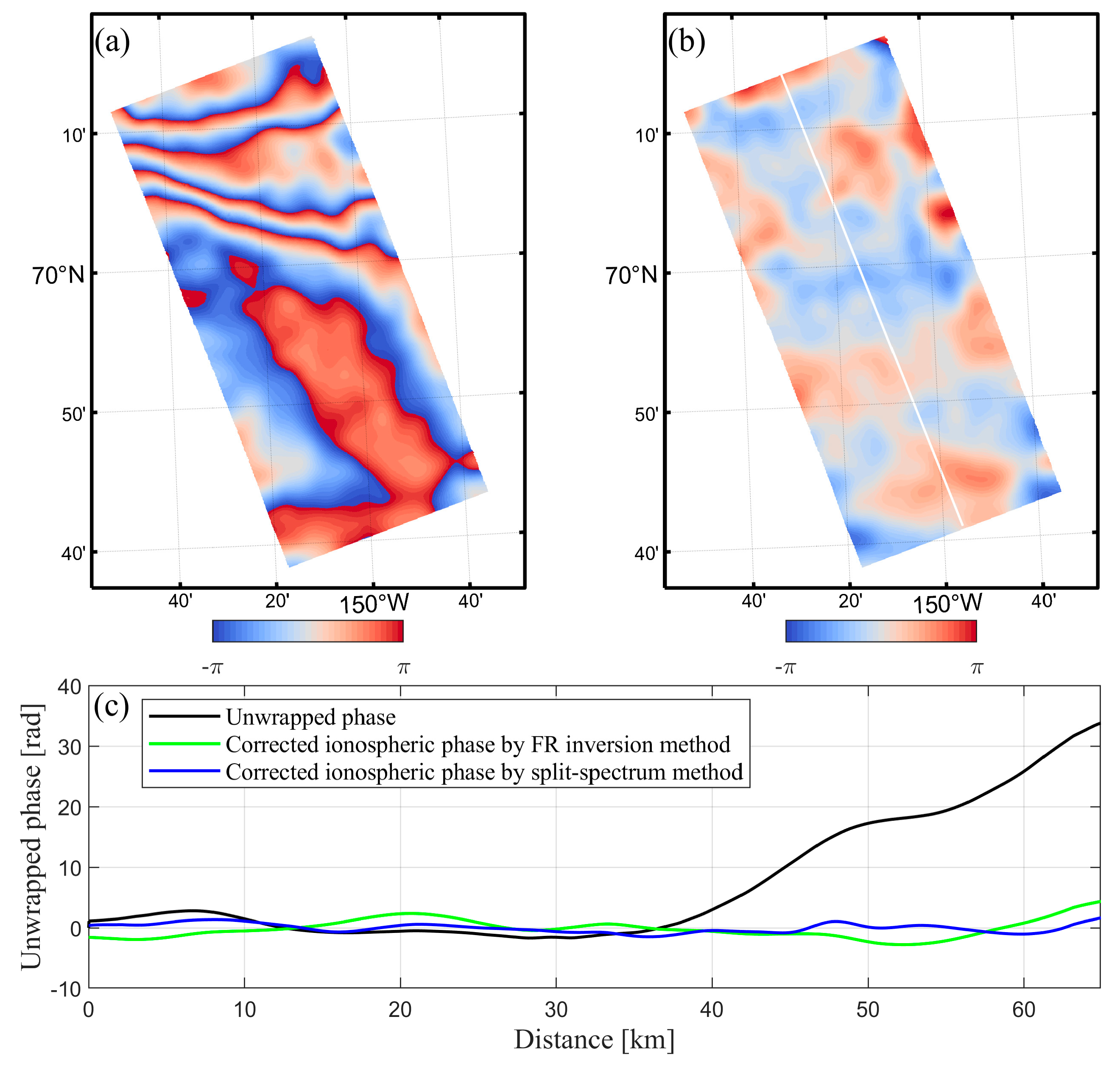
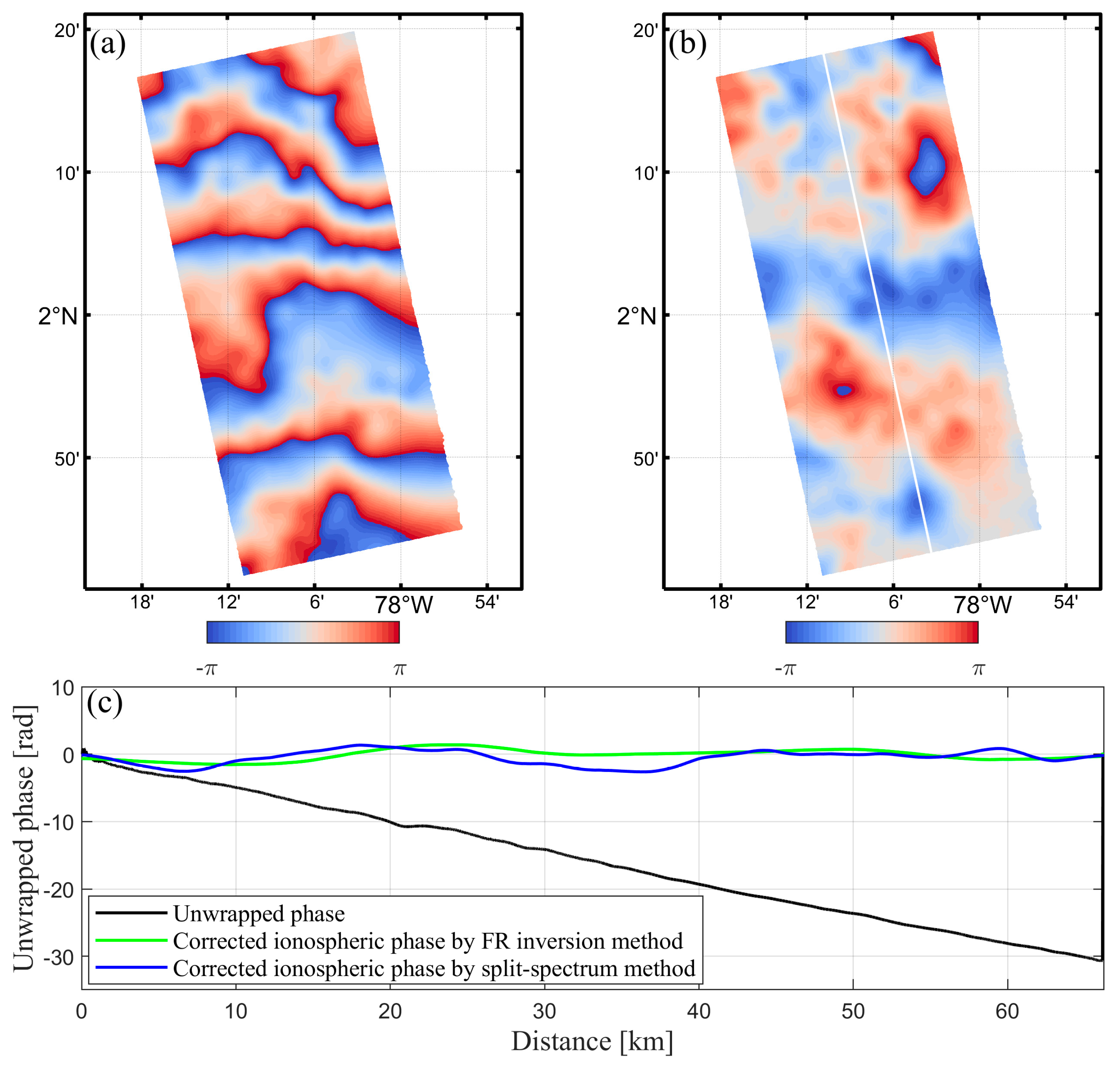
4.3. Ionospheric Phase Compensation
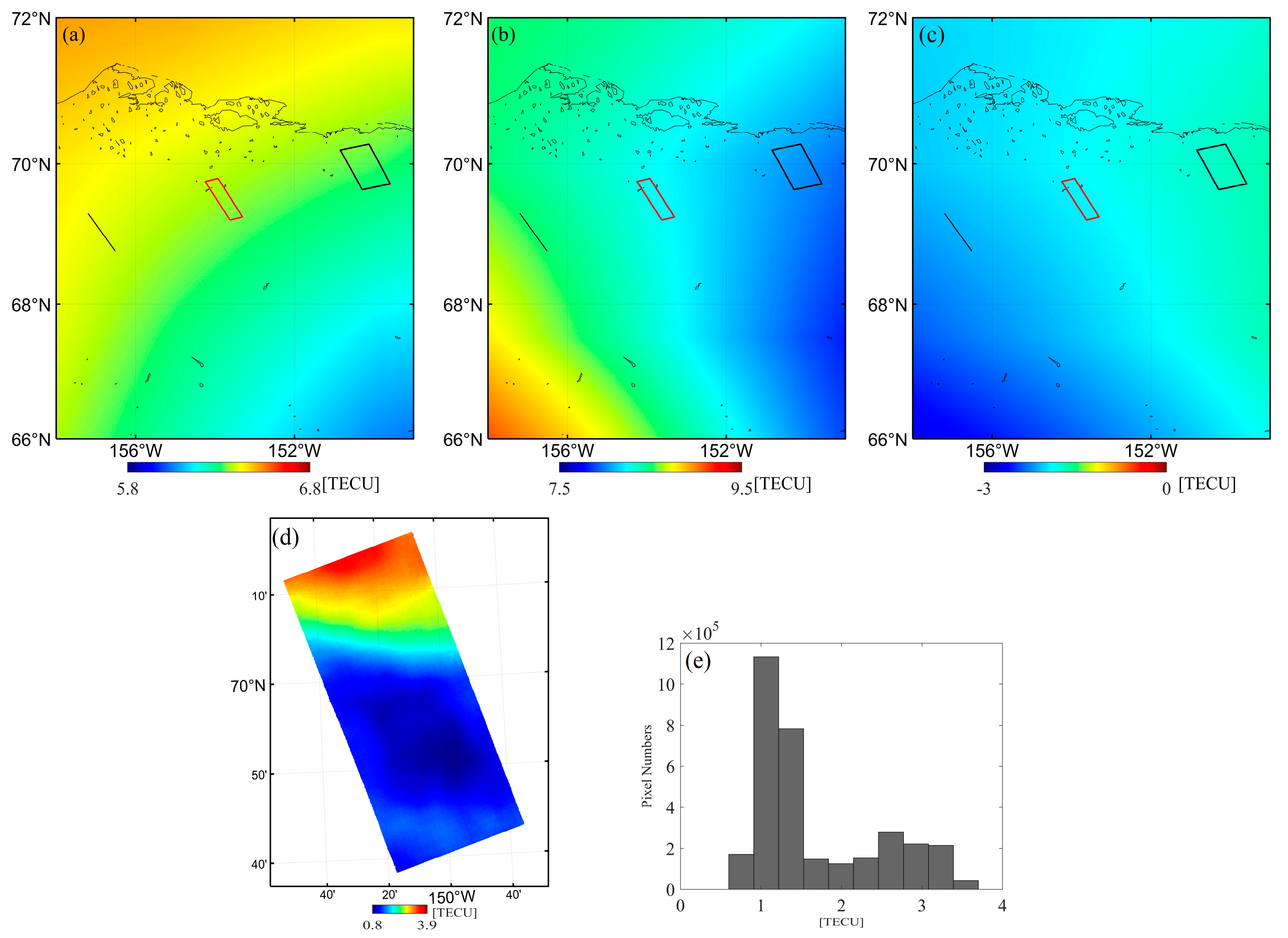
5. Validation and Discussion
5.1. Comparison with the Split-Spectrum Method
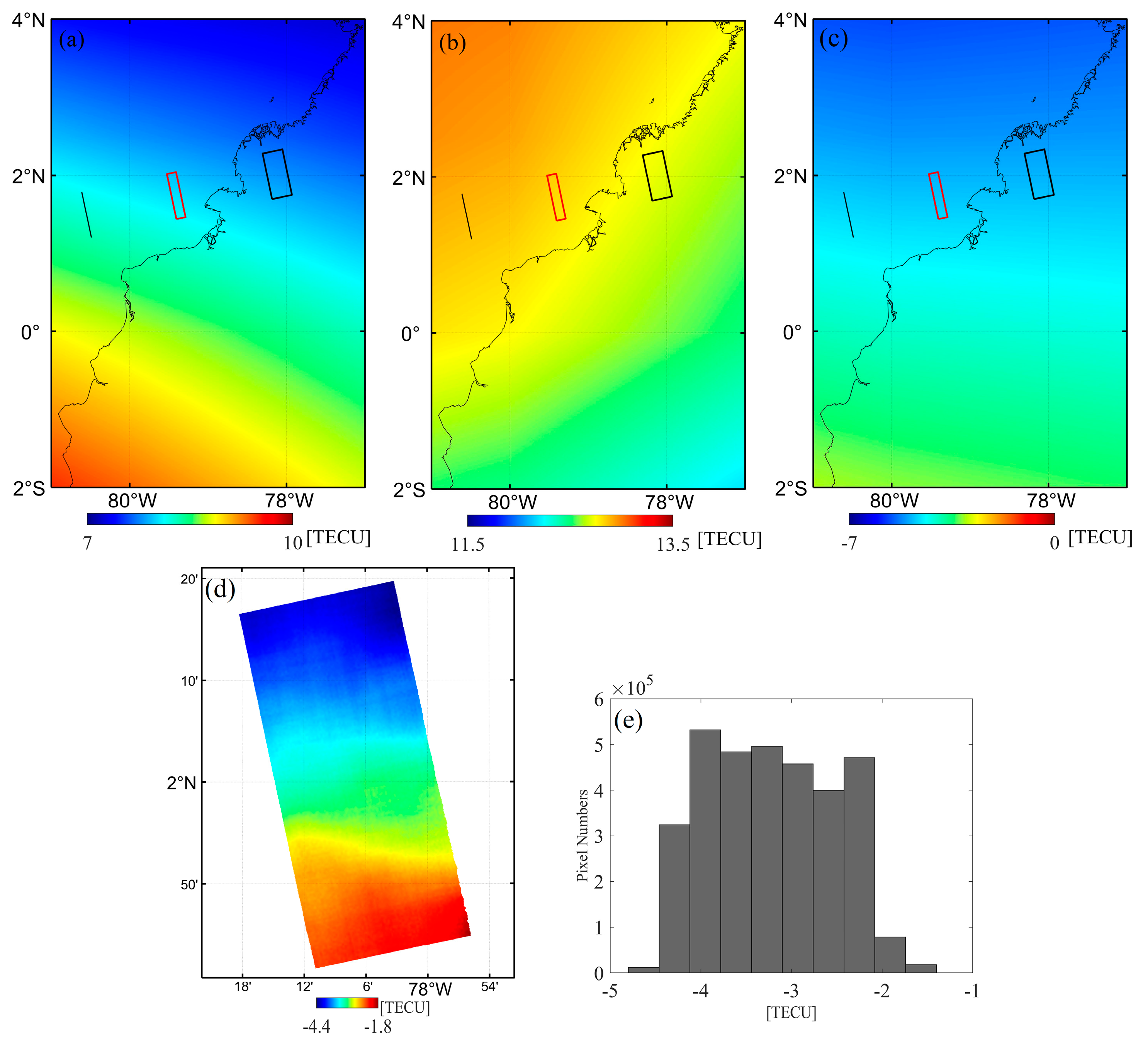
5.2. Comparison with TEC Maps
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, L.C. Emerging applications of interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) in geomorphology and hydrology. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2002, 92, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.L.; Mattar, K.E.; Sofko, G. Influence of ionospheric electron density fluctuations on satellite radar interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1451–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, E.; Chan, S.F.; Chapman, B.D.; Chen, C.W.; Martin, J.M.; Michel, T.R.; Muellerschoen, R.J.; Pi, X.; Rosen, P.A. Impact of the ionosphere on an L-band space based radar. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, NY, USA, 24–27 April 2006; pp. 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, F.J.; Nicoll, J. The impact of the ionosphere on interferometric SAR processing. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2008—2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008; pp. II-391–II-394. [Google Scholar]
- Belcher, D.; Rogers, N. Theory and simulation of ionospheric effects on synthetic aperture radar. IET RadarSonar Navig. 2009, 3, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.S. A survey of ionospheric effects on space-based radar. Waves Random Media 2004, 14, S189–S273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.; Bamler, R.; Jakowski, N.; Fritz, T. The potential of low-frequency SAR systems for mapping ionospheric TEC distributions. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.; Bamler, R.; Jakowski, N.; Fritz, T. The potential of broadband L-band SAR systems for small scale ionospheric TEC mapping. In Proceedings of the Fringe 2005 Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 28 November–2 December 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, F.J. Quantifying ionosphere-induced image distortions in L-band SAR data using the ionospheric scintillation model WBMOD. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2014, 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Berlin, Germany, 3–5 June 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, F. A review of ionospheric effects in low-frequency SAR—Signals, correction methods, and performance requirements. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Raucoules, D.; De Michele, M. Assessing ionospheric influence on L-band SAR data: Implications on coseismic displacement measurements of the 2008 Sichuan earthquake. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 7, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-S.; Lee, D.-T.; Lu, Z.; Won, J.-S. Ionospheric correction of SAR interferograms by multiple-aperture interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 51, 3191–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-S.; Lee, W.-J. An improvement of ionospheric phase correction by multiple-aperture interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4952–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strozzi, T.; Luckman, A.; Murray, T.; Wegmuller, U.; Werner, C.L. Glacier motion estimation using SAR offset-tracking procedures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2384–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechor, N.B.; Zebker, H.A. Measuring two-dimensional movements using a single InSAR pair. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brcic, R.; Parizzi, A.; Eineder, M.; Bamler, R.; Meyer, F. Estimation and compensation of ionospheric delay for SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 2908–2911. [Google Scholar]
- Brcic, R.; Parizzi, A.; Eineder, M.; Bamler, R.; Meyer, F. Ionospheric effects in SAR interferometry: An analysis and comparison of methods for their estimation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 1497–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Gomba, G.; Parizzi, A.; De Zan, F.; Eineder, M.; Bamler, R. Toward operational compensation of ionospheric effects in SAR interferograms: The split-spectrum method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 54, 1446–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomba, G.; González, F.R.; De Zan, F. Ionospheric phase screen compensation for the Sentinel-1 TOPS and ALOS-2 ScanSAR modes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 55, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, H.; Simons, M.; Agram, P. InSAR time-series estimation of the ionospheric phase delay: An extension of the split range-spectrum technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5984–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, C.; Ding, X.; Zhu, W.; Wu, S. Correction of ionospheric artifacts in SAR data: Application to fault slip inversion of 2009 Southern Sumatra Earthquake. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milczarek, W.; Kopeć, A.; Głąbicki, D. Estimation of Tropospheric and Ionospheric Delay in DInSAR Calculations: Case Study of Areas Showing (Natural and Induced) Seismic Activity. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Fu, H.; Zhu, J.; Zuo, T. A Framework for Correcting Ionospheric Artifacts and Atmospheric Effects to Generate High Accuracy InSAR DEM. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X. Ionospheric effects on spaceborne synthetic aperture radar and a new capability of imaging the ionosphere from space. Space Weather 2015, 13, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.; Freeman, A.; Chapman, B.; Rosen, P.; Li, Z. Imaging ionospheric inhomogeneities using spaceborne synthetic aperture radar. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoll, J.B.; Meyer, F.J. Mapping the ionosphere using L-band SAR data. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2008—2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008; pp. II-537–II-540. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Ding, X.-L.; Jung, H.-S.; Zhang, Q. Mitigation of ionospheric phase delay error for SAR interferometry: An application of FR-based and azimuth offset methods. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Jung, H.-S.; Chen, J.-Y. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (InSAR) Ionospheric Correction Based on Faraday Rotation: Two Case Studies. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, J.; Schuh, H. Atmospheric Effects in Space Geodesy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, J.; Scherliess, L.; Schunk, R.; Thompson, D. Spatial correlations of day-to-day ionospheric total electron content variability obtained from ground-based GPS. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, D. Theoretical limits on SAR imposed by the ionosphere. IET RadarSonar Navig. 2008, 2, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A. Calibration of linearly polarized polarimetric SAR data subject to Faraday rotation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, S.; Bates, R. Effects of magneto-ionic propagation on the polarization scattering matrix. Proc. IEEE 1965, 53, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.-Y.; Jin, Y.-Q. Analysis of the Effects of Faraday Rotation on Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Observations at P-Band. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Quegan, S. Improved estimators of Faraday rotation in spaceborne polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Dong, Z. Faraday rotation angle estimation from polarimetric covariance matrix. In Proceedings of the IET International Radar Conference 2013, Xi’an, China, 14–16 April 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, Z.; An, J.; Zhou, C.; Chen, Y. A New Faraday Rotation Estimator Based on Polarimetric Coherency Matrix and its Effect on Sea Ice. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 4571–4574. [Google Scholar]
- De Santis, A.; Tozzi, R.; Gaya-Piqué, L.R. Information content and K-entropy of the present geomagnetic field. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 218, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peddie, N.W. International geomagnetic reference field. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 1982, 34, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteo, N.; Morton, Y. Ionosphere geomagnetic field: Comparison of IGRF model prediction and satellite measurements 1991–2010. Radio Sci. 2011, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenqvist, A.; Shimada, M.; Ito, N.; Watanabe, M. ALOS PALSAR: A pathfinder mission for global-scale monitoring of the environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3307–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.J.; Nicoll, J.; Bristow, B. Mapping aurora activity with SAR—A case study. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; pp. IV-1–IV-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wing, S.; Johnson, J.; Jen, J.; Meng, C.I.; Sibeck, D.; Bechtold, K.; Freeman, J.; Costello, K.; Balikhin, M.; Takahashi, K. Kp forecast models. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Meyer, F.J.; Scheuchl, B.; Mouginot, J.; Joughin, I.; Rignot, E. Ionospheric correction of InSAR data for accurate ice velocity measurement at polar regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strozzi, T.; Wegmuller, U.; Tosi, L.; Bitelli, G.; Spreckels, V. Land subsidence monitoring with differential SAR interferometry. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2001, 67, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.; Sanz, J.; Orus, R.; Garcia-Rigo, A.; Feltens, J.; Komjathy, A.; Schaer, S.; Krankowski, A. The IGS VTEC maps: A reliable source of ionospheric information since 1998. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
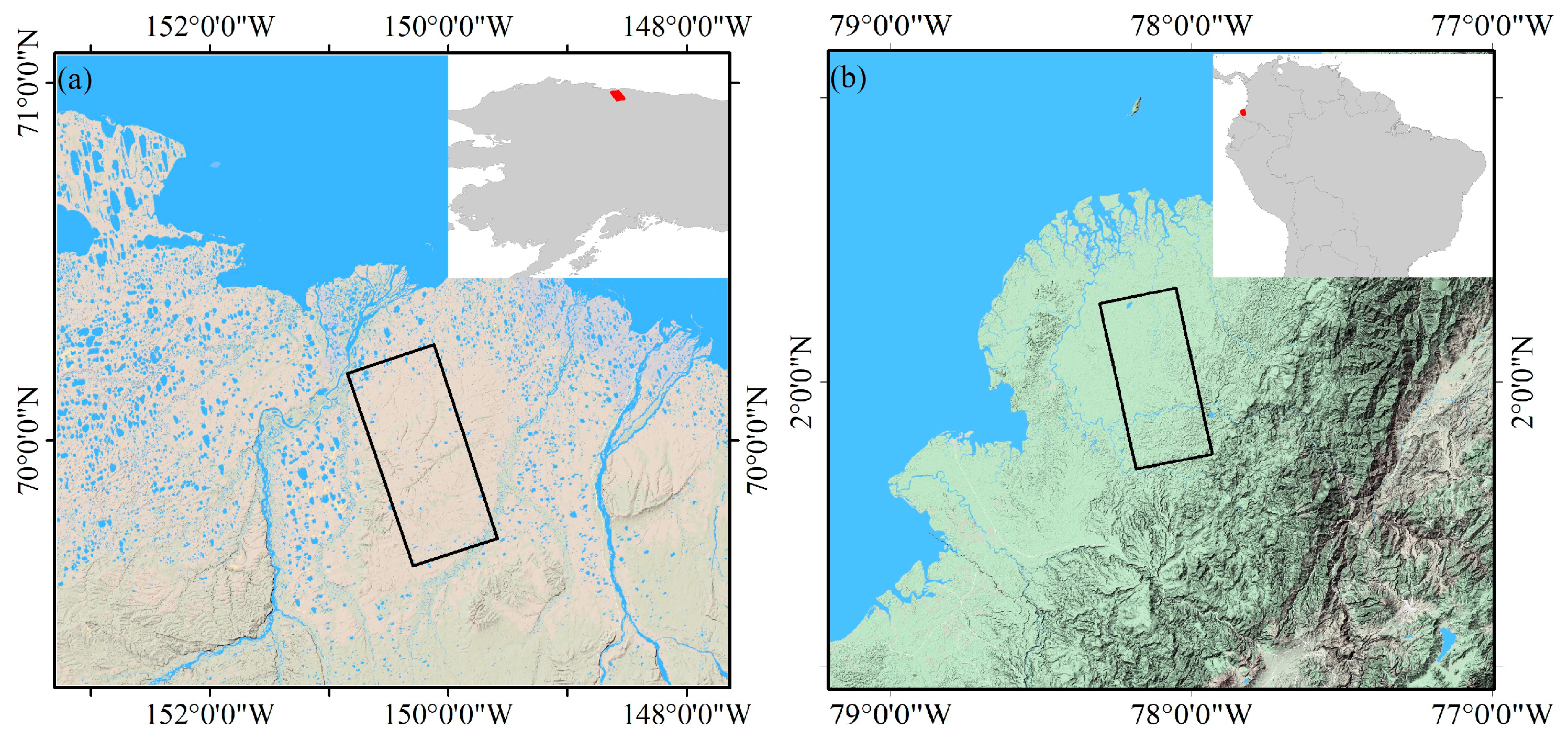
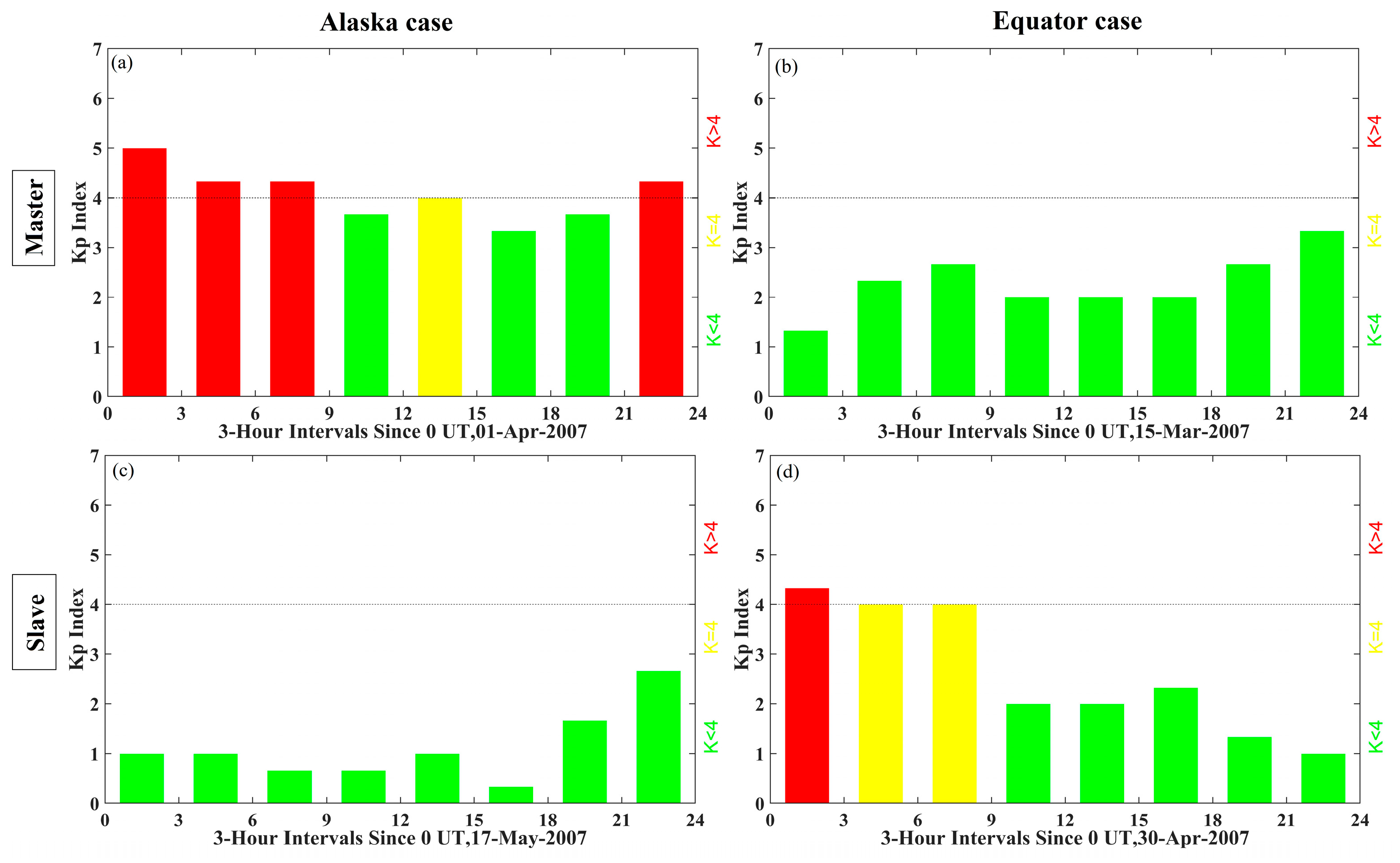

| Experiment Region | Track No. | Frame | Master | Slave |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alaska dataset | 243 | 1410 | 1 April 2007 | 17 May 2007 |
| Equator dataset | 150 | 0030 | 15 March 2007 | 30 April 2007 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Wang, Z.; An, J.; Zhang, B.; Geng, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, M.; Qian, Y. Ionospheric Phase Compensation for InSAR Measurements Based on the Faraday Rotation Inversion Method. Sensors 2020, 20, 6877. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236877
Li B, Wang Z, An J, Zhang B, Geng H, Ma Y, Li M, Qian Y. Ionospheric Phase Compensation for InSAR Measurements Based on the Faraday Rotation Inversion Method. Sensors. 2020; 20(23):6877. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236877
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bing, Zemin Wang, Jiachun An, Baojun Zhang, Hong Geng, Yuanyuan Ma, Mingci Li, and Yide Qian. 2020. "Ionospheric Phase Compensation for InSAR Measurements Based on the Faraday Rotation Inversion Method" Sensors 20, no. 23: 6877. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236877
APA StyleLi, B., Wang, Z., An, J., Zhang, B., Geng, H., Ma, Y., Li, M., & Qian, Y. (2020). Ionospheric Phase Compensation for InSAR Measurements Based on the Faraday Rotation Inversion Method. Sensors, 20(23), 6877. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236877





