EMG-Free Monitorization of the Acoustic Startle Reflex with a Mobile Phone: Implications of Sound Parameters with Posture Related Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
Purpose and Goals
2. Methods
2.1. Ethics and Environment
2.2. Recruitment
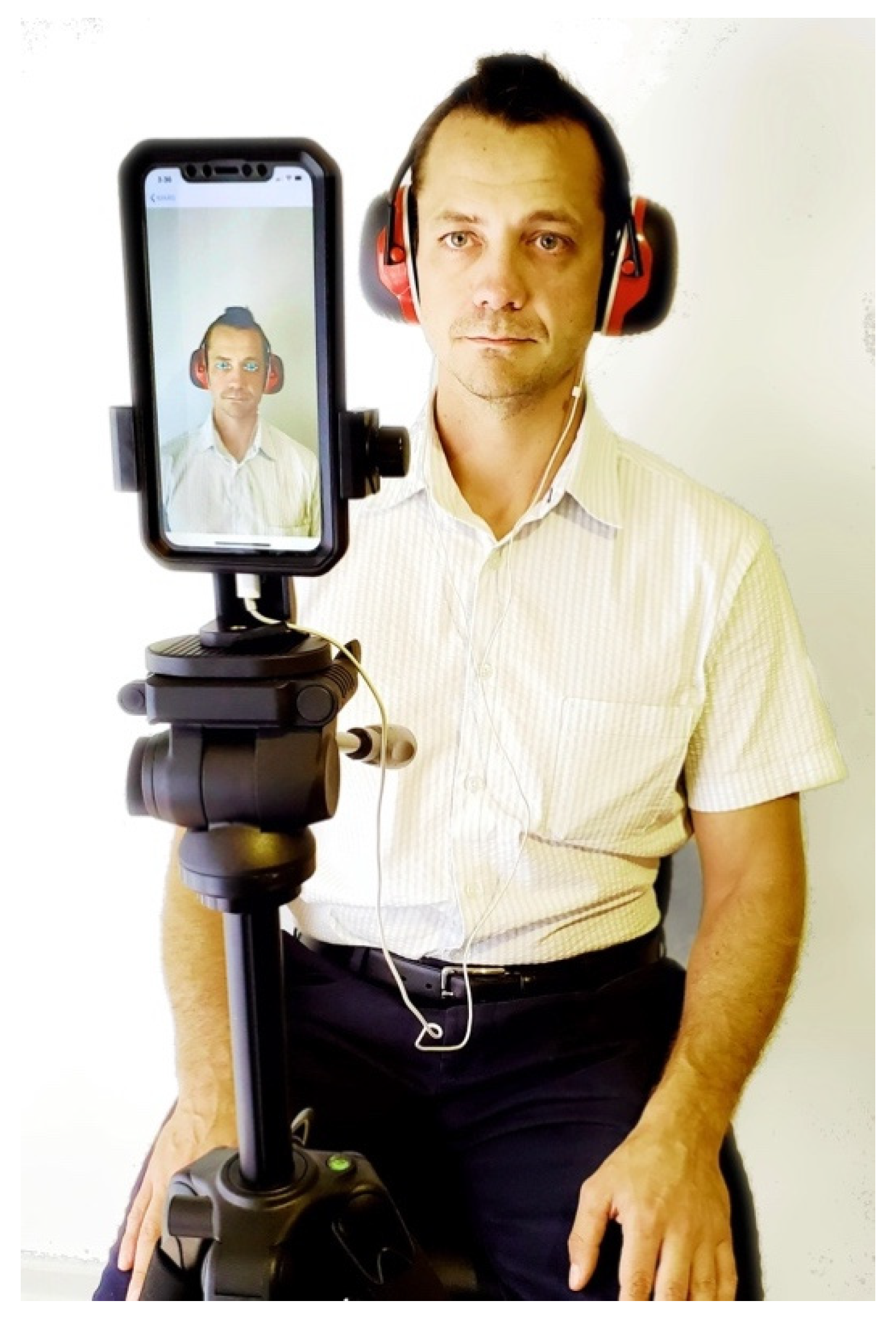
2.3. Hardware and Software
2.3.1. Mobile Sensing Platform Architecture
2.3.2. Application Overview
2.3.3. ASR Sound Stimulus Battery
2.4. Experimental Protocol
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Eye Synchronization
4.2. Blink Reaction Time and Response Amplitudes: Left and Right Eye, Sitting and Standing
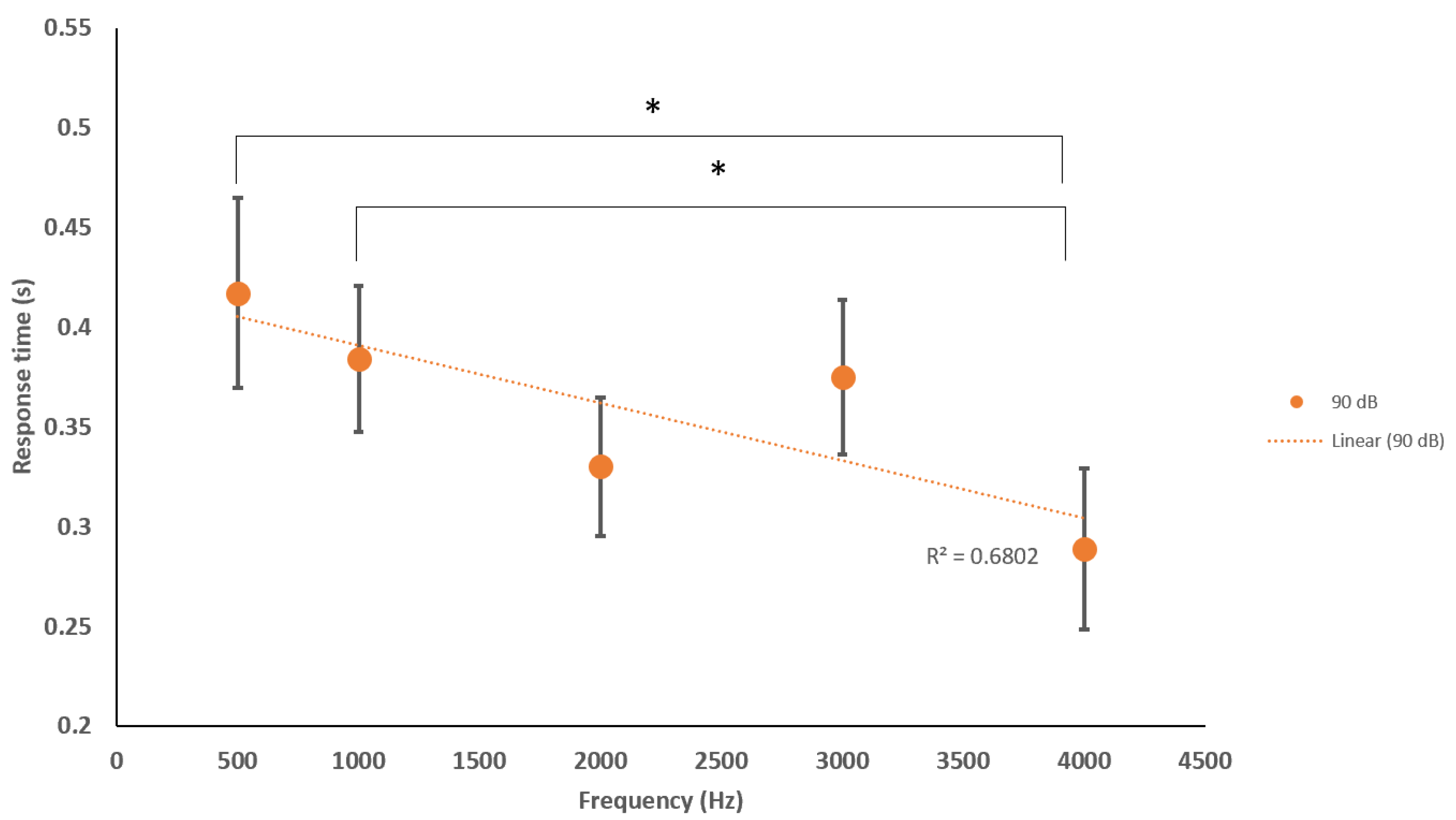
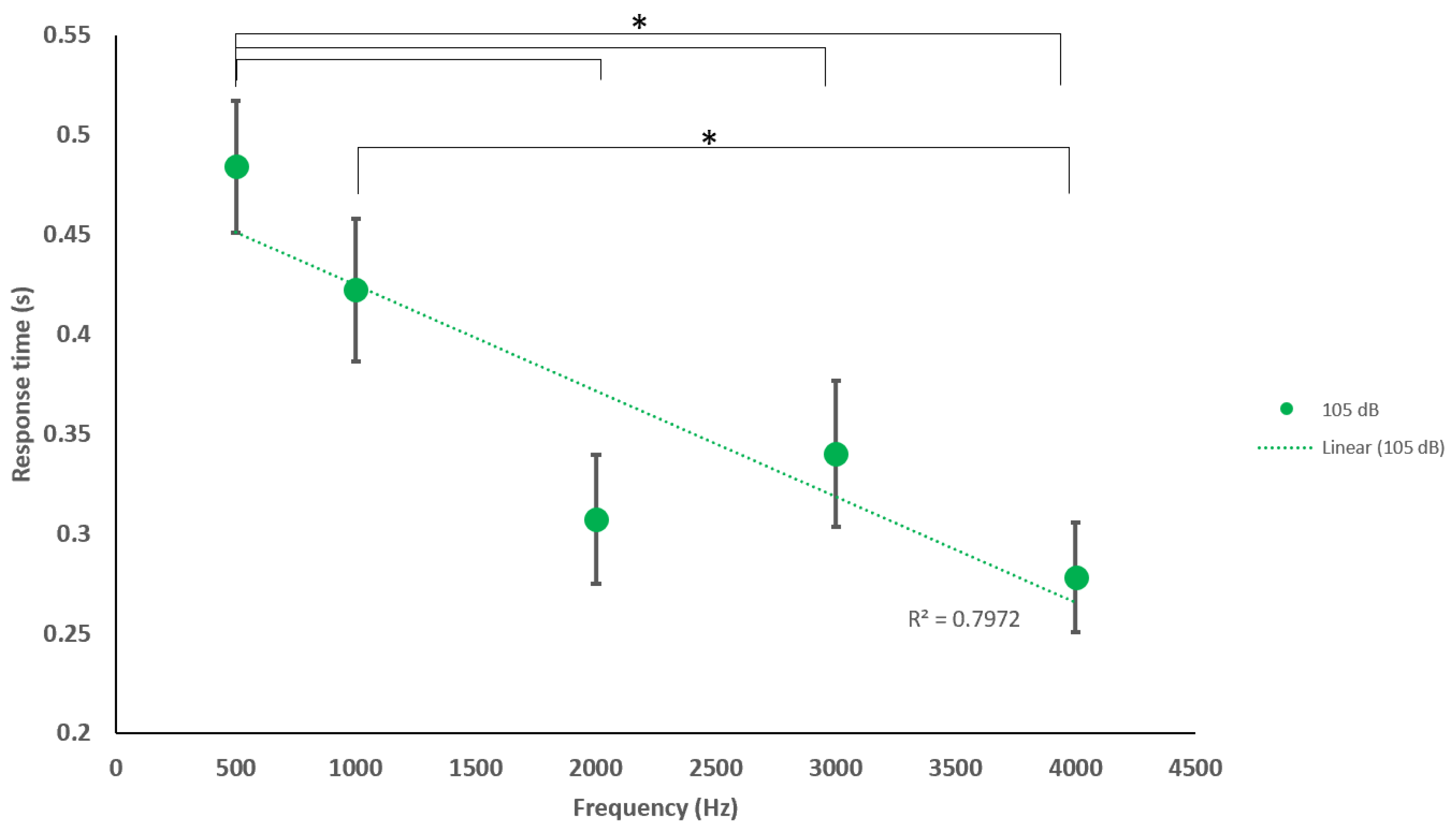
4.3. Response Times to Stimulus Parameters
5. Discussion
5.1. Limitations
5.2. Comparison with Prior Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASR | Acoustic startle reflex |
| OO | Orbicularis oculi |
| EAR | Eye Aspect Ratio |
| EMG | Electromyogram |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| DSM-V | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition |
| Hz | Hertz |
| dB | Decibels |
| N | Sample size |
| SLM | Sound level meter |
| MARS | Mobile acoustic-startle reflex monitoring system |
| RT | Reaction time |
| P | Probability value |
References
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders. In Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann, S.; Rehm, J.; Wittchen, H. The economic costs of mental disorders: Do our societies react appropriately to the burden of mental disorders? EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackett, P.T.; Cassem, H.N. Handbook of General Hospital Psychiatry, 2nd ed.; PSG Publishing Company, INC.: Littleton, MA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Rauch, S.L.; Whalen, P.J.; McInerney, S.C.; Macklin, M.L.; Lasko, N.B.; Orr, S.P.; Pitmman, R.K. Exagerated amygdala response to masked facial stimuli in posttraumatic stress disorder: A functional MRI study. Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 47, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsouleris, N.; Meisenzahl, E.M.; Borgwardt, S.; Rieher-Rossler, A.; Frodi, T.; Kambeitz, J.; Kohler, Y.; Falkai, P.; Moller, H.J.; Reiser, M.; et al. Individualized differential diagnosis of schizophrenia and mood disorders using neuroanatomical biomarkers. Brain J. Neurol. 2015, 7, 2059–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le-Niculescu, H.; Kurian, S.M.; Yehyawi, N.; Dike, C.; Patel, S.D.; Edenberg, H.J.; Tsuang, M.T.; Salomon, D.R.; Nurnberger, J.I., Jr.; Niculescu, A.B. Identifying blood biomarkers for mood disorders using convergent functional genomics. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A. The past, present, and future of psychiatric diagnosis. World Psychiatry 2013, 12, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders. In Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, K.A.; First, M.B.; Pincus, H.A. (Eds.) Advancing DSM: Dilemmas in Psychiatric Diagnosis; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- International Classification of Diseases. 6B40 Post Traumatic Stress Disorder, ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics (Version 04). Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en#/http://id.who.int/icd/entity/2070699808 (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Kaviani, H.; Gray, J.A.; Checkley, S.A.; Raven, P.W.; Wilson, G.D.; Kumari, V. Affective modulation of the startle response in depression: Influence of the severity of depression, anhedonia, and anxiety. J. Affect. Dis. 2004, 15, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P.J.; Bradley, M.M.; Cuthbert, B.N. Emotion, attention, and the startle reflex. Psychol. Rev. 1990, 3, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M.J.; Boer, F.; Benninga, M.A.; Koelman, J.H.T.M.; Tijssen, M.A.J. Increased Auditory Startle Reflex in Children with Functional Abdominal Pain. J. Pediatrics 2010, 156, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benning, S.D. Postauricular and superior auricular reflex modulation during emotional pictures and sounds. Psychophysiology 2011, 48, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, S.M.; Bianchin, M.; Angrilli, A. Effects of simulated microgravity on brain plasticity: A startle reflex habituation study. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanch, A.; Balada, F.; Aluja, A. Habituation in acoustic startle reflex: Individual differences in personality. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 91, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delwaide, P.J.; Shepens, B. Auditory startle (audio-spinal) reaction in normal man: EMG responses and H reflex changes in antagonistic lower limb muscles. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1995, 97, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillon, C.; Morgan, C.A.; Southwich, S.M.; Davis, M.; Charney, D.S. Baseline startle amplitude and prepulse inhibition in Vietnam veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Res. 1995, 64, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillon, C.; Pellowski, M.; Merikangas, K.R.; Davis, M. Darkness facilitates the acoustic startle reflex in humans. Biol. Psychiatry 1997, 42, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiziltan, M.E.; Gunduz, A.; Apaydin, H.; Ertan, S.; Kiziltan, G. Auditory startle reflex and startle reflex to somatosensory inputs in generalized dystonia. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, C.W.; Staib, M.; Tzovara, A.; Castegnetti, G.; Bach, D.R. A pupil size response model to assess fear learning. Psychophysiology 2017, 54, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, V.; Gray, J.A. Smoking withdrawal, Nicotine dependence and prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. Psychopharmacology 1999, 141, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.A.; Grillon, C.; Lubin, H.; Southwick, S.M. Startle Reflex Abnormalities in Women with Sexual Assault-Related Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 1997, 154, 1076–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, J.; Kofler, M.; Wenning, G.K.; Seppi, K.; Valls-Sole, S.; Poewe, W. Auditory startle response in cervical dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 1522–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnekes, J.; Geel, K.V.; Oude Nijhuis, L.B.; Bloem, B.R.; Geurts, A.C.; Weerdesteyn, V. Loading enhances the occurrence of startle responses in leg muscles. Neuroscience 2013, 240, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnekes, J.; Geurts, A.C.H.; Oude Nijhuis, L.B.; Geel, K.V.; Snijders, A.H.; Bloem, B.R.; Weerdesteyn, V. Reduced StartReact effect and freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease: Two of a kind? J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’beirne, G.A.; Patuzzi, R.B. Basic properties of the sound-evoked post-auricular muscle response (PAMR). Hear. Res. 1999, 138, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Jijhuis, L.B.; Allum, J.H.J.; Valls-Sole, J.; Overeem, S.; Bloem, B.R. First Trial Postural Reactions to Unexpected Balance Disturbances: A comparison With the Acoustic Startle Reaction. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 104, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rigato, S.; Rieger, G.; Romei, V. Multisensory signaling enhances pupil dilation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 6, 26188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, E.R.; Hou, R.H.; Langley, R.W.; Szabadi, E.; Bradshaw, C.M. Modulation of the Acoustic Startle Response by the Level of Arousal: Comparison of Clonidine and Modafinil in Healthy Volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 2405–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Siegelaar, S.E.; Olff, M.; Bour, L.J.; Veelo, D.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Bruggen, G.V.; Vries, G.J.D.; Raabe, S.; Cupido, C.; Koelman, J.H.T.M.; et al. The auditory startle response in post-traumatic stress disorder. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 174, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Nakahachi, T.; Komatsu, S.; Ogino, K.; Iida, Y.; Kamio, Y. Hyperreactivity to weak acoustic stimuli and prolonged acoustic startle latency in children with autism spectrum disorders. Mol. Autism 2014, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, H.S.; Kabel, A.H.; Khalil, L.H.; Said, N.M. Post Auricular Muscle Response in Auditory Neuropathy. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2010, 6, 360–364. [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal, T.D.; Cuthbert, B.N.; Filion, D.L.; Hackley, S.; Lipp, O.V.; van Boxtel, A. Committee report: Guidelines for human startle eyeblink electromyographic studies. Psychophysiology 2005, 42, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeomans, J.S.; Liang, L.; Scott, B.W.; Frankland, P.W. Tactile, acoustic and vestibular systems sum to elicit the startle reflex. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2001, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.; Flemming, J.; Zeffiro, T.; Rufer, M.; Orr, S.P.; Mueller-Pfeiffer, C. Effects of Posture and Stimulus Spectral Composition on Peripheral Physiological Responses to Loud Sounds. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlib C++ Library, Algorithm. Available online: http://dlib.net/algorithms.html#murmur_hash3 (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Soukupova, T.; Cech, J. Real-Time Eye Blink Detection using Facial Landmarks. In Proceedings of the 1st Computer Vision Winter Workshop, Rimske Toplice, Slovenia, 3–5 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Maeder, P.P.; Meuli, R.A.; Bellmann, A.; Fornari, E.; Thiran, J.-P.; Pittet, A.; Clarke, S. Distinct Pathways Involved in Sound Recognition and Localization: A Human fMRI Study. Neuroimage 2001, 14, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.W.; Wightman, F.L.; Brefczynski, J.A.; Phinney, R.E.; Binder, J.R.; DeYoe, E.A. Human brain regions involved in recognizing environmental sounds. Cereb. Cortex. 2004, 14, 1008–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboitiz, F. A Brain for Speech. Evolutionary Continuity in Primate and Human Auditory-Vocal Processing. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchi, C.; Severi, F.M.; Bruni, L.; Filardi, G.; Delia, A.; Boni, C.; Altomare, A.; Bellieni, C.V.; Petraglia, F. Ultrasound and Fetal Stress: Study of the Fetal Blink-Startle Reflex Evoked by Acoustic Stimuli. Neonatal Pain 2008, 4, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quam, R.; Martinez, I.; Lorenzo, C.; Bonmati, A.; Rosa-Zurera, M.; Jarabo, P.; Arsuaga, J.L. Studying audition in fossil hominins: A new approach to the evolution of language? In Psychology of Language; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa, T.; Cook, N.D. Identifying emotion in speech prosody using acoustical cues of harmony. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Spoken Language Processin INTERSPEECH, Jeju Island, Korea, 4–8 October 2004; pp. 1333–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Russel, J.A. A circumplex model of affect. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1980, 39, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagman, F. Emotional Response to Sound. Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Goteborg, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.-F.; Suzuki, S.S.; Siegel, J.M. Anatomical distribution and response patterns of reticular neurons active in relation to acoustic startle. Brain Res. 1988, 2, 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.A.; Plack, C.J. Pitch Processing Sites in the Human Auditory Brain. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 19, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, T.A. The Human Auditory System; Fundamental Organization and Clinical Disorders Chapter 2, Anatomic organization of the auditory cortex. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 129, 27–53. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.W. Chapter 22—Audio Processing/Human Hearing. In The Scientist and Engineer’s Guide to Digital Signal Processing; California Technical Publishing: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zivi, I.; Bertelli, E.; Bilotti, G.; Clemente, A.; Saltuari, L.; Frazzitta, G. Blink-associated contralateral eccentric saccades as a rare sign of unilateral brain injury. Neurology 2017, 88, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictionalclaims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
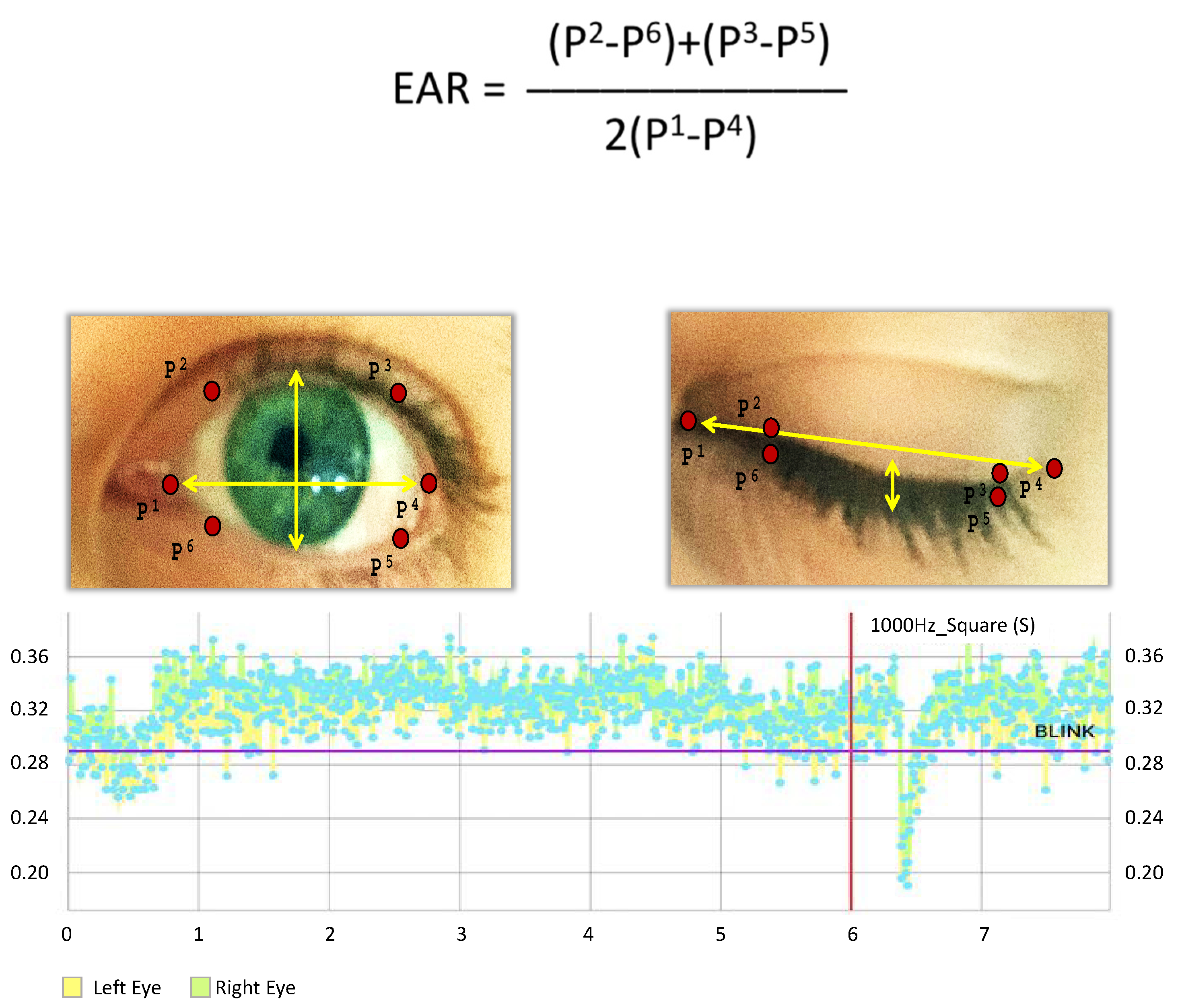

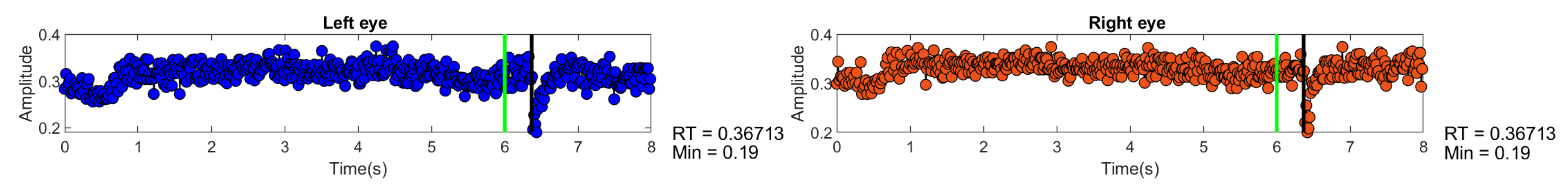

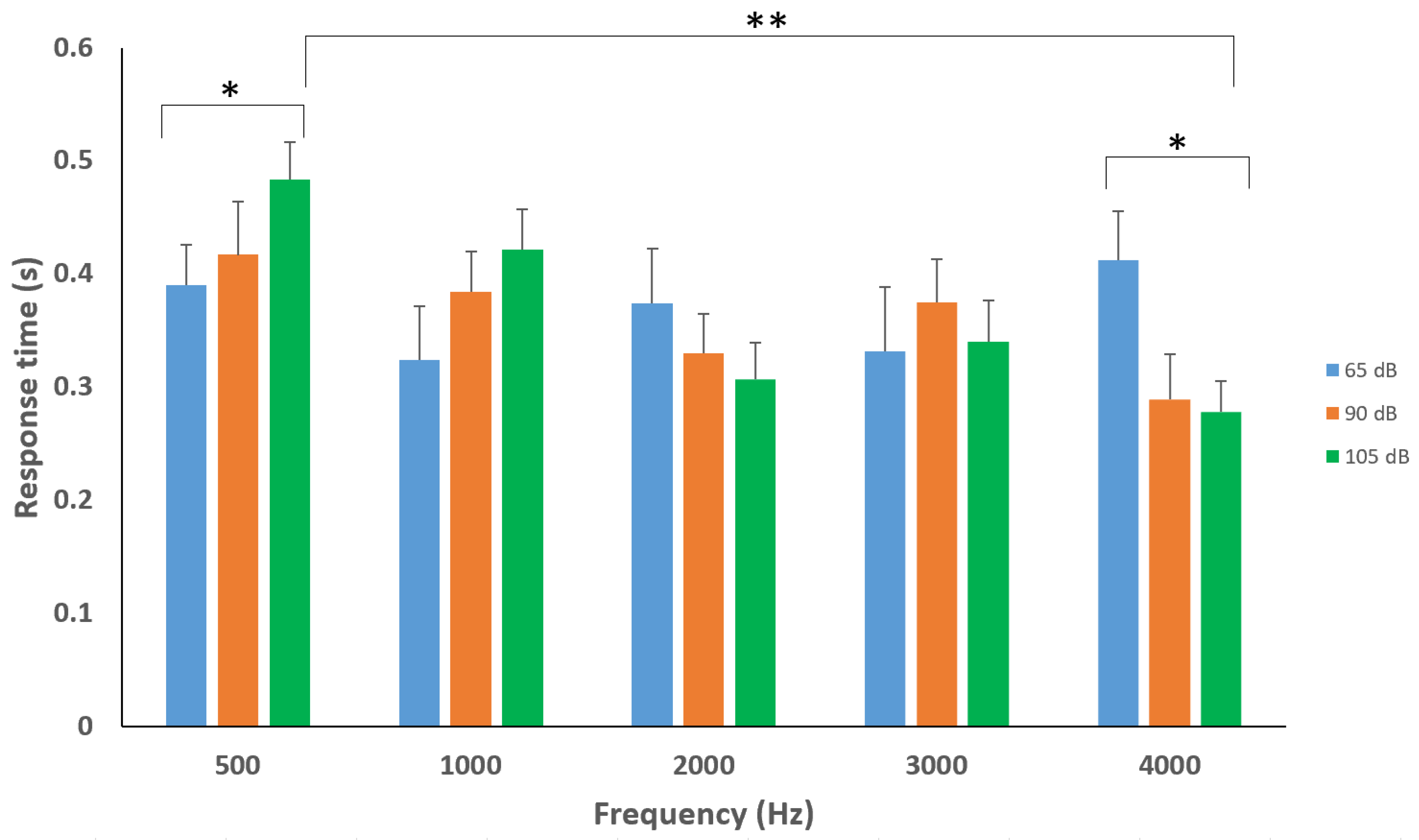
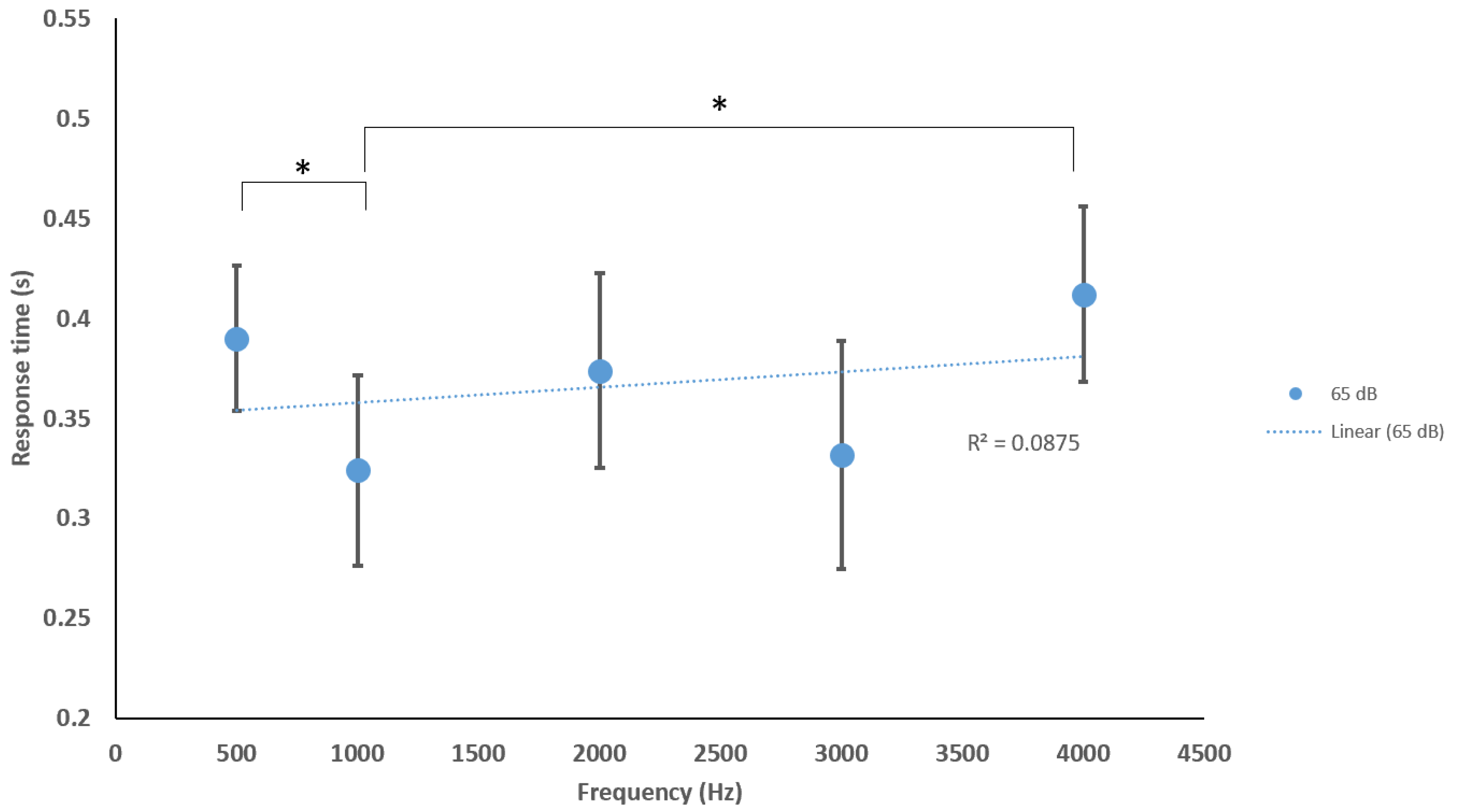
| Test Set | Frequency | ~Decibels | Delay to Startle (s) | Volume Scales (Phone) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500 | 65 | 5 | 2 |
| 2 | 1000 | 90 | 6 | 10 |
| 3 | 500 | 105 | 8 | 12 |
| 4 | 500 | 90 | 5 | 7 |
| 5 | 1000 | 65 | 8 | 4 |
| 6 | 2000 | 65 | 7 | 3 |
| 7 | 4000 | 90 | 7 | 10 |
| 8 | 2000 | 90 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 4000 | 105 | 5 | 14 |
| 10 | 3000 | 105 | 1 | 12 |
| 11 | 4000 | 65 | 3 | 3 |
| 12 | 1000 | 105 | 7 | 14 |
| 13 | 3000 | 65 | 8 | 3 |
| 14 | 2000 | 105 | 4 | 12 |
| 15 | 3000 | 90 | 9 | 12 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gowen, C.L.; Khwaounjoo, P.; Cakmak, Y.O. EMG-Free Monitorization of the Acoustic Startle Reflex with a Mobile Phone: Implications of Sound Parameters with Posture Related Responses. Sensors 2020, 20, 5996. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20215996
Gowen CL, Khwaounjoo P, Cakmak YO. EMG-Free Monitorization of the Acoustic Startle Reflex with a Mobile Phone: Implications of Sound Parameters with Posture Related Responses. Sensors. 2020; 20(21):5996. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20215996
Chicago/Turabian StyleGowen, Christopher L., Prashanna Khwaounjoo, and Yusuf O. Cakmak. 2020. "EMG-Free Monitorization of the Acoustic Startle Reflex with a Mobile Phone: Implications of Sound Parameters with Posture Related Responses" Sensors 20, no. 21: 5996. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20215996
APA StyleGowen, C. L., Khwaounjoo, P., & Cakmak, Y. O. (2020). EMG-Free Monitorization of the Acoustic Startle Reflex with a Mobile Phone: Implications of Sound Parameters with Posture Related Responses. Sensors, 20(21), 5996. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20215996





