Dual Oxygen and Temperature Luminescence Learning Sensor with Parallel Inference
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Measurement Principle
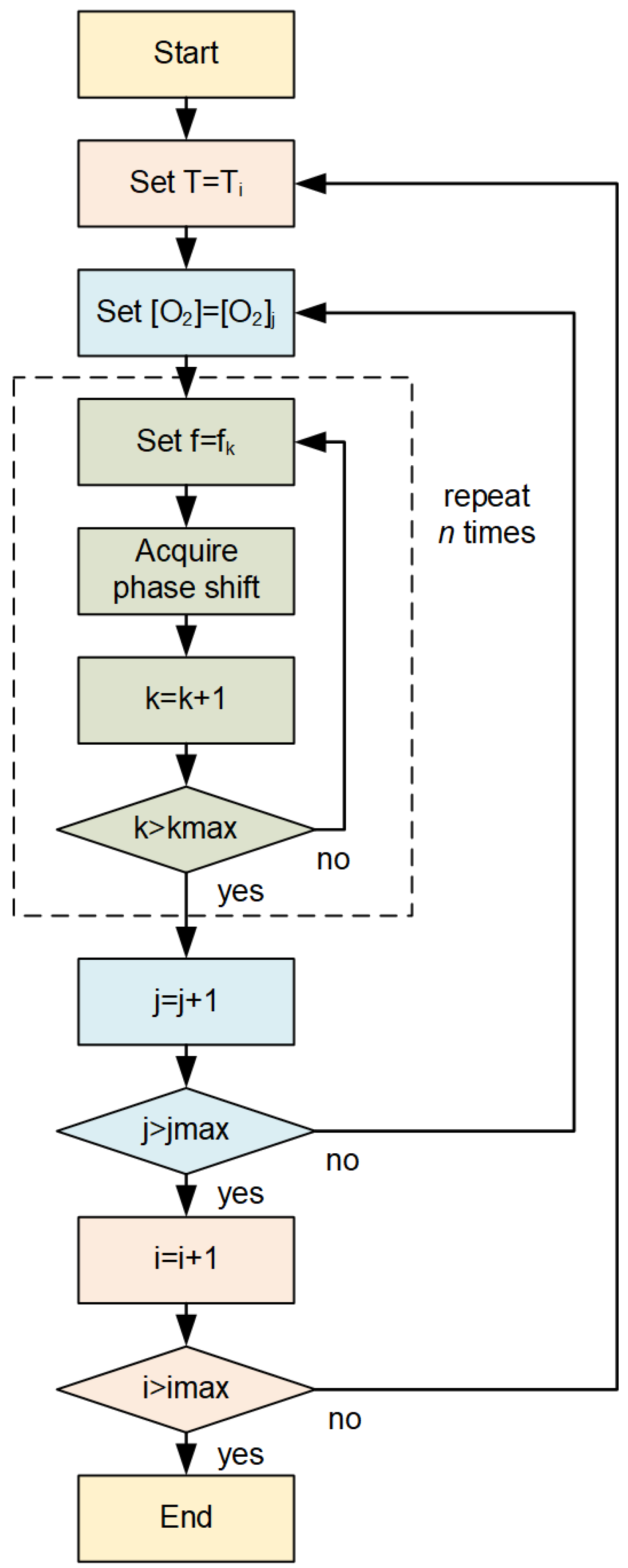
2.2. Experimental Setup and Dataset
2.3. Signal Processing Algorithm
2.4. Sensor Performance Evaluation
Error Limited Accuracy
3. Results and Discussion
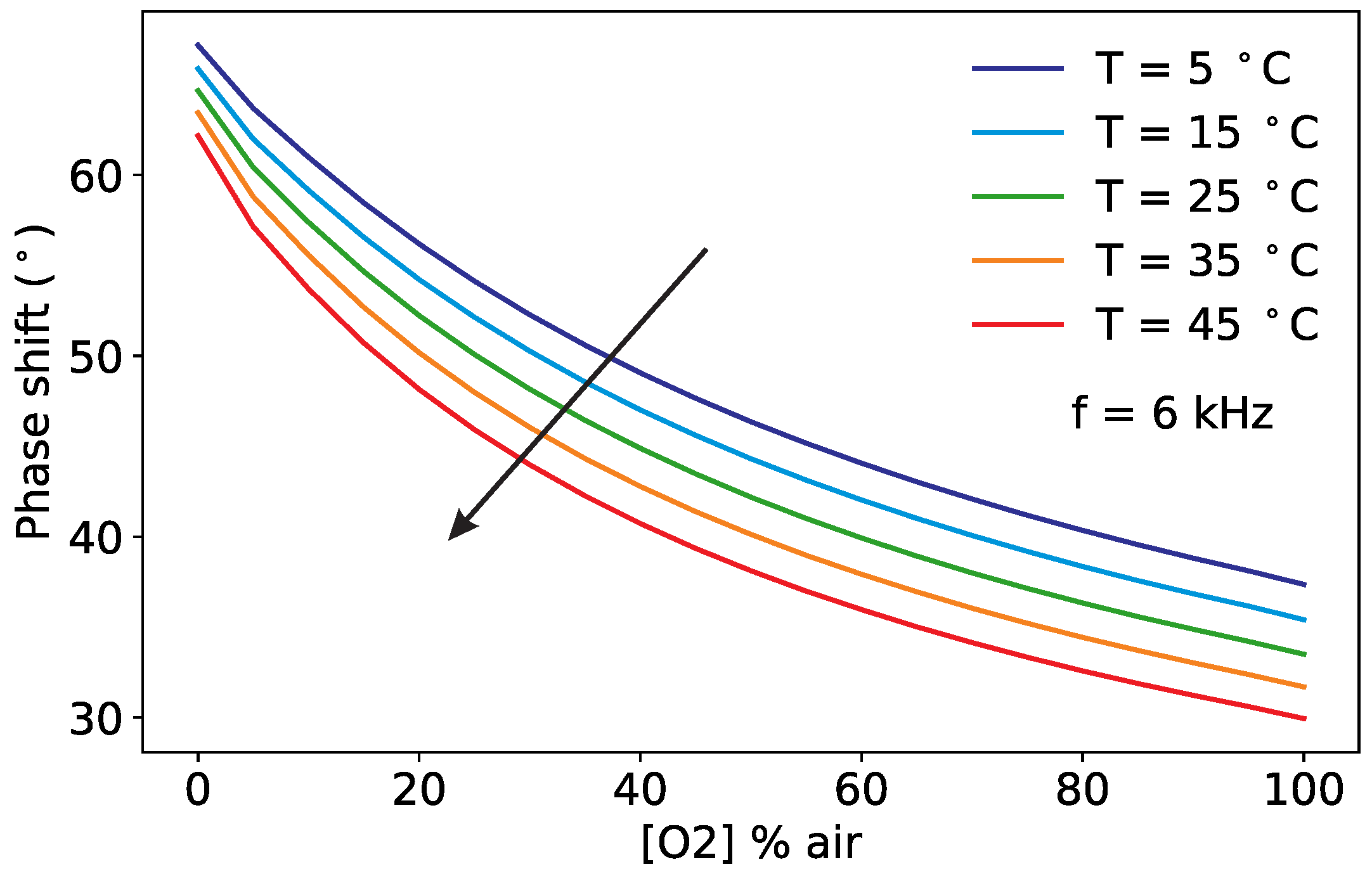
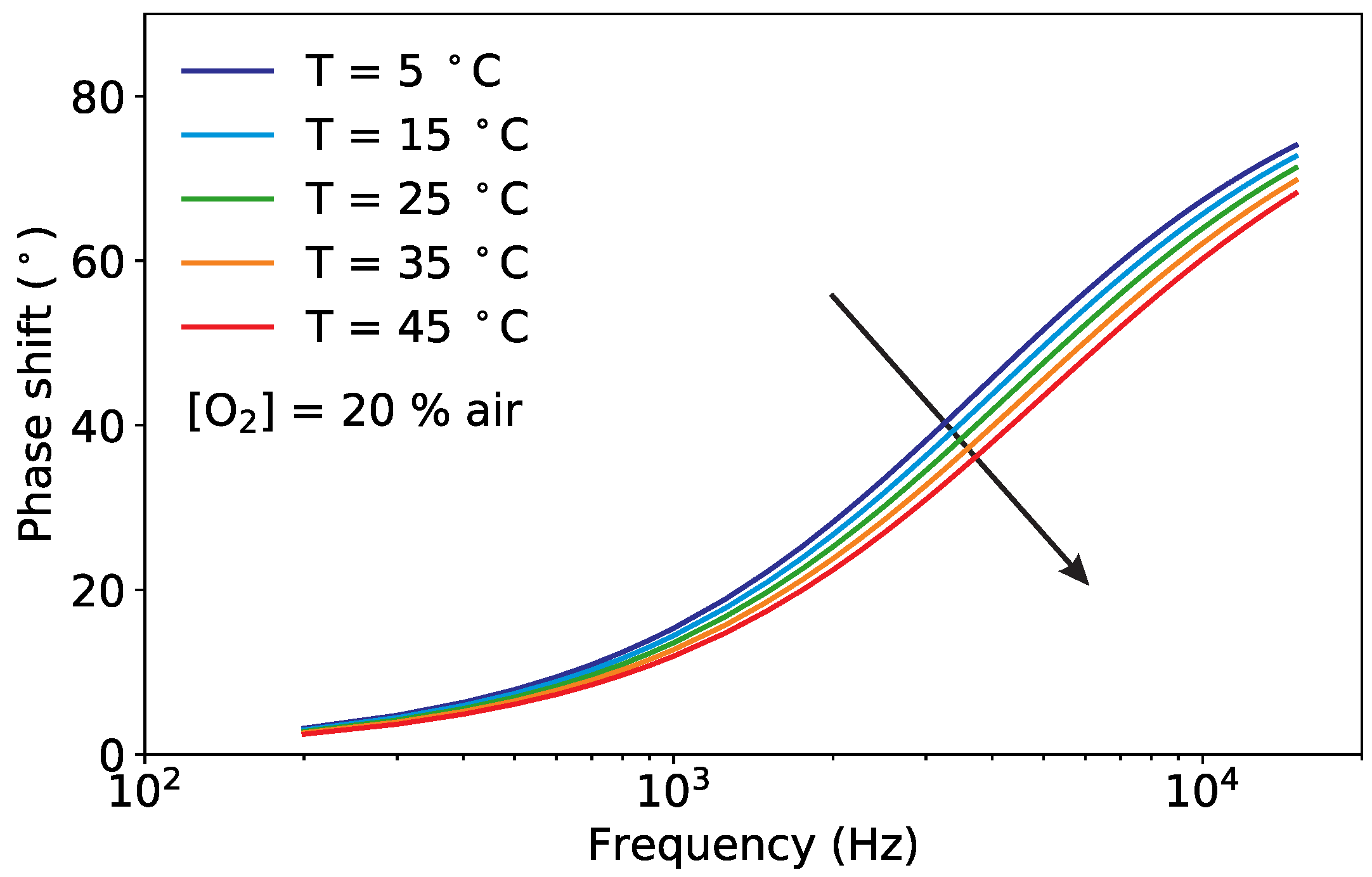
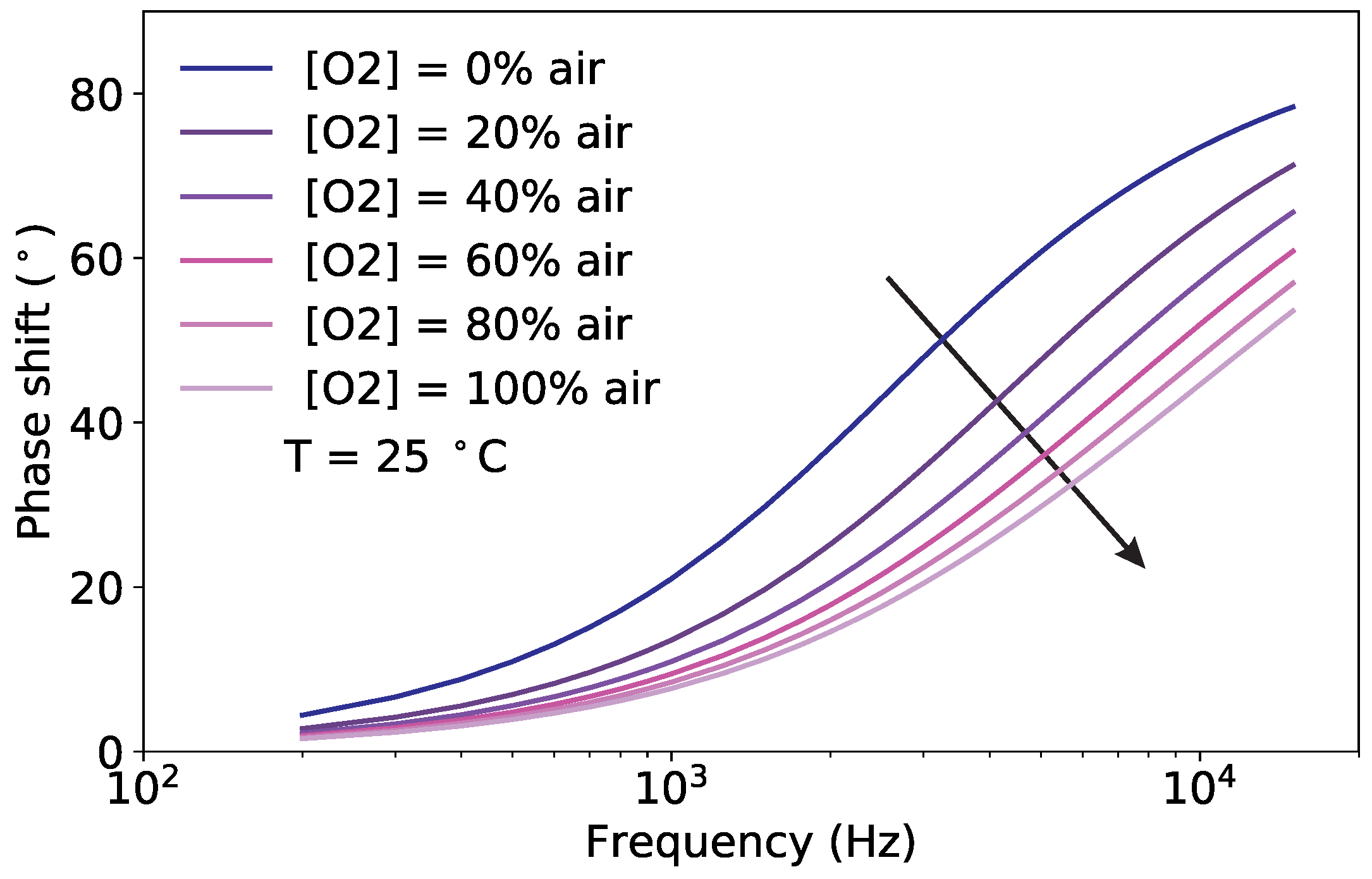
3.1. Pt-TFPP Luminescence
3.2. Sensor Performance
3.3. Error Limited Accuracy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SV | Stern–Volmer |
| Adam | Adaptive Moment Estimation |
| NNM | Neural Network Model |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| AE | Absolute Error |
| KDE | Kernel Density Estimate |
| ELA | Error Limited Accuracy |
References
- Stich, M.I.; Fischer, L.H.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Multiple fluorescent chemical sensing and imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3102–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borisov, S.M.; Seifner, R.; Klimant, I. A novel planar optical sensor for simultaneous monitoring of oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH and temperature. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 2463–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameya, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Egami, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Niimi, T. Dual luminescent arrays sensor fabricated by inkjet-printing of pressure-and temperature-sensitive paints. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Optical methods for sensing and imaging oxygen: Materials, spectroscopies and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3666–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, S.; Moro, A.; Portugal, C.; Crespo, J.; Coelhoso, I.; Lima, J. Development of oxygen and temperature sensitive membranes using molecular probes as ratiometric sensor. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biring, S.; Sadhu, A.S.; Deb, M. An Effective Optical Dual Gas Sensor for Simultaneous Detection of Oxygen and Ammonia. Sensors 2019, 19, 5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfbeis, O.S. Feasibility of optically sensing two parameters simultaneously using one indicator. In Chemical, Biochemical, and Environmental Fiber Sensors II; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1991; Volume 1368, pp. 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Zieger, S.E.; Steinegger, A.; Klimant, I.; Borisov, S.M. TADF-Emitting Zn (II)-Benzoporphyrin: An indicator for simultaneous sensing of oxygen and temperature. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, S.I.; Dasgupta, P.K.; Schug, K.A. Fiber optic sensor for simultaneous determination of atmospheric nitrogen dioxide, ozone, and relative humidity. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4183–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, B.B.; McShane, M.J. Time-resolved measurements of luminescence. J. Lumin. 2013, 144, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehning, C.; Holst, G.A. Addressing multiple indicators on a single optical fiber-digital signal processing approach for temperature compensated oxygen sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2004, 4, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, P.; Maule, C.; Silva, A.; Benrashid, R.; Santos, J.; Farahi, F. Dual sensing of oxygen and temperature using quantum dots and a ruthenium complex. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 606, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Moore, J.P.; Higgins, C.; McGaughey, O.; Lawless, B.G.; MacCraith, B.D. Exploiting sensor cross sensitivity: Achieving temperature compensation via a dual-element optical oxygen sensor. In Advanced Environmental, Chemical, and Biological Sensing Technologies IV; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006; Volume 6377, p. 63770I. [Google Scholar]
- Papkovsky, D.B.; Dmitriev, R.I. Biological detection by optical oxygen sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8700–8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, X. An intelligent optical dissolved oxygen measurement method based on a fluorescent quenching mechanism. Sensors 2015, 15, 30913–30926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; McDonough, R.C.; Langsdorf, B.; Demas, J.; DeGraff, B. Oxygen sensors based on luminescence quenching: Interactions of metal complexes with the polymer supports. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 4133–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, S.; Lippitsch, M.E.; Klimant, I.; Kraus, H.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Effects of polymer matrixes on the time-resolved luminescence of a ruthenium complex quenched by oxygen. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 3162–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, P.; Trettnak, W. Effects of polymer matrices on calibration functions of luminescent oxygen sensors based on porphyrin ketone complexes. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 2615–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A. Controlling the sensitivity of optical oxygen sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1998, 51, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badocco, D.; Mondin, A.; Pastore, P.; Voltolina, S.; Gross, S. Dependence of calibration sensitivity of a polysulfone/Ru (II)-Tris (4, 7-diphenyl-1, 10-phenanthroline)-based oxygen optical sensor on its structural parameters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 627, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, F.; Martinelli, E.; Paolesse, R.; Filippini, D.; D’Amico, A.; Lundström, I.; Di Natale, C. Polymer matrices effects on the sensitivity and the selectivity of optical chemical sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 154, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyriou, A.; Evgeniou, T.; Pontil, M. Multi-task feature learning. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’06), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 December 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Thrun, S. Is learning the n-th thing any easier than learning the first? In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’95), Denver, CO, USA, 27 November 1995; pp. 640–646. [Google Scholar]
- Caruana, R. Multitask learning. Mach. Learn. 1997, 28, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. A survey on multi-task learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.08114. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, J. A model of inductive bias learning. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2000, 12, 149–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thung, K.H.; Wee, C.Y. A brief review on multi-task learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 29705–29725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelucci, U.; Venturini, F. Multi-task learning for multi-dimensional regression: Application to luminescence sensing. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraway, E.; Demas, J.; DeGraff, B.; Bacon, J. Photophysics and photochemistry of oxygen sensors based on luminescent transition-metal complexes. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demas, J.N.; DeGraff, B.; Xu, W. Modeling of luminescence quenching-based sensors: Comparison of multisite and nonlinear gas solubility models. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelucci, U.; Baumgartner, M.; Venturini, F. Optical oxygen sensing with artificial intelligence. Sensors 2019, 19, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogurtsov, V.I.; Papkovsky, D.B. Modelling of phase-fluorometric oxygen sensors: Consideration of temperature effects and operational requirements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 113, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.L.; Chu, C.S.; Yur, J.P.; Chang, Y.C. Temperature compensation of fluorescence intensity-based fiber-optic oxygen sensors using modified Stern–Volmer model. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 131, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, N.; Melnikov, P.; Alferov, V.; Kopytin, A.; German, K. Stable optical oxygen sensing material based on perfluorinated polymer and fluorinated platinum (II) and palladium (II) porphyrins. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, F.; Michelucci, U.; Baumgartner, M. Dual oxygen and temperature sensing with single indicator using multi-task-learning neural networks. In Optical Sensing and Detection VI; Berghmans, F., Mignani, A.G., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11354, pp. 212–218. [Google Scholar]
- Michelucci, U. Applied Deep Learning—A Case-Based Approach to Understanding Deep Neural Networks; APRESS Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J.A. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
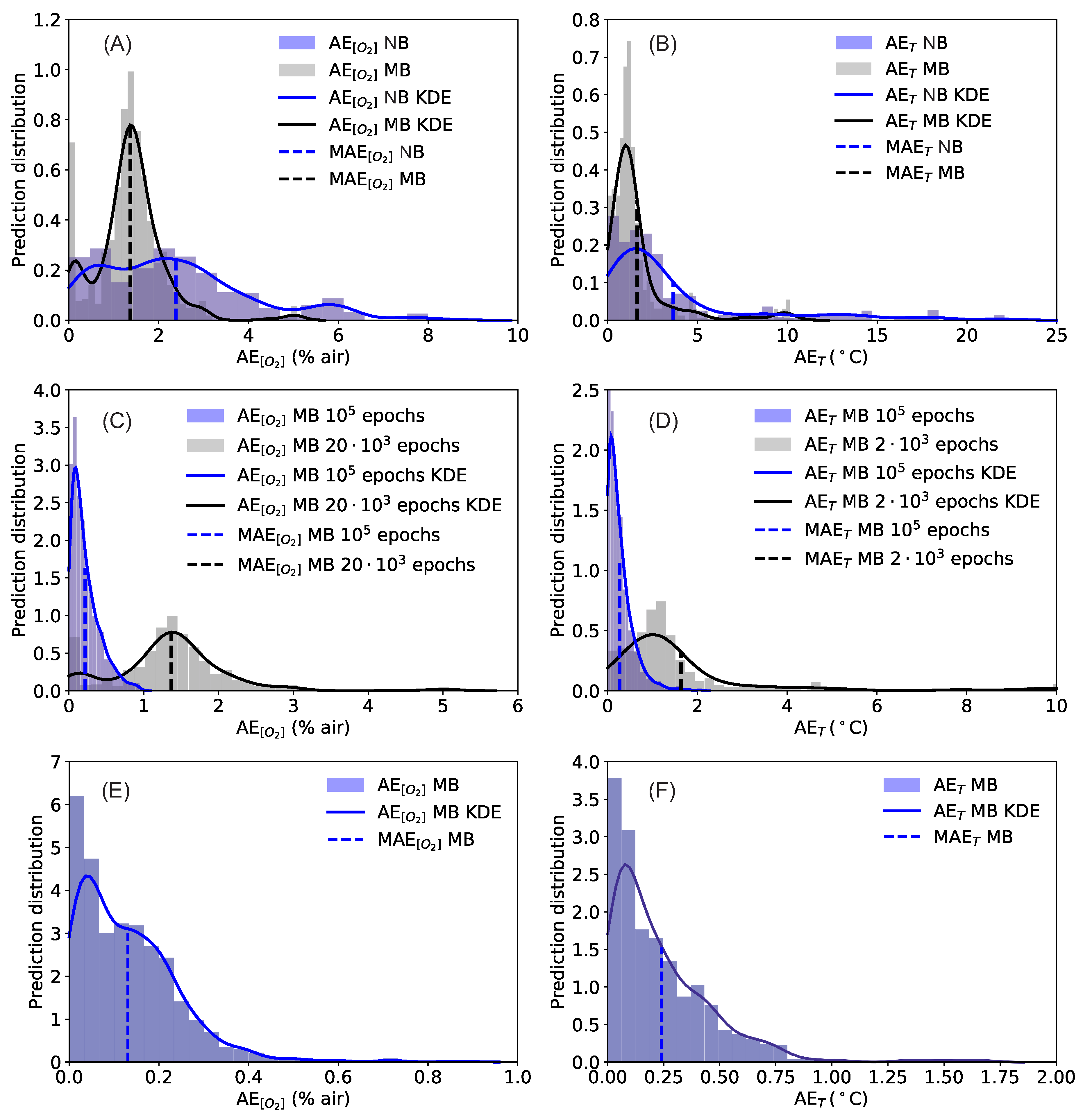

| Input | Epochs/Batch Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 20’000/no batch | 2.4% air | 3.6 °C | |
| 20’000/32 | 1.4% air | 1.6 °C | |
| 100’000/32 | 0.22% air | 0.27 °C | |
| 20’000/32 | 0.13% air | 0.24 °C |
| Input | Epochs/Batch Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 100’000/32 | 0.95% air | 2.1 °C | |
| 20’000/32 | 0.87% air | 1.7 °C |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venturini, F.; Michelucci, U.; Baumgartner, M. Dual Oxygen and Temperature Luminescence Learning Sensor with Parallel Inference. Sensors 2020, 20, 4886. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174886
Venturini F, Michelucci U, Baumgartner M. Dual Oxygen and Temperature Luminescence Learning Sensor with Parallel Inference. Sensors. 2020; 20(17):4886. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174886
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenturini, Francesca, Umberto Michelucci, and Michael Baumgartner. 2020. "Dual Oxygen and Temperature Luminescence Learning Sensor with Parallel Inference" Sensors 20, no. 17: 4886. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174886
APA StyleVenturini, F., Michelucci, U., & Baumgartner, M. (2020). Dual Oxygen and Temperature Luminescence Learning Sensor with Parallel Inference. Sensors, 20(17), 4886. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174886







