Simultaneous Coercivity and Size Determination of Magnetic Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
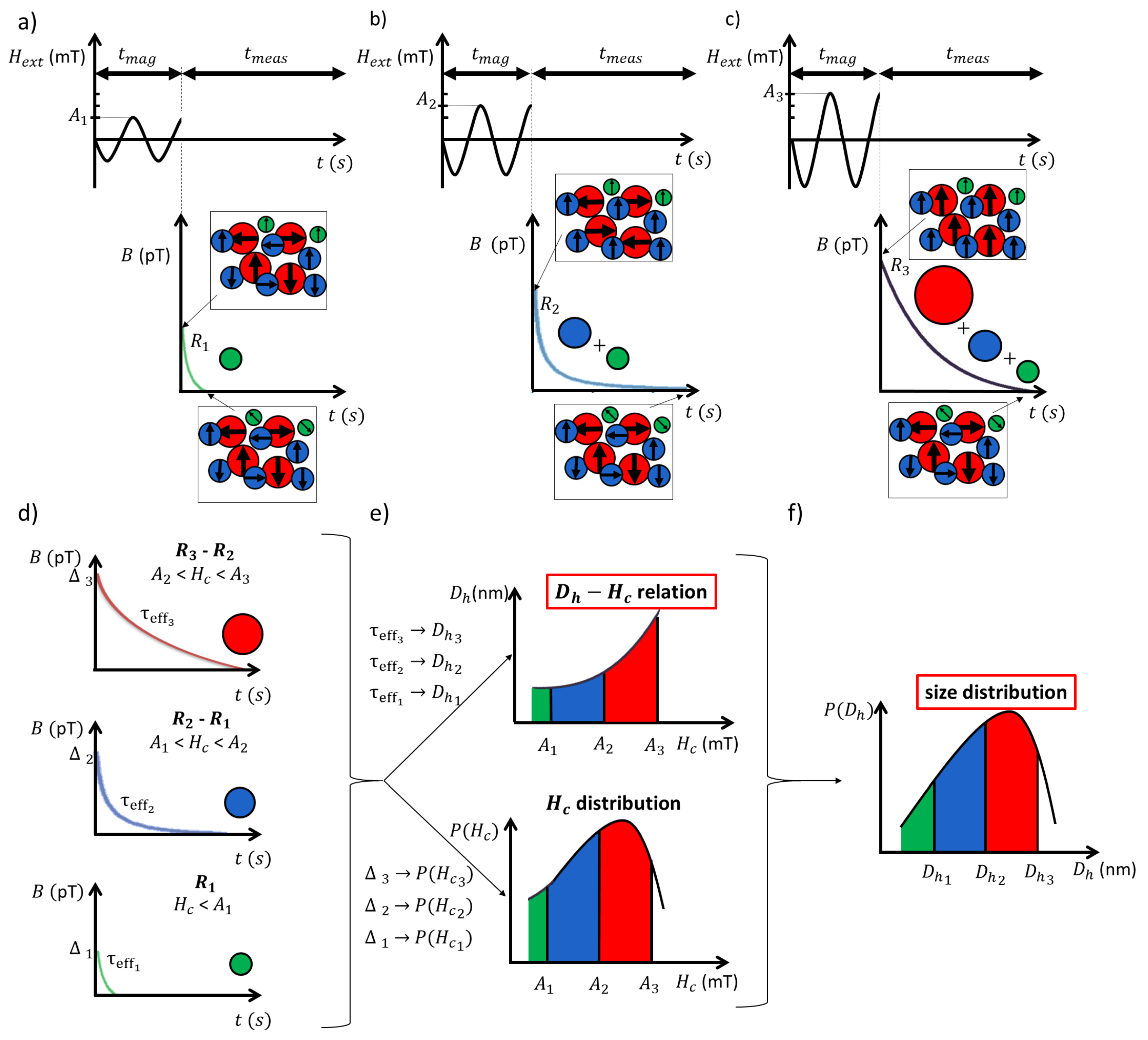
2. Overview of the Proposed Characterization Scheme
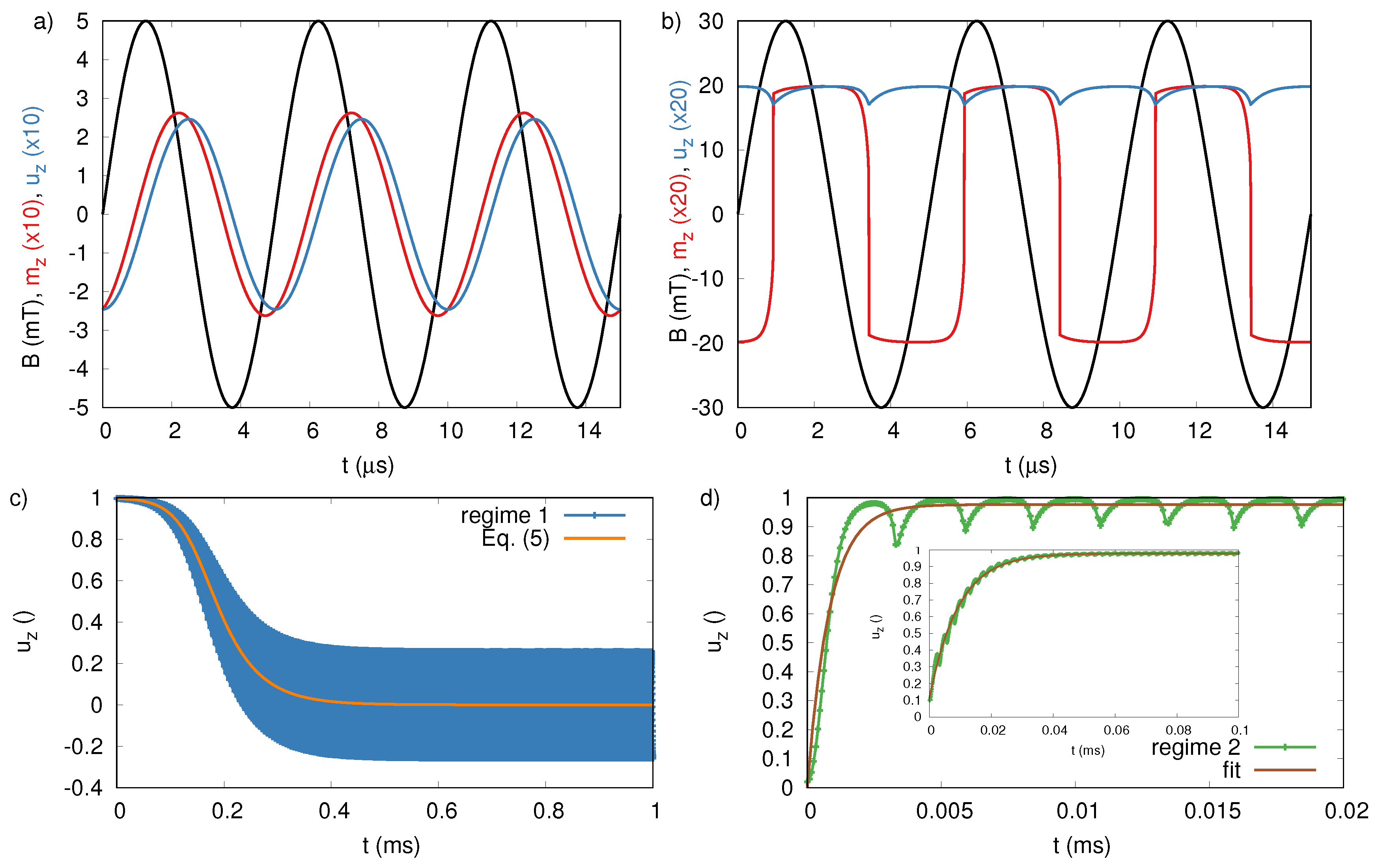
3. Magnetic Nanoparticle Dynamics
4. Magnetic Nanoparticle Response to AC Fields
4.1. Sinusoidal Externally Applied Field
4.2. Rotating Externally Applied Field
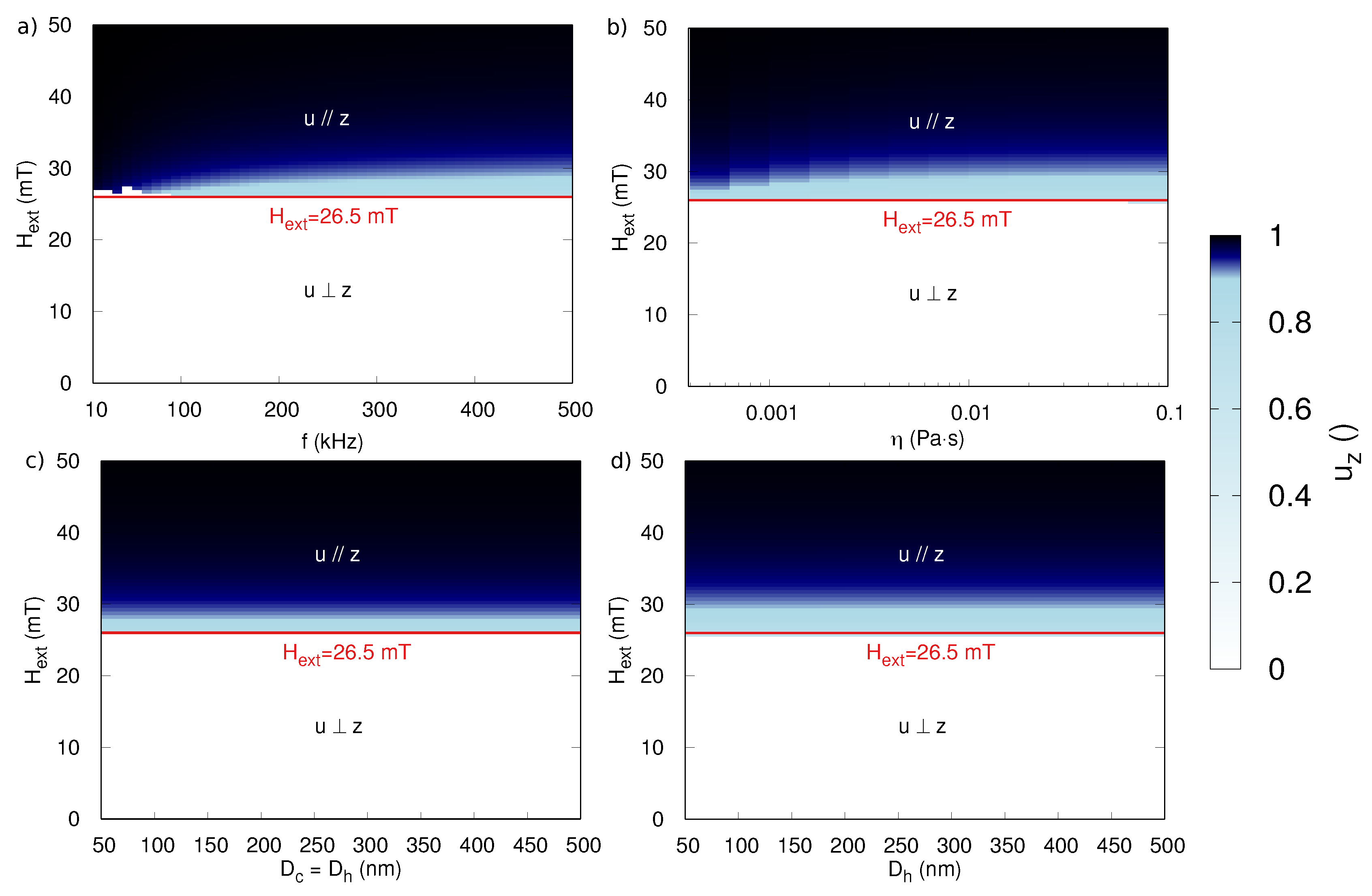
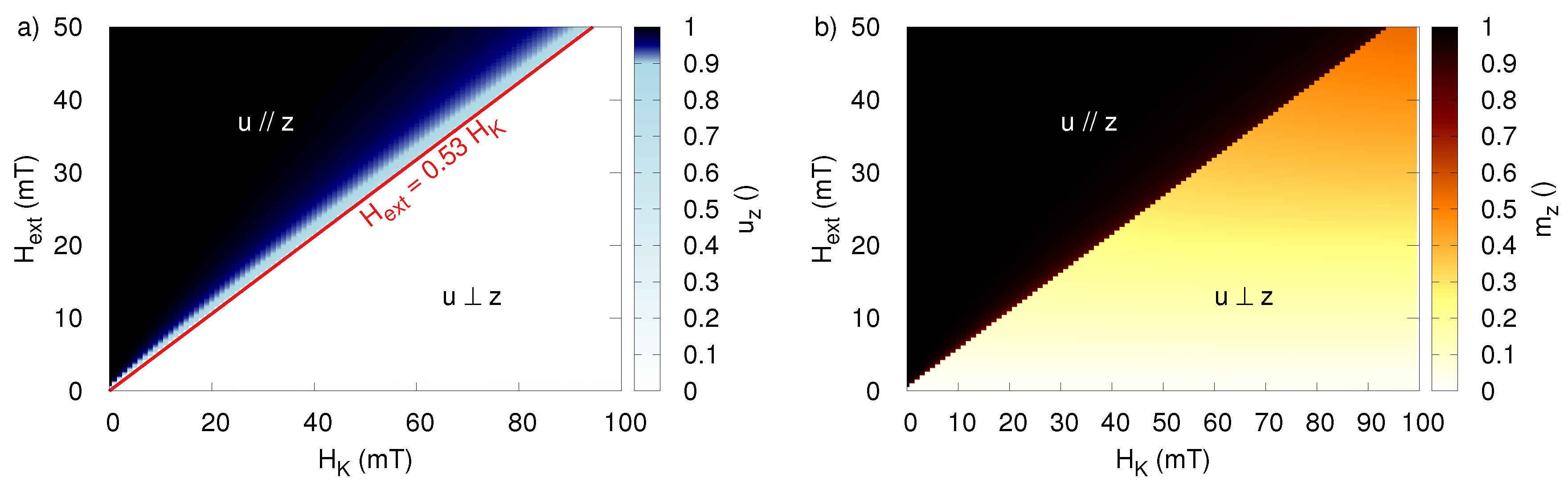
4.3. Comparison between Both Excitation Fields
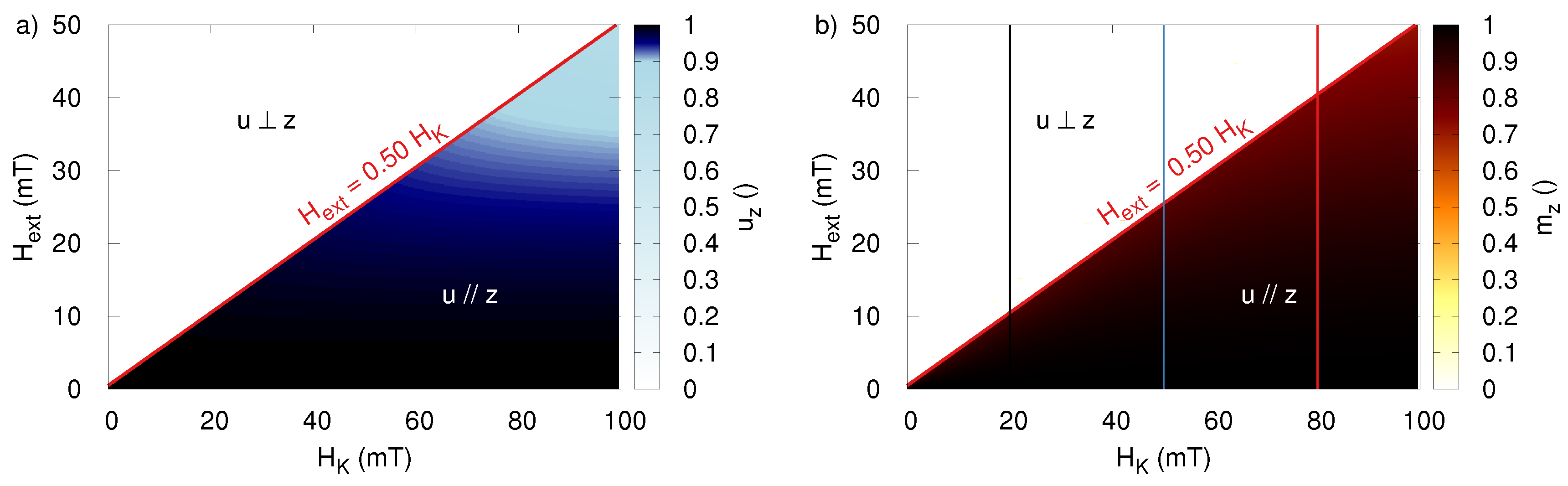
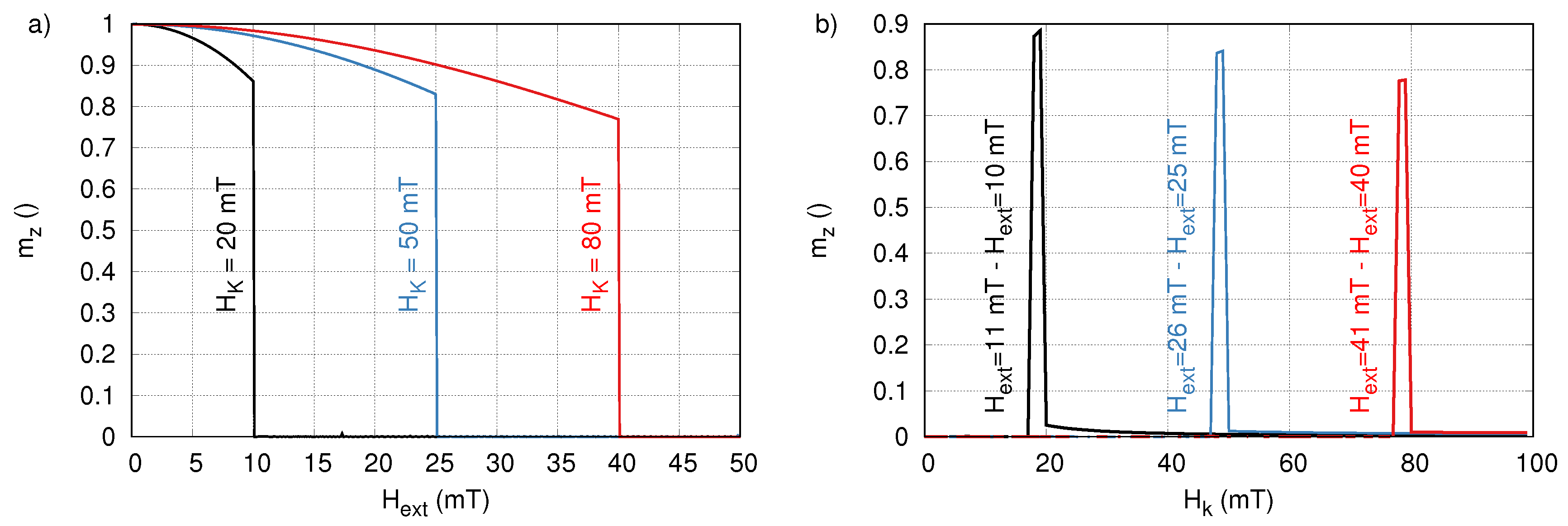
5. Particle Size-Dependent Coercivity
6. Magnetorelaxometry
7. Characterization Results
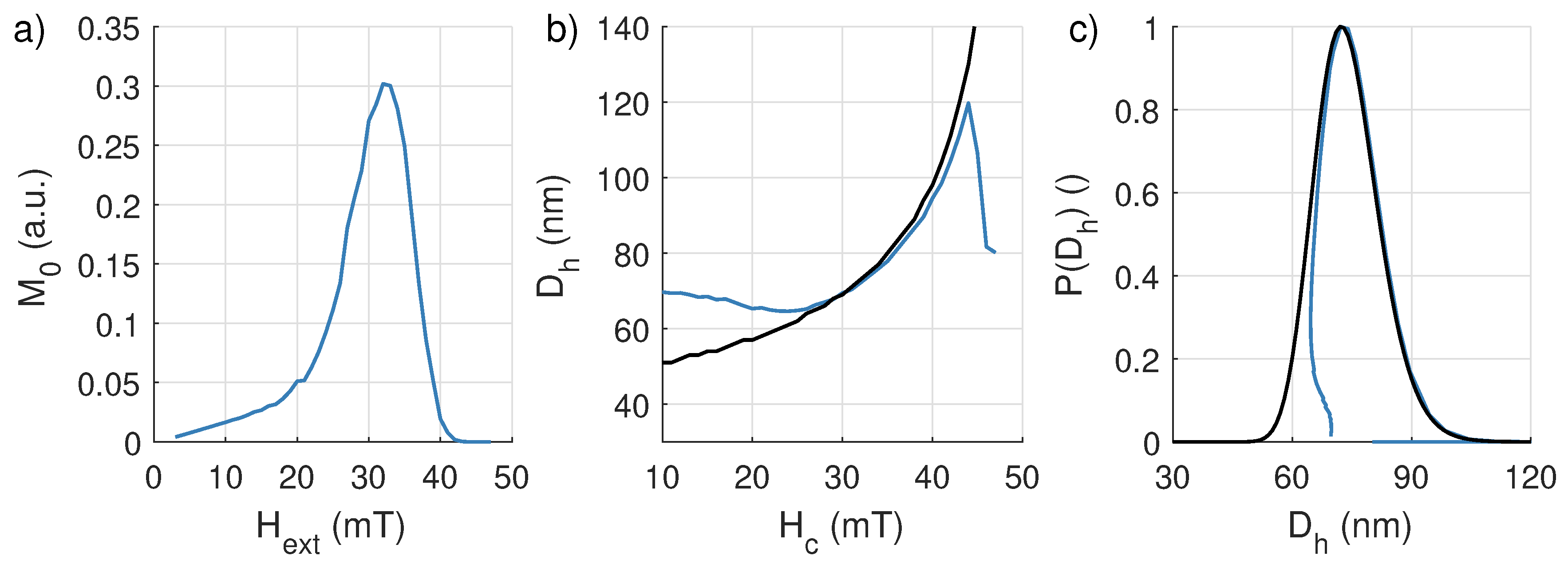
7.1. Sample 1: Lognormal Distribution of Single-Domain Particles
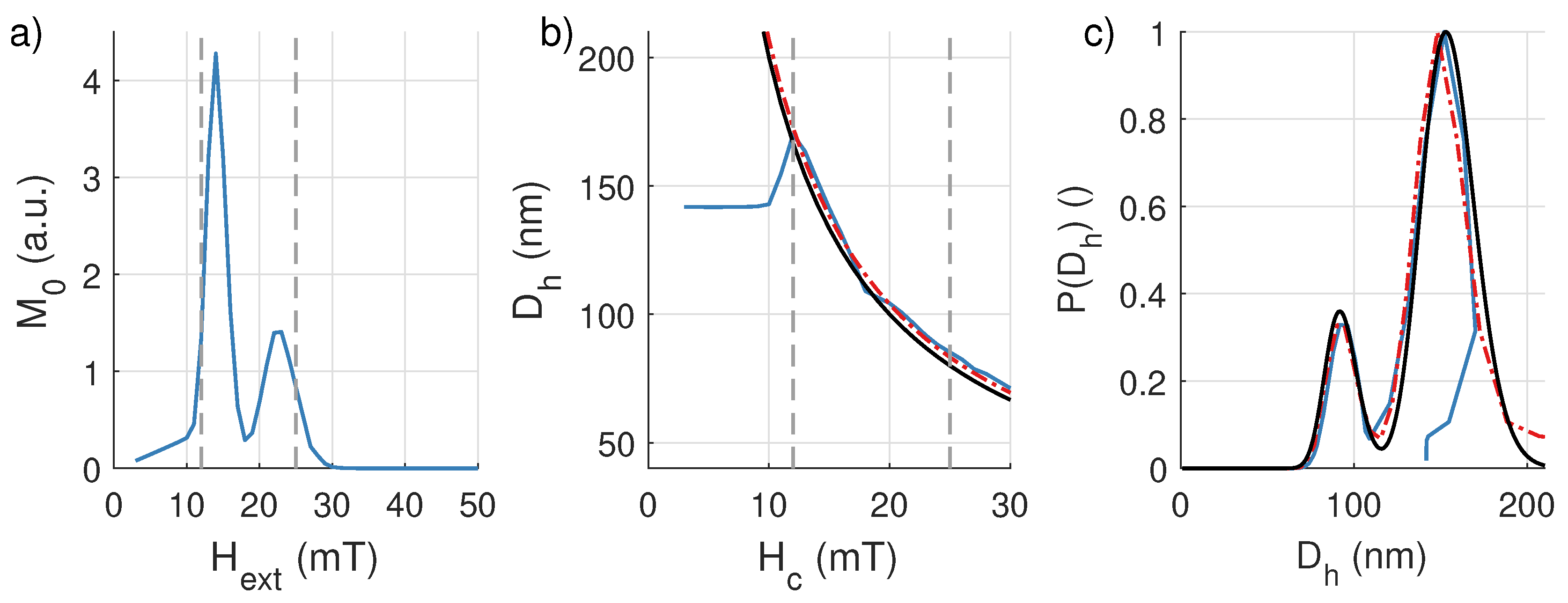
7.2. Sample 2: Bimodal Distribution of Multi-Domain Particles
8. Potential Use in Magnetic Nanoparticle Imaging
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pankhurst, Q.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Progress in applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 224001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wu, Z.; Yu, T.; Jiang, C.; Kim, W.S. Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 023501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadfar, S.M.; Roemhild, K.; Drude, N.I.; von Stillfried, S.; Knüchel, R.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Iron oxide nanoparticles: Diagnostic, therapeutic and theranostic applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 138, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Zhu, H.; Bao, G. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for disease detection and therapy. Mater. Today 2019, 31, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, L.H.; Arias, J.L.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Magnetic nanoparticles: Design and characterization, toxicity and biocompatibility, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5818–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jamal, K.T.; Bai, J.; Wang, J.T.W.; Protti, A.; Southern, P.; Bogart, L.; Heidari, H.; Li, X.; Cakebread, A.; Asker, D.; et al. Magnetic Drug Targeting: Preclinical in Vivo Studies, Mathematical Modeling, and Extrapolation to Humans. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 5652–5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haro, L.P.; Karaulanov, T.; Vreeland, E.C.; Anderson, B.; Hathaway, H.J.; Huber, D.L.; Matlashov, A.N.; Nettles, C.P.; Price, A.D.; Monson, T.C.; et al. Magnetic relaxometry as applied to sensitive cancer detection and localization. Biomed. Eng. Tech. 2015, 60, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, C.L.; Ivkov, R. Physics of heat generation using magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 29, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périgo, E.A.; Hemery, G.; Sandre, O.; Ortega, D.; Garaio, E.; Plazaola, F.; Teran, F.J. Fundamentals and advances in magnetic hyperthermia. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 041302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogren, S.; Fornara, A.; Ludwig, F.; del Puerto Morales, M.; Steinhoff, U.; Hansen, M.F.; Kazakova, O.; Johansson, C. Classification of Magnetic Nanoparticle Systems—Synthesis, Standardization and Analysis Methods in the NanoMag Project. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 20308–20325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harabech, M.; Leliaert, J.; Coene, A.; Crevecoeur, G.; Van Roost, D.; Dupré, L. The effect of the magnetic nanoparticle’s size dependence of the relaxation time constant on the specific loss power of magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 426, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, R.M.; Khandhar, A.P.; Kemp, S.J.; Arami, H.; Saritas, E.U.; Croft, L.R.; Konkle, J.; Goodwill, P.W.; Halkola, A.; Rahmer, J.; et al. Magnetic Particle Imaging With Tailored Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Tracers. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rijssel, J.; Kuipers, B.W.; Erné, B.H. Non-regularized inversion method from light scattering applied to ferrofluid magnetization curves for magnetic size distribution analysis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 353, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, F.; Mäuselein, S.; Heim, E.; Schilling, M. Magnetorelaxometry of magnetic nanoparticles in magnetically unshielded environment utilizing a differential fluxgate arrangement. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2005, 76, 106102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J.; Kotitz, R.; Haller, A.; Trahms, L.; Semmler, W.; Weitschies, W. Magnetorelaxometry—A new binding specific detection method based on magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 252, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, F.; Balceris, C.; Jonasson, C.; Johansson, C. Analysis of ac susceptibility spectra for the characterization of magnetic nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieckhoff, J.; Eberbeck, D.; Schilling, M.; Ludwig, F. Magnetic-field dependence of Brownian and Néel relaxation times. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 043903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzik, T.; Schilling, M.; Ludwig, F. Perspectives of magnetic particle spectroscopy for magnetic nanoparticle characterization. In Magnetic Particle Imaging; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Draack, S.; Lucht, N.; Remmer, H.; Martens, M.; Fischer, B.; Schilling, M.; Ludwig, F.; Viereck, T. Multiparametric magnetic particle spectroscopy of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles in viscous media. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 6787–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leliaert, J.; Coene, A.; Liebl, M.; Eberbeck, D.; Steinhoff, U.; Wiekhorst, F.; Fischer, B.; Dupré, L.; Van Waeyenberge, B. Thermal magnetic noise spectra of nanoparticle ensembles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 222401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leliaert, J.; Eberbeck, D.; Liebl, M.; Coene, A.; Steinhoff, U.; Wiekhorst, F.; Van Waeyenberge, B.; Dupré, L. The complementarity and similarity of magnetorelaxometry and thermal magnetic noise spectroscopy for magnetic nanoparticle characterization. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 085004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istratov, A.A.; Vyvenko, O.F. Exponential analysis in physical phenomena. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1999, 70, 1233–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, P.; Balceris, C.; Ludwig, F.; Posth, O.; Bogart, L.; Szczerba, W.; Castro, A.; Nilsson, L.; Costo, R.; Gavilán, H.; et al. Distribution functions of magnetic nanoparticles determined by a numerical inversion method. New J. Phys. 2017, 19, 073012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, P.; Fock, J.; Frandsen, C.; Hansen, M.F.; Balceris, C.; Ludwig, F.; Posth, O.; Wetterskog, E.; Bogart, L.K.; Southern, P.; et al. Relating magnetic properties and high hyperthermia performance of iron oxide nanoflowers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 3068–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberbeck, D.; Wiekhorst, F.; Steinhoff, U.; Trahms, L. Aggregation behaviour of magnetic nanoparticle suspensions investigated by magnetorelaxometry. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, S2829–S2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starsich, F.H.L.; Eberhardt, C.; Boss, A.; Hirt, A.M.; Pratsinis, S.E. Coercivity Determines Magnetic Particle Heating. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergt, R.; Hiergeist, R.; Zeisberger, M.; Glöckl, G.; Weitschies, W.; Ramirez, L.; Hilger, I.; Kaiser, W.A. Enhancement of AC-losses of magnetic nanoparticles for heating applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 280, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergt, R.; Dutz, S.; Röder, M. Effects of size distribution on hysteresis losses of magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2008, 20, 385214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heider, F.; Dunlop, D.J.; Sugiura, N. Magnetic Properties of Hydrothermally Recrystallized Magnetite Crystals. Science 1987, 236, 1287–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.; Lifshitz, E. Theory of the dispersion of magnetic permeability in ferromagnetic bodies. Phys. Z. Sowietunion 1935, 8, 153. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, W.F. Thermal Fluctuations of a Single-Domain Particle. Phys. Rev. 1963, 130, 1677–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, D.B.; Weaver, J.B. Combined Néel and Brown rotational Langevin dynamics in magnetic particle imaging, sensing, and therapy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 223106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leliaert, J.; Vansteenkiste, A.; Coene, A.; Dupré, L.; Van Waeyenberge, B. Vinamax: A macrospin simulation tool for magnetic nanoparticles. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2015, 53, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Leliaert, J.; Mulkers, J.; De Clercq, J.; Coene, A.; Dvornik, M.; Van Waeyenberge, B. Adaptively time stepping the stochastic Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert equation at nonzero temperature: Implementation and validation in MuMax3. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 125010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usadel, K.D.; Usadel, C. Dynamics of magnetic single domain particles embedded in a viscous liquid. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 234303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebl, M.; Wiekhorst, F.; Eberbeck, D.; Radon, P.; Gutkelch, D.; Baumgarten, D.; Steinhoff, U.; Trahms, L. Magnetorelaxometry procedures for quantitative imaging and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Biomed. Eng. Tech. 2015, 60, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiekhorst, F.; Steinhoff, U.; Eberbeck, D.; Trahms, L. Magnetorelaxometry assisting biomedical applications of magnetic nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, L.; Labaye, Y.; Tamine, M.; Coey, J.M.D. Ferromagnetic nanoparticles with strong surface anisotropy: Spin structures and magnetization processes. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 104431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, C.; del Puerto Morales, M.; Serna, C.J.; Vázquez, M. Multidomain to single-domain transition for uniform Co80Ni20nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2003, 14, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneller, E.F.; Luborsky, F.E. Particle Size Dependence of Coercivity and Remanence of Single-Domain Particles. J. Appl. Phys. 1963, 34, 656–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.F. The fundamental theorem of the theory of fine ferromagnetic particles. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1969, 147, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Cha, J.M.; Yoon, H.Y.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, Y.K. Magnetic multi-granule nanoclusters: A model system that exhibits universal size effect of magnetic coercivity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coene, A.; Leliaert, J.; Liebl, M.; Löwa, N.; Steinhoff, U.; Crevecoeur, G.; Dupré, L.; Wiekhorst, F. Multi-color magnetic nanoparticle imaging using magnetorelaxometry. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaufenthaler, A.; Schier, P.; Middelmann, T.; Liebl, M.; Wiekhorst, F.; Baumgarten, D. Quantitative 2D magnetorelaxometry imaging of magnetic nanoparticles using optically pumped magnetometers. Sensors 2020, 20, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einstein, A. Investigations on the Theory of the Brownian Movement; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Louis, N. Théorie du traînage magnétique des substances massives dans le domaine de Rayleigh. J. Phys. Radium 1950, 11, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leliaert, J.; Coene, A.; Crevecoeur, G.; Vansteenkiste, A.; Eberbeck, D.; Wiekhorst, F.; Van Waeyenberge, B.; Dupré, L. Regarding the Néel relaxation time constant in magnetorelaxometry. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 163914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberbeck, D.; Wiekhorst, F.; Wagner, S.; Trahms, L. How the size distribution of magnetic nanoparticles determines their magnetic particle imaging performance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 182502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Eberbeck, D.; Steinhoff, U.; Wiekhorst, F. Finding the magnetic size distribution of magnetic nanoparticles from magnetization measurements via the iterative Kaczmarz algorithm. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 431, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leliaert, J.; Schmidt, D.; Posth, O.; Liebl, M.; Eberbeck, D.; Coene, A.; Steinhoff, U.; Wiekhorst, F.; Waeyenberge, B.V.; Dupré, L. Interpreting the magnetorelaxometry signal of suspended magnetic nanoparticles with Kaczmarz’ algorithm. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 195002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usov, N.A. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Magnetic Hyperthermia. SPIN 2019, 9, 1940001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratta, G.D.; Serpico, C.; d’Aquino, M. A generalization of the fundamental theorem of Brown for fine ferromagnetic particles. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2012, 407, 1368–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Piper, J.A.; Zhang, F. Lifetime-engineered NIR-II nanoparticles unlock multiplexed in vivo imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, H.; Yang, L. Magnetic nanoparticles for precision oncology: Theranostic magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for image-guided and targeted cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmer, J.; Halkola, A.; Gleich, B.; Schmale, I.; Borgert, J. First experimental evidence of the feasibility of multi-color magnetic particle imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coene, A.; Crevecoeur, G.; Dupré, L. Adaptive control of excitation coil arrays for targeted magnetic nanoparticle reconstruction using magnetorelaxometry. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2842–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coene, A.; Leliaert, J.; Dupré, L.; Crevecoeur, G. Quantitative model selection for enhanced magnetic nanoparticle imaging in magnetorelaxometry. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 6853–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schier, P.; Liebl, M.; Steinhoff, U.; Handler, M.; Wiekhorst, F.; Baumgarten, D. Optimizing excitation coil currents for advanced magnetorelaxometry imaging. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2020, 62, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coene, A.; Leliaert, J. Simultaneous Coercivity and Size Determination of Magnetic Nanoparticles. Sensors 2020, 20, 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20143882
Coene A, Leliaert J. Simultaneous Coercivity and Size Determination of Magnetic Nanoparticles. Sensors. 2020; 20(14):3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20143882
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoene, Annelies, and Jonathan Leliaert. 2020. "Simultaneous Coercivity and Size Determination of Magnetic Nanoparticles" Sensors 20, no. 14: 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20143882
APA StyleCoene, A., & Leliaert, J. (2020). Simultaneous Coercivity and Size Determination of Magnetic Nanoparticles. Sensors, 20(14), 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20143882




