Potentiometric Solid-Contact Ion-Selective Electrode for Determination of Thiocyanate in Human Saliva
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Equipment
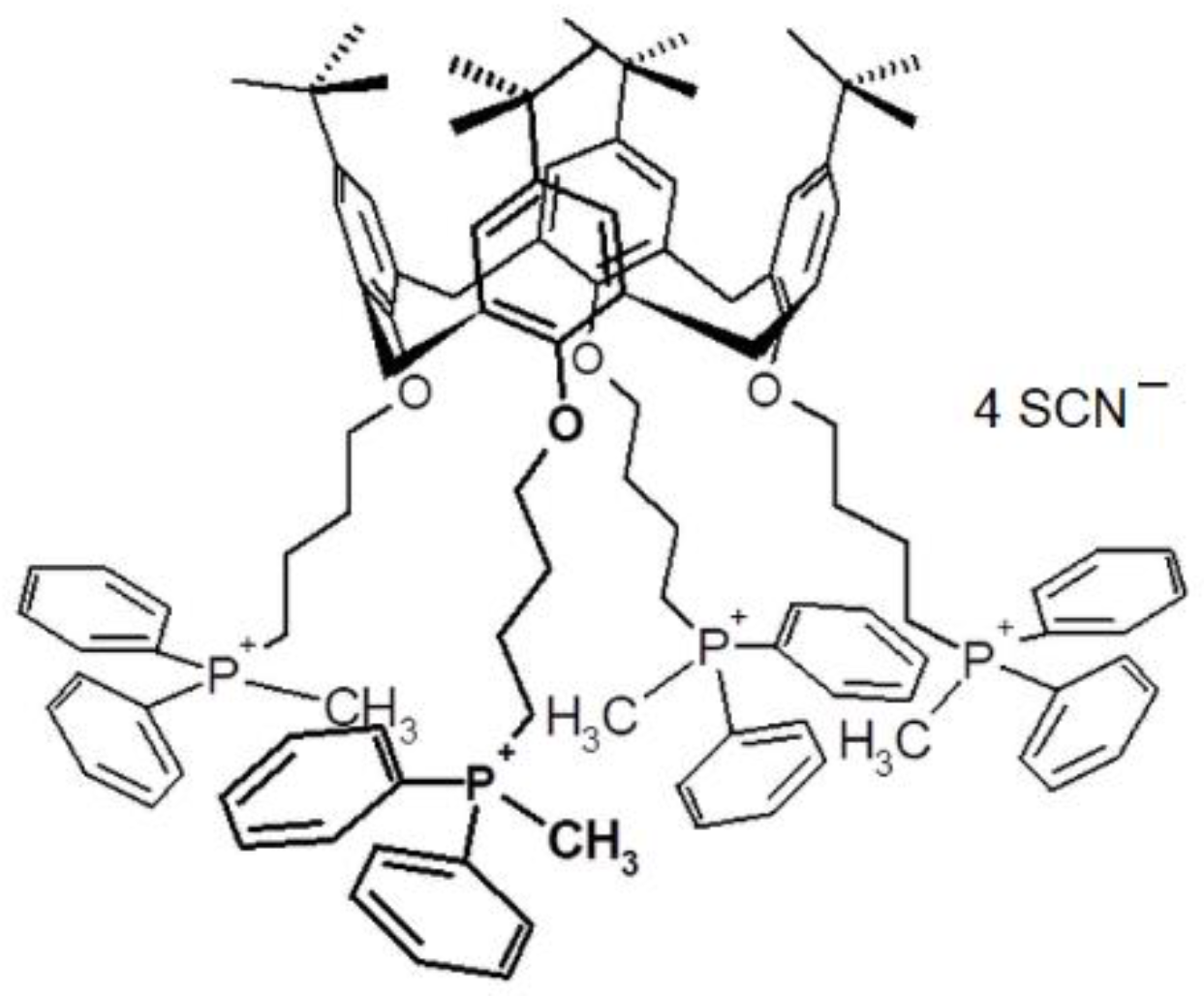
2.3. Thiocyanate-Solid State Ion Selective Electrodes (SCN-ISE)
2.4. Saliva’s Sampling and Measurement Protocol
3. Results
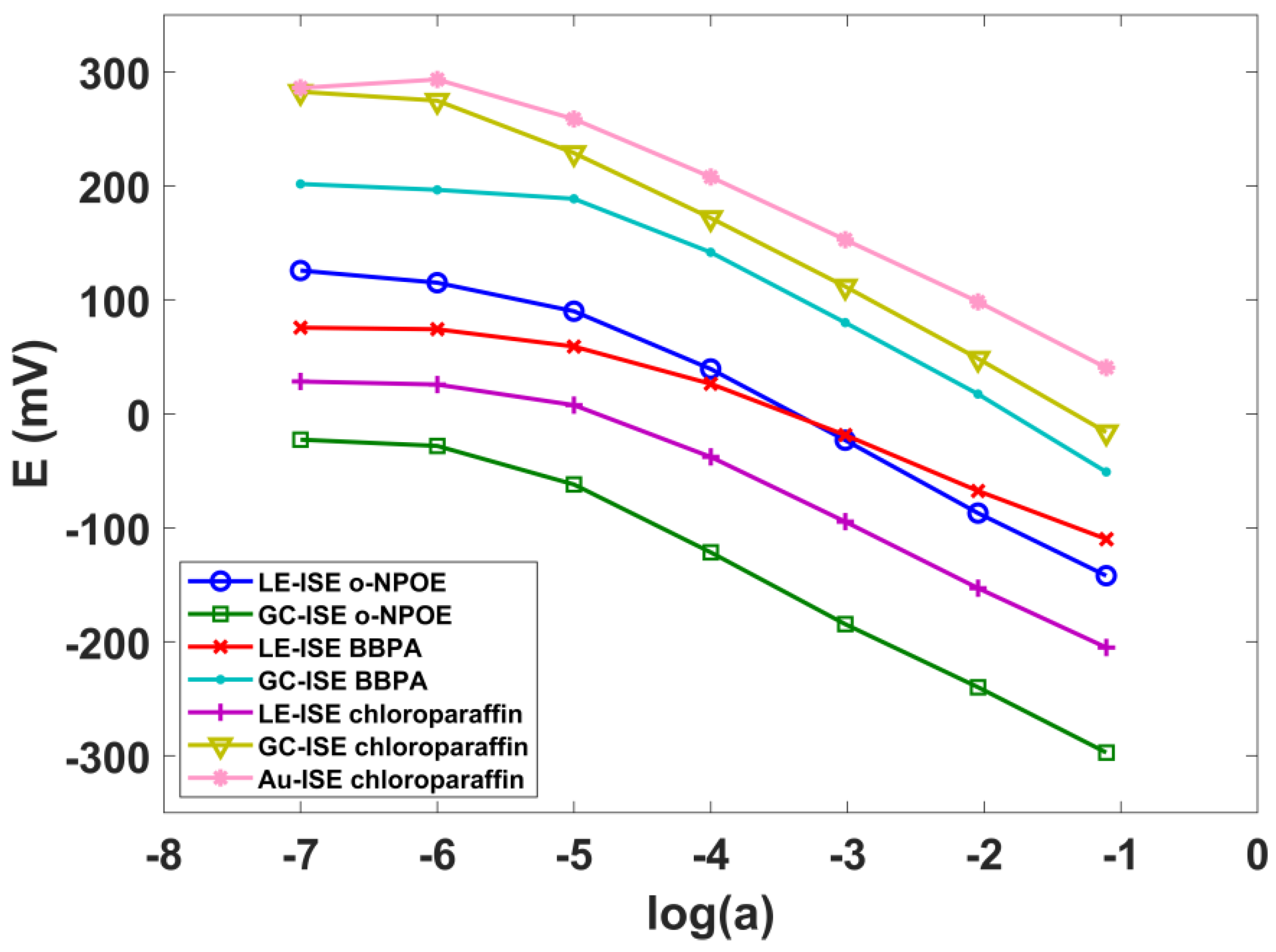
3.1. SCN-ISE Parameters
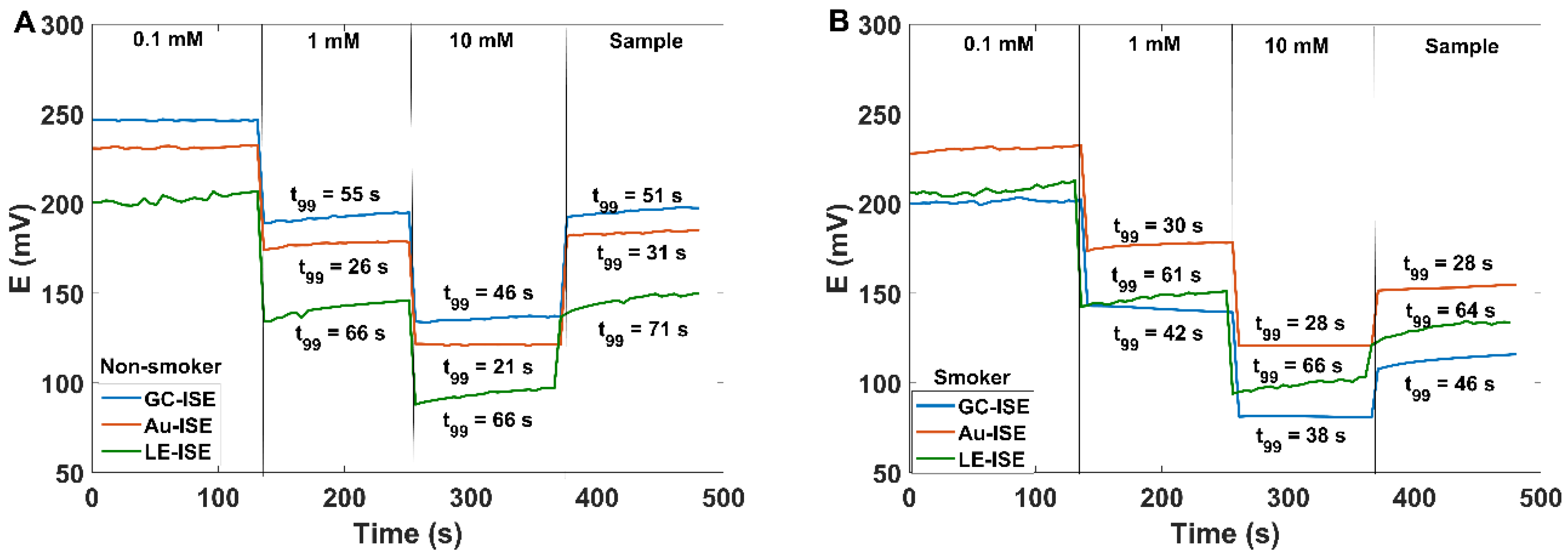
3.2. SCN− Determination in Human Saliva
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humphrey, S.P.; Williamson, R.T. A review of saliva: Normal composition, flow, and function. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steller, M.; Chou, L.; Daniels, T.E. Electrical Stimulation of Salivary Flow in Patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome. J. Dent. Res. 1988, 67, 1334–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, W.M. Saliva and dental health. Clinical implications of saliva: Report of a consensus meeting. Br. Dent. J. 1990, 169, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabak, L.A.; Levine, M.J.; Mandel, I.D.; Ellison, S.A. Role of salivary mucins in the protection of the oral cavity. J. Oral Pathol. 1982, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shern, R.J.; Fox, P.C.; Cain, J.L.; Li, S.-H. A Method for Measuring the Flow of Saliva from the Minor Salivary Glands. J. Dent. Res. 1990, 69, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navazesh, M. Methods for collecting saliva. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 694, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savica, V.; Calo, L.; Santoro, D.; Monardo, P.; Granata, A.; Bellinghieri, G. Salivary Phosphate Secretion in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2008, 18, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzalaf, M.A.; Hannas, A.R.; Kato, M.T. Saliva and dental erosion. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2012, 20, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; de Lima Marson, F.A.; de Holanda Mendonça, R.M.; Ribeiro, J.D.; Ribeiro, A.F.; Paschoal, I.A.; Levy, C.E. Saliva as a potential tool for cystic fibrosis diagnosis. Diag. Pathol. 2013, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraha, R.; Haratya, H.; Salameb, Z.; Faires, Y.; Ojcius, D.M.; Said Sadier, N. Salivary biomarkers for the diagnosisand monitoring of neurological diseases. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 63–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.B.; Faria, P.R.; Magna, L.A.; Correa, M.E.P.; De Sousa, C.A.; Almeida, O.P.; Cintra, M.L. Chronic GVHD in minor salivary glands and oral mucosa: Histopathological and immunohistochemical evaluation of 25 patients. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2005, 34, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilancio, G.; Cavallo, P.; Lombardi, C.; Guarino, E.; Cozza, V.; Giordano, F.; Palladino, G.; Cirillo, M. Saliva for assessing creatinine, uric acid, and potassium in nephropathic patients. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Vasudeva, S.B.; Vijayasarathy, S. Salivary gland disorders: A comprehensive review. World J. Stomatol. 2015, 4, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Månsson-Rahemtull, B.; Techanitisw, T.; Rahemtull, F.; McMillan, T.O.; Bradley, E.L.; Wahlin, Y.B. Analyses of salivary components in leukemia patients receiving chemotherapy. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. 1992, 74, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, M.; Vilpo, J. Spectrophotometric Determination of Thiocyanate in Human Saliva. J. Chem. Educ. 1999, 76, 1281–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.J.; Farias, M.A.; Silva, V.L.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M.; Araújo, A.N.; Lavorante, A.F.; Paim, A.P.S. Spectrophotometric Determination of Thiocyanate in Human Saliva Employing Micropumping Multicommutation Flow System. Spectrosc. Lett. 2010, 43, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenovuo, J.; Makinen, K.K. Concentration of Thiocyanate and Ionizable Iodine in Saliva of Smokers and Nonsmokers. J. Dent. Res. 1976, 55, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, B.A.; Reszka, K.J.; McCormick, M.L.; Britigan, B.E.; Evig, C.B.; Burns, P. Role of Thiocyanate, Bromide and Hypobromous Acid in Hydrogen Peroxide-induced Apoptosis. Free Radic. Res. 2004, 38, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolkiewicz, E.; Konopka, T.; Pupek, M.; Chybicka, A.; Mendak, M. Mucositis in children with leukemia and salivary defense factors. Dent. Med. Probl. 2007, 44, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kanthale, P.; Kumar, A.; Upadhyay, N.; Lal, D.; Rathod, G.; Sharma, V. Qualitative test for the detection of extraneous thiocyanate in milk. J. Food. Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1698–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ko, W.-C.; Liu, C.-L.; Lee, J.-J.; Liu, T.-P.; Yang, P.-S.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Cheng, S.-P. Negative Association between Serum Parathyroid Hormone Levels and Urinary Perchlorate, Nitrate, and Thiocyanate Concentrations in U.S. Adults: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005–2006. PLoS ONE 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, M.K.; Blount, B.C.; Valentin-Blasini, L.; Wapner, R.; Whyatt, R.; Gennings, C.; Factor-Litvak, P. CO-occurring exposure to perchlorate, nitrate and thiocyanate alters thyroid function in healthy pregnant women. Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ershad, S.; Sagathforoush, L.-A.; Karim-Nezhad, G. A Selective Optical Chemosensor Based on a Thia-containg Schiff-Base Iron(III) Complex for Thiocyanate Ion. Anal. Sci. 2009, 25, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Lavilla, I.; Bendicho, C. Paper-based analytical device for instrumental-free detection of thiocyanate in saliva as a biomarker of tobacco smoke exposure. Talanta 2016, 147, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettigrew, A.R.; Fell, G.S. Simplified Colorimetric Determination of Thiocyanate in Biological Fluids, and Its Application to Investigation of the Toxic Amblyopias. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammazzini, S.; Onor, M.; Pagliano, E.; Mester, Z.; Campanella, B.; Pitzalis, E.; Bramanti, E.; D’Ulivo, A. Determination of thiocyanate in saliva by headspace gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, following a single-step aqueous derivatization with triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1400, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Naruishi, N.; Fukuya, H.; Sakata, J.; Saito, K.; Wakida, S. Simultaneous determination of nitrite, nitrate, thiocyanate and uric acid in human saliva by capillary zone electrophoresis and its application to the study of daily variations. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1051, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinaka, S.; Takayama, N.; Michigami, Y.; Ueda, K. Simultaneous determination of cyanide and thiocyanate in blood by ion chromatography with fluorescence and ultraviolet detection. J. Chromatogr. B 1998, 713, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michigami, Y.; Fujii, K.; Ueda, K.; Yamamoto, Y. Determination of thiocyanate in human saliva and urine by ion chromatography. Analyst 1992, 117, 1855–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenkels, L.C.P.M.; Veerman, E.C.I.; Amerongen, A.V. Biochemical Composition of Human Saliva in Relation to Other Mucosal Fluids. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1995, 6, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Feng, S.; Pow, E.H.N.; Lam, O.L.; Mai, S.; Wang, H. Organic anion composition of human whole saliva as determined by ion chromatography. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 438, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaniotakis, N.A.; Chasser, A.M.; Meyerhoff, M.E.; Groves, J.T. Influence of Porphyrin Structure on Anion Selectivities of Manganese(III) Porphyrin Based Membrane Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.V.; Chaniotakis, N.A.; Lee, I.H.; Ma, S.C.; Park, S.B.; Meyerhoff, M.E.; Nick, R.J.; Groves, J.T. Mn(III)-Porphyrin-Based Thiocyanate-Selective Membrane Electrodes: Characterization and Application in Flow Injection Determination of Thiocyanate in Saliva. Electroanalysis 1989, 1, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Li, J.-Z.; Yu, R.-Q.; Zheng, G.-D. Metalloporphyrin Derivatives as Neutral Carriers for PVC Membrane Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 2245–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Gu, J.; Yu, R.-Q. Substituted metalloporphyrin derivatives as anion carrier for PVC membrane electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 302, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, J.H.; Amini, M.K.; Motaghi, M. Manganese porphyrin derivatives as ionophores for thiocyanate-selective electrodes: The influence of porphyrin substituents and additives on the response properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 87, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirmardi, A.; Shamsipur, M.; Akhond, M.; Monjezi, J. Electronic tongue for simultaneous determination of cyanide, thiocyanate and iodide. Measurement 2016, 88, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.K.; Shahrokhian, S.; Tangestaninejad, S. PVC-Based Cobalt and Manganese Phthalocyanine Coated Graphite Electrodes for Determination of Thiocyanate. Anal. Lett. 1999, 32, 2737–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.K.; Shahrokhian, S.; Tangestaninejad, S. Thiocyanate-selective electrodes based on nickel and iron phthalocyanines. Anal.Chim. Acta 1999, 402, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, M.M.; Sadeghi, A.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Highly selective and sensitive thiocyanate membrane electrode based on nickel(II)-1,4,8,11,15,18,22,25-octabutoxyphthalocyanine. Talanta 2005, 66, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, M.M.; Ensafi, A.A.; Niasaria, M.S.; Mirhoseini Chahooki, S. Selective thiocyanate poly(vinyl chloride) membrane based on a 1,8-dibenzyl-1,3,6,8,10,13-hexaazacyclotetradecane–Ni(II) perchlorate. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 462, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, A.; Kamyabi, M.A.; Esmaeilbeig, A.R.; Kia, R. Thiocyanate-selective electrode based on unsymmetrical benzoN4 nickel(II) macrocyclic complexes. Talanta 2002, 57, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjali, M.R.; Yousefi, M.; Javabakth, M.; Poursaberi, T.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Hajiagha-Babaei, L.; Latifi, E.; Shampsipur, M. Determination of SCN- in Urine and Saliva of Smokers and Non-Smokers by SCN- -Selective Polymeric Membrane Containing a Nickel(II)-Azamacrocycle Complex Coated on a Graphite Electrode. Anal. Sci. 2002, 18, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvand, M.; Zanjanchi, M.A.; Heydari, L. Novel thiocyanate-selective membrane sensor based on crown ether-cetyltrimethyl ammonium thiocyanate ion-pair as a suitable ionophore. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 122, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruoğlu, D.; Canel, E.; Memon, S.; Yilmaz, M.; Kiliȩ, E. Using of hydrogen ion-selective poly(vinyl chloride) membrane electrode based on calix[4]arene as thiocyanate ion-selective electrode. Anal. Sci. 2003, 19, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.M.; Elmosalamy, M.A.M.F. Liquid membrane electrode for selective determination of thiocyanate. Analyst 1987, 112, 1709–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-Q.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Yuan, R.; Ying, M.; Shen, G.-L.; Yu, R.-Q. Thiocyanate-selective PVC membrane electrodes based on Mn(II) complex of N,N′-bis-(4-phenylazosalicylidene) o-phenylene diamine as a neutral carrier. Electrochim. Acta 1999, 44, 2543–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjali, M.R.; Poursaberi, T.; Basiripour, F.; Salavati-Niassari, M.; Yousefi, M.; Shampsipur, M. Highly selective thiocyanate poly(vinyl chloride) membrane electrode based on a cadmium–Schiff’s base complex. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 2001, 370, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Wang, X.L.; Xu, L.; Chai, Y.Q.; Sun, Z.Y.; Huang, X.Q.; Li, Q.F.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, L. Highly selective thiocyanate electrode based on bis-bebzoin-semitriethylenetetraamine binuclear copper(II) complex as neutral carrier. Electrochem. Commun. 2003, 5, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.M.; Ghali, M.H.A.; Amr, A.-G.M.; Mohamed, A.H.K. Novel thiocyanate-selective membrane sensors based on di-, tetra-, and hexa-imidepyridine ionophores. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 482, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.K.; Rafi, A.; Ghaedi, M.; Zohory, M.M. Bis(2-mercaptobenzoxazolato)mercury(II) and bis(2-pyridinethiolato)mercury(II) complexes as carriers for thiocyanate selective electrodes. Microchem. J. 2003, 75, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühlmann, P.; Yahya, L.; Enderes, R. Ion-Selective Electrodes for Thiocyanate Based on the Dinuclear Zinc(II) Complex of a Bis-N,O-bidentate Schiff Base. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.-Q.; Dai, J.Y.; Yuan, R.; Zhong, X.; Liu, Y.; Tang, D.-T. Highly thiocyanate-selective membrane electrodes based on the N,N′-bis-(benzaldehyde)-glycine copper(II) complex as a neutral carrier. Desalination 2005, 180, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Ershad, S.; Samadi, N.; Rezvani, A.R.; Haddadzadeh, H. The first use of a Rh(III) complex as a novel ionophore for thiocyanate-selective polymeric membrane electrodes. Talanta 2005, 65, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, U.P.; Mehtab, S.; Aggarwal, V. Thiocyanate selective sensor based on tripodal zinc complex for direct determination of thiocyanate in biological samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Rawat, A.; Sarkar, A. Thiocyanate-Selective PVC Membrane Electrode Based on Copper and Nickel Complexes of Para-tolualdehydesemicarbazone as Carrier. Anal. Lett. 2010, 41, 3058–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Aggarwal, V.; Singh, U.P.; Mehtab, S. Nickel pyrazolyl borate complexes: Synthesis, structure and analytical application in biological and environmental samples as anion selective sensors. Talanta 2008, 77, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrollahi, A.; Ghaedi, M.; Ghaedi, H.; Kianfar, A.H. Thiocyanate-selective membrane electrode based on cobalt(III) Schiff base as a charge carrier. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2008, 88, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.S.; Hong, T.K.; Lee, Y.H. Thiocyanate ion selective solid contact electrode based on Mn complex of N,N′-bis-(4-phenylazosalicylidene)-O-phenylene diamine ionophore. AJAC 2011, 2, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvidi, A.; Ghanbarzadeh, M.T.; Dehghan, M.; Mazloum-Ardakani, M.; Vafazadeh, R. Thiocyanate ion selective electrode based on bis(N-3-methylphenyl salicylidenaminato)copper(II) ionophore. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 1639–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehab, O.R.; Mansour, A.M. New thiocyanate potentiometric sensors based on sulfadimidine metal complexes: Experimental and theoretical studies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 57, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, S.; Hooda, S.; Tomar, P.K.; Malik, A.; Kumar, A.; Malik, S.; Gautam, S. Synthesis and characterization of bis nitrato[4-hydroxyacetophenonesemicarbazone) nickel(II) complex as ionophore for thiocyanate-selective electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewenstam, A. Electrochemical Sensor Analysis. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Alegret, S., Merkoci, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lewenstam, A. Routines and Challenges in Clinical Application of Electrochemical Ion-Sensors. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Nostro, P.; Ninham, B.W. Hofmeister Phenomena: An Update on Ion Specificity in Biology. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2286–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janata, J. Electrochemistry of chemically sensitive field effect transistors. Sens. Actuators 1983, 4, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomecko, R.; Asfari, Z.; Hubscher-Bruder, V.; Bochenska, M.; Arnaud-Neu, F. Anion recognition by phosphonium calix[4]arenes: Synthesis and physico-chemical studies. Supramol. Chem. 2010, 22, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Urbanowicz, M.; Pijanowska, D.G.; Jasiński, A.; Ekman, M.; Bocheńska, M.K. A miniaturized solid-contact potentiometric multisensor platform for determination of ionic profiles in human saliva. J. Solid State Electochem. 2019, 23, 3299–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanowicz, M.; Jasiński, A.; Jasińska, M.; Drucis, K.; Ekman, M.; Szarmach, A.; Suchodolski, R.; Pomećko, R.; Bocheńska, M. Simultaneous determination of Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and Cl- in unstimulated and stimulated human saliva using all solid state multisensor platform. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 2232–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanowicz, M.; Pijanowska, D.G.; Jasiński, A.; Bocheńska, M. The Computational Methods in the Development of a Novel Multianalyte Calibration Technique for Potentiometric Integrated Sensors Systems. J Solid State Electrochem. 2019, 23, 2251–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiński, A.; Urbanowicz, M.; Guziński, M.; Bocheńska, M. Potentiometric Solid-Contact Multisensor System for Simultaneous Measurement of Several Ions. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E. Determination of Unbiased Selectivity Coefficients of Neutral Carrier-Based Cation-Selective Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, R.P.; Linder, E. Recommendations for nomenclature of ion-selective electrodes. Pure. Appl. Chem. 1994, 68, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, R.W.; Covington, A.K.; Andersen, N.F. Use of Ion-Selective Electrodes for Blood-Electrolyte Analysis. Recommendations for Nomenclature, Definitions and Conventions. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2000, 38, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, E.; Pretsch, E.; Buhlmann, P. Selectivity of Potentiometric Ion Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, Y.; Buhlmann, P.; Umezawa, K.; Tohda, K.; Amemiya, S. Potentiometric selectivity coefficients of ion-selective electrodes Part I. Inorganic cations (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Apply. Chem. 2000, 72, 1851–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E. Selectivity of liquid membrane ion-selective electrodes. Electroanalysis 1997, 9, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechenkina, I.A.; Mikhelson, K.N. Materials for the Ionophore Based Membranes for Ion Selective Electrodes: Problems and Achievements (Review Paper). Russ. J. Electrochem. 2015, 51, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aps, J.K.M.; Martens, L.C. Review: The physiology of saliva and transfer of drugs into saliva. Forensic Sci. Int. 2005, 150, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardow, A.; Madsen, J.; Nauntofte, B. The bicarbonate concentration in human saliva does not exceed theplasma level under normal physiological conditions. Clin. Oral. Invest 2000, 4, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobey, S.L.; Anslyn, E.V. Determination of Inorganic Phosphate in Serum and Saliva Using a Synthetic Receptor. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 2029–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa Novoa, D.; Eisenhardt Melloa, J.; Rondana, F.S. Bromine and iodine determination in human saliva: Challenges in thedevelopment of an accurate method. Talanta 2019, 191, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, D.K.; Harden, R.M.; Alexander, W.D. The influence of flow rate on the salivary iodide concentration in man. Arch. Oral. Biol. 1966, 11, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannana, K.; Praamsmaa, M.L.; Oldi, J.F. Occurrence of perchlorate in drinking water, groundwater, surface waterand human saliva from India. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umezawa, Y.; Umezawa, K.; Buhlmann, P.; Hamada, N.; Aoki, H.; Nakanishi, J.; Sato, M.; Xiao, K.P.; Nishimura, Y. Potentiometric selectivity coefficients of ion-selective electrodes Part II. Inorganic anions (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Apply. Chem. 2002, 74, 923–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ISE Type | S (mV/dec) | Low Limit of Detection (logaSCN−) | Lifetime (Month) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LE-ISEBBPA | −47.4 ± 3.8 | −4.67 | < 1 |
| GC-ISE BBPA | −61.9 ± 3.2 | −4.82 | < 1 |
| LE-ISE o-NPOE | −60.6 ± 1.7 | −5.20 | 3 |
| GC-ISE o-NPOE | −60.4 ± 1.2 | −5.20 | 3 |
| LE-ISE Chloroparaffin | −55.5 ± 2.1 | −5.20 | 3 |
| GC-ISE Chloroparaffin | −59.9 ± 0.3 | −5.80 | 3 |
| Au-ISE Chloroparaffin | −53.3 ± 2.1 | −5.50 | 3 |
| ISE Type | Separate Solution Method (SD ± 0.1) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl− | H2PO4− | HCO3− | Ac− | Bz− | NO3− | Br− | I− | SCN− | ClO4− | |
| LE-ISE | −3.2 | −4.5 | −3.4 | −3.1 | −2.0 | −1.6 | −2.0 | −0.2 | 0.0 | 0.7 |
| GC-ISE | −4.0 | −4.0 | −3.9 | −2.1 | −3.8 | −1.6 | −2.5 | −0.3 | 0.0 | 0.7 |
| Au-ISE | −3.8 | −4.2 | −3.0 | −2.4 | −3.6 | −2.0 | −2.6 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.8 |
| Fix Interference Method (SD ± 0.1) | ||||||||||
| LE-ISE | −3.9 | −4.6 | −3.4 | −2.7 | −2.0 | −1.8 | −2.1 | −0.4 | 0.0 | 0.6 |
| GC-ISE | −3.9 | −4.2 | −3.9 | −2.2 | −3.9 | −1.8 | −2.2 | −0.5 | 0.0 | 0.5 |
| Au-ISE | −3.8 | −4.4 | −3.6 | −2.3 | −3.6 | −1.8 | −2.2 | −0.4 | 0.0 | 0.6 |
| Interfering Ion | Selectivity Coefficient for Au-ISE | Required Selectivity Coefficient | Representative Interfering Ion Concentration in Human Saliva (mM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cl− | −3.9 | −3.1 | 30 [79] |
| HCO3− | −3.6 | −3.1 | 30 [80] |
| H2PO4− | −4.4 | −2.6 | 10 [81] |
| AcO− | −2.4 | −1 | 0.24 [31] |
| Bz− | −3.2 | 1 | 2.5 × 10−3 [82] |
| NO3− | −1.8 | −1.3 | 0.76 [31] |
| Br− | −2.2 | 2.8 | 4 × 10−5 [82] |
| I− | −0.4 | 4.2 | 1.4 × 10−6 [83] |
| ClO4− | 0.6 | 3.3 | 1.3 × 10−5 [84] |
| Sample | Concentration of SCN− (mM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LE-ISE | GC-ISE | Au-ISE | UV-Vis | |
| I (non-smoker) | 0.85 ± 0.14 | 0.87 ± 0.09 | 0.79 ± 0.06 | 0.82 ± 0.01 |
| II (smoker) | 5.31 ± 0.06 | 5.38 ± 0.05 | 5.49 ± 0.06 | 5.50 ± 0.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urbanowicz, M.; Sadowska, K.; Pijanowska, D.G.; Pomećko, R.; Bocheńska, M. Potentiometric Solid-Contact Ion-Selective Electrode for Determination of Thiocyanate in Human Saliva. Sensors 2020, 20, 2817. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102817
Urbanowicz M, Sadowska K, Pijanowska DG, Pomećko R, Bocheńska M. Potentiometric Solid-Contact Ion-Selective Electrode for Determination of Thiocyanate in Human Saliva. Sensors. 2020; 20(10):2817. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102817
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrbanowicz, Marcin, Kamila Sadowska, Dorota G. Pijanowska, Radosław Pomećko, and Maria Bocheńska. 2020. "Potentiometric Solid-Contact Ion-Selective Electrode for Determination of Thiocyanate in Human Saliva" Sensors 20, no. 10: 2817. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102817
APA StyleUrbanowicz, M., Sadowska, K., Pijanowska, D. G., Pomećko, R., & Bocheńska, M. (2020). Potentiometric Solid-Contact Ion-Selective Electrode for Determination of Thiocyanate in Human Saliva. Sensors, 20(10), 2817. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102817







