Screen Printed Based Impedimetric Immunosensor for Rapid Detection of Escherichia coli in Drinking Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
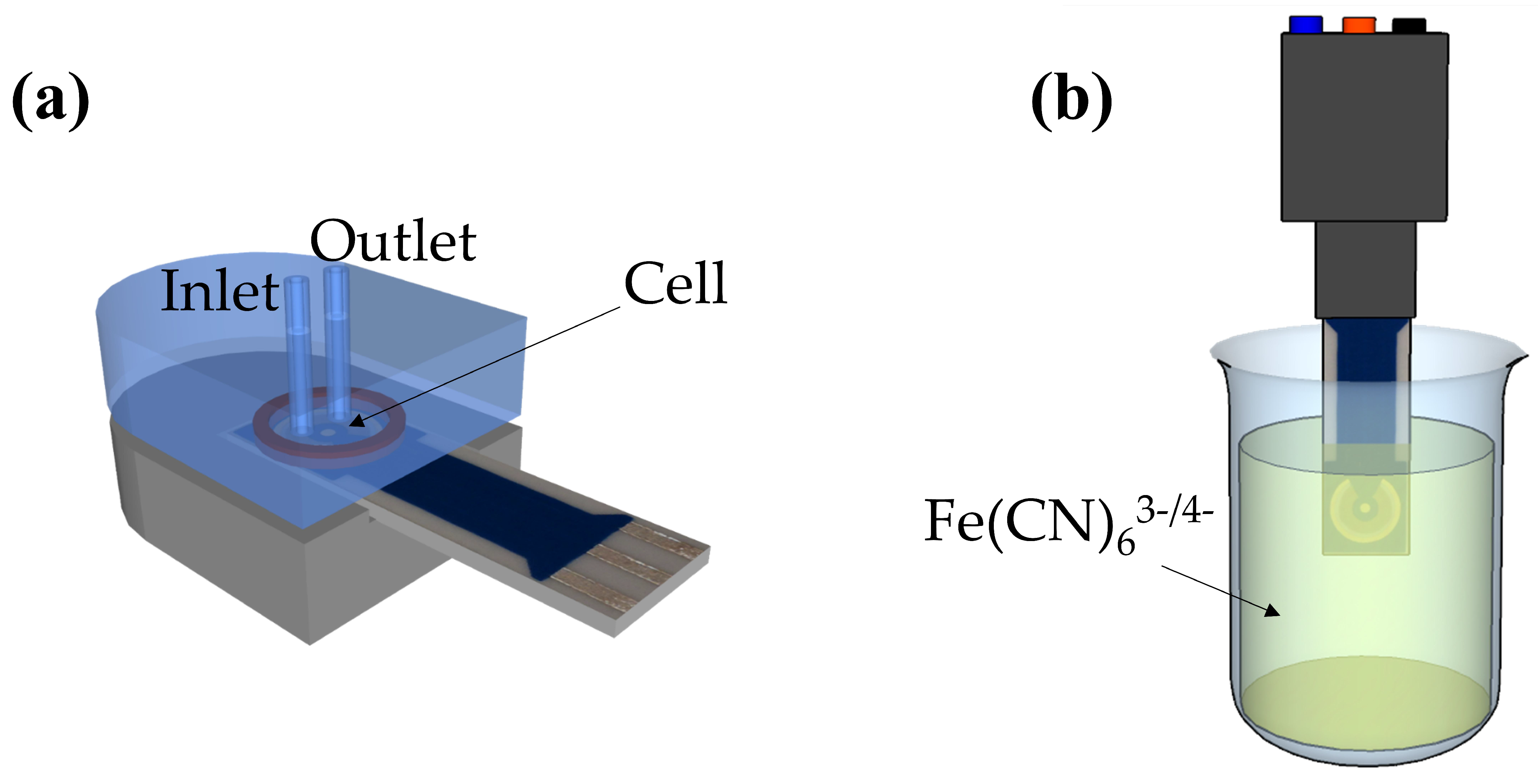
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Preparation of the Biological Sample
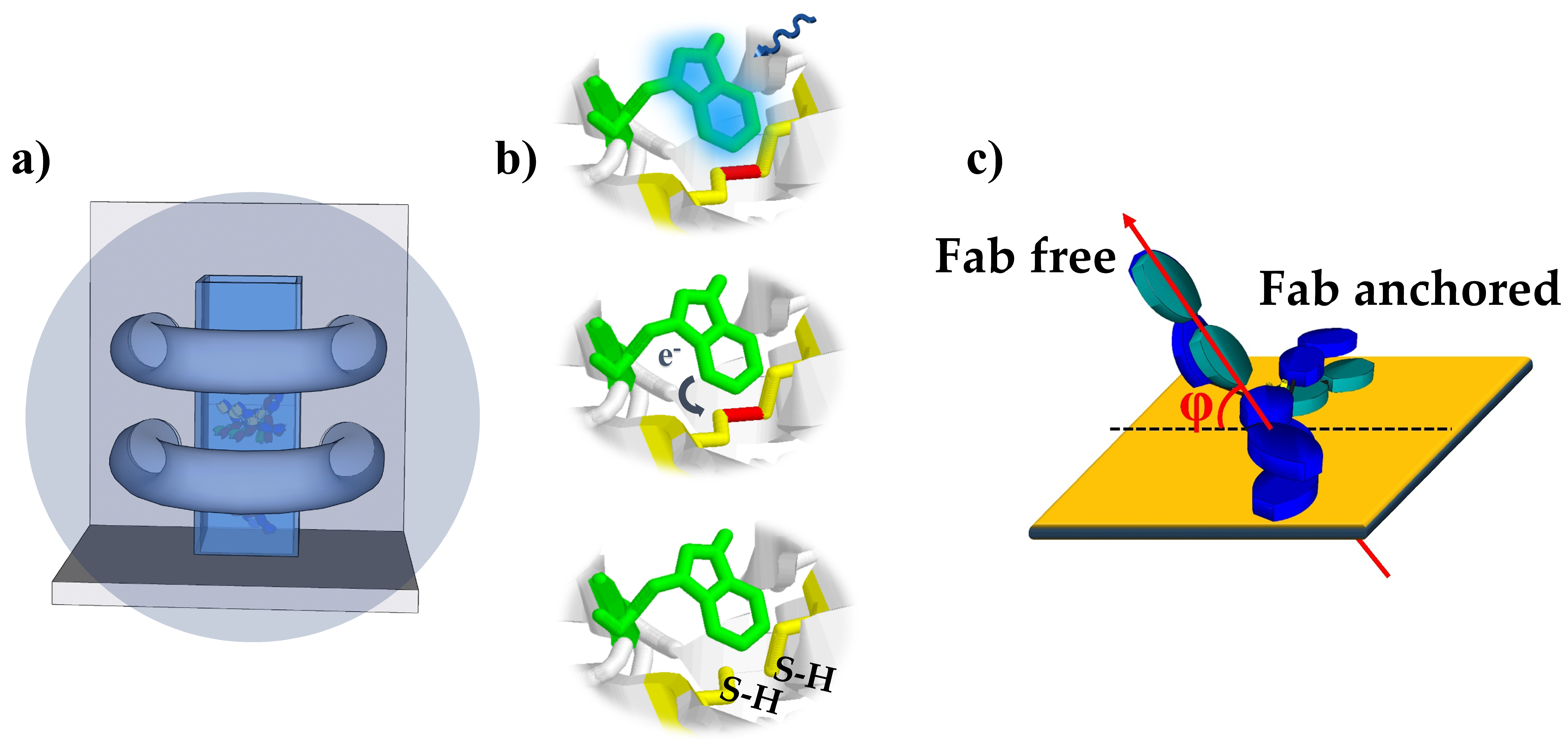
2.4. UV Activation of Antibody Solution
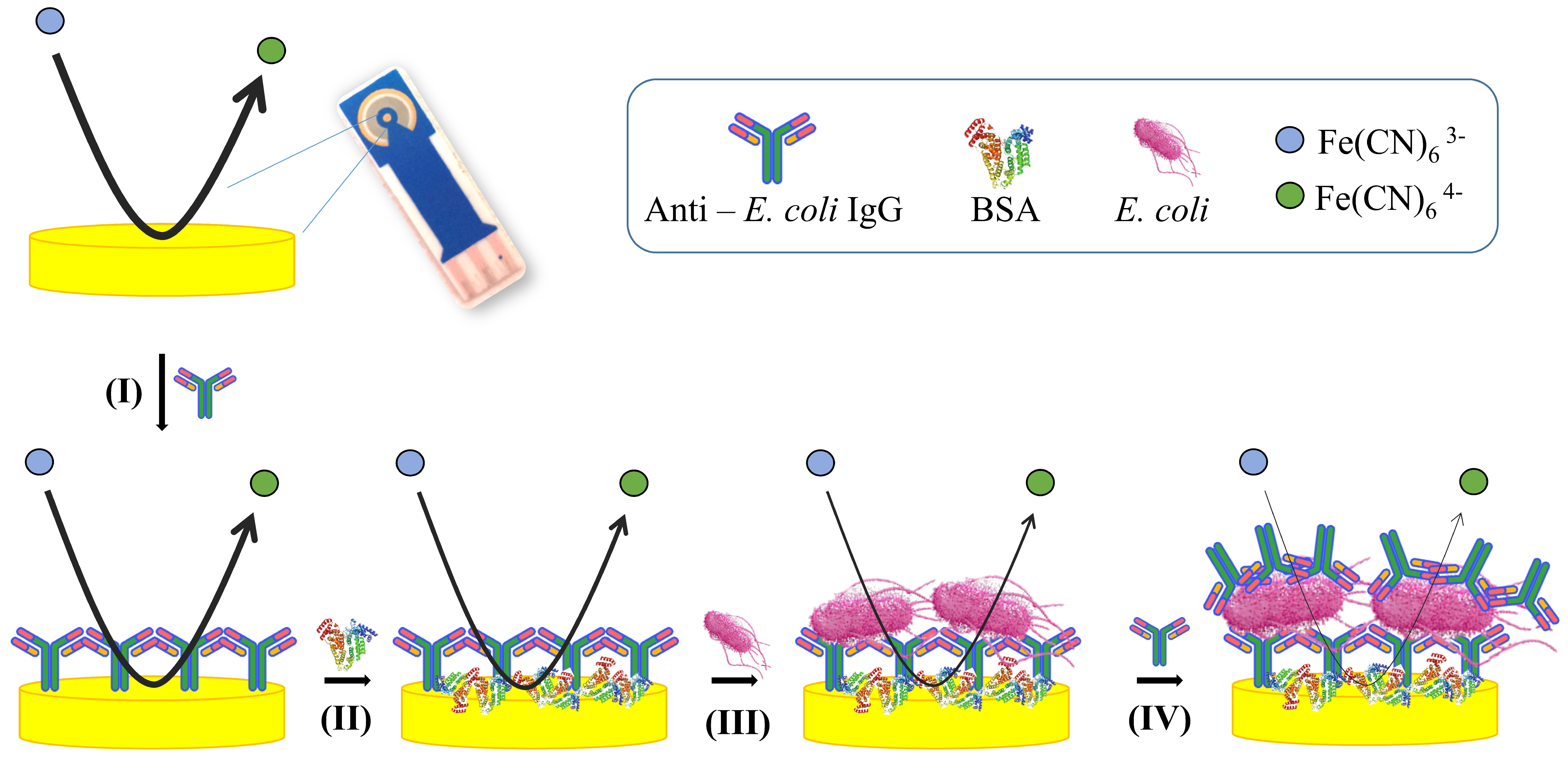
2.5. Immunosensor Development and E. coli Detection
2.6. Enhanced Sensitivity Protocol
3. Results and Discussion
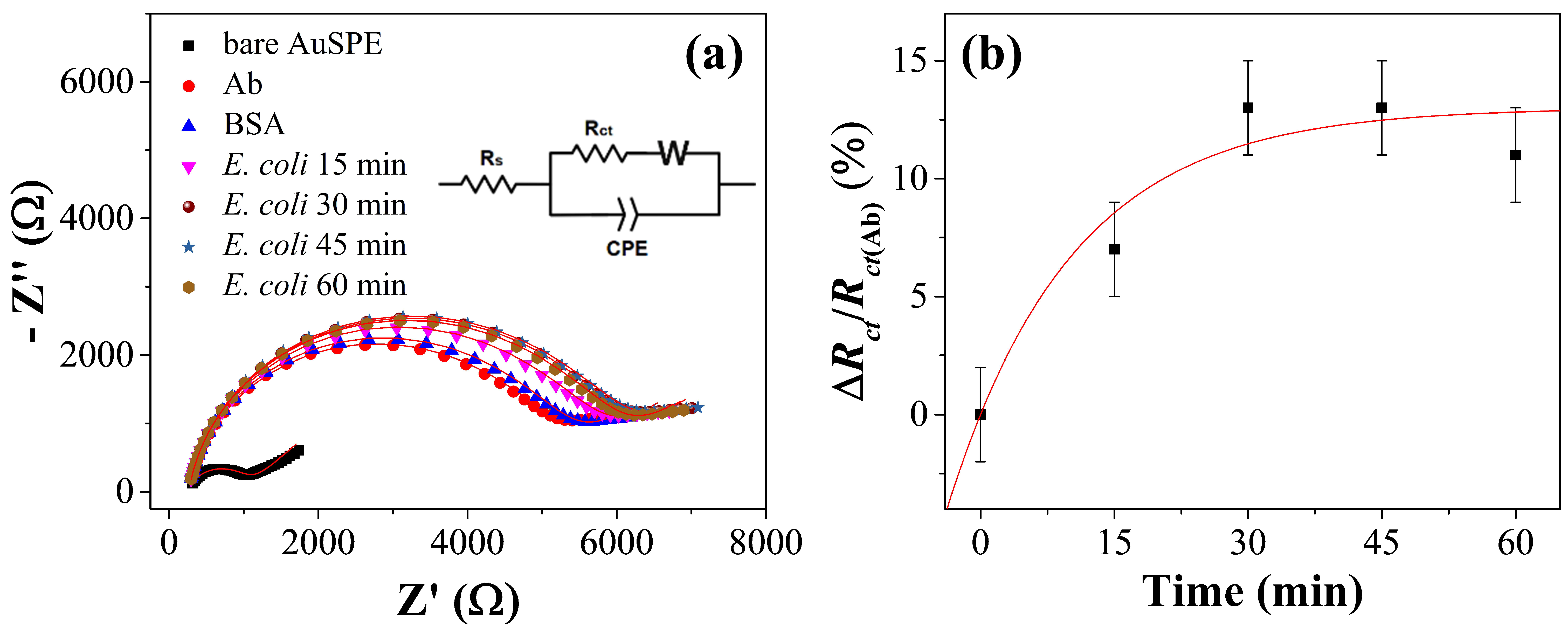
3.1. Principle of the Impedimetric Biosensor
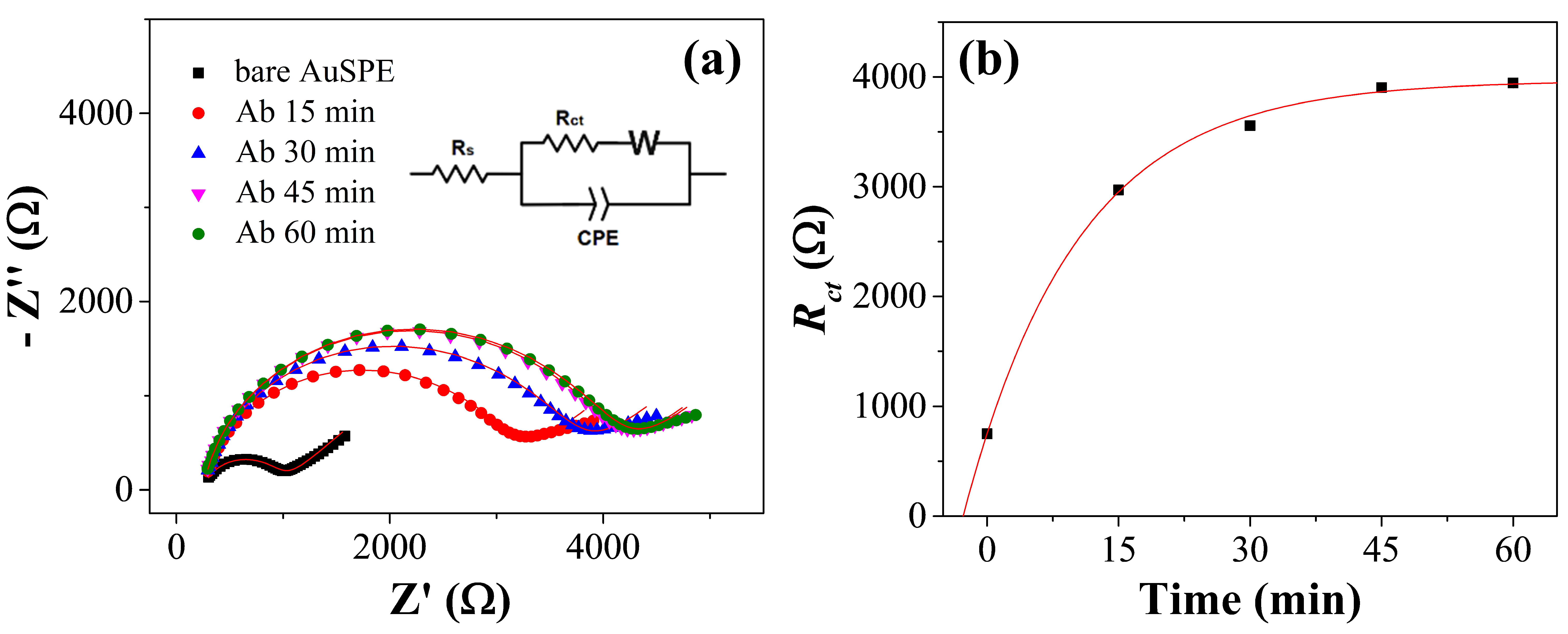
3.2. Kinetics of the Functionalization and Detection
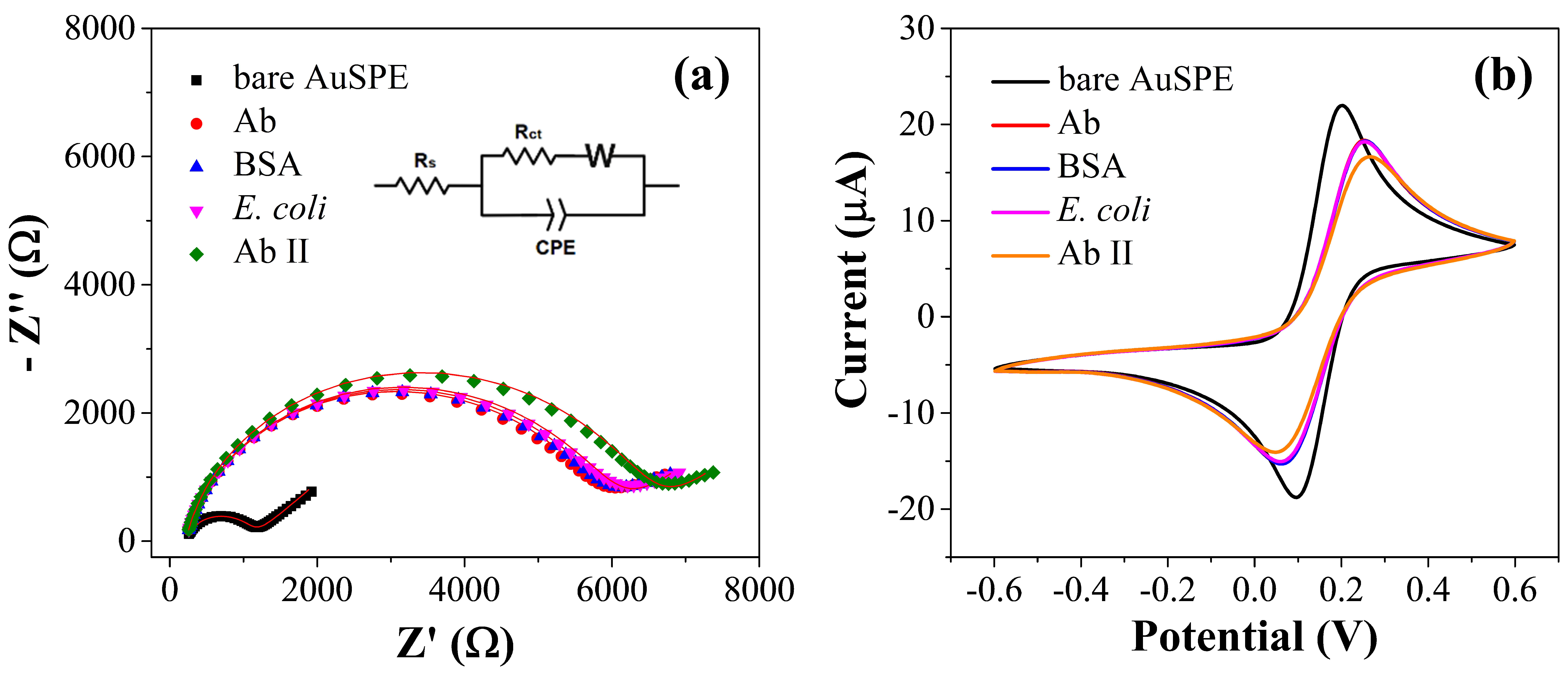
3.3. Electrochemical Characterization of the Immunosensor Preparation
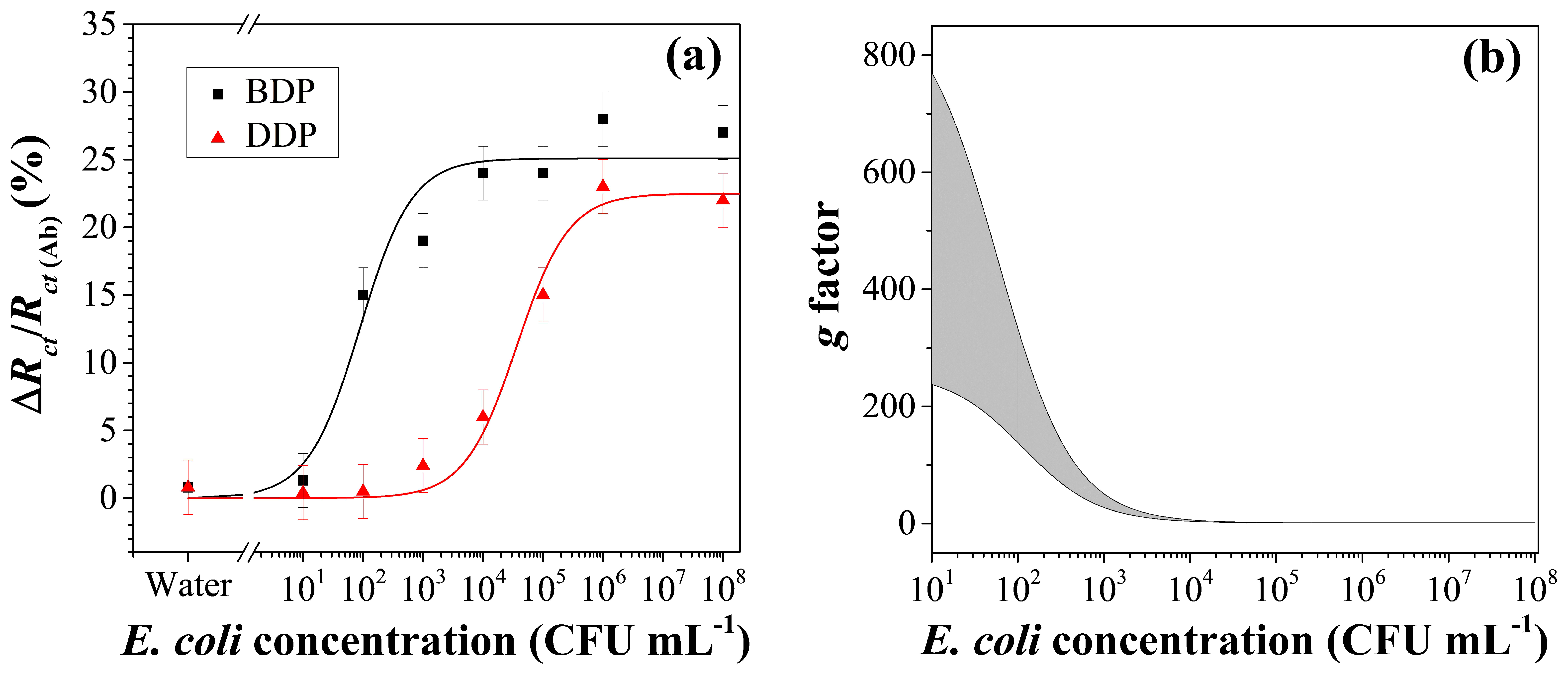
3.4. Immunosensor Analytical Performance
3.5. Data Fitting
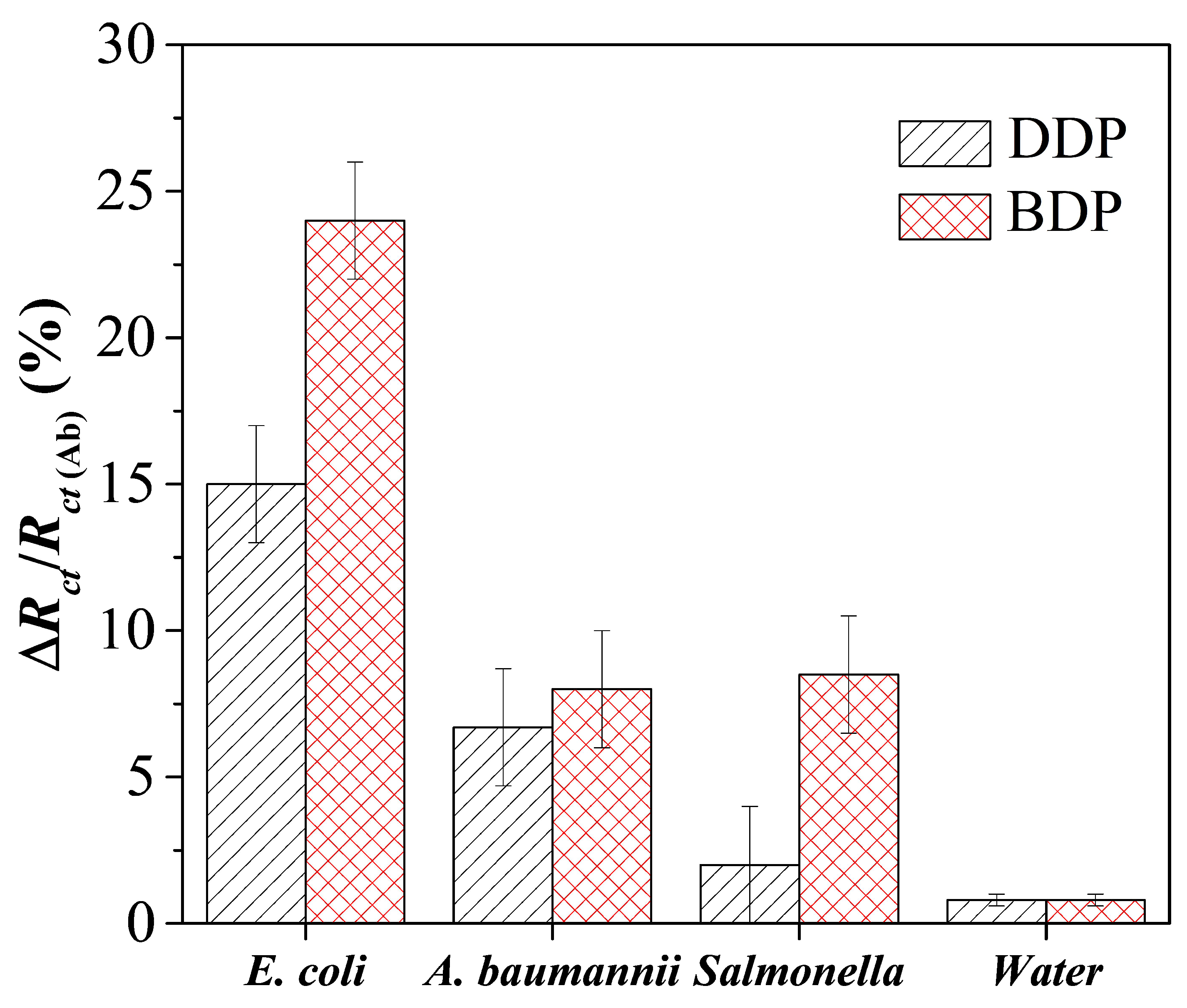
3.6. Immunosensor Specificity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Odonkor, S.T.; Ampofo, J.K. Escherichia coli as an indicator of bacteriological quality of water: An overview. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 4, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, J.P.S. Water microbiology. Bacterial pathogens and water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3657–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Drinking-Water. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water (accessed on 17 September 2019).
- Price, R.G.; Wildeboer, D. E. coli as an Indicator of Contamination and Health Risk in Environmental Waters. In Escherichia coli—Recent Advances on Physiology, Pathogenesis and Biotechnological Applications; InTech: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Velusamy, V.; Arshak, K.; Korostynska, O.; Oliwa, K.; Adley, C. An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: In the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Huang, W.C.; Yang, S.T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in surface enhanced poly(methyl methacrylate) microchannels. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 98, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.L.; Louie, L.; Simor, A.E.; Louie, M. PCR detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 directly from stools: Evaluation of commercial extraction methods for purifying fecal DNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4108–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Levin, R.E. Quantitative detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in ground beef by the polymerase chain reaction. Food Microbiol. 2002, 19, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deisingh, A.K.; Thompson, M. Detection of infectious and toxigenic bacteria. Analyst 2002, 127, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Váradi, L.; Luo, J.L.; Hibbs, D.E.; Perry, J.D.; Anderson, R.J.; Orenga, S.; Groundwater, P.W. Methods for the detection and identification of pathogenic bacteria: Past, present, and future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4818–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furst, A.L.; Francis, M.B. Impedance-Based Detection of Bacteria. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 700–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, M.; Kotian, A.; Marathe, S.; Chakravortty, D. Detection of microorganisms using biosensors—A smarter way towards detection techniques. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Electrochemical biosensors for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Talanta 2017, 162, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudak, F.C.; Boyaci, I.H. Development of an immunosensor based on surface plasmon resonance for enumeration of Escherichia coli in water samples. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lin, C.S.; Chen, S.H.; Ye, R.; Wu, V.C.H. A piezoelectric immunosensor for specific capture and enrichment of viable pathogens by quartz crystal microbalance sensor, followed by detection with antibody-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leahy, S.; Lai, Y. A cantilever biosensor based on a gap method for detecting E. coli in real time. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, F.S.; Angnes, L. Electrochemical immunosensors—A powerful tool for analytical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollarasouli, F.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Ozkan, S.A. The Role of Electrochemical Immunosensors in Clinical Analysis. Biosensors 2019, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Du, X. Electrochemical Biosensors for Detection of Foodborne Pathogens. Micromachines 2019, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalouf, R.; Fournier-Wirth, C.; Coste, J.; Chebib, H.; Saïkali, Y.; Vittori, O.; Errachid, A.; Cloarec, J.P.; Martelet, C.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Label-free detection of bacteria by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: Comparison to surface plasmon resonance. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4879–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla-Gómez, V.; Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; Pingarrón, J.M. Gold screen-printed-based impedimetric immunobiosensors for direct and sensitive Escherichia coli quantisation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3365–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, P.; Zhang, X.; Meng, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Jin, L.; Feng, Z.; Wu, Z. Self-assembled monolayers-based immunosensor for detection of Escherichia coli using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 4663–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, H.; Hao, H.; Gong, Q.; Nie, K. Detection of Escherichia coli with a label-free impedimetric biosensor based on lectin functionalized mixed self-assembled monolayer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 229, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvano, F.; Pilloton, R.; Albanese, D. Label-free impedimetric biosensors for the control of food safety—A review. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, N.G.; Scoble, J.A.; Muir, B.W.; Pigram, P.J. Orientation and characterization of immobilized antibodies for improved immunoassays (Review). Biointerphases 2017, 12, 02D301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Fang, Y.; Ramasamy, R.P. Non-covalent functionalization of carbon nanotubes for electrochemical biosensor development. Sensors 2019, 19, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Byrne, H.; O’Kennedy, R.J. Antibodies and antibody-derived analytical biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Um, H.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Min, J.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, Y. Electrochemically oriented immobilization of antibody on poly-(2-cyano-ethylpyrrole)-coated gold electrode using a cyclic voltammetry. Talanta 2011, 84, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, N.J.; Kiziltepe, T.; Bilgicer, B. Oriented surface immobilization of antibodies at the conserved nucleotide binding site for enhanced antigen detection. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9640–9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.A.; Hsu, W.; Liao, W.; Chiu, J.; Chen, M.; Chang, H.; Li, C. Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of biotin using electrically addressable site-oriented antibody immobilization approach via aminophenyl boronic acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, S.K.; Dixit, C.K.; MacCraith, B.D.; O’Kennedy, R. Effect of antibody immobilization strategies on the analytical performance of a surface plasmon resonance-based immunoassay. Analyst 2011, 136, 4431–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Park, J.S.; Shim, Y.B. An impedimetric immunosensor for the label-free detection of bisphenol A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2464–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, A.C.; Collyer, S.D.; Davis, F.; Garifallou, G.; Tsekenis, G.; Tully, E.; Kennedy, R.O.; Gibson, T.; Millner, P.A.; Higson, S.P.J. Labeless AC impedimetric antibody-based sensors with pg mL−1 sensitivities for point-of-care biomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouerghi, O.; Touhami, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Martelet, C.; Ouada, H.B.; Cosnier, S. Impedimetric immunosensor using avidin—Biotin for antibody immobilization. Bioelectrochemistry 2002, 56, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, C.S.; Kwon, Y.; Ha, J.H.; Choi, S.S.; Cha, H.J. A comparative study on antibody immobilization strategies onto solid surface. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkpen, M.S.; Liu, Z.-F.; Li, H.; Campos, L.M.; Neaton, J.B.; Venkataraman, L. Non-chemisorbed gold–sulfur binding prevails in self-assembled monolayers. Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharafeldin, M.; Rusling, J.F. Influence of antibody immobilization strategy on carbon electrode immunoarrays. Analyst 2019, 144, 5108–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, J.M.; Stuart, M.C.; Wong, D.K.Y. Self-assembled layer of thiolated protein G as an immunosensor scaffold. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Du, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Li, Q. A label-free electrochemical immunosensor for carbofuran detection based on a sol-gel entrapped antibody. Sensors 2011, 11, 9520–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereli, N.; Ertürk, G.; Tümer, M.A.; Denizli, A. Oriented immobilized anti-hIgG via Fc fragment-imprinted PHEMA cryogel for IgG purification. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschallski, M.; Evers, A.; Brandstetter, T.; Rühe, J. Sensitivity of microarray based immunoassays using surface-attached hydrogels. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 781, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, H. Antibody immobilization technique using protein film for high stability and orientation control of the immobilized antibody. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icoz, K.; Soylu, M.C.; Canikara, Z.; Unal, E. Quartz-crystal Microbalance Measurements of CD19 Antibody Immobilization on Gold Surface and Capturing B Lymphoblast Cells: Effect of Surface Functionalization. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiros dos Santos, M.; Agusil, J.P.; Prieto-Simón, B.; Sporer, C.; Teixeira, V.; Samitier, J. Highly sensitive detection of pathogen Escherichia coli O157:H7 by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvano, F.; Pilloton, R.; Albanese, D. Sensitive Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Food Products by Impedimetric Immunosensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Ai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, X.; Gao, Q.; Cheng, Z. Signal-off impedimetric immunosensor for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Pillai, R.G.; Lee, W.E.; Jemere, A.B. An impedimetric biosensor for E. coli O157:H7 based on the use of self-assembled gold nanoparticles and protein G. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, A.D.; De, A.; Chaudhuri, C.R.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Sen, P. Label free polyaniline based impedimetric biosensor for detection of E. coli O157:H7 Bacteria. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vericat, C.; Vela, M.E.; Benitez, G.; Carro, P.; Salvarezza, R.C. Self-assembled monolayers of thiols and dithiols on gold: New challenges for a well-known system. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1805–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandler, D.; Kraus-Ophir, S. Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) for electrochemical sensing. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2011, 15, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaki, N.K.; Vijayamohanan, K. Self-assembled monolayers as a tunable platform for biosensor applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Canavan, H.E.; Gamble, L.J.; Castner, D.G. Evidence of impurities in thiolated single-stranded DNA oligomers and their effect on DNA self-assembly on gold. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5134–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, A.; Blues, E.; Williamson, P.; Cardona, M.; Gray, L.; Corrigan, D.K. SAM composition and electrode roughness affect performance of a DNA biosensor for antibiotic resistance. Biosensors 2019, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimers, J.R.; Ford, M.J.; Marcuccio, S.M.; Ulstrup, J.; Hush, N.S. Competition of van der Waals and chemical forces on gold-sulfur surfaces and nanoparticles. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häkkinen, H. The gold-sulfur interface at the nanoscale. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pensa, E.; Cortés, E.; Corthey, G.; Carro, P.; Vericat, C.; Fonticelli, M.H.; Benítez, G.; Rubert, A.A.; Salvarezza, R.C. The chemistry of the sulfur-gold interface: In search of a unified model. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Ventura, B.; Banchelli, M.; Funari, R.; Illiano, A.; De Angelis, M.; Taroni, P.; Amoresano, A.; Matteini, P.; Velotta, R. Biosensor surface functionalization by a simple photochemical immobilization of antibodies: Experimental characterization by mass spectrometry and surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2019, 144, 6871–6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Ventura, B.; Schiavo, L.; Altucci, C.; Esposito, R.; Velotta, R. Light assisted antibody immobilization for bio-sensing. Biomed. Opt. Express 2011, 2, 3223–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaglione, R.; Dell’Olmo, E.; Bosso, A.; Chino, M.; Pane, K.; Ascione, F.; Itri, F.; Caserta, S.; Amoresano, A.; Lombardi, A.; et al. Novel human bioactive peptides identified in Apolipoprotein B: Evaluation of their therapeutic potential. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 130, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, R.; Della Ventura, B.; Altucci, C.; Offenhäusser, A.; Mayer, D.; Velotta, R. Single Molecule Characterization of UV-Activated Antibodies on Gold by Atomic Force Microscopy. Langmuir 2016, 32, 8084–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves-Petersen, M.T.; Gryczynski, Z.; Lakowicz, J.; Fojan, P.; Pedersen, S.; Petersen, E.; Bjørn Petersen, S. High probability of disrupting a disulphide bridge mediated by an endogenous excited tryptophan residue. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue Sulfyd Groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, R.; Della Ventura, B.; Carrieri, R.; Morra, L.; Lahoz, E.; Gesuele, F.; Altucci, C.; Velotta, R. Detection of parathion and patulin by quartz-crystal microbalance functionalized by the photonics immobilization technique. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funari, R.; Della Ventura, B.; Schiavo, L.; Esposito, R.; Altucci, C.; Velotta, R. Detection of parathion pesticide by quartz crystal microbalance functionalized with UV-activated antibodies. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6392–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Ventura, B.; Sakač, N.; Funari, R.; Velotta, R. Flexible immunosensor for the detection of salivary α-amylase in body fluids. Talanta 2017, 174, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funari, R.; Terracciano, I.; Della Ventura, B.; Ricci, S.; Cardi, T.; D’Agostino, N.; Velotta, R. Label-Free Detection of Gliadin in Food by Quartz Crystal Microbalance-Based Immunosensor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulgione, A.; Cimafonte, M.; Della Ventura, B.; Iannaccone, M.; Ambrosino, C.; Capuano, F.; Proroga, Y.T.R.; Velotta, R.; Capparelli, R. QCM-based immunosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in food. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iarossi, M.; Schiattarella, C.; Rea, I.; De Stefano, L.; Fittipaldi, R.; Vecchione, A.; Velotta, R.; Della Ventura, B. Colorimetric Immunosensor by Aggregation of Photochemically Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 3805–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, J.S.; Pourmand, N. Label-Free Impedance Biosensors: Opportunities and Challenges. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 1239–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Functionalization Scheme | Functionalization Time (h) | LOD (CFU mL−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Au-MHDA-Ab | 18 * | 2 | [44] |
| Au-Cys-Ferrocene-Ab | 20 * | 3 | [45] |
| Au-MUA/UDT-Ab | 20 * | 100 | [46] |
| Au-PrG thiol-Ab | 10 | 140 | [47] |
| Au-AuNPs-PrG thiol-Ab | 24 * | 48 | [47] |
| Au-PANI-Glu-Ab | >2 | 100 | [48] |
| Au-Ab (PIT activated) | 1 | 30 | This work |
| DDP | 0.185 ± 0.007 | (3.0 ± 0.7) × 104 |
| BDP | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 70 ± 26 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cimafonte, M.; Fulgione, A.; Gaglione, R.; Papaianni, M.; Capparelli, R.; Arciello, A.; Bolletti Censi, S.; Borriello, G.; Velotta, R.; Della Ventura, B. Screen Printed Based Impedimetric Immunosensor for Rapid Detection of Escherichia coli in Drinking Water. Sensors 2020, 20, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010274
Cimafonte M, Fulgione A, Gaglione R, Papaianni M, Capparelli R, Arciello A, Bolletti Censi S, Borriello G, Velotta R, Della Ventura B. Screen Printed Based Impedimetric Immunosensor for Rapid Detection of Escherichia coli in Drinking Water. Sensors. 2020; 20(1):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010274
Chicago/Turabian StyleCimafonte, Martina, Andrea Fulgione, Rosa Gaglione, Marina Papaianni, Rosanna Capparelli, Angela Arciello, Sergio Bolletti Censi, Giorgia Borriello, Raffaele Velotta, and Bartolomeo Della Ventura. 2020. "Screen Printed Based Impedimetric Immunosensor for Rapid Detection of Escherichia coli in Drinking Water" Sensors 20, no. 1: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010274
APA StyleCimafonte, M., Fulgione, A., Gaglione, R., Papaianni, M., Capparelli, R., Arciello, A., Bolletti Censi, S., Borriello, G., Velotta, R., & Della Ventura, B. (2020). Screen Printed Based Impedimetric Immunosensor for Rapid Detection of Escherichia coli in Drinking Water. Sensors, 20(1), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010274






