The Piezo-resistive MC Sensor is a Fast and Accurate Sensor for the Measurement of Mechanical Muscle Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Tensiomyographic (TMG) Measurements
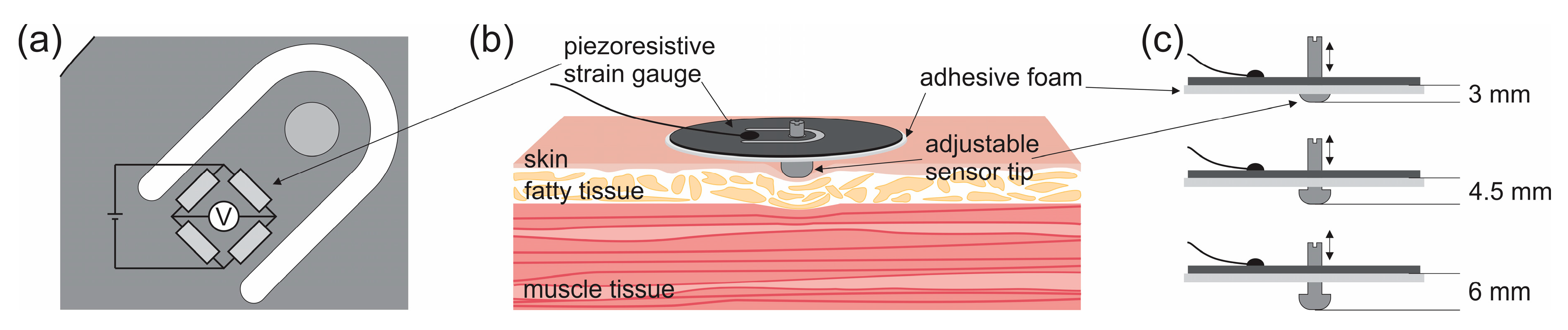
2.3. MC Measurements
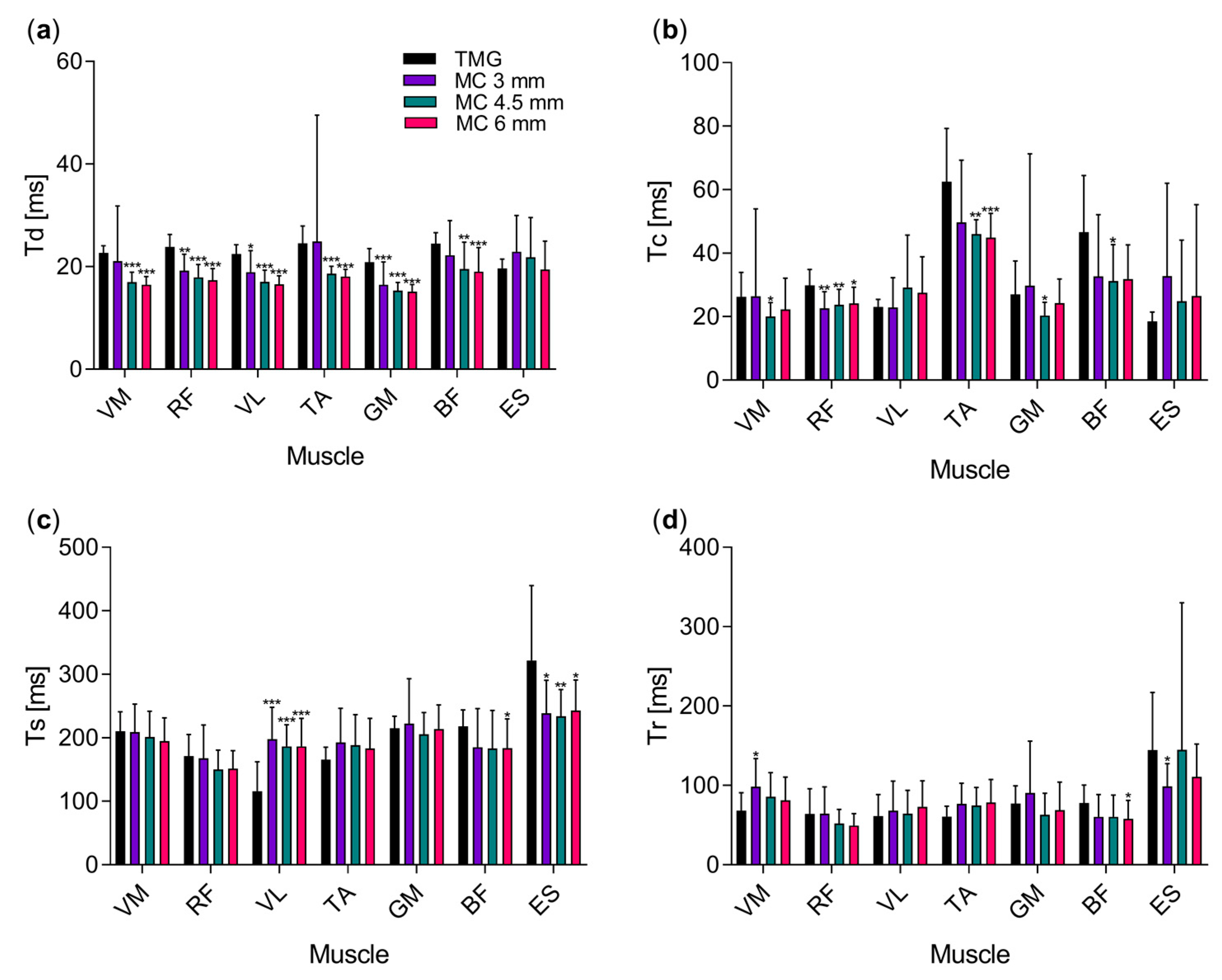
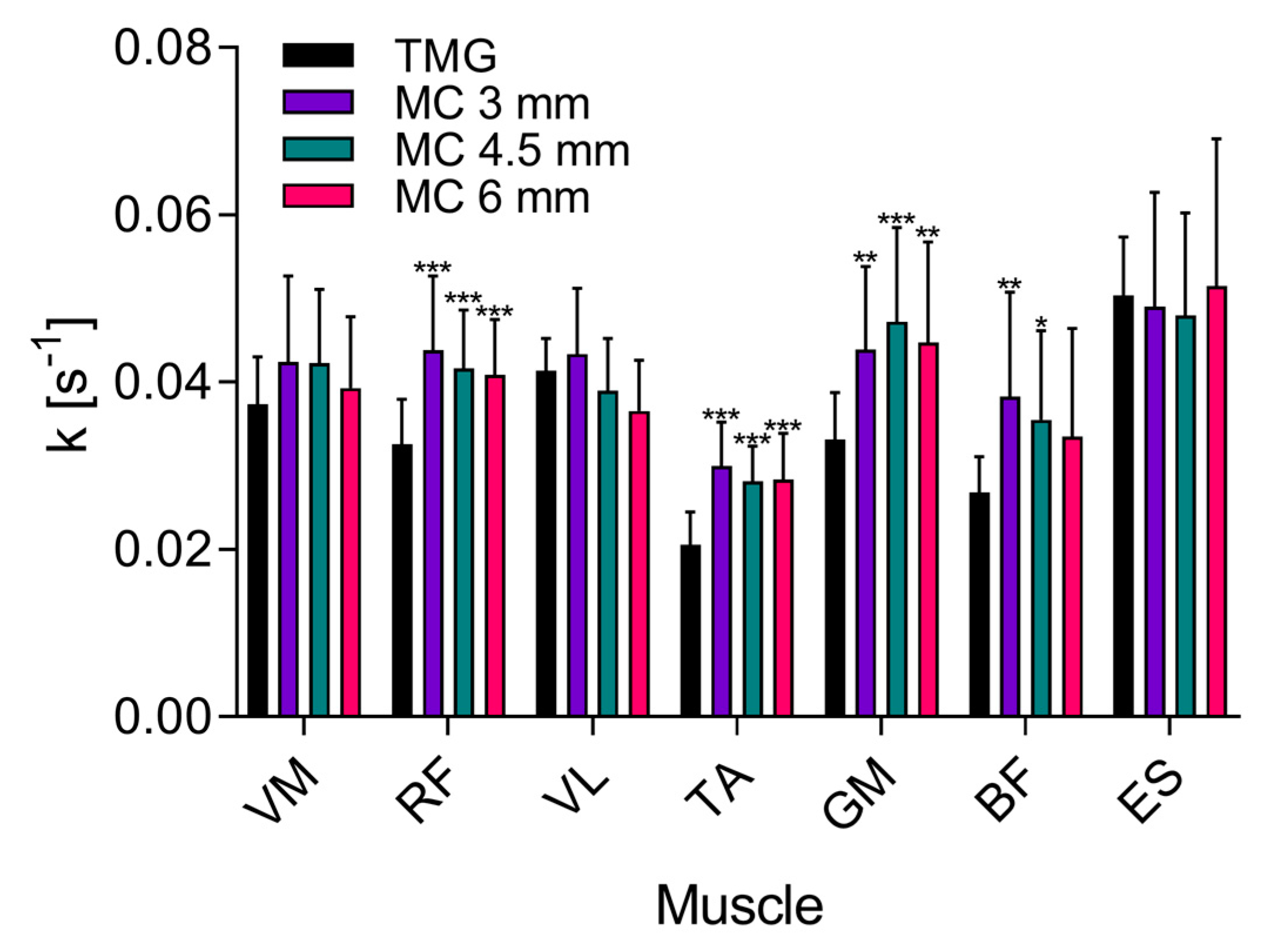
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esposito, D.; Andreozzi, E.; Fratini, A.; Gargiulo, G.; Savino, S.; Niola, V.; Bifulco, P. A Piezoresistive Sensor to Measure Muscle Contraction and Mechanomyography. Sensors 2018, 18, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Sundholm, M.; Cheng, J.; Cruz, H.; Lukowicz, P. Measuring muscle activities during gym exercises with textile pressure mapping sensors. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2017, 38, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Zheng, Y.P.; Xie, H.B.; Chen, X. Continuous monitoring of electromyography (EMG), mechanomyography (MMG), sonomyography (SMG) and torque output during ramp and step isometric contractions. Med. Eng. Phys. 2010, 32, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, L.P.J.; Lisitsa, I.; Bowker, P.; Heath, G.H.; Howard, D. Dimensional change in muscle as a control signal for powered upper limb prostheses: A pilot study. Med. Eng. Phys. 1999, 21, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harridge, S.D.; White, M.J. A comparison of voluntary and electrically evoked isokinetic plantar flexor torque in males. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1993, 66, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritani, T.; deVries, H.A. Reexamination of the relationship between the surface integrated electromyogram (IEMG) and force of isometric contraction. Am. J. Phys. Med. 1978, 57, 263–277. [Google Scholar]
- Bigland-Ritchie, B. EMG/force relations and fatigue of human voluntary contractions. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 1981, 9, 75–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hof, A.L.; Van den Berg, J. EMG to force processing I: An electrical analogue of the Hill muscle model. J. Biomech. 1981, 14, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, A.L.; Van den Berg, J. EMG to force processing II: Estimation of parameters of the Hill muscle model for the human triceps surae by means of a calfergometer. J. Biomech. 1981, 14, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, A.L.; Van den Berg, J. EMG to force processing III: Estimation of model parameters for the human triceps surae muscle and assessment of the accuracy by means of a torque plate. J. Biomech. 1981, 14, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, A.L.; Van den Berg, J. EMG to force processing IV: Eccentric-concentric contractions on a spring-flywheel set up. J. Biomech. 1981, 14, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disselhorst-Klug, C.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Rau, G. Surface electromyography and muscle force: Limits in sEMG–force relationship and new approaches for applications. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, G.R.; Duvoisin, M.R.; Dudley, G.A. Magnetic resonance imaging and electromyography as indexes of muscle function. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 73, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, T.; Ito, M.; Ichinose, Y.; Kuno, S.; Kawakami, Y.; Fukashiro, S. Tendinous movement of a human muscle during voluntary contractions determined by real-time ultrasonography. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 81, 1430–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Orizio, C. Sound myogram and EMG cross-spectrum during exhausting isometric contractions in humans. J. Electromyogr. Kines. 1992, 2, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orizio, C. Muscle sound: Bases for the introduction of a mechanomyographic signal in muscle studies. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1993, 21, 201–243. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, T.W.; Housh, T.J.; Cramer, J.T.; Weir, J.P.; Johnson, G.O.; Coburn, J.W.; Malek, M.H.; Mielke, M. Mechanomyographic amplitude and frequency responses during dynamic muscle actions: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Eng. Online 2005, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Hamada, T.; Watanabe, T.; Maeda, A.; Oya, T.; Moritani, T. Mechanomyographic responses in human biceps brachii and soleus during sustained isometric contraction. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 92, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orizio, C. Electromyography: Physiology, Engineering, and Noninvasive Applications; Merletti, R., Parker, P., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 305–322. [Google Scholar]
- Valenčič, V.; Knez, N. Measuring of skeletal muscles dynamic properties. Artif. Organs 1997, 21, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenčič, V.; Djordjevič, S. Influence of acute physical exercise on twitch response elicited by stimulation of skeletal muscles in man. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Valenčič, V.; Knez, N.; Šimunič, B. Tensiomyography: Detection of skeletal muscle response by means of radial muscle belly displacement. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Križaj, D.; Šimunič, B.; Žagar, T. Short-term repeatability of parameters extracted from radial displacement of muscle belly. J. Electromyogr. Kines. 2008, 18, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tous-Fajardo, J.; Moras, G.; Rodriguez-Jimenez, S.; Usach, R.; Doutres, D.M.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Inter-rater reliability of muscle contractile property measurements using noninvasive tensiomyography. J. Electromyogr. Kines. 2010, 20, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimunič, B. Between-day reliability of a method for non-invasive estimation of muscle composition. J. Electromyogr. Kines. 2012, 2, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditroilo, M.; Smith, I.J.; Fairweather, M.M.; Hunter, A.M. Long-term stability of tensiomyography measured under different muscle conditions. J. Electromyogr. Kines. 2013, 23, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula Simola, R.Á.; Harms, N.; Raeder, C.; Kellmann, M.; Meyer, T.; Pfeiffer, M.; Ferrauti, A. Tensiomyography reliability and prediction of changes in muscle force following heavy eccentric strength exercise using muscle mechanical properties. Sports Tech. 2015, 8, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pišot, R.; Narici, M.V.; Šimunič, B.; De Boer, M.; Seynnes, O.; Jurdana, M.; Biolo, G.; Mekjavić, I.B. Whole muscle contractile parameters and thickness loss during 35-day bed rest. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula Simola, R.Á.; Reader, C.; Wiewelhove, T.; Kellmann, M.; Meyer, T.; Pfeiffer, M.; Ferrauti, A. Muscle mechanical properties of strength and endurance athletes and changes after one week of intensive training. J. Electromyogr. Kines. 2016, 30, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Manso, J.M.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, D.; Rodríguez-Matoso, D.; de Saá, Y.; Sarmiento, S.; Quiroga, M. Assessment of muscle fatigue after an ultra-endurance triathlon using tensiomyography (TMG). J. Sport Sci. 2011, 29, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, O.; Hernández-Mendo, A.; Serrano-Gómez, V.; Morales-Sánchez, V. Application of the generalizability theory of tensiomyography analysis of professional road cyclists. Rev. Psicol. Deporte 2013, 22, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Dahmane, R.; Valenčič, V.; Knez, N.; Eržen, I. Evaluation of the ability to make non-invasive estimation of muscle contractile properties on the basis of the muscle belly response. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2001, 39, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmane, R.; Djordjevič, S.; Šimunič, B.; Valenčič, V. Spatial fiber type distribution in normal human muscle: histochemical and tensiomiographical evaluation. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimunič, B.; Degens, H.; Rittweger, J.; Narici, M.; Mekjavić, I.B.; Pišot, R. Noninvasive estimation of myosin heavy chain composition in human skeletal muscle. Med. Sci. Sport. Exer. 2011, 43, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, H.; Valenčič, V.; Marinček, Č.; Kogovšek, N. Properties of musculus gluteus maximus in above-knee amputees. Clin. Biomech. 1996, 11, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula Simola, R.Á.; Harms, N.; Raeder, C.; Kellmann, M.; Meyer, T.; Pfeiffer, M.; Ferrauti, A. Assessment of neuromuscular function after different strength training protocols using tensiomyography. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Manso, J.M.; Rodríguez-Matoso, D.; Sarmiento, S.; de Saa, Y.; Vaamonde, D.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, D. Effect of high-load and high-volume resistance exercise on the tensiomyographic twitch response of biceps brachii. J. Electromyogr. Kines. 2012, 22, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hunter, A.M.; Galloway, S.D.; Smith, I.J.; Tallent, J.; Ditroilo, M.; Fairweather, M.M. Assessment of eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage of the elbow flexors by tensiomyography. J. Electromyogr. Kines. 2012, 22, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đorđević, S.; Stančin, S.; Meglič, A.; Milutinović, V.; Tomažič, S. MC Sensor—A Novel Method for Measurement of Muscle Tension. Sensors 2011, 11, 9411–9425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đorđević, S.; Tomažič, S.; Narici, M.; Pišot, R.; Meglič, A. In-Vivo Measurement of Muscle Tension: Dynamic Properties of the MC Sensor during Isometric Muscle Contraction. Sensors 2014, 14, 17848–17863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krašna, S.; Đorđević, S.; Hribernik, M.; Trajkovski, A. A Novel Approach to Measuring Muscle Mechanics in Vehicle Collision Conditions. Sensors 2017, 17, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.Z.; Hamzaid, N.A.; Davis, G.G.; Wahab, A.K.A.; Hasnan, N. Mechanomyography and Torque during FES-Evoked Muscle Contractions to Fatigue in Individuals with Spinal Cord Injury. Sensors 2017, 17, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perotto, A.O.; Delagi, E.F.; Lazzeti, J.; Morrison, D. Anatomic Guide for the Electromyographer: the Limbs; Charles C. Thomas Publisher: Springfield, IL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Maganaris, C.N.; Baltzopoulos, V.; Sargeant, A.J. In vivo measurements of the triceps surae complex architecture in man: implications for muscle function. J. Physiol. 1998, 512, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Muscle | R(3 mm) | R(4.5 mm) | R(6 mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| vastus medialis | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.84 |
| rectus femoris | 0.72 | 0.80 | 0.84 |
| vastus lateralis | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.76 |
| tibialis anterior | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.71 |
| gastrocnemius medialis | 0.68 | 0.76 | 0.72 |
| biceps femoris | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.66 |
| erector spinae | 0.62 | 0.49 | 0.44 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meglič, A.; Uršič, M.; Škorjanc, A.; Đorđević, S.; Belušič, G. The Piezo-resistive MC Sensor is a Fast and Accurate Sensor for the Measurement of Mechanical Muscle Activity. Sensors 2019, 19, 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092108
Meglič A, Uršič M, Škorjanc A, Đorđević S, Belušič G. The Piezo-resistive MC Sensor is a Fast and Accurate Sensor for the Measurement of Mechanical Muscle Activity. Sensors. 2019; 19(9):2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092108
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeglič, Andrej, Mojca Uršič, Aleš Škorjanc, Srđan Đorđević, and Gregor Belušič. 2019. "The Piezo-resistive MC Sensor is a Fast and Accurate Sensor for the Measurement of Mechanical Muscle Activity" Sensors 19, no. 9: 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092108
APA StyleMeglič, A., Uršič, M., Škorjanc, A., Đorđević, S., & Belušič, G. (2019). The Piezo-resistive MC Sensor is a Fast and Accurate Sensor for the Measurement of Mechanical Muscle Activity. Sensors, 19(9), 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092108





