Efficient Modulation and Processing Method for Closed-Loop Fiber Optic Gyroscope with Piezoelectric Modulator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Phase Modulation in an I-FOG with a PEM
2.2. Closed-Loop Fully Harmonic Modulation
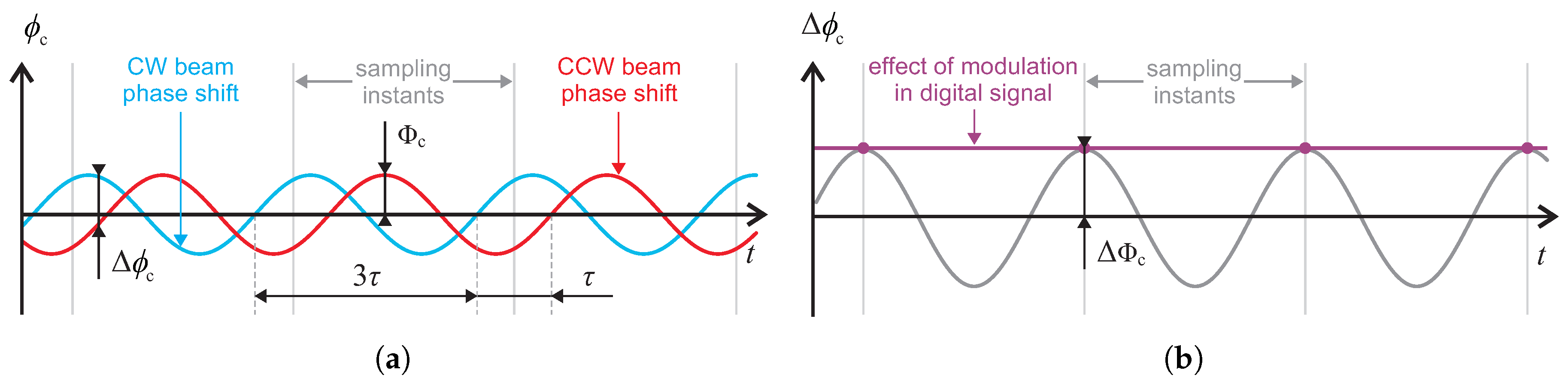
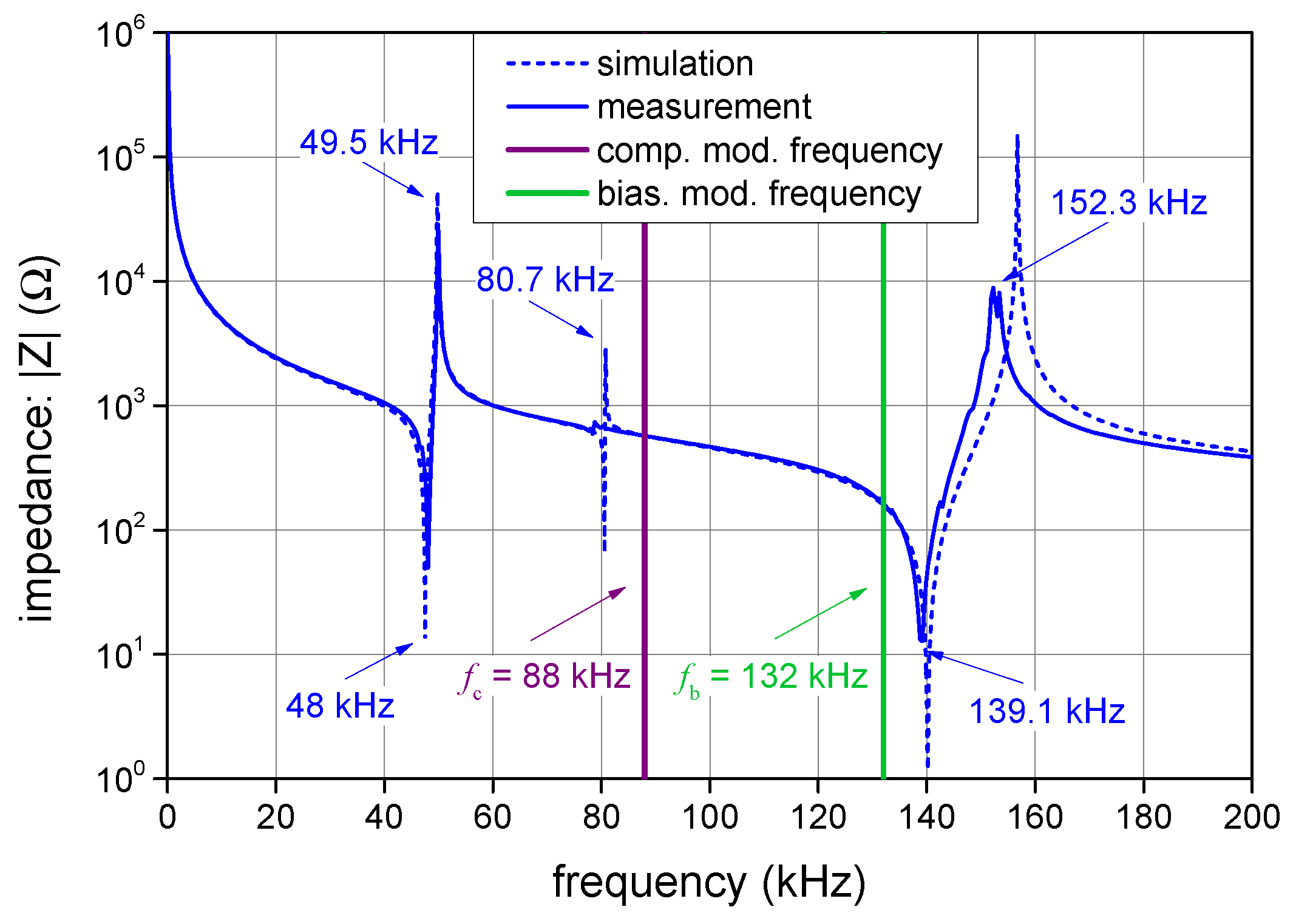
2.3. Parasitic Effects of the Proposed Method
3. Experimental Setup
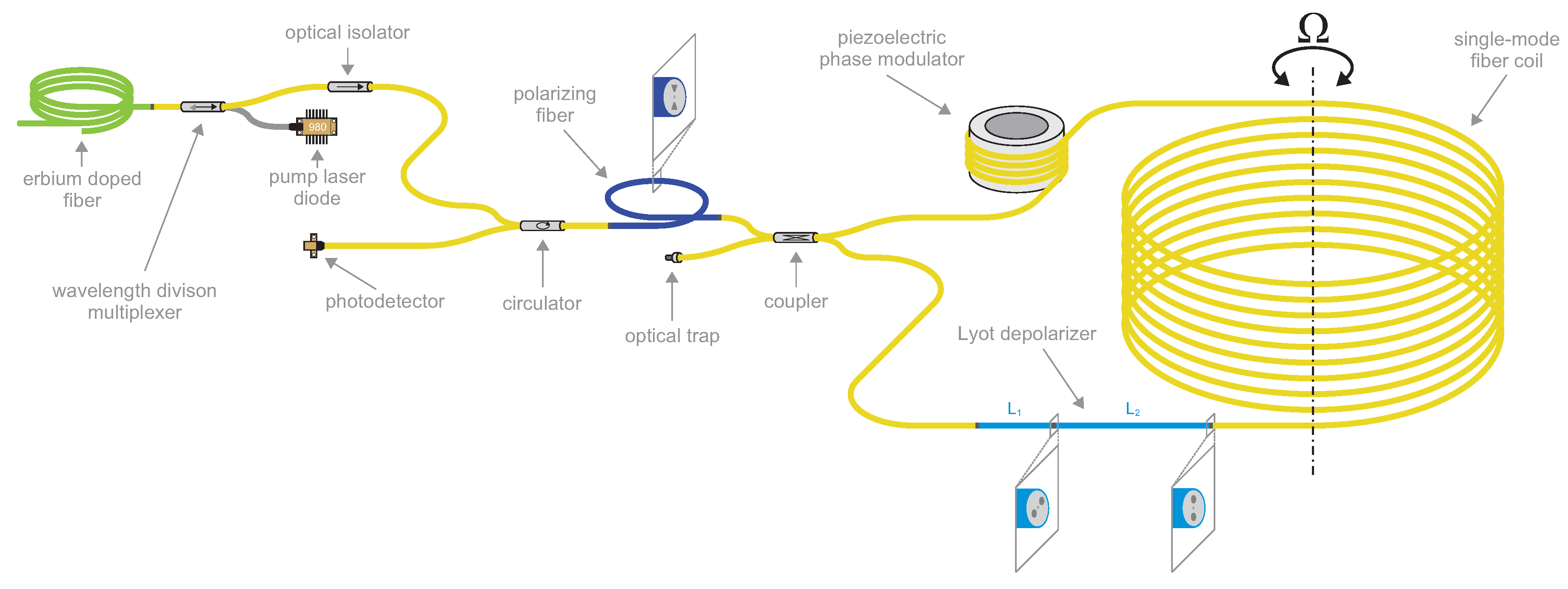
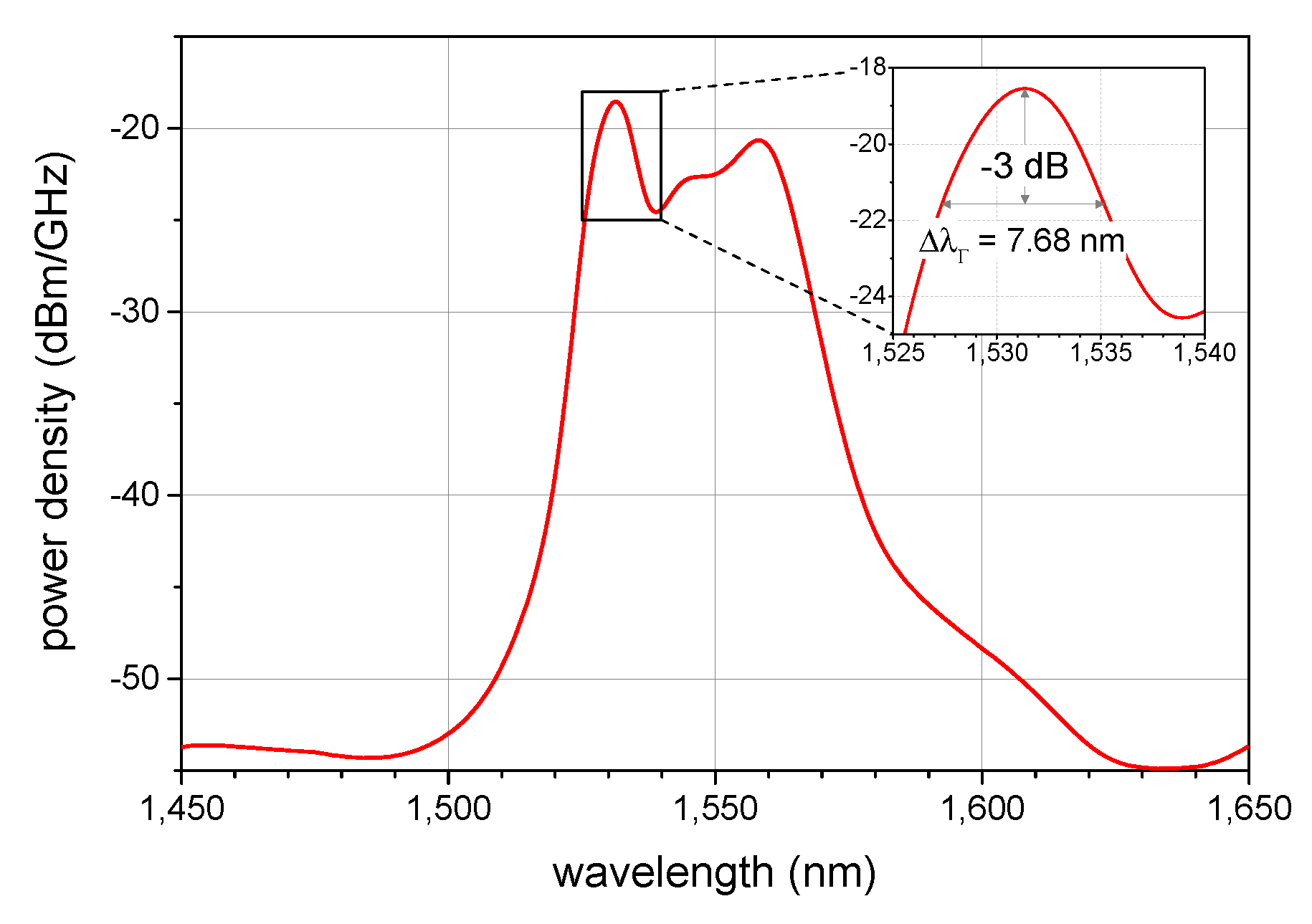
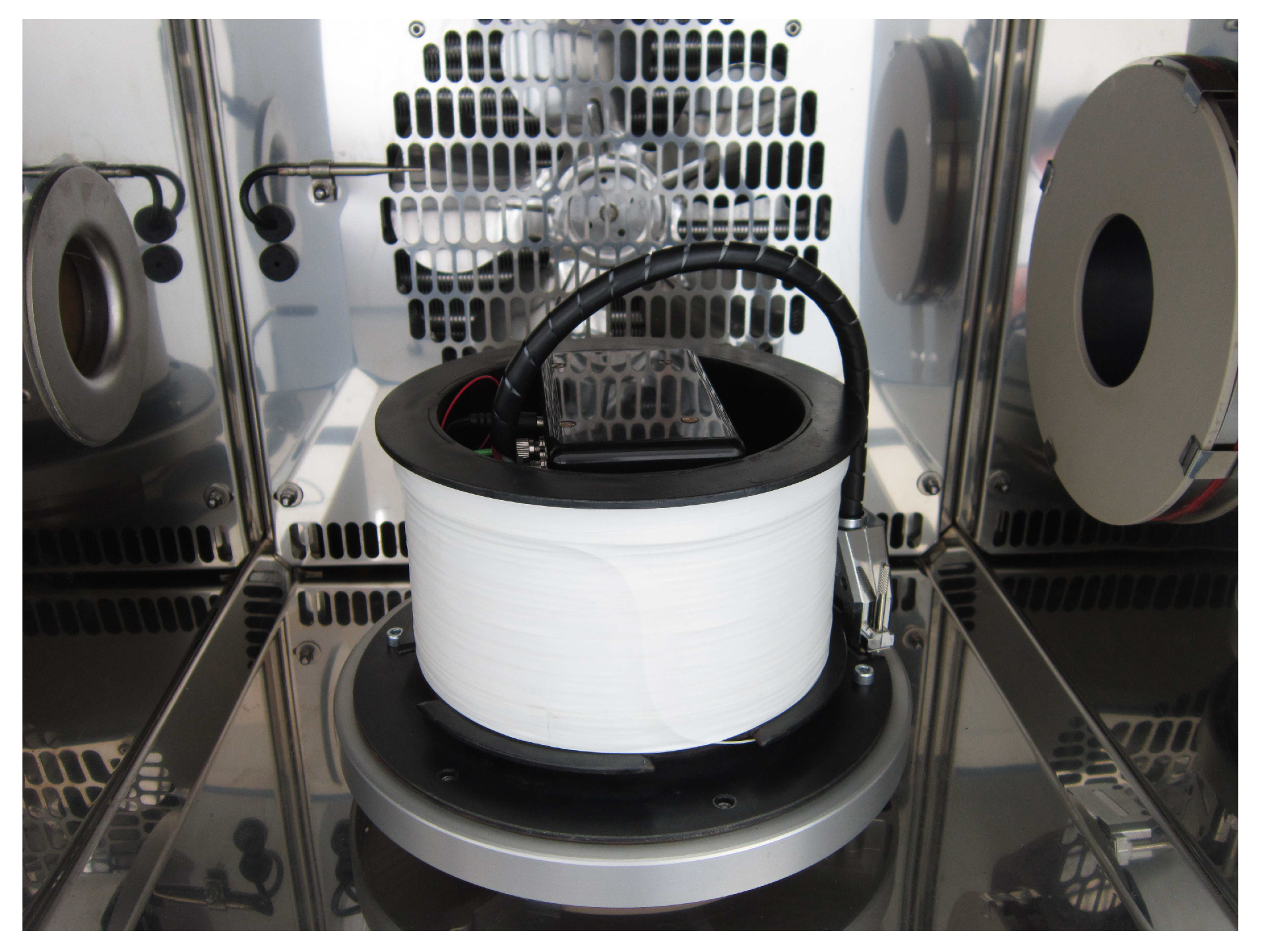
3.1. Optical Design
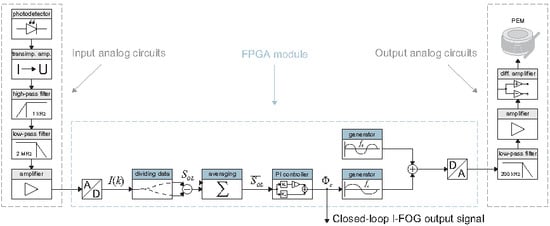
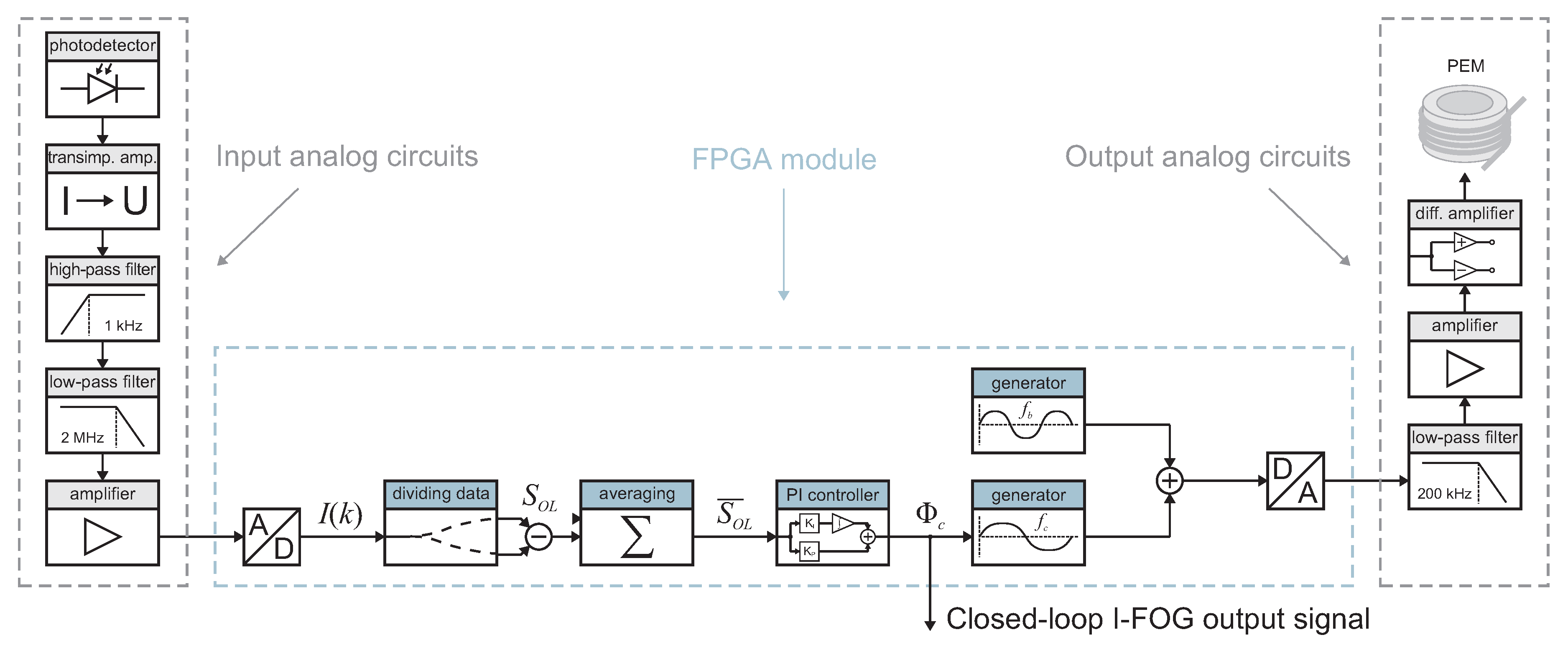
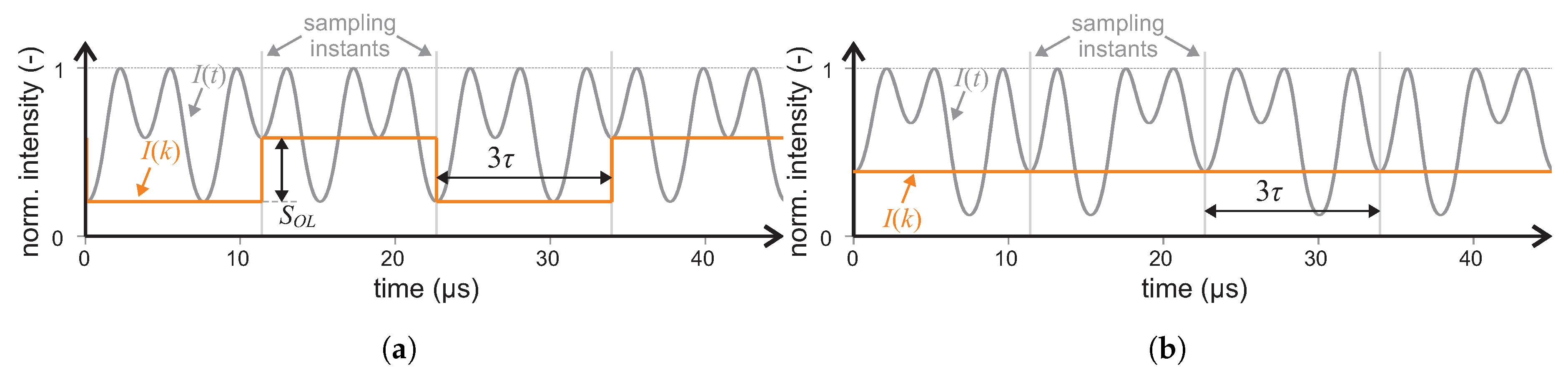
3.2. Signal Processing and Closed-Loop Control
4. Results and Discussion
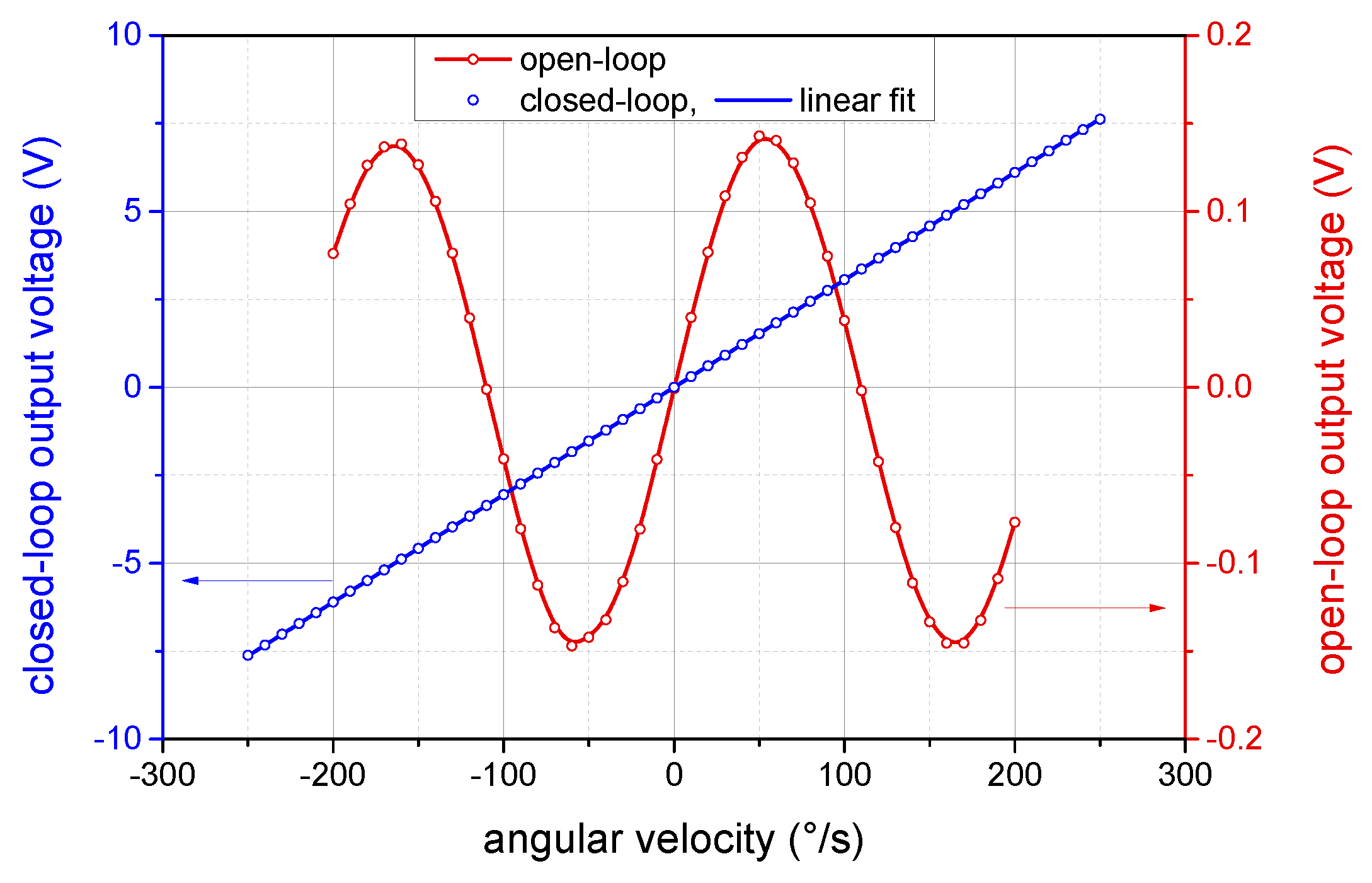
4.1. Output Characteristics of the Open-Loop and Closed-Loop I-FOG
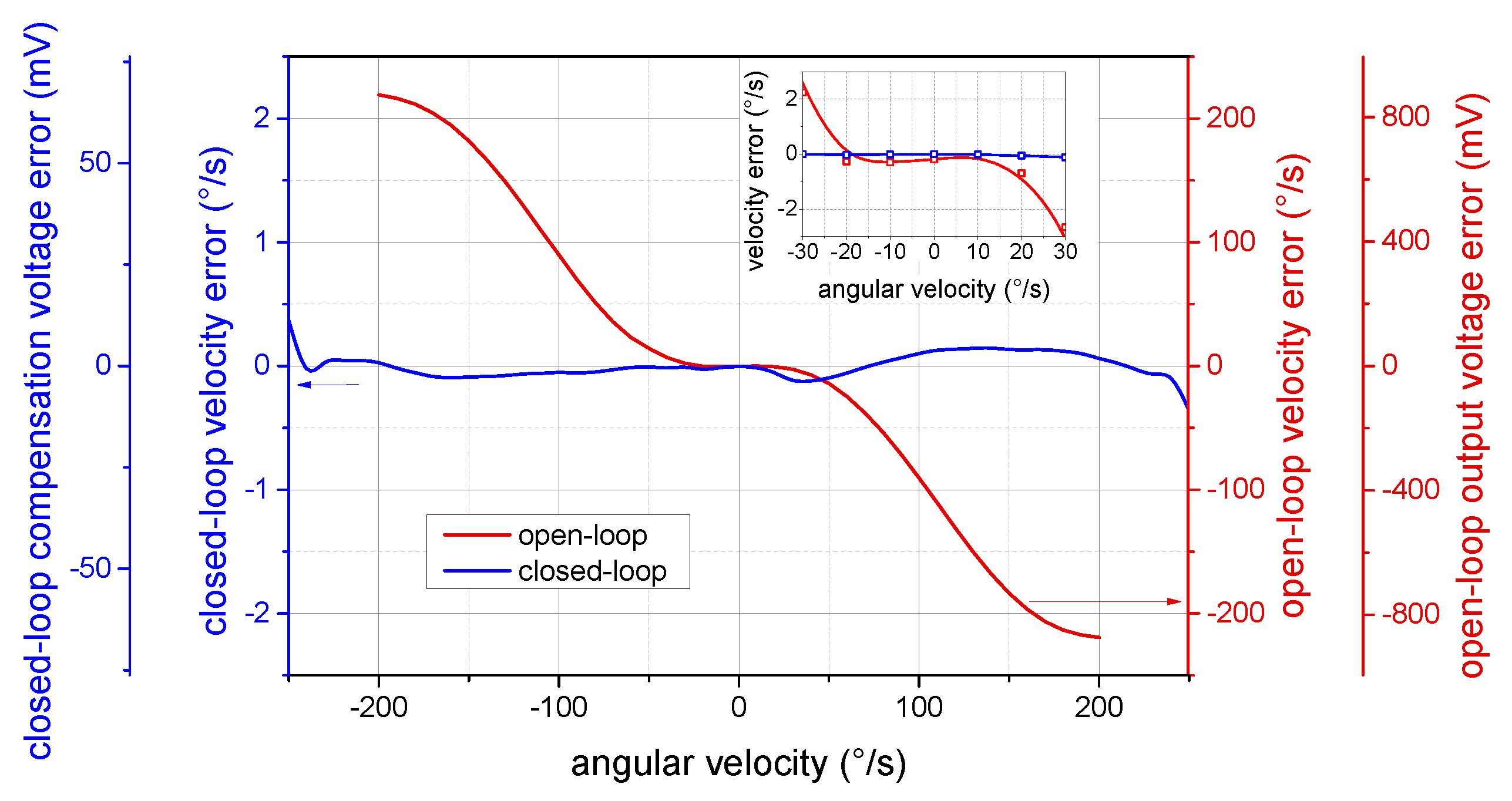
4.2. Output Linearity
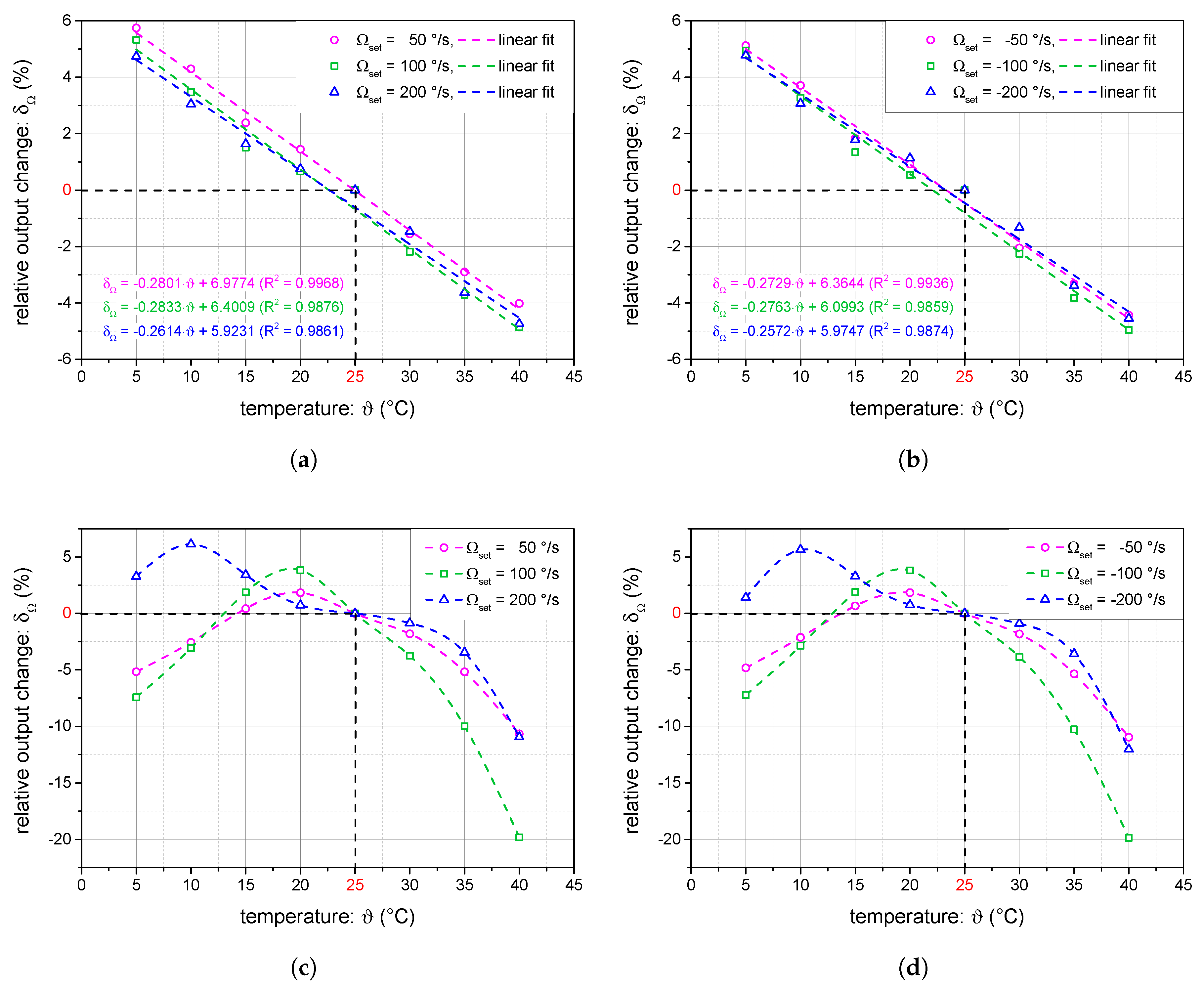
4.3. Temperature Dependence
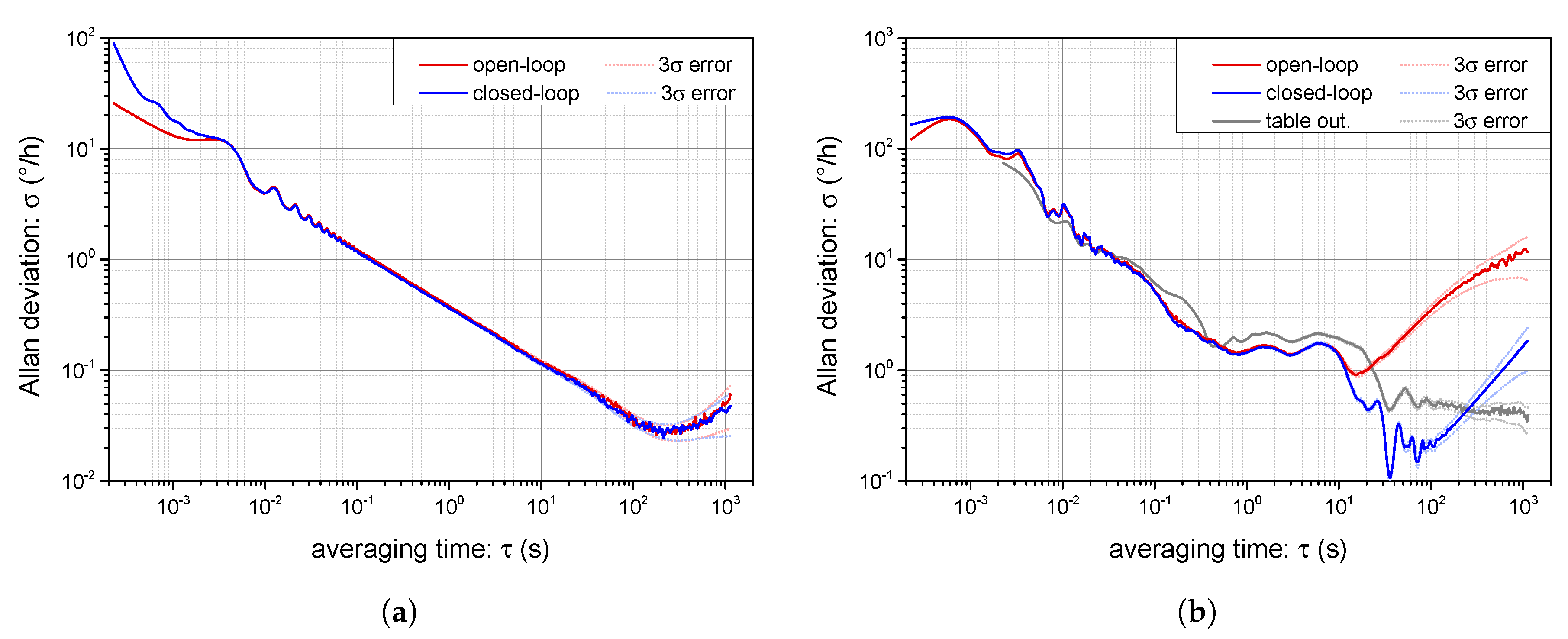
4.4. Allan Deviation and Time Stability
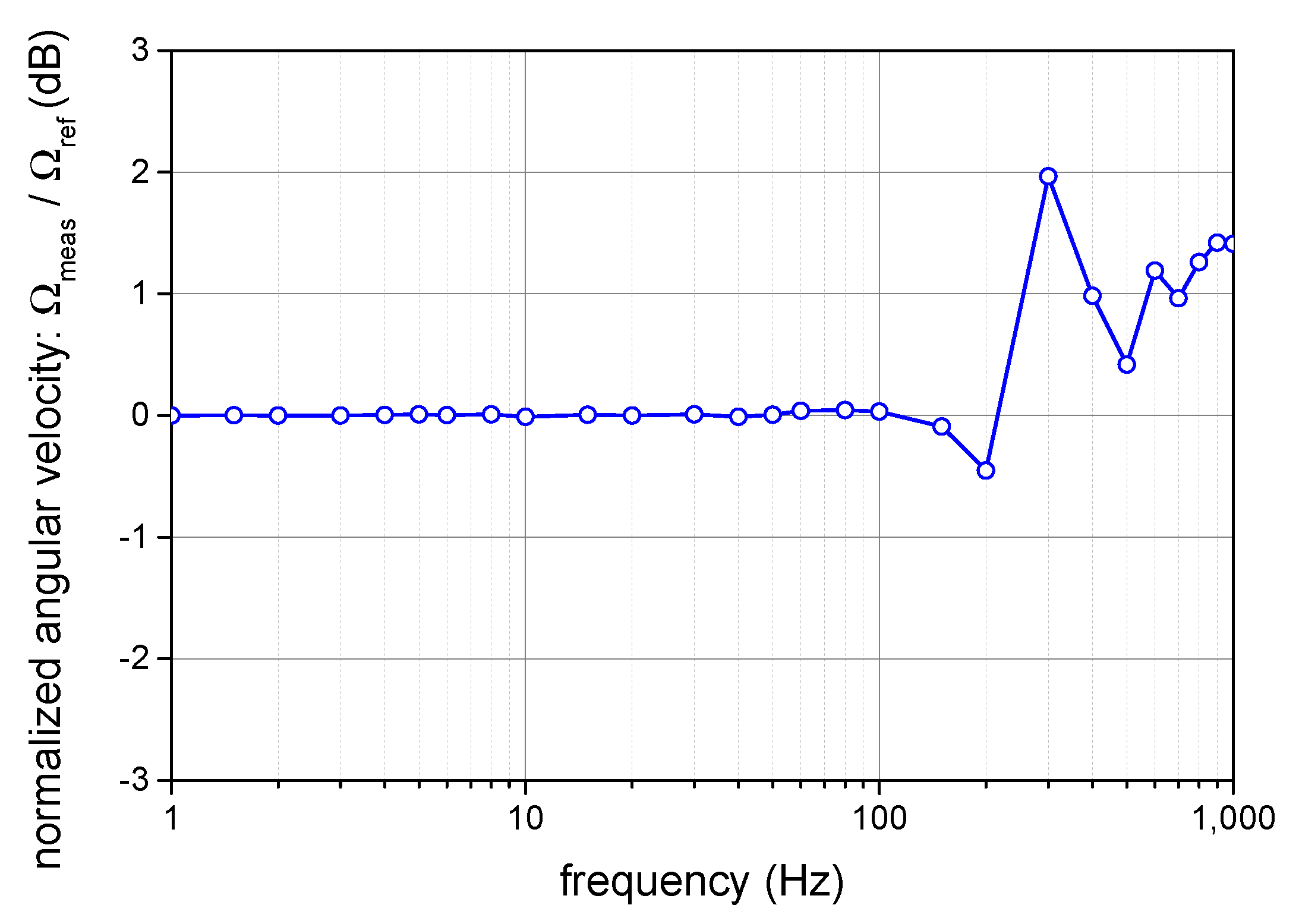
4.5. Closed-Loop System Dynamic Performances
4.6. Comparing the Proposed Harmonic Closed-Loop and the Standard Open-Loop Configurations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARW | angle random walk |
| FPGA | field-programmable gate-array |
| I-FOG | interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope |
| MEMS | microelectromechanical systems |
| PEM | piezoelectric modulator |
| PM | polarization-maintaining |
| RLG | ring laser gyroscope |
| SFS | superfluorescent fiber source |
| SLD | superluminescent diode |
| SM | single-mode |
References
- Passaro, V.M.N.; Cuccovillo, A.; Vaiani, L.; De Carlo, M.; Campanella, C.E. Gyroscope Technology and Applications: A Review in the Industrial Perspective. Sensors 2017, 17, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlo, S.; Norgia, M.; Donati, S. Fiber gyroscope principles. In Handbook of Optical Fibre Sensing Technology; López-Higuera, J.M., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 331–348. ISBN 978-0-471-82053-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ciminelli, C.; Dell’Olio, F.; Campanella, C.E.; Armenise, M.N. Photonic technologies for angular velocity sensing. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2010, 2, 370–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, G.A.; Szafraniec, B. Progress in fiber-optic gyroscope applications II with emphasis on the theory of depolarized gyros. In Optical Gyros and Their Application; Loukianov, D., Rodloff, R., Sorg, H., Stieler, B., Eds.; RTO NATO AGARDograph: Neuilly-sur-Seine, France, 1999; pp. 1–42. ISBN 92-837-1014-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lefèvre, H.C. The fiber-optic gyroscope: Challenges to become the ultimate rotation-sensing technology. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2013, 19, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deppe, O.; Dorner, G.; König, S.; Martin, T.; Voigt, S.; Zimmermann, S. MEMS and FOG Technologies for Tactical and Navigation Grade Inertial Sensors-Recent Improvements and Comparison. Sensors 2017, 17, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlath, G.A.; Shaw, H.J. Birefringence and polarization effects in fiber gyroscopes. Appl. Opt. 1982, 21, 1752–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, W.K.; Kersey, A.D. Fiber-optic gyroscopes with depolarized light. J. Light Technol. 1992, 10, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celikel, O.; San, S.E. Establishment of All Digital Closed-Loop Interferometric Fiber-Optic Gyroscope and Scale Factor Comparison for Open-Loop and All Digital Closed-Loop Configurations. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronau, Y.; Tur, M. Digital signal processing for an open-loop fiber-optic gyroscope. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 5849–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Lu, P.; Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z. All-Depolarized Interferometric Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Based on Optical Compensation. IEEE Photonics J. 2014, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahalom, R.; Moslehi, B.; Oblea, L.; Sotoudeh, V.; Ha, J.C. Low-cost, compact Fiber-Optic Gyroscope for super-stable Line-of-Sight stabilization. In Proceedings of the IEEE-ION Position Location and Navigation Symposium, Indian Wells, CA, USA, 8 July 2010; pp. 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lefèvre, H.C. The Fiber-Optic Gyroscope, 2nd ed.; Artech House: London, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-1-60807-695-6. [Google Scholar]
- Arditty, H.J.; Lefèvre, H.C. Sagnac effect in fiber gyroscopes. Opt. Lett. 1981, 6, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, S.; Jin, J.; Song, N. Novel Compensation Scheme for the Modulation Gain to Suppress the Quantization-Induced Bias in a Fiber Optic Gyroscope. Sensors 2017, 17, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Shaw, H.J. Gated phase-modulation feedback approach to fiber-optic gyroscopes. Opt. Lett. 1984, 9, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Shaw, H.J. Gated phase-modulation approach to fiber-optic gyroscope with linearized scale factor. Opt. Lett. 1984, 9, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.; Chung, M.; Kim, Y. Effects of the second harmonic and the duty cycle on the scale factor of a fiber-optic gyroscope with gated two-harmonic phase modulation. Opt. Lett. 1988, 13, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, P.Y.; Pan, C.L. Deep phase-modulation approach to an open-loop fiber optic gyroscope. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 1991, 3, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronova, I.A.; Malykin, G.B. Physical problems of fiber gyroscopy based on the Sagnac effect. Phys.-Uspek. 2002, 45, 793–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malykin, G.B.; Malykin, É.G. On possibility of using the lowest odd harmonics of the phase modulation frequency in the output signal of the fiber-optic ring interferometer for detection of the sagnac effect. Opt. Spectr. 2008, 105, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malykin, G.B. Effect of nonsinusoidal phase modulation on the zero shift in a fiber ring interferometer. Radiophys. Quant. Electron. 1994, 37, 870–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malykin, G.B. Effect of higher harmonics of phase-modulation frequency on zero drift in a fiber ring interferometer. Radiophys. Quant. Electron. 1996, 39, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, R.; Álvarez, I.; Enguita, J. Theoretical Design of a Depolarized Interferometric Fiber-Optic Gyroscope (IFOG) on SMF-28 Single-Mode Standard Optical Fiber Based on Closed-Loop Sinusoidal Phase Modulation with Serrodyne Feedback Phase Modulation Using Simulation Tools for Tactical and Industrial Grade Applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arditty, H.J.; Puech, C.; Papuchon, M. Device for Measuring a Phase Shift Which Is Not Reciprocal Produced in a Ring Interferometer. U.S. Patent 5,056,919, 15 October 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, A. The Interferometric Fiber-Optic Gyro. In Modern Inertial Technology: Navigation, Guidance, and Control; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 189–207. ISBN 0-387-97868-2. [Google Scholar]
- Georges Sabat, R.; Mukherjee, B.K.; Ren, W.; Yang, G. Temperature dependence of the complete material coefficients matrix of soft and hard doped piezoelectric lead zirconate titanate ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 064111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergh, R.A. Dual-Ramp Closed-Loop Fiber-Optic Gyroscope. In Proceedings of the SPIE 1169, Fiber Optic and Laser Sensors VII, Boston, MA, USA, 13 February 1990; pp. 429–439. [Google Scholar]
- Skalský, M.; Havránek, Z.; Fialka, J. Fibre optic gyroscope with single-mode fibre and loop-back phase shift compensation. In Proceedings of the SPIE 10603, Photonics, Devices, and Systems VII, Prague, Czech Republic, 1 December 2017; p. 1060309. [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki, P.F.; Digonnet, M.J.F.; Kim, B.Y.; Shaw, H.J. Characteristics of erbium-doped superfluorescent fiber sources for interferometric sensor applications. J. Light Technol. 1994, 12, 550–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafraniec, B.; Sanders, G.A. Theory of polarization evolution in interferometric fiber-optic depolarized gyros. J. Light Technol. 1999, 17, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredricks, R.J.; Ulrich, R. Phase error bounds of fibre gyro with imperfect polariser/depolariser. Electron. Lett. 1984, 20, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE. IEEE Std 952-1997: IEEE Standard Specification Format Guide and Test Procedure for Single-Axis Interferometric Fiber Optic Gyros; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 43–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. A New Open-Loop Fiber Optic Gyro Error Compensation Method Based on Angular Velocity Error Modeling. Sensors 2015, 15, 4899–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| I-FOG Parameter | Open-Loop | Closed-Loop |
|---|---|---|
| bias stability | 0.03/h | 0.03/h |
| ARW | 0.006 | 0.006 |
| SFS stability (at 10/s) | /h | no impact |
| linearity error | nonlinear | <0.08% (/s) |
| temp. dependence (5–40 C) | sine | linearized |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skalský, M.; Havránek, Z.; Fialka, J. Efficient Modulation and Processing Method for Closed-Loop Fiber Optic Gyroscope with Piezoelectric Modulator. Sensors 2019, 19, 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071710
Skalský M, Havránek Z, Fialka J. Efficient Modulation and Processing Method for Closed-Loop Fiber Optic Gyroscope with Piezoelectric Modulator. Sensors. 2019; 19(7):1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071710
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkalský, Michal, Zdeněk Havránek, and Jiří Fialka. 2019. "Efficient Modulation and Processing Method for Closed-Loop Fiber Optic Gyroscope with Piezoelectric Modulator" Sensors 19, no. 7: 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071710
APA StyleSkalský, M., Havránek, Z., & Fialka, J. (2019). Efficient Modulation and Processing Method for Closed-Loop Fiber Optic Gyroscope with Piezoelectric Modulator. Sensors, 19(7), 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071710