A Human–Machine Interface Based on Eye Tracking for Controlling and Monitoring a Smart Home Using the Internet of Things
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. User-Centered Design (UCD)
2.1.1. Usability
2.1.2. System Usability Scale (SUS)
- (1)
- I think that I would like to use this system frequently.
- (2)
- I found the system unnecessarily complex.
- (3)
- I thought the system was easy to use.
- (4)
- I think that I would need the support of a technical person to be able to use this system.
- (5)
- I found the various functions in this system were well integrated.
- (6)
- I thought there was too much inconsistency in this system.
- (7)
- I would imagine that most people would learn to use this system very quickly.
- (8)
- I found the system very cumbersome to use.
- (9)
- I felt very confident using the system.
- (10)
- I needed to learn a lot of things before I could get going with this system.
- For odd-numbered items: subtract 1 from the user response;
- For even-numbered items: subtract the user responses from 5;
- This scales all values from 0 to 4 (with 4 being the most positive response).
- Add the converted responses for each user and multiply that total by 2.5. This converts the range of possible values from 0 to 100 instead of from 0 to 40.
2.2. Eye Tracking
2.3. Smart Homes
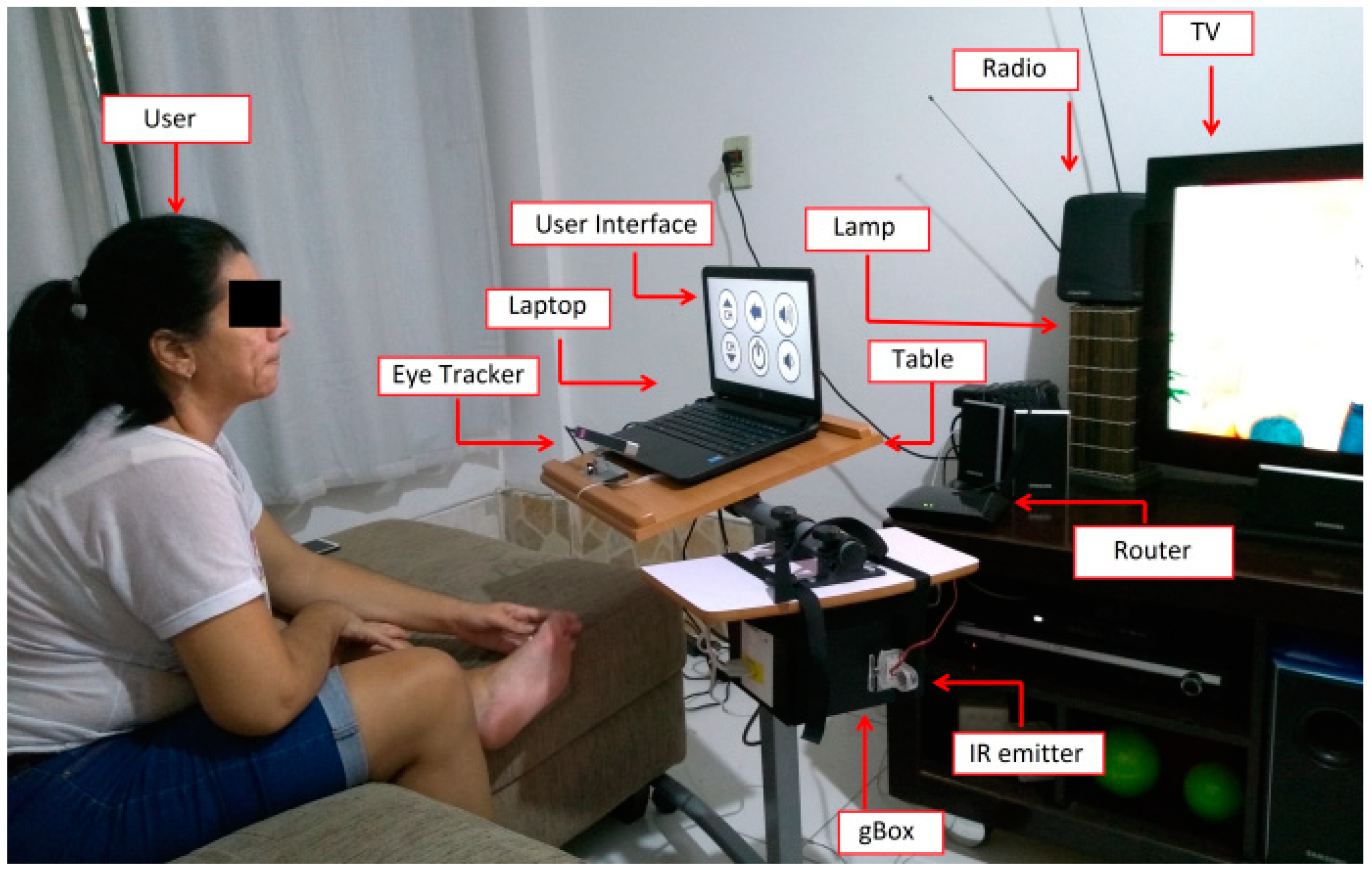
3. Proposed Assistive System
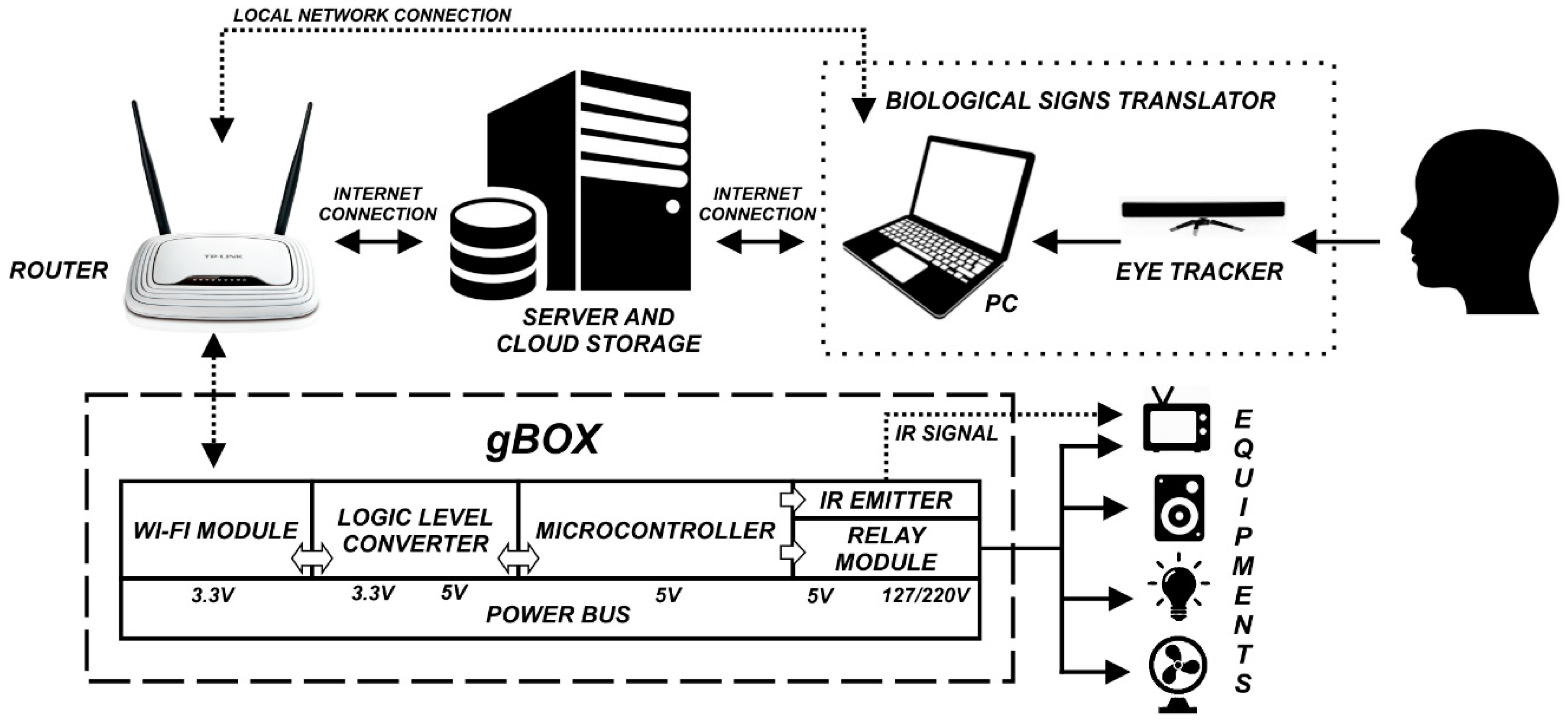
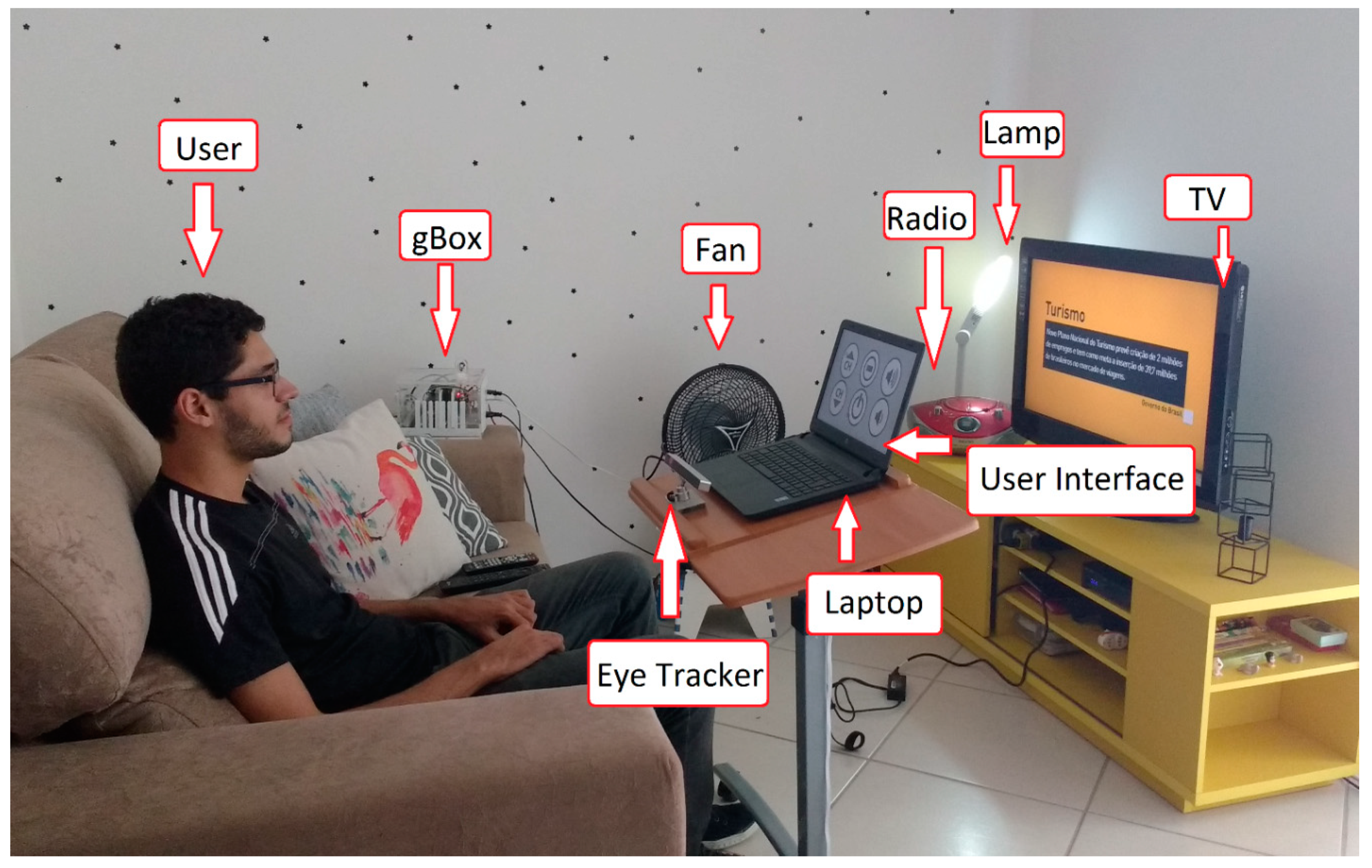
3.1. System Architecture
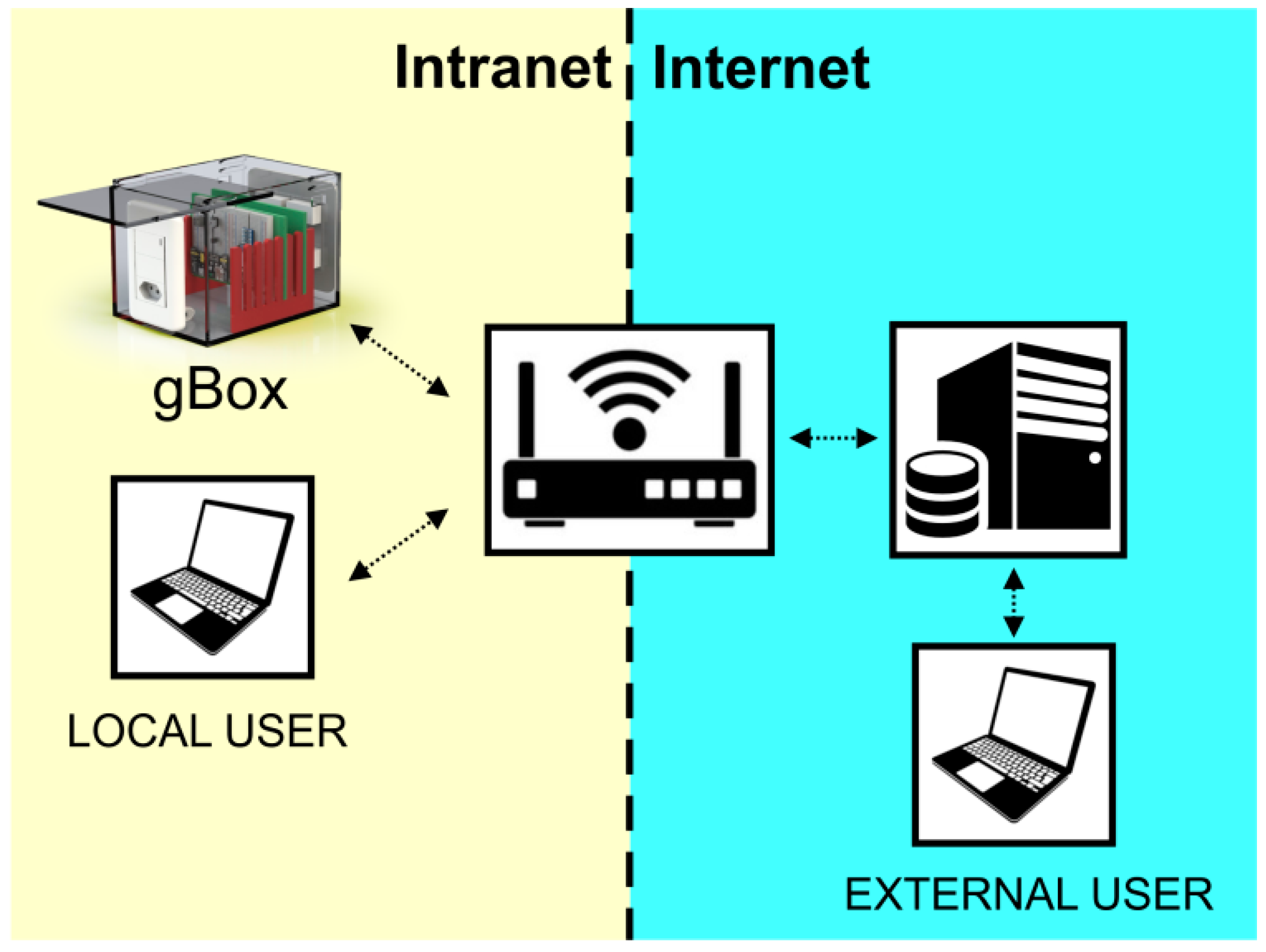
3.2. Connectivity
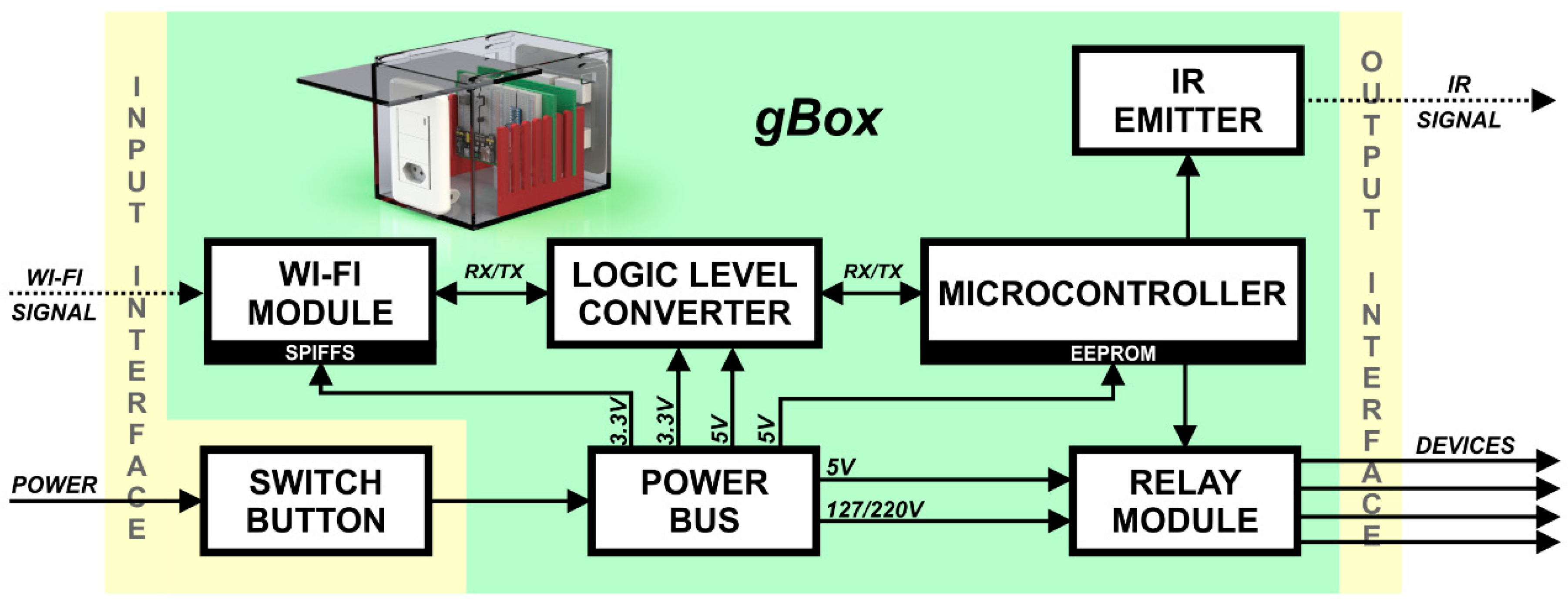
3.3. GlobalBox (gBox)
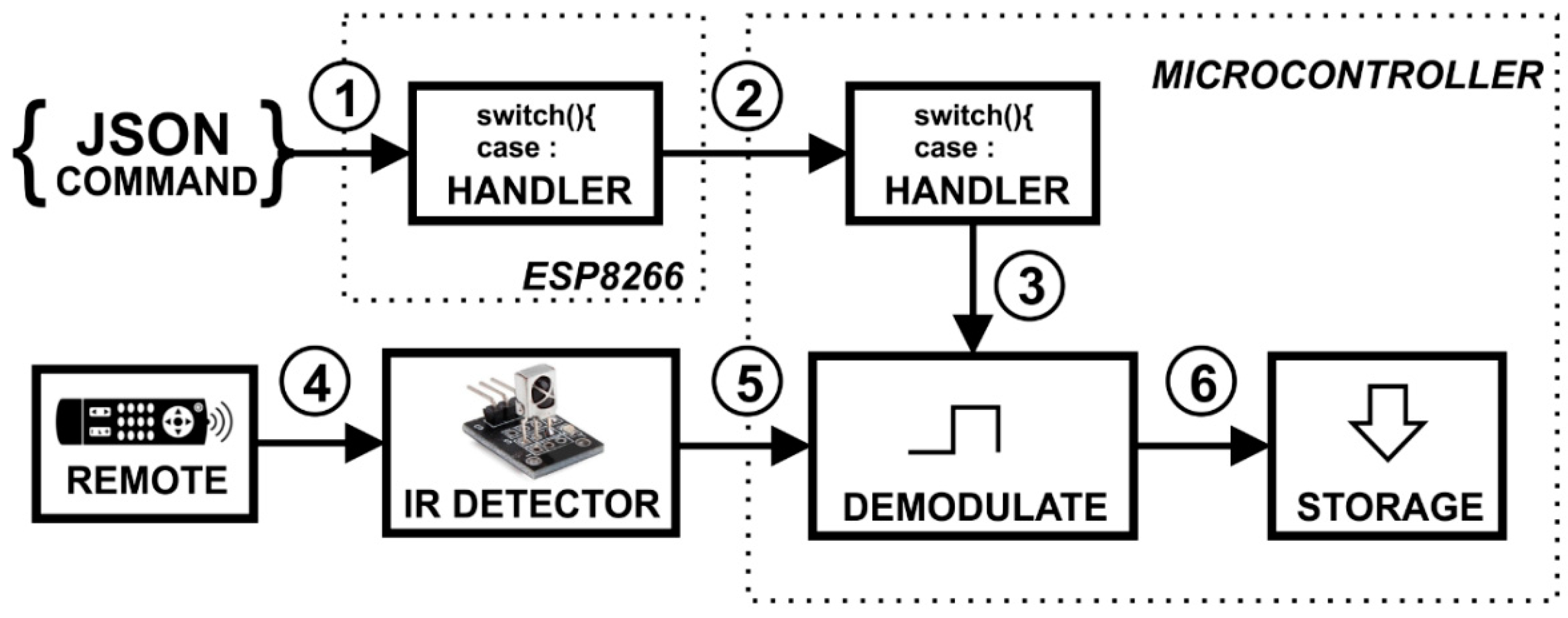
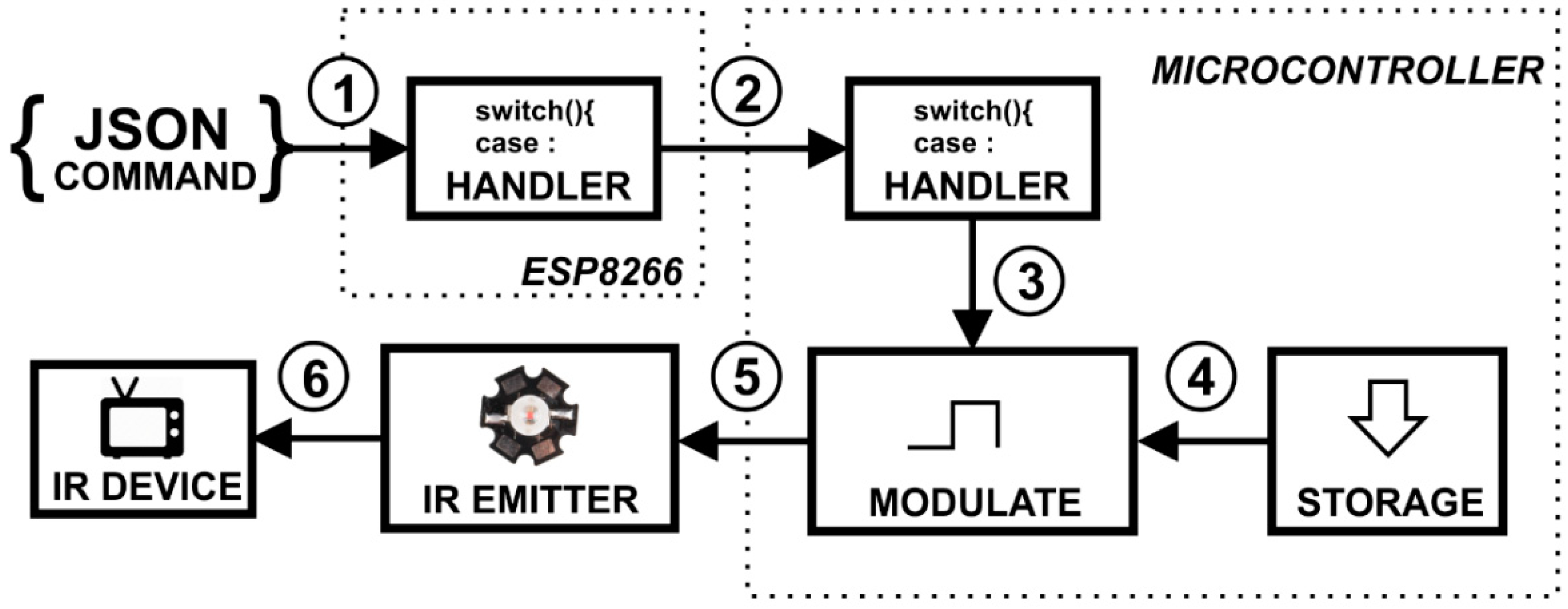
3.4. Wireless Infrared Communication
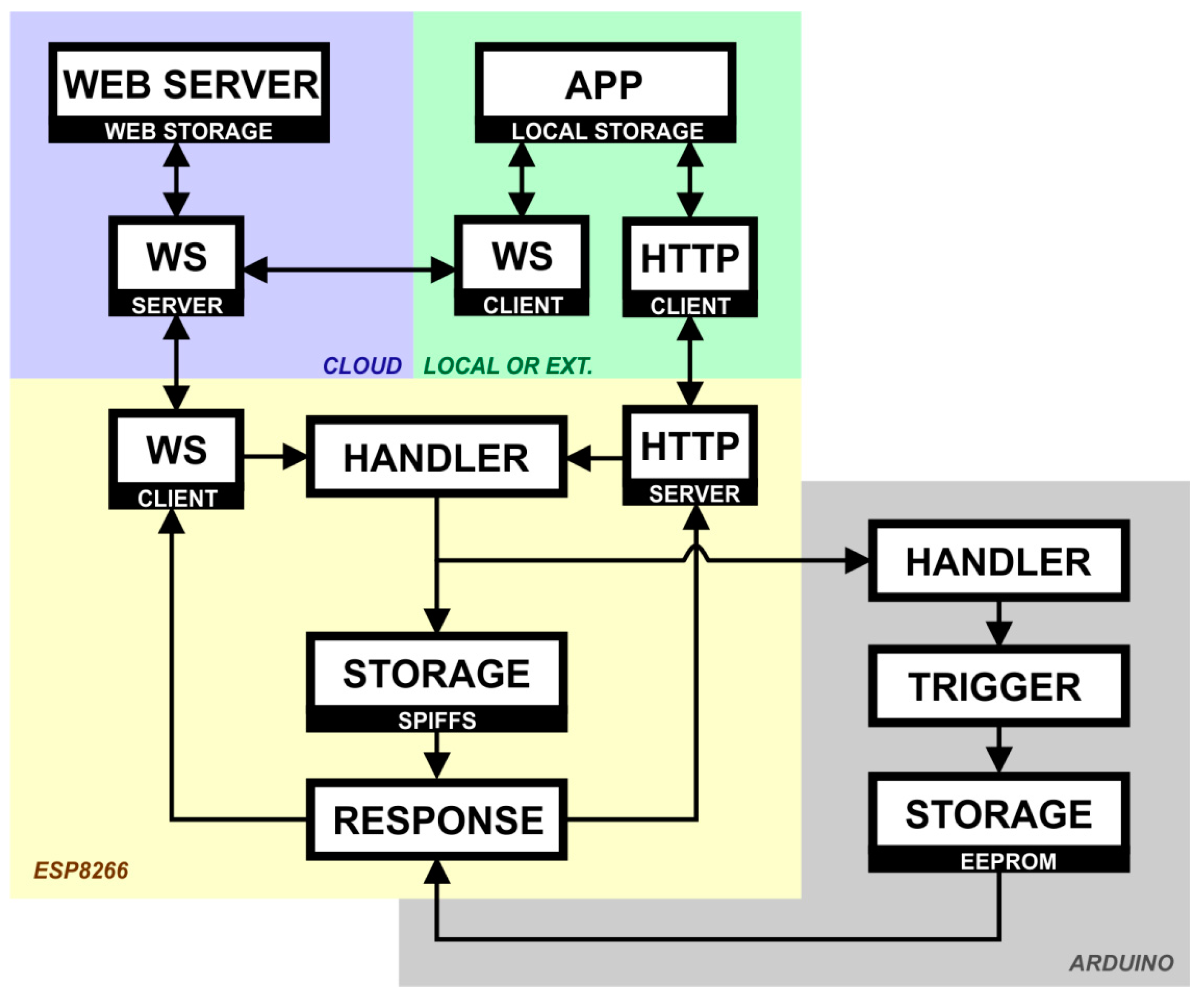
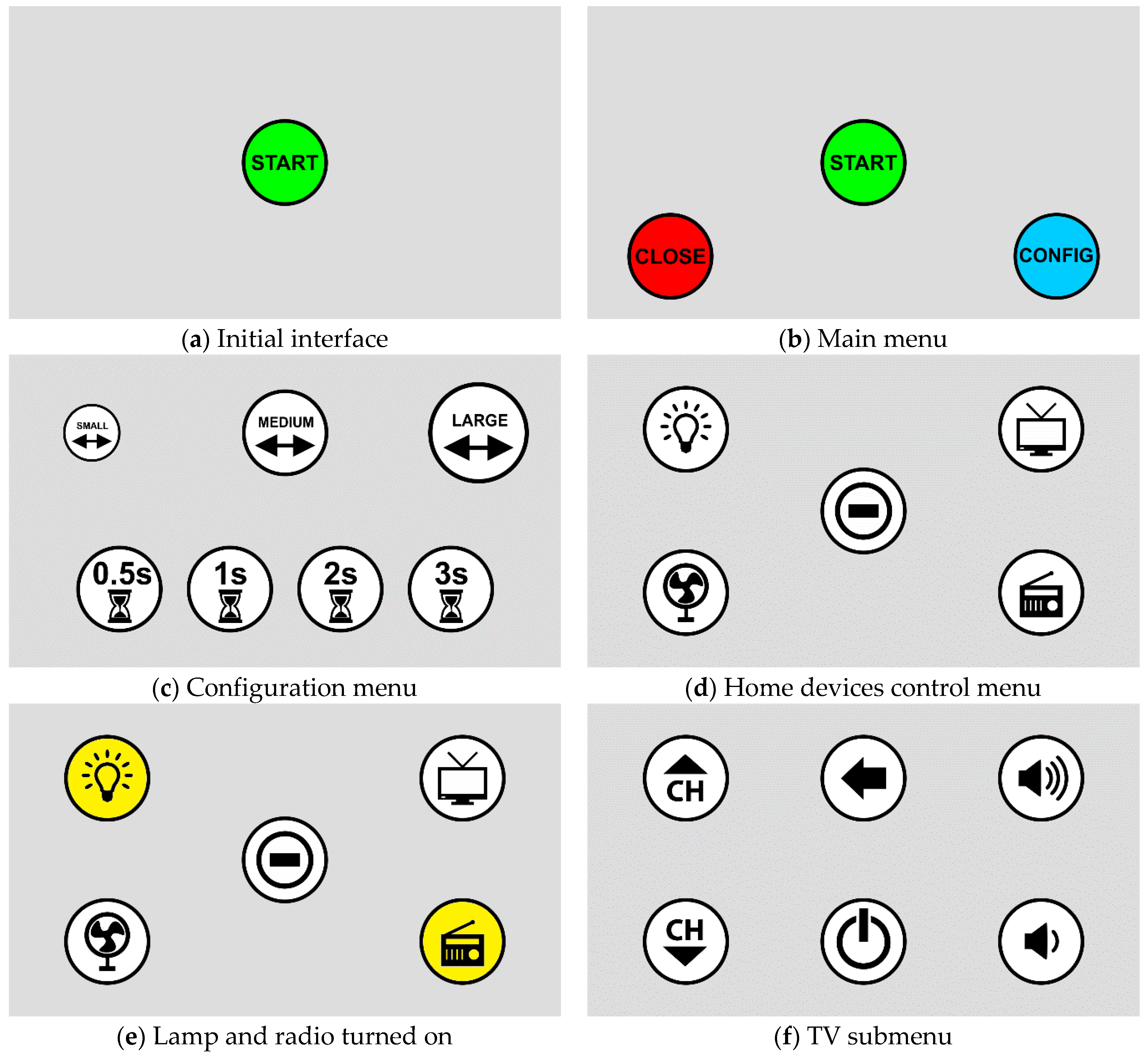
3.5. User Interface
3.6. Caregiver Interface
- Connected via WS. This is the best connection. It occurs when the connection between the application and the physical device is done by Internet; that way, user commands are stored on the server instantly.
- Connected via AJAX. This occurs when the connection between the application and the physical device is made by the Intranet, so the commands are stored temporarily on the user’s computer until a connection via WS is established.
- Not Connected. This occurs when there is no connection between the application and the physical device. In this case, it is suggested to refresh the site and check the connections with the physical device.
4. Tests, Results, and Discussion
4.1. Tests with a Group of Able-Bodied Participants
4.1.1. Pre-Test Preparation
4.1.2. Participants
4.1.3. Experimental Sessions
4.1.4. Results and Discussion
4.2. Tests with a Person with Disabilities
4.2.1. Pre-Test Preparation
4.2.2. Participant Background
4.2.3. Experimental Sessions
4.2.4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AJAX | Asynchronous JavaScript and XML |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| CEP/UFES | Committee of Ethics in Human Beings Research of the Federal University of Espirito Santo |
| EEPROM | Electrically-Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory |
| EOG | Electrooculography |
| HCI | Human-Computer Interaction |
| HMI | Human-Computer Interface |
| HTTP | Hypertext Transfer Protocol |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| IP | Internet Protocol |
| IR | Infrared |
| IROG | Infrared Oculography |
| JSON | JavaScript Object Notation |
| SPIFFS | Serial Peripheral Interface Flash File System |
| SSC | Scleral Search Coil |
| SSID | Service Set IDentifier |
| SUS | System Usability Scale |
| TCP | Transmission Control Protocol |
| UCD | User-Centered Design |
| UI | User Interface |
| VOG | Video-Oculography |
| WS | WebSocket |
References
- Tang, L.Z.W.; Ang, K.S.; Amirul, M.; Yusoff, M.B.M.; Tng, C.K.; Alyas, M.D.B.M.; Lim, J.G.; Kyaw, P.K.; Folianto, F. Augmented reality control home (ARCH) for disabled and elderlies. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Tenth International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing (ISSNIP), Singapore, 7–9 April 2015; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Schwiegelshohn, F.; Wehner, P.; Rettkowski, J.; Gohringer, D.; Hubner, M.; Keramidas, G.; Antonopoulos, C.; Voros, N.S. A holistic approach for advancing robots in ambient assisted living environments. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 13th International Conference on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing, Porto, Portugal, 21–23 October 2015; pp. 140–147. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinidis, E.I.; Antoniou, P.E.; Bamparopoulos, G.; Bamidis, P.D. A lightweight framework for transparent cross platform communication of controller data in ambient assisted living environments. Inf. Sci. (NY) 2015, 300, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumpa, E.; Charalampou, I.; Gkogkidis, A.; Ntaliani, A.; Kokkinou, E.; Kakarountas, A. Assistive System for Elders Suffering of Dementia. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 8th International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Berlin, Germany, 2–5 September 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Brazil Assistive Technology. In Proceedings of the National Undersecretary for the Promotion of the Rights of People with Disabilities; Technical Assistance Committee: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Elakkiya, J.; Gayathri, K.S. Progressive Assessment System for Dementia Care Through Smart Home. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Algorithms, Methodology, Models and Applications in Emerging Technologies (ICAMMAET), Chennai, India, 16–18 Febuary 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rafferty, J.; Nugent, C.D.; Liu, J.; Chen, L. From Activity Recognition to Intention Recognition for Assisted Living within Smart Homes. IEEE Trans. Hum. -Mach. Syst. 2017, 47, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, T.; Fornaser, A.; Suwa, H.; Yasumoto, K.; Cecco, M. De Kinect-based micro-behavior sensing system for learning the smart assistance with human subjects inside their homes. In Proceedings of the 2018 Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 and IoT, Brescia, Italy, 16–18 April 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Daher, M.; El Najjar, M.E.; Diab, A.; Khalil, M.; Charpillet, F. Multi-sensory Assistive Living System for Elderly In-home Staying. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computer and Applications (ICCA), Beirut, Lebanon, 25–26 August 2012; pp. 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Ghayvat, H.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Shenjie, B.; Chouhan, A.; Chen, W. Smart Home Based Ambient Assisted Living Recognition of Anomaly in the Activity of Daily Living for an Elderly Living Alone. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Houston, TX, USA, 14–17 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.; Li, M.; Grady, M.J.O.; Hare, G.M.P.O.; Gu, X.; Alawlaqi, M.A.A.H. Time-bounded Activity Recognition for Ambient Assisted Living. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2018, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristály, D.M.; Moraru, S.-A.; Neamtiu, F.O.; Ungureanu, D.E. Assistive Monitoring System Inside a Smart House. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Symposium in Sensing and Instrumentation in IoT Era (ISSI), Shanghai, China, 6–7 September 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Falcó, J.L.; Vaquerizo, E.; Artigas, J.I. A Multi-Collaborative Ambient Assisted Living Service Description Tool. Sensors 2014, 14, 9776–9812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadão, C.; Caldeira, E.; Bastos-filho, T.; Frizera-neto, A.; Carelli, R. A New Controller for a Smart Walker Based on Human-Robot Formation. Sensors 2016, 16, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y. Wheelchair Navigation System for Disabled and Elderly People. Sensors 2016, 16, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, C.; Dawes, H. Disrupting the world of Disability: The Next Generation of Assistive Technologies and Rehabilitation Practices. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, D.M.C.D.; Emmel, M.L.G. Assistive Technology Public Policies in Brazil: A Study about Usability and Abandonment by People with Physical Disabilities. Rev. Fac. St. Agostinho 2015, 12, 79–106. [Google Scholar]
- Da Costa, C.R.; Ferreira, F.M.R.M.; Bortolus, M.V.; Carvalho, M.G.R. Assistive technology devices: Factors related to abandonment. Cad. Ter. Ocup. UFSCar 2015, 23, 611–624. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, D.M.C.D.; Emmel, M.L.G. Use and abandonment of assistive technology for people with physical disabilities in Brazil. Available online: https://www.efdeportes.com/efd173/tecnologia-assistiva-com-deficiencia-fisica.htm (accessed on 19 February 2019).
- Marcos, P.M.; Foley, J. HCI (human computer interaction): Concepto y desarrollo. El Prof. La Inf. 2001, 10, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lamberti, F.; Sanna, A.; Carlevaris, G.; Demartini, C. Adding pluggable and personalized natural control capabilities to existing applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 2832–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisio, I.; Lavagetto, F.; Marchese, M.; Sciarrone, A. Smartphone-Centric Ambient Assisted Living Platform for Patients Suffering from Co-Morbidities Monitoring. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Shao, Y.; Shu, L.; Han, G.; Zhu, C. LDPA: A Local Data Processing Architecture in Ambient Assisted Living Communications. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Basterretxea, A.; Mendez-Zorrilla, A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. Eye/head tracking technology to improve HCI with iPad applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 2244–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butala, P.M.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, D.C.; Wagenaar, R.C. Wireless System for Monitoring and Real-Time Classification of Functional Activity. In Proceedings of the 2012 Fourth International Conference Communication Systems Networks (COMSNETS 2012), Bangalore, India, 3–7 January 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ahamed, M.M.; Bakar, Z.B.A. Triangle Model Theory for Enhance the Usability by User Centered Design Process in Human Computer Interaction. Int. J. Contemp. Comput. Res. 2017, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Iivari, J.; Iivari, N. Varieties of user-centredness: An analysis of four systems development methods. J. Inf. Syst. 2011, 21, 125–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, D.A. The Design of Everyday Things; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Preece, J.; Rogers, Y.; Sharp, H. Interaction Design-Beyond Human-Computer Interaction; John Wiley Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 168–186. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, E.; Stolterman, E.; Wakkary, R. Understanding Interaction Design Practices. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–11 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Begum, I. HCI and its Effective Use in Design and Development of Good User Interface. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2014, 3, 176–179. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9241-210–Ergonomics of Human-System Interaction—Part 210: Human-Centred Design for Interactive Systems; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Brooke, J. System Usability Scale (SUS): A Quick-and-Dirty Method of System Evaluation User Information; Digital Equipment Co Ltd.: Reading, UK, 1986; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.S.A.; Tien, G.; Atkins, M.S.; Zheng, B.; Panton, O.N.M.; Meneghetti, A.T. Analysis of eye gaze: Do novice surgeons look at the same location as expert surgeons during a laparoscopic operation. Surg. Endosc. 2012, 26, 3536–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richstone, L.; Schwartz, M.J.; Seideman, C.; Cadeddu, J.; Marshall, S.; Kavoussi, L.R. Eye metrics as an objective assessment of surgical skill. Ann. Surg. 2010, 252, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.; McGrath, J.; Vine, S.; Brewer, J.; Defriend, D.; Masters, R. Psychomotor control in a virtual laparoscopic surgery training environment: Gaze control parameters differentiate novices from experts. Surg. Endosc. 2010, 24, 2458–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.R.; McGrath, J.S.; Vine, S.J.; Brewer, J.; Defriend, D.; Masters, R.S.W. Perceptual impairment and psychomotor control in virtual laparoscopic surgery. Surg. Endosc. 2011, 27, 2268–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Xia, J.; Nadarajah, N.; Falkmer, T.; Foster, J.; Lee, H. Assessing drivers’ visual-motor coordination using eye tracking, GNSS and GIS: A spatial turn in driving psychology. J. Spat. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.; Vine, S.J.; Cooke, A.M.; Ring, C. Quiet eye training expedites motor learning and aids performance under heightened anxiety: The roles of response programming and external attention. Psychophysiology 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, M.A.; Giakoumidis, N.; El-Saddik, A. A Novel Eye-Gaze-Controlled Wheelchair System for Navigating Unknown Environments: Case Study with a Person with ALS. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 558–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, R.G.; Ungureanu, F. Mobile Embedded System for Human Computer Communication in Assistive Technology. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 8th International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 30 August–1 September 2012; pp. 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Lupu, R.G.; Ungureanu, F.; Siriteanu, V. Eye tracking mouse for human computer interaction. In Proceedings of the 2013 E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 21–23 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, N.; Green, C.; Fairley, S. Investigation of the use of eye tracking to examine tourism advertising effectiveness. Curr. Issues Tour. 2015, 19, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecotti, H. A Multimodal Gaze-Controlled Virtual Keyboard. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2016, 46, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.; Pereira, T.; Almeida, D. Smart scrolling based on eye tracking. Design an eye tracking mouse. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 80, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Nehete, M.; Lokhande, M.; Ahire, K. Design an Eye Tracking Mouse. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 2013, 2, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Frutos-Pascual, M.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. Assessing visual attention using eye tracking sensors in intelligent cognitive therapies based on serious games. Sensors 2015, 15, 11092–11117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yoo, J.; Han, G. Gaze-assisted user intention prediction for initial delay reduction in web video access. Sensors 2015, 15, 14679–14700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, K.; Takahashi, K.; Takamatsu, J. Estimating 3-D Point-of-Regard in a Real Environment Using a Head-Mounted Eye-Tracking System. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2014, 44, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, H.; Fukumoto, M.; Yagi, T. Direct Gaze Estimation Based on Nonlinearity of EOG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzman, P.S.; Proctor, L.R.; Hughes, D.W. Eye-tracking patterns in schizophrenia. Science 1973, 181, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaghy, C.; Thurtell, M.J.; Pioro, E.P.; Gibson, J.M.; Leigh, R.J. Eye movements in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and its mimics: A review with illustrative cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, C.A.; Barreto, A.; Cremades, J.G.; Adjouadi, M. Integrated electromyogram and eye-gaze tracking cursor control system for computer users with motor disabilities. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2008, 45, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missimer, E.; Betke, M. Blink and wink detection for mouse pointer control. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Pervasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments (PETRA ’10), Samos, Greece, 23–25 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wankhede, S.; Chhabria, S. Controlling Mouse Cursor Using Eye Movement. Int. J. Appl. Innov. Eng. Manag. 2013, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Meghna, S.M.A.; Kachan, K.L.; Baviskar, A. Head tracking virtual mouse system based on ad boost face detection algorithm. Int. J. Recent Innov. Trends Comput. Commun. 2016, 4, 921–923. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, J.; Wai, A.A.P.; Tolstikov, A.; Kenneth, L.J.H.; Maniyeri, J.; Victor, F.S.F.; Lee, A.; Phua, C.; Jiaqi, Z.; Hoa, H.T.; et al. From context to micro-context–Issues and challenges in sensorizing smart spaces for assistive living. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2011, 5, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visutsak, P.; Daoudi, M. The Smart Home for the Elderly: Perceptions, Technologies and Psychological Accessibilities. In Proceedings of the 2017 XXVI International Conference on Information, Communication and Automation Technologies (ICAT), Sarajevo, Bosnia-Herzegovina, 26–28 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Beligianni, F.; Alamaniotis, M.; Fevgas, A.; Tsompanopoulou, P.; Bozanis, P.; Tsoukalas, L.H. An internet of things architecture for preserving privacy of energy consumption. In Proceedings of the Mediterranean Conference on Power Generation, Transmission, Distribution and Energy Conversion (MedPower 2016), Belgrade, Serbia, 6–9 November 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchet, O.; Javaudin, J.; Kortebi, A.; El-Abdellaouy, H.; Lebouc, M.; Fontaine, F.; Jaffré, P.; Celeda, P.; Mayer, C.; Guan, H. ACEMIND: The smart integrated home network. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Intelligent Environments, Shanghai, China, 30 June–4 July 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Buhl, J.; Hasselkuß, M.; Suski, P.; Berg, H. Automating Behavior? An Experimental Living Lab Study on the Effect of Smart Home Systems and Traffic Light Feedback on Heating Energy Consumption. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 22, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Lim, S.Y.; Nguyen, M.D.; Li, C.; Tan, Y. Bridging Between universAAL and ECHONET for Smart Home Environment. In Proceedings of the 2017 14th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI), Jeju, South Korea, 28 June–1 July 2017; pp. 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.M.; Chen, M.T. Design and Implementation of a Smart Home Energy Saving System with Active Loading Feature Identification and Power Management. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 3rd International Future Energy Electronics Conference and ECCE Asia (IFEEC 2017–ECCE Asia), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 3–7 June 2017; pp. 739–742. [Google Scholar]
- Soe, W.T.; Mpawenimana, I.; Difazio, M.; Belleudy, C.; Ya, A.Z. Energy Management System and Interactive Functions of Smart Plug for Smart Home. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Energ. Electron. Commun. Eng. 2017, 11, 824–831. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Hu, X.; Teng, Y.; Qian, S.; Cheng, R. Optimal integration of a hybrid solar-battery power source into smart home nanogrid with plug-in electric vehicle. J. Power Sources 2017, 363, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melhem, F.Y.; Grunder, O.; Hammoudan, Z. Optimization and Energy Management in Smart Home considering Photovoltaic, Wind, and Battery Storage System with Integration of Electric Vehicles. Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2017, 40, 128–138. [Google Scholar]
- Başol, G.; Güntürkün, R.; Başol, E. Smart Home Design and Application. World Wide J. Multidiscip. Res. Dev. 2017, 3, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Choi, C.; Park, W.; Lee, I.; Kim, S.; Architecture, A.S. Smart Home Energy Management System Including Renewable Energy Based on ZigBee and PLC. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2014, 60, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Luo, F.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; An, Y.; Li, X. Smart Home Energy Management with Vehicle-to-Home Technology. In Proceedings of the 2017 13th IEEE International Conference on Control & Automation (ICCA), Ohrid, Macedonia, 3–6 July 2017; pp. 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Kiat, L.Y.; Barsoum, N. Smart Home Meter Measurement and Appliance Control. Int. J. Innov. Res. Dev. 2017, 6, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oliveira, E.L.; Alfaia, R.D.; Souto, A.V.F.; Silva, M.S.; Francês, C.R. SmartCoM: Smart Consumption Management Architecture for Providing a User-Friendly Smart Home based on Metering and Computational Intelligence. J. Microw. Optoelectron. Electromagn. Appl. 2017, 16, 732–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kibria, M.G.; Jarwar, M.A.; Ali, S.; Kumar, S.; Chong, I. Web Objects Based Energy Efficiency for Smart Home IoT Service Provisioning. In Proceedings of the 2017 Ninth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Milan, Italy, 4–7 July 2017; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, S.K. Towards Securing Discovery Services in Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 7–11 January 2016; pp. 506–507. [Google Scholar]
- Huth, C.; Duplys, P.; Tim, G. Secure Software Update and IP Protection for Untrusted Devices in the Internet of Things Via Physically Unclonable Functions. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communication Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Sydney, Australia, 14–18 March 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, R.A.; Shah, B. Security analysis of IoT protocols: A focus in CoAP. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd MEC International Conference on Big Data and Smart City (ICBDSC), Muscat, Oman, 15–16 March 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rajiv, P.; Raj, R.; Chandra, M. Email based remote access and surveillance system for smart home infrastructure. Perspect. Sci. 2016, 8, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, J.; Hoang, K.; Arias, O.; Sadeghi, A.; Jin, Y. Security Analysis on Consumer and Industrial IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 2016 21st Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC), Macau, China, 25–28 January 2016; pp. 519–524. [Google Scholar]
- Arabo, A. Cyber Security Challenges within the Connected Home Ecosystem Futures. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 61, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golait, S.S. 3-Level Secure Kerberos Authentication for Smart Home Systems Using IoT. In Proceedings of the 2015 1st International Conference on Next Generation Computing Technologies (NGCT), Dehradun, India, 4–5 September 2015; pp. 262–268. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.H.; Kim, J. Security Considerations for Secure and Trustworthy Smart Home System in the IoT Environment. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, South Korea, 28–30 October 2015; pp. 1116–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Huth, C.; Zibuschka, J.; Duplys, P.; Tim, G. Securing Systems on the Internet of Things via Physical Properties of Devices and Communications. In Proceedings of the 2015 Annual IEEE Systems Conference (SysCon) Proceedings, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 13–16 April 2015; pp. 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsson, A.; Davidsson, P. Towards a Model of Privacy and Security for Smart Homes. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 2nd World Forum Internet Things, Milan, Italy, 4–16 December 2015; pp. 727–732. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Kato, T.; Takahashi, H.; Kinoshita, T. Intelligent Home Security System Using Agent-based IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 4th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Osaka, Japan, 27–30 October 2015; pp. 313–314. [Google Scholar]
- Peretti, G.; Lakkundit, V.; Zorzi, M. BlinkToSCoAP: An End-to-End Security Framework for the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2015 7th International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks (COMSNETS), Bangalore, India, 6–10 January 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Santoso, F.K.; Vun, N.C.H. Securing IoT for Smart Home System. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Symposium on Consumer Electronics (ISCE), Madrid, Spain, 24–26 June 2015; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Schiefer, M. Smart Home Definition and Security Threats. In Proceedings of the 2015 Ninth International Conference on IT Security Incident Management & IT Forensics, Magdeburg, Germany, 18–20 May 2015; pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Alohali, B.; Merabti, M.; Kifayat, K. A Secure Scheme for a Smart House Based on Cloud of Things (CoT). In Proceedings of the 2014 6th Computer Science and Electronic Engineering Conference (CEEC), Colchester, UK, 25–26 September 2014; pp. 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaraman, V.; Gharakheili, H.H.; Vishwanath, A.; Boreli, R.; Mehani, O. Network-Level Security and Privacy Control for Smart-Home IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 11th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob), Abu Dhabi, United Arab, 19–21 October 2015; pp. 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Amadeo, M.; Briante, O.; Campolo, C.; Molinaro, A.; Ruggeri, G. Information-centric networking for M2M communications: Design and deployment. Comput. Commun. 2016, 89–90, 105–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Seed, D.; Flynn, B.; Mladin, C.; Di Girolamo, R. Enabling Semantics in an M2M/IoT Service Delivery Platform. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Tenth International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC), Laguna Hills, CA, USA, 4–6 Febuary 2016; pp. 206–213. [Google Scholar]
- Rizopoulos, C. Implications of Theories of Communication and Spatial Behavior for the Design of Interactive Environments. In Proceedings of the 2011 Seventh International Conference on Intelligent Environments, Nottingham, UK, 25–28 July 2011; pp. 286–293. [Google Scholar]
- Waltari, O.; Kangasharju, J. Content-Centric Networking in the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th IEEE Annual Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9–12 January 2016; pp. 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, D.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.Y. Hybrid reality-based user experience and evaluation of a context-aware smart home. Comput. Ind. 2016, 76, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadeo, M.; Campolo, C.; Iera, A.; Molinaro, A. Information Centric Networking in IoT scenarios: The Case of a Smart Home. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), London, UK, 8–12 June 2015; pp. 648–653. [Google Scholar]
- Elkhodr, M.; Shahrestani, S.; Cheung, H. A Smart Home Application based on the Internet of Things Management Platform. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Data Intensive Systems, Sydney, Australia, 11–13 December 2015; pp. 491–496. [Google Scholar]
- Bhide, V.H.; Wagh, S. I-learning IoT: An intelligent self learning system for home automation using IoT. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Communications and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Melmaruvathur, India, 2–4 April 2015; pp. 1763–1767. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, J.; Fan, D.; Zhang, J. The new intelligent home control system based on the dynamic and intelligent gateway. In Proceedings of the 2011 4th IEEE International Conference on Broadband Network and Multimedia Technology, Shenzhen, China, 28–30 October 2011; pp. 526–530. [Google Scholar]
- Cheuque, C.; Baeza, F.; Marquez, G.; Calderon, J. Towards to responsive web services for smart home LED control with Raspberry Pi. A first approach. In Proceedings of the 2015 34th International Conference of the Chilean Computer Science Society (SCCC), Santiago, Chile, 9–13 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hasibuan, A.; Mustadi, M.; Syamsudin, D.I.E.Y.; Rosidi, I.M.A. Design and Implementation of Modular Home Automation Based on Wireless Network, REST API and WebSocket. In Proceedings of the Internastional Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ISPACS), Nusa Dua, Indonesia, 9–12 November 2015; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, M.E.P.; Reiff-Marganiec, S. Autonomous and self controlling smart objects for the future Internet. In Proceedings of the 2015 3rd International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud, Rome, Italy, 24–26 August 2015; pp. 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsson, A.; Boldt, M.; Carlsson, B. A risk analysis of a smart home automation system. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2016, 56, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsson, A.; Boldt, M.; Carlsson, B. On the risk exposure of smart home automation systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud, Barcelona, Spain, 27–29 August 2014; pp. 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarevic, I.; Sekulic, M.; Savic, M.S.; Mihic, V. Modular home automation software with uniform cross component interaction based on services. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 5th International Conference on Consumer Electronics Berlin (ICCE-Berlin), Berlin, Germany, 6–9 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.M.; Teng, W.G.; Hou, T.W. Point-n-Press: An Intelligent Universal Remote Control System for Home Appliances. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2016, 13, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeazell, S.C. Teaching Supplemental Jurisdiction. Indiana Law J. 1998, 74, 222–249. [Google Scholar]
- Miclaus, A.; Riedel, T.; Beigl, M. Computing Corner. Teach. Stat. 1990, 12, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, Y.; Toshniwal, P.; Sharma, S.; Singhal, D.; Gupta, R.; Mittal, V.K. A voice-controlled multi-functional Smart Home Automation System. In Proceedings of the 2015 Annual IEEE India Conference (INDICON), New Delhi, India, 17–20 December 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Moravcevic, V.; Tucic, M.; Pavlovic, R.; Majdak, A. An approach for uniform representation and control of ZigBee devices in home automation software. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 5th International Conference on Consumer Electronics - Berlin (ICCE-Berlin), Berlin, Germany, 6–9 September 2015; pp. 237–239. [Google Scholar]
- Papp, I.; Velikic, G.; Lukac, N.; Horvat, I. Uniform representation and control of Bluetooth Low Energy devices in home automation software. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 5th International Conference on Consumer Electronics - Berlin (ICCE-Berlin), Berlin, Germany, 6–9 September 2015; pp. 366–368. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, J.L. Home automation. IEE Rev. 1988, 34, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-T.; Hsiao, W.-H.; Huang, C.-M.; Chou, S.-C.T. An Integrated Cloud-Based Smart Home Management System with Community Hierarchy. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2016, 62, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaris, L.; Kokkinis, A.; Fortino, G.; Liotta, A.; Stavrou, S. Sample Size Determination Algorithm for fingerprint-based indoor localization systems. Comput. Netw. 2016, 101, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, L.Y.; Faiçal, B.S.; Nakamura, L.H.V.; Gomes, P.H.; Libralon, G.L.; Meneguete, R.I.; Filho, G.P.R.; Giancristofaro, G.T.; Pessin, G.; Krishnamachari, B.; et al. Exploiting IoT technologies for enhancing Health Smart Homes through patient identification and emotion recognition. Comput. Commun. 2016, 89–90, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjal, S.V.; Talmale, G.R. Medicine Reminder and Monitoring System for Secure Health Using IOT. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 78, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhole, M.; Phull, K.; Jose, A.; Lakkundi, V. Delivering Analytics Services for Smart Homes. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Wireless Sensors (ICWiSe), Melaka, Malaysia, 24–26 August 2015; pp. 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, S.; Bourobou, M.; Yoo, Y. User Activity Recognition in Smart Homes Using Pattern Clustering Applied to Temporal ANN Algorithm. Sensors 2015, 15, 11953–11971. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, M.; Flehmig, G.; Schmidtke, H.R.; Scholz, G.H. Powering Smart Home intelligence using existing entertainment systems. In Proceedings of the 2011 Seventh International Conference on Intelligent Environments, Nottingham, UK, 25–28 July 2011; Volume 970, pp. 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Peng, J.; Lu, Z.; Jiao, J. 802.11ad Key Performance Analysis and Its Application in Home Wireless Entertainment. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 17th International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering, Chengdu, China, 19–21 December 2014; Volume 5, pp. 1595–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Technologies, I. Analyzing Social Networks Activities to Deploy Entertainment Services in HRI-based Smart Environments. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), Naples, Italy, 9–12 July 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.A.; Alamri, A.; Parra, J. Context-Aware Elderly Entertainment Support System in Assisted Living Environment. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo Workshops (ICMEW), San Jose, CA, USA, 15–19 July 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dooley, J.; Henson, M.; Callaghan, V.; Hagras, H.; Al-Ghazzawi, D.; Malibari, A.; Al-Haddad, M.; Al-ghamdi, A.A. A Formal Model For Space Based Ubiquitous Computing. In Proceedings of the 2011 Seventh International Conference on Intelligent Environments, Nottingham, UK, 25–28 July 2011; pp. 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- De Morais, W.O.; Wickström, N. A “Smart Bedroom” as an Active Database System. In Proceedings of the 2013 9th International Conference on Intelligent Environments, Athens, Greece, 16–17 July 2013; pp. 250–253. [Google Scholar]
- Gaikwad, P.P.; Gabhane, J.P.; Golait, S.S. Survey based on Smart Homes System Using Internet-of-Things. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computation of Power, Energy, Information and Communication (ICCPEIC), Chennai, India, 22–23 April 2015; pp. 330–335. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, S.S.I. A Review of Connectivity Challenges in IoT-Smart Home. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd MEC International Conference on Big Data and Smart City (ICBDSC), Muscat, Oman, 15–16 March 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Jeon, Y.; Chong, I.; Lee, S.H. Orchestration in distributed web-of-objects for creation of user-centered iot service capability. In Proceedings of the 2013 Fifth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Da Nang, Vietnam, 2–5 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, T.; Kawarada, A.; Nambu, M.; Tsukada, A.; Sasaki, K.; Yamakoshi, K. E-Healthcare at an Experimental Welfare Techno House in Japan. Open Med. Inform. J. 2007, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohktar, M.S.; Sukor, J.A.; Redmond, S.J.; Basilakis, J.; Lovell, N.H. Effect of Home Telehealth Data Quality on Decision Support System Performance. Proc. Comput. Sci. 2015, 64, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matsuoka, K. Aware Home Understanding Life Activities. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Smart Homes Health Telematics (ICOST 2004), Ames, IA, USA, 28 June–2 July 2004; Volume 14, pp. 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, T.; Noguchi, H.; Takada, A.; Sato, T. Sensing room environment: Distributed sensor space for measurement of human dialy behavior. Ransaction Soc. Instrum. Control Eng. 2006, 1, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Kim, Y.-T.; Jung, J.-W.; Park, K.-H.; Kim, D.-J.; Bang, B.; Bien, Z.Z. A 24-hour health monitoring system in a smart house. Gerontechnol. J. 2008, 7, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubihome|Mind the Gap. Available online: https://mindthegap.agency/client/ubihome (accessed on 30 November 2018).
- ubiHome. Available online: http://ubihome.me/Home (accessed on 30 November 2018).
- Oh, Y.; Lee, S.; Woo, W. User-Centric Integration of Contexts for a Unified Context-Aware Application Model. CEUR Workshop Proceeding. 2005, pp. 9–16. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/User-centric-Integration-of-Contexts-for-A-Unified-Oh-Lee/0b36ca616e47b66487372625df44aeb1d919fe48 (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Oh, Y.; Woo, W. A Unified Application Service Model for ubiHome by Exploiting Intelligent Context-Awareness. In International Symposium on Ubiquitious Computing Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germnay, 2004; pp. 192–202. [Google Scholar]
- Bien, Z.Z.; Park, K.-H.; Bang, W.-C.; Stefanov, D.H. LARES: An Intelligent Sweet Home for Assisting the Elderly and the Handicapped. 1st International Conference Smart Homes Health Telematics, Assistive Technology, 2003. pp. 151–158. Available online: https://edurev.in/studytube/LARES-An-Intelligent-Sweet-Home-for-Assisting-the-/bf43423b-0daf-42b3-bf3f-54c8fa4e2bbd_p (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Minoh, M. Experiences in UKARI Project. J. Natl. Inst. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2007, 54, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Tetsuya, F.; Hirotada, U.; Michihiko, M. A Looking-for-Objects Service in Ubiquious Home. J. Natl. Inst. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2007, 54, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Toyota Dream House PAPI. Available online: http://tronweb.super-nova.co.jp/toyotadreamhousepapi.html (accessed on 30 November 2018).
- Junestrand, S.; Keijer, U.; Tollmar, K. Private and Public Digital Domestic Spaces. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2001, 54, 753–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orpwood, R.; Gibbs, C.; Adlam, T.; Faulkner, R.; Meegahawatte, D. The Gloucester Smart House for People with Dementia—User-Interface Aspects. In Designing a More Inclusive World; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004; pp. 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, G.; Wiratunga, N.; Taylor, B.; Craw, S. Matching smarthouse technology to needs of the elderly and disabled. In Proceedings of the Workshop Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Case-Based Reasoning, Trondheim, Norway, 23–26 June 2003; pp. 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrotra, S.; Dhande, R. Smart cities and smart homes: From realization to reality. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Green Computing and Internet of Things (ICGCIoT), Noida, India, 8–10 October 2015; pp. 1236–1239. [Google Scholar]
- myGEKKO. Available online: https://www2.my-gekko.com/en/ (accessed on 30 November 2018).
- MATCH–Mobilising Advanced Technologies for Care at Home. Available online: http://www.cs.stir.ac.uk/~kjt/research/match/main/main.html (accessed on 30 November 2018).
- The Adaptive House Boulder, Colorado. Available online: http://www.cs.colorado.edu/~mozer/index.php?dir=/Research/Projects/Adaptive house/ (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Lindsey, R.; Daluiski, A.; Chopra, S.; Lachapelle, A.; Mozer, M.; Sicular, S.; Hanel, D.; Gardner, M.; Gupta, A.; Hotchkiss, R.; et al. Deep neural network improves fracture detection by clinicians. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aware Home Research Initiative (AHRI). Available online: http://awarehome.imtc.gatech.edu/ (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- MavHome: Managing an Adaptive Versatile Home. Available online: http://ailab.wsu.edu/mavhome/ (accessed on 30 November 2018).
- Cook, D.J.; Youngblood, M.; Heierman, E.O.; Gopalratnam, K.; Rao, S.; Litvin, A.; Khawaja, F. MavHome: An agent-based smart home. In Proceedings of the First IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, 2003. (PerCom 2003), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 26 March 2003; pp. 521–524. [Google Scholar]
- House_n Materials and Media. Available online: http://web.mit.edu/cron/group/house_n/publications.html (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Intille, S.S. The Goal: Smart People, Not Smart Homes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Homes and Health Telematics, Belfast, Northern Ireland, 26–28 June 2006; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Shafer, S.; Krumm, J.; Brumitt, B.; Meyers, B.; Czerwinski, M.; Robbins, D. The New EasyLiving Project at Microsoft Research. In Proceedings of the Joint DARPA/NIST Smart Spaces Workshop, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 30–31 Jully 1998; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Helal, A.; Mann, W. Gator Tech Smart House: A Programmable Pervasive Space. IEEE Comput. Mag. 2005, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigot, H.; Lefebvre, B. The Role of Intelligent Habitats in Upholding Elders in Residence. WIT Trans. Biomed. Health 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, V.; Atighetchi, M.; Benyo, B.; Horling, B.; Raja, A.; Vincent, R.; Wagner, T.; Xuan, P.; Zhang, S. A Multi-Agent System for Intelligent Environment Control; UMass Computer Science Technical Report 1998-40; University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- CASAS–Center for Advanced Studies in Adaptive Systems. Available online: http://casas.wsu.edu/ (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Ghods, A.; Caffrey, K.; Lin, B.; Fraga, K.; Fritz, R.; Schmitter-Edgecombe, M.; Hundhausen, C.; Cook, D.J. Iterative Design of Visual Analytics for a Clinician-in-the-loop Smart Home. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Inf. 2018, 2168–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.I.; Babbitt, R.; Wong, J.; Chang, C.K. A framework for service morphing and heterogeneous service discovery in smart environments. In International Conference on Smart Homes and Health Telematics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Heinz, M.; Martin, P.; Margrett, J.A.; Yearns, M.; Franke, W.; Yang, H.I. Perceptions of technology among older adults. J. Gerontol. Nurs. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Skubic, M.; Rantz, M.; Cuddihy, P.E. Quantitative gait measurement with pulse-doppler radar for passive in-home gait assessment. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 2434–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochester. Available online: https://www.rochester.edu/pr/Review/V64N3/feature2.html (accessed on 30 November 2018).
- Du, K.K.; Wang, Z.L.; Hong, M. Human machine interactive system on smart home of IoT. J. China Univ. Posts Telecommun. 2013, 20, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissoli, A.L.C. Multimodal Solution for Interaction with Assistance and Communication Devices; Federal University of Espirito Santo (UFES): Vitoria, Espirito Santo, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bangor, A.; Philip, K.; James, M. Determining what individual SUS scores mean: Adding an adjective rating scale. J. Usability Stud. 2009, 4, 114–123. [Google Scholar]

| Date | Start | End | Duration | Commands |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 09/14/2018 | 14:20 | 18:10 | 03:50:00 | 163 |
| 09/28/2018 | 12:51 | 19:49 | 06:58:00 | 131 |
| 09/20/2018 | 13:58 | 15:55 | 01:57:00 | 36 |
| 09/22/2018 | 15:52 | 17:36 | 01:44:00 | 18 |
| 10/02/2018 | 17:38 | 18:01 | 00:23:00 | 31 |
| 10/04/2018 | 14:15 | 18:04 | 03:49:00 | 88 |
| 10/05/2018 | 14:35 | 15:56 | 01:21:00 | 75 |
| Total | 20:02:00 | 542 |
| From | To | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | Day 6 | Day 7 | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | 12 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0% |
| 12 | 13 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0% |
| 13 | 14 | 0 | 62 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13% |
| 14 | 15 | 94 | 7 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 31 | 42% |
| 15 | 16 | 57 | 21 | 7 | 13 | 0 | 3 | 44 | 27% |
| 16 | 17 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1% |
| 17 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 22 | 8 | 0 | 6% |
| 18 | 19 | 12 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 4% |
| 19 | 20 | 0 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6% |
| 20 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0% |
| 21 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 1% |
| 22 | 00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0% |
| Total | 163 | 131 | 36 | 18 | 31 | 88 | 75 | 542 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bissoli, A.; Lavino-Junior, D.; Sime, M.; Encarnação, L.; Bastos-Filho, T. A Human–Machine Interface Based on Eye Tracking for Controlling and Monitoring a Smart Home Using the Internet of Things. Sensors 2019, 19, 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040859
Bissoli A, Lavino-Junior D, Sime M, Encarnação L, Bastos-Filho T. A Human–Machine Interface Based on Eye Tracking for Controlling and Monitoring a Smart Home Using the Internet of Things. Sensors. 2019; 19(4):859. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040859
Chicago/Turabian StyleBissoli, Alexandre, Daniel Lavino-Junior, Mariana Sime, Lucas Encarnação, and Teodiano Bastos-Filho. 2019. "A Human–Machine Interface Based on Eye Tracking for Controlling and Monitoring a Smart Home Using the Internet of Things" Sensors 19, no. 4: 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040859
APA StyleBissoli, A., Lavino-Junior, D., Sime, M., Encarnação, L., & Bastos-Filho, T. (2019). A Human–Machine Interface Based on Eye Tracking for Controlling and Monitoring a Smart Home Using the Internet of Things. Sensors, 19(4), 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040859






