Abstract
By the assist of remotely sensed data, this study examines the viability of slope stability monitoring using two novel conventional models. The proposed models are considered to be the combination of neuro-fuzzy (NF) system along with invasive weed optimization (IWO) and elephant herding optimization (EHO) evolutionary techniques. Considering the conditioning factors of land use, lithology, soil type, rainfall, distance to the road, distance to the river, slope degree, elevation, slope aspect, profile curvature, plan curvature, stream power index (SPI), and topographic wetness index (TWI), it is aimed to achieve a reliable approximation of landslide occurrence likelihood for unseen environmental conditions. To this end, after training the proposed EHO-NF and IWO-NF ensembles using training landslide events, their generalization power is evaluated by receiving operating characteristic curves. The results demonstrated around 75% accuracy of prediction for both models; however, the IWO-NF achieved a better understanding of landslide distribution pattern. Due to the successful performance of the implemented models, they could be promising alternatives to mathematical and analytical approaches being used for discerning the relationship between the slope failure and environmental parameters.
1. Introduction
The use of traditional methods for slope stability analysis has been associated with some constraints. Above all, solving problems with complicated situations is time-consuming and costly [1]. Providing design charts is known as a fundamental approach for determining the pattern of the safety factor of slopes [2,3,4,5]. Many scholars have tried to explain the relationship between a slope and its geometrical factors. One of the first studies in this subject was accomplished by Taylor [6]. He generated the slope stability design charts, which were widely used for years. Additionally, some mathematical solutions such as robust design [7,8,9,10,11] and random field theory [12,13] are still receiving considerable attention in the field of slope analysis. More recently, intelligent techniques such as the support vector machine and artificial neural network (ANN) have been broadly-used for exploring the relationship between landslide and causative factors [14,15]. The adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) is also known as a leading method for landslide susceptibility analysis [16]. Different methods of the ANFIS were tested by Polykretis, et al. [17]. Referring to the findings (Accuracy > 70%), they showed that the ANFIS is a capable tool for this purpose.
Moreover, the advent of natural-inspired metaheuristic techniques (such as artificial bee colony (ABC) and particle swarm optimization (PSO)) introduced numerous optimization opportunities to typical predictive models like ANN and ANFIS in natural hazard modelling [18,19]. In this sense, Nguyen, et al. [20] found that the ABC and PSO could act promisingly in the field of landslide modelling to enhance the performance of ANN with nearly 77% accuracy to around 80% and 86%, respectively. Similarly, Moayedi, et al. [21] used the Harris hawks optimization algorithm to increase the accuracy of the ANN in slope stability analysis. Accordingly, the performance error of the ANN was reduced by nearly 20% and 27% in terms of Root mean square error and mean absolute error, respectively. Additionally, in the case of ANFIS, many studies have conducted the optimization of this tool using hybrid evolutionary algorithms in simulating various natural phenomena like landslide, flood [22,23], groundwater spring potential [24,25] and so on. In research by Chen, et al. [26] the ANFIS achieved more than 75% accuracy for landslide susceptibility modelling when was incorporated with genetic algorithm (GA), PSO, and differential evolution techniques. Similarly, Chen, et al. [27] employed shuffled frog leaping algorithm (SFLA) and PSO to optimize the ANFIS for spatial prediction of landslide in Langao County of China. In this work, step-wise assessment ratio analysis (SWARA) was used to assess the relationship between landslide events and environmental factors. The results revealed that both ANFIS-SFLA and ANFIS-PSO models achieve the same accuracy (89%). They also found that the PSO optimizes the fuzzy system far faster than the SFLA.
The proposed methodology of the current paper comprises two major items, namely, remote sensing and metaheuristic science, for investigating the viability of slope stability monitoring. Although metaheuristic techniques have shown high robustness in natural hazard modelling, the used algorithms have been mostly selected among broadly-used ones like the PSO, imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA), and GA [28,29,30,31]. In other words, the lack of studies focusing on evaluating the optimization capability of new metaheuristic algorithms is an appreciable gap of knowledge in the mentioned field. Therefore, this research is conducted to pursue two novel objectives: (a) development of two new predictive models using invasive weed optimization and elephant herding optimization for landslide probability assessment which has not been explored in earlier studies and (b) studying a new region in a landslide-prone area of Iran.
2. Study Area and Data Collection
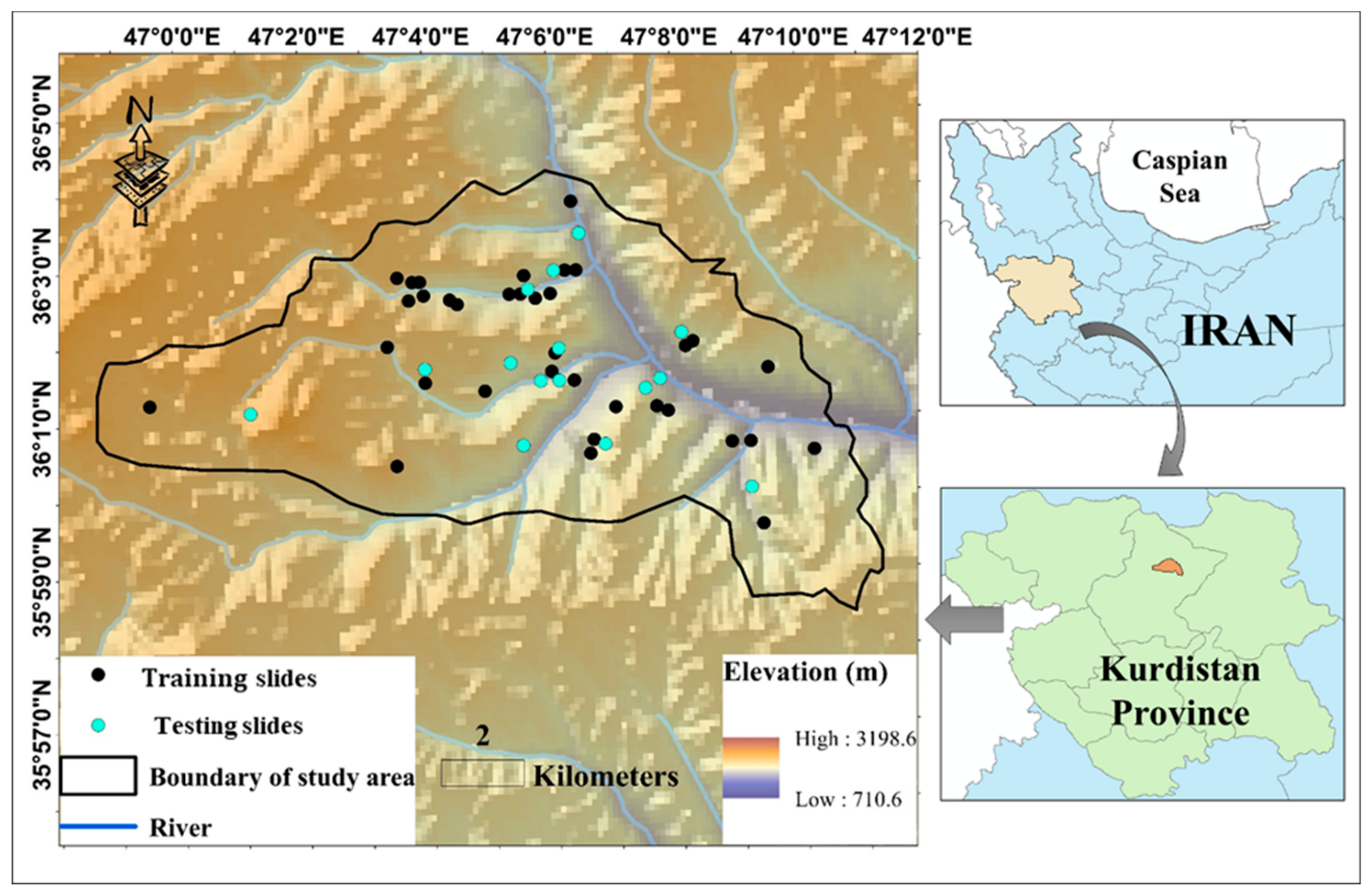
The location of the study area is illustrated in Figure 1. It is situated within the longitude 46°59′ to 47°11′ E and latitude 35°58′ to 36°04′ N, in the northern part of the Kurdistan Province, West of Iran. Kurdistan is a mountainous area comprising Zagros mountains. “Semi-arid with cold winters” and “temperate” are two common climates that have been mentioned in this area [32].
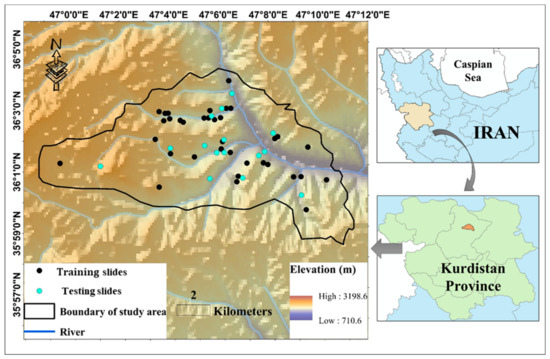
Figure 1.
The location of the study area and the marked landslide incidents.
In this paper, utilizing remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS), the information of 13 landslide influential factors, including land use, lithology, soil type, rainfall, distance to the road, distance to the river, slope degree, elevation, slope aspect, profile curvature, plan curvature, stream power index (SPI), and topographic wetness index (TWI) were extracted. The information about the type and source of these layers is presented in Table 1. Figure 1 also shows the location of 56 historical landslides (occurred over the past 20 years). As can be seen, they have mostly occurred along with the rivers. The same number of non-landslide points are also produced within the areas devoid of landslide occurrence records. Note that the landslide susceptibility value (LSV) for the landslide and non-landslide points is considered 1 and 0, respectively. Next, out of 112 data records, 70% (i.e., 78 samples) are used for training the proposed intelligent models. The accuracy of the models is then evaluated by the remaining 30% (i.e., 34 samples).

Table 1.
List and source of the spatial database.
The digital elevation model (DEM) of the Kurdistan province was created using topographic data at 1:25,000 scale. Then, the map of five conditioning factors of elevation, slope degree, profile curvature, plan curvature, and slope aspect were directly derived from the DEM. The altitude varies from around 710 to 3200 m above the sea level. The slopes are mainly gentle and their value range in [0, 25°]. Additionally, the maximum distances from the rivers and road is around 4353 and 13,346 m. The land use in the whole area is dry farming and agriculture where there are two soil categories namely, “Inceptisols” and “Rock Outcrops/Inceptisols”. The description of the geology units is also presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
The description of the lithology units.
3. Methodology
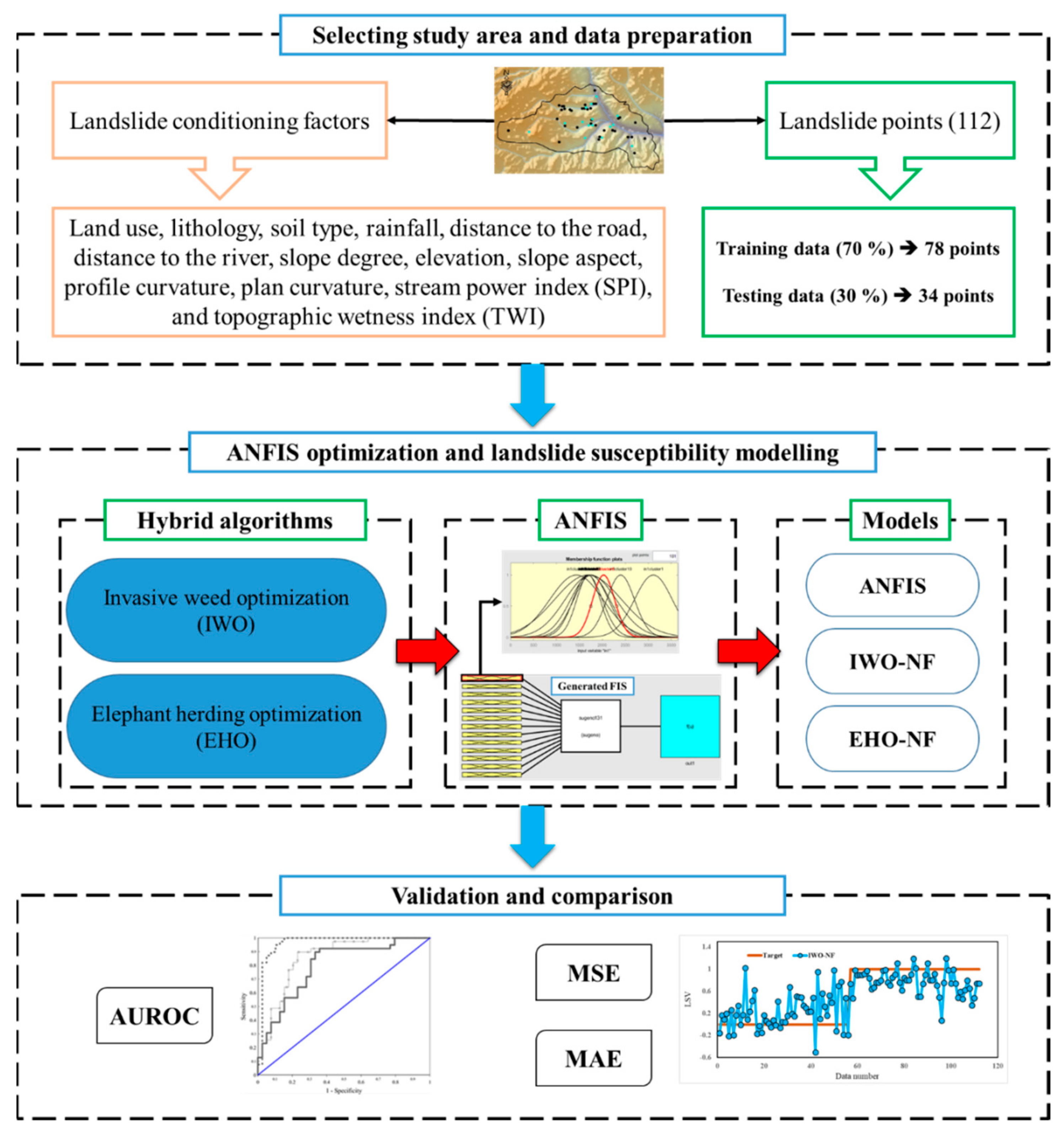
Figure 2 shows the overall steps taken for meeting the objective of this paper. After providing a proper spatial database, it was divided into the training and testing subsets. The proposed metaheuristic algorithms of the EHO and IWO were then synthesized with the ANFIS to predict the LSV. After determining the best structure of each fuzzy ensemble, the outputs were compared with actual LSVs to examine the efficiency of the applied algorithms. The results were then compared to determine the best model of the study. In this work, the accuracy of the prediction was evaluated by area under the receiving operating characteristic (AUROC) curve. The AUROC is known as a common manner for accuracy assessment of natural hazard simulation [33]. Additionally, the performance error is also measured by mean square error (MSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) criteria which are formulated as follows:
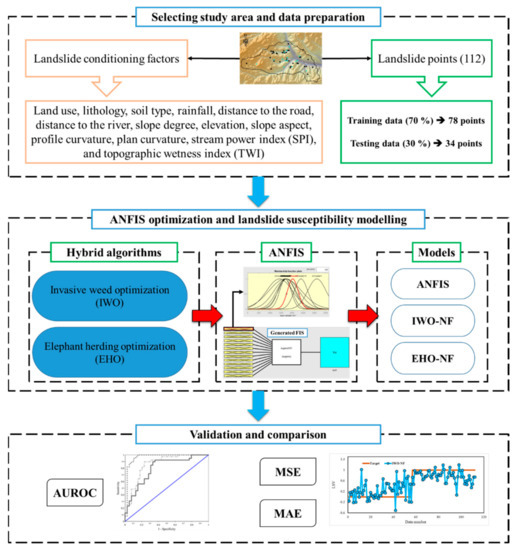
Figure 2.
The graphical methodology of this study.
In the above equations, N represents the number of data. Moreover, Yi observed and Yi predicted denote the observed (i.e., 0 and 1) and estimated values of LSV, respectively.
The description of the used algorithms is presented in the next section.
3.1. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System
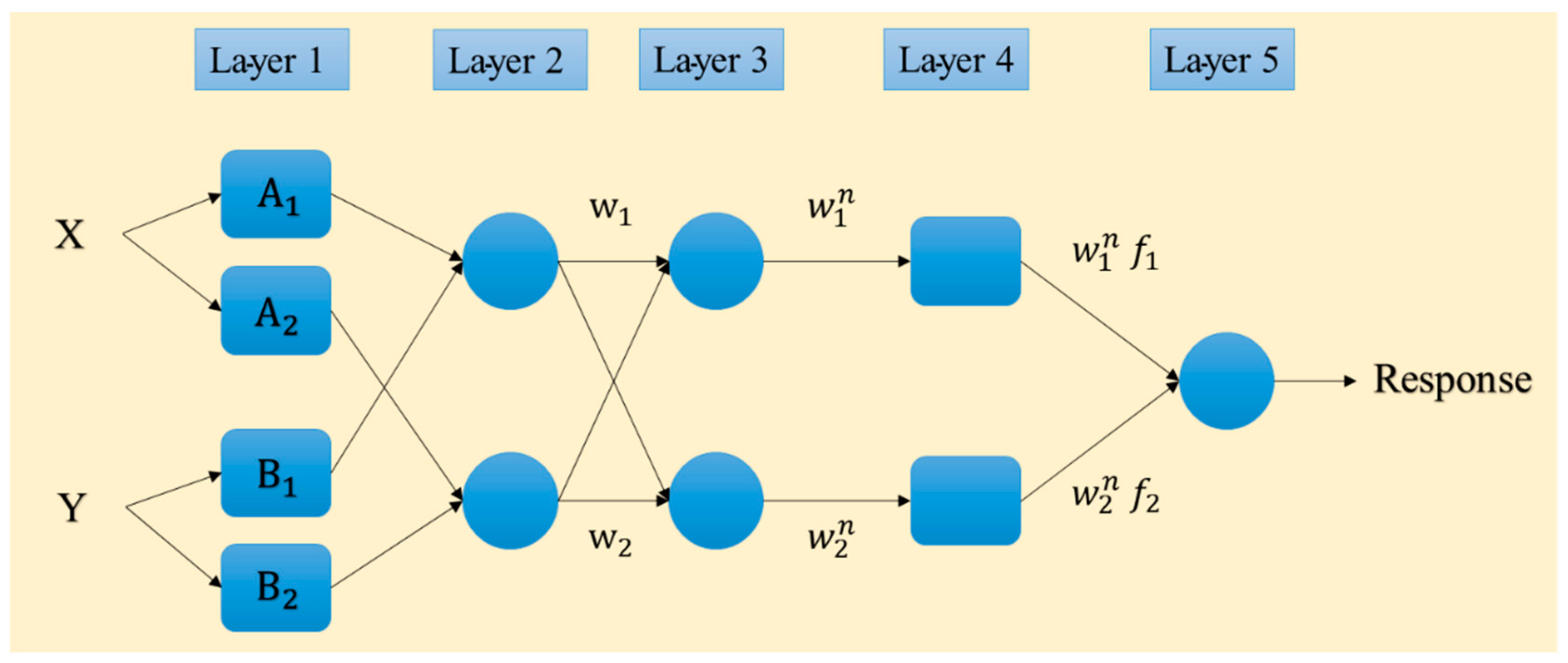
Proposed by Jang [34], the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) is based on the fuzzy theory and if-then rules. It is a robust predictive tool which benefits both ideas of neural and fuzzy computing [35]. Hence, the ANFIS has been considered to produce more consistent results compared to typical FIS. The back-propagation gradient descent and least-squares methods are combined in this tool for adjusting the membership function (MF) parameters. Figure 3 shows the structure of the ANFIS. As is seen, there are five layers. Input data (X and Y) are received by the adaptive nodes in the first layer. In the next layer, the output of each node (W1 and W2) is produced by all input signals. These products are then normalized in the third layer ( and ). Next, using some specific parameters (also called result parameters) of the node, a function is applied to produce the output of the fourth layer ( and ), and eventually, the node in the last layer gives the overall response as the sum of all input signals [22].
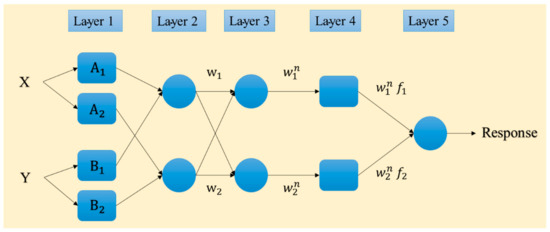
Figure 3.
Typical structure of the ANFIS network.
3.2. Hybrid Optimization Techniques
Two recently-developed hybrid metaheuristic algorithms, namely elephant herding optimization (EHO) and invasive weed optimization (IWO), were used to optimize the performance of the ANFIS. The EHO and IWO are population-based techniques that attempt to find the best solution for a defined problem. In this work, fine-tuning the MF parameters of the ANFIS was the main contribution of the mentioned optimization algorithms to the problem of the landslide susceptibility analysis [36].
In brief, the EHO was introduced by Wang, et al. [37] in 2015. This algorithm mimics the herding behavior of elephants and draws on two major stages: (a): clan updating (in which the position of the elephant is updated based on the behavior of the matriarch) and (b): separation (which describes the solitary life of the weakest elephant living in each generation). More details about the EHO algorithm can be found in previous literature [38,39].
Based on the colonizing behavior of weeds, the IWO was suggested by Mehrabian and Lucas [40] in 2006. In this method, the main objective is to find the optimal place for the growth and reproduction of weeds. It has been widely used for various optimization aims because of its merits such as high robustness and simple structure. Five major components including: (a) initialization, (b) reproduction, (c) spatial dispersal, (d) competitive exclusion, and (e) termination condition are considered to reproduce seeds and creating future generation. The mechanism of the IWO is well-detailed in previous works [41,42,43].
4. Results and Discussion
This part is composed of two major sections that report the results of the optimization process and the main findings of this paper. The main concern of this work lies in evaluating the potential of EHO and IWO evolutionary techniques in fine-tuning of ANFIS in predicting the landslide occurrence. ANFIS is a leading predictive model in the field of landslide modelling. In the literature, Oh and Pradhan [16] revealed the applicability of this tool for regional landslide susceptibility modelling at Penang Island of Malaysia. In fact, they conducted a comparative study for testing various MFs of the ANFIS. The results showed that the susceptibility maps produced by a trapezoidal, triangular, polynomial, and generalized bell MFs (accuracy ≈ 84%) had more accuracy than those produced by four Gaussian and Sigmoidal-based MFs. There are also plenty of works that have tried using metaheuristic techniques like GA and PSO for optimizing the ANFIS [27].
4.1. Optimizing the ANFIS Using EHO and IWO
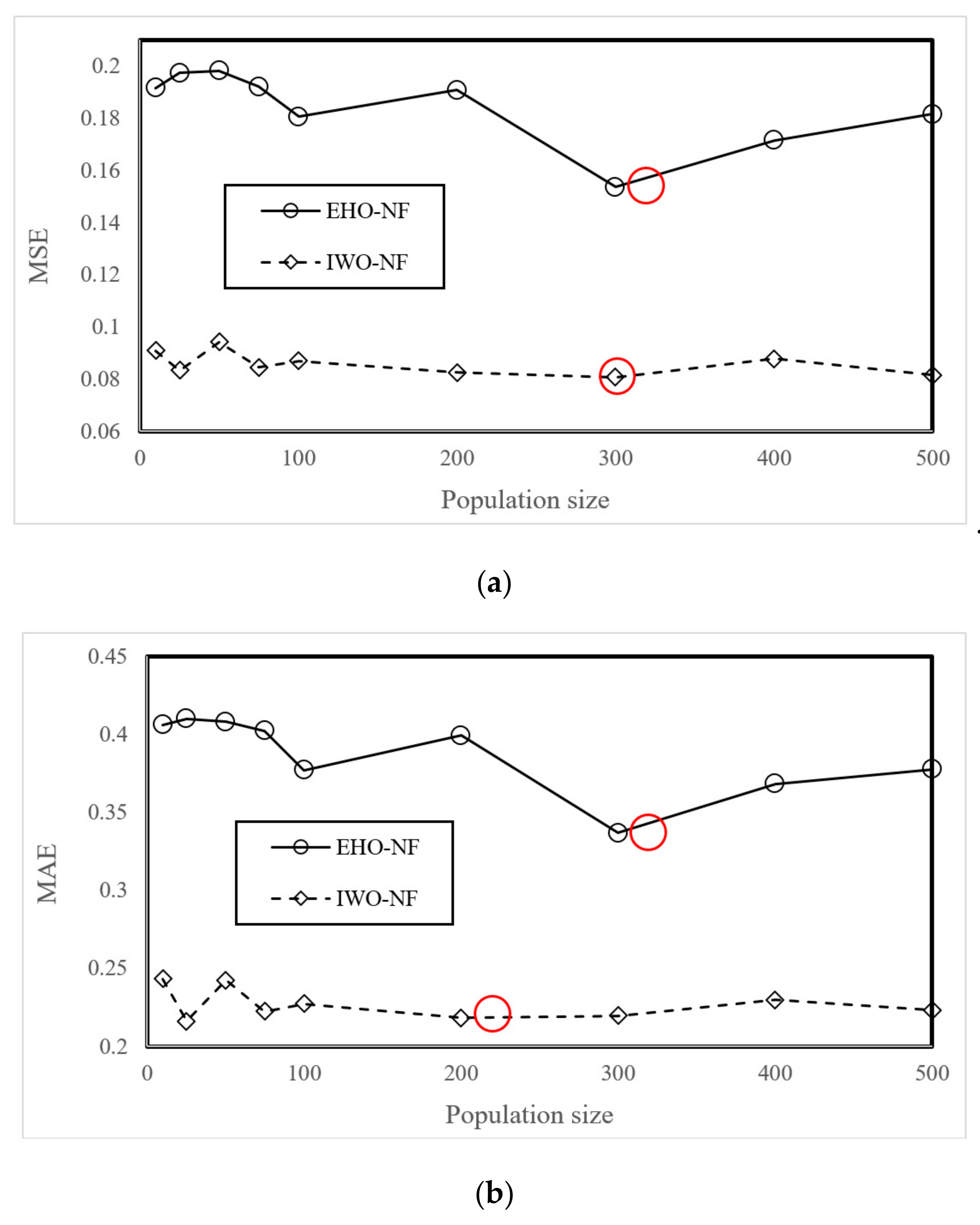
The EHO and IWO algorithms were coupled with the neuro-fuzzy system using the programming language of MATLAB 2014. The outcome of this task was two fuzzy-metaheuristic ensembles of EHO-NF and IWO-NF. Next, an extensive trial and error process was conducted to determine the best-fitted structure of the used models. The models were tested within 1000 repetitions by taking into consideration nine population sizes of 10, 25, 50, 75, 100, 200, 300, 400, and 500. Remarkably, the MSE index was used as the objective function in this study. The results are presented in Figure 4a,b. These figures show the MSE and MAE obtained at the end of the 1000th iteration. As is seen, regarding the calculated value of MSE, both EHO and IWO ensembles optimized the NF by population size = 300 more efficiently than other tested values. Moreover, the calculated MAEs confirm the results for the EHO; however, a slightly lower MAE is obtained for the IWO with population size = 200. Additionally, the calculation time for the EHO-NF and IWO-NF networks obtained 4052 and 4965 s, respectively, on the operating system at 2.5 GHz and six gigabytes of RAM.
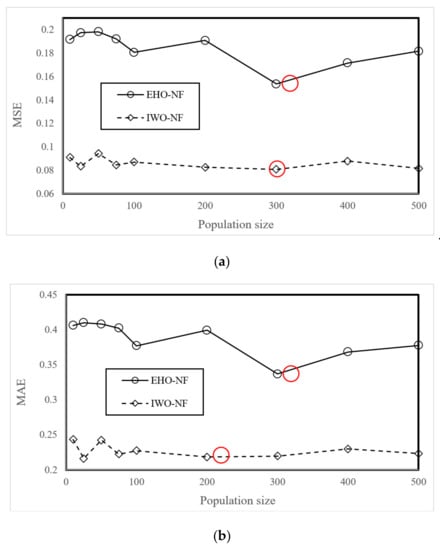
Figure 4.
The results of the sensitivity analysis of the EHO-NF and IWO-NF based on (a) MSE and (b) MAE criteria.
4.2. Model Assessment
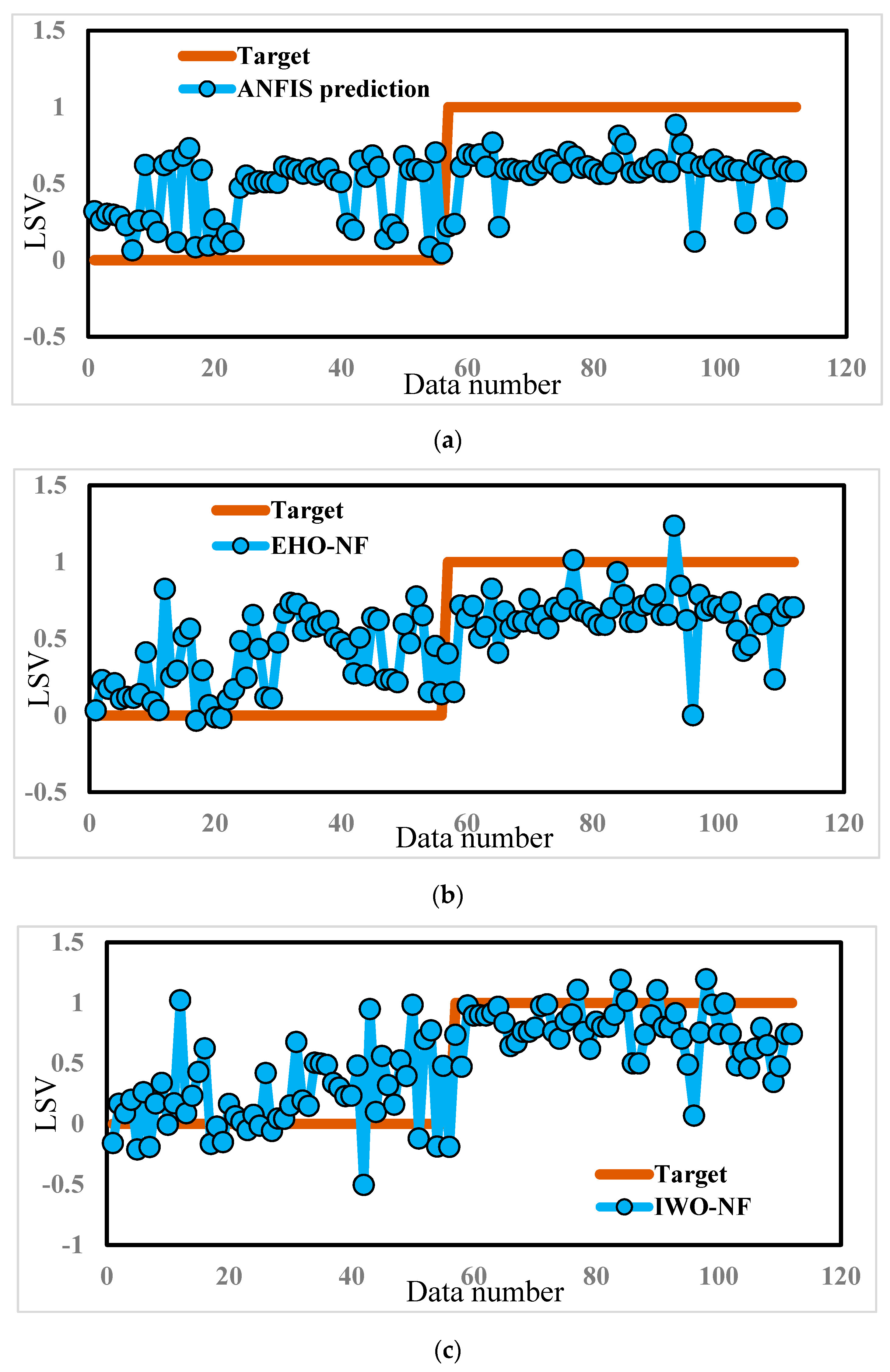
The response of each model for the training and testing samples was then extracted and compared to the expected LSVs. In other words, each one of ANFIS, EHO-NF, and IWO-NF used the training landslides to recognize the pattern between the landslide occurrence and considered conditioning factors. Then, they applied the gained knowledge to the unseen environmental conditions (i.e., the testing inputs) to estimate the LSV. Figure 5 depicts a graphical comparison between the actual and predicted LSVs, suggested by ANFIS, EHO-NF, and IWO-NF models (for the whole data).
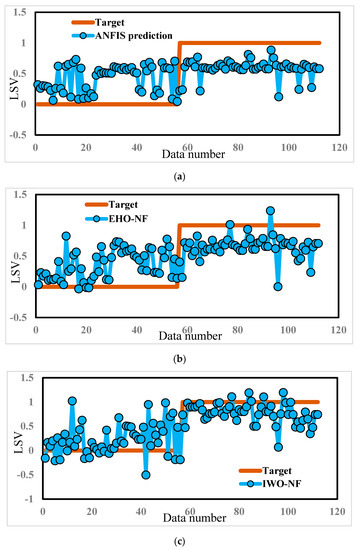
Figure 5.
The results obtained by (a) typical ANFIS, (b) EHO-NF, and (c) IWO-NF for the whole dataset.
As mentioned previously, to have a quantitative understanding of the accuracy of the models in the training and testing stages, the error of performance is calculated by means of the MSE and MAE criteria. According to these values, both proposed evolutionary algorithms showed a high capability for optimizing the ANFIS. Overall, the IWO achieved a considerably more accurate understanding of the relationship between the landslide and conditioning factors. The results of the pairwise comparison (using the method by Hanley and McNeil [44]) for the training ROC curves support this claim. Accordingly, p-values for the comparison between the performance of ANFIS~IWO-NF and ANFIS~EHO-NF were shown to be 0.0002 and 0.0059, respectively, which indicates a statistically significant difference between the performance of the typical and improved fuzzy networks.
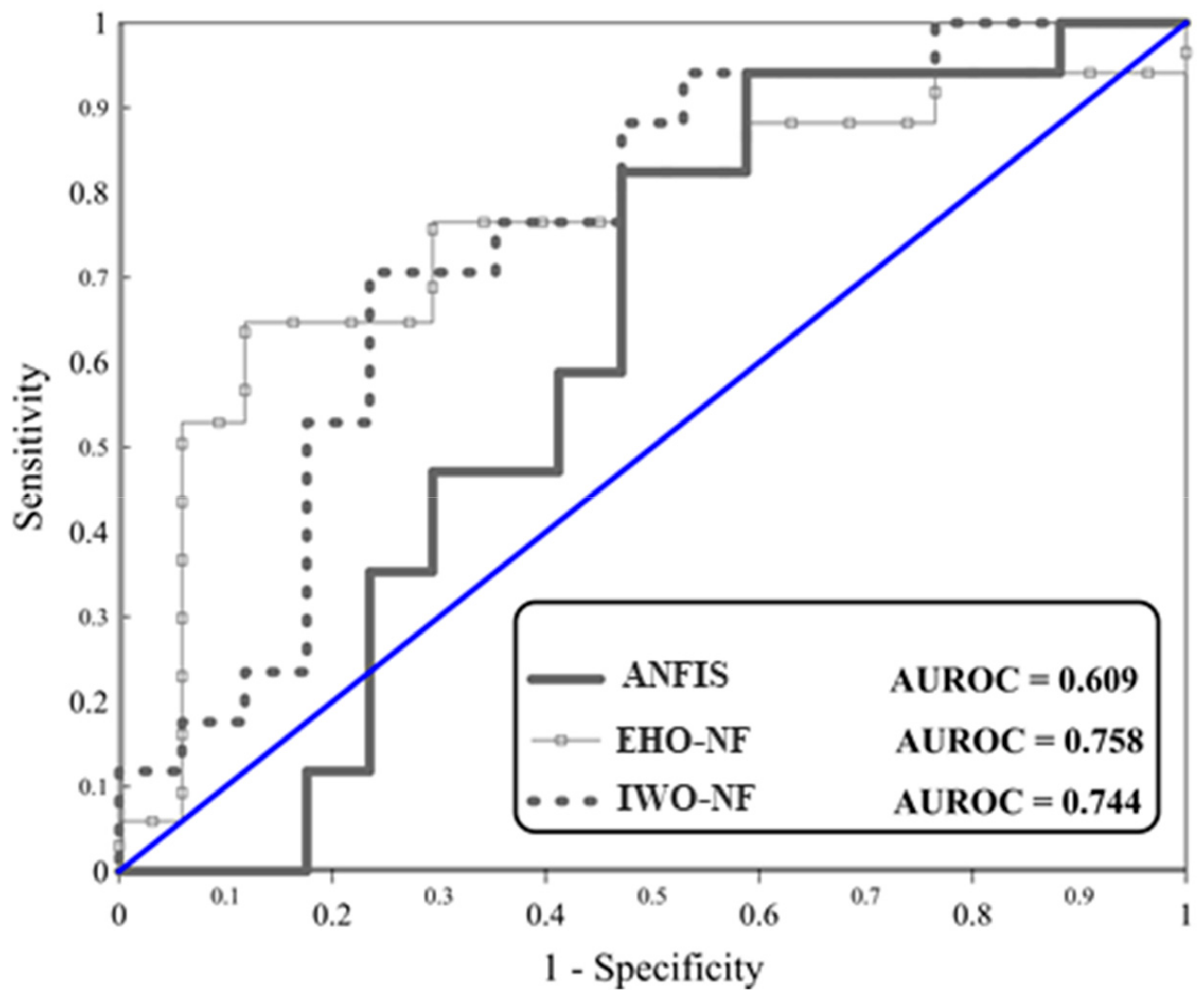
Regarding testing landslides, referring to the obtained MSEs (0.2380, 0.2112, and 0.2255) and MAEs (0.4457, 0.4160, and 0.4019), it can be derived that the performance error of both EHO-NF and IWO-NF is lower than the typical ANFIS. This indicates that the mentioned algorithm could enhance the generalization power of the neuro-fuzzy system. Moreover, Figure 6 depicts the ROC curves of the used models. Note that plotting this curve is a common way for evaluating the accuracy of prediction for diagnostic problems [45], and shows the specificity versus sensitivity [46,47]. According to this figure, the EHO surpasses other models as it achieved the largest accuracy of prediction (AUROC = 0.758). Additionally, the IWO-NF emerged as the second reliable model, due to its larger accuracy compared to the typical ANFIS (AUROCANFIS = 0.609 and AUROCIWO-NF = 0.744). Table 3 shows the results of the statistical analysis of the results.
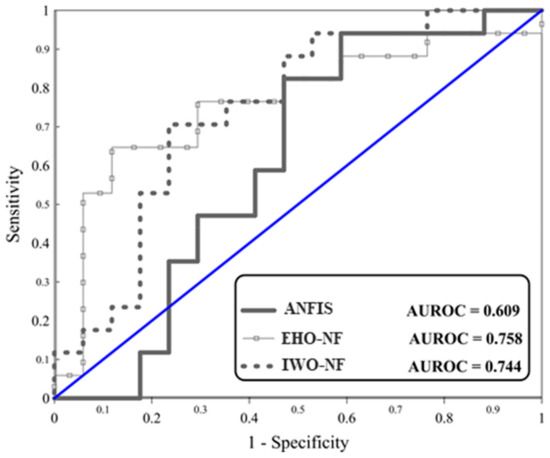
Figure 6.
The ROC diagrams for the used models.

Table 3.
The results of the statistical analysis of testing ROC curves.
All in all, similar to many previous studies, it was demonstrated that synthesizing hybrid algorithms leads to improving the accuracy of the neuro-fuzzy system. Jaafari, et al. [48] showed the efficiency of GA, PSO, ICA, and SFLA for prevailing the overfitting of typical ANFIS in fire susceptibility analysis. In this work, the prediction accuracy of the ANFIS experienced around a 15% and 14% increase, which is considerably higher than what we achieved in previous research, such as [49]. Furthermore, considering 75% an acceptable level of accuracy [26], applying the IWO and EHO helped the ANFIS to achieve it from nearly 60% accuracy.
Moreover, evaluating the results of this study reflects a discrepancy between the learning capability and generalization potential of the used hybrid ensembles. As mentioned in Section 4.2, the IWO-based model achieved the highest learning accuracy in terms of MAE and MSE. Table 4 summarizes the obtained values of the MSE, MAE, and AUROC. Based on this table, the EHO-NF performed more promisingly in the second phase. This claim can be supported by the lowest testing MSE as well as the highest AUROC. Regarding the mentioned issue, a score-based ranking system is developed in this table to determine the most efficient model. To do this, each model received three partial scores (for three accuracy indices). In this process, the more accurate the index indicates, the higher score it gains. Eventually, the summation of these reflects the overall ranking score (ORS). As the table outlines, the least ORS is obtained for the ANFIS which presented the poorest prediction. After that, the EHO (ORS = 8) emerged as the most capable algorithm of this study, followed by the IWO (ORS = 7). It should be mentioned that both ensembles used the same complexity (i.e., the population size = 300), to find the best-fitted solution.

Table 4.
The obtained accuracy criteria for the used models.
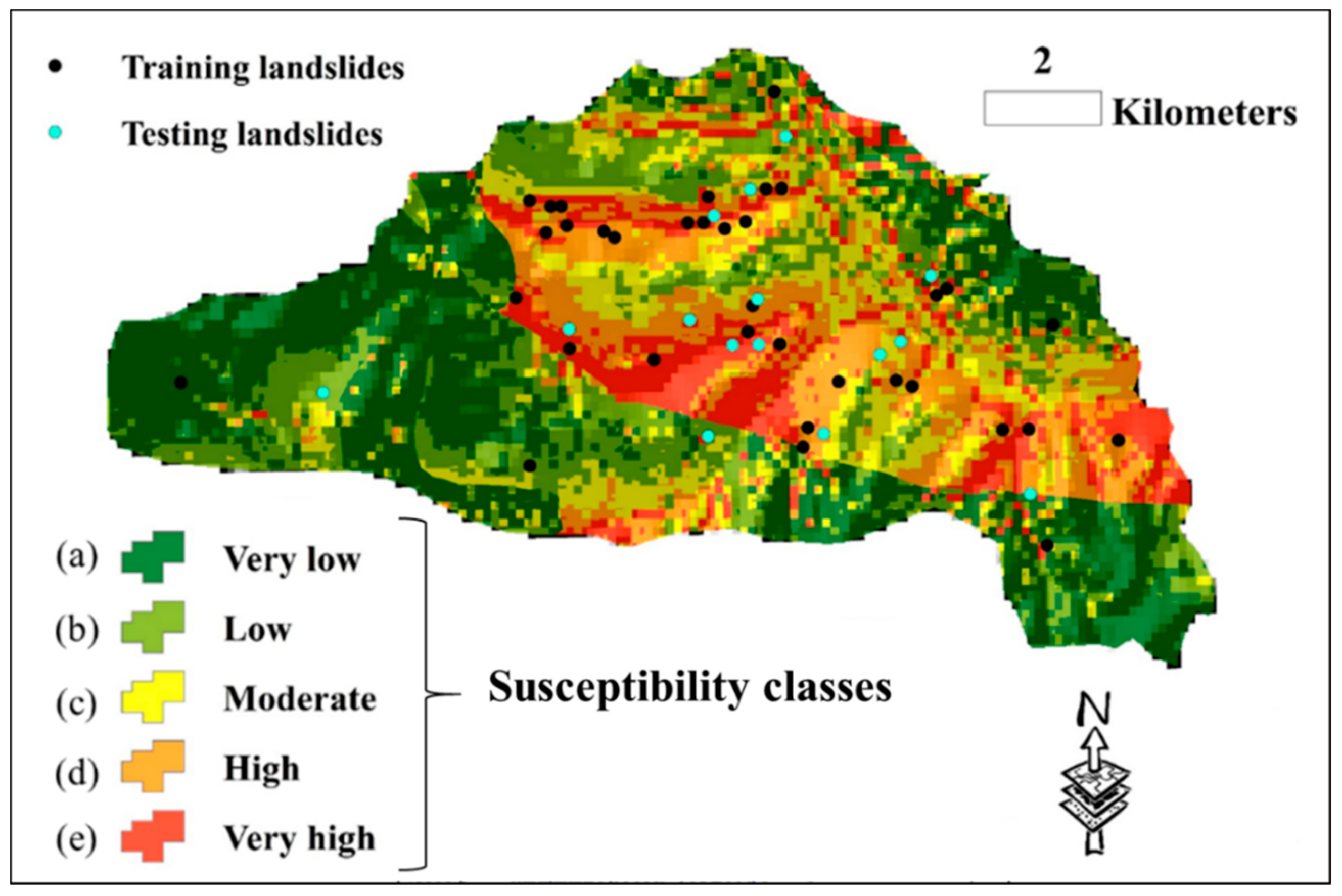
Lastly, the susceptibility map of the study area is generated using the elite model (i.e., the EHO-NF). To do this, the model was applied to the whole area to estimate the LSV. Then, the outputs are converted to raster in the GIS environment. Next, it was divided into five susceptibility classes (including “Very low”, “Low”, “Moderate”, “High”, and “Very high”) using the natural break classification method which is the most common method for this task [49,50,51]. The developed landslide susceptibility map is shown in Figure 7. As can be seen, the majority of landslide points have been correctly located in highly susceptible regions.
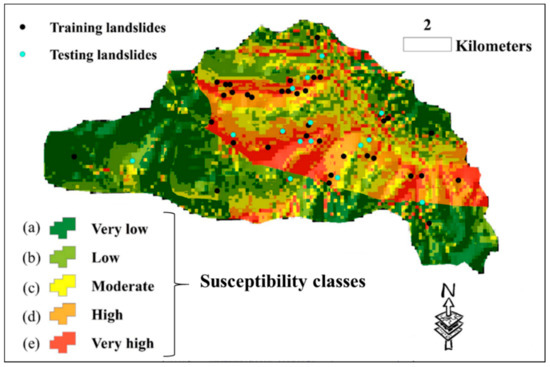
Figure 7.
The susceptibility map of the whole area, generated by the EHO-NF model.
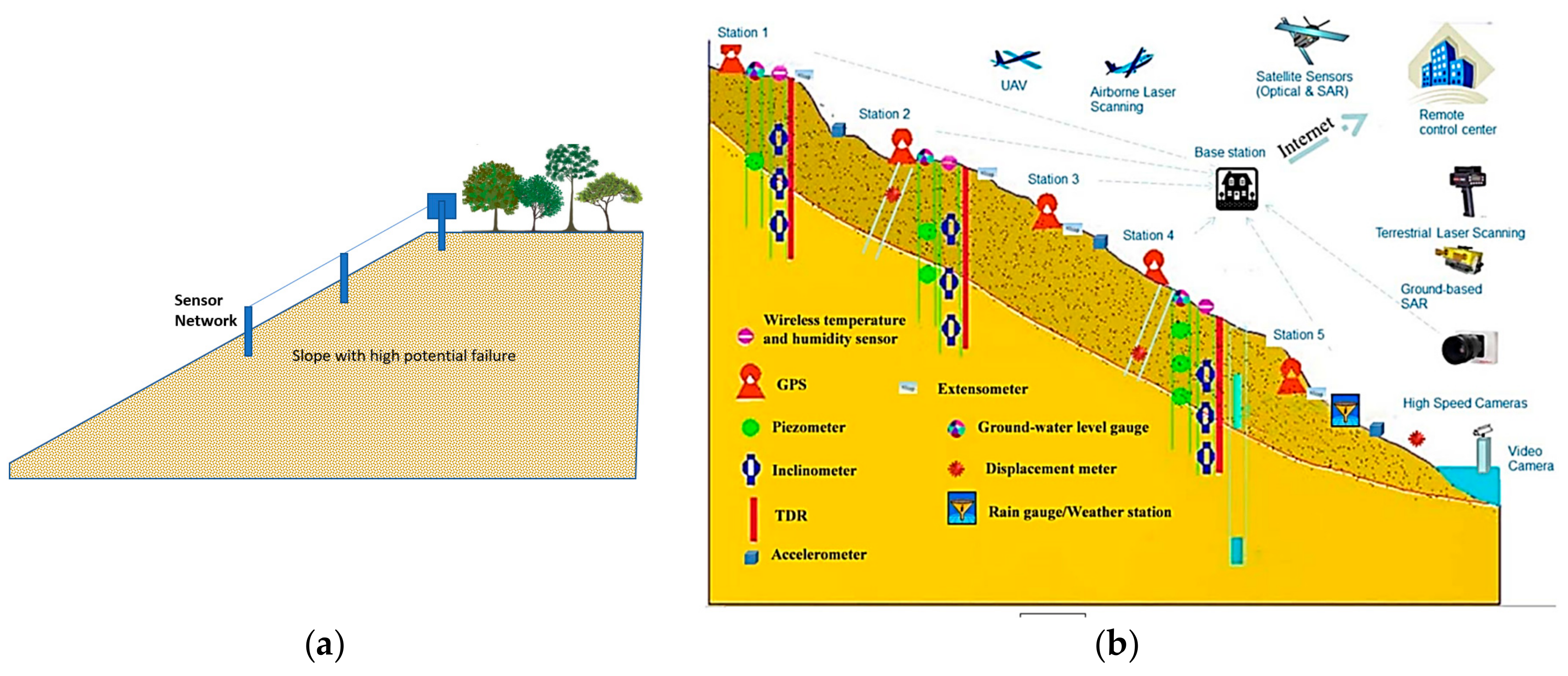
As Figure 7 illustrates, there are some regions in the study area that are recognized to have high landslide susceptibility. Previous studies (e.g., [52,53]) focused on the development of landslide early warning and monitoring systems; these landslide-prone areas, and especially their critical slopes, need to monitored and investigated for early prediction of landslides in order to alleviate the damages caused by this natural disaster. This process is performed using special sensors (Figure 8). In the first stage, sensors detect small motions when the sliding part is getting separated from the static one. Once the slip surface is detected, they aim to separate the subset of sensors which moved from the stabile ones. This work was carried out by conducting a distributed voting algorithm. Next, the displacement of the moved components was measured, and eventually, the position of the slip surface was estimated using the information obtained from the moved nodes [54,55].
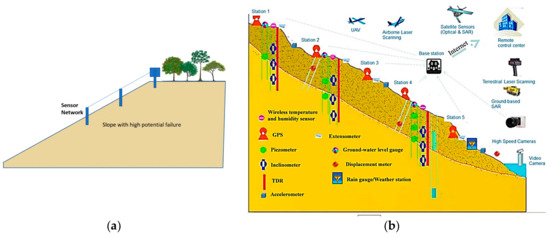
Figure 8.
Proper location of landslide detection sensor: (a) column sensor installation on the slope and (b) an example of used sensor network for landslide early detection in Reference [56].
5. Conclusions
Considering the importance of engineering modellings for predicting the occurrence likelihood of landslide, the main objective of this paper was to investigate and compare the applicability of two wise hybrids of ANFIS for predicting the landslide susceptibility in Western Iran. To this end, after providing the spatial dataset through remotely sensed conditioning factors, the invasive weed optimization, and elephant herding optimization algorithms are coupled with the neuro-fuzzy system in order to find the optimal parameters of its membership functions. The outcomes of the sensitivity analysis reported the value of 300 as the most suitable population size for both algorithms. Additionally, the results showed that both EHO and IWO metaheuristic algorithms could help the ANFIS to overcome computational drawbacks as the error of the ANFIS decreased by nearly 20% and 60% for the training data, and around 11% and 5% for the testing data. It was also concluded that regarding the developed ranking system in testing phase, the EHO surpassed IWO in optimizing the ANFIS in landslide probability assessment.
Author Contributions
H.M., performed experiments and field data collection; H.M. and D.T.B. wrote the manuscript, L.K.F. discussion and analyzed the data. H.M., and D.T.B. edited, restructured, and professionally optimized the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Ton Duc Thang University and the University of South-East Norway.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yuan, C.; Moayedi, H. The performance of six neural-evolutionary classification techniques combined with multi-layer perception in two-layered cohesive slope stability analysis and failure recognition. Eng. Comput. 2019, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusharar, S.W.; Han, J. Two-dimensional deep-seated slope stability analysis of embankments over stone column-improved soft clay. Eng. Geol. 2011, 120, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, K. Undrained Bearing Capacity of Strip Footings on Slopes. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2010, 136, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.J.; Khoo, S.Y.; Wang, Y.; Lyamin, A.V. Application of Neural Network to Rock Slope Stability Assessments; Crc Press-Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 473–478. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z.G.; Li, A.J.; Merifield, R.S.; Lyamin, A.V. Slope stability charts for two-layered purely cohesive soils based on finite-element limit analysis methods. Int. J. Geomech. 2014, 15, 06014022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.W. Stability of earth slopes. J. Boston Soc. Civ. Eng. 1937, 24, 197–246. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Tien, Y.M.; Chen, J.-M.; Juang, C.H. Robust design of rock slopes with multiple failure modes: Modeling uncertainty of estimated parameter statistics with fuzzy number. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 2957–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wang, W.; Dimitrov, D.; Wang, Y. Nano properties analysis via fourth multiplicative ABC indicator calculating. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnevisan, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, L.; Juang, C.H. Robust design in geotechnical engineering–An update. Georisk Assess. Manag. Risk Eng. Syst. Geohazards 2014, 8, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Dimitrov, D.; Abdo, H. Tight independent set neighborhood union condition for fractional critical deleted graphs and ID deleted graphs. Discrete Cont. Dyn.-S 2018, 12, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Guirao, J.L.G.; Abdel-Aty, M.; Xi, W. An independent set degree condition for fractional critical deleted graphs. Discrete Cont. Dyn.-S 2019, 12, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-P.; Zhu, B.-Z.; Juang, C.-H.; Wong, L.N.Y. A stability analysis of a layered-soil slope based on random field. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2018, 78, 2611–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-Q.; Jiang, S.-H.; Cao, Z.-J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, C.-B.; Zhang, L.-M. A multiple response-surface method for slope reliability analysis considering spatial variability of soil properties. Eng. Geol. 2015, 187, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, I. Landslide susceptibility mapping using frequency ratio, logistic regression, artificial neural networks and their comparison: A case study from Kat landslides (Tokat—Turkey). Comput. Geosci. 2009, 35, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ryu, J.-H.; Won, J.-S.; Park, H.-J. Determination and application of the weights for landslide susceptibility mapping using an artificial neural network. Eng. Geol. 2004, 71, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.-J.; Pradhan, B. Application of a neuro-fuzzy model to landslide-susceptibility mapping for shallow landslides in a tropical hilly area. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 37, 1264–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polykretis, C.; Chalkias, C.; Ferentinou, M. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) modeling for landslide susceptibility assessment in a Mediterranean hilly area. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 1173–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Mehrabi, M.; Mosallanezhad, M.; Rashid, A.S.A.; Pradhan, B. Modification of landslide susceptibility mapping using optimized PSO-ANN technique. Eng. Comput. 2018, 35, 967–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, W.; Li, G.; Moayedi, H.; Nguyen, H. A particle-based optimization of artificial neural network for earthquake-induced landslide assessment in Ludian county, China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 1750–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Mehrabi, M.; Kalantar, B.; Moayedi, H.; Abdullahi, M.a.M. Potential of hybrid evolutionary approaches for assessment of geo-hazard landslide susceptibility mapping. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 1667–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Osouli, A.; Nguyen, H.; Rashid, A.S.A. A novel Harris hawks’ optimization and k-fold cross-validation predicting slope stability. Eng. Comput. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termeh, S.V.R.; Kornejady, A.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Keesstra, S. Flood susceptibility mapping using novel ensembles of adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system and metaheuristic algorithms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadlou, M.; Karimi, M.; Alizadeh, S.; Shirzadi, A.; Parvinnejhad, D.; Shahabi, H.; Panahi, M. Flood susceptibility assessment using integration of adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and biogeography-based optimization (BBO) and BAT algorithms (BA). Geocarto Int. 2018, 34, 1252–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, K.; Panahi, M.; Tien Bui, D. Spatial Prediction of Groundwater Spring Potential Mapping Based on Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System and Metaheuristic Optimization. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Panahi, M.; Khosravi, K.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Rezaie, F.; Parvinnezhad, D. Spatial prediction of groundwater potentiality using ANFIS ensembled with Teaching-learning-based and Biogeography-based optimization. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tsangaratos, P.; Ilia, I.; Duan, Z.; Chen, X. Groundwater spring potential mapping using population-based evolutionary algorithms and data mining methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Panahi, M.; Pourghasemi, H.R. Performance evaluation of GIS-based new ensemble data mining techniques of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) with genetic algorithm (GA), differential evolution (DE), and particle swarm optimization (PSO) for landslide spatial modelling. Catena 2017, 157, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, D.T.; Bui, Q.-T.; Nguyen, Q.-P.; Pradhan, B.; Nampak, H.; Trinh, P.T. A hybrid artificial intelligence approach using GIS-based neural-fuzzy inference system and particle swarm optimization for forest fire susceptibility modeling at a tropical area. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 32–44. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Guirao, J.L.G.; Basavanagoud, B.; Wu, J. Partial multi-dividing ontology learning algorithm. Inform. Sci. 2018, 467, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien Bui, D.; Shahabi, H.; Shirzadi, A.; Chapi, K.; Hoang, N.-D.; Pham, B.; Bui, Q.-T.; Tran, C.-T.; Panahi, M.; Bin Ahamd, B. A novel integrated approach of relevance vector machine optimized by imperialist competitive algorithm for spatial modeling of shallow landslides. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wu, H.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Baig, A.Q. Study of biological networks using graph theory. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzadi, A.; Chapi, K.; Shahabi, H.; Solaimani, K.; Kavian, A.; Ahmad, B.B. Rock fall susceptibility assessment along a mountainous road: An evaluation of bivariate statistic, analytical hierarchy process and frequency ratio. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beguería, S. Validation and evaluation of predictive models in hazard assessment and risk management. Nat. Hazards 2006, 37, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-S. ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. ManCybern. 1993, 23, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-S.; Sun, C.-T. Neuro-fuzzy modeling and control. Proc. IEEE 1995, 83, 378–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Mehrabi, M.; Kalantar, B.; Abdullahi Mu’azu, M.A.; Rashid, A.S.; Foong, L.K.; Nguyen, H. Novel hybrids of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) with several metaheuristic algorithms for spatial susceptibility assessment of seismic-induced landslide. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 1879–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-G.; Deb, S.; Coelho, L.d.S. Elephant Herding Optimization, 2015 3rd. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Computational and Business Intelligence ISCBI, Basel, Switzerland, 27–29 August 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Vijay, R. Optimal Allocation of Electric Power Distributed Generation on Distributed Network Using Elephant Herding Optimization Technique. Cvr J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, N.K.; Parashar, S.; Swarnkar, A.; Gupta, N.; Niazi, K.R. Improved elephant herding optimization for multiobjective DER accommodation in distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 14, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabian, A.R.; Lucas, C. A novel numerical optimization algorithm inspired from weed colonization. Ecol. Inform. 2006, 1, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien Bui, D.; Khosravi, K.; Li, S.; Shahabi, H.; Panahi, M.; Singh, V.; Chapi, K.; Shirzadi, A.; Panahi, S.; Chen, W. New hybrids of anfis with several optimization algorithms for flood susceptibility modeling. Water 2018, 10, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, Y.R.; Ojha, A. A hybrid version of invasive weed optimization with quadratic approximation. Soft Comput. 2015, 19, 3581–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Ghavidel, S.; Akbari, E.; Vahed, A.A. Solving non-linear, non-smooth and non-convex optimal power flow problems using chaotic invasive weed optimization algorithms based on chaos. Energy 2014, 73, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. A method of comparing the areas under receiver operating characteristic curves derived from the same cases. Radiology 1983, 148, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, J.P. Signal Detection Theory and {ROC} Analysis; Psychology Press: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Tien Bui, D.; Le, K.-T.; Nguyen, V.; Le, H.; Revhaug, I. Tropical forest fire susceptibility mapping at the Cat Ba National Park Area, Hai Phong City, Vietnam, using GIS-based kernel logistic regression. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, U.S.; Pradhan, B.; Yusoff, Z.B.M.; Abdallah, A.F.B.; Aryal, J.; Park, H.-J. Data mining and statistical approaches in debris-flow susceptibility modelling using airborne LiDAR data. Sensors 2019, 19, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafari, A.; Zenner, E.K.; Panahi, M.; Shahabi, H. Hybrid artificial intelligence models based on a neuro-fuzzy system and metaheuristic optimization algorithms for spatial prediction of wildfire probability. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 266, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, D.T.; Moayedi, H.; Kalantar, B.; Osouli, A.; Gör, M.; Pradhan, B.; Nguyen, H.; Rashid, A.S.A. Harris Hawks Optimization: A Novel Swarm Intelligence Technique for Spatial Assessment of Landslide Susceptibility. Sensors 2019, 19, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourghasemi, H.R.; Pradhan, B.; Gokceoglu, C.; Moezzi, K.D. A comparative assessment of prediction capabilities of Dempster–Shafer and weights-of-evidence models in landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2013, 4, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafari, A.; Najafi, A.; Pourghasemi, H.; Rezaeian, J.; Sattarian, A. GIS-based frequency ratio and index of entropy models for landslide susceptibility assessment in the Caspian forest, northern Iran. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 909–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gian, Q.A.; Tran, D.-T.; Nguyen, D.C.; Nhu, V.H.; Tien Bui, D. Design and implementation of site-specific rainfall-induced landslide early warning and monitoring system: A case study at Nam Dan landslide (Vietnam). Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2017, 8, 1978–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barla, M.; Antolini, F. An integrated methodology for landslides’ early warning systems. Landslides 2016, 13, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, G.S.; Metha, M.; Ahmed, M.Y.; Chowdhury, M.A.I. Landslide monitoring by using sensor and wireless technique: A review. Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 2014, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Terzis, A.; Anandarajah, A.; Moore, K.; Wang, I. Slip Surface Localization in Wireless Sensor Networks for Landslide Prediction. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–21 April 2006; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, G.; Lu, P.; Scaioni, M.; Xu, S.; Tong, X.; Feng, T.; Wu, H.; Chen, W.; Tian, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Landslide Investigation with Remote Sensing and Sensor Network: From Susceptibility Mapping and Scaled-down Simulation towards in situ Sensor Network Design. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4319–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).