Optical Detection of Fe3+ Ions in Aqueous Solution with High Selectivity and Sensitivity by Using Sulfasalazine Functionalized Microgels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Sulfasalazine Functionalized Microgels (SSZ-MGs)
2.3. Optical Detection of Fe3+ Ions in Aqueous Solution
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
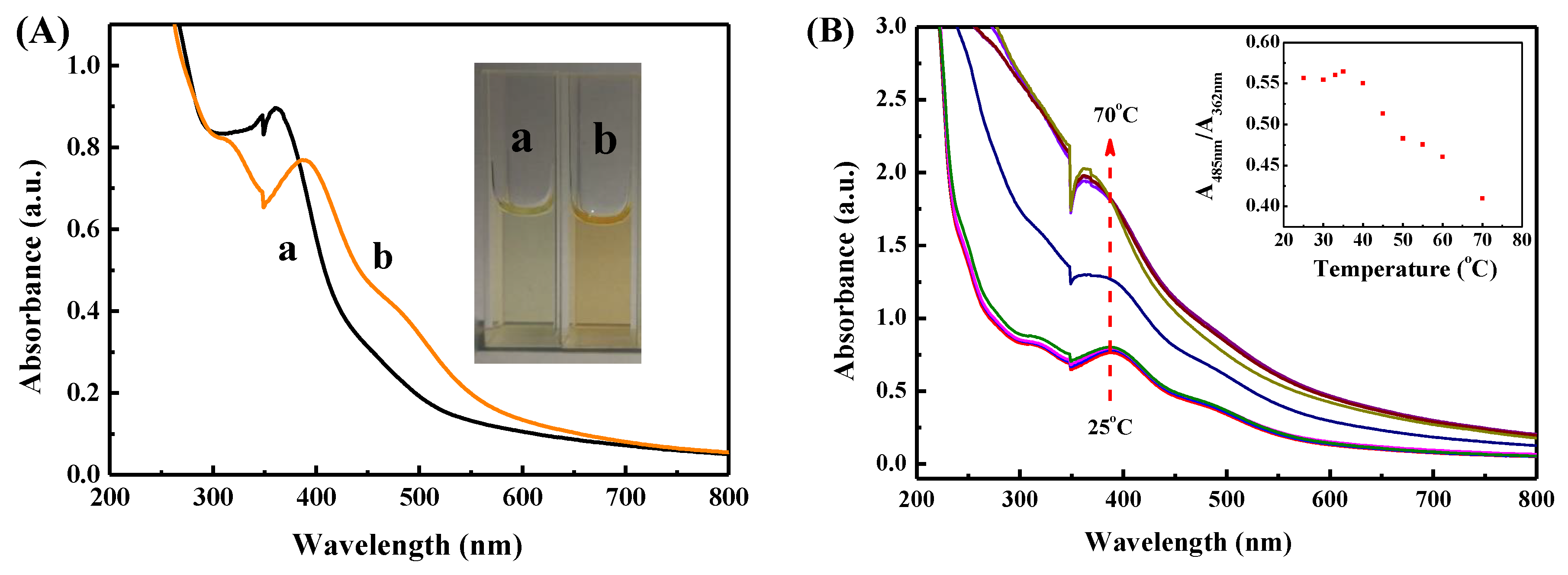
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of SSZ-MGs
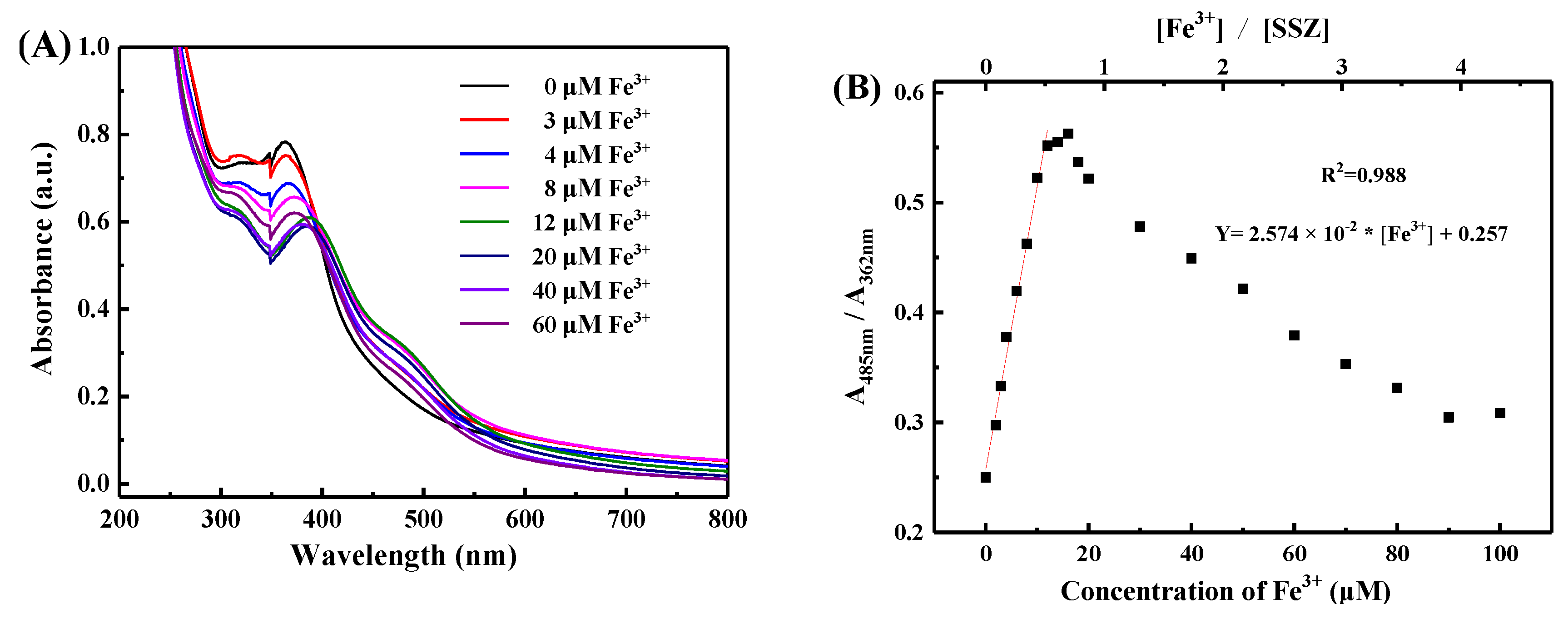
3.2. Optical Detection of Fe3+ Ions in Aqueous Solution
3.3. Selectivity and Interference Study over Other Metal Ions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaplan, C.D.; Kaplan, J. Iron Acquisition and Transcriptional Regulation. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4536–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentze, M.W.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Galy, B.; Camaschella, C. Two to Tango: Regulation of Mammalian Iron Metabolism. Cell 2010, 142, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eisenstein, R.S. Iron regulatory proteins and the molecular control of mammalian iron metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2000, 20, 627–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, J.R.; Menzies, S.L.; Martin, S.M.S.; Mufson, E.J. A histochemical study of iron, transferrin, and ferritin in Alzheimer’s diseased brains. Neurosci. Res. J. 1992, 31, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, D.; Gerlach, M.; Youdim, M.B.; Double, K.L.; Zecca, L.; Riederer, P.; Becker, G. Brain iron pathways and their relevance to Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem. J. 2001, 79, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivetta, T.; Masuri, S.; Cabiddu, M.G.; Caltagirone, C.; Pintus, A.; Massa, M.; Isaia, F.; Cadoni, E. A novel ratiometric and turn-on fluorescent coumarin-based probe for Fe(iii). New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 12032–12041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hai, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Sun, S. Selective Detection of Iron(III) by Rhodamine-Modified Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 4680–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, D.; Wang, C.-C.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, Y. Three colorimetric and off-on fluorescent chemosensors for Fe3+ in aqueous media. Luminescence 2013, 28, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Voelcker, N.H. Rhodamine-Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots for Detection of Fe3+ in Cancer Stem Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23958–23966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Wei, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Ge, X.; Shi, L. Nile Red Derivative-Modified Nanostructure for Upconversion Luminescence Sensing and Intracellular Detection of Fe3+ and MR Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagit, R.; Yildirim, M.; Ozay, O.; Yesilot, S.; Ozay, H. Phosphazene Based Multicentered Naked-Eye Fluorescent Sensor with High Selectivity for Fe3+ Ions. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 2144–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Van Giap, T.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kang, C.; Kim, J.S. A novel strategy to selectively detect Fe(III) in aqueous media driven by hydrolysis of a rhodamine 6G Schiff base. Chem. Comm. 2010, 46, 1407–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiffert, S. Microgel Capsules Tailored by Droplet-Based Microfluidics. Chemphyschem 2013, 14, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigolaeva, L.V.; Gladyr, S.Y.; Gelissen, A.P.H.; Mergel, O.; Pergushov, D.V.; Kurochkin, I.N.; Plamper, F.A.; Richtering, W. Dual-Stimuli-Sensitive Microgels as a Tool for Stimulated Spongelike Adsorption of Biomaterials for Biosensor Applications. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3735–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, K.; Nie, J.; Du, B.; Tang, G. Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidinone) Microgels: Preparation, Biocompatibility, and Potential Application as Drug Carriers. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuckling, D.; Vo, C.D.; Wohlrab, S.E. Preparation of Nanogels with Temperature-Responsive Core and pH-Responsive Arms by Photo-Cross-Linking. Langmuir 2002, 18, 4263–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Tong, Z.; Lyon, L.A. Multicompartment Core/Shell Microgels. Am. Chem. Soc. J. 2010, 132, 11470–11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuckling, D.; Vo, C.D.; Adler, H.-J.P.; Völkel, A.; Colfen, H. Preparation and Characterization of Photo-Cross-Linked Thermosensitive PNIPAAm Nanogels. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plamper, F.A.; Richtering, W. Functional Microgels and Microgel Systems. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bütün, V.; Atay, A.; Tuncer, C.; Baş, Y. Novel Multiresponsive Microgels: Synthesis and Characterization Studies. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12657–12665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Nie, J.; Du, B. Functionalized Ionic Microgel Sensor Array for Colorimetric Detection and Discrimination of Metal Ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 20913–20921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Nie, J.; Du, B. 4-(2-Pyridylazo)-resorcinol Functionalized Thermosensitive Ionic Microgels for Optical Detection of Heavy Metal Ions at Nanomolar Level. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 21966–21974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, B.; Xue, J.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Q.; Nie, J.; Xu, J.; Du, B. Highly Selective and Sensitive Detection of Pb2+ in Aqueous Solution Using Tetra(4-pyridyl)porphyrin-Functionalized Thermosensitive Ionic Microgels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 25706–25716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigolaeva, L.V.; Gladyr, S.Y.; Mergel, O.; Gelissen, A.P.H.; Noyong, M.; Simon, U.; Pergushov, D.V.; Kurochkin, I.N.; Plamper, F.A.; Richtering, W. Easy-Preparable Butyrylcholinesterase/Microgel Construct for Facilitated Organophosphate Biosensing. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6091–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Serpe, M.J. Polymer-based devices for the label-free detection of DNA in solution: Low DNA concentrations yield large signals. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 4777–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lifson, M.A.; Roy, D.B.; Miller, B.L. Enhancing the Detection Limit of Nanoscale Biosensors via Topographically Selective Functionalization. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Ahiabu, A.; Li, X.; Serpe, M.J. Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) Microgel-Based Optical Devices for Sensing and Biosensing. Sensors 2014, 14, 8984–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narayan, N.; Rigby, S.; Carlucci, F. Sulfasalazine induced immune thrombocytopenia in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheu. 2017, 36, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ol’khovich, M.V.; Sharapova, A.V.; Blokhina, S.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Sulfasalazine: Dissolution and Distribution in Pharmaceutically Relevant Mediums. Chem. Eng. Data J. 2017, 62, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Nie, J.; Ji, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Du, B. Thermosensitive Ionic Microgels via Surfactant-Free Emulsion Copolymerization and in Situ Quaternization Cross-Linking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 4498–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Nie, J.; Wang, Q.; Du, B. Thermosensitive Ionic Microgels with pH Tunable Degradation via in Situ Quaternization Cross-Linking. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 3130–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygård, B.; Olofsson, J.; Sandberg, M. Some physico-chemical properties of salicylazosulphapyridine, including its solubility, protolytic constants and general spectrochemical and polarographic behaviour. Acta Pharm. Suec. 1966, 3, 313. [Google Scholar]
- El-Safty, S.A.; Ismail, A.A.; Matsunaga, H.; Nanjo, H.; Mizukami, F. Uniformly mesocaged cubic Fd3ml monoliths as modal carriers for optical chemosensors. Phys. Chem. C J. 2008, 112, 4825–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, N.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, G.; Guang, S.; Xu, H. Highly selective chemosensor for repetitive detection of Fe3+ in pure water and bioimaging. Analyst 2019, 144, 3414–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Cheng, X. Novel Fluorescence Signal Magnified Chemosensors for Detection of Fe3+ and Hg2+ Ions. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesi, H.A.; Hildebrand, J.H. A Spectrophotometric Investigation of the Interaction of Iodine with Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Am. Chem. Soc. J. 1949, 71, 2703–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.; Wang, C.; Pan, Y.; Shiao, Y.; Yen, J.; Shu, C.; Lee, G.; Peng, S.; Chung, W. Upper Rim Allyl- and Arylazo-Coupled Calix [4]arenes as Highly Sensitive Chromogenic Sensors for Hg2+ Ion. Org. Chem. J. 2005, 70, 2912–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisham, M.B.; Ware, K.; Marshall, S.; Yamada, T.; Sandhu, I.S. Prooxidant properties of 5-aminosalicylic acid. Possible mechanism for its adverse side effects. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1992, 37, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, W.; Zhu, Z.; Dong, S.; Nie, J.; Du, B. Optical Detection of Fe3+ Ions in Aqueous Solution with High Selectivity and Sensitivity by Using Sulfasalazine Functionalized Microgels. Sensors 2019, 19, 4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194223
Ji W, Zhu Z, Dong S, Nie J, Du B. Optical Detection of Fe3+ Ions in Aqueous Solution with High Selectivity and Sensitivity by Using Sulfasalazine Functionalized Microgels. Sensors. 2019; 19(19):4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194223
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Weiming, Zumei Zhu, Shunni Dong, Jingjing Nie, and Binyang Du. 2019. "Optical Detection of Fe3+ Ions in Aqueous Solution with High Selectivity and Sensitivity by Using Sulfasalazine Functionalized Microgels" Sensors 19, no. 19: 4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194223
APA StyleJi, W., Zhu, Z., Dong, S., Nie, J., & Du, B. (2019). Optical Detection of Fe3+ Ions in Aqueous Solution with High Selectivity and Sensitivity by Using Sulfasalazine Functionalized Microgels. Sensors, 19(19), 4223. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194223






