Hybrid IRBM-BPNN Approach for Error Parameter Estimation of SINS on Aircraft
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Traditional neural network methods for integrated navigation system have focused on the estimation and compensation of navigation state parameter error, where the estimation of IMU instrument errors has been rarely reported. What’s more, few studies have been conducted on parameter estimation and compensation of SINS that consider the IMU instrument errors and initial alignment errors. In this study, an artificial neural network method is used to simultaneously estimate and forecast the IMU instrument errors and initial alignment errors, and the research content is in-depth and challenging;
- (2)
- For the design of neural network structure, previous studies have mainly regarded the navigation state parameters or navigation deviations of integrated navigation system as the inputs or outputs of the neural network and have not utilized the pulse information from IMU. In this paper, the network structure is improved, the gyroscope pulse signal and accelerometer pulse signal are taken as the inputs of the neural network, and the data are more fully utilized, which are conducive to the estimation of SINS error parameters;
- (3)
- In this paper, an RBM model is used to initialize the BPNN for obtaining good initial network values to avoid the neural network falling into local optimal. An RBM-BPNN forecast model is constructed by combining RBM and BPNN networks to improve the forecast accuracy of SINS error parameters.
- (4)
- Unsupervised feature learning mechanism is introduced in the field of integrated navigation and SINS error parameters estimation, which enhances the processing and adaptability of the neural network model to the measurement data of integrated navigation system and provides new insight into the error parameter estimation and navigation accuracy improvement of SINS.
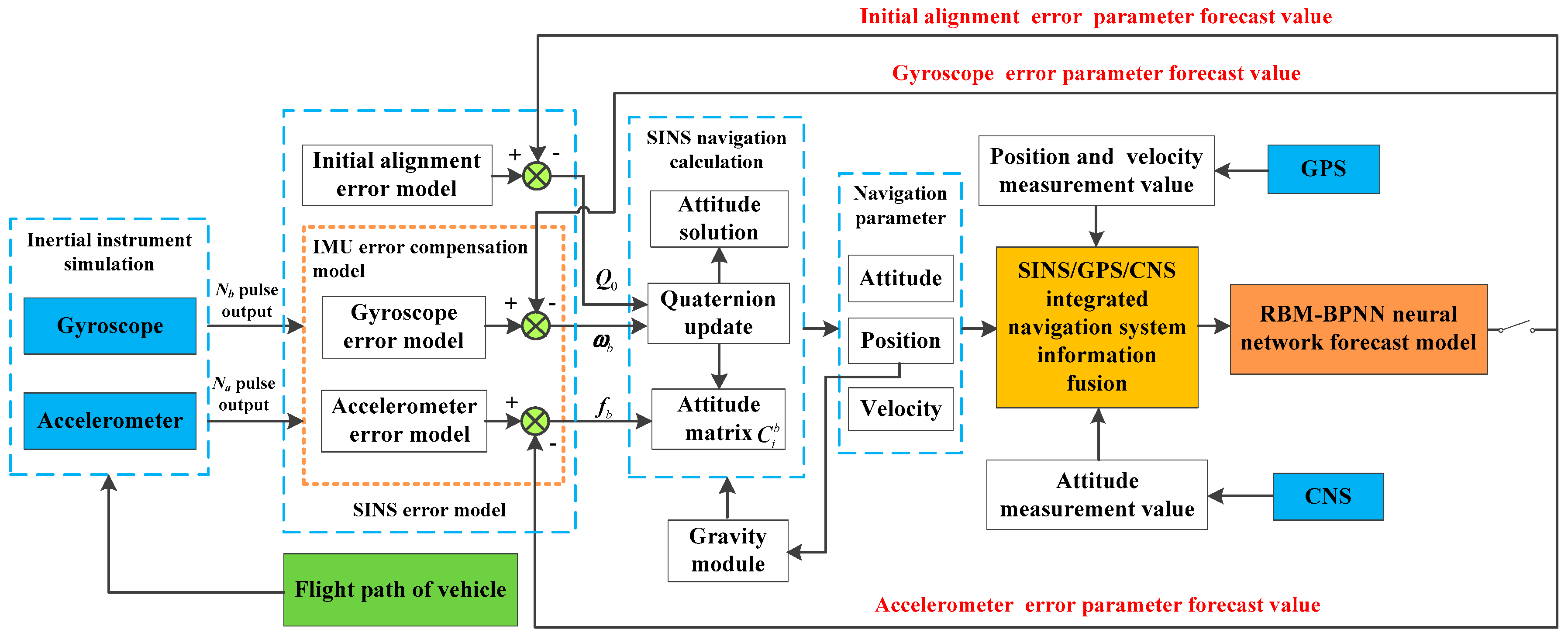
2. Overall Error Estimation Scheme Design
3. SINS Error Model Establishment
3.1. Initial Alignment Error Model of SINS
3.2. IMU Instrument Error Model of SINS
4. RBM-BPNN Method Design for SINS Error Estimation
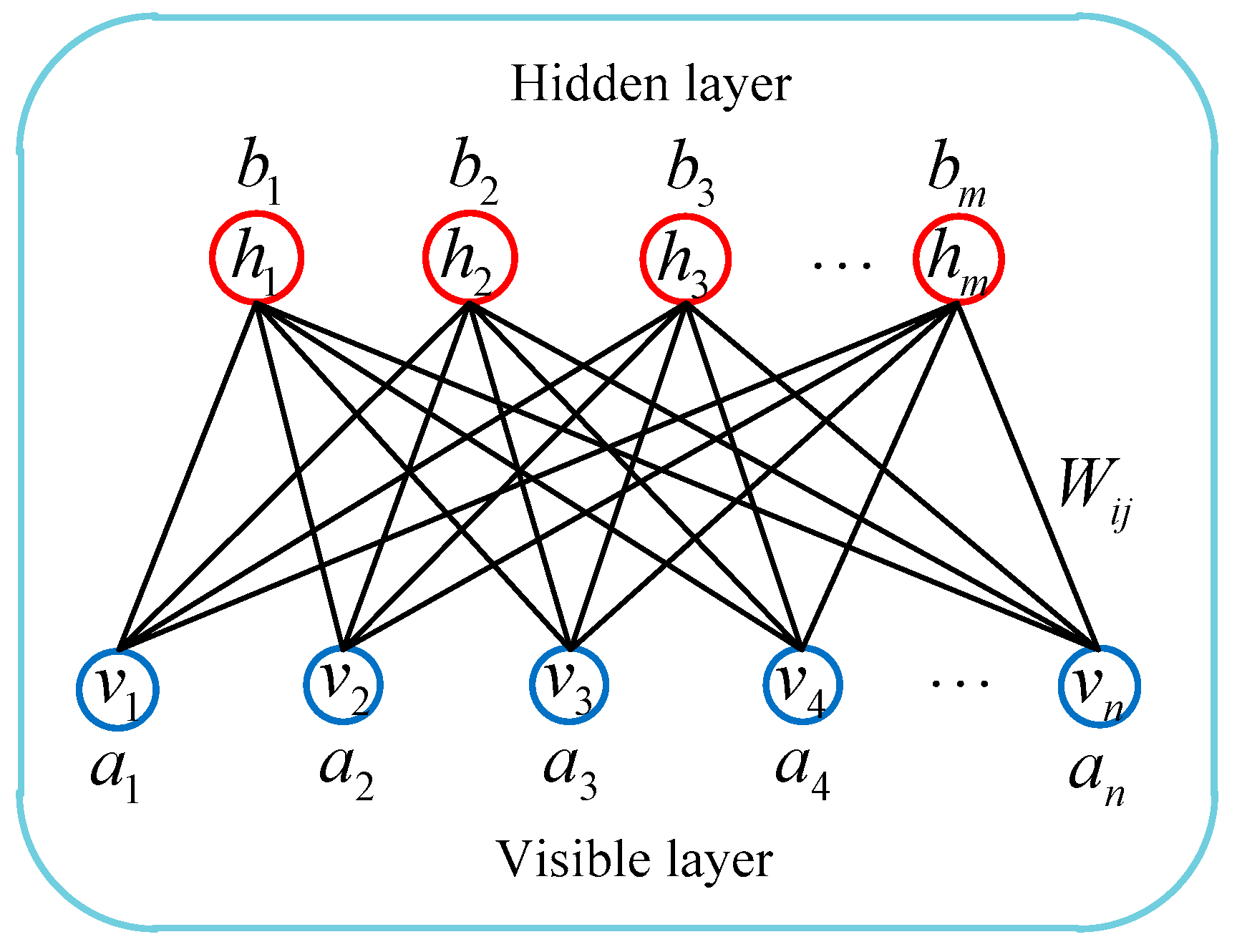
4.1. Introduction of Basic Principles of RBM
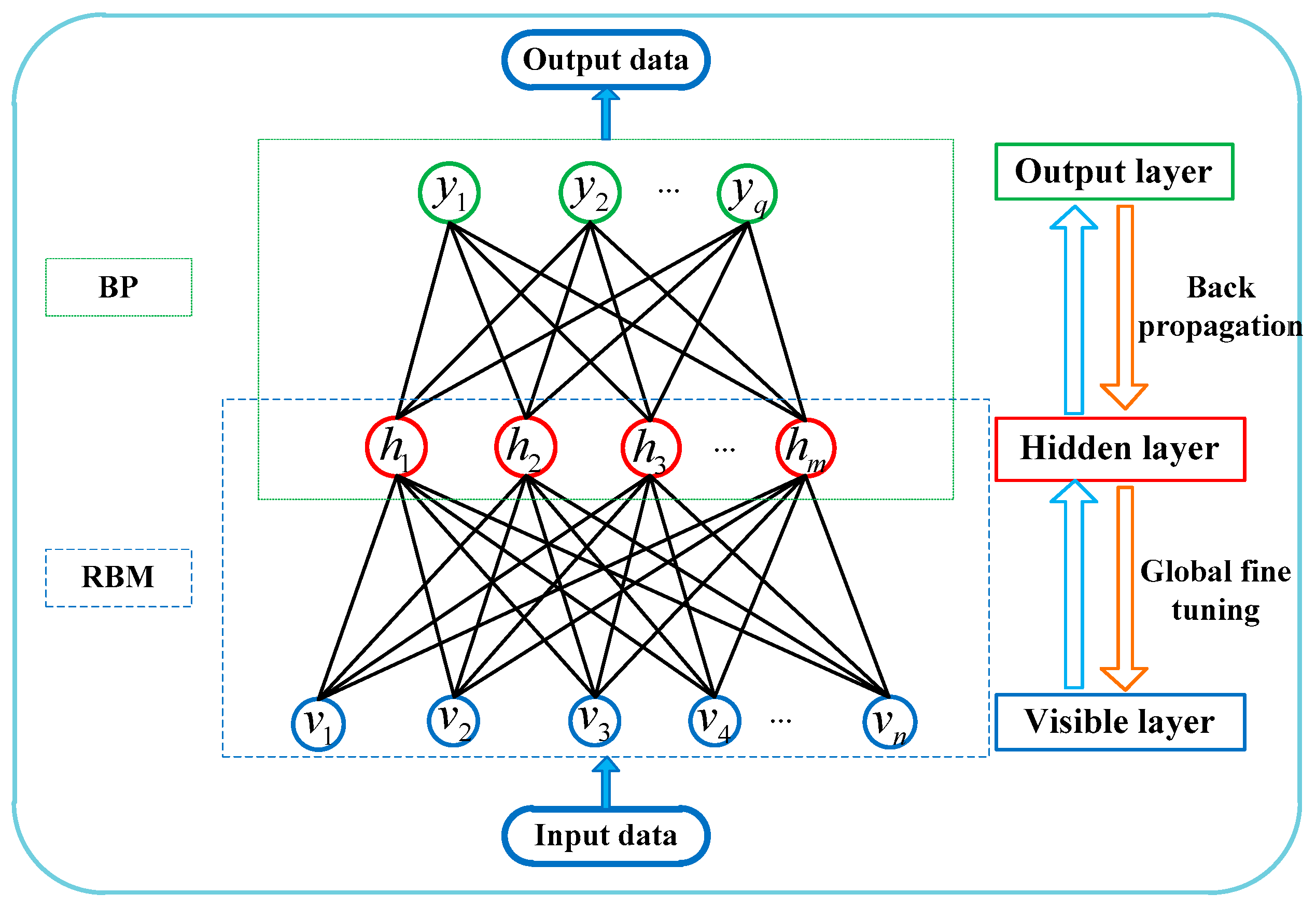
4.2. RBM-BPNN Forecast Model Construction
- (1)
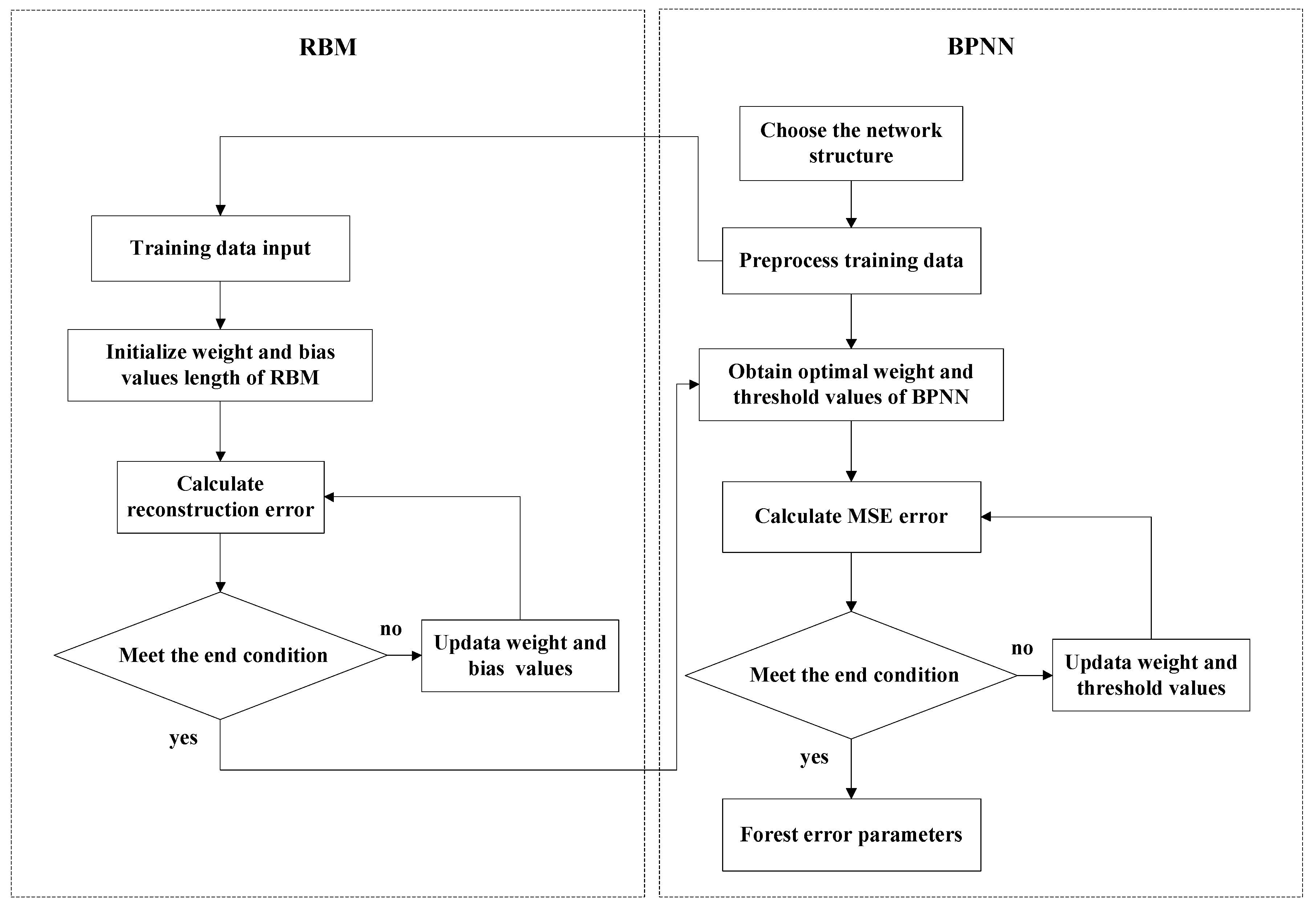
- Data preprocess. The sample data are collected based on SINS/GPS/CNS integrated navigation system measurement and SINS error parameter information. Then, the sample data are normalized and mapped to the interval of [0, 1], which is expressed as:where and are the maximum value and minimum value of the sample data, respectively;
- (2)
- The training sample is input into the RBM model, the RBM structure is trained by using a greedy learning algorithm without supervision, and the deep feature information of the input data is extracted. Then, the weight and bias of the RBM structure are determined;
- (3)
- The BPNN is initialized based on the RBM training results. The weight and threshold between input layer and hidden layer of BPNN are replaced by the weight and bias of RBM;
- (4)
- The weight and threshold value of the entire network of RBM-BPNN are fine-tuned by using a BP algorithm, and the mapping relationship between the input layer and output layer is obtained, that is, the RBM-BPNN structure;
- (5)
- The trained RBM-BPNN model is evaluated by testing samples, and the generalization ability and error parameter forecast effect of the model are verified.
5. Simulation Experiments and Result Analysis
5.1. Simulation Condition Settings
- (1)
- (2)
- The initial launch parameters of aircraft. The coordinate of the launch point is (118°E, 32°N, 0.0 m), and the launch azimuth is 90° [28];
- (3)
- The initial alignment error parameters of SINS. The standard deviation of the initial pitch angle error is 60″, the standard deviation of the initial yaw angle error is 60″, and the standard deviation of the initial roll angle error is 90″ [29];
- (4)
5.2. Sample Generation and RBM-BPNN Structure Training
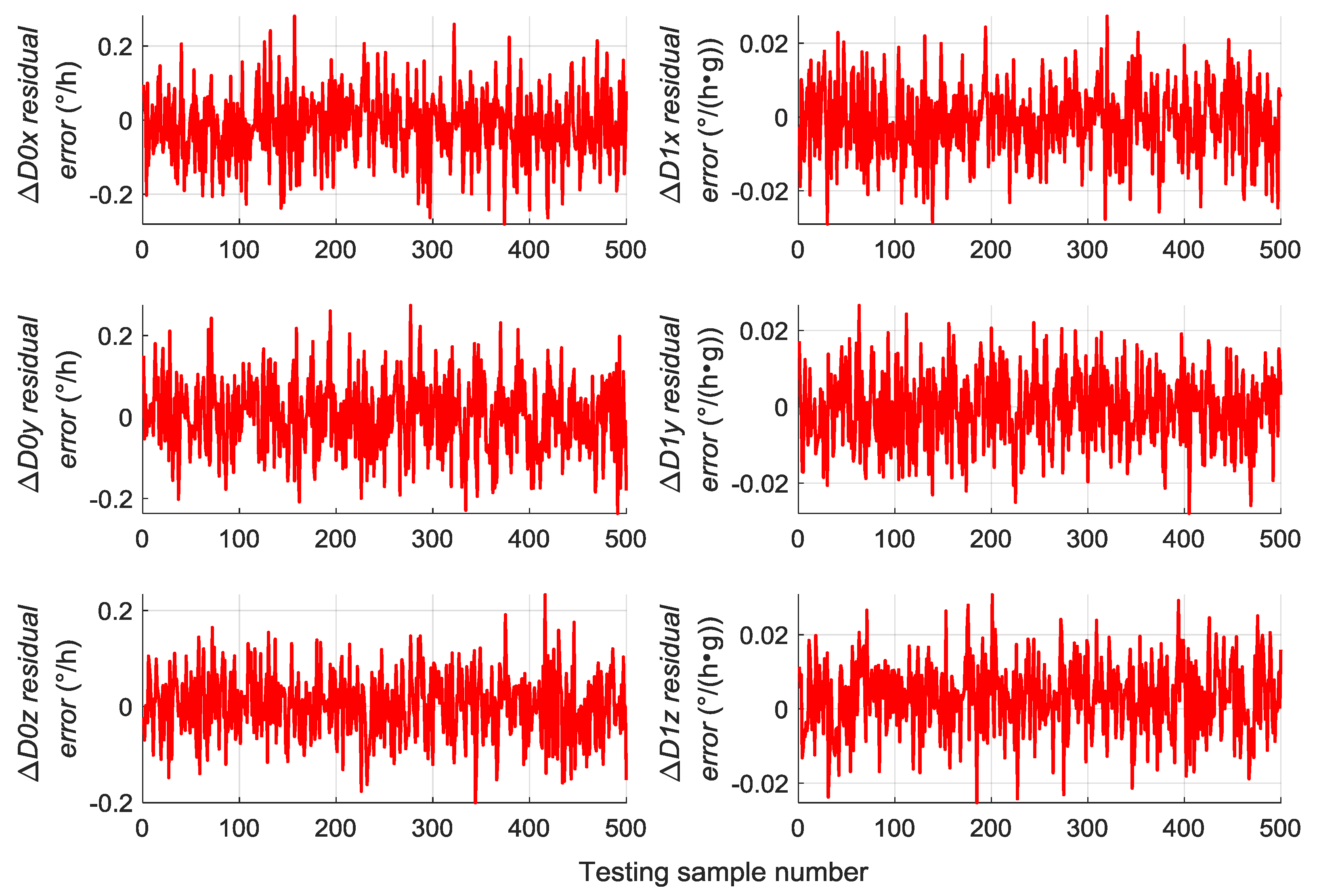
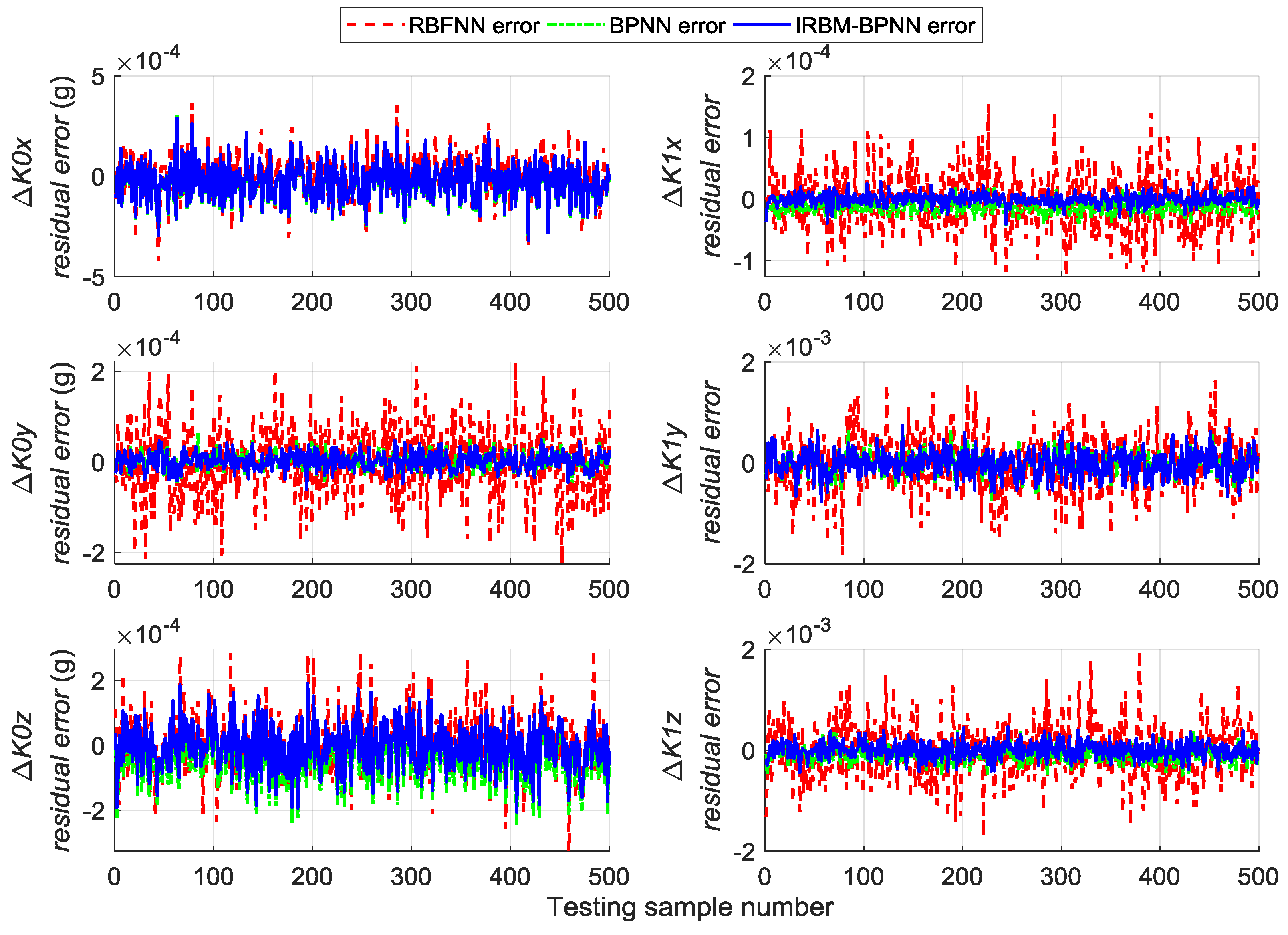
5.3. Error Parameter Forecast Results by RBM-BPNN
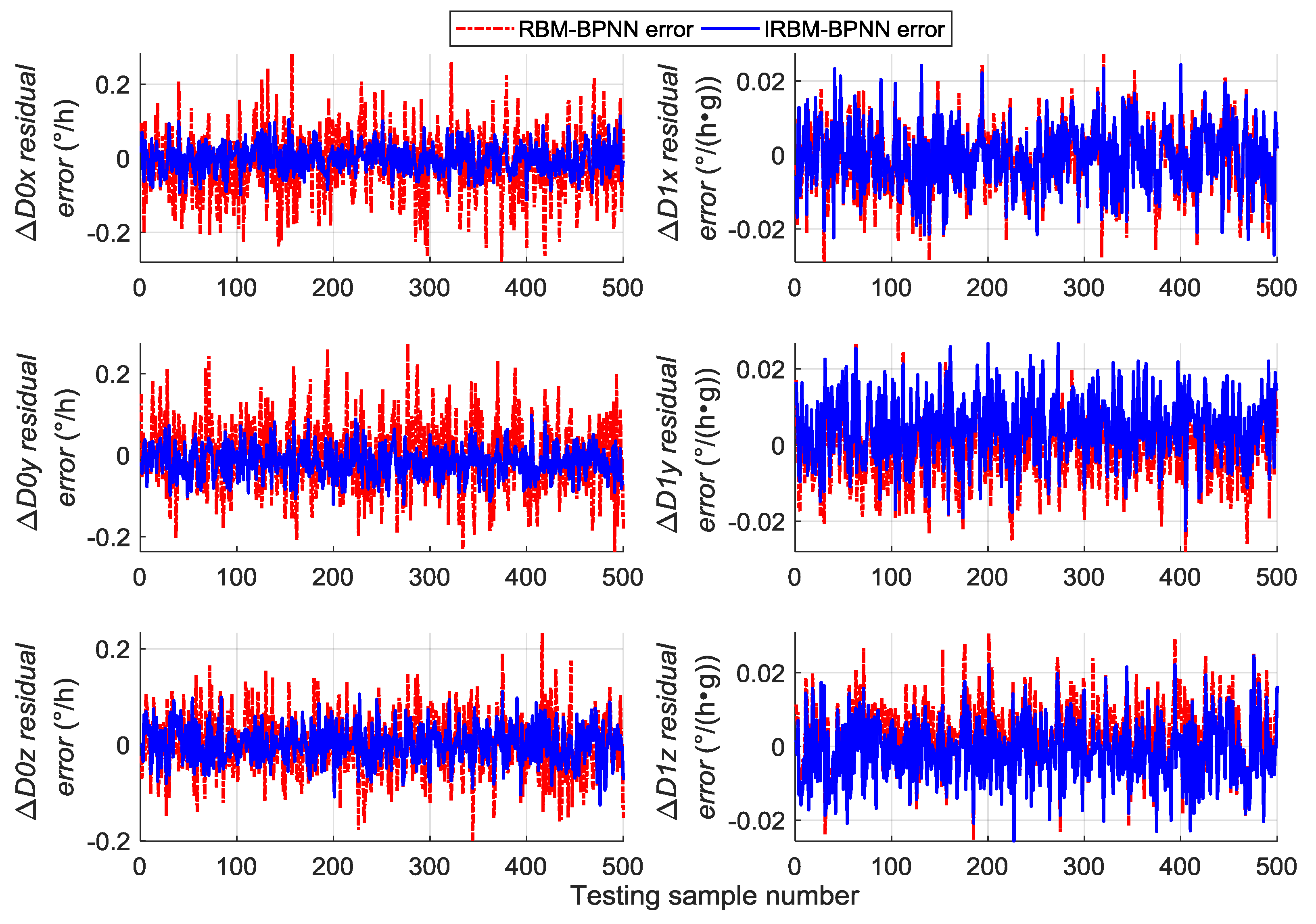
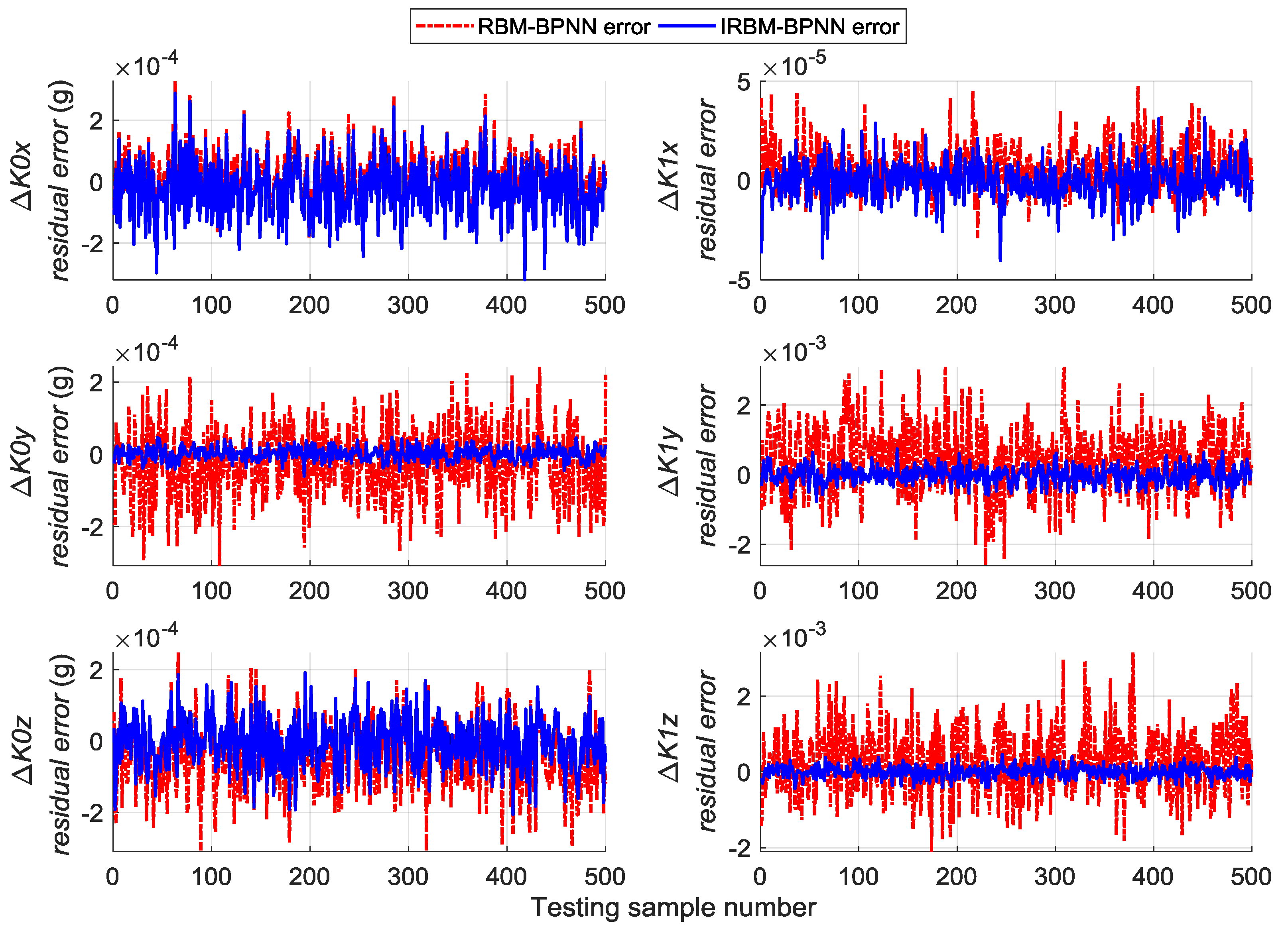
5.4. RBM-BPNN Method Improvement and Simulation
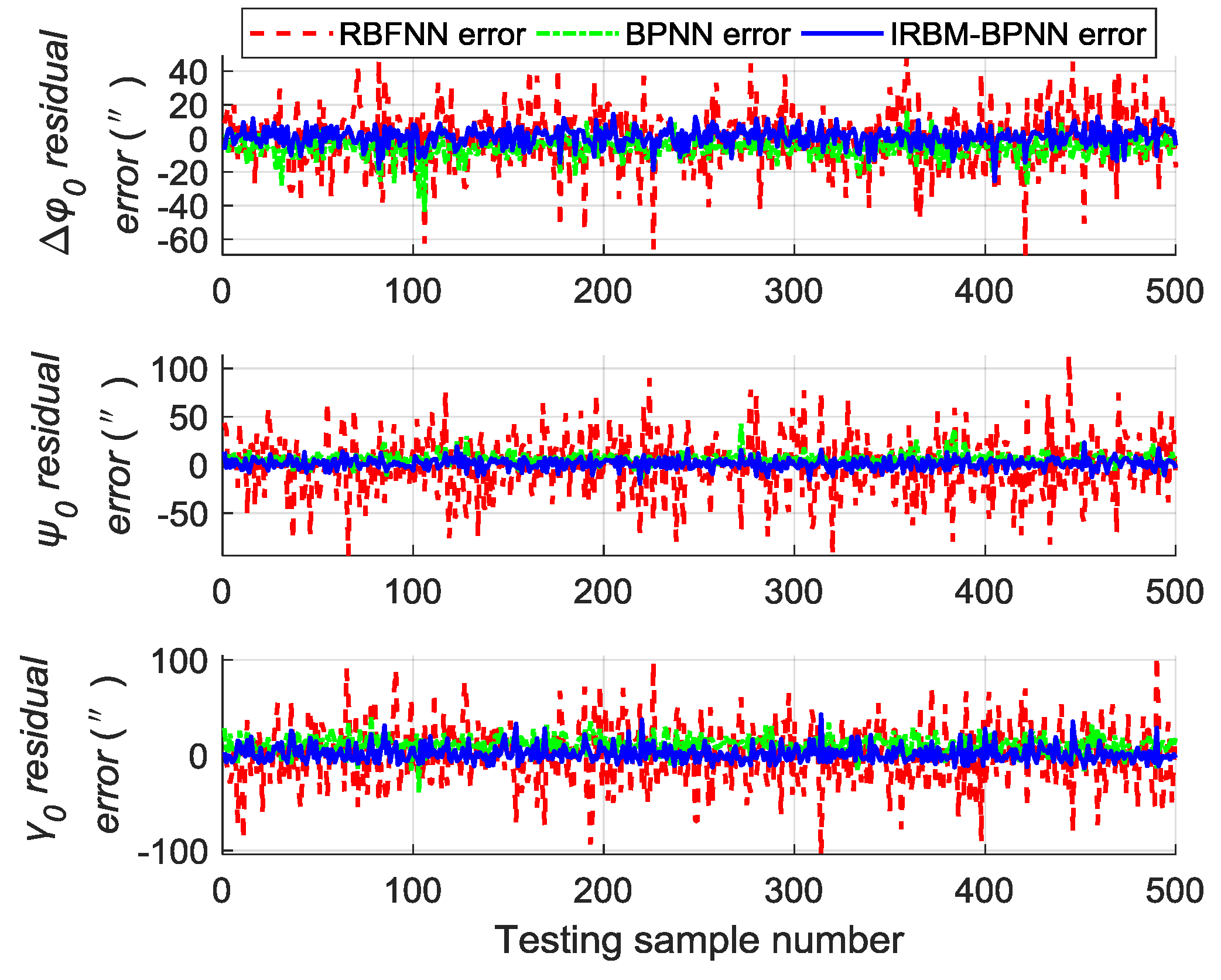
5.5. Design of Simulation Comparison Experiments
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.J.; Yang, H.B.; Lu, H.P.; Zhang, S.F.; Cai, H.; Qian, S. Cubature Kalman filtering for relative spacecraft attitude and position estimation. Acta Astronaut. 2014, 105, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xiong, Z.; Shi, L.J.; Yu, F.; Liu, J.Y. A robust filtering algorithm for integrated navigation system of aerospace vehicle in launch inertial coordinate. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.D.; Wang, J.L.; Chris, R.; Doug, K. Improving adaptive Kalman estimation in GPS/INS integration. J. Navig. 2007, 60, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Xu, J.N.; He, H.Y.; Guo, S.L. Initial alignment method of strapdown gyrocompass based on particle swarm optimization algorithm. J. Chin. Inert. Technol. 2017, 25, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.L.; Xian, Y.; Li, B.; Ren, L.L. Initial alignment error on-line identification based on adaptive particle swarm optimization algorithm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3486492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.Y.; Xu, J.N.; Qin, F.J.; Li, F. Genetic algorithm based fast alignment method for strap-down inertial navigation system with large azimuth misalignment. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2015, 86, 1930–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.W.; Wang, K.H.; Dai, H.D. A rapid calibration method for accelerometer based on PSO algorithm. Electron. Opt. Control 2014, 21, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, K.W.; Chang, H.W. Intelligent sensor positioning and orientation through constructive neural network-embedded INS/GPS integration algorithms. Sensors 2010, 10, 9252–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.M.; Samsudin, K.; Ramli, A.R. GPS/INS integration based on dynamic ANFIS network. Int. J. Control Autom. 2012, 5, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Saadeddin, K.; Abdel-Hafez, M.F.; Jaradat, M.A.; Jarrah, M.A. Optimization of intelligent approach for low-cost INS/GPS navigation system. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2014, 73, 325–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.P.; Wang, J.; Han, H.Z.; Tan, X.L.; Liu, T.J. An optimal radial basis function neural network enhanced adaptive robust Kalman filter for GNSS/INS integrated systems in complex urban areas. Sensors 2018, 18, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.Q.; Xu, X.S.; Zhu, C.C.; Chan, C.Y. A hybrid fusion algorithm for GPS/INS integration during GPS outages. Measurement 2017, 103, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Li, Y.B.; Diao, M.; Gao, W.; Qi, Z. Performance enhancement of INS/CNS integration navigation system based on particle swarm optimization back propagation neural network. Ocean Eng. 2015, 108, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Z.; Hang, Y.N.; Ma, H.K. Application of the hybrid BP/GA algorithm in simple integrated navigation system. J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2005, 31, 535–538. [Google Scholar]
- Sharaf, R.; Noureldin, A.; Osman, A.; Ei-Sheimy, N. Online INS/GPS integration with a radial basis function neural network. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2005, 20, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzi, M.; Testolin, A.; Stoianov, I.P. Modeling language and cognition with deep unsupervised learning: A tutorial overview. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Sejnowski, T.J. Learning and relearning in Boltzmann machines. Cogn. Sci. 1986, 9, 147–169. [Google Scholar]
- Smolensky, P. Information processing in dynamical systems: Foundations of harmony theory. In Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; Volume 1, pp. 194–281. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 2006, 313, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, P.; Yadav, S.K. Restricted Boltzmann machines and softmax regression for fault detection and classification. Complex Syst. 2017, 4, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.X.; Jin, W.J.; Pavel, R. Enhanced restricted Boltzmann machine with prognosability regularization for prognostics and health assessment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7076–7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.C.; Guo, J.M.; Sun, W.D. Object-oriented ensemble classification for polarimetric SAR imagery using restricted Boltzmann machines. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuremoto, T.; Kimura, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Obayashi, M. Time series forecasting using a deep belief network with restricted Boltzmann machines. Neurocomputing 2014, 137, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.H.; Xiao, L.X. Research on ballistic missile laser SIMU error propagation mechanism. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2008, 19, 356–362. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, Y.; Li, G. Research on SINS error transfer model of ballistic missile. Acta Armamentarii 2009, 30, 338–341. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Geoffrey, E. Training products of experts by minimizing contrastive divergence. Neural Comput. 2002, 14, 1771–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, R.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, C. A new dynamic calibration method for IMU deterministic errors of the INS on the hypersonic cruise vehicles. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.L.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, L.N.; Yu, F.; Zhao, H.; Liu, A.J. A simplified UKF algorithm for SINS/GPS/CNS integrated navigation system in launch inertial coordinate system. Acta Armamentarii 2015, 36, 484–491. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.D. Research on Integrated Navigation Technology for Hypersonic Vehicle; National University of Defense Technology: Changsha, China, 2010; pp. 46–50. [Google Scholar]







| Senor | Error Parameters | Error Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gyroscope | Zero-order error | 0.1 | |
| Zero-order error | 0.1 | ||
| Zero-order error | 0.1 | ||
| First-order error | 0.01 | ||
| First-order error | 0.01 | ||
| First-order error | 0.01 | ||
| White noise | 0.01 | ||
| Accelerometer | Zero-order error | 1.0 × 10−4 | |
| Zero-order error | 1.0 × 10−4 | ||
| Zero-order error | 1.0 × 10−4 | ||
| First-order error | 1.0 × 10−4 | - | |
| First-order error | 1.0 × 10−3 | - | |
| First-order error | 1.0 × 10−3 | - | |
| White noise | 1.0 × 10−5 |
| Error Parameter | Maximum Value | Minimum Value | MAE | MAPE/(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /(″) | 12.8593 | −14.3543 | 4.0847 | 17.69 |
| /(″) | 23.1374 | −26.5427 | 7.1069 | 27.72 |
| /(″) | 41.0735 | −46.3723 | 12.0742 | 28.41 |
| /() | 2.8065 × 10−1 | −2.8068 × 10−1 | 7.5766 × 10−2 | 85.63 |
| /() | 2.7374 × 10−1 | −2.3656 × 10−1 | 7.3499 × 10−2 | 78.21 |
| /() | 2.3289 × 10−1 | −2.0062 × 10−1 | 5.3618 × 10−2 | 62.39 |
| /() | 2.7299 × 10−2 | −2.9003 × 10−2 | 7.9876 × 10−3 | 92.51 |
| /() | 2.6547 × 10−2 | −2.7958 × 10−2 | 7.8484 × 10−3 | 87.86 |
| /() | 3.0782 × 10−2 | −2.5271 × 10−2 | 8.1292 × 10−3 | 81.94 |
| /() | 3.2797 × 10−4 | −3.1048 × 10−4 | 7.5387 × 10−5 | 92.22 |
| /() | 2.4197 × 10−4 | −3.0791 × 10−4 | 8.1093 × 10−5 | 81.02 |
| /() | 2.4728 × 10−4 | −3.0946 × 10−4 | 8.6272 × 10−5 | 77.54 |
| 4.7426 × 10−5 | −2.9022 × 10−5 | 1.0119 × 10−5 | 21.05 | |
| 3.0925 × 10−3 | −2.6130 × 10−3 | 8.8878 × 10−4 | 83.01 | |
| 3.1416 × 10−3 | −2.0996 × 10−3 | 7.4163 × 10−4 | 79.66 |
| Error Parameter | Maximum Value | Minimum Value | MAE | MAPE/(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /(″) | 15.1057 | −25.2937 | 4.2752 | 17.32 |
| /(″) | 23.1410 | −19.3652 | 4.2384 | 17.57 |
| /(″) | 42.4832 | −13.4244 | 6.3805 | 17.24 |
| /() | 1.1449 × 10−1 | −1.1188 × 10−1 | 3.2479 × 10−2 | 52.06 |
| /() | 9.7487 × 10−2 | −1.2024 × 10−1 | 3.4799 × 10−2 | 53.14 |
| /() | 1.1065 × 10−1 | −1.2577 × 10−1 | 3.2075 × 10−2 | 47.47 |
| /() | 2.4441 × 10−2 | −2.7048 × 10−2 | 7.2427 × 10−3 | 79.74 |
| /() | 2.6639 × 10−2 | −2.2403 × 10−2 | 7.9801 × 10−3 | 76.89 |
| /() | 2.4528 × 10−2 | −2.5661 × 10−2 | 6.9553 × 10−3 | 72.46 |
| /() | 2.8906 × 10−4 | −3.1930 × 10−4 | 7.6031 × 10−5 | 82.18 |
| /() | 4.8948 × 10−5 | −6.0603 × 10−5 | 1.4845 × 10−5 | 32.22 |
| /() | 1.9109 × 10−4 | −2.0527 × 10−4 | 5.7869 × 10−5 | 67.25 |
| 3.1575 × 10−5 | −4.0429 × 10−5 | 7.2550 × 10−6 | 17.17 | |
| 7.3813 × 10−4 | −7.6925 × 10−4 | 2.0235 × 10−4 | 38.87 | |
| 4.6047 × 10−4 | −4.4187 × 10−4 | 1.2891 × 10−4 | 30.32 |
| Error parameter | RBFNN | BPNN | IRBM-BPNN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MAPE/(%) | MAE | MAPE/(%) | MAE | MAPE/(%) | |
| /(″) | 14.4716 | 39.47 | 6.7169 | 23.55 | 4.2752 | 17.32 |
| /(″) | 25.3949 | 55.02 | 6.9855 | 25.24 | 4.2384 | 17.57 |
| /(″) | 26.1093 | 44.47 | 12.0992 | 30.68 | 6.3805 | 17.24 |
| /() | 5.1322 × 10−2 | 63.57 | 3.7878 × 10−2 | 56.65 | 3.2479 × 10−2 | 52.06 |
| /() | 4.4252 × 10−2 | 58.66 | 3.2558 × 10−2 | 51.09 | 3.4799 × 10−2 | 53.14 |
| /() | 4.8451 × 10−2 | 58.59 | 3.3190 × 10−2 | 47.74 | 3.2075 × 10−2 | 47.47 |
| /() | 8.3080 × 10−3 | 80.47 | 7.3119 × 10−3 | 79.45 | 7.2427 × 10−3 | 79.74 |
| /() | 8.2976 × 10−3 | 79.67 | 7.1242 × 10−3 | 76.23 | 7.9801 × 10−3 | 76.89 |
| /() | 8.0855 × 10−3 | 77.00 | 8.0056 × 10−3 | 76.19 | 6.9553 × 10−3 | 72.46 |
| /() | 8.6713 × 10−5 | 82.33 | 7.7971 × 10−5 | 80.14 | 7.6031 × 10−5 | 82.18 |
| /() | 6.0672 × 10−5 | 70.41 | 1.5862 × 10−5 | 34.22 | 1.4845 × 10−5 | 32.22 |
| /() | 7.6700 × 10−5 | 78.39 | 6.7325 × 10−5 | 70.40 | 5.7869 × 10−5 | 67.25 |
| 3.7834 × 10−5 | 52.52 | 1.4592 × 10−5 | 32.65 | 7.2550 × 10−6 | 17.17 | |
| 4.4197 × 10−4 | 59.16 | 2.0157 × 10−4 | 38.75 | 2.0235 × 10−4 | 38.87 | |
| 4.4192 × 10−4 | 60.16 | 1.5053 × 10−4 | 33.97 | 1.2891 × 10−4 | 30.32 | |
| Error Parameter | Actual Value | RBFNN | BPNN | IRBM-BPNN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated Value | Relative Error /(%) | Estimated Value | Relative Error /(%) | Estimated Value | Relative Error /(%) | ||
| /(″) | 60 | 69.250841 | 15.42 | 66.372812 | 10.62 | 64.152852 | 6.92 |
| /(″) | 60 | 22.492555 | 62.51 | 47.194597 | 21.34 | 50.519926 | 15.80 |
| /(″) | 90 | 71.941863 | 20.06 | 66.508608 | 26.10 | 78.082916 | 13.24 |
| /() | 0.1 | 0.104901 | 4.90 | 0.145416 | 45.42 | 0.115932 | 15.93 |
| /() | 0.1 | 0.074452 | 25.55 | 0.120273 | 20.27 | 0.136983 | 36.98 |
| /() | 0.1 | 0.076391 | 23.61 | 0.077471 | 22.53 | 0.085497 | 14.50 |
| /() | 0.01 | −0.001552 | 100.00 | 0.003833 | 61.67 | 0.004844 | 51.56 |
| /() | 0.01 | 0.013379 | 33.79 | 0.002648 | 73.52 | 0.001272 | 87.28 |
| /() | 0.01 | 0.002397 | 76.03 | 0.013044 | 30.44 | 0.012514 | 25.13 |
| /() | 1.0 × 10−4 | 6.4540 × 10−5 | 35.46 | 1.2107 × 10−5 | 87.89 | 1.4009 × 10−5 | 85.99 |
| /() | 1.0 × 10−4 | 5.1649 × 10−5 | 48.35 | 7.0472 × 10−5 | 29.53 | 1.2214 × 10−4 | 22.14 |
| /() | 1.0 × 10−4 | −7.7172 × 10−5 | 100.00 | 1.0760 × 10−4 | 7.60 | 7.1746 × 10−5 | 28.25 |
| 1.0 × 10−4 | 1.3814 × 10−5 | 86.19 | 1.1293 × 10−4 | 12.93 | 9.5368 × 10−5 | 4.63 | |
| 1.0 × 10−3 | 1.9599 × 10−4 | 80.40 | 7.0701 × 10−4 | 29.30 | 8.4009 × 10−4 | 15.99 | |
| 1.0 × 10−3 | 1.5141 × 10−3 | 51.41 | 9.0074 × 10−4 | 9.93 | 8.2878 × 10−4 | 17.12 | |
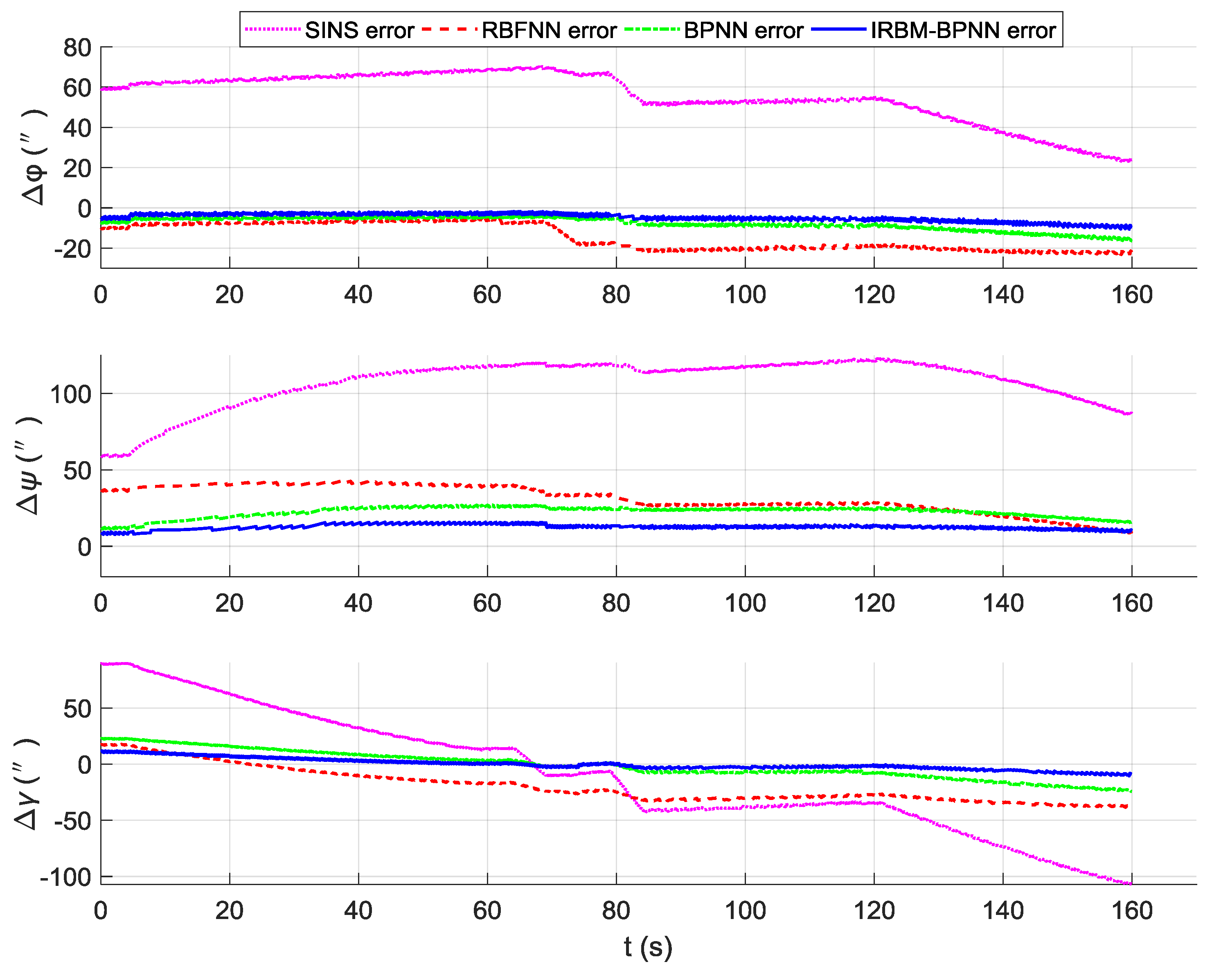
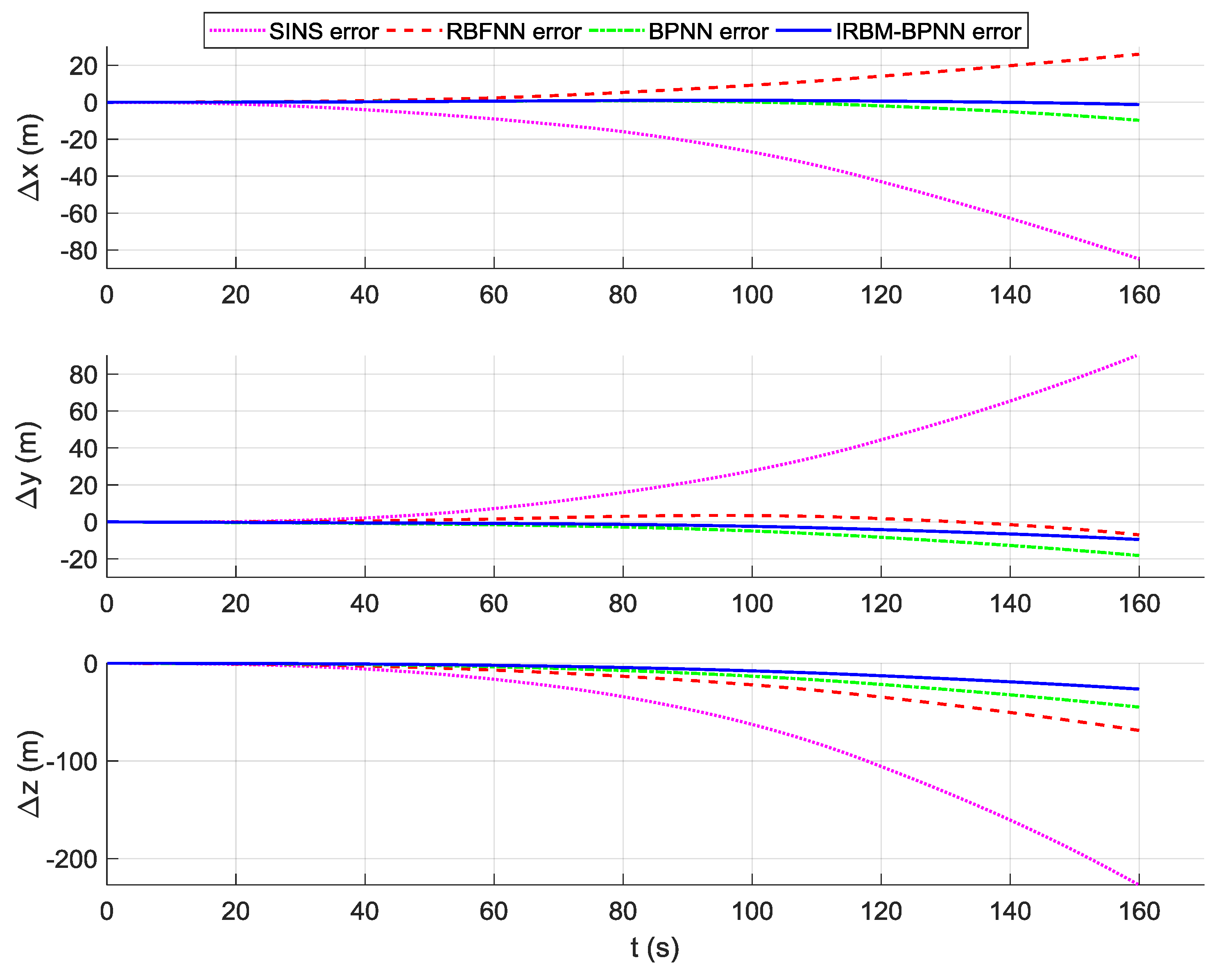
| Error Type | Navigation Parameter | Pure SINS Error | RBFNN Error | BPNN Error | IRBM-BPNN Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attitude error/(″) | 56.836476 | 15.927349 | 8.308803 | 5.122294 | |
| 108.665519 | 32.575822 | 22.702491 | 12.773308 | ||
| 53.972813 | 24.864880 | 12.464985 | 5.130052 | ||
| Position error/(m) | 35.629810 | 11.301681 | 2.967975 | 0.636830 | |
| 37.127953 | 2.393230 | 7.208955 | 3.692268 | ||
| 90.433416 | 28.697697 | 18.219801 | 10.700961 | ||
| Velocity error/(m/s) | 0.649370 | 0.195083 | 0.108240 | 0.028812 | |
| 0.709428 | 0.124732 | 0.146494 | 0.078337 | ||
| 1.824331 | 0.527373 | 0.354347 | 0.208763 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, W.; Xian, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, B.; Ren, L. Hybrid IRBM-BPNN Approach for Error Parameter Estimation of SINS on Aircraft. Sensors 2019, 19, 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19173682
Guo W, Xian Y, Zhang D, Li B, Ren L. Hybrid IRBM-BPNN Approach for Error Parameter Estimation of SINS on Aircraft. Sensors. 2019; 19(17):3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19173682
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Weilin, Yong Xian, Daqiao Zhang, Bing Li, and Leliang Ren. 2019. "Hybrid IRBM-BPNN Approach for Error Parameter Estimation of SINS on Aircraft" Sensors 19, no. 17: 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19173682
APA StyleGuo, W., Xian, Y., Zhang, D., Li, B., & Ren, L. (2019). Hybrid IRBM-BPNN Approach for Error Parameter Estimation of SINS on Aircraft. Sensors, 19(17), 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19173682




