A Data-Based Framework for Identifying a Source Location of a Contaminant Spill in a River System with Random Measurement Errors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
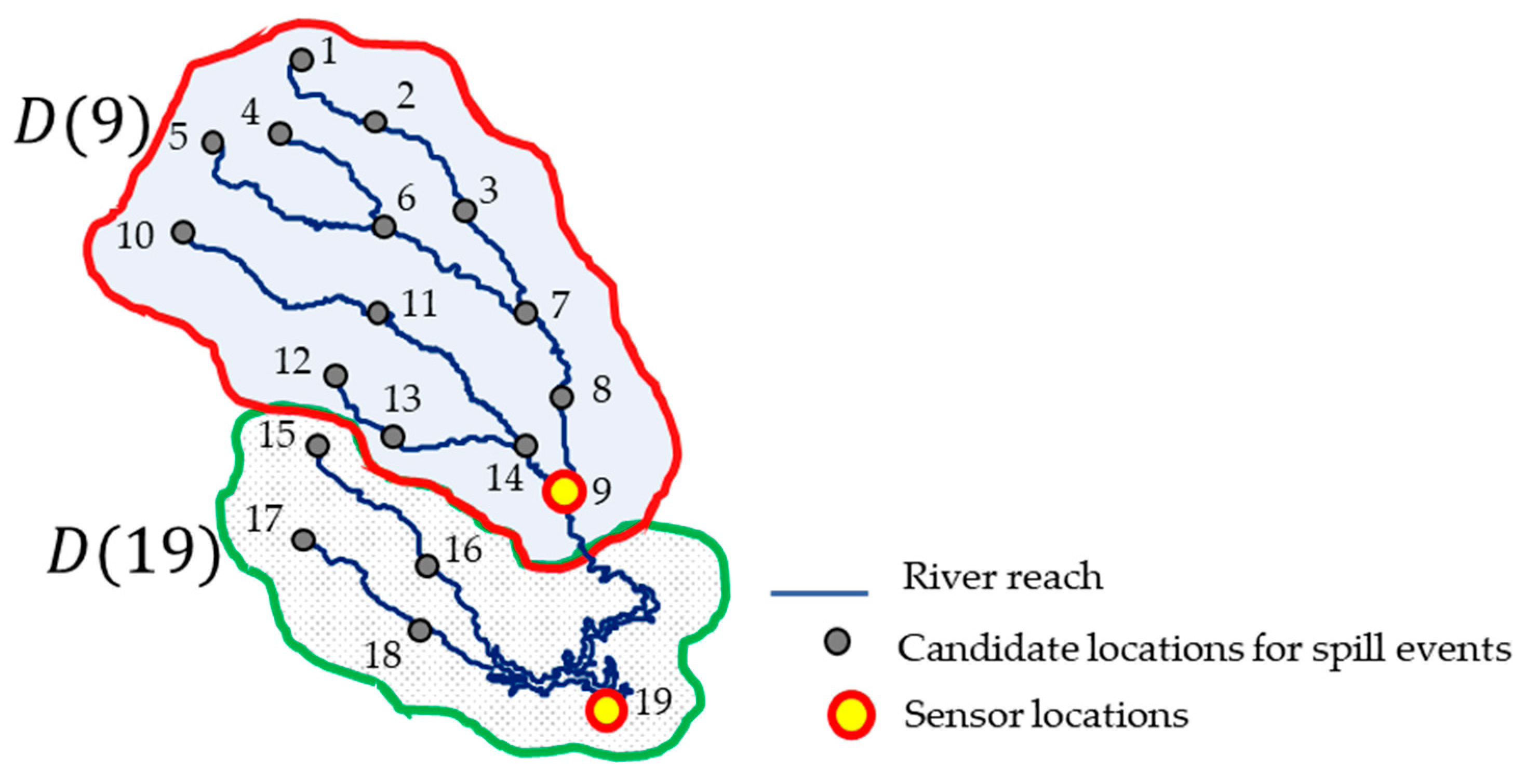
2.1. Problem Description
2.2. Data Acquisition with Simulation
3. Methods
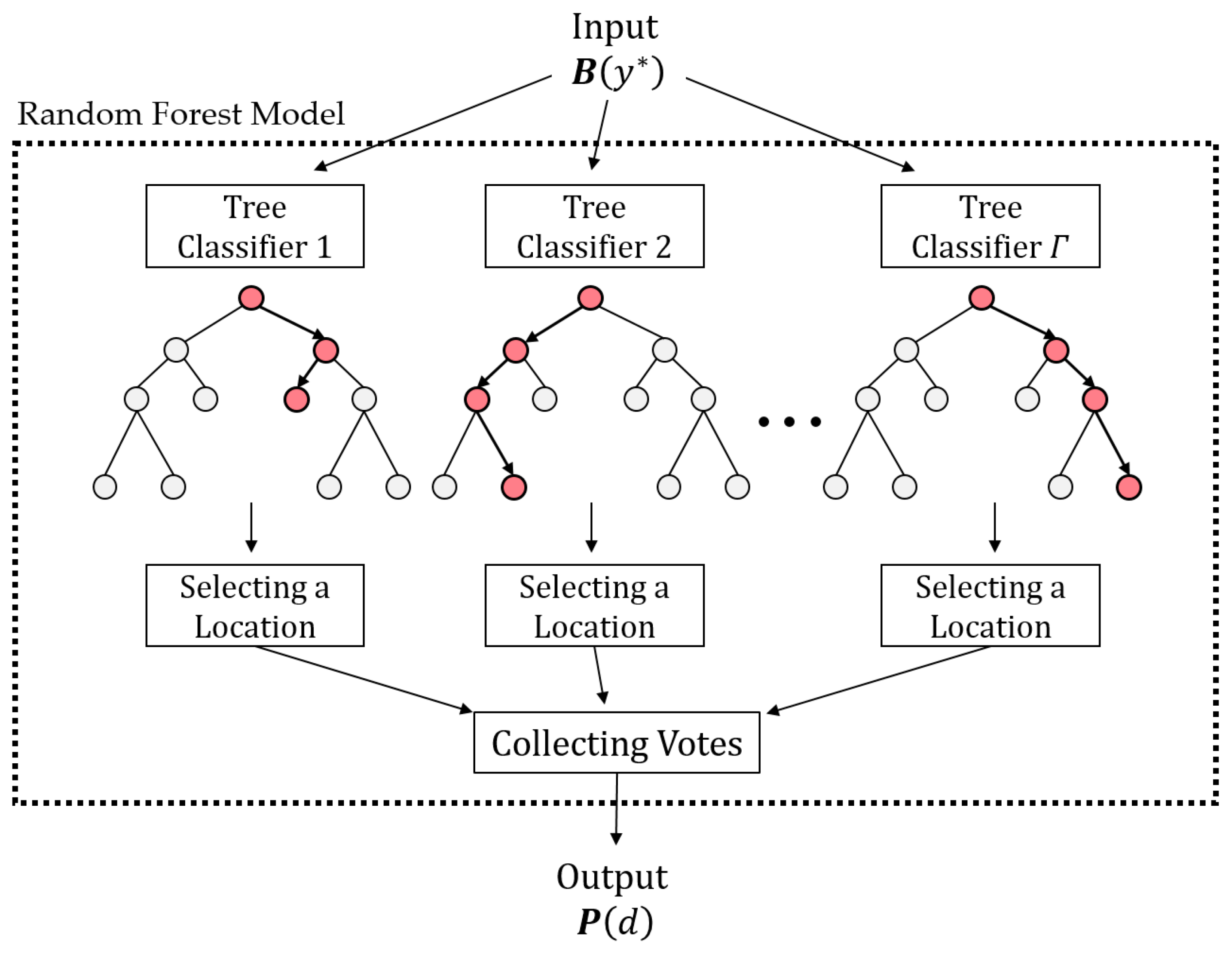
3.1. Overall Description of the Proposed Framework
| the discretized time index at which each sensor returns an observation; | |
| the location index of the sensor that raises the first alarm; | |
| the point of time when the first alarm is on by the sensor at | |
| the point of time when the first alarm is off by the sensor at | |
| the concentration level reported by the sensor at at time (i.e., ; | |
| a pre-specified window length for spill detection; | |
| a lag parameter pre-designated by users to determine ; | |
| a nonlinear regression model for in the time period [ | |
| a vector representing the curvature characteristics of ; | |
| the set of candidate spill locations that can be identified only by the sensor at and | |
| the random forest model corresponding to the sensor at |
3.2. Spill Detection
| Constructing CUSUM monitoring statistics |
| Set and . |
| Whiledo |
| . |
| . |
| end while |
3.3. Data Preprocessing
3.4. Source Identification
4. Case Study
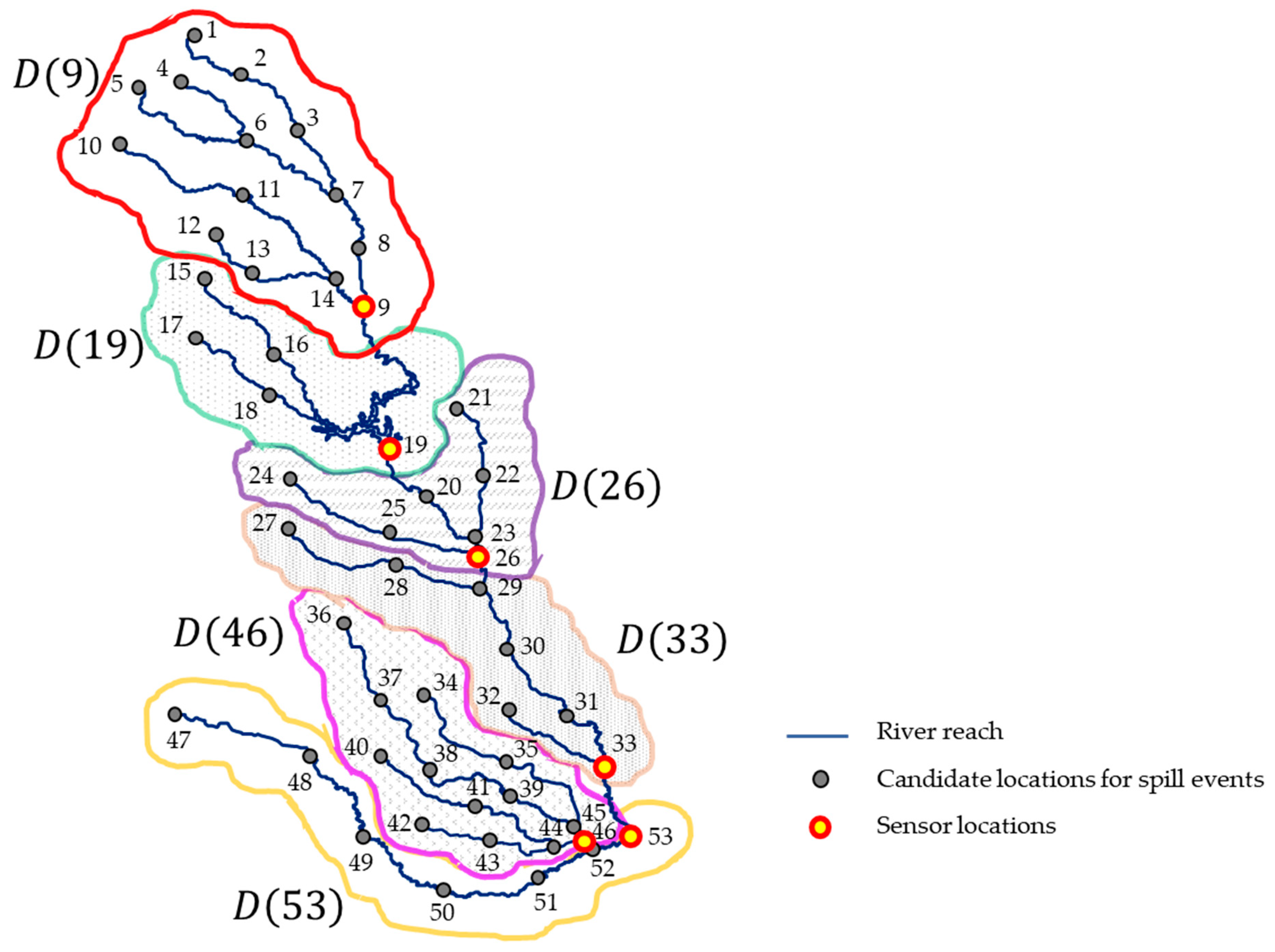
4.1. Simulation Setup for the Targeted River System
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aral, M.M.; Guan, J. Genetic algorithms in search of groundwater pollution sources. In Advances in Groundwater Pollution Control and Remediation, 2nd ed.; Aral, M.M., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 9, pp. 347–369. ISBN 978-94-009-0205-3. [Google Scholar]
- Aral, M.M.; Guan, J.; Maslia, M.L. Identification of contaminant source location and release history in aquifers. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2001, 6, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, S.M.; Evans, B.; Remson, I. Identifying sources of groundwater pollution: An optimization approach. Water Resour. Res. 1983, 19, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.M.; Datta, B. Identification of groundwater pollution sources using GA-based linked simulation optimization model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2006, 11, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.Y.; Painter, S.L.; Wittmeyer, G.W. A robust approach for iterative contaminant source location and release history recovery. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2006, 88, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neupauer, R.M.; Lin, R. Identifying sources of a conservative groundwater contaminant using backward probabilities conditioned on measured concentrations. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupauer, R.M.; Wilson, J.L. Numerical implementation of a backward probabilistic model of ground water contamination. Groundwater 2004, 42, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.Y. A robust geostatistical approach to contaminant source identification. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.M.; Datta, B. Artificial neural network modeling for identification of unknown pollution sources in groundwater with partially missing concentration observation data. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.M.; Datta, B.; Jain, A. Identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources using artificial neural networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2004, 130, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Singh, R.M. Breakthrough curves characterization and identification of an unknown pollution source in groundwater system using an artificial neural network (ANN). Environ. Forensics 2014, 15, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boano, F.; Revelli, R.; Ridolfi, L. Source identification in river pollution problems: A geostatistical approach. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wu, Y.; Gao, S.; Cao, W.; Bo, Y.; Shang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhou, F. Spatio-temporal patterns and source identification of water pollution in lake taihu (China). Water 2016, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghane, A.; Mazaheri, M.; Samani, J.M.V. Location and release time identification of pollution point source in river networks based on the backward probability method. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telci, I.T.; Aral, M.M. Contaminant source location identification in river networks using water quality monitoring systems for exposure analysis. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2011, 2, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Park, C.; Lee, M.L. Identification of a contaminant source location in a river system using random forest model. Water 2018, 10, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Aral, M.M.; Eun, Y.; Park, J.J.; Park, C. Impact of sensor measurement error on sensor positioning in water quality monitoring networks. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2017, 31, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C. Introduction to Statistical Quality Control; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 047151988X. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-H.; Alexopoulos, C.; Tsui, K.L.; Wilson, J.R. A distribution-free tabular CUSUM chart for autocorrelated data. IIE Trans. 2007, 39, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, L.A. Storm Water Management Model User’s Manual, Version 5.0; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2004.
- Cleveland, W.S. Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.K. The random subspace method for constructing decision forests. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mech. Intell. 1998, 20, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Telci, I.T.; Kim, S.-H.; Aral, M.M. Designing an optimal water quality monitoring network for river systems using constrained discrete optimization via simulation. Eng. Optim. 2014, 46, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telci, I.T.; Nam, K.; Guan, J.; Aral, M.M. Optimal water quality monitoring network design for river systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2987–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Sensor Location | Random Forest Model | Set of Candidate Spill Locations | % of OOB Error (L, L) | % of OOB Error (H, H) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 29.34 | 33.84 | ||
| 19 | 21.08 | 26.68 | ||
| 26 | 4.49 | 7.43 | ||
| 33 | 4.46 | 9.83 | ||
| 46 | 30.82 | 35.17 | ||
| 53 | 4.4 | 10.11 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.L.; Park, C. A Data-Based Framework for Identifying a Source Location of a Contaminant Spill in a River System with Random Measurement Errors. Sensors 2019, 19, 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19153378
Kim JH, Lee ML, Park C. A Data-Based Framework for Identifying a Source Location of a Contaminant Spill in a River System with Random Measurement Errors. Sensors. 2019; 19(15):3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19153378
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jun Hyeong, Mi Lim Lee, and Chuljin Park. 2019. "A Data-Based Framework for Identifying a Source Location of a Contaminant Spill in a River System with Random Measurement Errors" Sensors 19, no. 15: 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19153378
APA StyleKim, J. H., Lee, M. L., & Park, C. (2019). A Data-Based Framework for Identifying a Source Location of a Contaminant Spill in a River System with Random Measurement Errors. Sensors, 19(15), 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19153378





