Integrating Remote Sensing and Geophysics for Exploring Early Nomadic Funerary Architecture in the “Siberian Valley of the Kings”
Abstract
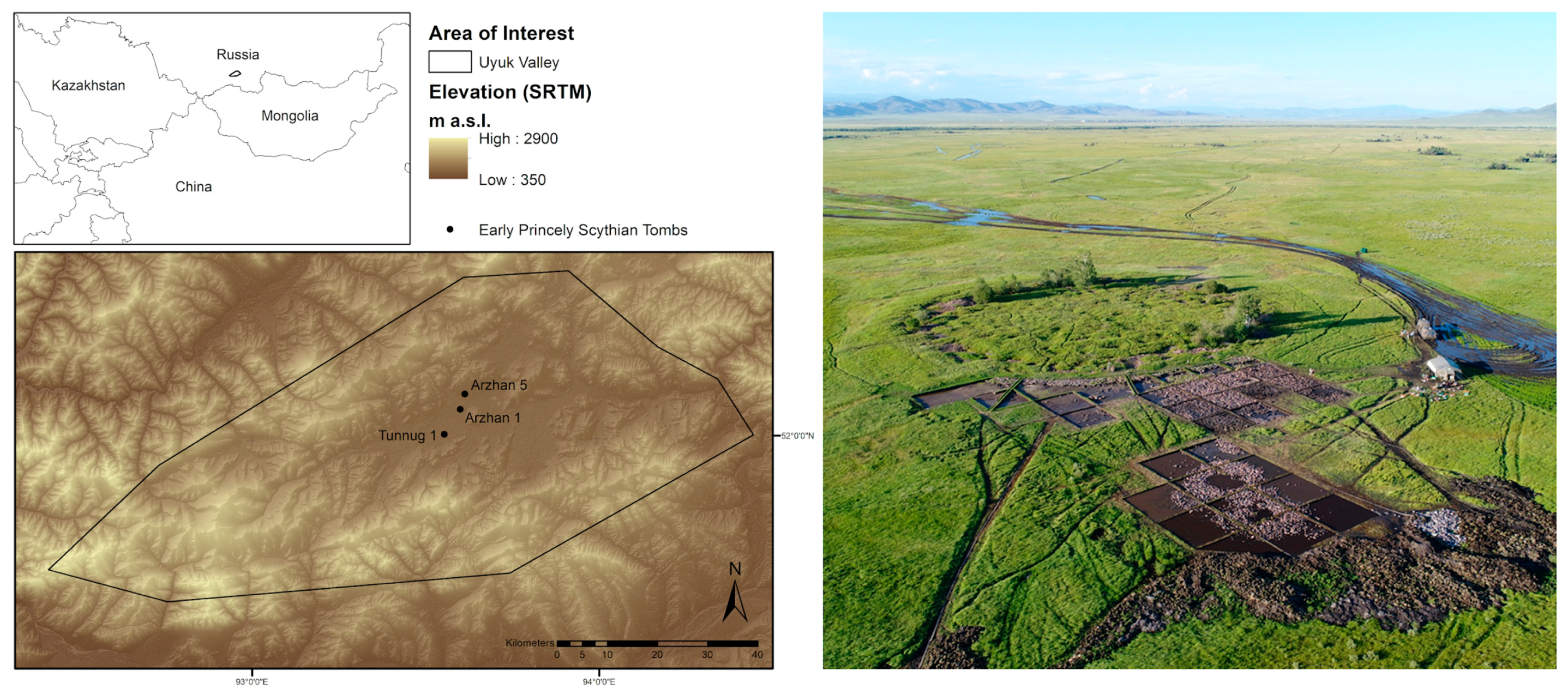
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Visual Interpretation of WorldView-2 Data
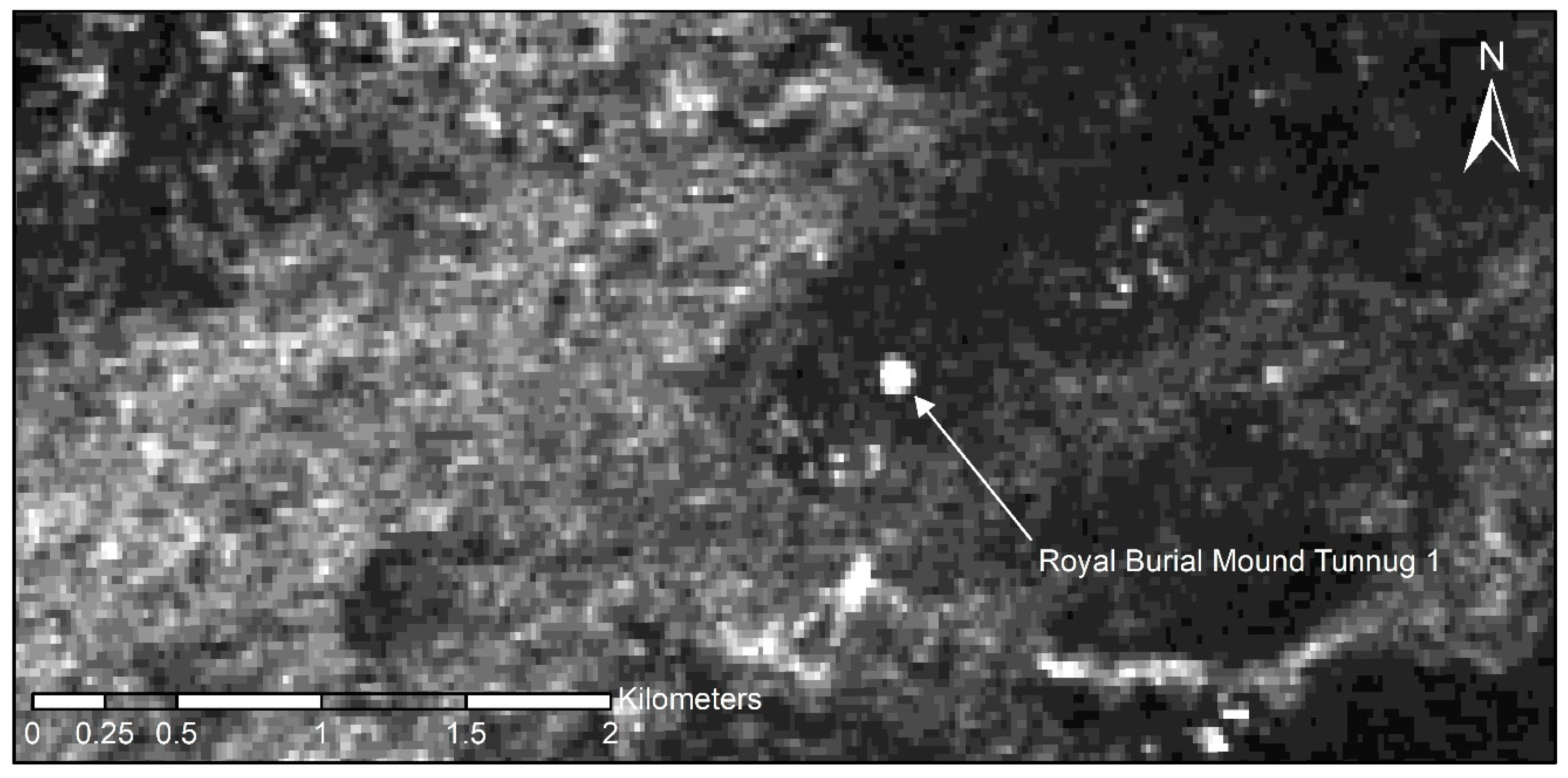
2.2. Multipolarization SAR Amplitude Data Analysis
2.3. Drone Survey and Photogrammetry-Based Digital Elevation Model
2.4. Geoelectric Resistivity Survey
2.5. Geomagnetic Survey
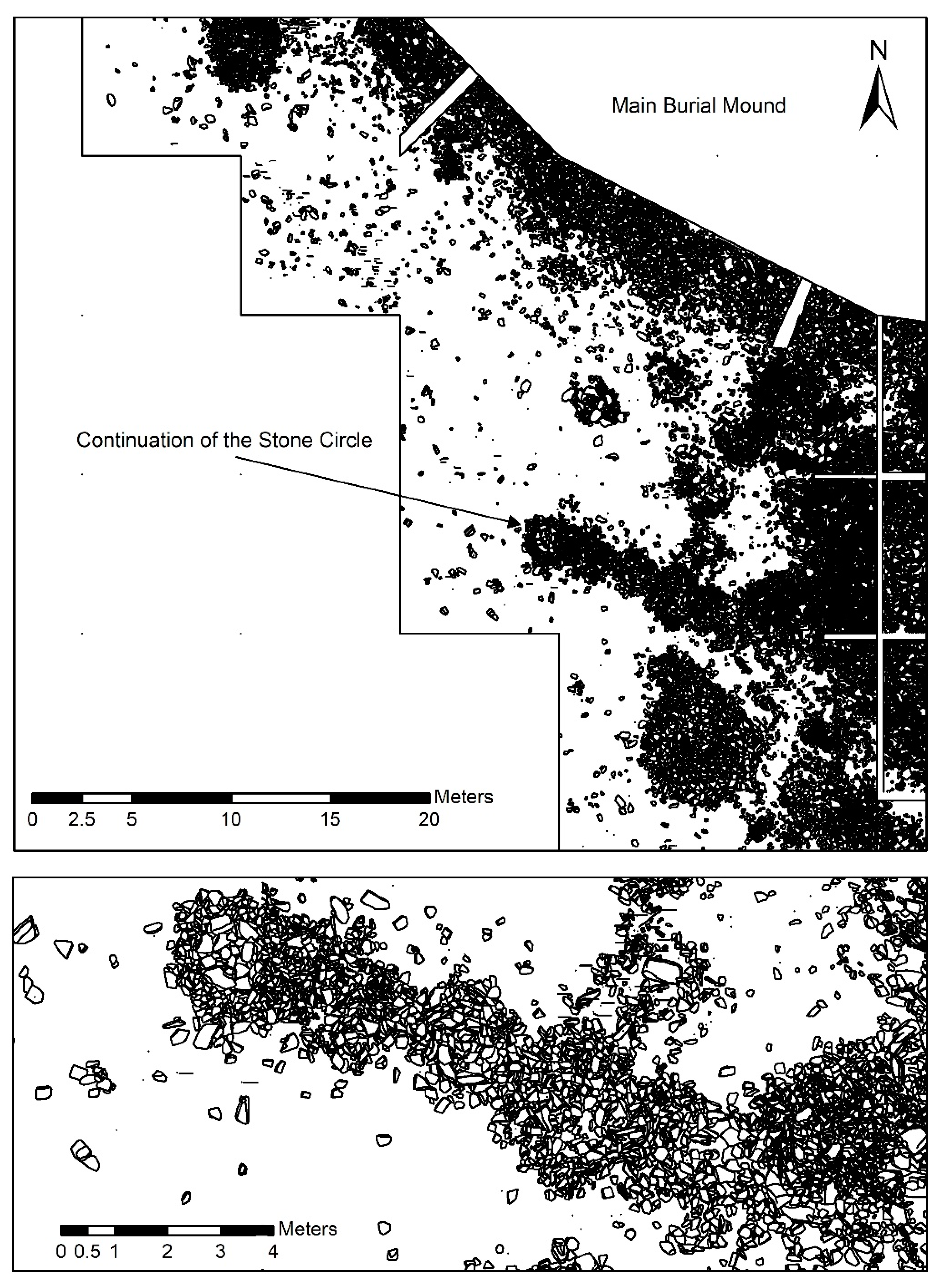
2.6. Excavation
3. Results
3.1. Visual Interpretation of WorldView-2 Data
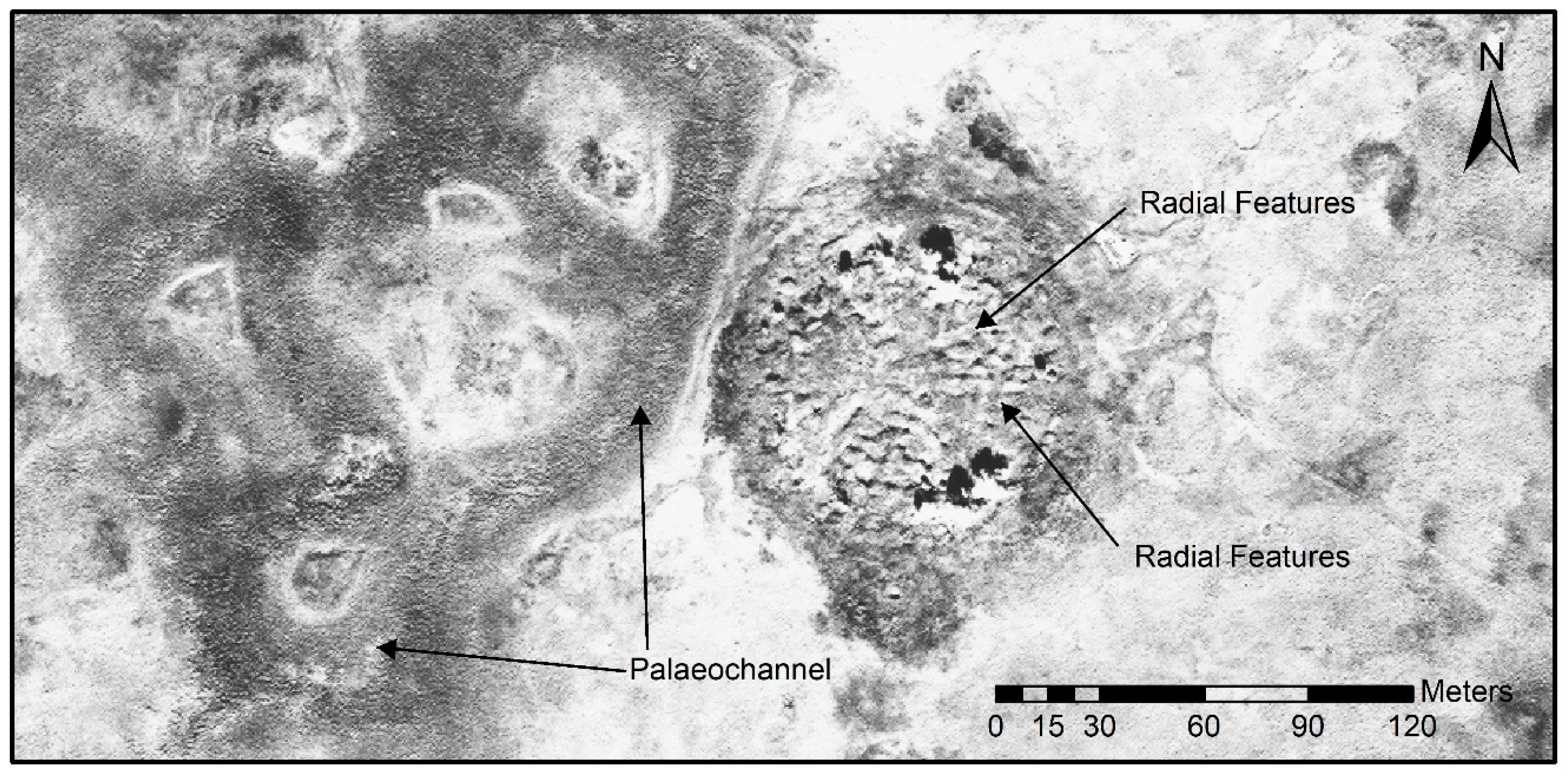
3.2. Multipolarization SAR Amplitude Analysis
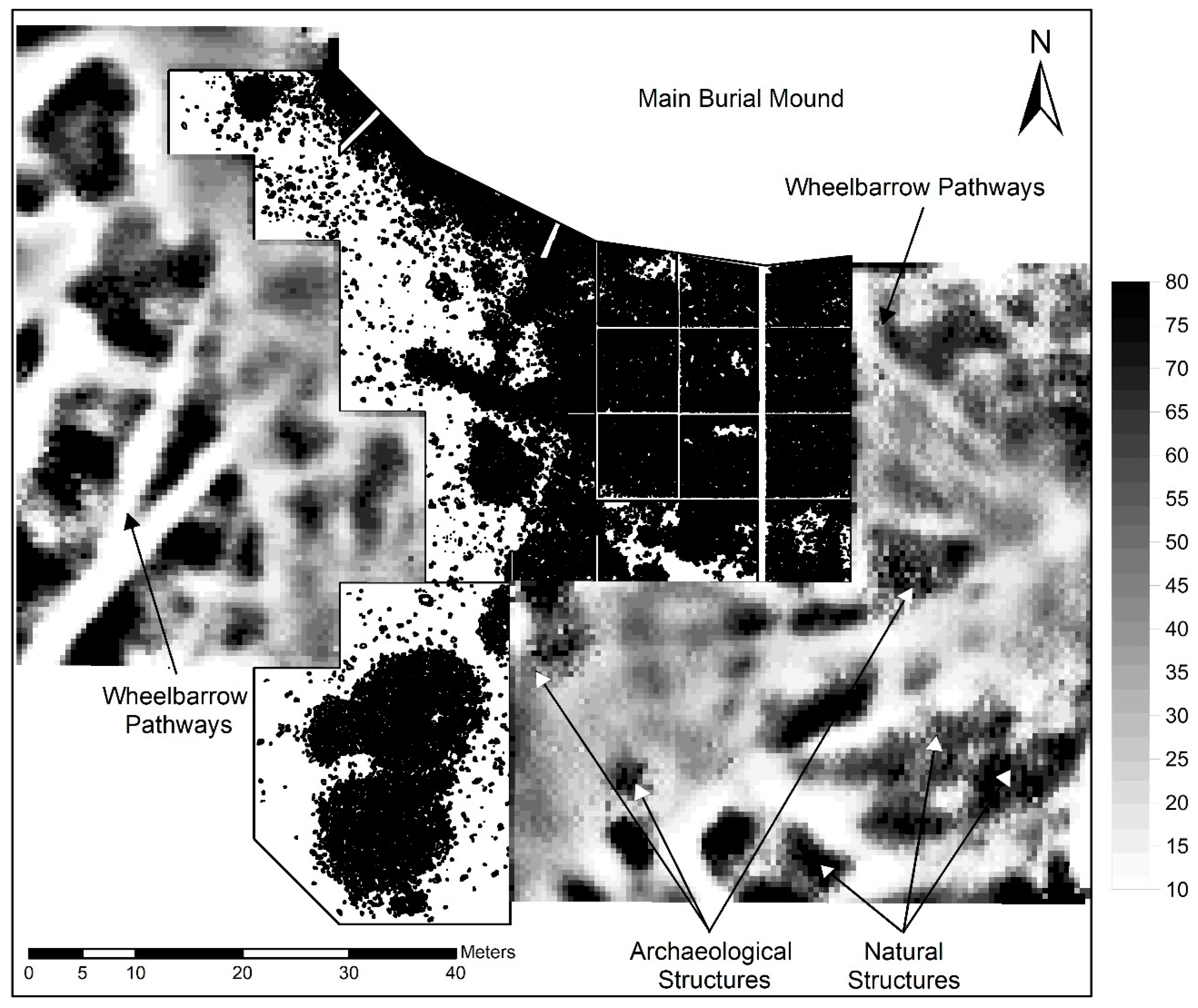
3.3. Drone Survey and Photogrammetry-Based Digital Elevation Model
3.4. Geoelectric Resistivity Survey
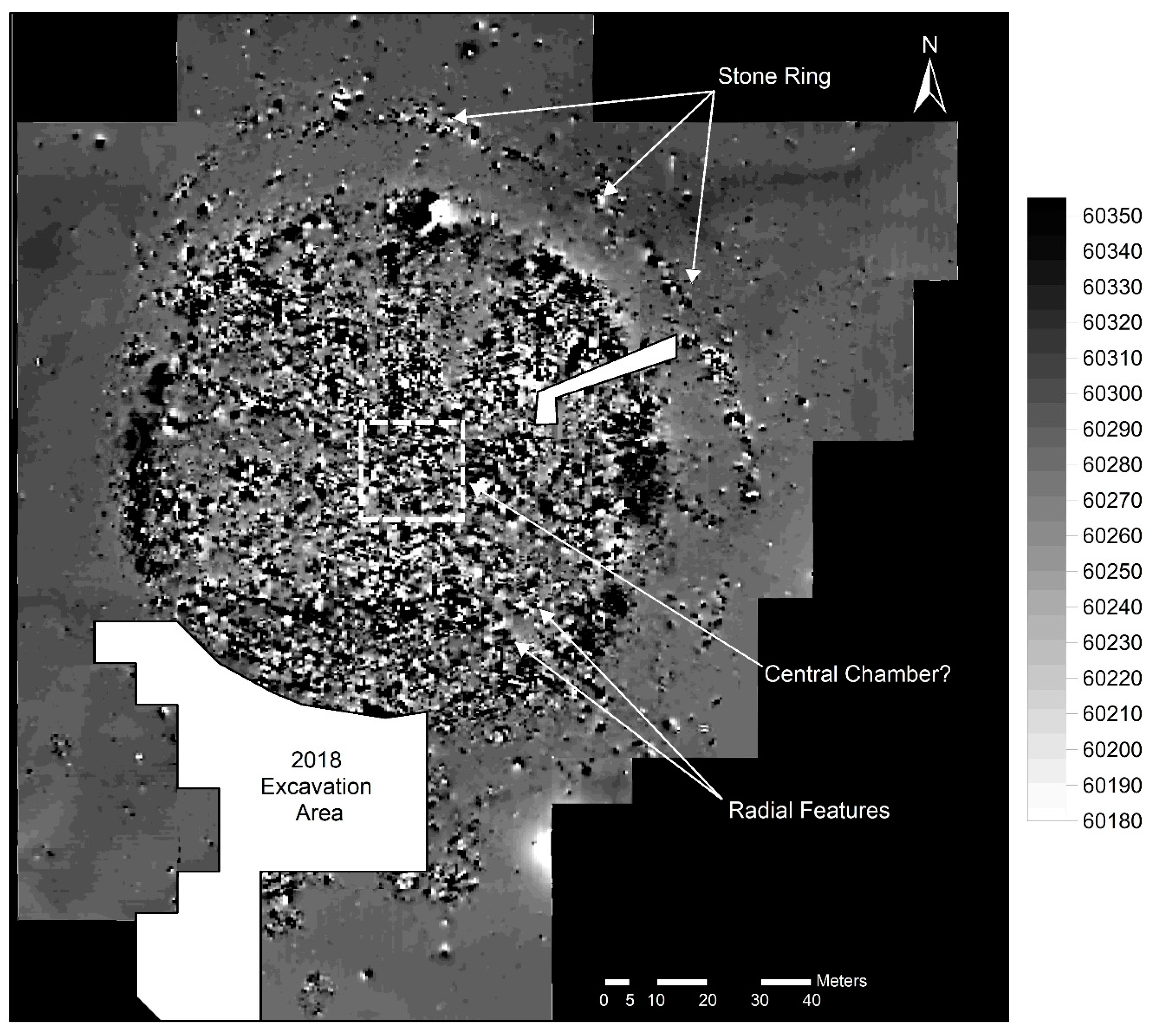
3.5. Geomagnetic Survey
3.6. Excavation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuzmina, E. The Prehistory of the Silk Road: Encounters with Asia; University of Pennsylvania Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmina, E. The Eurasian steppes the transition from early urbanism to nomadism. In Kurgans, Ritual Sites and Settlements Eurasian Bronze and Iron Age; Davis-Kimball, J., Murphy, E.M., Koryakova, L., Yablonsky, L.T., Eds.; BAR International Series: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 118–189. [Google Scholar]
- Khazanov, A.M. Nomads and the Outside World; University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Golden, P.B. Central Asia in World History; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Galanina, L.; Pjotrovskij, B. Scythian Art. The Legacy of the Scythian World: Mid-7th to 3rd Century BC; Aurora Art Publishers: Leningrad, Russia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Van Geel, B.; Bokovenko, N.A.; Burova, N.D.; Chugunov, K.V.; Dergachev, V.A.; Dirksen, V.G.; Kulkova, M.; Nagler, A.; Parzinger, H.; Van der Plicht, J.; et al. Climate change and the expansion of the Scythian culture after 850 BC: A hypothesis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2004, 31, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Yablonsky, L.T. “Scythian Triad” and “Scythian World” Kurgans. In Ritual Sites, and Settlements: Eurasian Bronze and Iron Age; Davis-Kimball, J., Murphy, E.M., Koryakova, L., Yablonsky, L.T., Eds.; BAR 890: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, M.; Wu, X.; Tarasov, P.; Aisha, A.; Ramsey, C.B.; Schultz, M.; Schmidt-Schultz, T.; Gresky, J. Radiocarbon-dated archaeological record of early first millennium BC mounted pastoralists in the Kunlun Mountains, China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15733–15738. [Google Scholar]
- Gryaznov, M.P. Kurgan Arzhan (Arzhan Barrow); Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Zaitseva, G.I.; Chugunov, K.V.; Alekseev, A.Y.; Dergachev, V.A.; Vasiliev, S.S.; Sementsov, A.A.; Cook, G.; Scott, E.M.; van Der Plicht, J.; Parzinger, H.; et al. Chronology of key barrows belonging to different stages of the Scythian period in Tuva (Arzhan-1 and Arzhan-2 barrows). Radiocarbon 2007, 49, 645–658. [Google Scholar]
- Caspari, G.; Sadykov, T.; Blochin, J.; Hajdas, I. Tunnug 1 (Arzhan 0)—An early Scythian kurgan in Tuva Republic, Russia. Archaeol. Res. Asia 2018, 15, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Parzinger, H. Die frühen Völker Eurasiens: Vom Neolithikum bis zum Mittelalter; CH Beck: München, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rukavishnikova, I.; Gladchenkov, A. Studies of Arzhan-5 in the Turan-Uyuk Basin (Рукавишникoва И.В., Гладченкoв A.A. Исследoвания Aржана-5 в Туранo-Уюкскoй кoтлoвине//KCИA). KSIA 2016, 243, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Fassbinder, J.W.E.; Becker, H. Die Magnetometerprospektion. In Der skythenzeitliche Fürstenkurgan von Aržan 2 in Tuva; Čugunov, K.V., Parzinger, H., Nagler, A., Eds.; Philipp von Zabern: Mainz, Germany, 2010; pp. 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fassbinder, J.W.E.; Gorka, T.; Chemyakina, M.; Molodin, V.; Parzinger, H.; Nagler, A. Prospecting of kurgans by magnetometry: Case studies from Kazakhstan, Siberia and the northern Caucasus. In Virtual Archaeology; The State Heremitage Publishers: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2013; pp. 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- WorldView-2 Satellite Sensor (0.46 m). Available online: https://www.satimagingcorp.com/satellite-sensors/worldview-2/ (accessed on 21 May 2019).
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. Image Enhancement, Feature Extraction and Geospatial Analysis in an Archaeological Perspective. In Satellite Remote Sensing: A New Tool for Archaeology; Lasaponara, R., Masini, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 17–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, M. ALOS-2 science program. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium-IGARSS, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 2400–2403. [Google Scholar]
- Curlander, J.C.; McDonough, R.N. Synthetic Aperture Radar—Systems and Signal Processing; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- De Reu, J.; De Smedt, P.; Herremans, D.; Van Meirvenne, M.; Laloo, P.; De Clercq, W. On introducing an image-based 3D reconstruction method in archaeological excavation practice. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 41, 251–262. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, A. Earth Resistance for Archaeologists; AltaMira Press: Lanham, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Aspinall, A.; Gaffney, C.; Schmidt, A. Magnetometry for Archaeologists; Alta-Mira Press: Lanham, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zickgraf, B. Geomagnetische und geoelektrische Prospektion in der Archäologie; Marie Leidorf GmbH: Rahden, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Caspari, G. Assessing Looting from Space: The Destruction of Early Iron Age Burials in Northern Xinjiang. Heritage 2018, 1, 320–327. [Google Scholar]
- Agapiou, A.; Lysandrou, V.; Sarris, A.; Papadopoulos, N.; Hadjimitsis, D. Fusion of satellite multispectral images based on ground-penetrating radar (GPR) data for the investigation of buried concealed archaeological remains. Geosciences 2017, 7, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Ciminale, M.; Gallo, D.; Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. A multiscale approach for reconstructing archaeological landscapes: Applications in Northern Apulia (Italy). Archaeol. Prospect. 2009, 16, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Sadykov, T.; Caspari, G.; Blochin, E. The Early Scythian Burial Mound Tunnug 1: Preliminary Results of the Excavation of the Southern Periphery (РАННЕСКИФСКИЙ КУРГАН ТУННУГ-1: РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ ПЕРВЫХ РАБОТ НА ЮЖНОЙ ПЕРИФЕРИИ ПАМЯТНИКА). Theory Pract. Archaeol. Res. 2019, 25, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Masini, N.; Yang, R.; Milillo, P.; Feng, D.; Lasaponara, R. A space view of radar archaeological marks: First applications of COSMO-SkyMed X-band data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 24–50. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, C. Detection of archaeological residues in vegetated areas using satellite synthetic aperture radar. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Masini, N.; Capozzoli, L.; Chen, P.; Chen, F.; Romano, G.; Lu, P.; Tang, P.; Sileo, M.; Ge, Q.; Lasaponara, R. Towards an operational use of geophysics for archaeology in Henan (China): Methodological approach and results in Kaifeng. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 809. [Google Scholar]
- Schneidhofer, P.; Nau, E.; Leigh McGraw, J.; Tonning, C.; Draganits, E.; Gustavsen, L.; Trinks, I.; Filzwieser, R.; Aldrian, L.; Gansum, T.; et al. Geoarchaeological evaluation of ground penetrating radar and magnetometry surveys at the Iron Age burial mound Rom in Norway. Archaeol. Prospect. 2017, 24, 425–443. [Google Scholar]
- Tonkov, N.; Loke, M.H. A resistivity survey of a burial mound in the ‘Valley of the Thracian Kings’. Archaeol. Prospect. 2006, 13, 129–136. [Google Scholar]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caspari, G.; Sadykov, T.; Blochin, J.; Buess, M.; Nieberle, M.; Balz, T. Integrating Remote Sensing and Geophysics for Exploring Early Nomadic Funerary Architecture in the “Siberian Valley of the Kings”. Sensors 2019, 19, 3074. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19143074
Caspari G, Sadykov T, Blochin J, Buess M, Nieberle M, Balz T. Integrating Remote Sensing and Geophysics for Exploring Early Nomadic Funerary Architecture in the “Siberian Valley of the Kings”. Sensors. 2019; 19(14):3074. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19143074
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaspari, Gino, Timur Sadykov, Jegor Blochin, Manuel Buess, Matthias Nieberle, and Timo Balz. 2019. "Integrating Remote Sensing and Geophysics for Exploring Early Nomadic Funerary Architecture in the “Siberian Valley of the Kings”" Sensors 19, no. 14: 3074. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19143074
APA StyleCaspari, G., Sadykov, T., Blochin, J., Buess, M., Nieberle, M., & Balz, T. (2019). Integrating Remote Sensing and Geophysics for Exploring Early Nomadic Funerary Architecture in the “Siberian Valley of the Kings”. Sensors, 19(14), 3074. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19143074





