CA-CWA: Channel-Aware Contention Window Adaption in IEEE 802.11ah for Soft Real-Time Industrial Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a channel-aware contention window adaption (CA-CWA) algorithm, which dynamically increases and decreases the CW according to the channel status in order to improve the real-time performance of the RAW mechanism in IEEE 802.11ah.
- To eliminate the influence of the interference in real wireless environment, the CW adaption process is integrated with an external interference discrimination method. This method can improve the performance of CA-CWA algorithm effectively in the wireless environment with interference.
2. Background
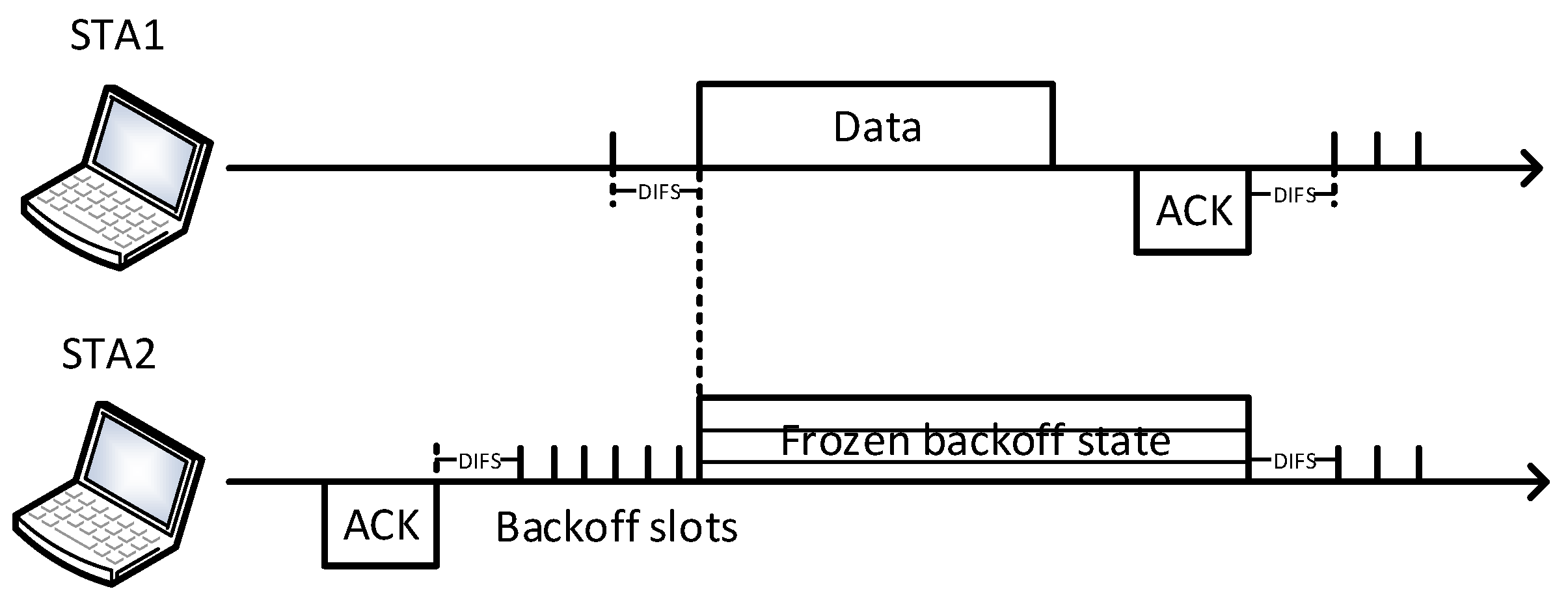
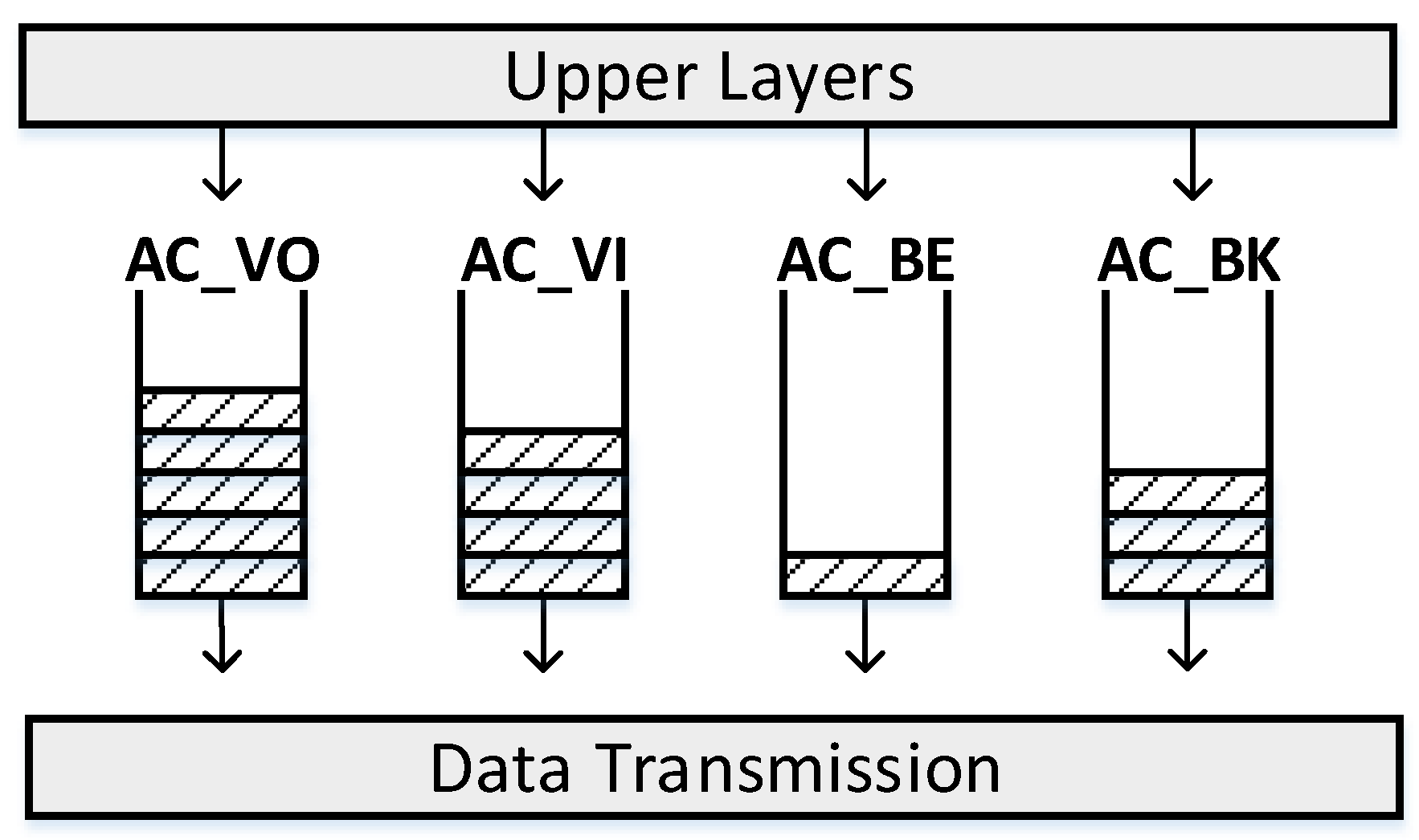
2.1. IEEE 802.11 DCF and EDCA
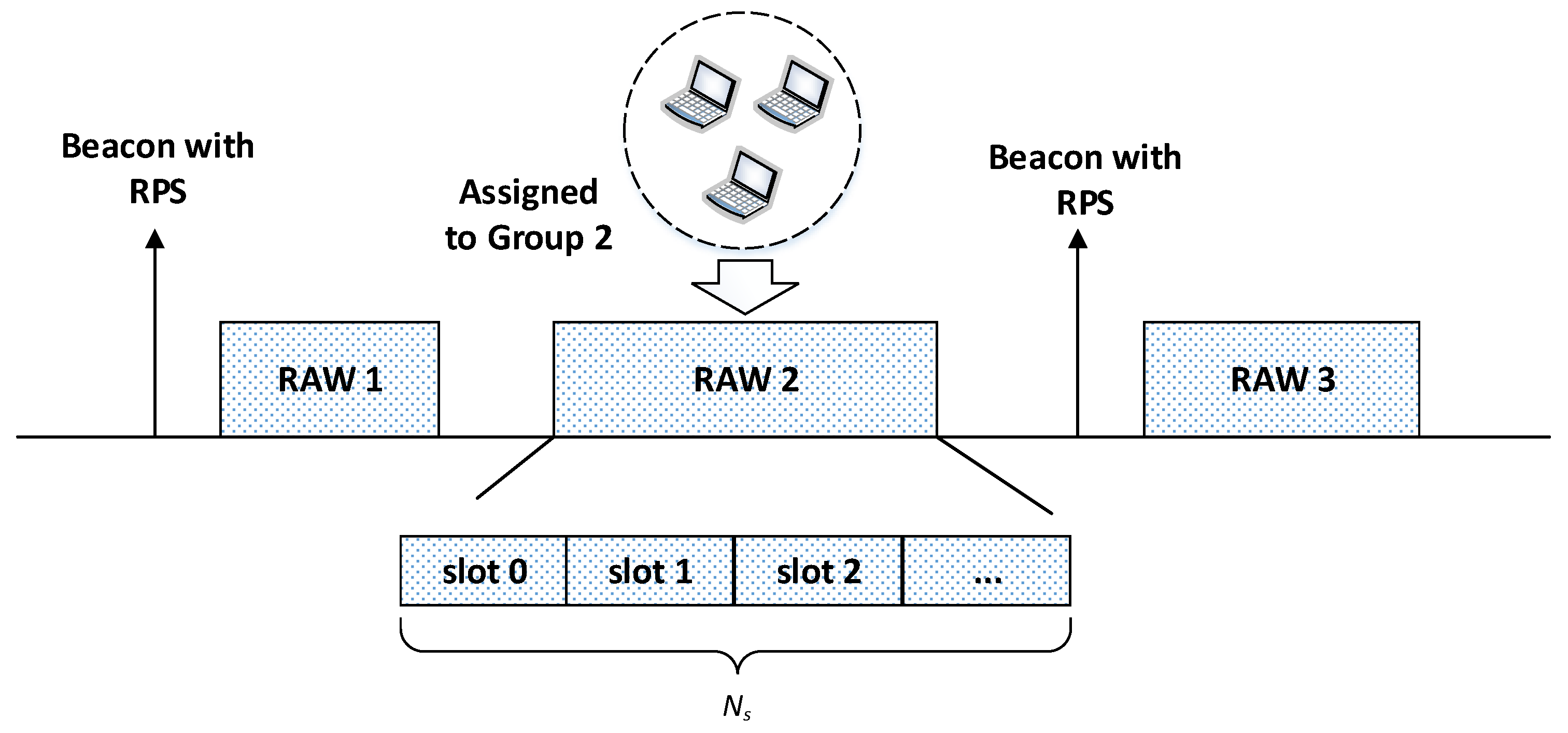
2.2. IEEE 802.11ah RAW
2.3. Contention Window Adaption
3. The Proposed CA-CWA Algorithm
3.1. Congestion Status Estimation
3.2. The Contention Window Adaption Scheme
| Algorithm 1 Channel-aware CW adaption algorithm. |
|
4. Performance Evaluation
4.1. Simulation Environment
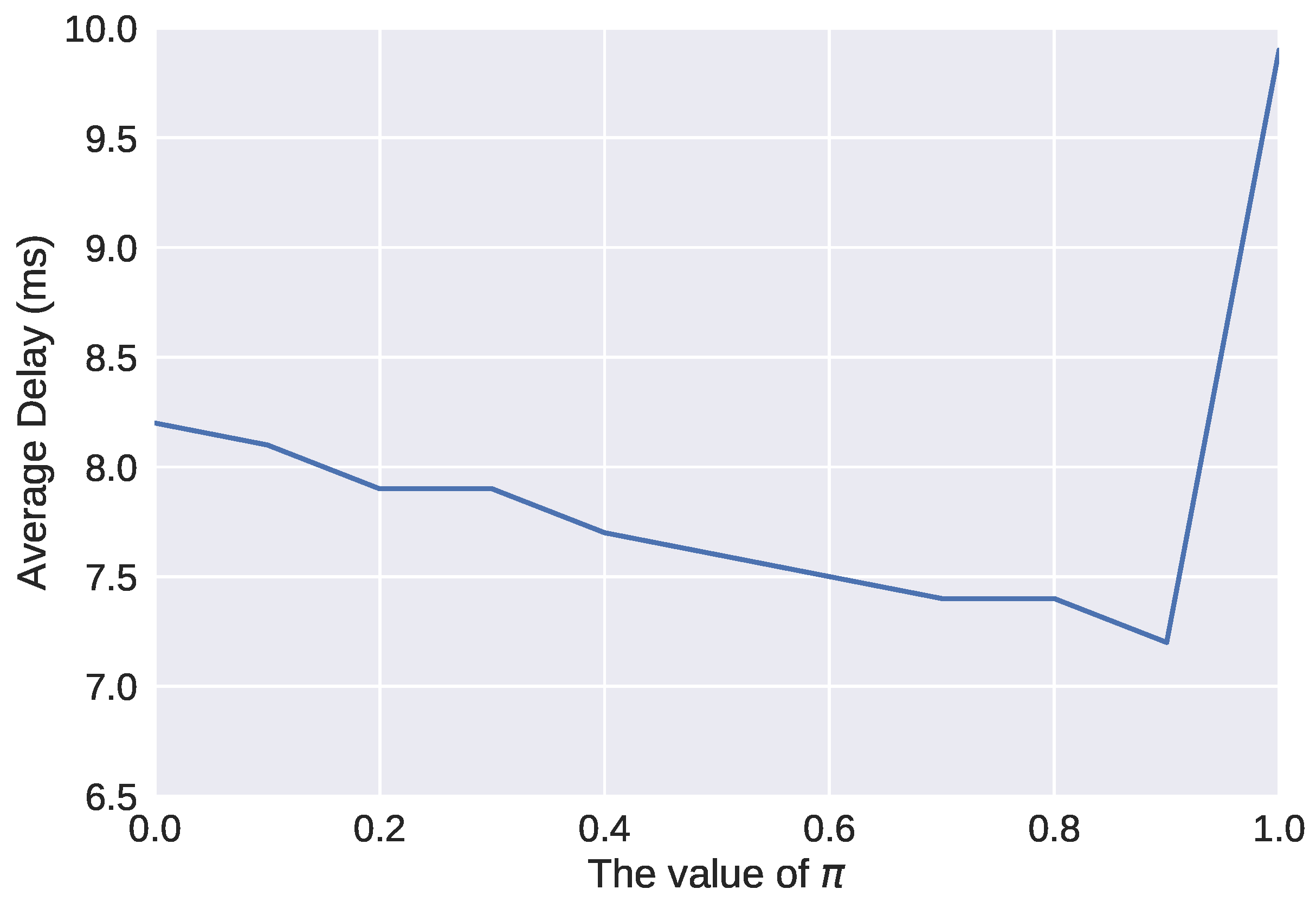
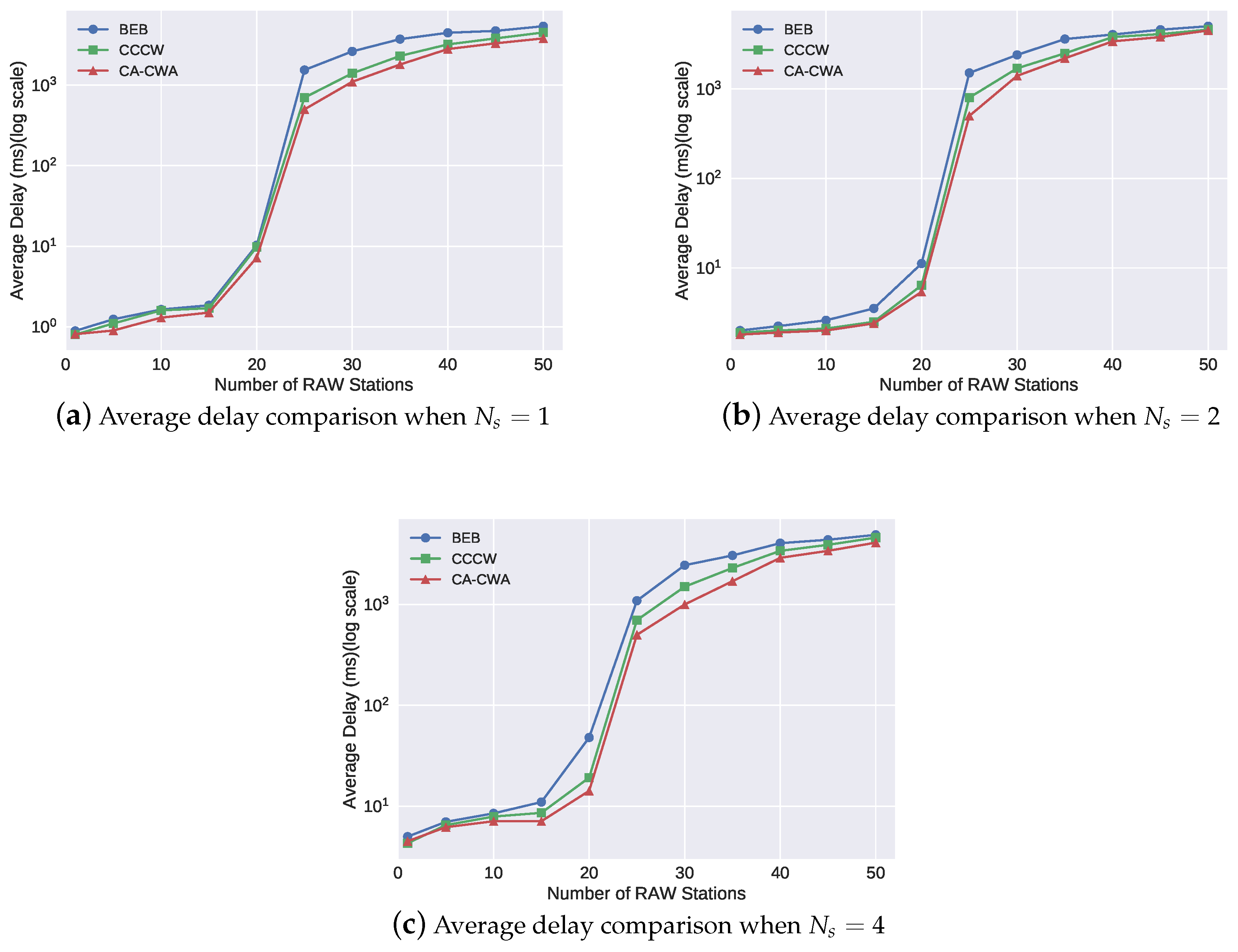
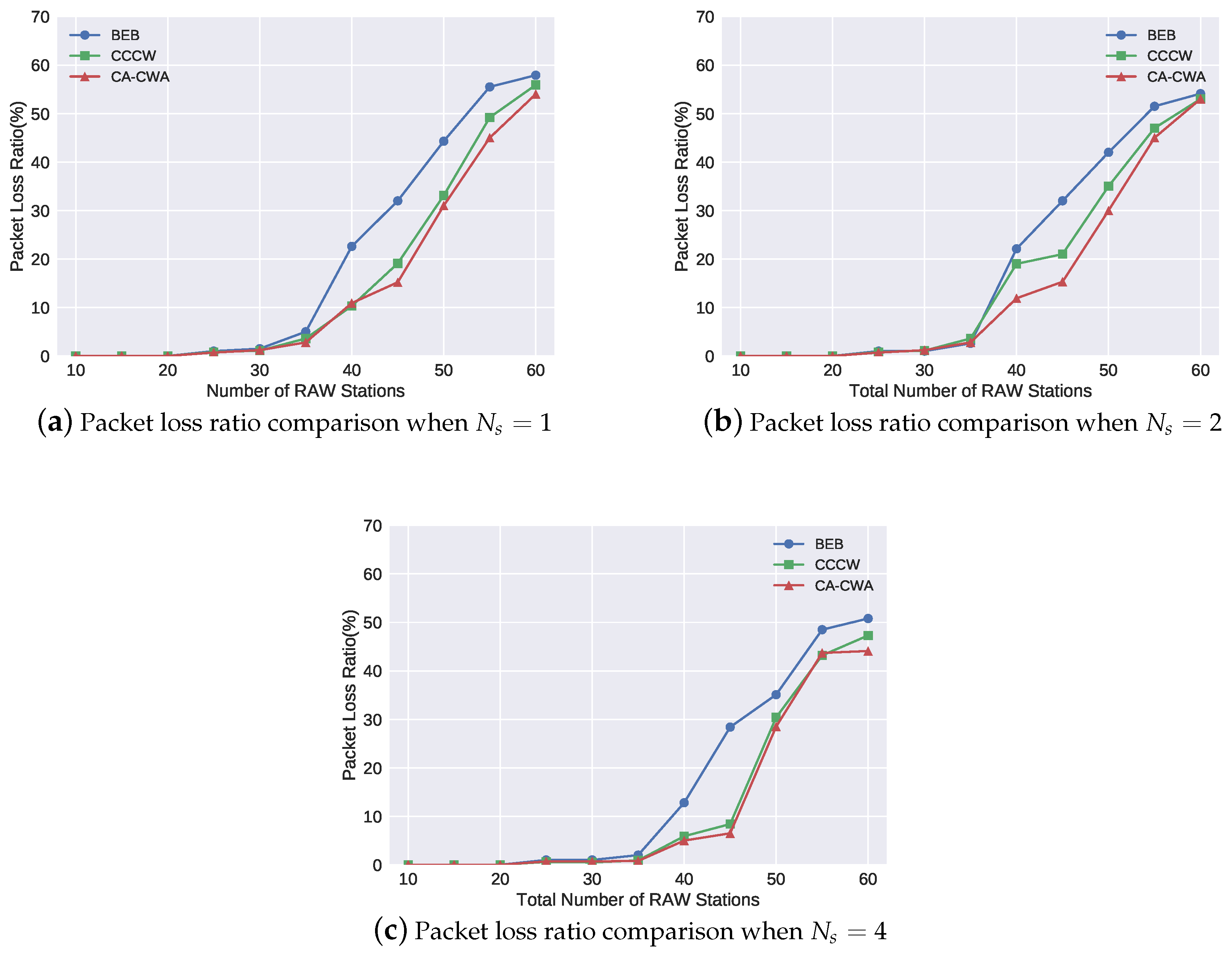
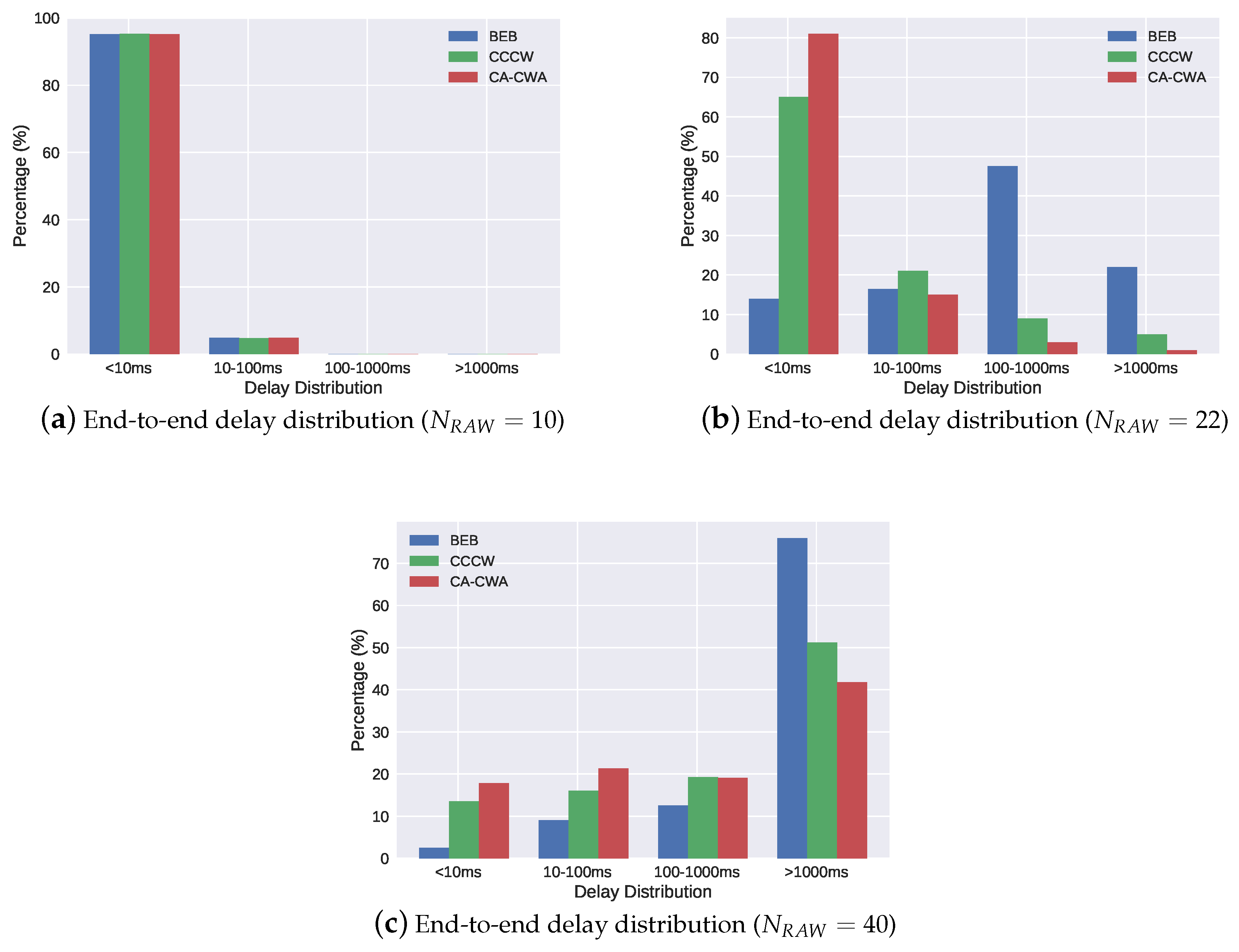
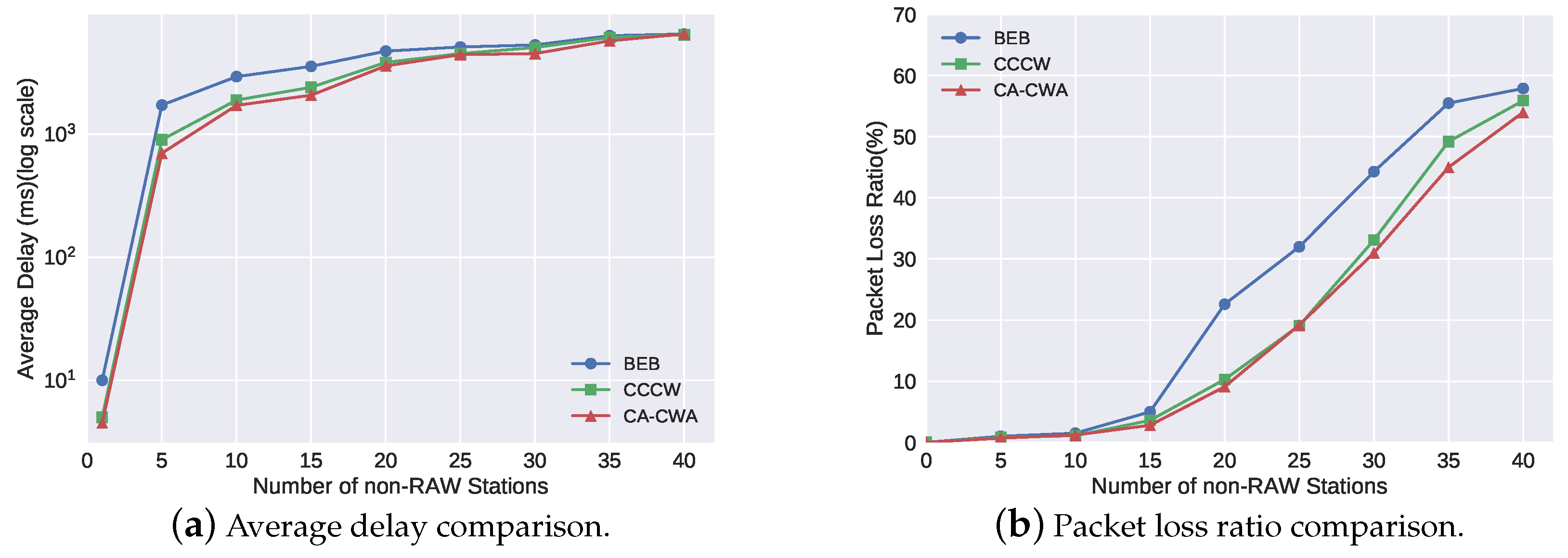
4.2. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magno, M.; Boyle, D.; Brunelli, D.; O’Flynn, B.; Popovici, E.; Benini, L. Extended wireless monitoring through intelligent hybrid energy supply. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhou, H. Det-LB: A Load Balancing Approach in 802.11 Wireless Networks for Industrial Soft Real-Time Applications. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 32054–32063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Qiu, J.; Yin, S.; Gao, H.; Fan, J.; Chai, T. Performance-based adaptive fuzzy tracking control for networked industrial processes. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2016, 46, 1760–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre-Blanes, J.; Almeida, L.; Marau, R.; Pedreiras, P. Online QoS management for multimedia real-time transmission in industrial networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 58, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seno, L.; Cena, G.; Valenzano, A.; Zunino, C. Bandwidth management for soft real-time control applications in industrial wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 2484–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seno, L.; Cena, G.; Scanzio, S.; Valenzano, A.; Zunino, C. Enhancing communication determinism in Wi-Fi networks for soft real-time industrial applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M. IEEE 802.11 ah: Sub-1-GHz license-exempt operation for the internet of things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Molnár, M.; Hanzálek, Z. Experiments for real-time communication contracts in IEEE 802.11e EDCA networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Factory Communication Systems, Dresden, Germany, 21–23 May 2008; pp. 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes, R.; Portugal, P.; Vasques, F.; Fonseca, J.A. Limitations of the IEEE 802.11e EDCA protocol when supporting real-time communication. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Factory Communication Systems, Dresden, Germany, 21–23 May 2008; pp. 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Cena, G.; Seno, L.; Valenzano, A.; Zunino, C. On the performance of IEEE 802.11e wireless infrastructures for soft-real-time industrial applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2010, 6, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, V.C.; Hancke, G.P. Industrial wireless sensor networks: Challenges, design principles, and technical approaches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 4258–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, B.S.; Park, Y. Design of MAC layer resource allocation schemes for IEEE 802.11 ax: Future directions. IETE Tech. Rev. 2018, 35, 28–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, N.; Ali, R.; Kim, Y.T. Hybrid Slotted-CSMA/CA-TDMA for Efficient Massive Registration of IoT Devices. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 18366–18382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y. Channel condition based contention window adaptation in IEEE 802.11 WLANs. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2012, 60, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatua, M.; Misra, S. D2D: Delay-aware distributed dynamic adaptation of contention window in wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2016, 15, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bononi, L.; Conti, M.; Donatiello, L. Design and performance evaluation of a distributed contention control (DCC) mechanism for IEEE 802.11 wireless local area networks. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2000, 60, 407–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bononi, L.; Conti, M.; Gregori, E. Runtime optimization of IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs performance. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2004, 15, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.J.; Ke, C.H.; Chen, H.H.; Huang, Y.M. Contention window optimization for IEEE 802.11 DCF access control. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2008, 7, 5129–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusse, M.; Rousseau, F.; Guillier, R.; Duda, A. Idle sense: An optimal access method for high throughput and fairness in rate diverse wireless LANs. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 22–26 August 2005; Volume 35, pp. 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano, P.; Banchs, A.; Patras, P.; Azcorra, A. Optimal configuration of 802.11e EDCA for real-time and data traffic. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2010, 59, 2511–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patras, P.; Banchs, A.; Serrano, P.; Azcorra, A. A control-theoretic approach to distributed optimal configuration of 802.11 WLANs. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2011, 10, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Roy, S. Contention window and transmission opportunity adaptation for dense IEEE 802.11 WLAN based on loss differentiation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, Beijing, China, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 2556–2560. [Google Scholar]
- Malone, D.; Clifford, P.; Leith, D.J. MAC layer channel quality measurement in 802.11. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2007, 11, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Deronne, S.; Latré, S.; Famaey, J. Implementation and Validation of an IEEE 802.11 ah Module for ns-3. In Proceedings of the Workshop on ns-3, Seattle, WA, USA, 15–16 June 2016; pp. 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Moyne, J.R.; Tilbury, D.M. The emergence of industrial control networks for manufacturing control, diagnostics, and safety data. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.M.; Saccucci, M.S. Exponentially Weighted Moving Average Control Schemes: Properties and Enhancements. Technometrics 1990, 32, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willig, A.; Kubisch, M.; Hoene, C.; Wolisz, A. Measurements of a wireless link in an industrial environment using an IEEE 802.11-compliant physical layer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 1265–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeesi, O.; Pirskanen, J.; Hazmi, A.; Levanen, T.; Valkama, M. Performance evaluation of IEEE 802.11 ah and its restricted access window mechanism. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC), Sydney, Australia, 11–14 June 2014; pp. 460–466. [Google Scholar]
- Badihi, B.; Del Carpio, L.F.; Amin, P.; Larmo, A.; Lopez, M.; Denteneer, D. Performance evaluation of IEEE 802.11 ah actuators. In Proceedings of the IEEE 83rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Nanjing, China, 15–18 May 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]

| 3 | 7 | 2 | 28 | |
| 7 | 15 | 2 | 28 | |
| 15 | 1023 | 3 | 37 | |
| 15 | 1023 | 7 | 73 |
| Basic Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Reception energy threshold | −116.0 dbm |
| CCA threshold | −119.0 dbm |
| Noise figure | 3 db |
| Channel bandwidth | 1 MHz |
| Path loss model | Log-distance |
| Path loss exponent | 3.67 |
| Data rate | 2.4 Mbps |
| Maximal distance between AP and stations | 250 m |
| 15 | |
| 1023 | |
| UDP traffic interval | 0.05 s |
| Packet payload size | 100 bytes |
| RAW Parameters | |
| RAW slot format | 0 |
| C | 100 |
| D | 12.5 ms |
| Number of group | 1 |
| Algorithm Parameters | |
| 5 ms | |
| 0.2 | |
| 2 | |
| 0.9 | |
| 0.82 |
| 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2% | 14% | 35% | 53% | 89% | 92% | 94% | 95% | 98% | 98% | 98% | |
| 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.35 | 0.53 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 |
| 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80% | 92% | 94% | 95% | 97% | 98% | 98% | |
| 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yang, D. CA-CWA: Channel-Aware Contention Window Adaption in IEEE 802.11ah for Soft Real-Time Industrial Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19133002
Cheng Y, Zhou H, Yang D. CA-CWA: Channel-Aware Contention Window Adaption in IEEE 802.11ah for Soft Real-Time Industrial Applications. Sensors. 2019; 19(13):3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19133002
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yujun, Huachun Zhou, and Dong Yang. 2019. "CA-CWA: Channel-Aware Contention Window Adaption in IEEE 802.11ah for Soft Real-Time Industrial Applications" Sensors 19, no. 13: 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19133002
APA StyleCheng, Y., Zhou, H., & Yang, D. (2019). CA-CWA: Channel-Aware Contention Window Adaption in IEEE 802.11ah for Soft Real-Time Industrial Applications. Sensors, 19(13), 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19133002





