Improving Short Term Clock Prediction for BDS-2 Real-Time Precise Point Positioning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Improved Model
2.1. Quadratic Polynomial Model
2.2. Spectrum Analysis Model
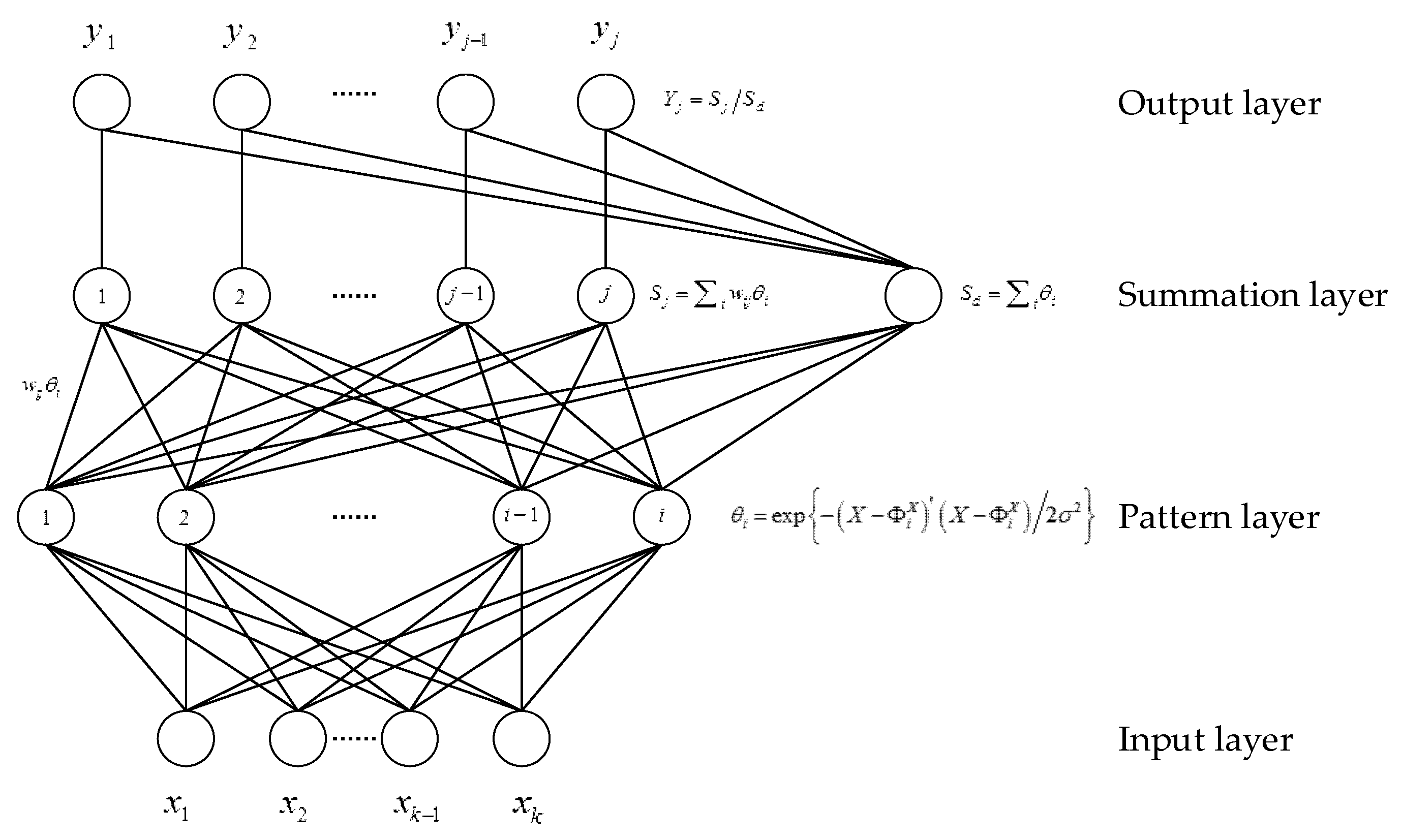
2.3. GRNN Model
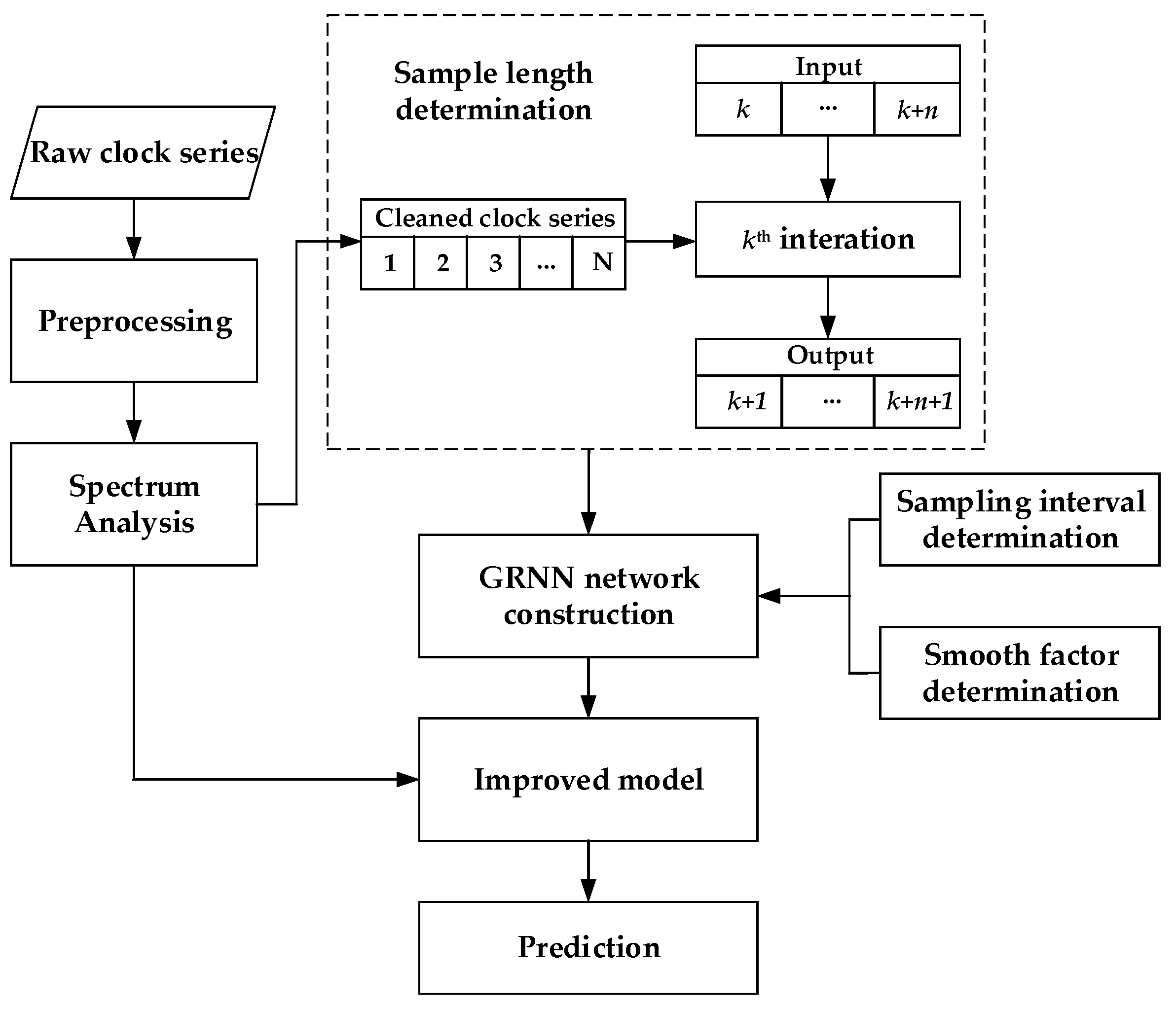
2.4. The Improved Model
3. Realization of the Improved Model
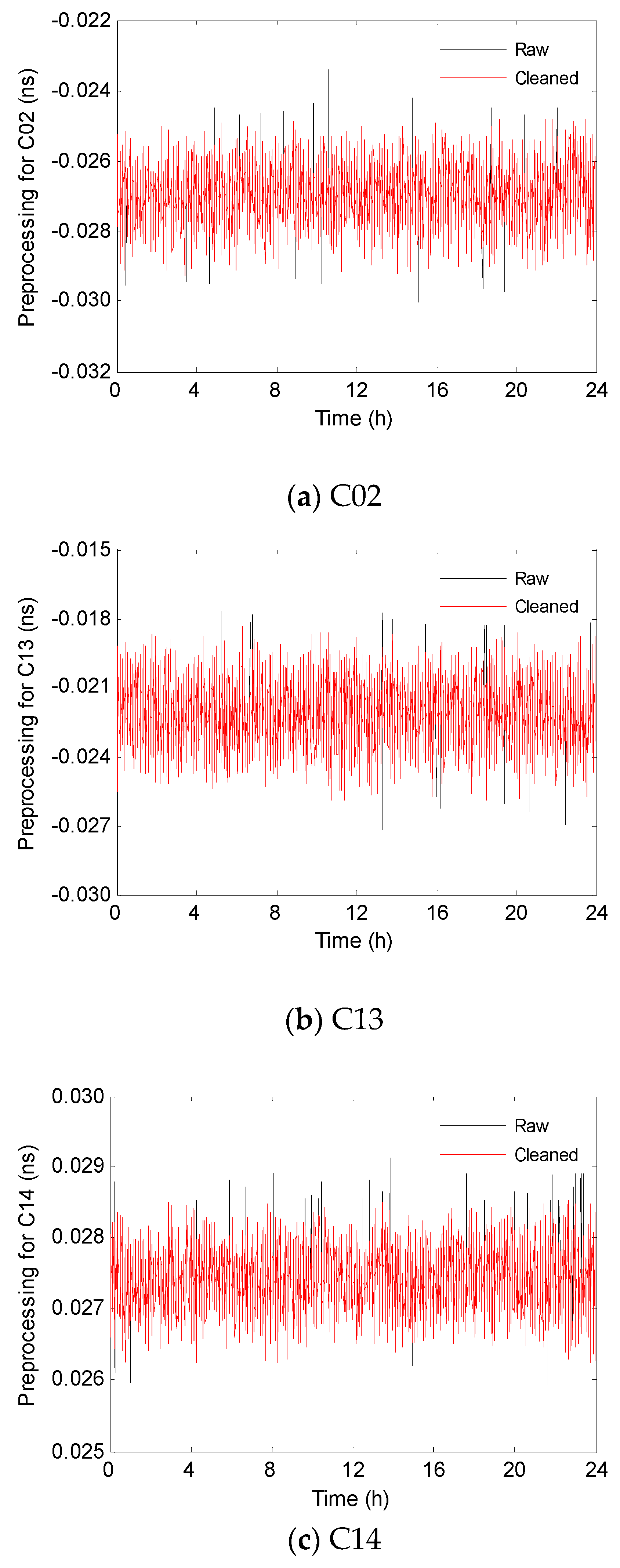
3.1. Preprocessing for Satellite Clock Offset
3.2. Determination of Periodic Terms
3.3. Impact of the Length of Input Data
3.4. Impact of the Sampling Interval of Input Data
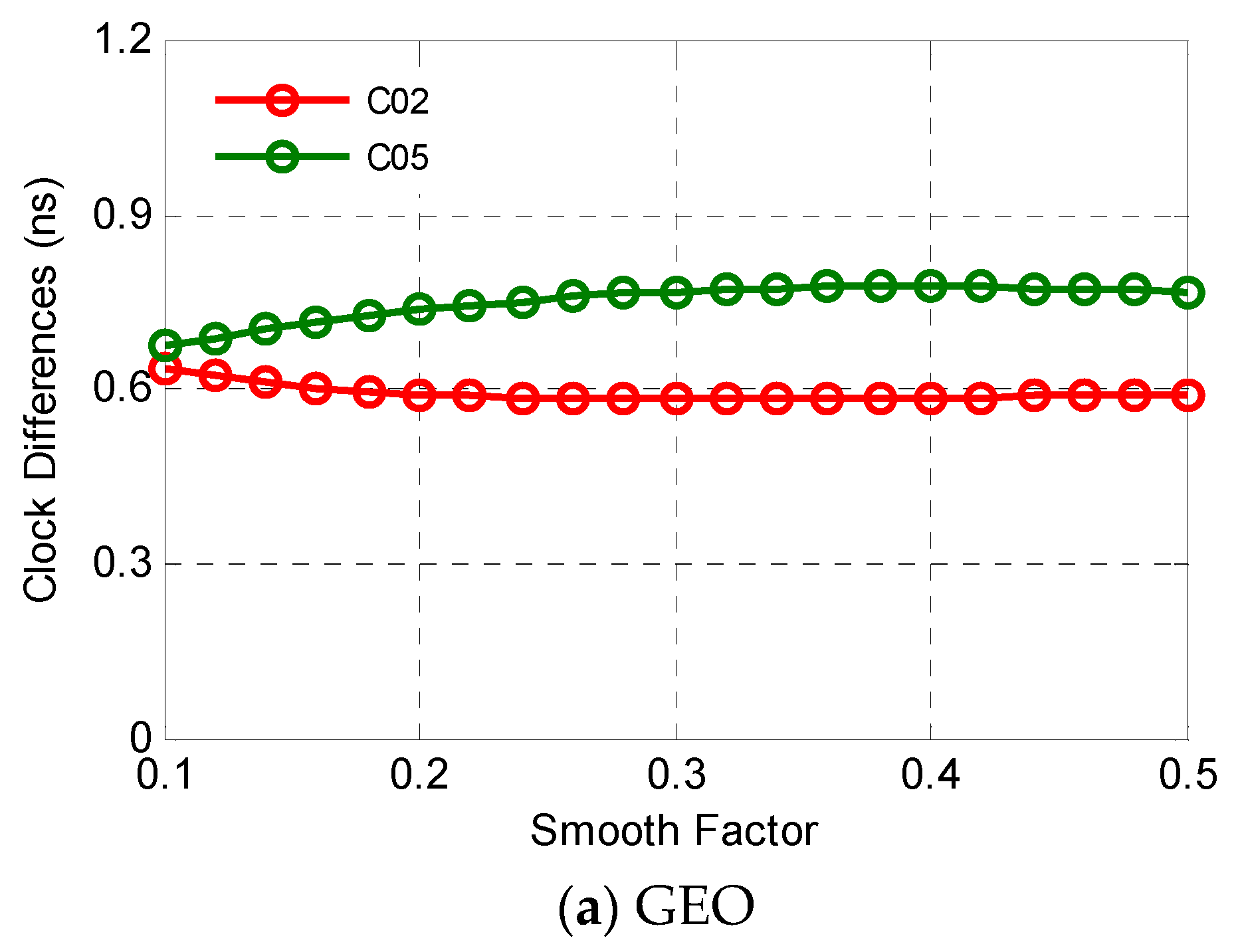
3.5. Determination of the Smooth Factor
4. Validation of the Predicted Clocks
4.1. Clock Comparison
4.2. PPP Validation
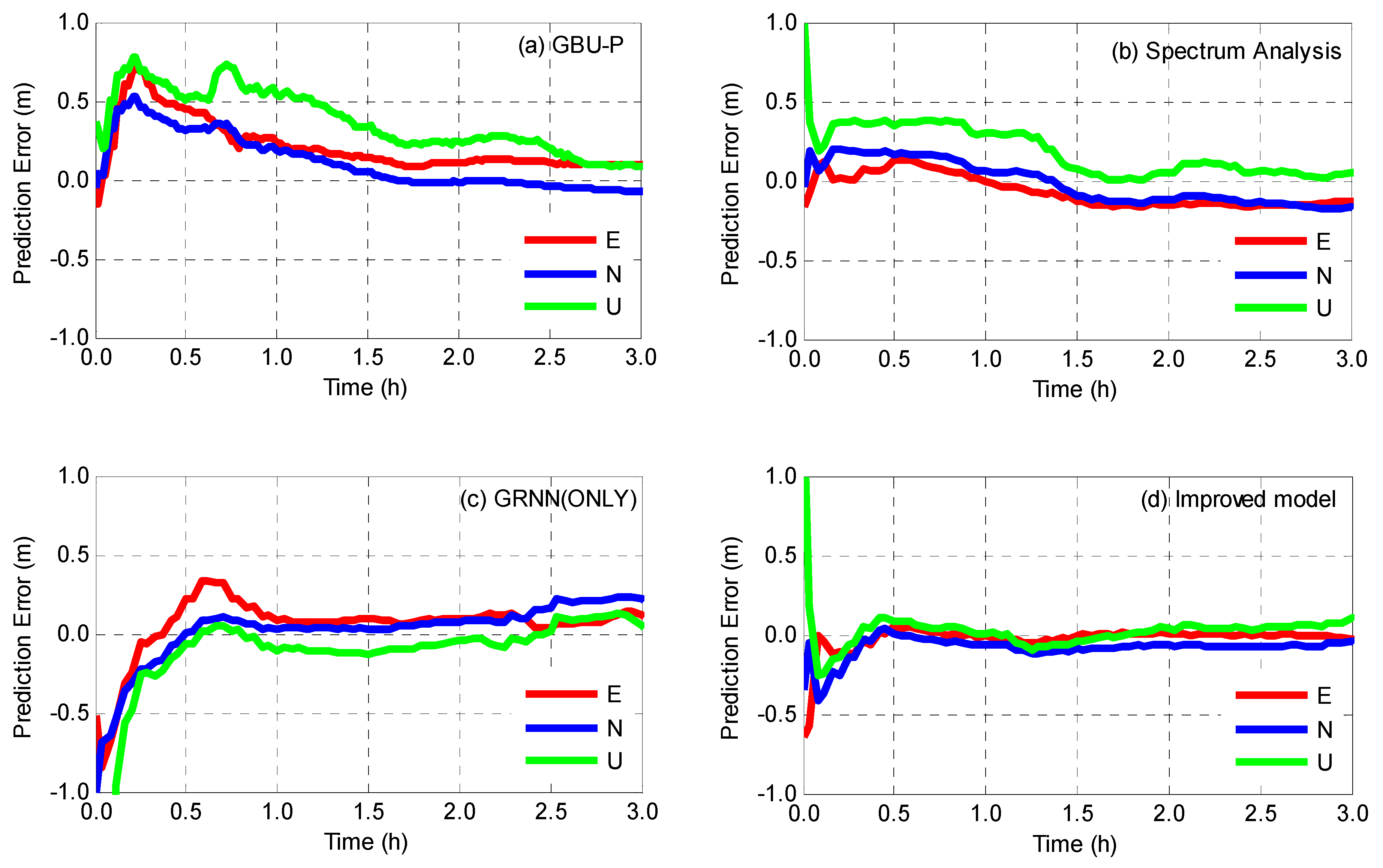
4.2.1. Static PPP Validation
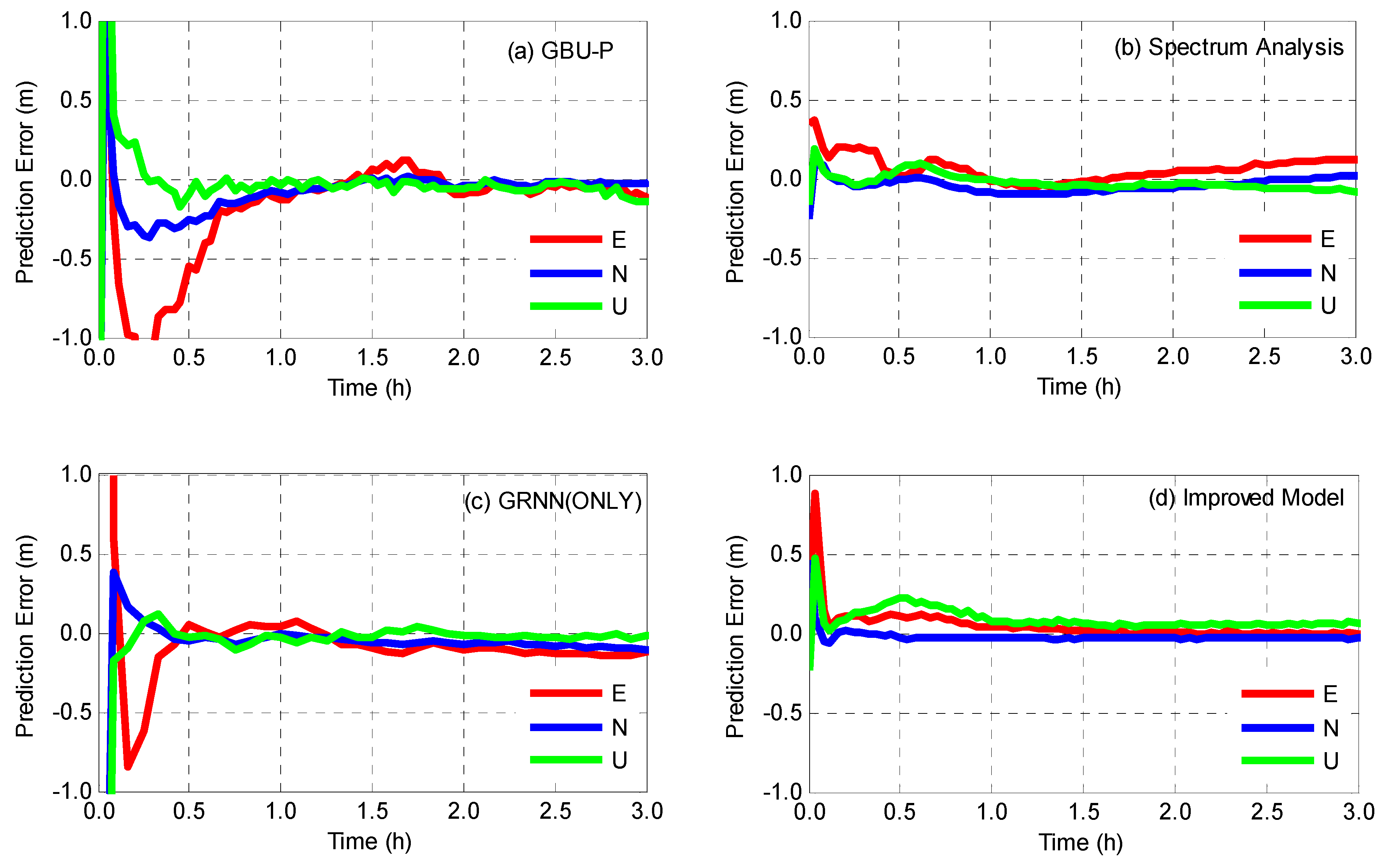
4.2.2. Kinematic PPP Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teferle, F.N.; Orliac, E.J.; Bingley, R.M. An assessment of Bernese GPS software precise point positioning using IGS final products for global site velocities. GPS Solut. 2007, 11, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Xu, Z.; Xu, X. Precise Point Positioning Using the Regional BeiDou Navigation Satellite Constellation. J. Navig. 2014, 67, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.R.; Chen, J.P.; Dousa, J.; Gendt, G.; Wickert, J. A computationally efficient approach for estimating high-rate satellite clock corrections in realtime. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L. The multi GNSS experiment (MGEX) of the international GNSS service (IGS)—Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; A Guide to Using International GNSS Service (IGS) Products. Taken from IGS Website. Available online: https://kb.igs.org/hc/en-us/articles/201271873-A-Guide-to-Using-the-IGS-Products (accessed on 25 January 2017).
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Hu, Z.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Initial results of precise orbit and clock determination for compass navigation satellite system. J. Geodesy 2013, 87, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O. Orbit and clock analysis of Compass GEO and IGSO satellites. J. Geodesy 2013, 87, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Ge, M.; Wang, J.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Experimental study on the precise orbit determination of the beidou navigation satellite system. Sensors 2013, 13, 2911–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Gao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Xu, C. Evaluation and analysis of real-time precise orbits and clocks products from different IGS analysis centers. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 2942–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P. Short-term analysis of GNSS clocks. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Dai, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J. Improved short-term clock prediction method for real-time positioning. Sensors 2017, 17, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.W.; Cui, B.B.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, W.J.; Li, P.L. An Improved Predicted Model for BDS Ultra-Rapid Satellite Clock Offsets. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, W.A. Time and frequency (Time-Domain) Characterization, Estimation, and Prediction of Precision Clocks and Oscillators. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1987, UFFC-34, 647–654. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, Y.J.; Cho, J. Improving prediction accuracy of GPS satellite clocks with periodic variation behavior. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 073001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucca, C.; Tavella, P. A mathematical model for the atomic clock error in case of jumps. Metrologia 2015, 52, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Navigation satellite clock error prediction based on functional network. Neural Process. Lett. 2013, 38, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.C.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, R.P. Fusion-based Satellite Clock Bias Prediction Considering Characteristics and Fitted Residue. J. Navig. 2018, 71, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackman, C. Accuracy/precision of USNO predicted clock estimates for GPS satellites. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual PTTI Systems and Applications Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 26–29 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- El-Mowafy, A.; Deo, M.; Kubo, N. Maintaining real-time precise point positioning during outages of orbit and clock corrections. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadas, T.; Bosy, J. IGS RTS precise orbits and clocks verification and quality degradation over time. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.W.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, G.C. Real-time clock offset prediction with an improved model. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, K.L.; Ray, J.R.; Beard, R.L. Characterization of periodic variations in the GPS satellite clocks. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, M.; Freed, G. , Rajan, J. GPS IIR Rubidium Clocks: In-Orbit Performance Aspects; ITT Aerospace/Communications Div: Clifton, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Q.S.; Xu, T.H.; Li, J.J.; Xiong, H.W. The short-term forecast of BeiDou satellite clock bias based on wavelet neural network. In China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2016 Proceedings; Sun, J., Liu, J., Fan, S., Wang, F., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2016; Volume I, pp. 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Qu, Y. Improving prediction performance of GPS satellite clock bias based on wavelet neural network. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O.; Sleewaegen, J.M.; Huisman, L.; Teunissen, P.J. Characterization of COMPASS M-1 signals. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, D.F. A general regression neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1991, 2, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Lou, Y.; Liu, J. Analysis of BDS satellite clocks in orbit. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, M.T.; Chen, A.S.; Daouk, H. Forecasting exchange rates using general regression neural networks. Comput. Oper. Res. 2000, 27, 1093–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leys, C.; Ley, C.; Klein, O.; Bernard, P.; Licata, L. Detecting outliers: Do not use standard deviation around the mean, use absolute deviation around the median. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2013, 49, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ge, M. PANDA software and its preliminary result of positioning and orbit determination. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2003, 8, 603–609. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Rothacher, M.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Resolution of GPS carrier-phase ambiguities in Precise Point Positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J. Geodesy 2008, 82, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
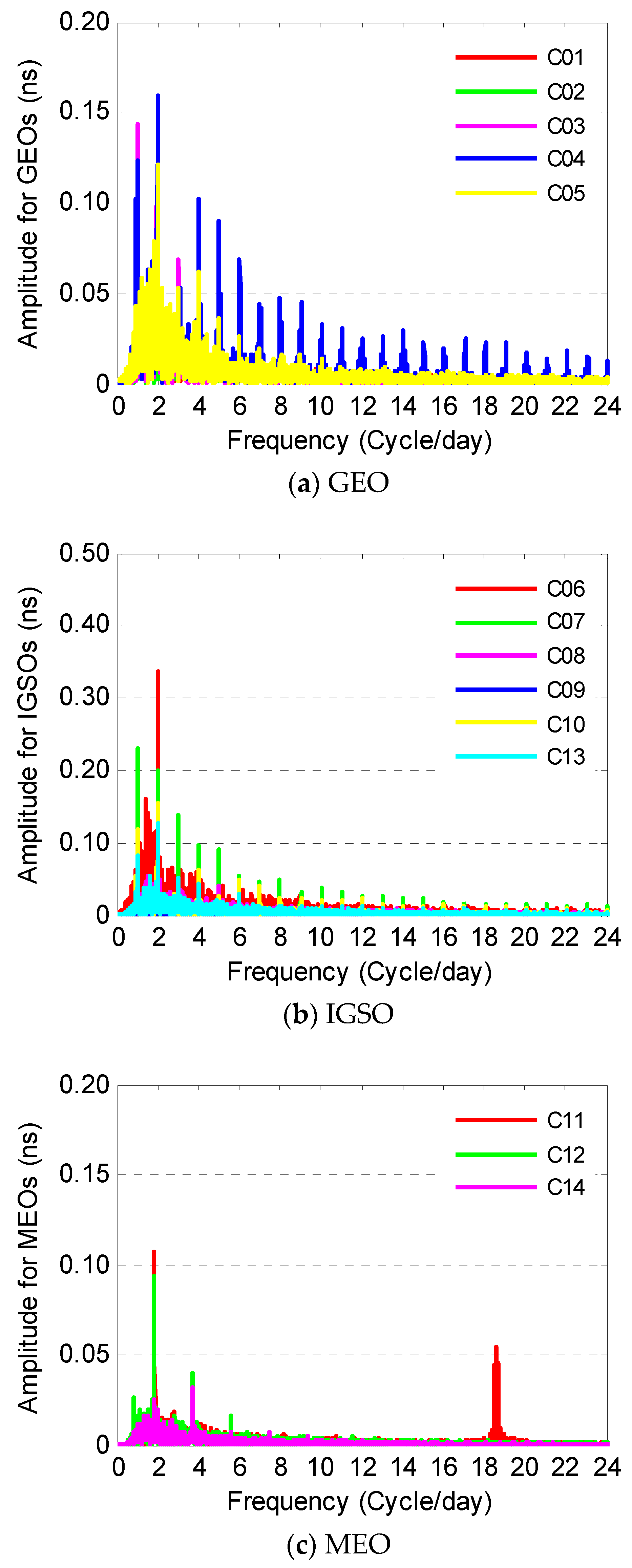
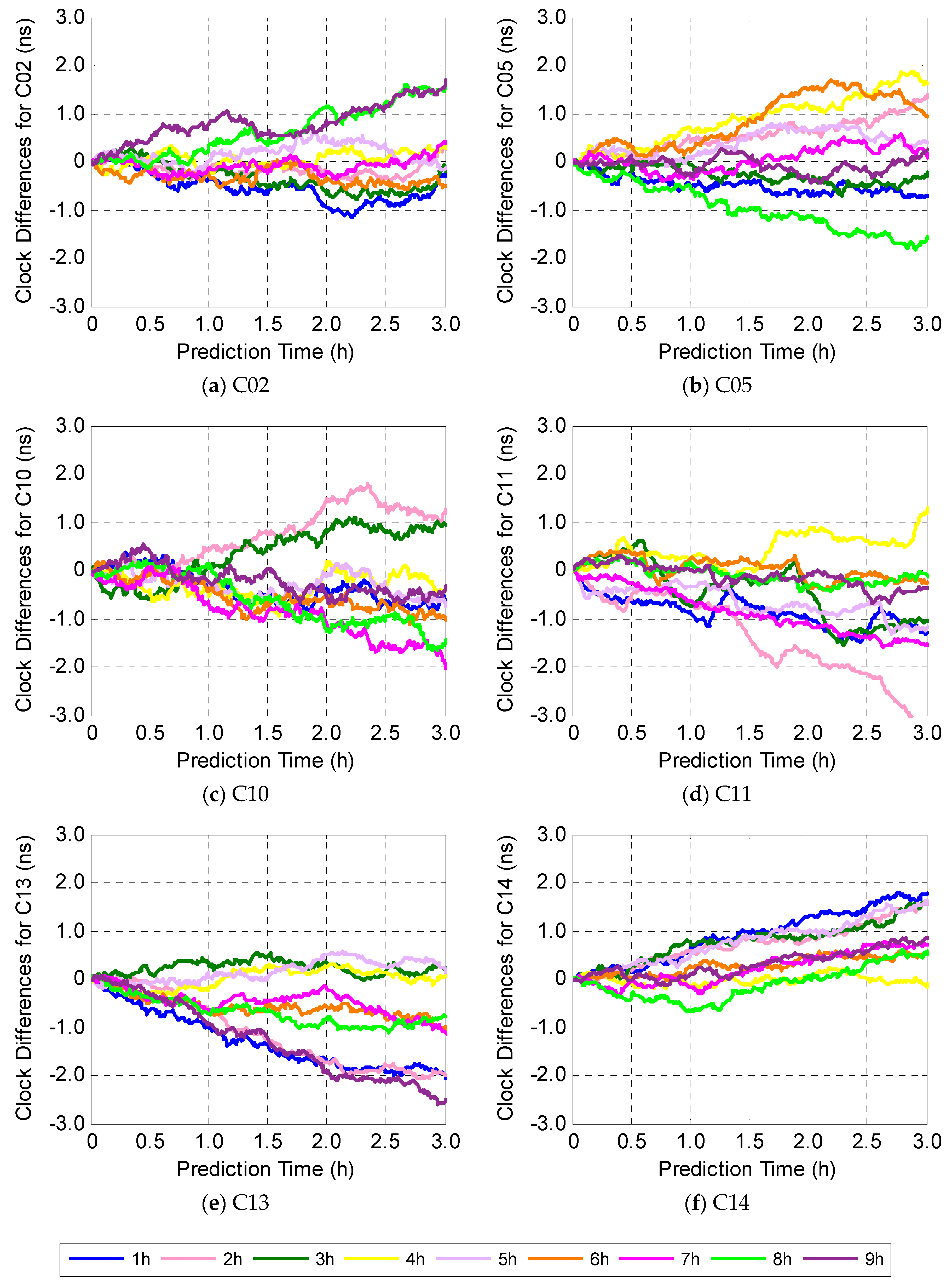
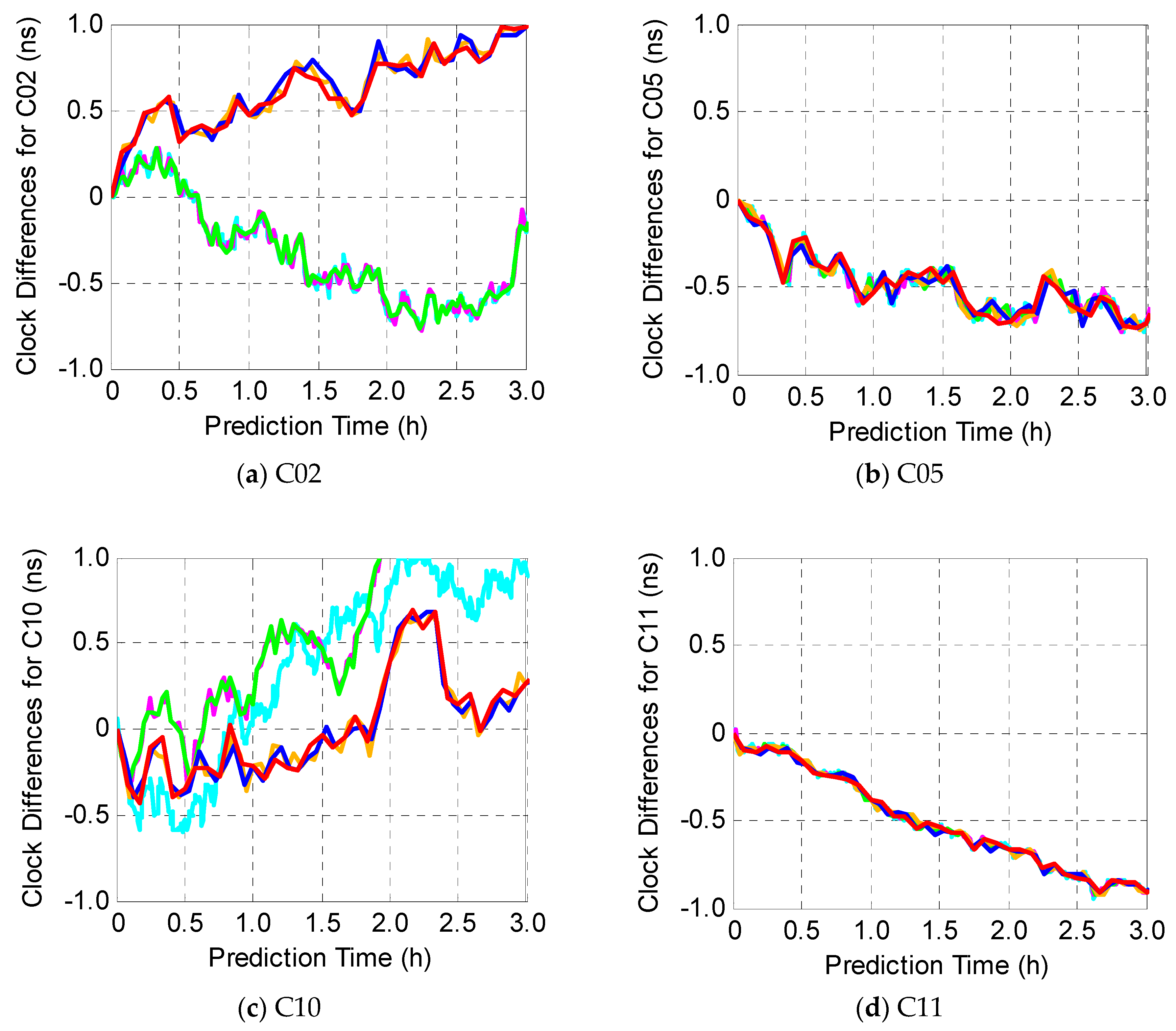
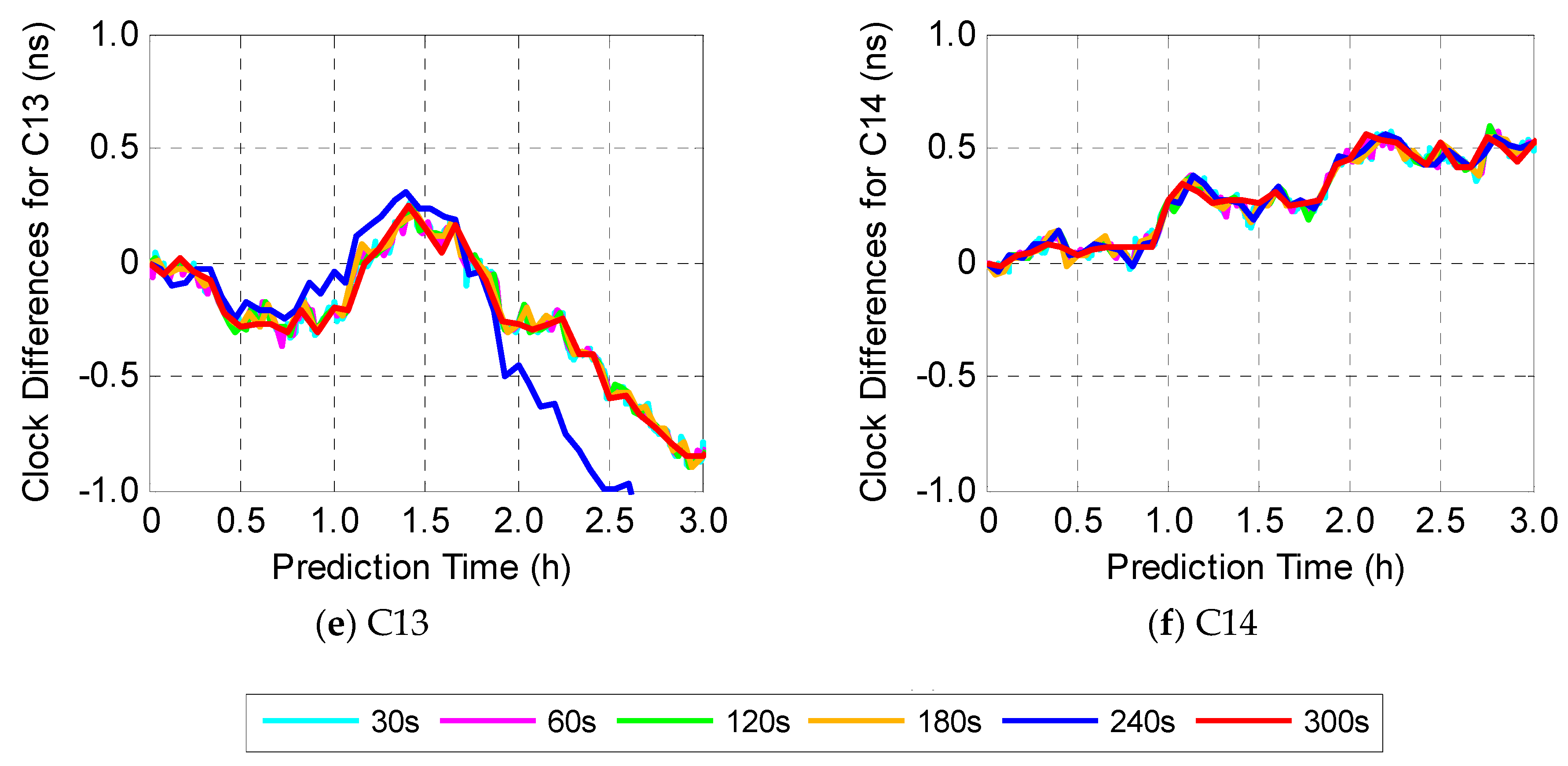



| Type | Satellite | Main Period (h) | Secondary Period (h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GEO | C01 | 5.9850 | 24.0059 |
| C02 | 7.9727 | 12.0029 | |
| C03 | 23.7449 | 11.8725 | |
| C04 | 11.9373 | 23.2397 | |
| C05 | 11.9700 | 5.9850 | |
| IGSO | C06 | 11.9373 | 23.6166 |
| C07 | 23.8747 | 11.9700 | |
| C08 | 11.9700 | 23.8747 | |
| C09 | 23.8747 | 11.9373 | |
| C10 | 11.9373 | 23.8747 | |
| C13 | 11.9700 | 23.8747 | |
| MEO | C11 | 12.8125 | 1.2922 |
| C12 | 12.8502 | 6.4157 | |
| C14 | 6.4063 | 12.8125 |
| Type | Satellite | Smooth Factor |
|---|---|---|
| GEO | C01 | 0.10 |
| C02 | 0.26 | |
| C03 | 0.10 | |
| C04 | 0.10 | |
| C05 | 0.10 | |
| IGSO | C06 | 0.10 |
| C07 | 0.50 | |
| C08 | 0.38 | |
| C09 | 0.10 | |
| C10 | 0.10 | |
| C13 | 0.10 | |
| MEO | C11 | 0.26 |
| C12 | 0.50 | |
| C14 | 0.20 |
| Prediction Time (h) | GBU-P (ns) | SA (ns)1 | GRNN (ns) | IM (ns) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 1.541 | 1.486 | 0.429 | 0.412 |
| 1.0 | 1.631 | 1.523 | 0.513 | 0.437 |
| 2.0 | 2.226 | 1.946 | 0.915 | 0.505 |
| 3.0 | 3.051 | 2.512 | 1.578 | 0.841 |
| Solutions | Setting |
|---|---|
| Software used | PANDA |
| Tracking stations | Eight stations in Asia-Pacific Area |
| Observations | Ionospheric-free linear combination |
| Sample rate | 30 s |
| Elevation cutoff angle | 7° |
| Weight | Elevation dependent |
| Orbit | GFZ ultra-rapid orbit |
| Trop zenith delay | Initial model (Global Mapping Function) and random walk |
| Phase windup | Phase windup correction |
| Earth tides correction | Solid |
| Earth Rotation Parameters | Products by GFZ |
| Differential code biases | Products by CODE |
| Receiver clock | White noise parameter |
| Ambiguity | Real constants |
| Parameter estimator | Least square method and Kalman Filter |
| Station | E (m) | N (m) | U (m) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GBU-P | SA1 | GRNN | IM1 | GBU-P | SA1 | GRNN | IM1 | GBU-P | SA1 | GRNN | IM 1 | |
| CEDU | 0.132 | 0.130 | 0.103 | 0.094 | 0.120 | 0.122 | 0.110 | 0.092 | 0.147 | 0.144 | 0.135 | 0.130 |
| COCO | 0.135 | 0.133 | 0.110 | 0.083 | 0.132 | 0.131 | 0.132 | 0.086 | 0.184 | 0.190 | 0.175 | 0.162 |
| DARW | 0.097 | 0.089 | 0.092 | 0.084 | 0.095 | 0.107 | 0.099 | 0.076 | 0.115 | 0.082 | 0.088 | 0.095 |
| HKSL | 0.152 | 0.153 | 0.122 | 0.092 | 0.150 | 0.132 | 0.132 | 0.114 | 0.192 | 0.139 | 0.140 | 0.120 |
| IISC | 0.188 | 0.173 | 0.133 | 0.116 | 0.122 | 0.113 | 0.111 | 0.083 | 0.181 | 0.185 | 0.174 | 0.116 |
| KRGG | 0.150 | 0.138 | 0.108 | 0.105 | 0.162 | 0.151 | 0.136 | 0.112 | 0.166 | 0.154 | 0.133 | 0.101 |
| LHAZ | 0.183 | 0.167 | 0.170 | 0.112 | 0.168 | 0.120 | 0.109 | 0.098 | 0.325 | 0.241 | 0.201 | 0.186 |
| MRO1 | 0.132 | 0.125 | 0.118 | 0.098 | 0.120 | 0.121 | 0.094 | 0.088 | 0.172 | 0.146 | 0.133 | 0.135 |
| Method | DARW | MRO1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E (m) | N (m) | U (m) | E (m) | N (m) | U (m) | |
| GBU-P | 0.131 | 0.127 | 0.176 | 0.140 | 0.135 | 0.161 |
| SA 1 | 0.119 | 0.113 | 0.153 | 0.129 | 0.118 | 0.153 |
| GRNN | 0.117 | 0.110 | 0.142 | 0.123 | 0.109 | 0.149 |
| IM 1 | 0.112 | 0.095 | 0.125 | 0.118 | 0.110 | 0.140 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, L.; Zhou, H.; Wen, Y.; He, X. Improving Short Term Clock Prediction for BDS-2 Real-Time Precise Point Positioning. Sensors 2019, 19, 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122762
He L, Zhou H, Wen Y, He X. Improving Short Term Clock Prediction for BDS-2 Real-Time Precise Point Positioning. Sensors. 2019; 19(12):2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122762
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Lina, Hairui Zhou, Yuanlan Wen, and Xiufeng He. 2019. "Improving Short Term Clock Prediction for BDS-2 Real-Time Precise Point Positioning" Sensors 19, no. 12: 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122762
APA StyleHe, L., Zhou, H., Wen, Y., & He, X. (2019). Improving Short Term Clock Prediction for BDS-2 Real-Time Precise Point Positioning. Sensors, 19(12), 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122762




