A Possible Way for the Detection and Identification of Dangerous Substances in Ternary Mixtures Using THz Pulsed Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
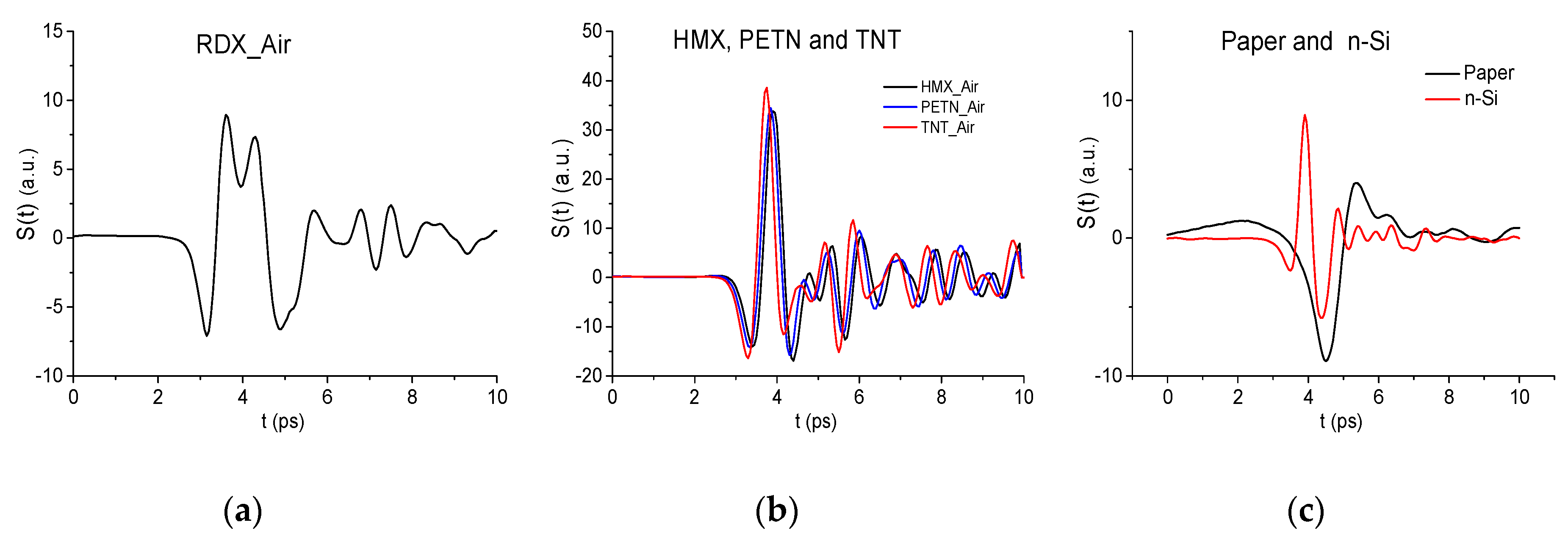
2. Identification of Ternary Mixtures of Explosives in Reflection Mode
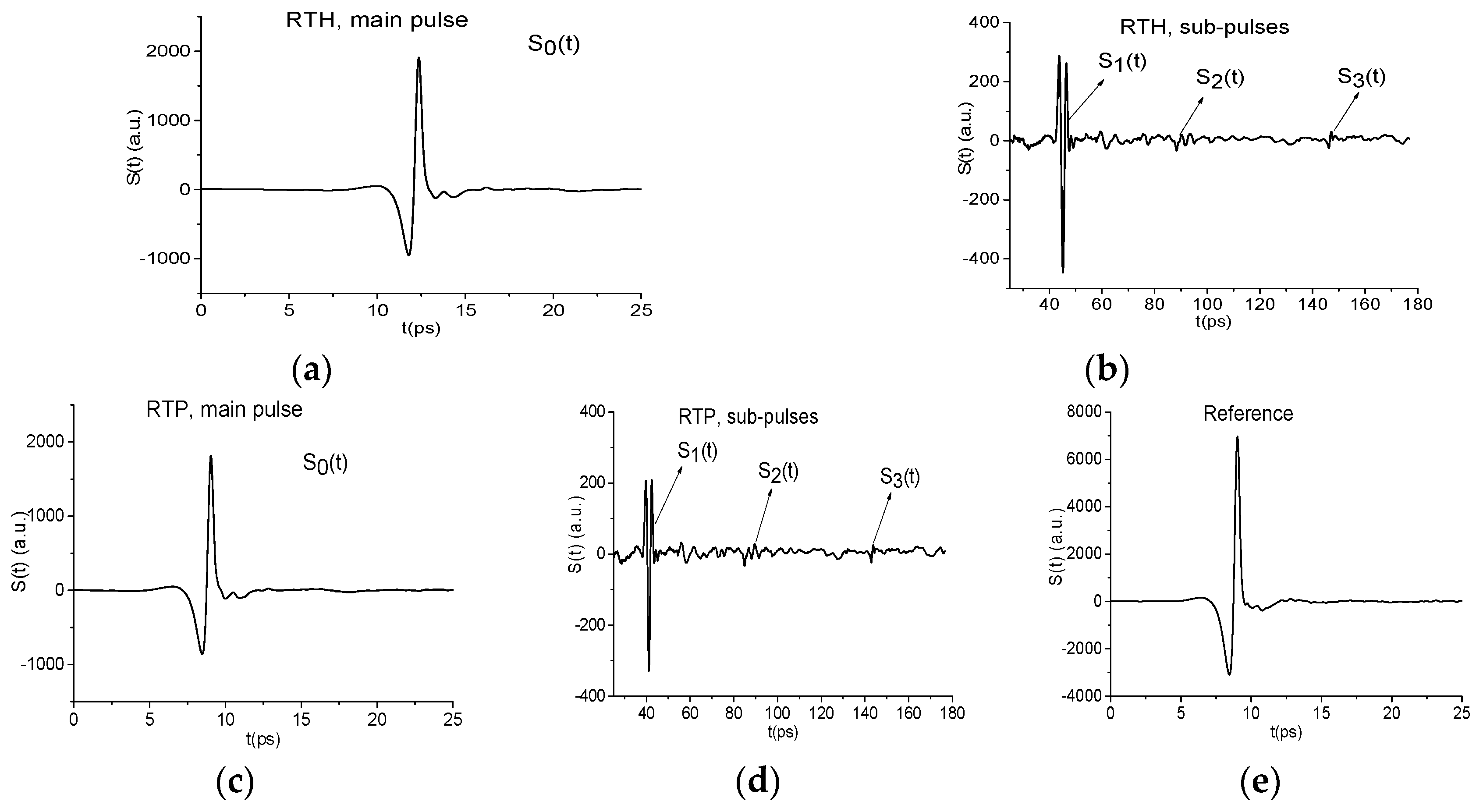
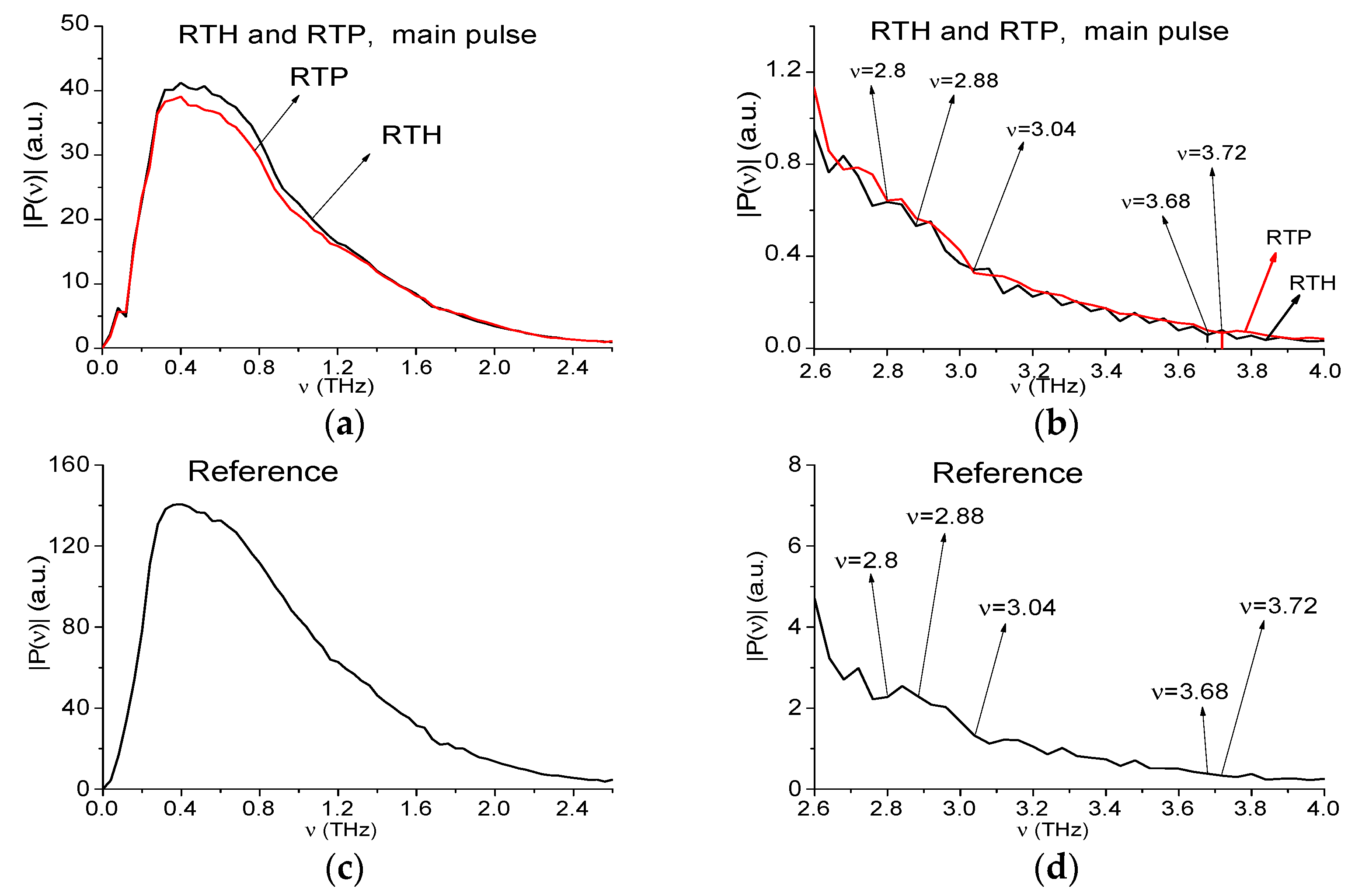
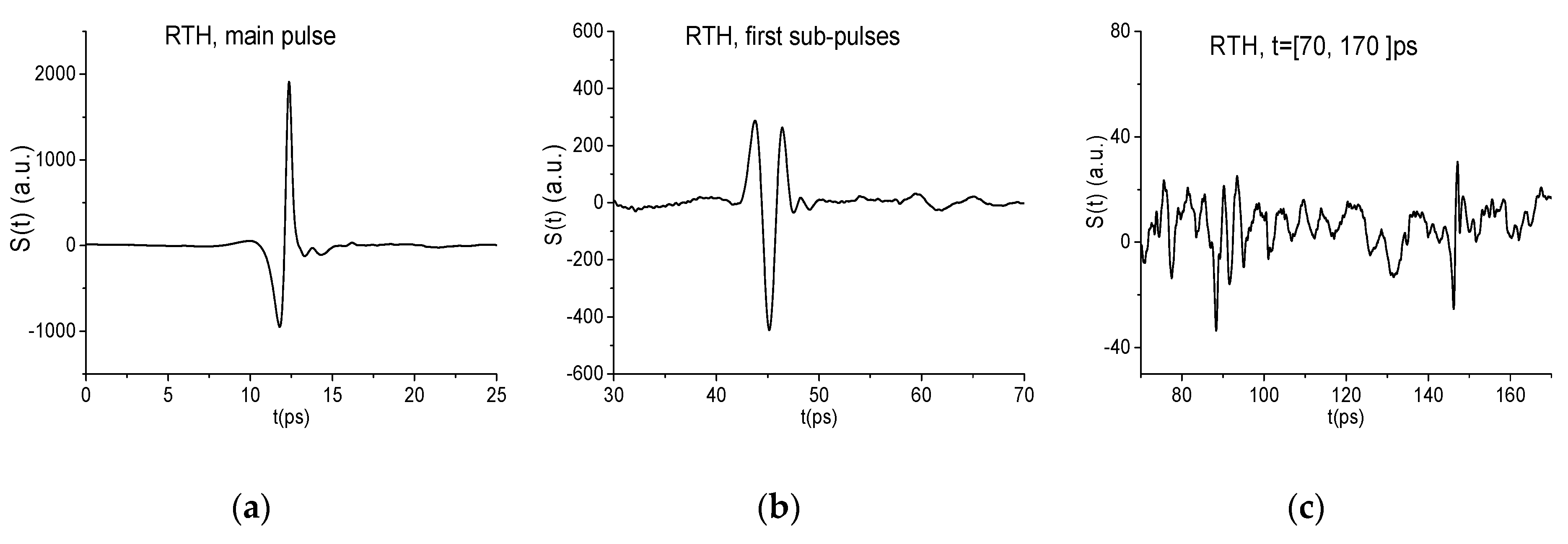
2.1. Temporal Structure of the Reflected Signals RTH, RTP and Spectra of Their Main Pulses
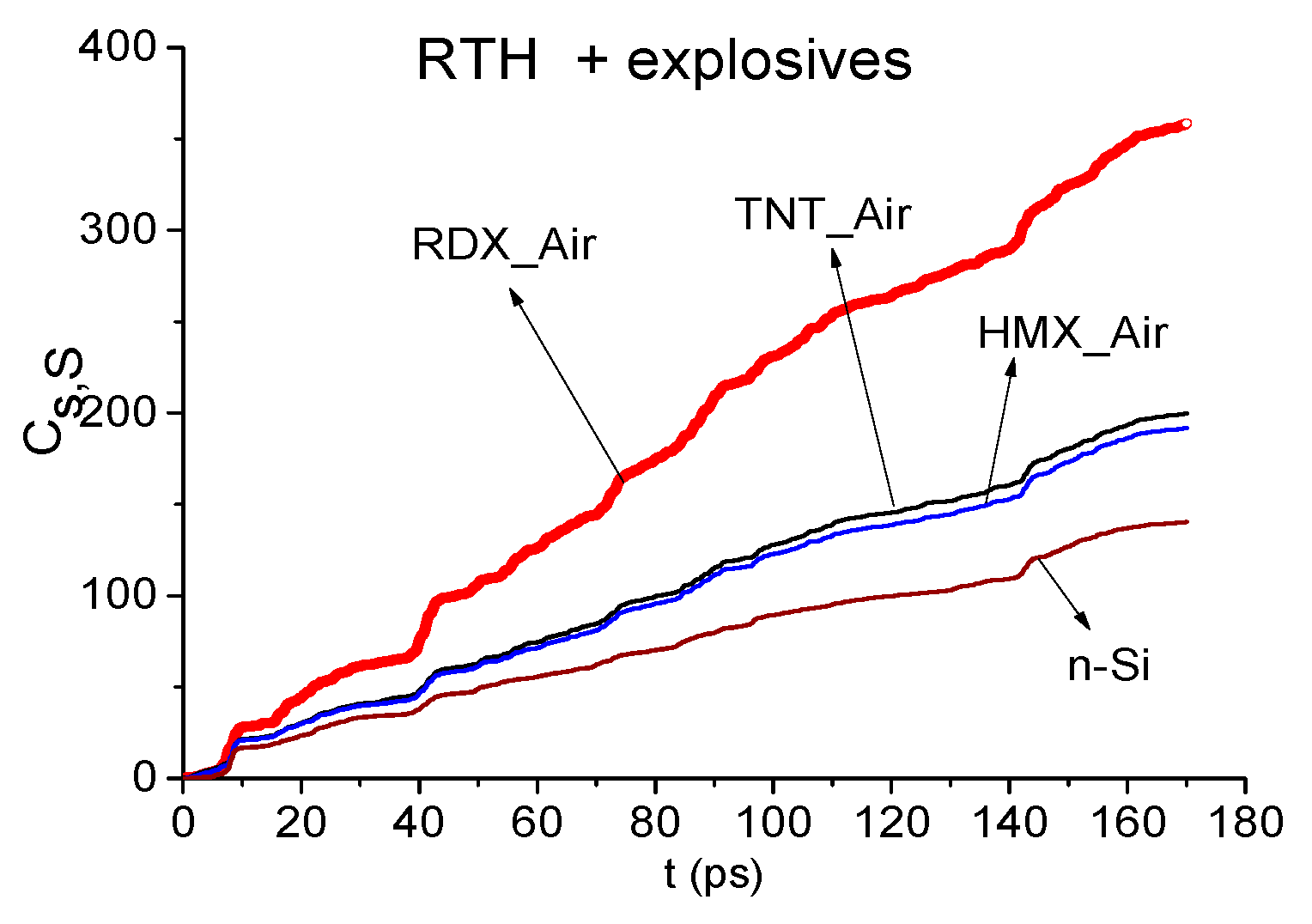
2.2. Brief Overview of Integral Correlation Criteria and the SDA-Method
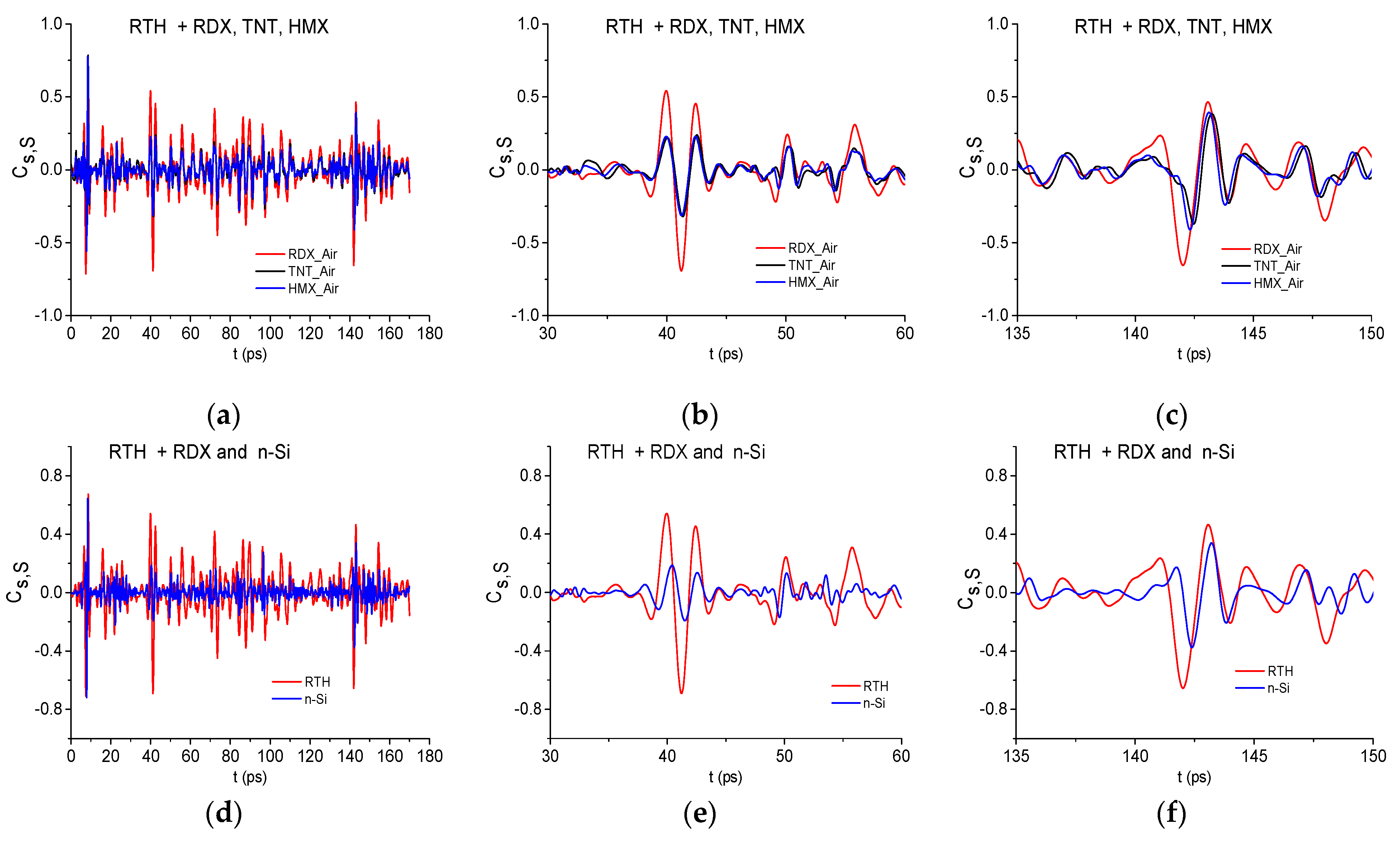
2.3. Time-Dependent Analysis of the Similarity between the RTH Signal and the Standard THz Signals
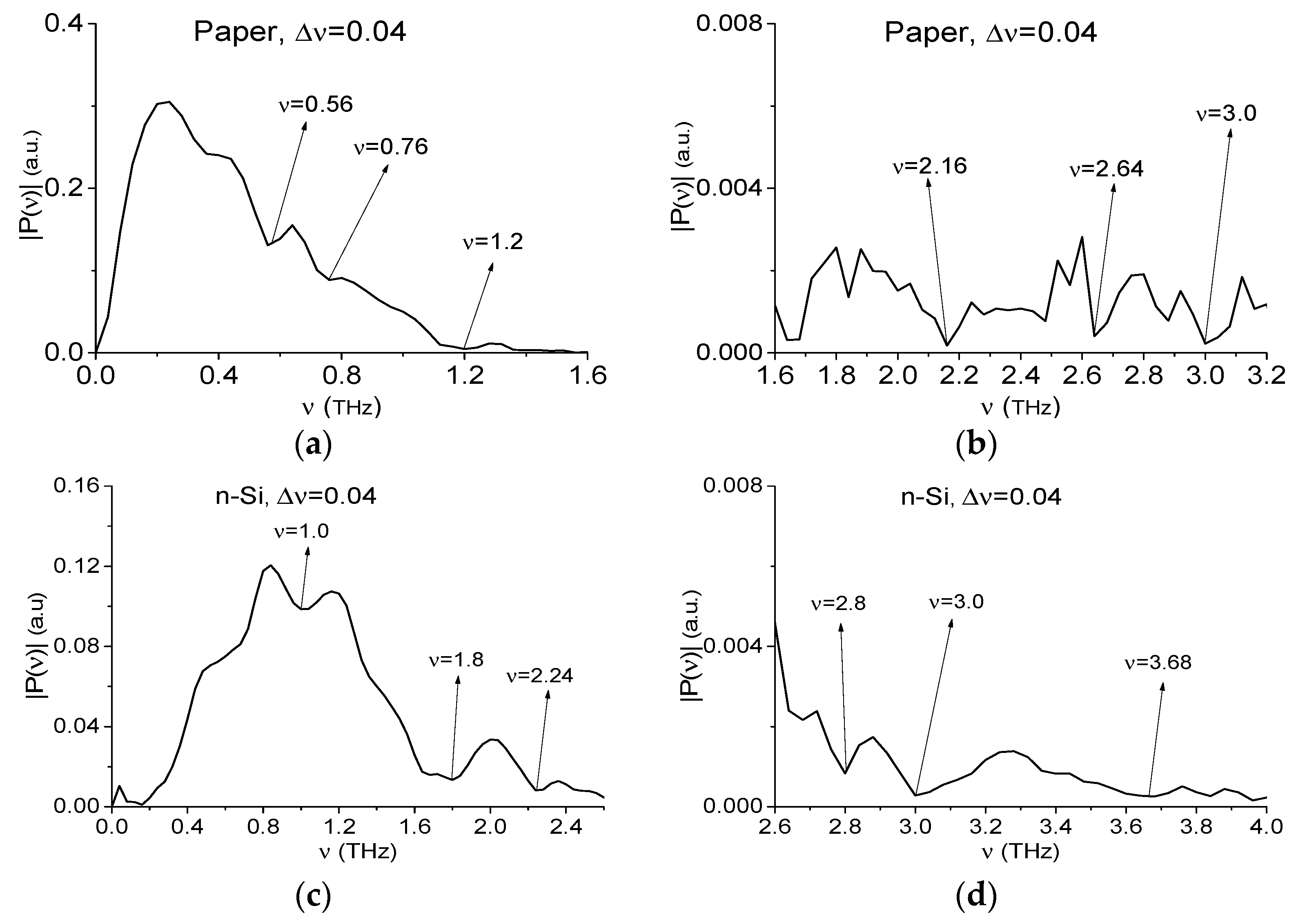
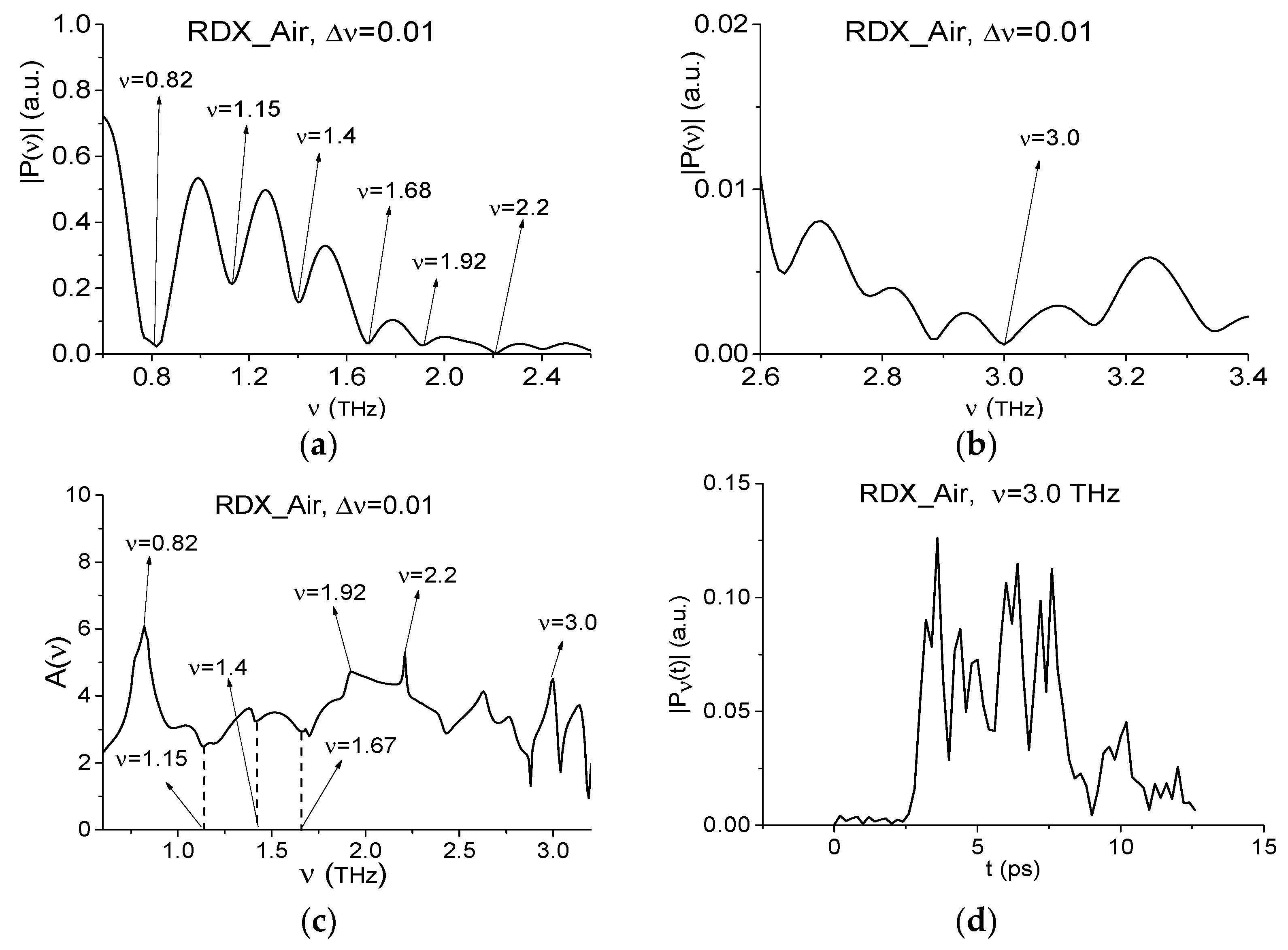
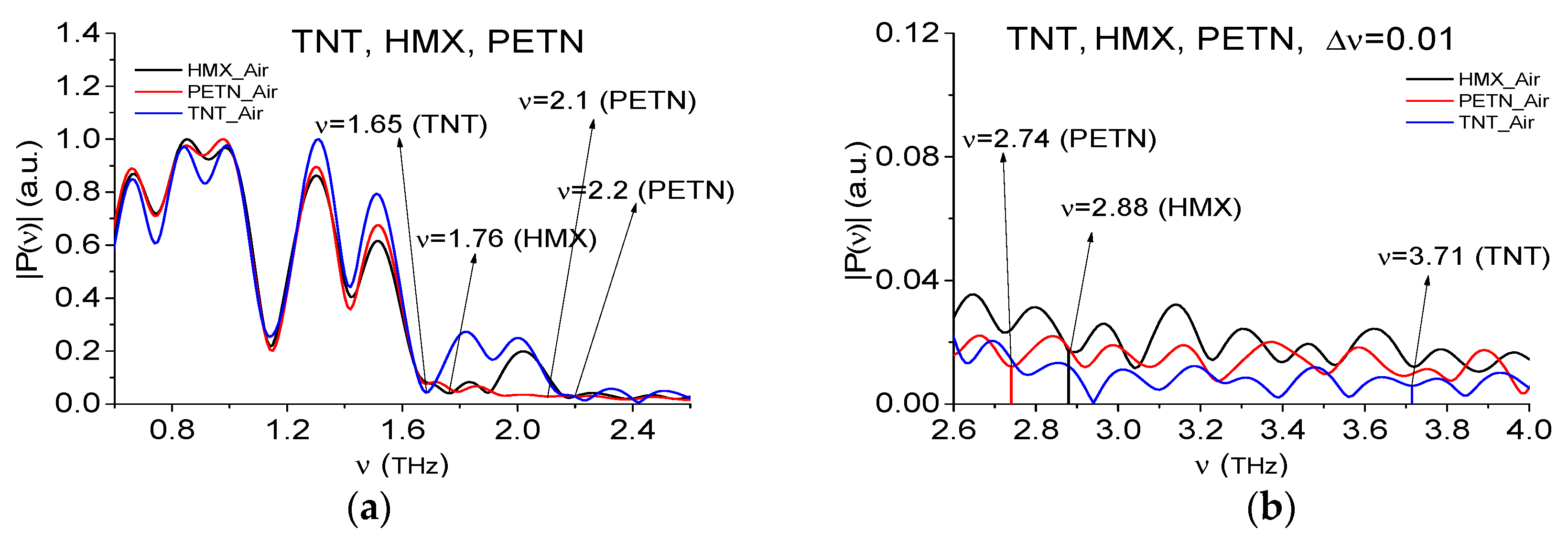
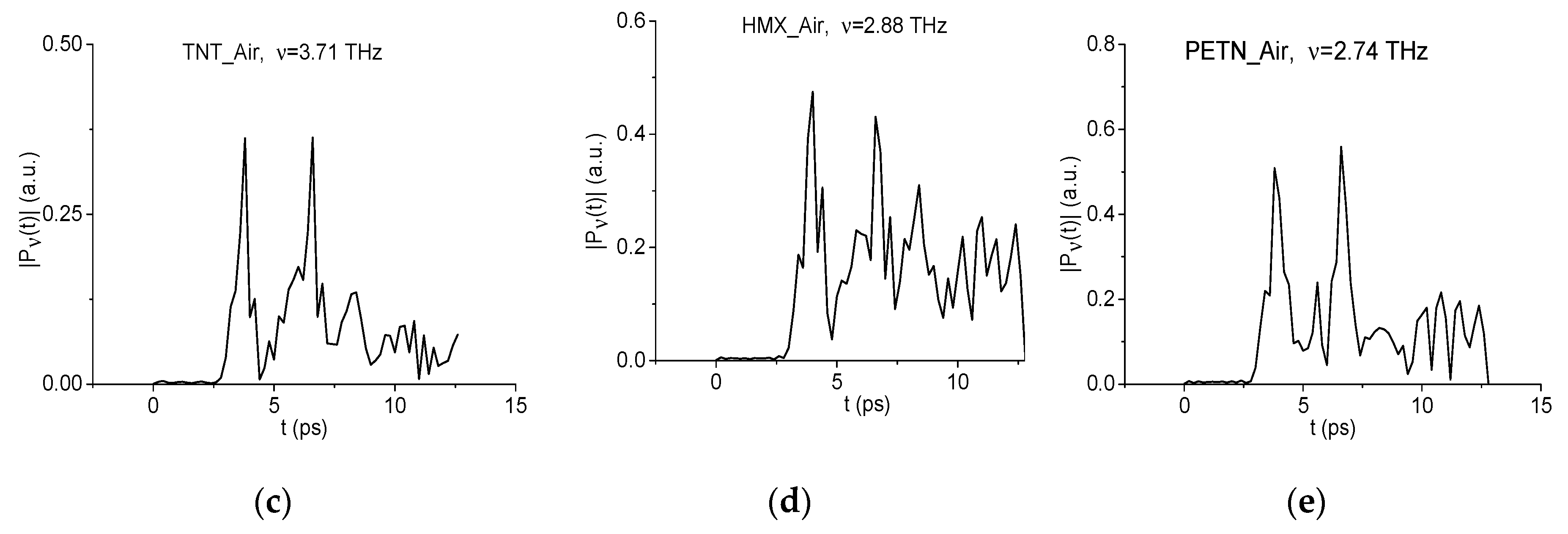
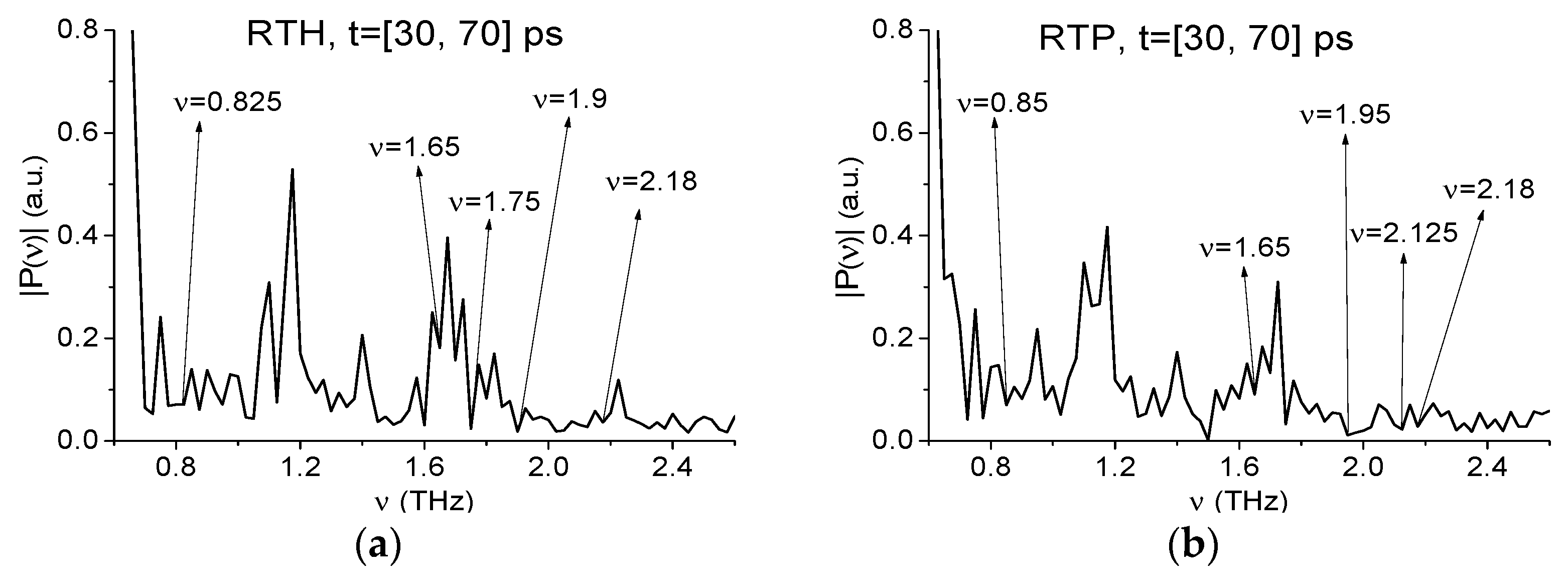
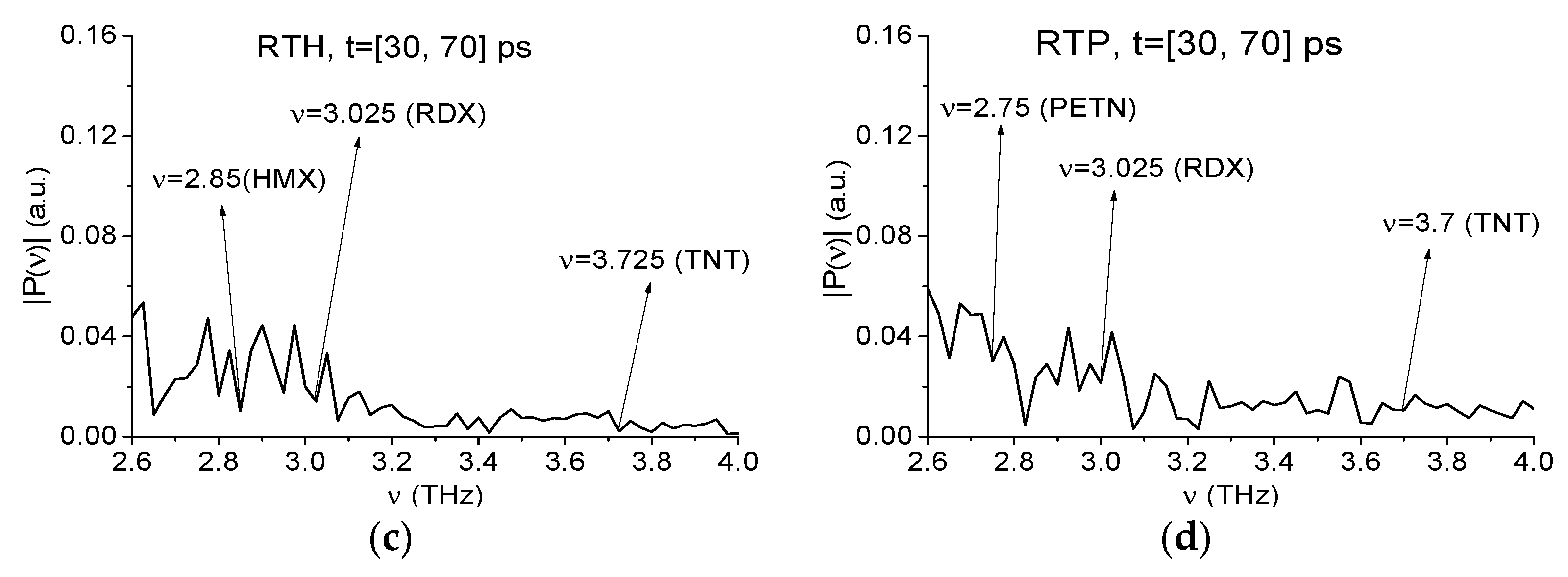
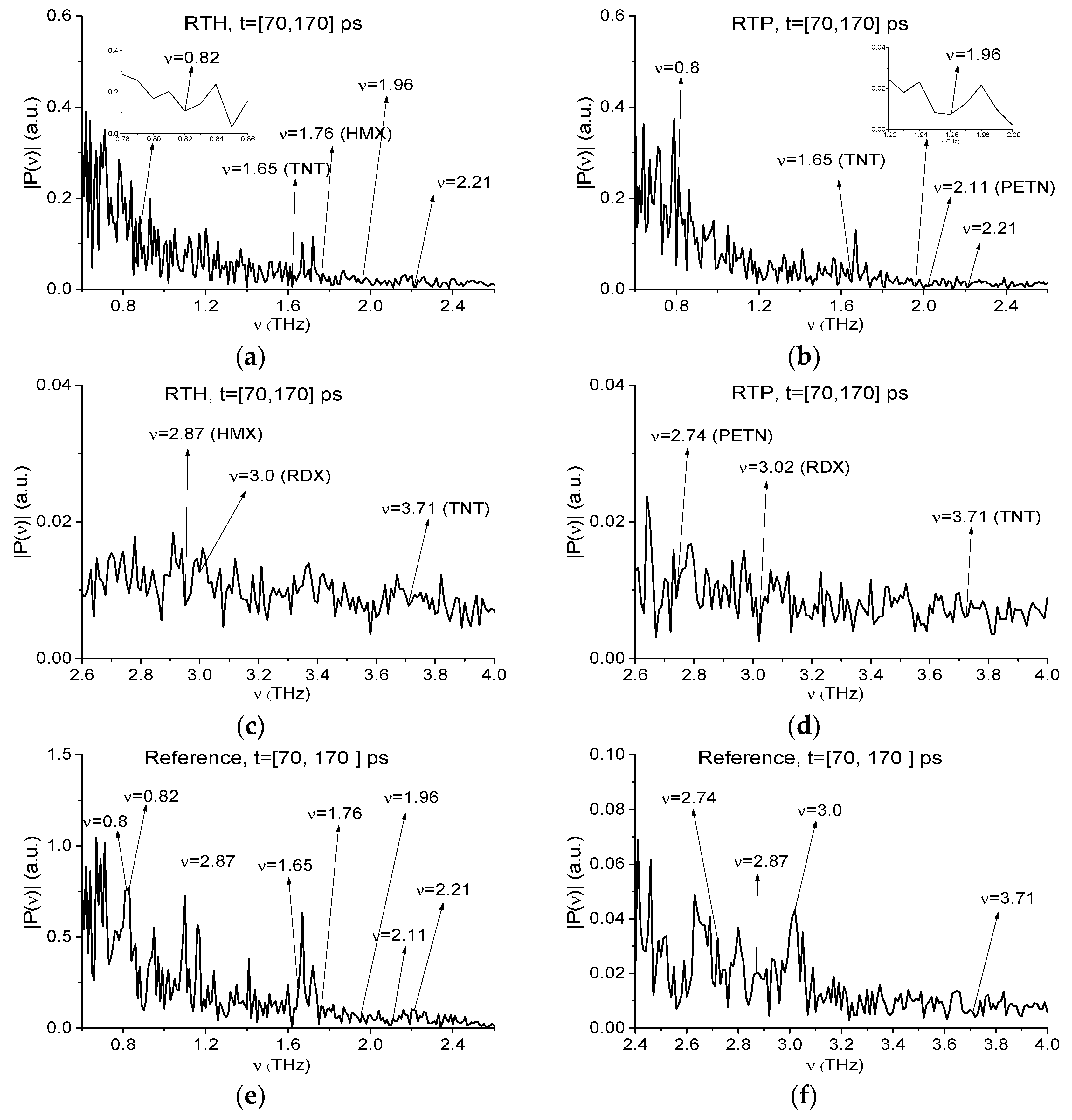
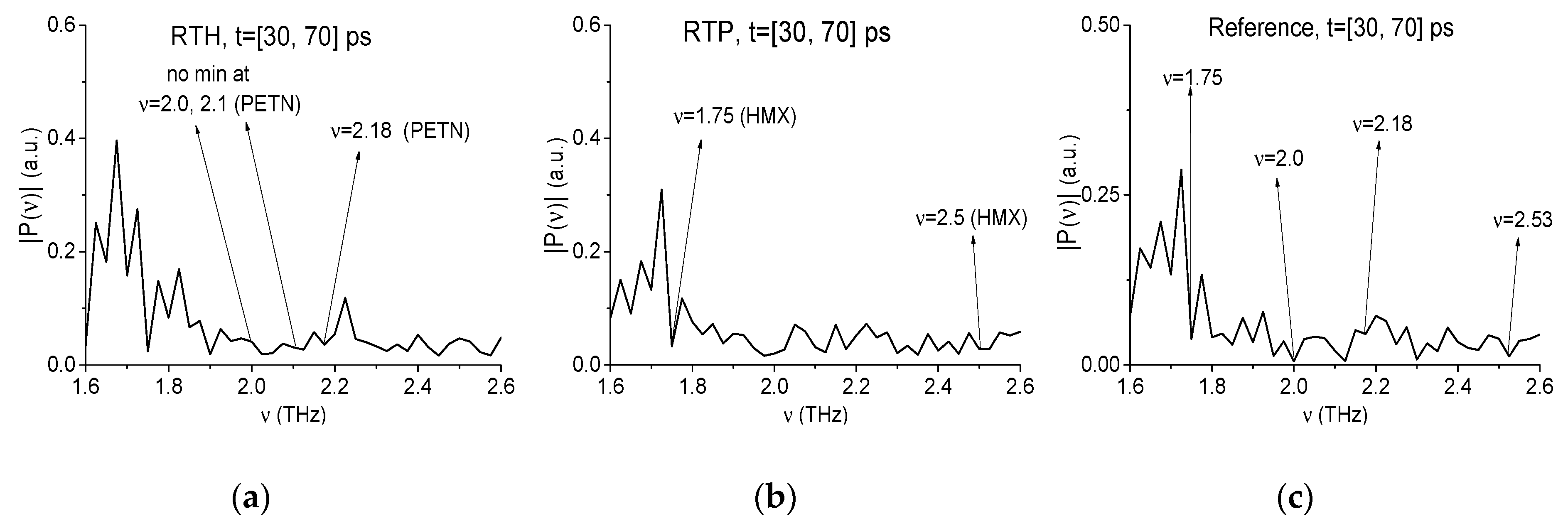
2.4. Absorption Frequencies of the Standard THz Signals
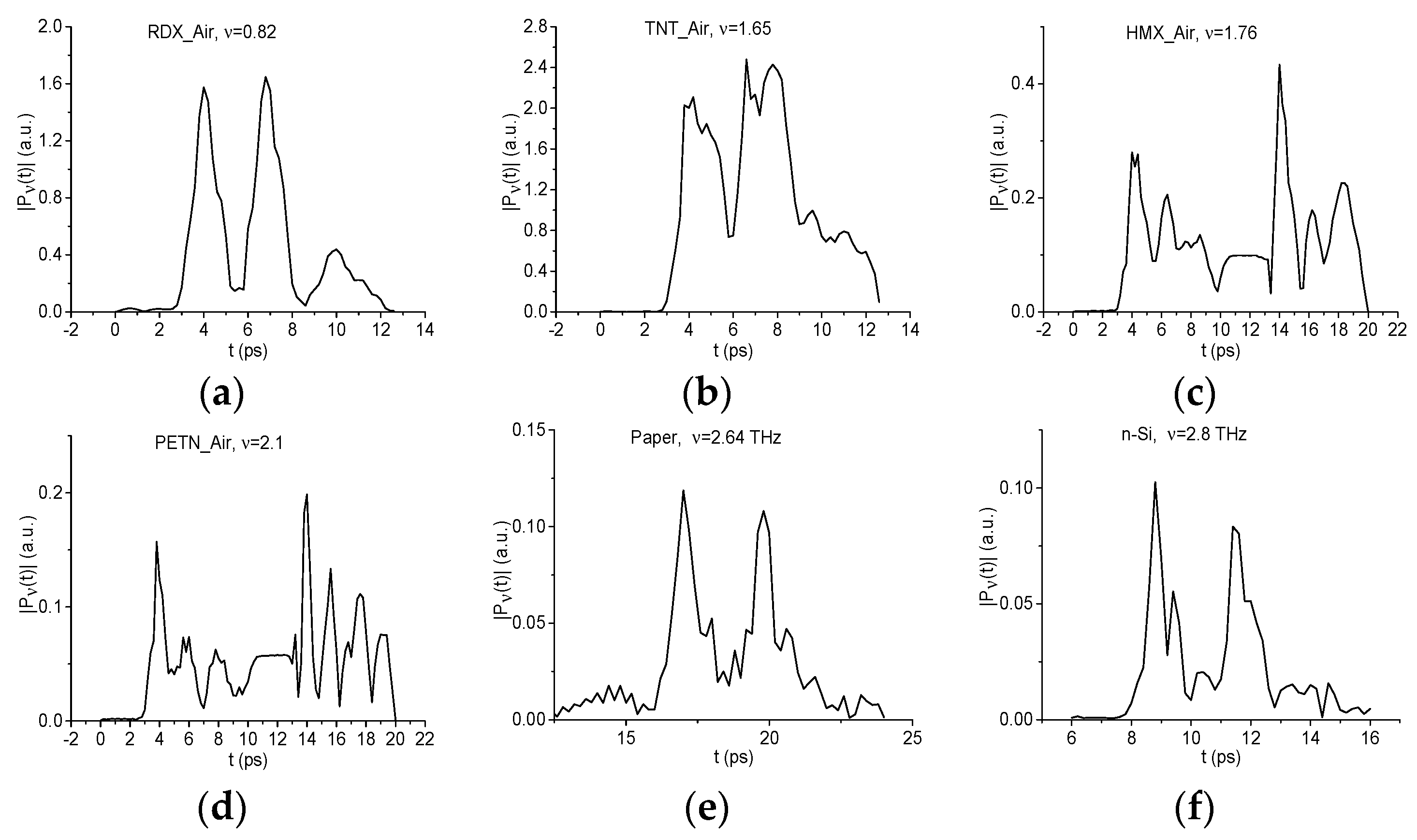
2.5. Similarity of the Spectral Line Dynamics Shape for the Standard Signals
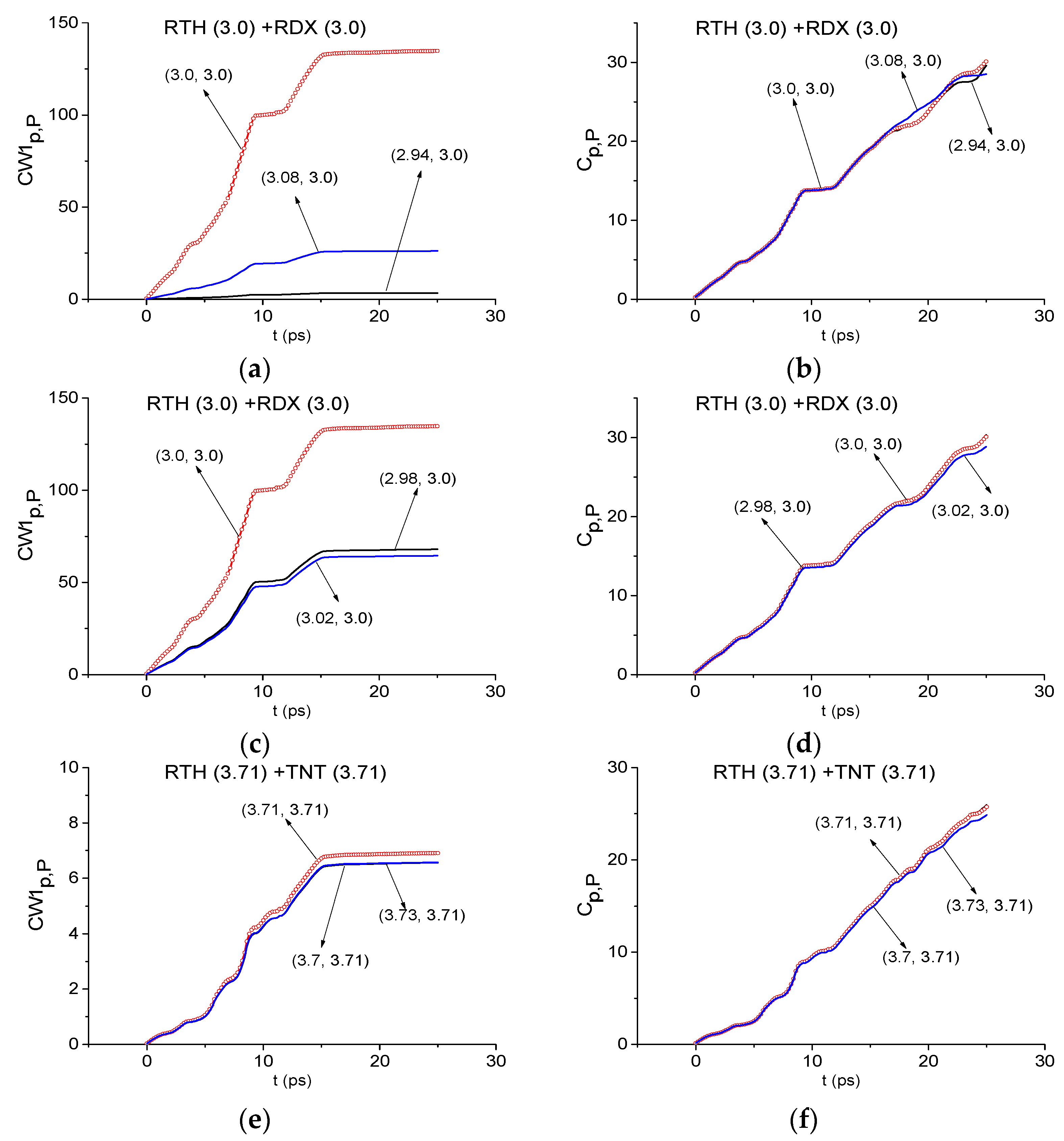
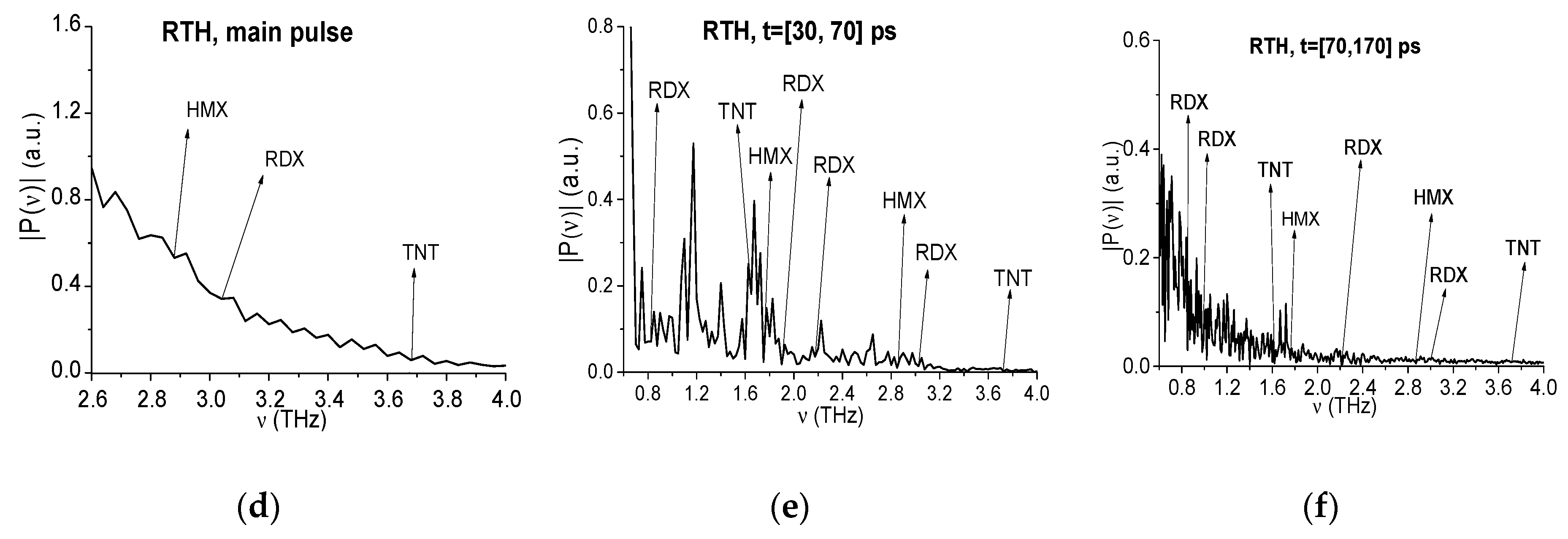
2.6. Efficiency of Substance Detection in the Time Interval t = [0, 25] ps, Containing the Main Reflected Pulse
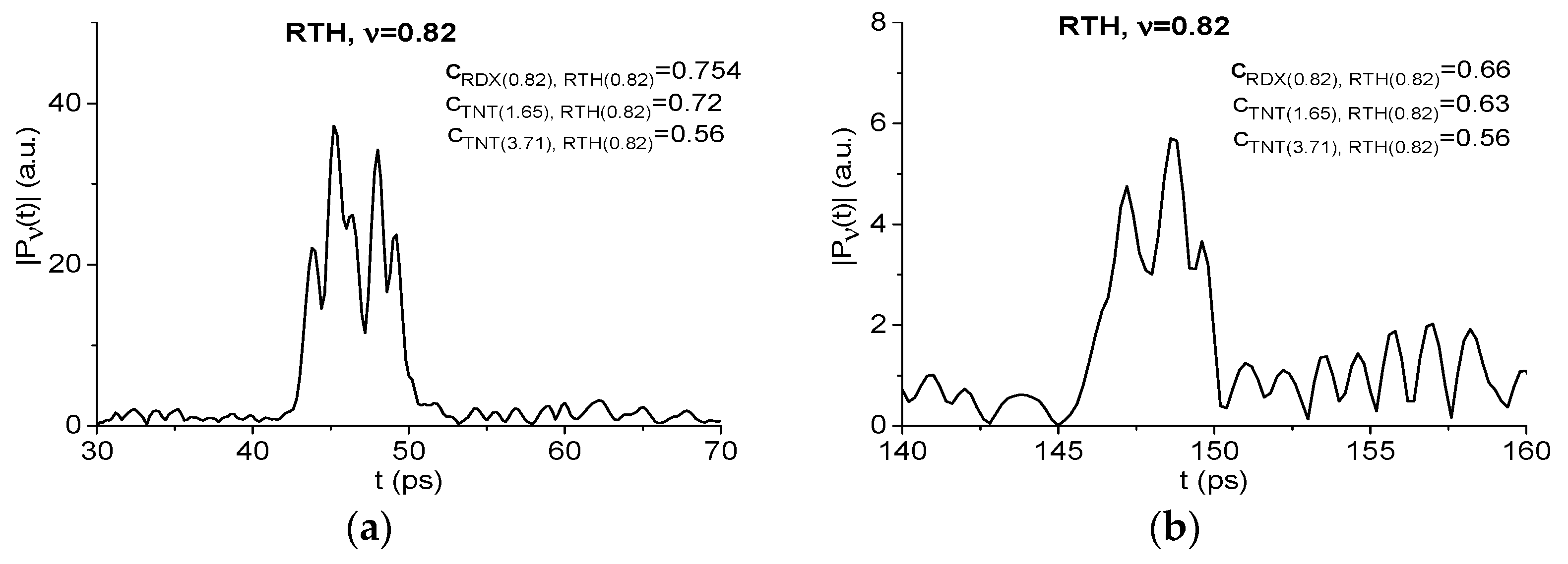
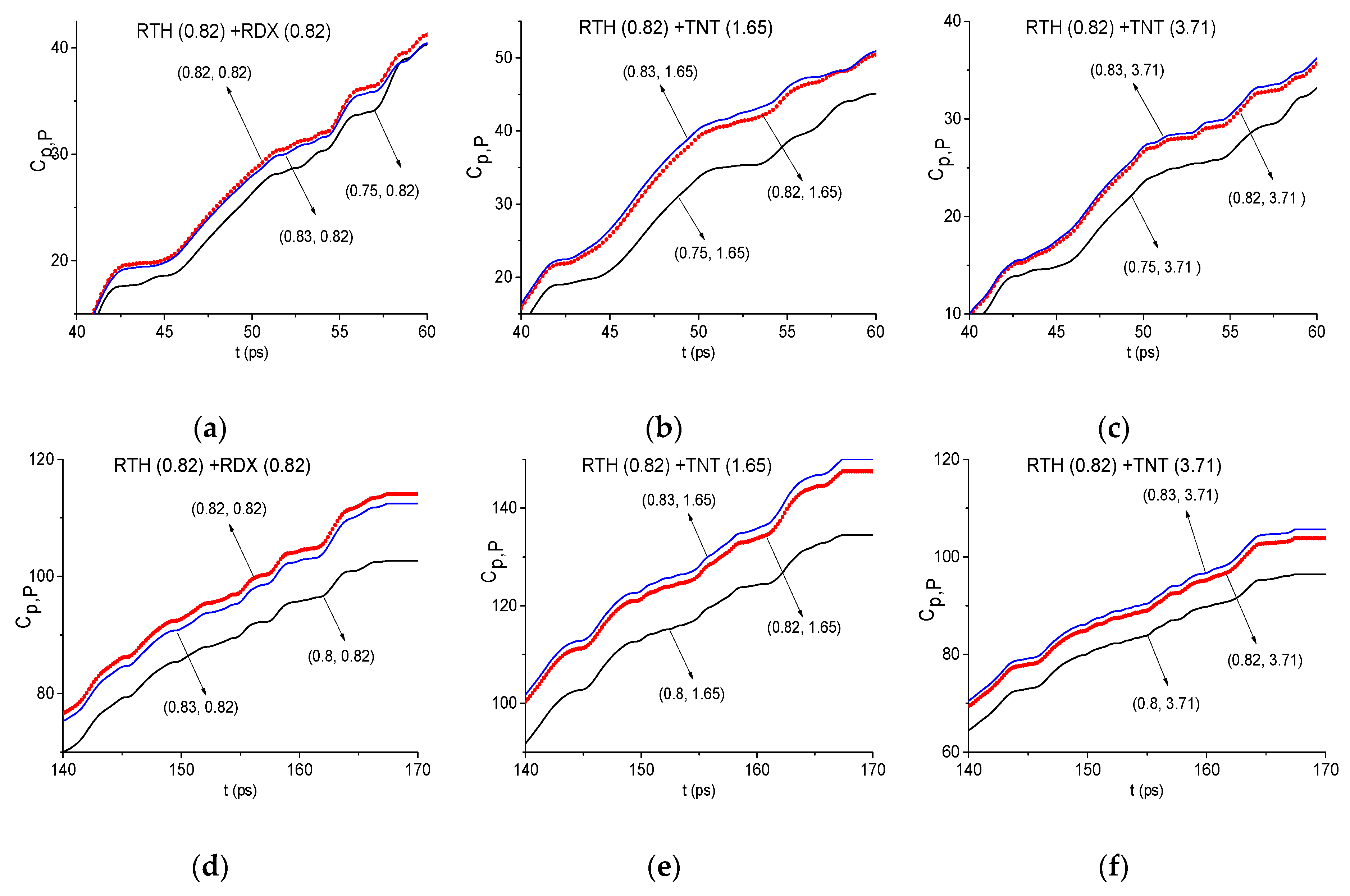
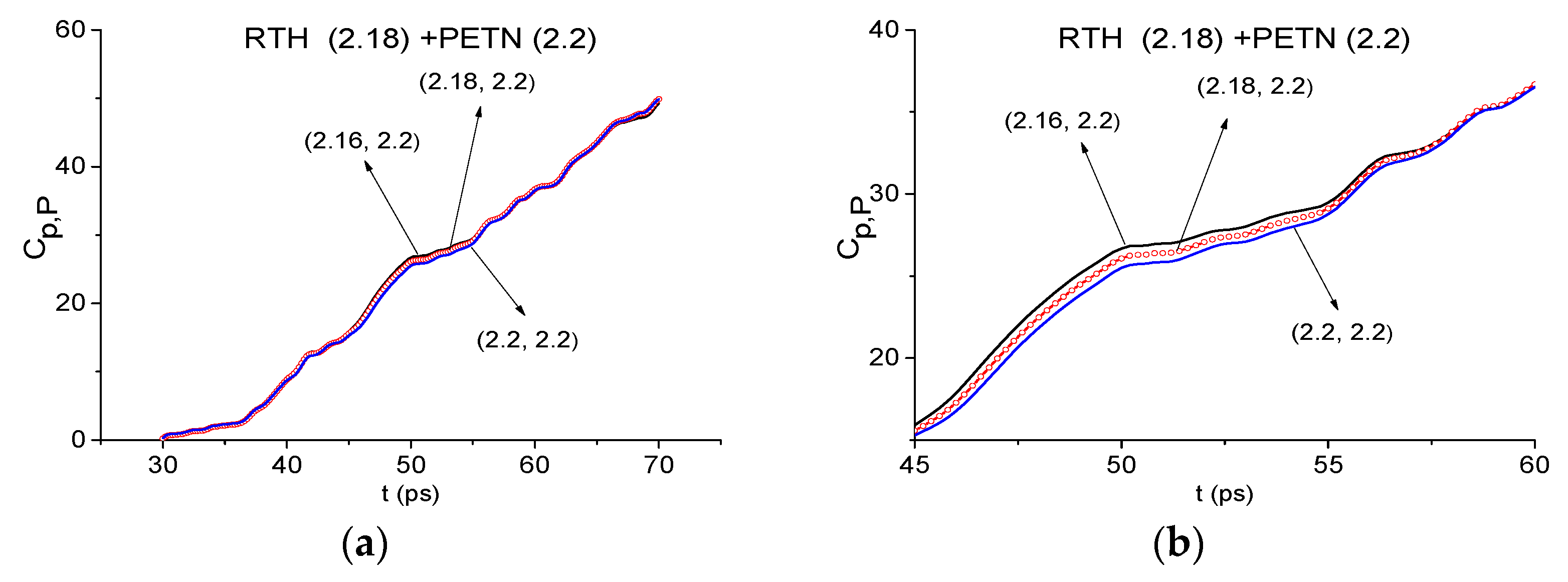
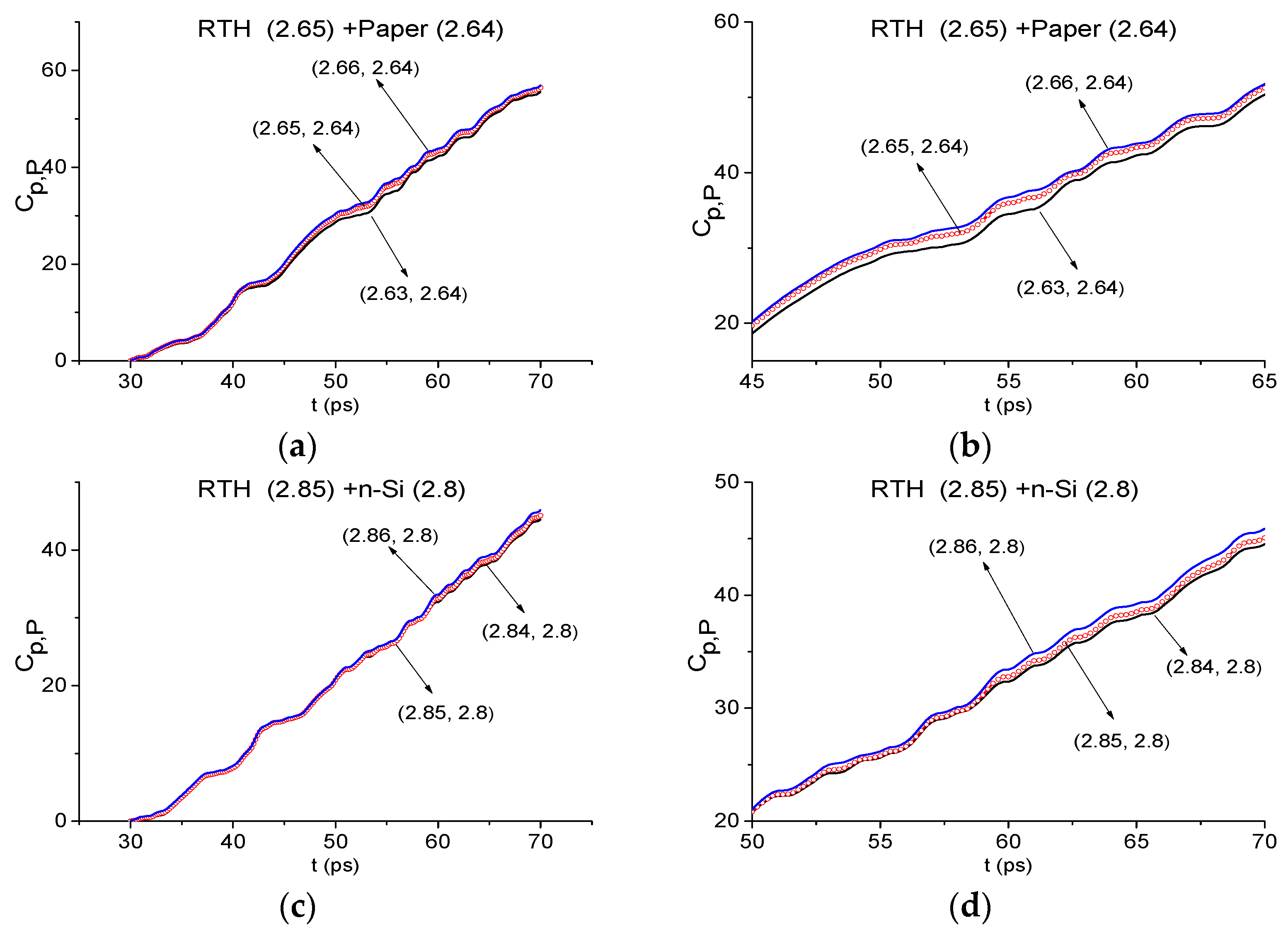
2.7. The Substance Detection Using the First Sub-Pulse (Time Interval t = [30, 70 ps)
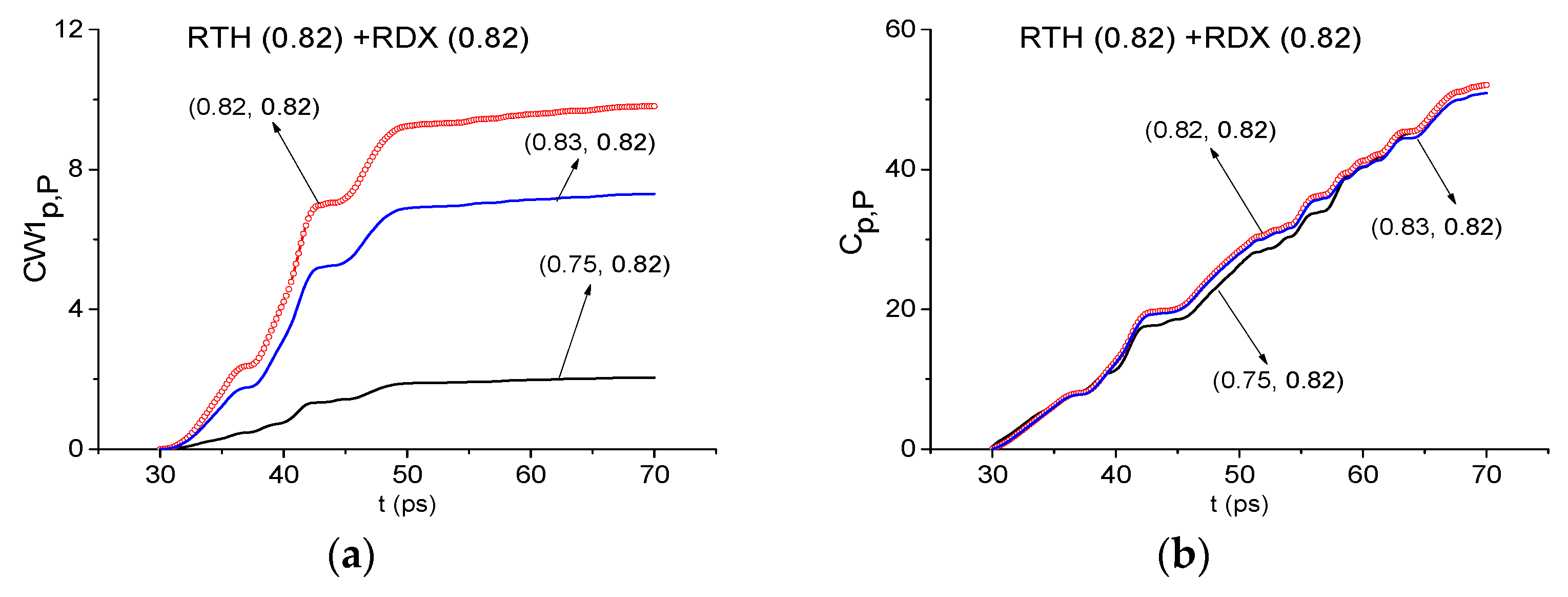
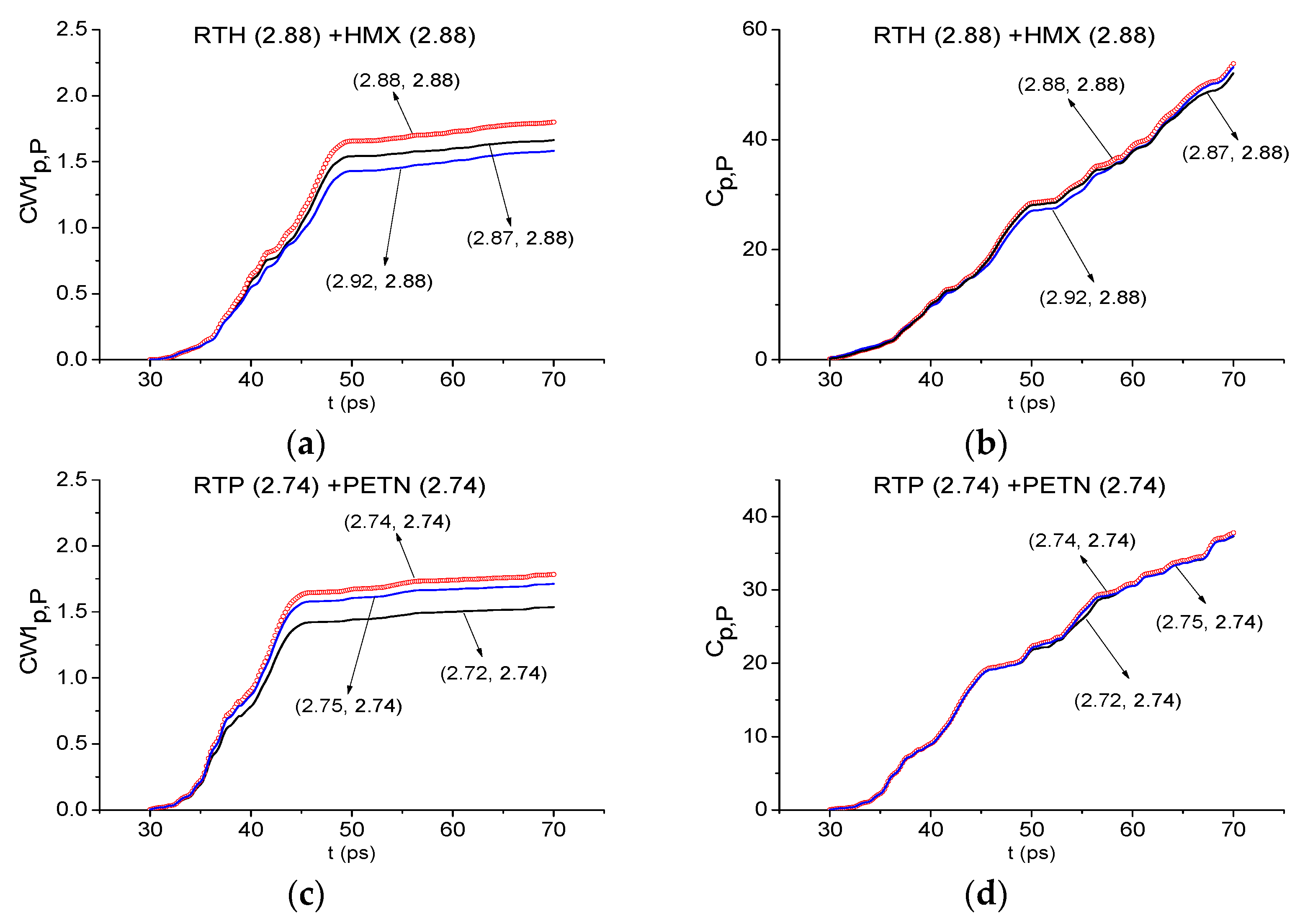
2.7.1. Detection of the Mixture Components in the Low Frequency Range ν < 2.6 THz.
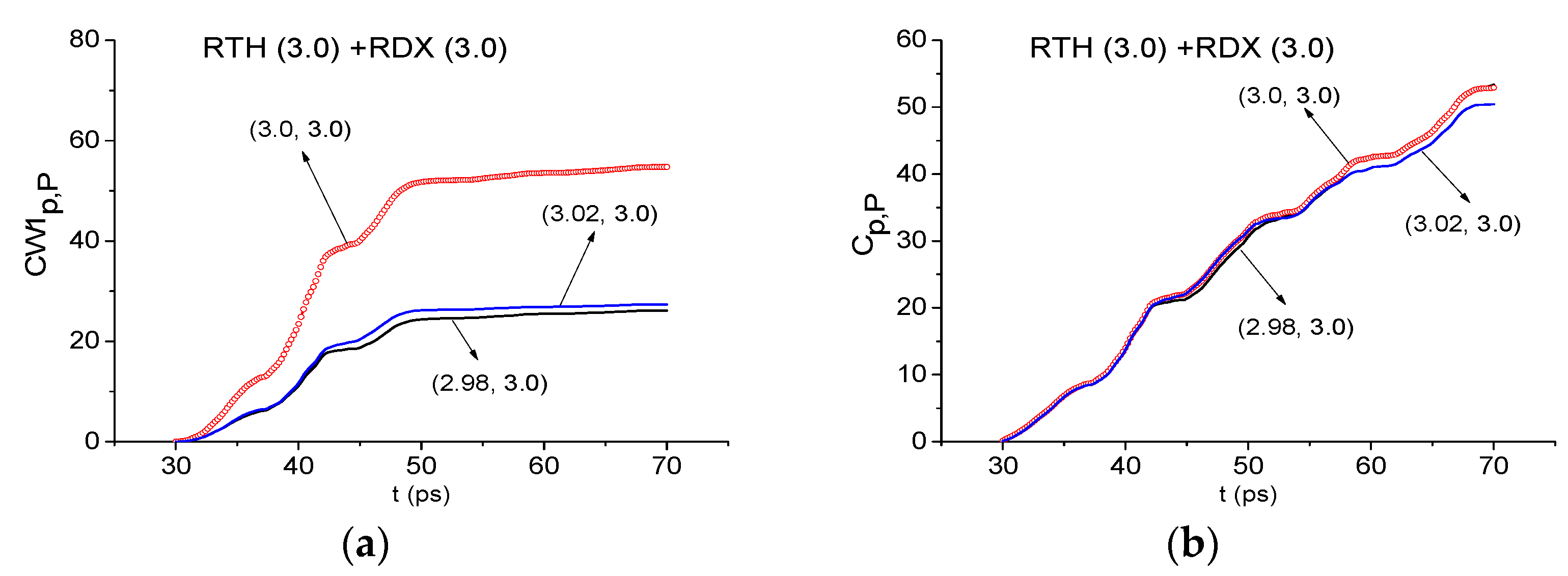
2.7.2. Detection of the Mixture Components in the High Frequency Range ν > 2.6 THz.
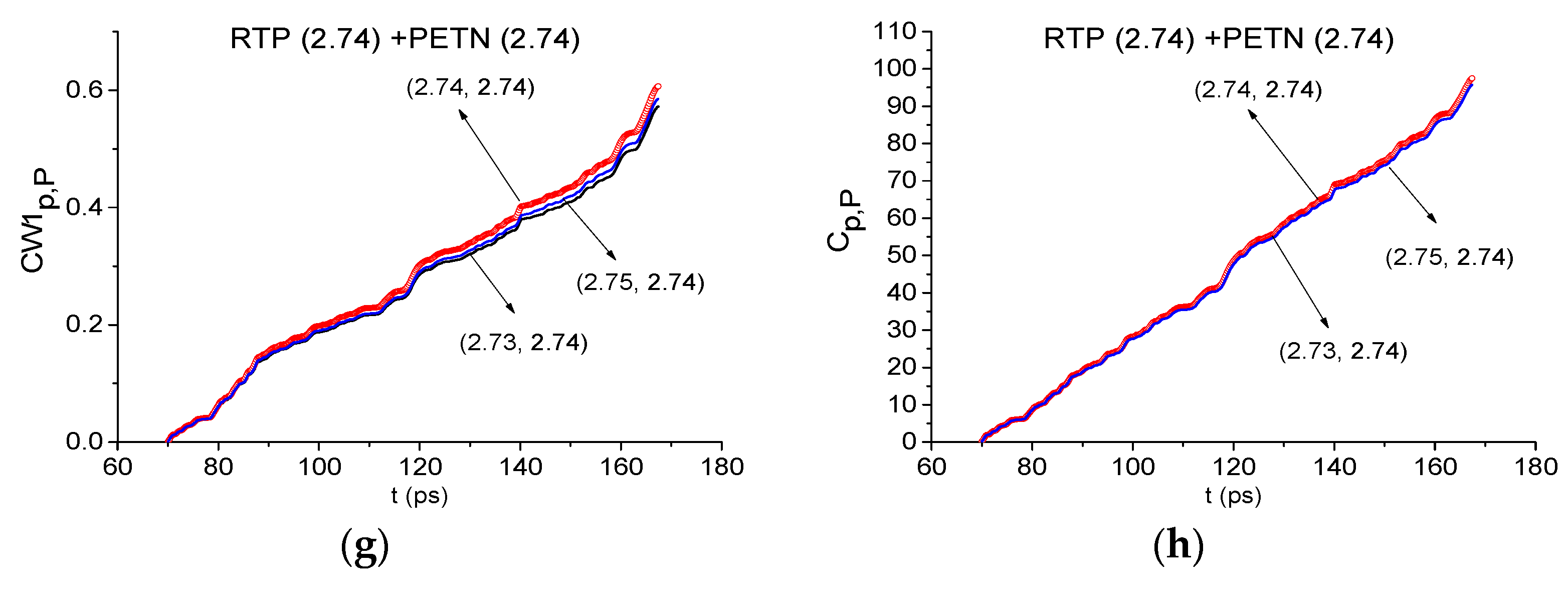
2.8. The Substance Detection Using the Time Interval t = [70, 170] ps
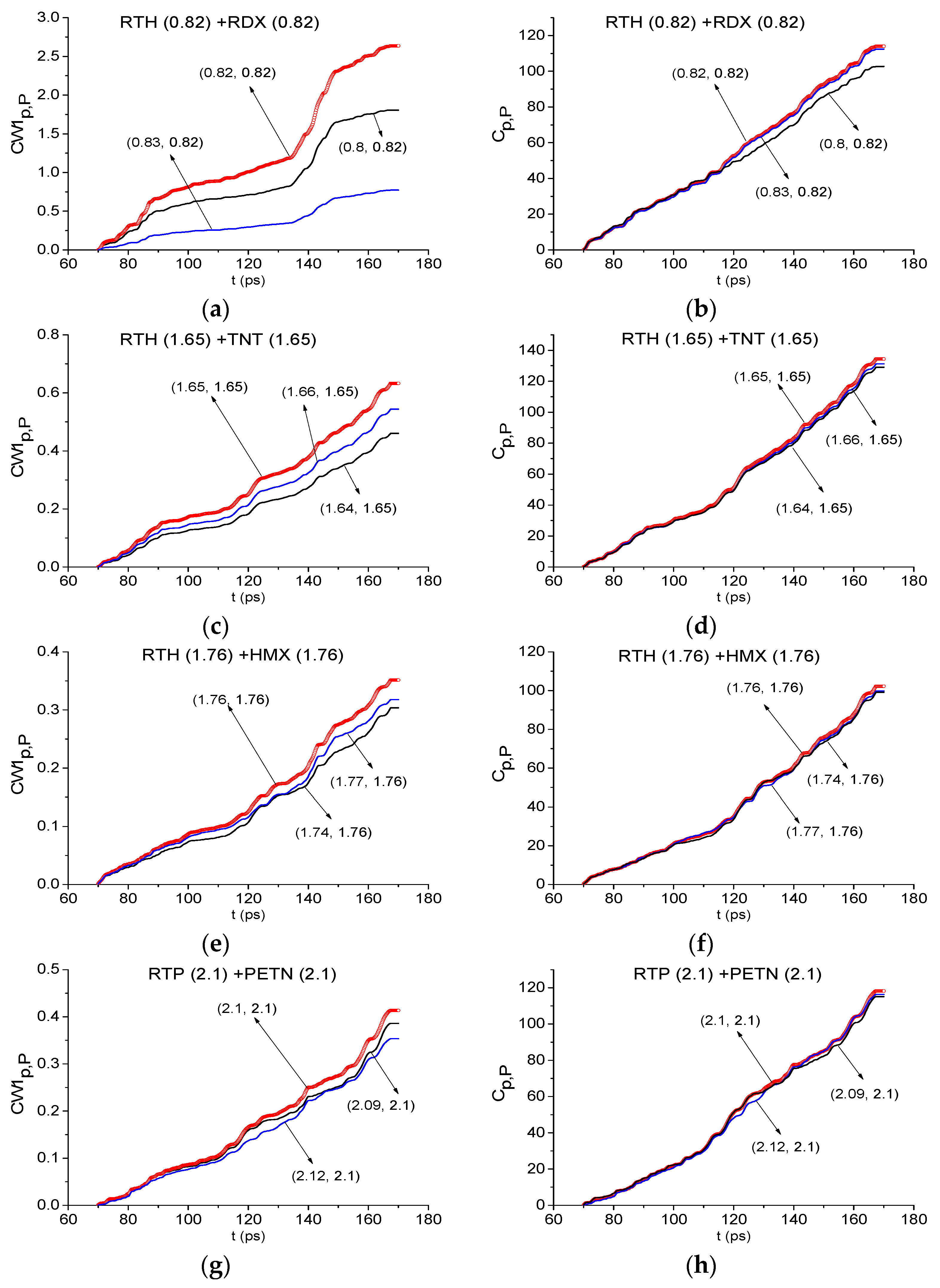
2.8.1. Detection of the Mixture Components in The Low Frequency Range ν < 2.6 THz.
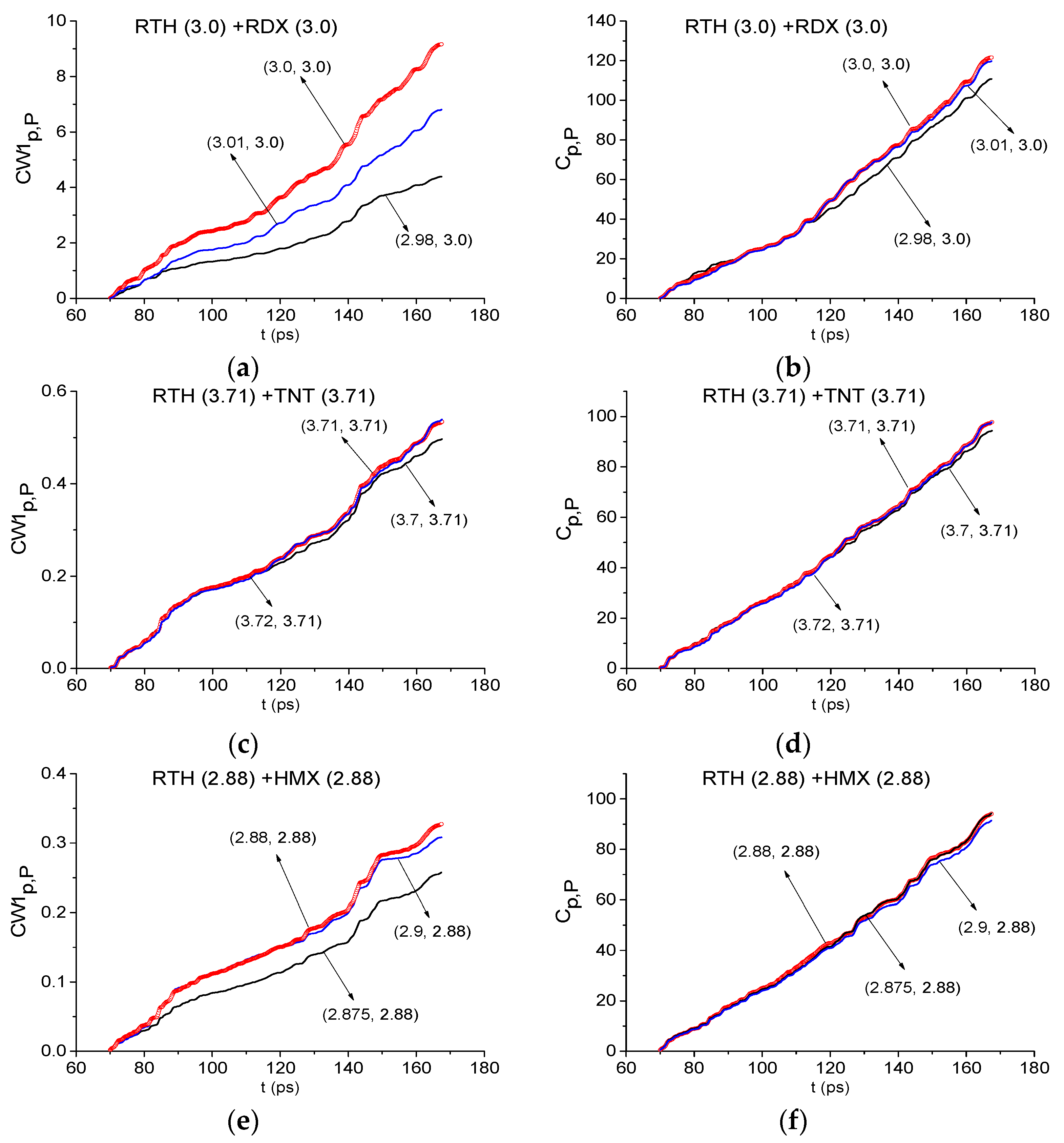
2.8.2. Detection of the Mixture Components in the High Frequency Range ν > 2.6 THz.
2.9. Can Criteria Distinguish the Frequencies Possessing the Similar Time-Dependent Spectral Line Dynamics?
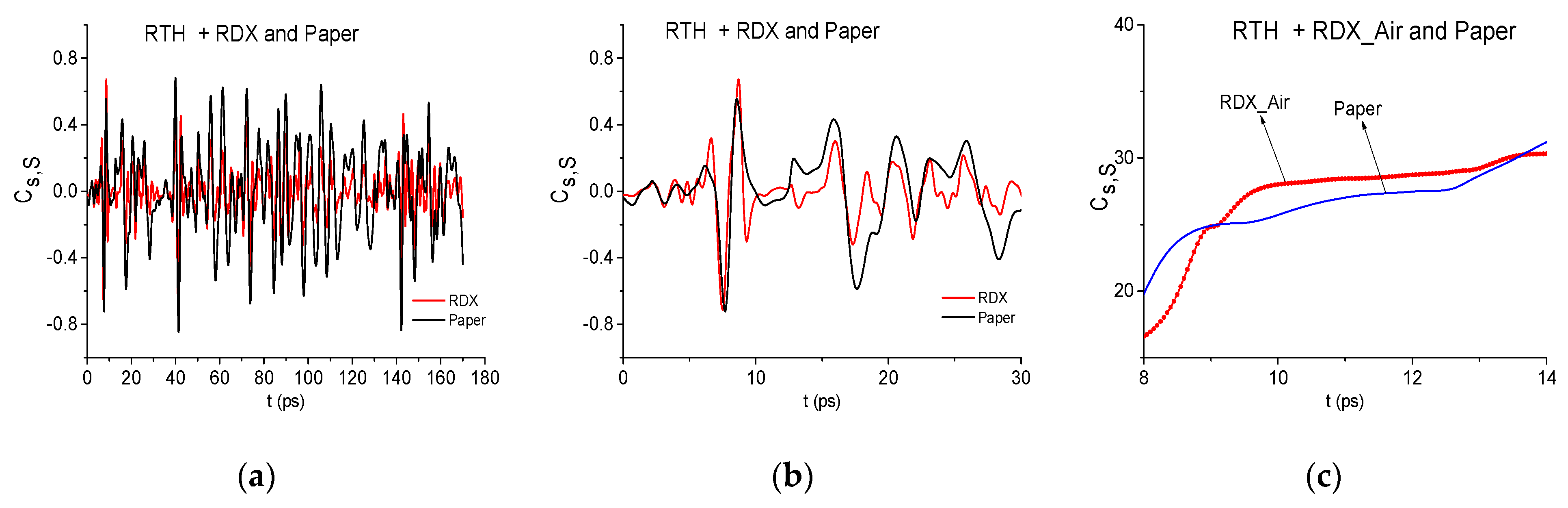
2.10. How to Distinguish the Mixtures RTH and RTP and to Exclude The False Presence Of Paper and Semiconductors in Them?
3. Conclusions and Summarizing
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Federici, J.F.; Schulkin, B.; Huang, F.; Gary, D.; Barat, R.; Oliveira, F.; Zimdars, D. THz imaging and sensing for security applications—Explosives, weapons and drugs. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, S266–S280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Shen, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liang, L.; Xu, X. Detection and identification of illicit drugs using terahertz imaging. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 103104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobroiu, A.; Sasaki, Y.; Shibuya, T.; Otani, C.; Kawase, K. THz-wave spectroscopy applied to the detection of illicit drugs in mail. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 1566–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Bastiaans, G.J.; Zhang, X.-C. Absorption coefficients of selected explosives and related compounds in the range of 0.1–2.8 THz. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 12060–12067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leahy-Hoppa, M.R.; Fitch, M.J.; Zheng, X.; Hayden, L.M.; Osiander, R. Wideband terahertz spectroscopy of explosives. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 434, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Chen, Y.; Bastiaans, G.J.; Zhang, X.C. Detection and identification of explosive RDX by THz diffuse reflection spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palka, N. THz reflection spectroscopy of explosives measured by time domain spectroscopy. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2011, 120, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, M.C. Explosives detection by terahertz spectroscopy—A bridge too far? IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puc, U.; Abina, A.; Rutar, M.; Zidanšek, A.; Jeglič, A.; Valušis, G. Terahertz spectroscopic identification of explosive and drug simulants concealed by various hiding techniques. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 4495–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slocum, D.M.; Slingerland, E.J.; Giles, R.H.; Goyette, T.M. Atmospheric absorption of terahertz radiation and water vapor continuum effects. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2013, 127, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahi, K.; Anwar, M. Advanced terahertz techniques for quality control and counterfeit detection. Proc. SPIE 2016, 9856, 98560G. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer, T.; Weber, S.; Klier, J.; Bachtler, S.; Molter, D.; Jonuscheit, J.; Von Freymann, G. Terahertz thickness determination with interferometric vibration correction for industrial applications. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 12558–12568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretti, R.; Mitryukovskiy, S.; Froberger, K.; Mebarki, M.A.; Eliet, S.; Vanwolleghem, M.; Lampin, J.F. THz-TDS time-trace analysis for the extraction of material and metamaterial parameters. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Khan, M. THz spectroscopy: An emerging technology for pharmaceutical development and pharmaceutical Process Analytical Technology (PAT) applications. J. Mol. Struct. 2012, 1020, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, T.; Kajiki, K.; Koizumi, T.; Itsuji, T.; Koyama, Y.; Sekiguchi, R.; Kawase, K. Terahertz imaging system for medical applications and related high efficiency terahertz devices. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2014, 35, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaliūnas, M.; Nasser, K.E.; Urbanowicz, A.; Kašalynas, I.; Bražinskienė, D.; Asadauskas, S.; Valušis, G. Non-destructive inspection of food and technical oils by terahertz spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 18025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schecklman, S.; Zurk, L.M.; Henry, S.; Kniffin, G.P. Terahertz material detection from diffuse surface scattering. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 094902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Kawase, K.; Ikari, T. Component spatial pattern analysis of chemicals using terahertz spectroscopic imaging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Kawase, K.; Ikari, T.; Ito, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Minamide, H. Component analysis of chemical mixtures using terahertz spectroscopic imaging. Opt. Commun. 2004, 234, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B.; Hoffmann, M.; Helm, H.; Modjesch, G.; Jepsen, P.U. Chemical recognition in terahertz time-domain spectroscopy and imaging. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, S246–S253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, S.; Zhao, H.; Ma, X.; Wang, W. Quantitative measurement of mixtures by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. J. Chem. Sci. 2009, 121, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, Z.; Hu, F.R.; Mo, W. Quantitative analysis of mixtures using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy and different PLS algorithms. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 804, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abina, A.; Puc, U.; Jeglič, A.; Prah, J.; Venckevičius, R.; Kašalynas, I.; Valušis, G.; Zidanšek, A. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of calcium-based microfillers using terahertz spectroscopy and imaging. Talanta 2015, 143, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, P.; Hou, D.; Cai, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G. The spectral resolution of unknown mixture based on THz spectroscopy with self-modeling technique. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2016, 150, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Ryu, S.Y.; Kwon, W.S.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, S. Compound explosives detection and component analysis via terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 2013, 17, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, J.B.; El Haddad, J.; Perraud, J.B.; Bassel, L.; Bousquet, B.; Palka, N.; Mounaix, P. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Explosives by Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy: Application to Imaging. In Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz waves (IRMMW-THz), Tucson, AZ, USA, 14–19 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sleiman, J.B.; Bousquet, B.; Palka, N.; Mounaix, P. Quantitative analysis of hexahydro-1, 3, 5-trinitro-1, 3, 5, triazine/pentaerythritol tetranitrate (RDX-PETN) mixtures by terahertz time domain spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2015, 69, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, J.B.; Perraud, J.B.; Bousquet, B.; Guillet, J.P.; Palka, N.; Mounaix, P. Discrimination and identification of RDX/PETN explosives by chemometrics applied to terahertz time-domain spectral imaging. Proc. SPIE 2015, 9651, 965109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhao, S.; Shen, J. Quantitative analysis of the mixtures of illicit drugs using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Proc. SPIE 2008, 6840, 68400U. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, Y. Quantitative measurements of binary amino acids mixtures in yellow foxtail millet by terahertz time domain spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, S.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Simultaneous determination of amino acid mixtures in cereal by using terahertz time domain spectroscopy and chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2017, 164, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.H.; Li, B.; Zhai, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z. An effective approach to quantitative analysis of ternary amino acids in foxtail millet substrate based on terahertz spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Shi, C.; Xu, M.; Xu, M.; Kou, T.; Wu, X.; Song, B.; Ma, H.; Guo, S.; Liu, L.; et al. Qualitative and quantitative identification of components in mixture by Terahertz spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Zhao, K.; Bao, R.; Xiao, L. Monitoring PM2.5 in the atmosphere by using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2016, 37, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaks, V.; Domracheva, E.; Sobakisnakaya, E.; Chernyaeva, M. Sub-THz Spectroscopy for Security Related Gas Detection. In Terahertz and Mid Infrared Radiation: Detection of Explosives and CBRN (Using Terahertz); Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, M.F.; Zubelli, J.P.; Winge, D.; Wacker, A.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Anfertev, V. Theory and measurements of harmonic generation in semiconductor superlattices with applications in the 100 GHz to 1 THz range. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 045306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.-C. Identification of explosive media using spectrum dynamics under the action of a THz pulse. Proc. SPIE 2009, 7486, 74860A. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Zhang, C.; Shen, J.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, Y. 2D signature for identification of drugs. Proc. SPIE 2011, 8040, 804007. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Szustakowski, M.; Palka, N. Detection and identification of compound explosive using the SDA method of the reflected THz signal. Proc. SPIE 2012, 8382, 83820B. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. Effective criteria for the identification of substance using the spectral lines dynamics of reflected THz signal. Proc. SPIE 2013, 8901, 890106. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. Effective criteria developing for the identification of substance using the reflected THz signal. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9082, 90820B. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. Real-time criteria based on spectral dynamics of medium response for the detection and identification of substance using THz signal. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9253, 925305. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Trofimov, V.V. Possibility of the detection and identification of substance at long distance using the noisy reflected THz pulse under real conditions. Proc. SPIE 2015, 9483, 94830P. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. An effective method for substance detection using the broad spectrum THz signal: A “terahertz nose”. Sensors 2015, 15, 12103–12132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. Detection and identification of drugs under real conditions by using noisy terahertz broadband pulse. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 9605–9618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Tikhomirov, V.V.; Trofimov, V.V. High effective THz-TDS method for the detection and identification of substances in real conditions. Proc. SPIE 2016, 9836, 98362. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Zakharova, I.G.; Zagursky, D.Y.; Varentsova, S.A. Detection and identification of substances using noisy THz signal. Proc. SPIE 2017, 10194, 101942O. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Palka, N.; Szustakowski, M.; Trzcinski, T.; Lan, S.; Liu, H.Y. An influence of the absolute phase of THz pulse on linear and nonlinear medium response. Proc. SPIE 2011, 8195, 81951W. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.H.; Shen, J.L.; Liang, L.S.; Xu, X.Y.; Liu, H.B.; Zhang, C.L. Experimental investigation on terahertz spectra of amphetamine type stimulants. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2005, 22, 3176–3178. [Google Scholar]
- Newport Corporation Spectra-Physics. Mai Tai Ti: Sapphire Oscillator. Available online: http://www.spectra-physics.com/products/ultrafast-lasers/mai-tai#specs (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Rice, A.; Jin, Y.; Ma, X.F.; Zhang, X.-C.; Bliss, D.; Larkin, J.; Alexander, M. Terahertz optical rectification from <110> zinc-blende crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1994, 64, 1324–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Dai, Q.F.; Wu, L.J.; Lan, S.; Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. Effects of p-type doping on the optical properties of InAs/GaAs quantum dots. Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Zakharova, I.G.; Zagursky, D.Y. New possibilities of substance identification based on THz TDS using cascade mechanism of high energy level excitation. Sensors 2017, 17, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. The anomalous influence of spectral resolution on pulsed THz time domain spectroscopy under real conditions. Sensors 2017, 17, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RIKEN THz database. Available online: http://www.riken.jp/THzdatabase/ (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Peccianti, M.; Fastampa, R.; Mosca Conte, A.; Pulci, O.; Violante, C.; Łojewska, J.; Clerici, M.; Morandotti, R.; Missori, M. Terahertz absorption by cellulose: Application to ancient paper artifacts. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2017, 7, 064019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palka, N.; Szustakowski, M.; Kowalski, M.; Trzcinski, T.; Ryniec, R.; Piszczek, M.; Ciurapinski, W.; Zyczkowski, M.; Zagrajek, P.; Wrobel, J. THz Spectroscopy and Imaging in Security Applications. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Microwaves, Radar & Wireless Communications, Warsaw, Poland, 21–23 May 2012; Volume 1, pp. 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. High effective time-dependent THz spectroscopy method for the detection and identification of substances with inhomogeneous surface. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. A Possible Way for the Detection and Identification of Dangerous Substances in Ternary Mixtures Using THz Pulsed Spectroscopy. Sensors 2019, 19, 2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102365
Trofimov VA, Varentsova SA. A Possible Way for the Detection and Identification of Dangerous Substances in Ternary Mixtures Using THz Pulsed Spectroscopy. Sensors. 2019; 19(10):2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102365
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrofimov, Vyacheslav A., and Svetlana A. Varentsova. 2019. "A Possible Way for the Detection and Identification of Dangerous Substances in Ternary Mixtures Using THz Pulsed Spectroscopy" Sensors 19, no. 10: 2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102365
APA StyleTrofimov, V. A., & Varentsova, S. A. (2019). A Possible Way for the Detection and Identification of Dangerous Substances in Ternary Mixtures Using THz Pulsed Spectroscopy. Sensors, 19(10), 2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102365




