Ultracompact Multielectrode Array for Neurological Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
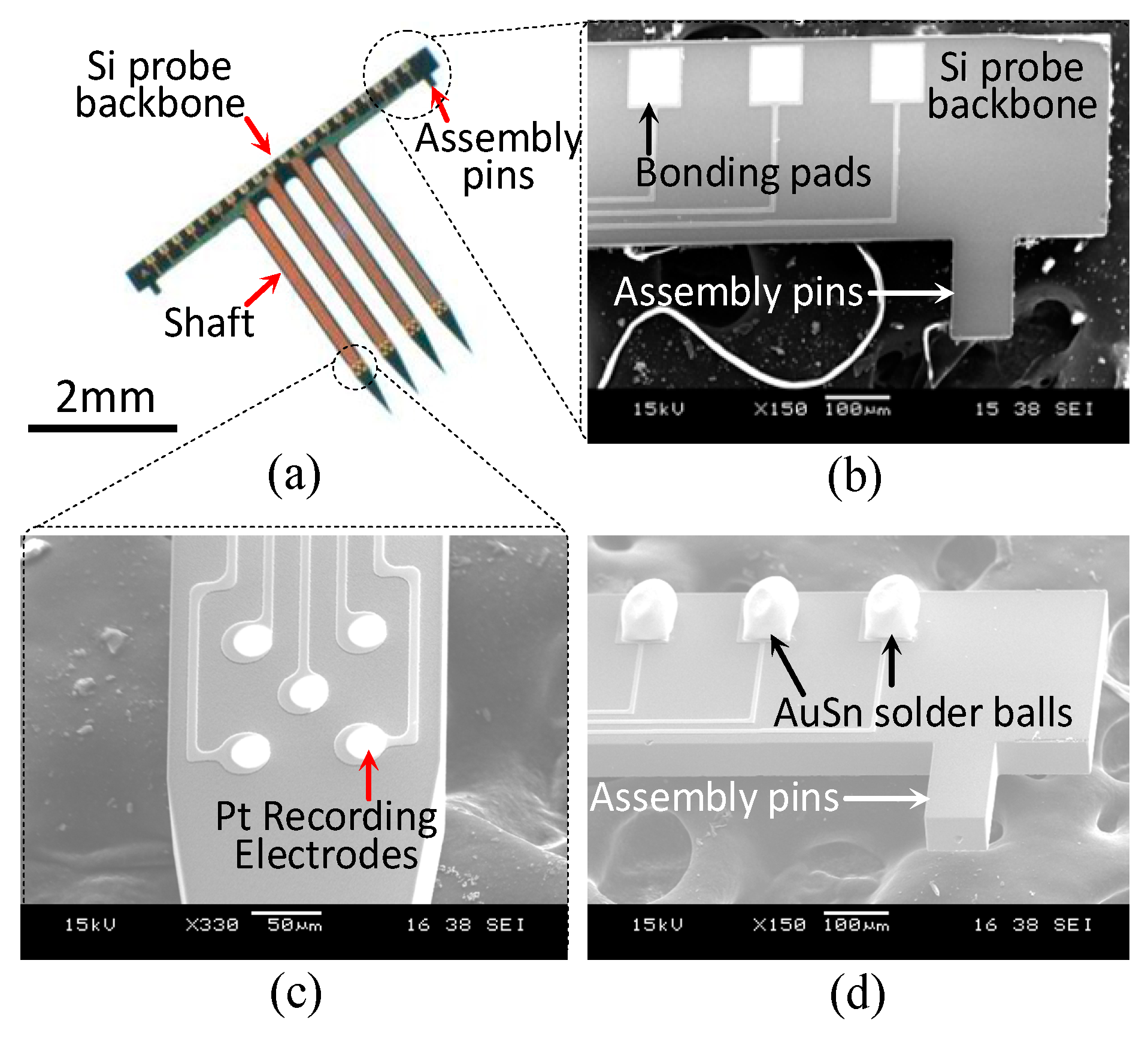
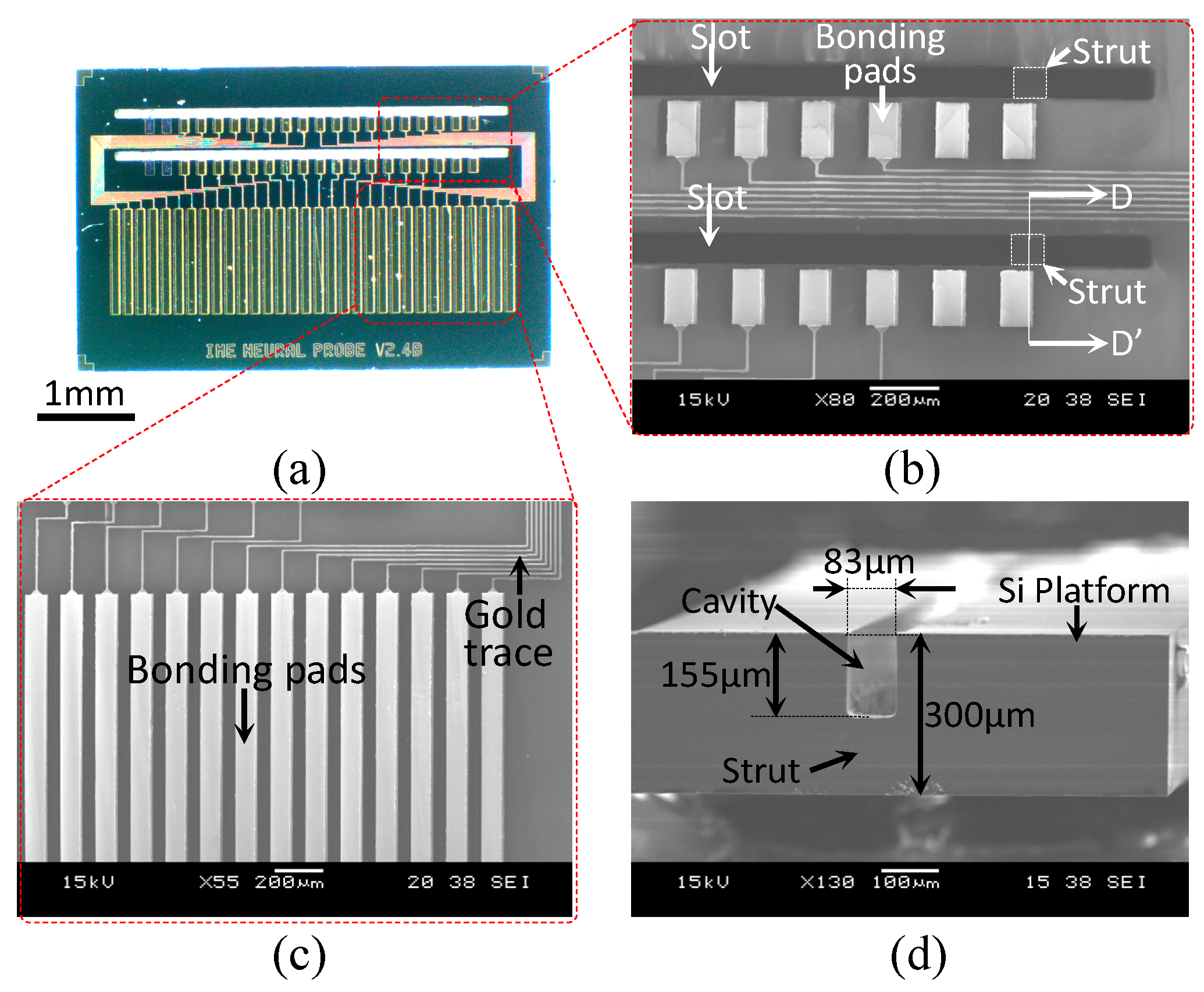
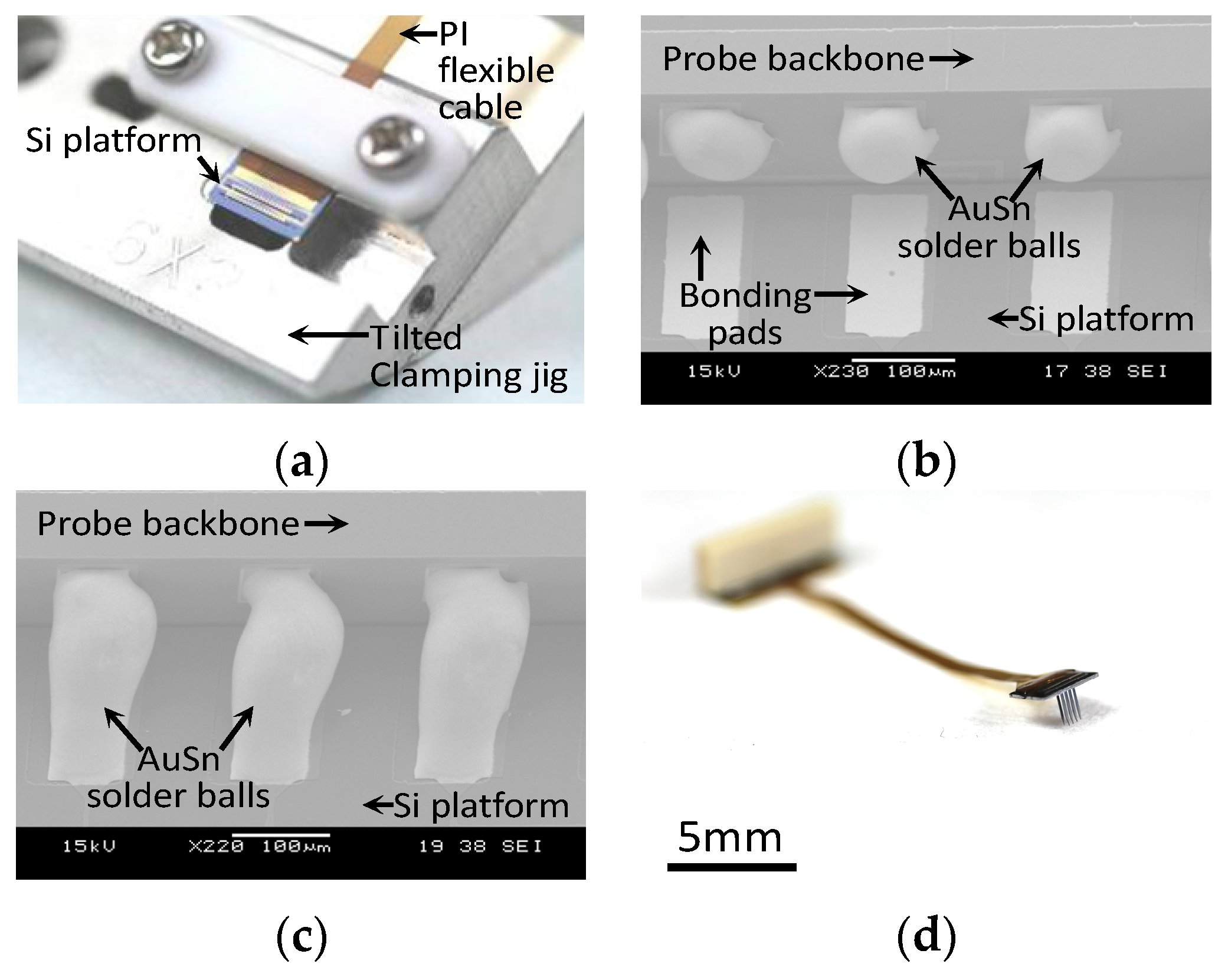
3. Fabrication and Packaging
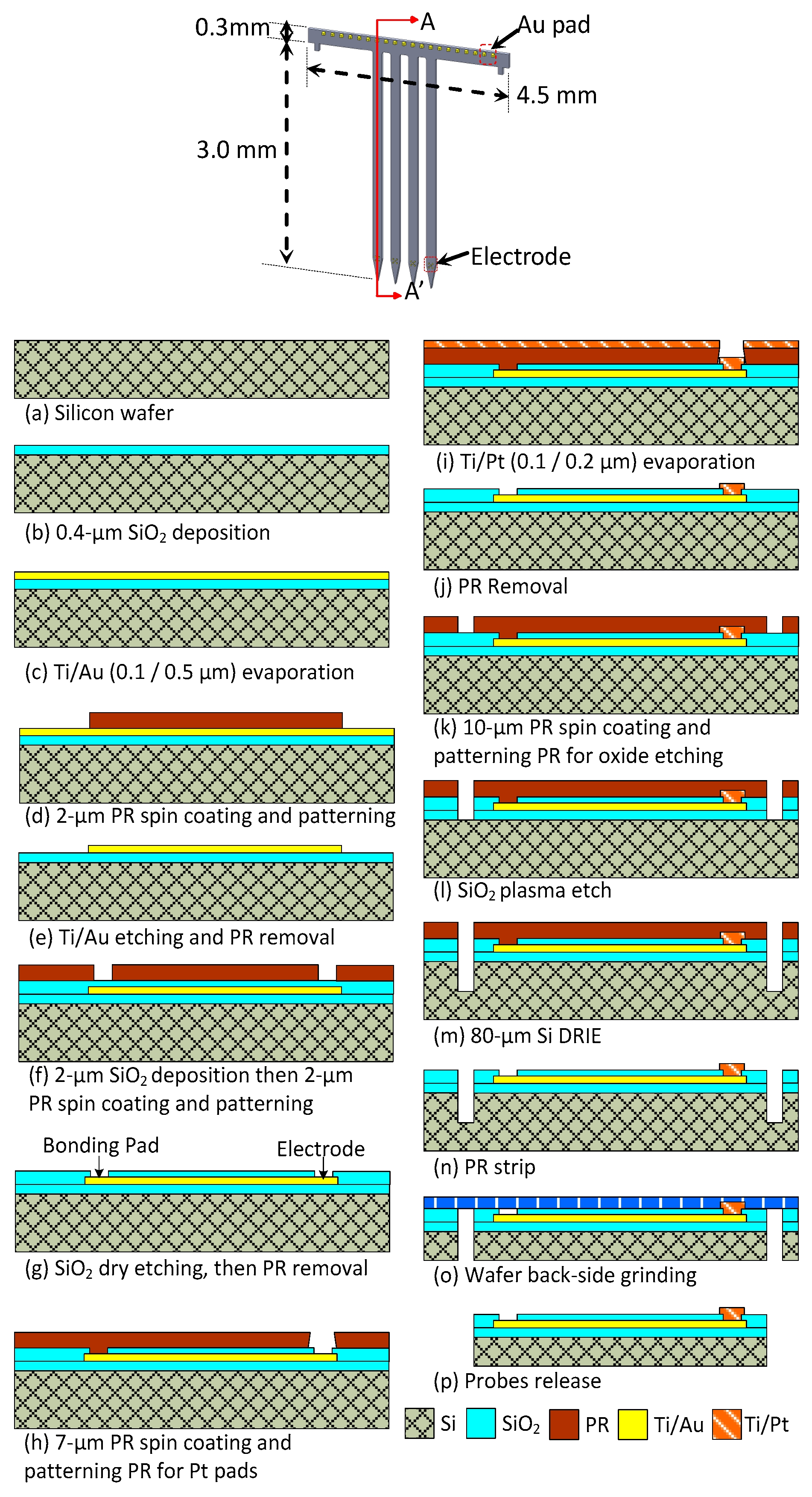
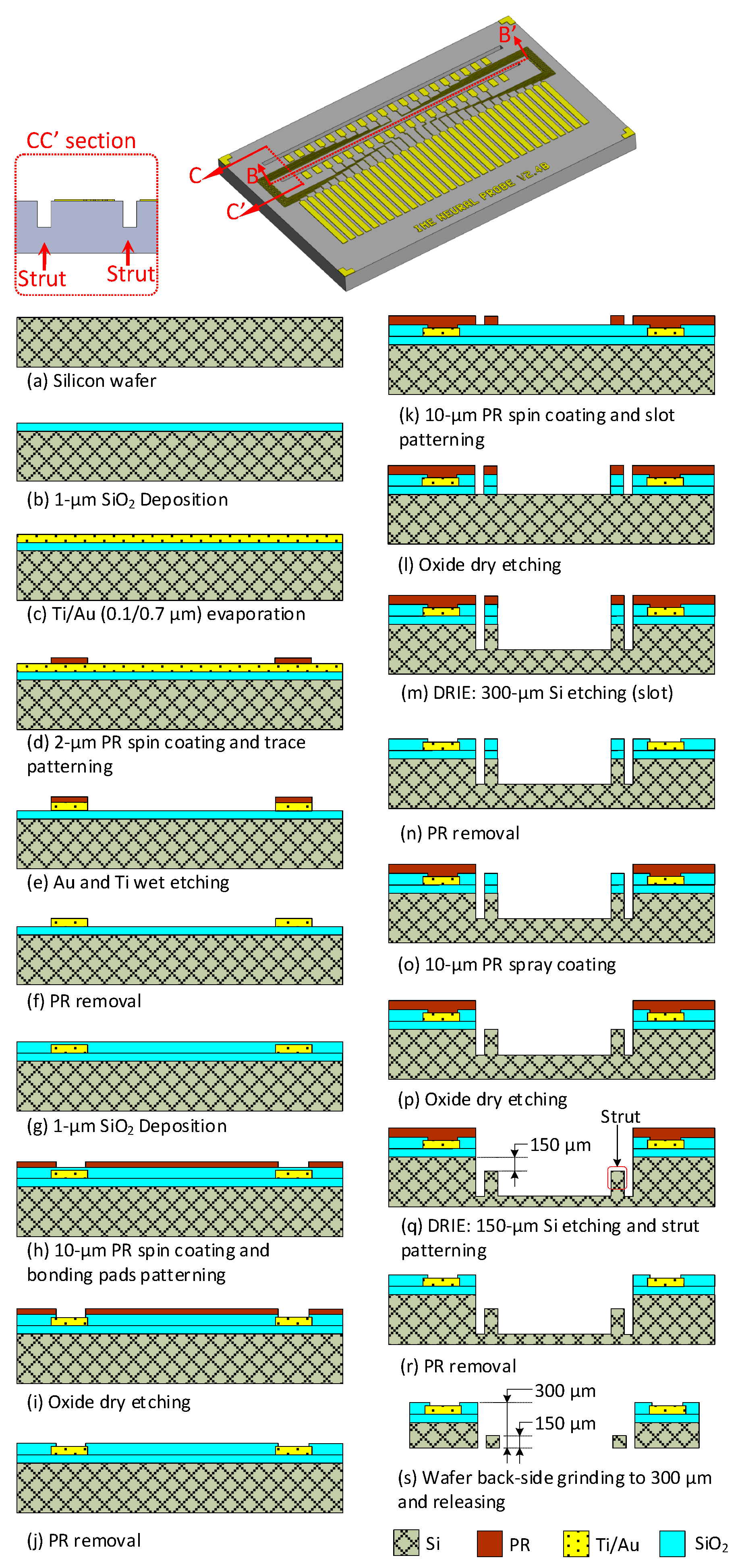
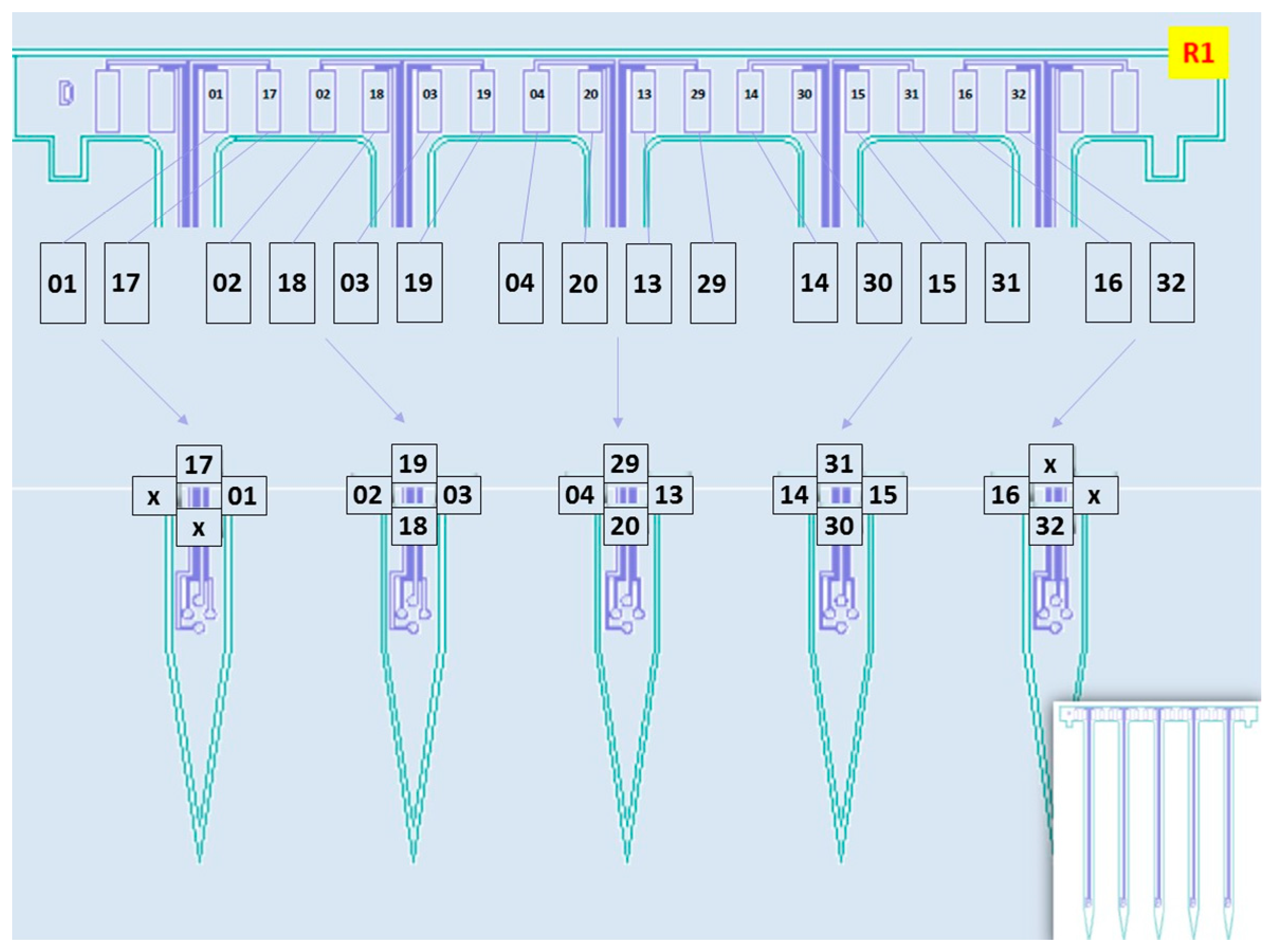
3.1. Fabrication
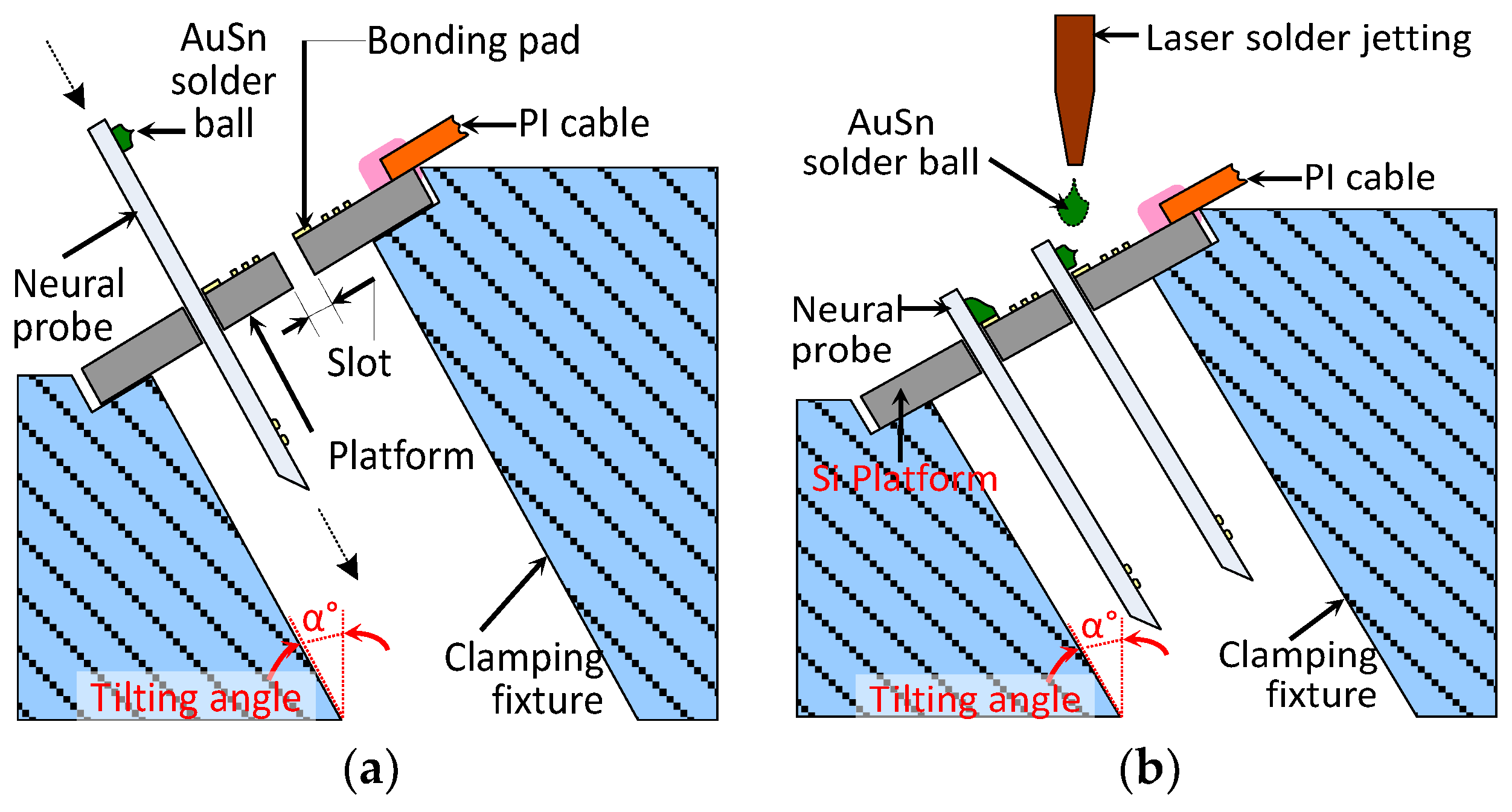
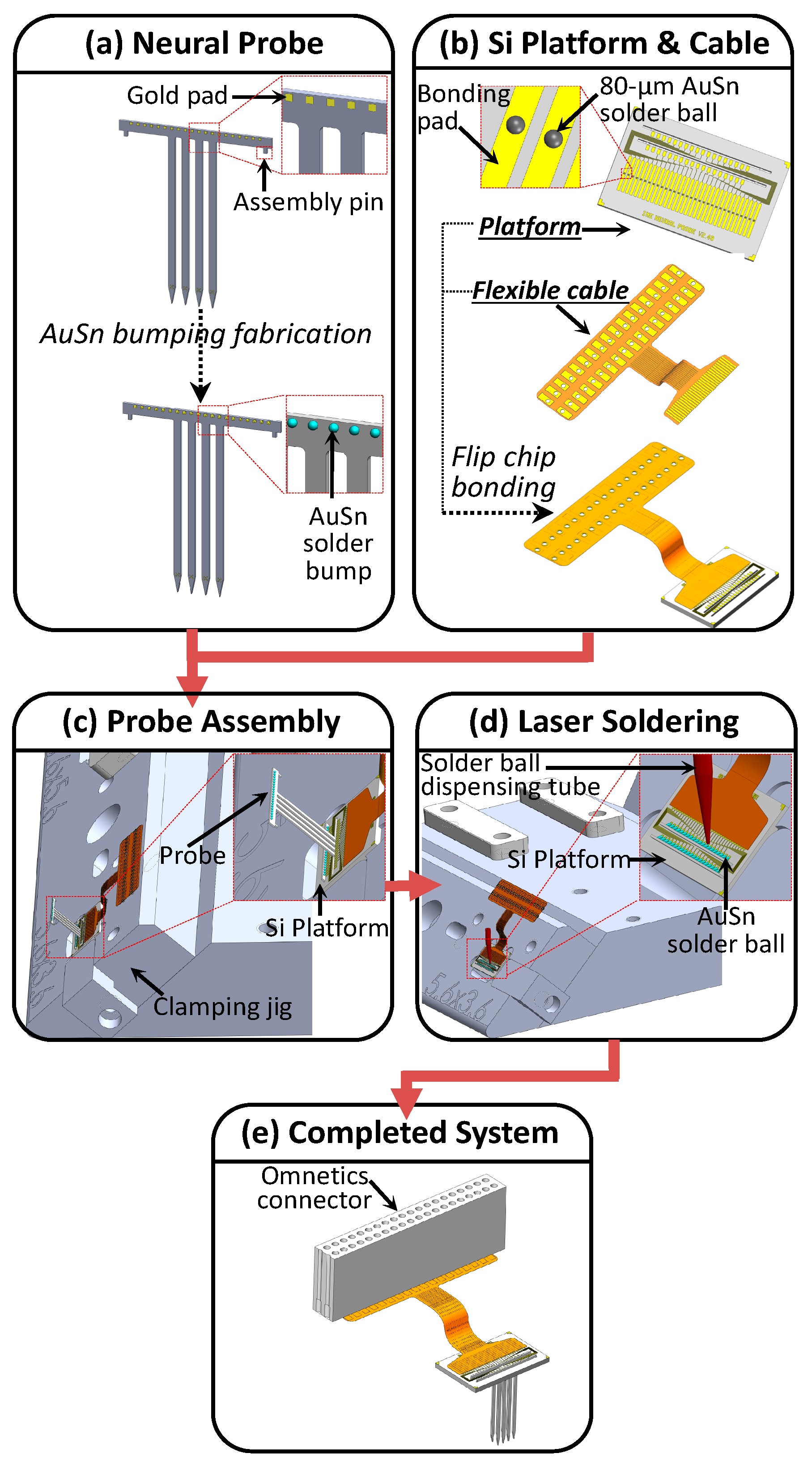
3.2. Packaging
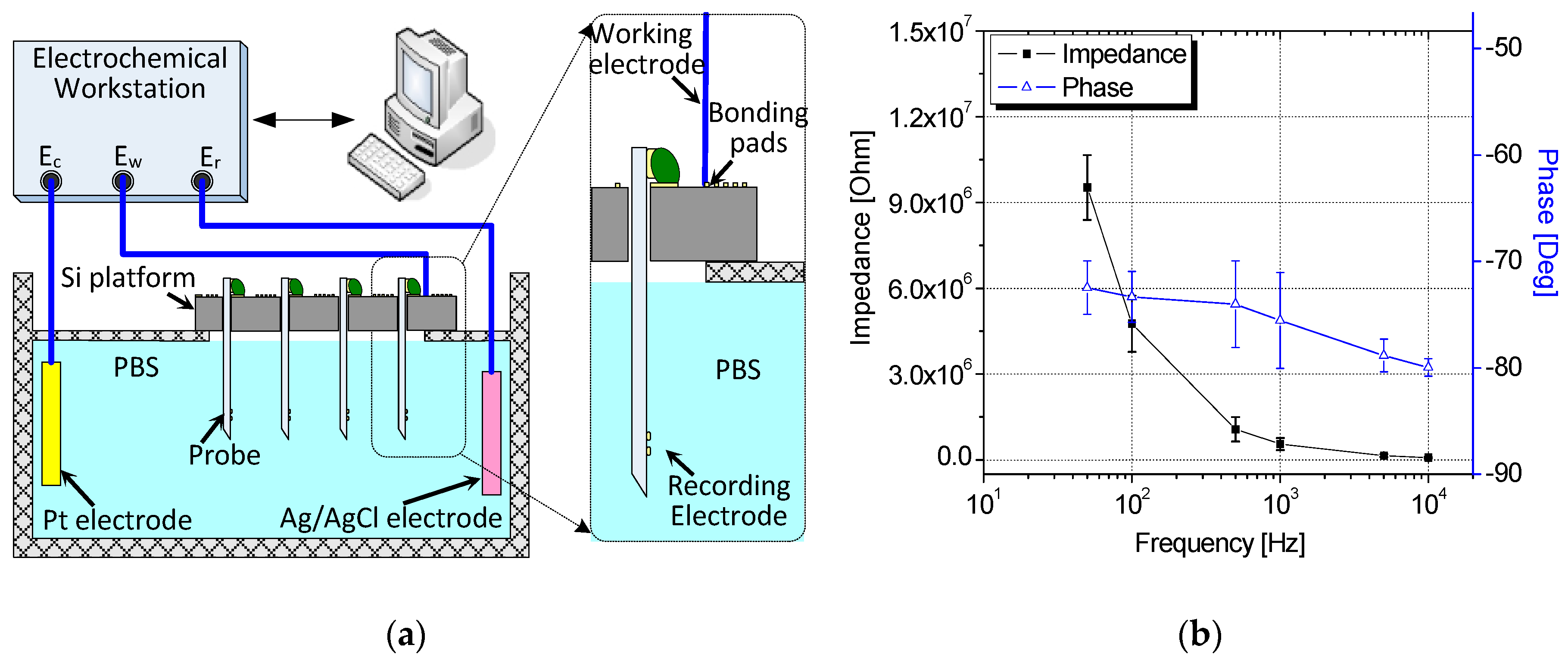
4. Testing Results and Discussion
4.1. Benchtop Signal Acquisition and Impedance Measurement of the Assembled Neural Device
4.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Testing Preparation
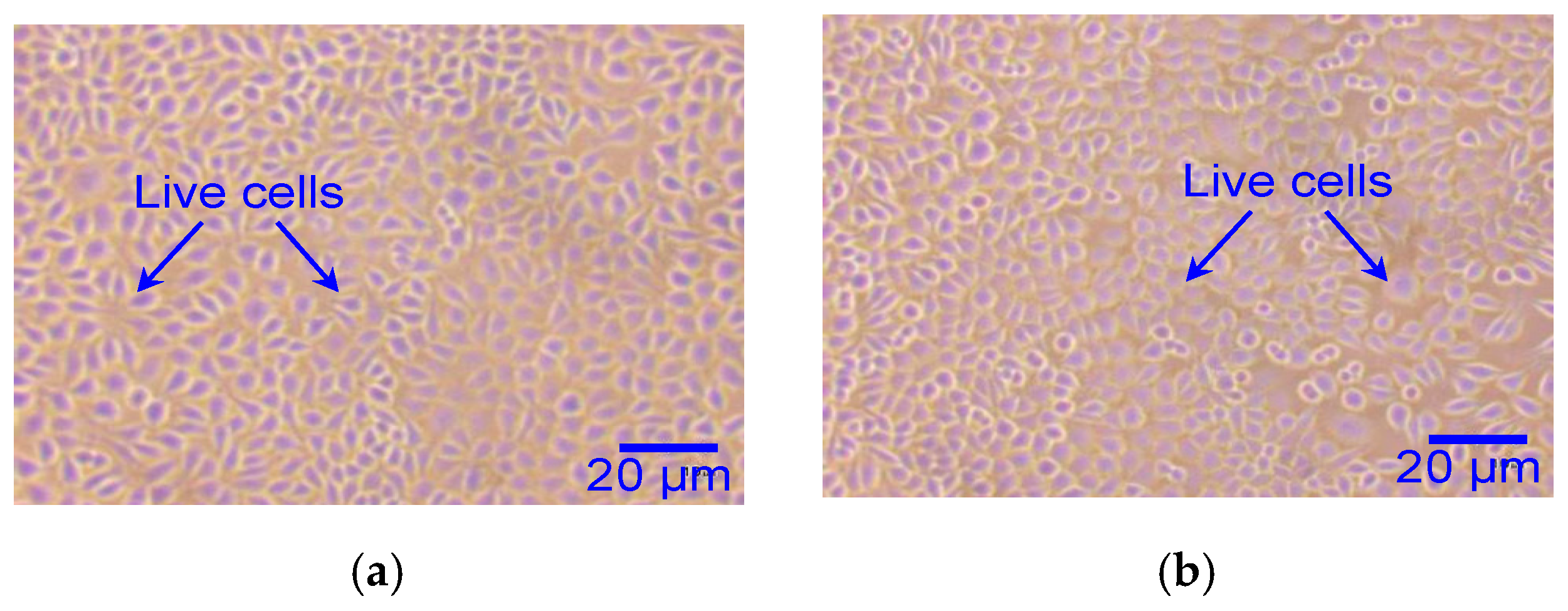
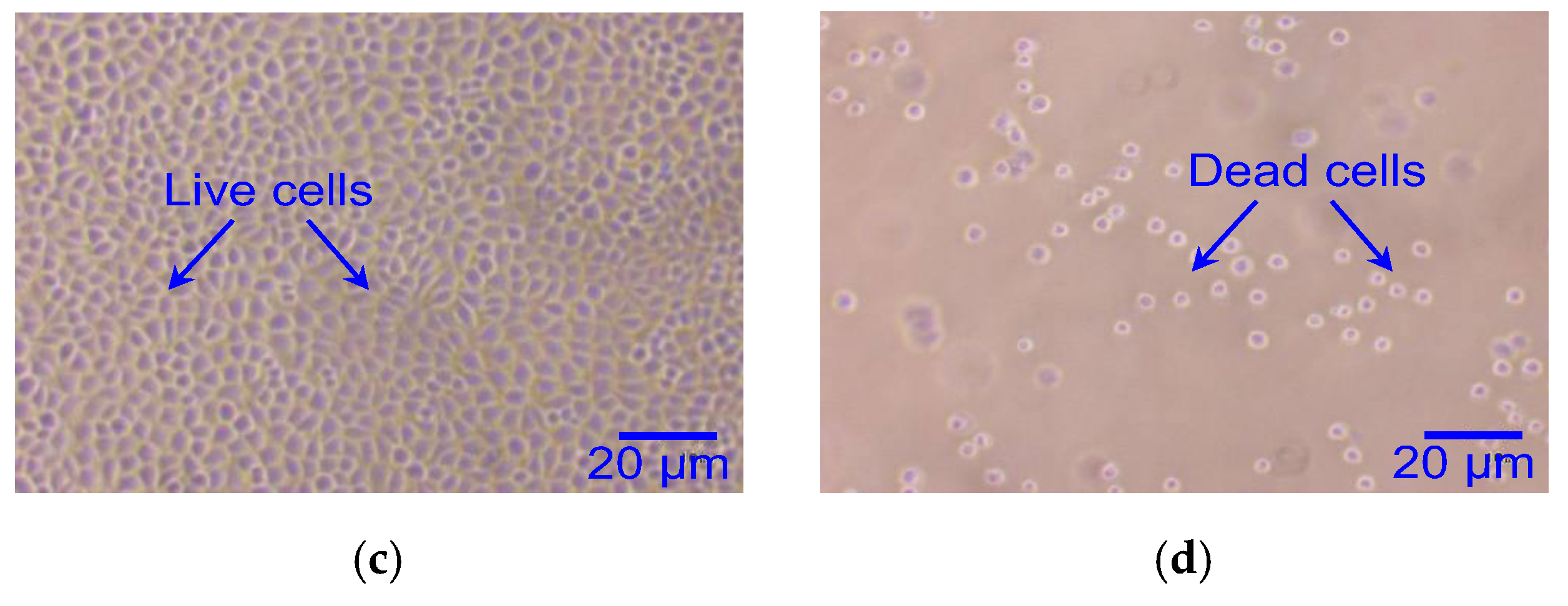
4.3. Biocompatibility Test
4.4. In Vivo Testing Preparation: Surgery and Electrophysiological Recordings
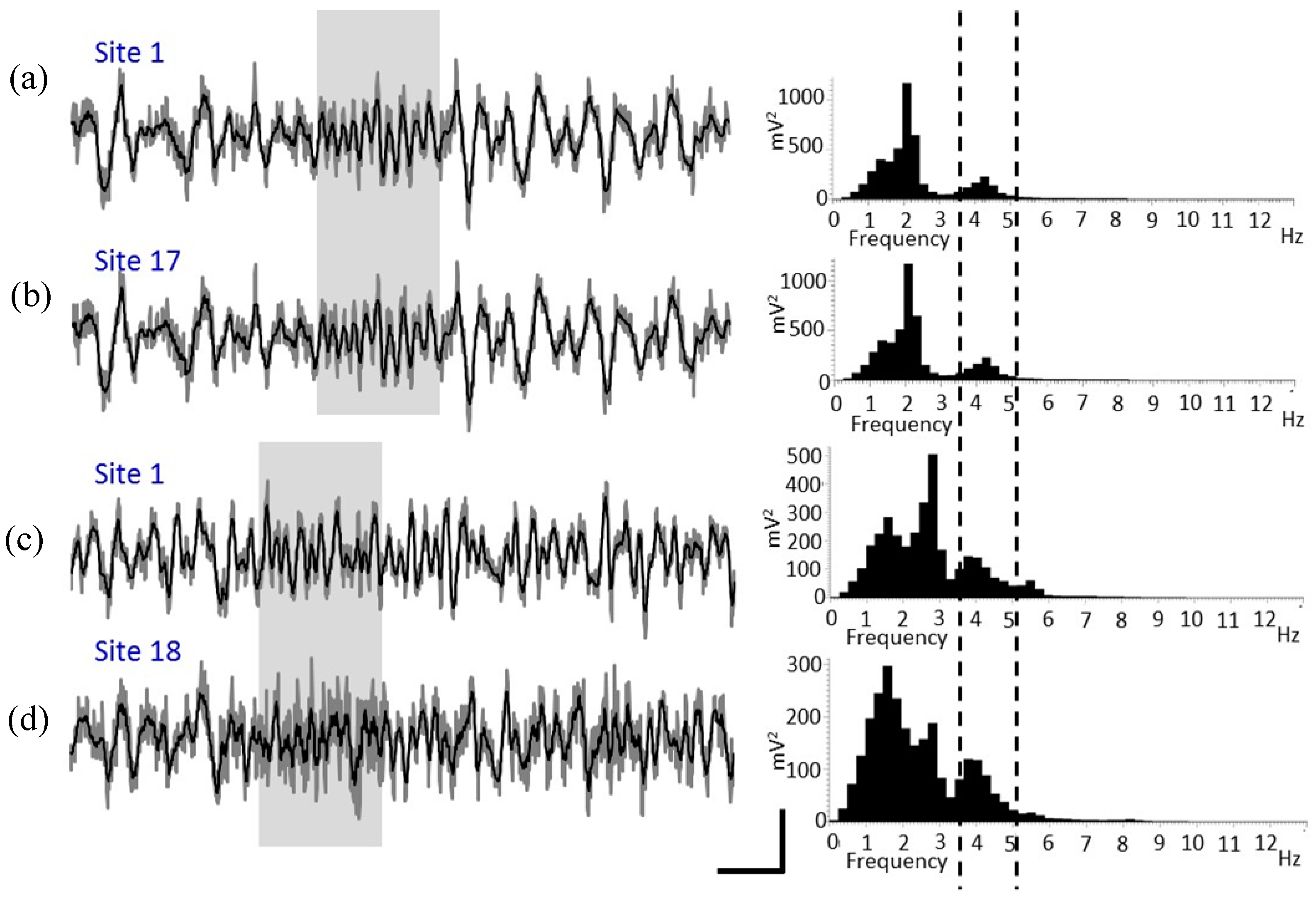
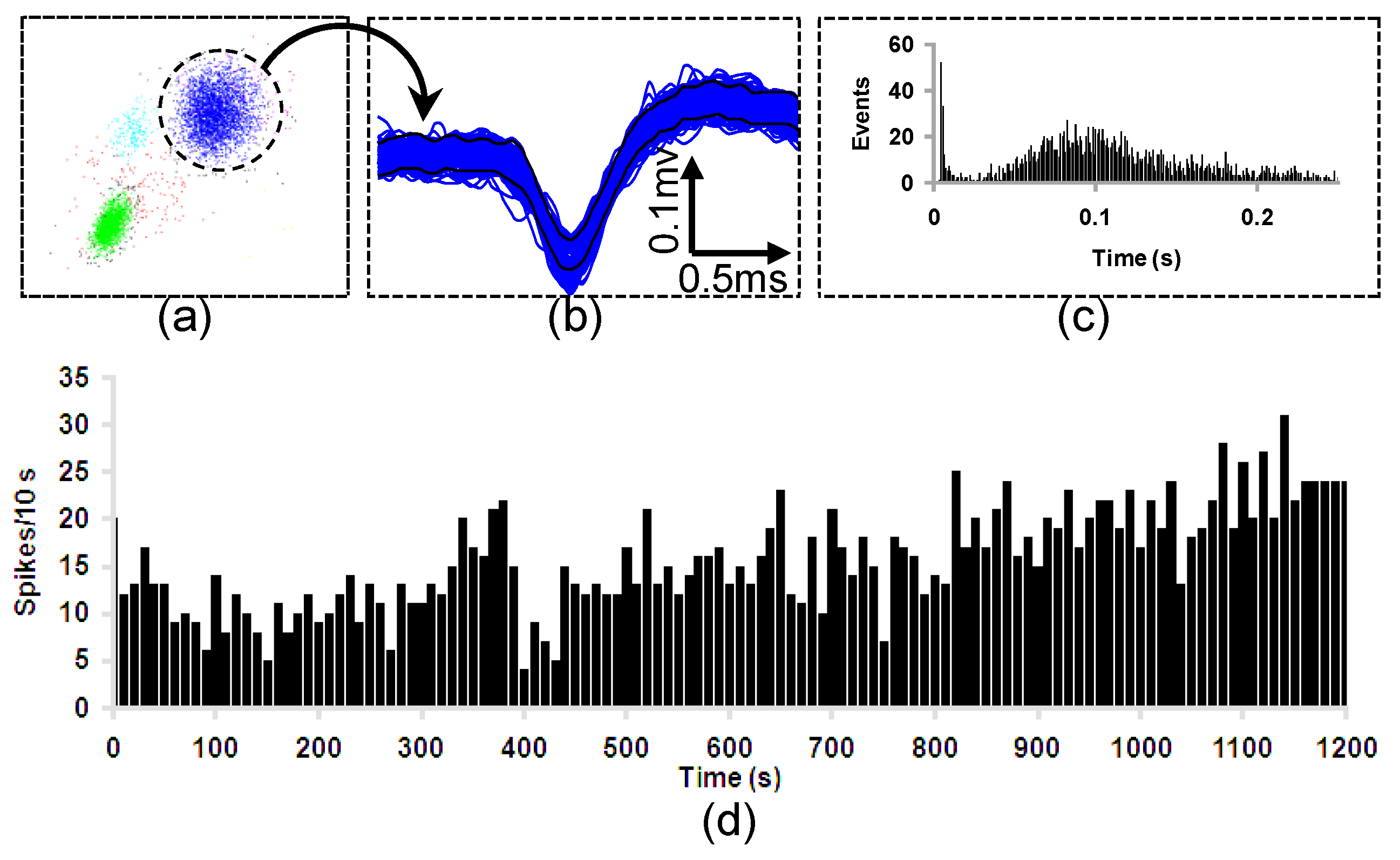
4.5. In Vivo Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armour, B.S.; Courtney-Long, E.A.; Fox, M.H.; Fredine, H.; Cahill, A. Prevalence and Causes of Paralysis—United States, 2013. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 1855–1857. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, L.R.; Serruya, M.D.; Friehs, G.M.; Mukand, J.A.; Saleh, M.; Caplan, A.H.; Branner, A.; Chen, D.; Penn, R.D.; Donoghue, J.P. Neuronal ensemble control of prosthetic devices by a human with tetraplegia. Nature 2006, 442, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velliste, M.; Perel, S.; Spalding, M.C.; Whitford, A.S.; Schwartz, A.B. Cortical control of a prosthetic arm for self-feeding. Nature 2008, 453, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, L.R.; Bacher, D.; Jarosiewicz, B.; Masse, N.Y.; Simeral, J.D.; Vogel, J.; Haddadin, S.; Liu, J.; Cash, S.S.; Van Der Smagt, P.; et al. Reach and grasp by people with tetraplegia using a neurally controlled robotic arm. Nat. Cell Boil. 2012, 485, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, G.W.V.; Rynes, M.L.; Kelliher, Z.; Goodwin, S.J. Review of Brain-Machine Interfaces Used in Neural Prosthetics with New Perspective on Somatosensory Feedback through Method of Signal Breakdown. Scientifica 2016, 2016, 8956432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzsáki, G.; Anastassiou, C.A.; Koch, C. The origin of extracellular fields and currents—EEG, ECoG, LFP and spikes. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorfia, M.; Skousenb, J.L.; Wedera, C.; Capadona, J.R. Progress Towards Biocompatible Intracortical Microelectrodes for Neural Interfacing Applications. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kmon, P. Low-power low-area techniques for multichannel recording circuits dedicated to biomedical experiments. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2016, 64, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musallam, S.; Bak, M.J.; Troyk, P.R.; Andersen, R.A. A floating metal microelectrode array for chronic implantation. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 160, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Bhandari, R.; Klein, M.; Negi, S.; Rieth, L.; Tathireddy, P.; Toepper, M.; Oppermann, H.; Solzbacher, F. Integrated Wireless Neural Interface Based on the Utah Electrode Array. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, C.M.; Andrei, A.; Mitra, S.; Welkenhuysen, M.; Eberle, W.; Bartic, C.; Puers, R.; Yazicioglu, R.F.; Gielen, G.G.E. An Implantable 455-Active-Electrode 52-Channel CMOS Neural Probe. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, E.M.; Nordhausen, C.T.; Normann, R.A. The Utah Intracortical Electrode Array: A recording structure for potential brain-computer interfaces. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 102, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, K.; Schwaerzle, M.; Ulbert, I.; Neves, H.P.; Paul, O.; Ruther, P. CMOS-Based High-Density Silicon Microprobe Arrays for Electronic Depth Control in Intracortical Neural Recording-Characterization and Application. J. Microelectromechan. Syst. 2011, 21, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barz, F.; Paul, O.; Ruther, P. Modular assembly concept for 3D neural probe prototypes offering high freedom of design and alignment precision. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 3977–3980. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-W.; Chiou, J.-C. Development of a Three Dimensional Neural Sensing Device by a Stacking Method. Sensors 2010, 10, 4238–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.-F.; Maleki, T.; Ziaie, B. A self-assembled 3D microelectrode array. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 35013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Riedel-Kruse, I.H.; Nawroth, J.C.; Roukes, M.L.; Laurent, G.; Masmanidis, S.C. High-Resolution Three-Dimensional Extracellular Recording of Neuronal Activity With Microfabricated Electrode Arrays. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 101, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herwik, S.; Kisban, S.; A A Aarts, A.; Seidl, K.; Girardeau, G.; Benchenane, K.; Zugaro, M.B.; I Wiener, S.; Paul, O.; Neves, H.P.; et al. Fabrication technology for silicon-based microprobe arrays used in acute and sub-chronic neural recording. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 74008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, A.A.A.; Neves, H.; Ulbert, I.; Wittner, L.; Grand, L.; Fontes, M.B.A.; Herwik, S.; Kisban, S.; Paul, O.; Ruther, P.; et al. A 3D slim-base probe array for in vivo recorded neuron activity. In Proceedings of the 2008 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–25 August 2008; pp. 5798–5801. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.-Y.; Je, M.; Tan, K.L.; Tan, E.L.; Lim, R.; Yao, L.; Li, P.; Park, W.-T.; Phua, E.J.R.; Gan, C.L.; et al. A low-profile three-dimensional neural probe array using a silicon lead transfer structure. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 95013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.C.; A Hippensteel, J.; Dilgen, J.; Shain, W.; Kipke, D.R. Complex impedance spectroscopy for monitoring tissue responses to inserted neural implants. J. Neural Eng. 2007, 4, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Method of Cytotoxicity Testing for ISO 10993 Standard. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: In Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/36406.html (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Sample Preparation of Cytotoxicity Testing for ISO 10993 Standard. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 12: Sample Preparation and Reference Materials. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/53468.html (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Farooq, U.; Rajkumar, R.; Sukumaran, S.; Wu, Y.; Tan, W.H.; Dawe, G.S. Corticotropin-releasing factor infusion into nucleus incertus suppresses medial prefrontal cortical activity and hippocampo-medial prefrontal cortical long-term potentiation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 38, 2516–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, M.-Y.; Damalerio, R.B.; Chen, W.; Rajkumar, R.; Dawe, G.S. Ultracompact Multielectrode Array for Neurological Monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102286
Cheng M-Y, Damalerio RB, Chen W, Rajkumar R, Dawe GS. Ultracompact Multielectrode Array for Neurological Monitoring. Sensors. 2019; 19(10):2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102286
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Ming-Yuan, Ramona B. Damalerio, Weiguo Chen, Ramamoorthy Rajkumar, and Gavin S. Dawe. 2019. "Ultracompact Multielectrode Array for Neurological Monitoring" Sensors 19, no. 10: 2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102286
APA StyleCheng, M.-Y., Damalerio, R. B., Chen, W., Rajkumar, R., & Dawe, G. S. (2019). Ultracompact Multielectrode Array for Neurological Monitoring. Sensors, 19(10), 2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102286




