Robust Entangled-Photon Ghost Imaging with Compressive Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
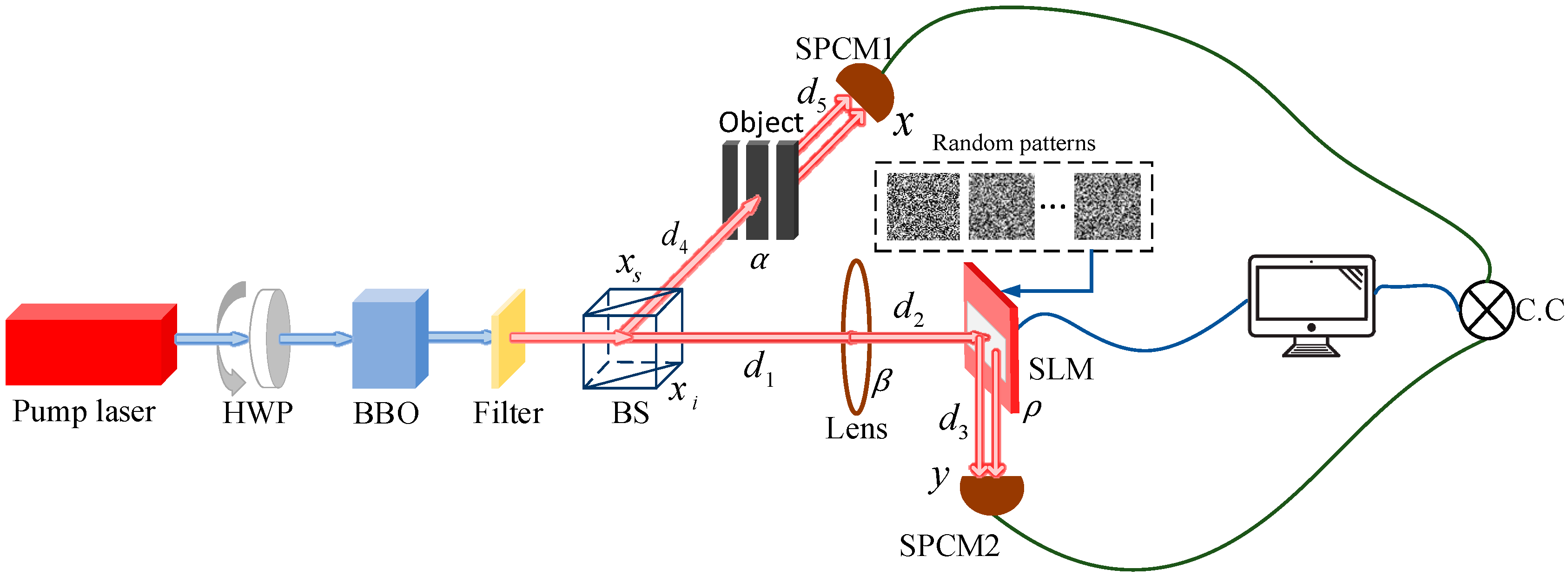
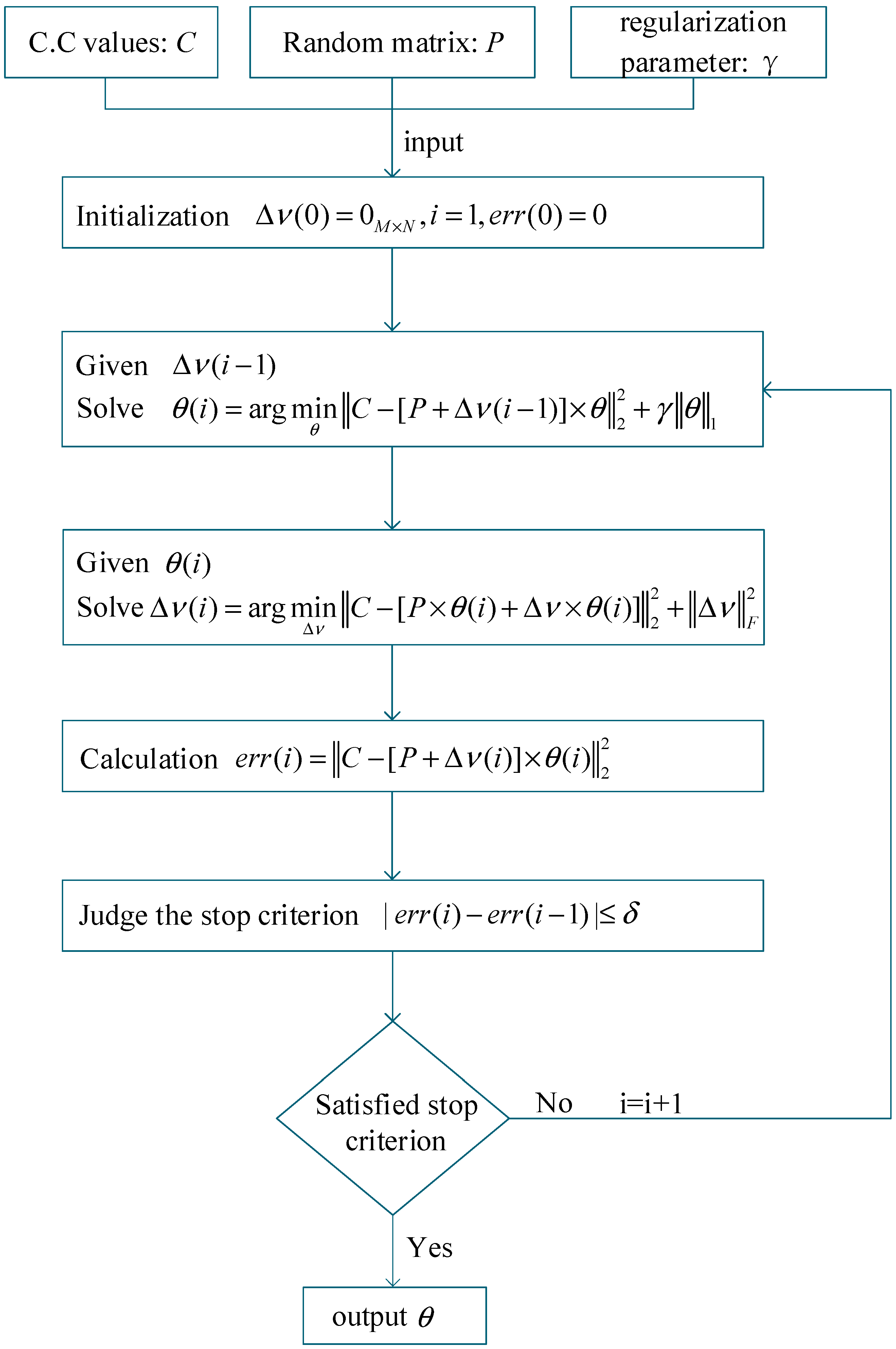
2. Robust Ghost Imaging Based on STLS
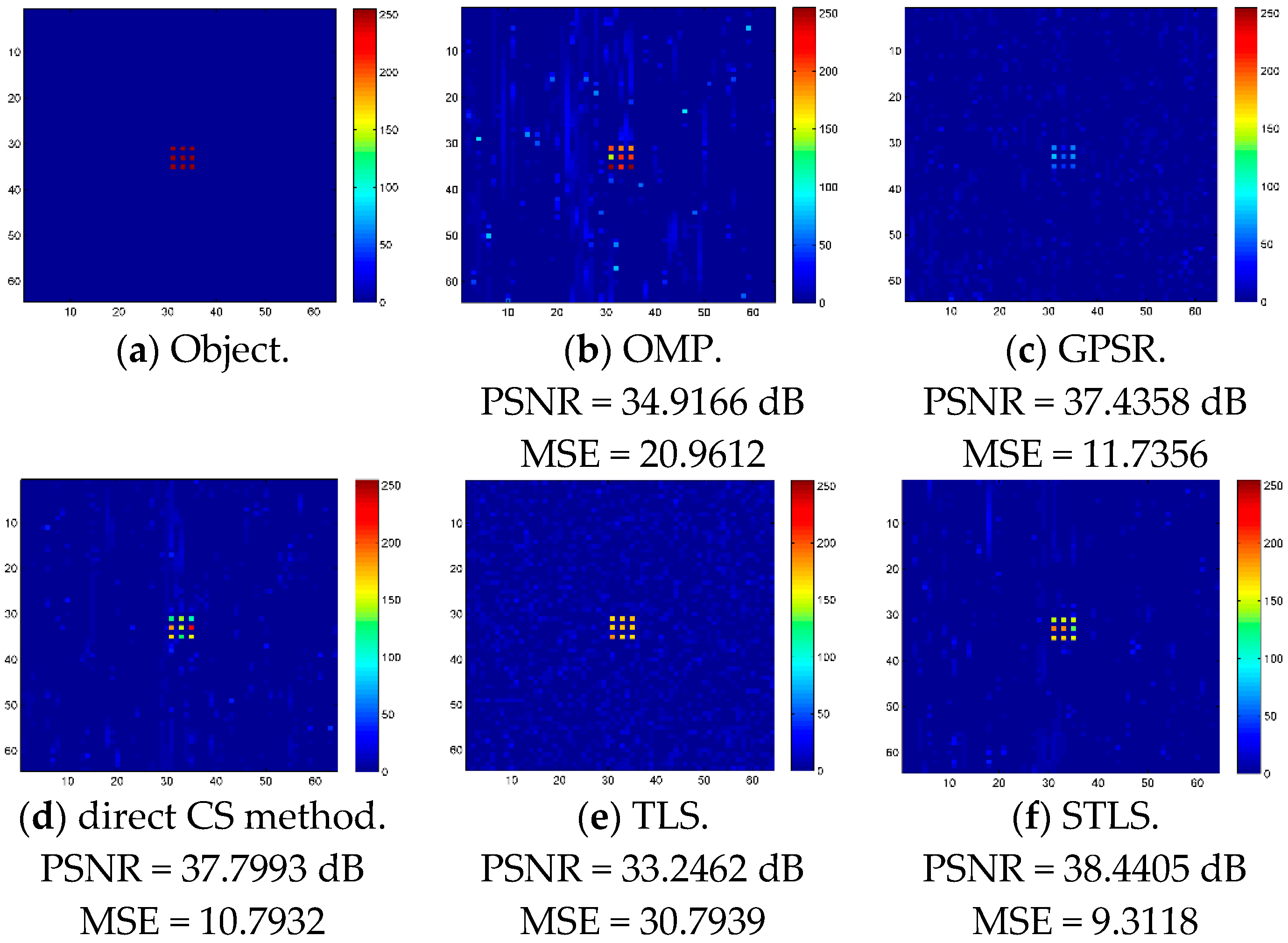
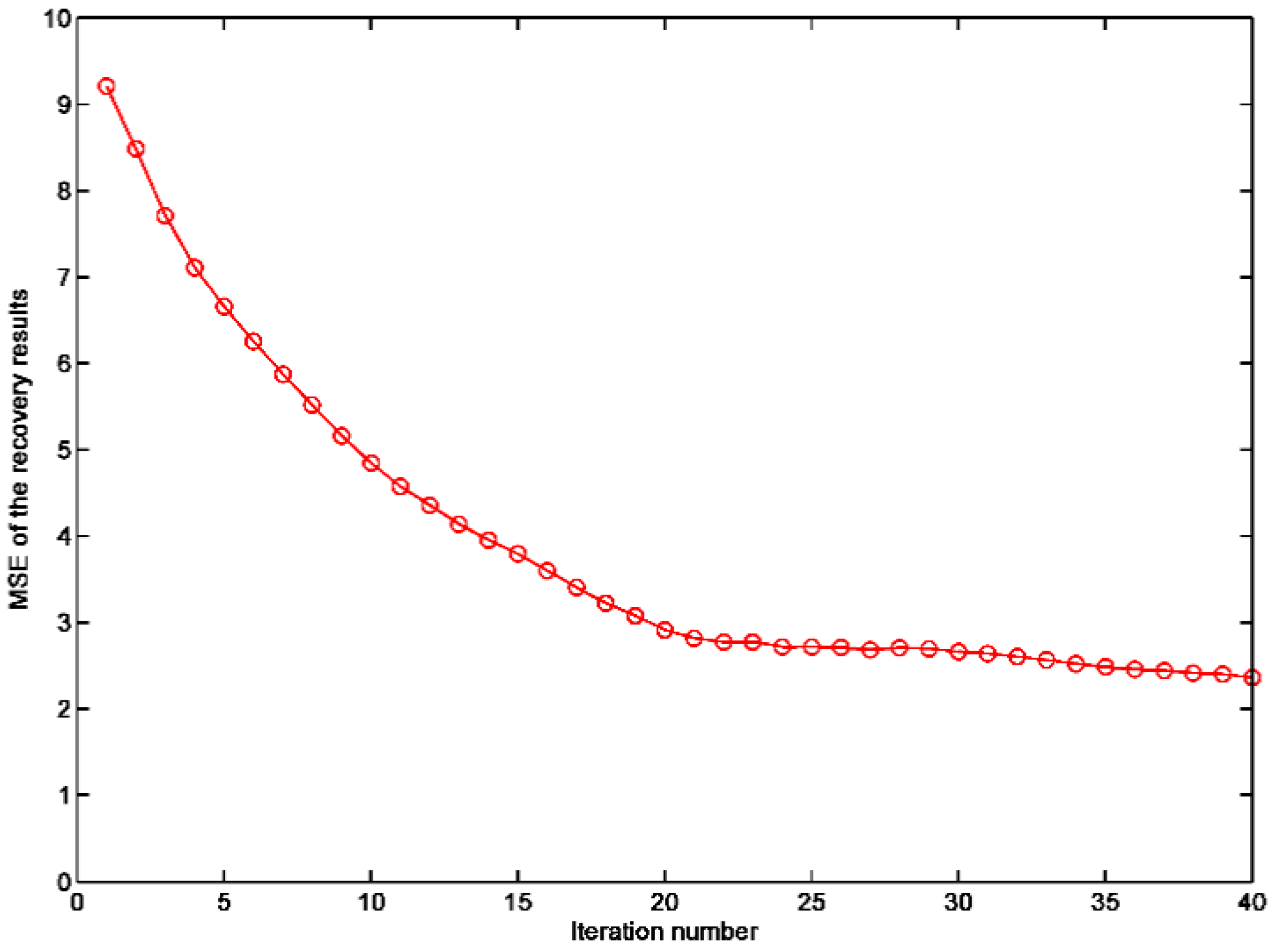
3. Numerical Simulation Results
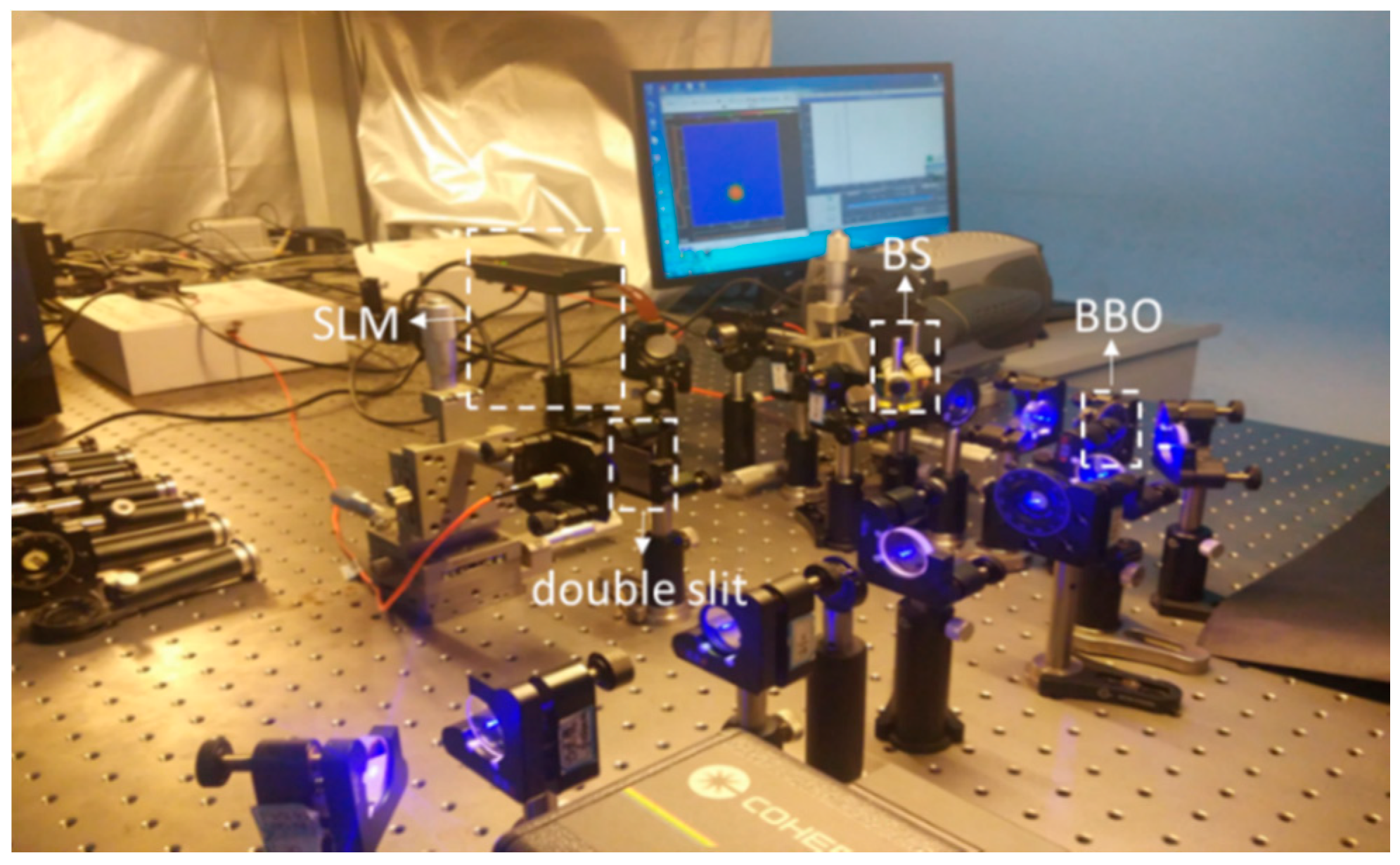
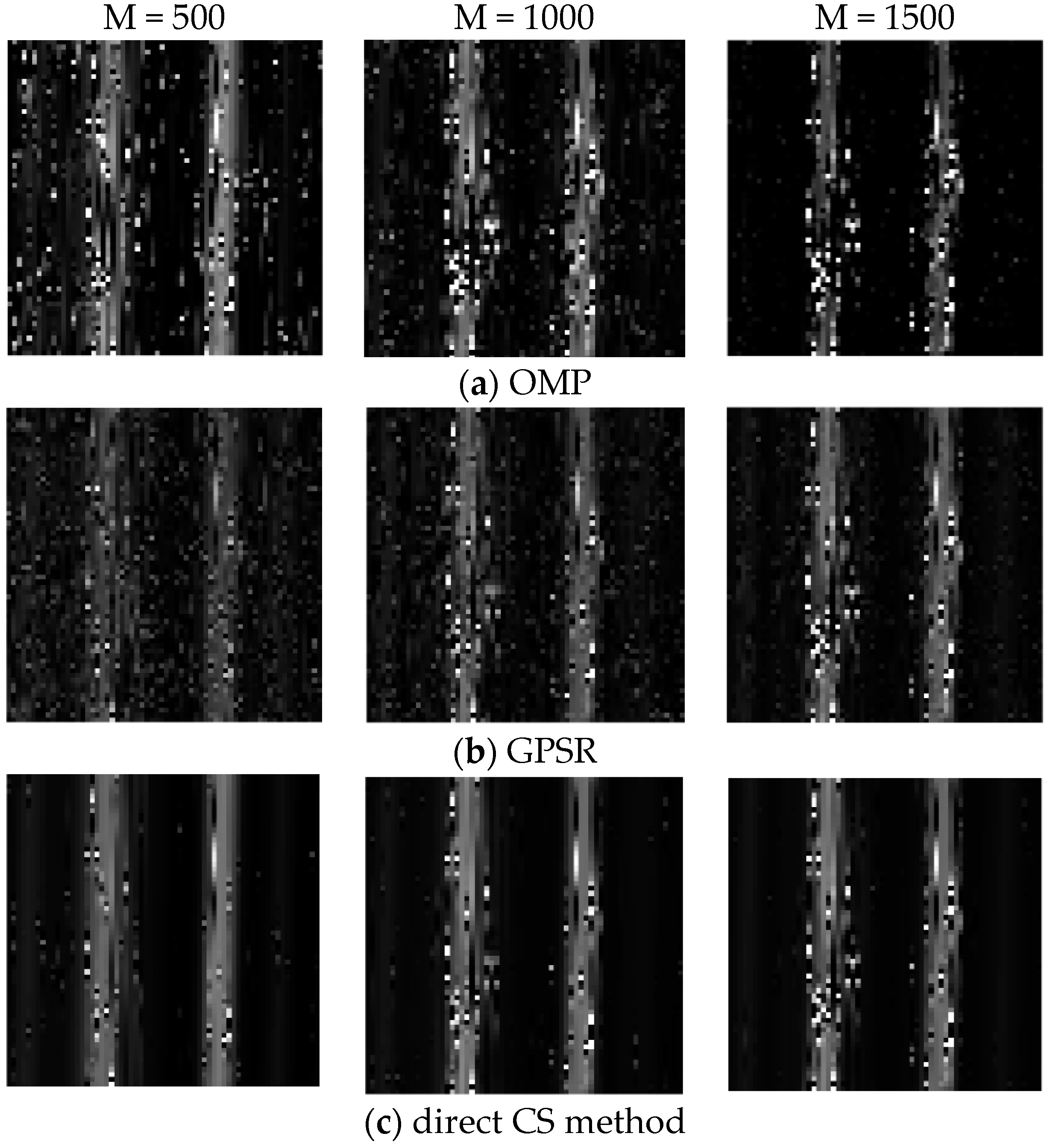
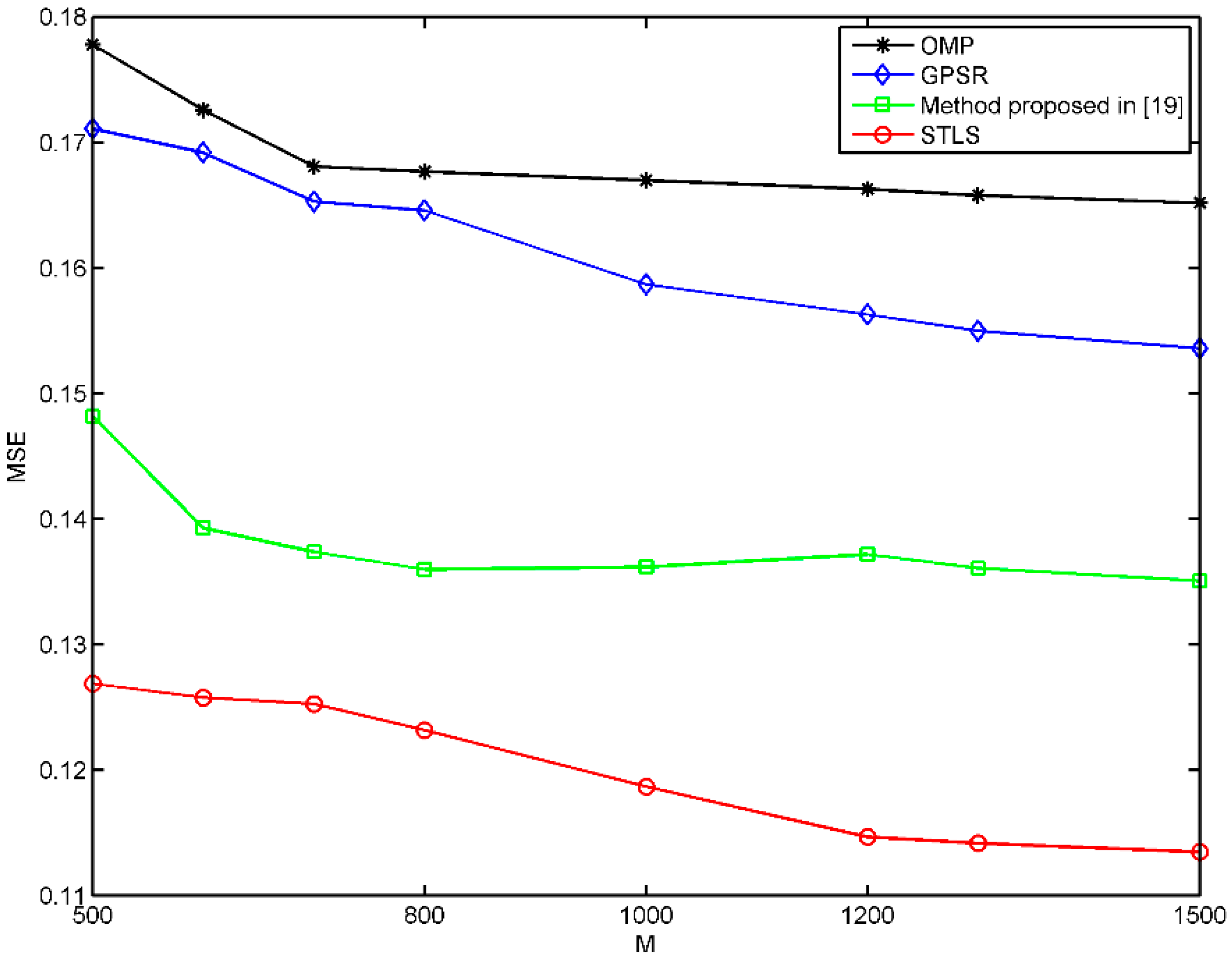
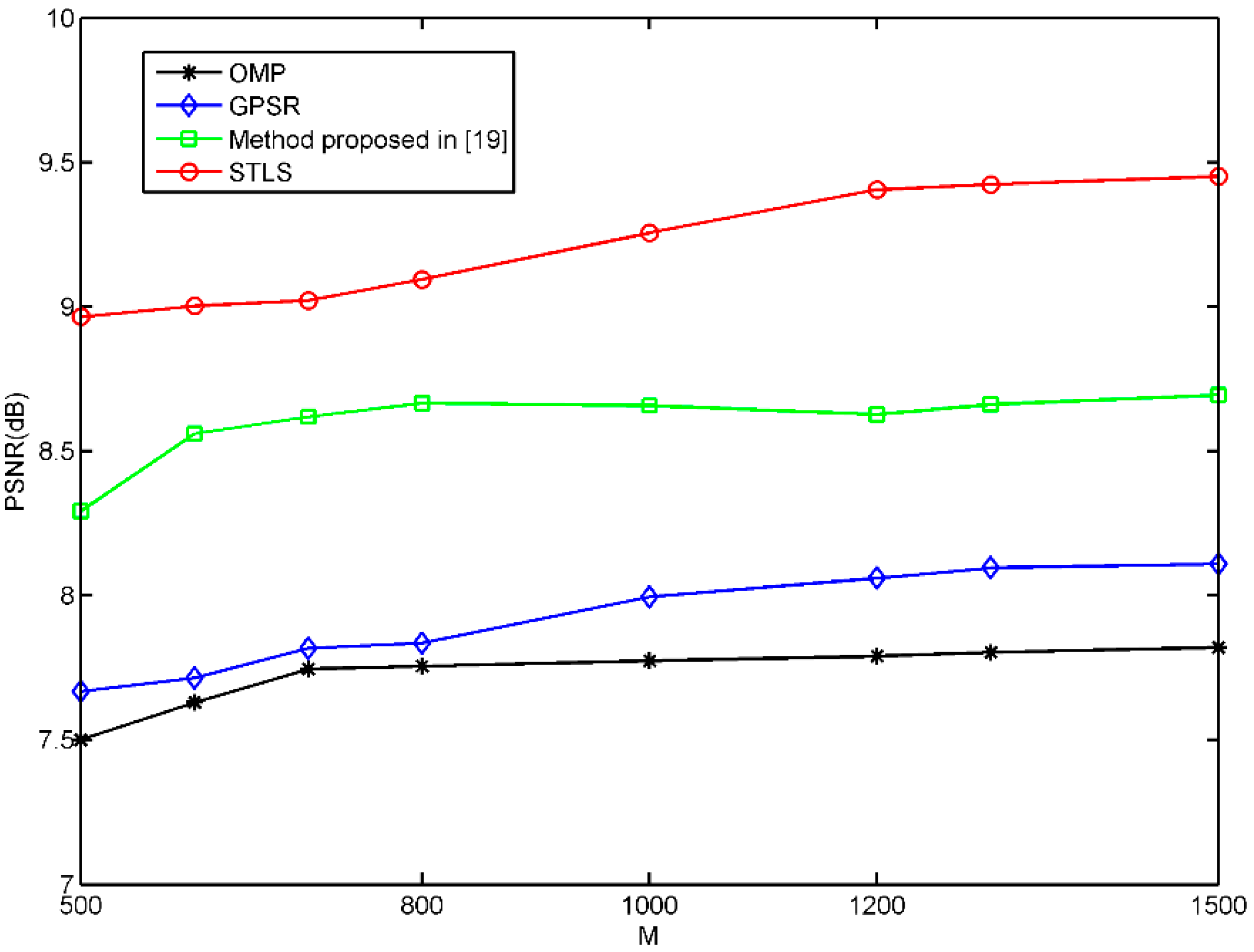
4. Experimental Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morris, P.A.; Aspden, R.S.; Bell, J.E.; Boyd, R.W.; Padgett, M.J. Imaging with a small number of photons. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, P.; Durán, V.; Tajahuerce, E.; Lancis, J. Optical encryption based on computational ghost imaging. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 2391–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, J.H.; Boyd, R.W. The physics of ghost imaging. Quantum Inf. Process. 2012, 11, 949–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magana-Loaiza, O.S.; Howland, G.A.; Malik, M.; Howell, J.C.; Boyd, R.W. Compressive object tracking using entangled photons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 231104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strekalov, D.V.; Sergienko, A.V.; Klyshko, D.N.; Shih, Y.H. Observation of two-photon “ghost” interference and diffraction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittman, T.B.; Shih, Y.H.; Strekalov, D.V.; Sergienko, A.V. Optical imaging by means of two-photon quantum entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 1995, 52, R3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, M.; Shih, Y.H. Quantum imaging. Laser Phys. Lett. 2010, 2, 567–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, O.; Bromberg, Y.; Silberberg, Y. Compressive ghost imaging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Lei, B. Robust Facial Expression Recognition via Compressive Sensing. Sensors 2012, 12, 3747–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Truong, T.K. Simultaneous Radio Frequency and Wideband Interference Suppression in SAR Signals via Sparsity Exploitation in Time-Frequency Domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5780–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.K.; Li, M.F.; Yao, X.R.; Liu, X.F.; Wu, L.A.; Zhai, G.J. Adaptive compressive ghost imaging based on wavelet trees and sparse representation. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 7133–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tropp, J.A.; Gilbert, A.C. Signal Recovery from Random Measurements via Orthogonal Matching Pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2007, 53, 4655–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brida, G.; Chekhova, M.V.; Fornaro, G.A.; Genovese, M.; Lopaeva, E.D.; Berchera, I.R. Systematic analysis of signal-to-noise ratio in bipartite ghost imaging with classical and quantum light. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 83, 063807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennink, R.S.; Bentley, S.J.; Boyd, R.W. “Two-Photon” coincidence imaging with a classical source. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 113601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.; Han, S. Super-resolution ghost imaging via compressive sampling reconstruction. arXiv, 2009; arXiv:0910.4823. [Google Scholar]
- Genovese, M. Real applications of quantum imaging. J. Opt. 2016, 18, 073002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, M.W.; Seong, W.; Ye, J.C. Compressed sensing metal artifact removal in dental CT. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Boston, MA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bobin, J.; Starck, J.L.; Ottensamer, R. Compressed Sensing in Astronomy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2008, 2, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajkowski, K.M.; Pastuszczak, A.; Kotynski, R. Real-time single-pixel video imaging with Fourier domain regularization. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1804.10008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zheng, G.; Zhong, J. Fast Fourier single-pixel imaging via binary illumination. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, C.F.; Murray-Smith, R.; Padgett, M.J.; Edgar, M.P. Deep learning for real-time single-pixel video. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennink, R.S.; Bentley, S.J.; Boyd, R.W.; Howell, J.C. Quantum and classical coincidence imaging. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 033601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Pan, L.; Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Gong, W.; Han, S. Performance analysis of ghost imaging lidar in background light environment. Photonics Res. 2017, 5, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.A.; Toninelli, E.; Morris, P.A.; Aspden, R.S.; Gregory, T.; Spalding, G.; Boyd, R.W.; Padgett, M.J. Resolution limits of quantum ghost imaging. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 7528–7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Han, S.; Kolobov, M.I. Quantum limits of super-resolution of optical sparse objects via sparsity constraint. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 23235–23252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, B.E.; Abouraddy, A.F.; Sergienko, A.V.; Teich, M.C. Duality between partial coherence and partial entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 2000, 62, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerom, P.; Chan, K.W.; Howell, J.C.; Boyd, R.W. Entangled-photon compressive ghost imaging. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 84, 061804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyshko, D.N. Photons Nonlinear Optics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Pittman, T.B.; Strekalov, D.V.; Klyshko, D.N.; Rubin, M.H.; Sergienko, A.V.; Shih, Y.H. Two-photon geometric optics. Phys. Rev. A 1996, 53, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilanci, M.; Arikan, O. Recovery of sparse perturbations in Least Squares problems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Candès, E.J.; Romberg, J.K.; Tao, T. Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 2006, 59, 1207–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrholz, E.; Teschke, G. Compressive sensing principles and iterative sparse recovery for inverse and ill-posed problems. Inverse Probl. 2010, 26, 125012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candes, E.J.; Romberg, J.; Tao, T. Robust Uncertainty Principles: Exact Signal Reconstruction from Highly Incomplete Frequency Information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candes, E.J.; Tao, T. Near-Optimal Signal Recovery from Random Projections: Universal Encoding Strategies? IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 5406–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Methods | OMP | GPSR | Method Proposed in [19] | STLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Runtime | 7.8582 s | 29.5845 s | 30.1480 s | 102.5624 s |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Gao, W.; Qian, J.; Guo, Q.; Xi, J.; Ritz, C.H. Robust Entangled-Photon Ghost Imaging with Compressive Sensing. Sensors 2019, 19, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010192
Li J, Gao W, Qian J, Guo Q, Xi J, Ritz CH. Robust Entangled-Photon Ghost Imaging with Compressive Sensing. Sensors. 2019; 19(1):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010192
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jun, Wenyu Gao, Jiachuan Qian, Qinghua Guo, Jiangtao Xi, and Christian H. Ritz. 2019. "Robust Entangled-Photon Ghost Imaging with Compressive Sensing" Sensors 19, no. 1: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010192
APA StyleLi, J., Gao, W., Qian, J., Guo, Q., Xi, J., & Ritz, C. H. (2019). Robust Entangled-Photon Ghost Imaging with Compressive Sensing. Sensors, 19(1), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010192





