Reliability Modeling for Humidity Sensors Subject to Multiple Dependent Competing Failure Processes with Self-Recovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
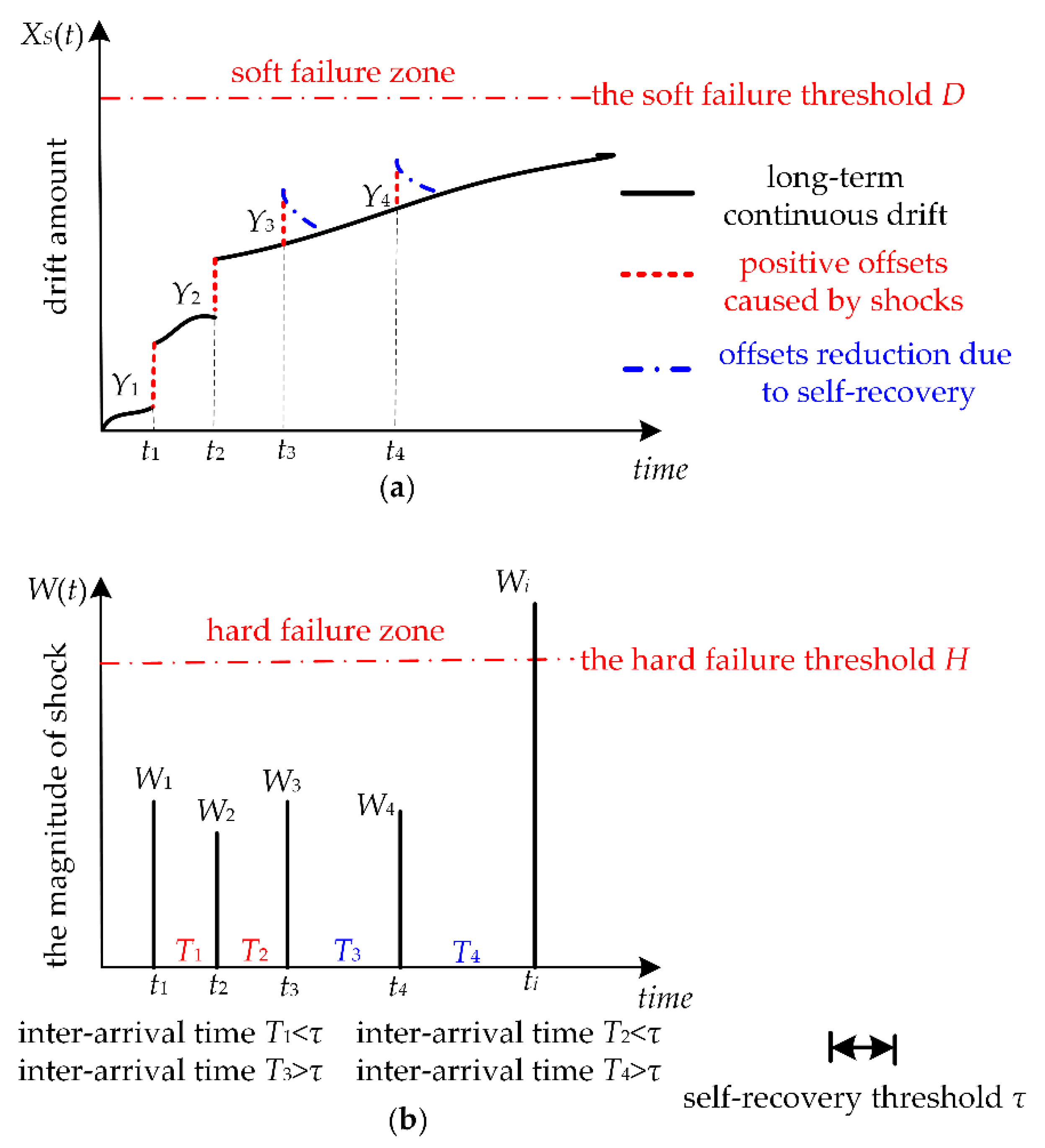
2. Description of Humidity Sensors Failure Process
3. Reliability Modeling for Humidity Sensors with Considering Self-Recovery
3.1. Reliability Modeling for Humidity Sensors Subject to Soft Failure
3.2. Reliability Modeling for Humidity Sensors Subject to Random Shocks
3.3. Reliability Modeling for Humidity Sensors Subject to MDCFPs
3.4. Some Special Cases
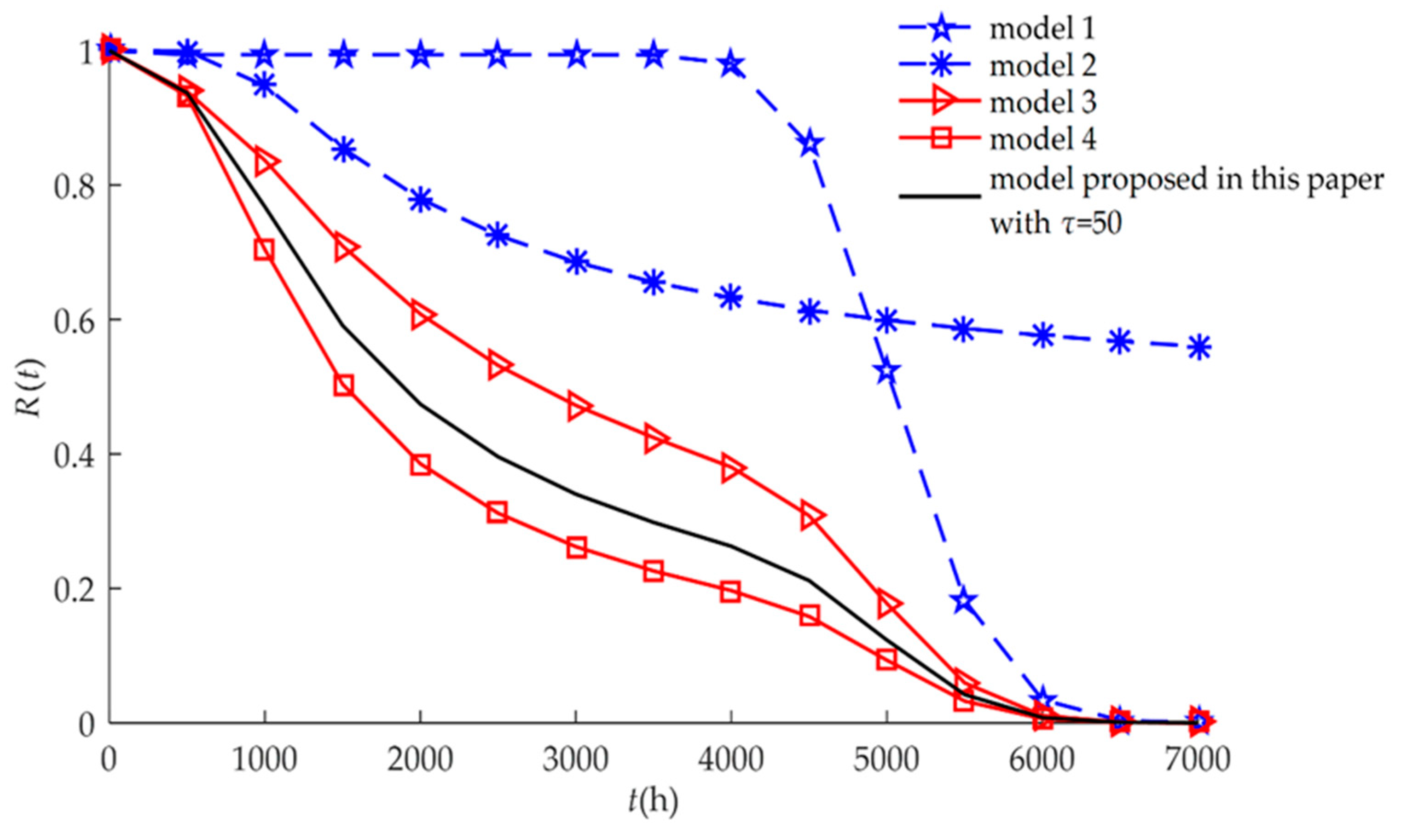
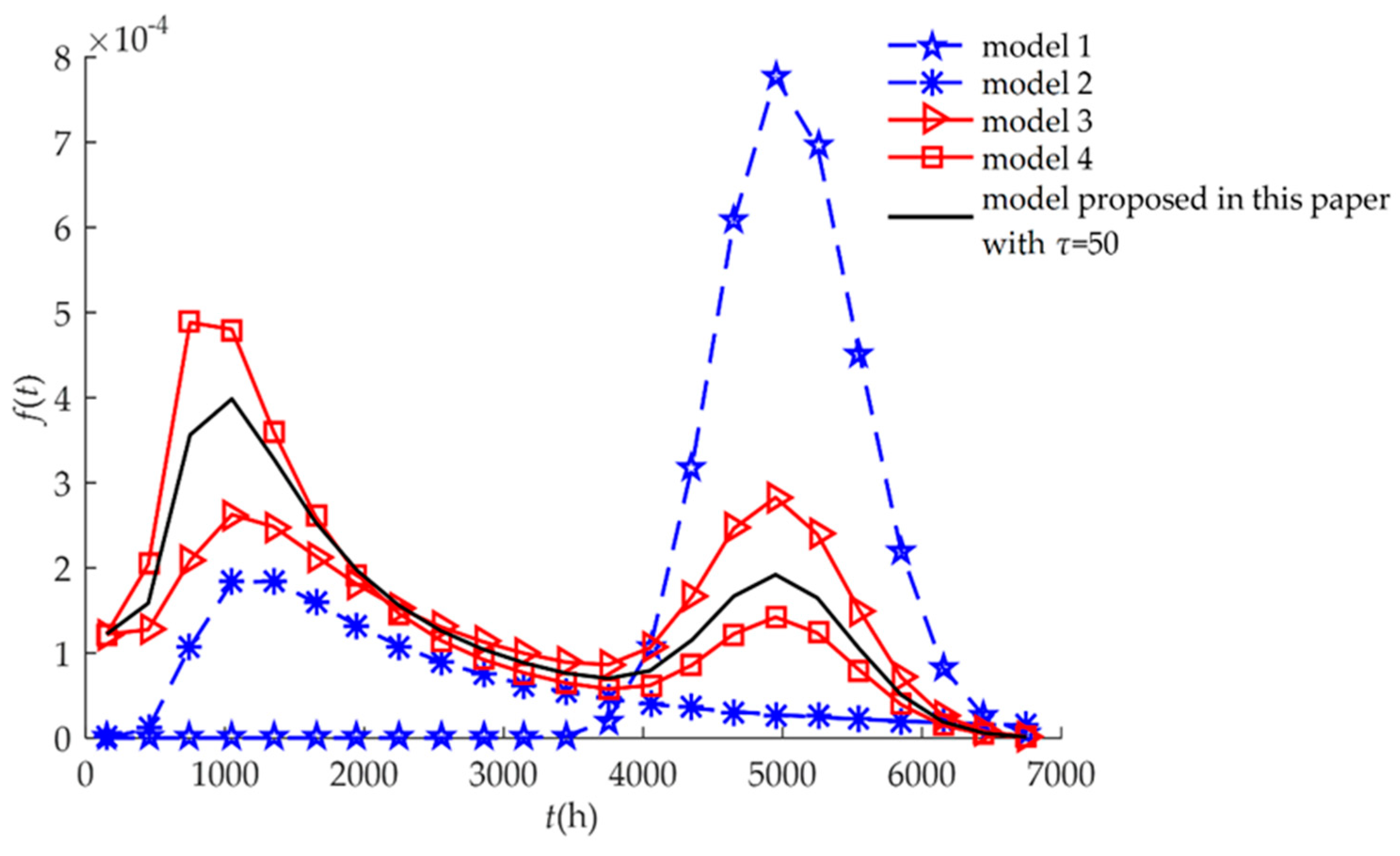
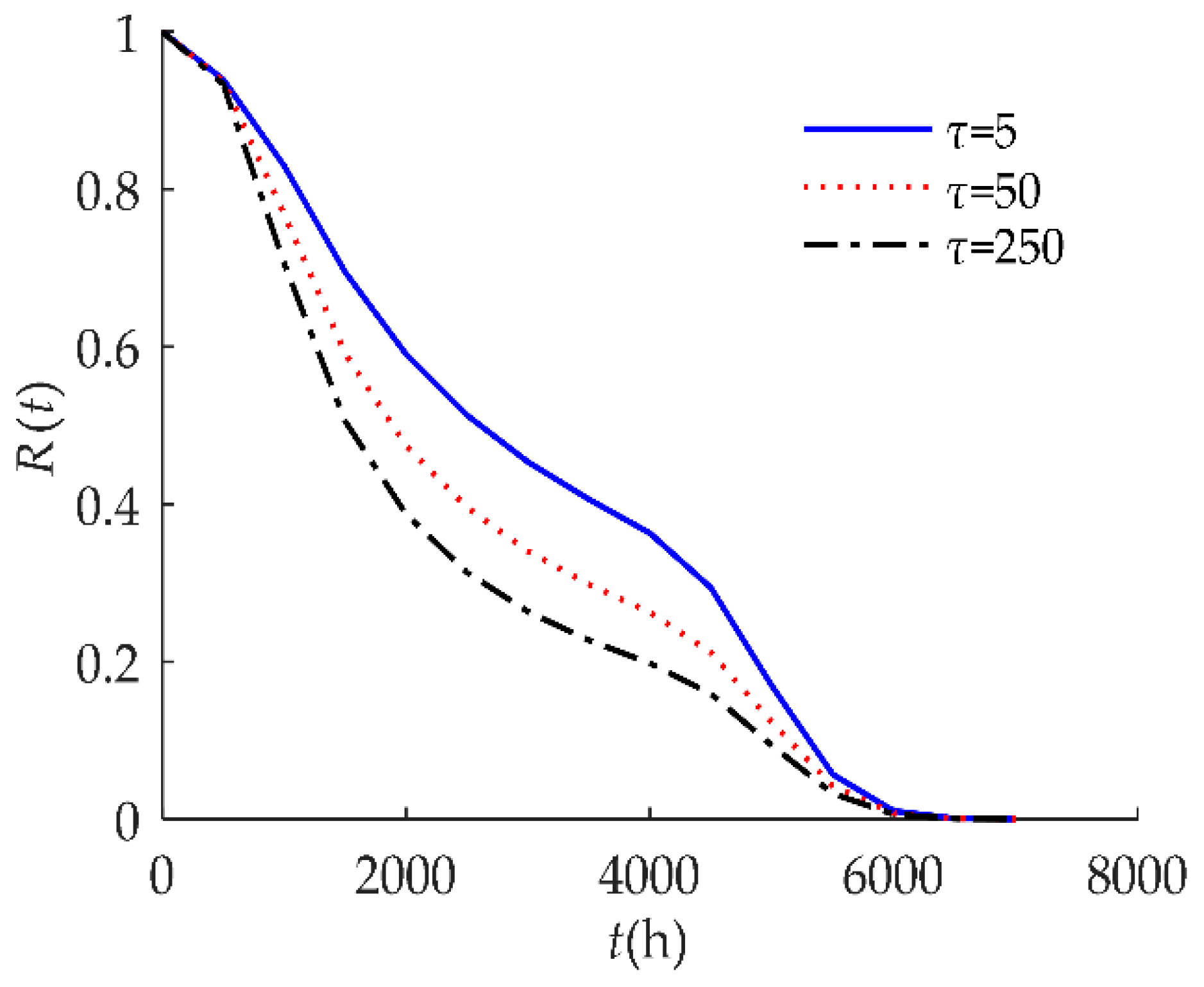
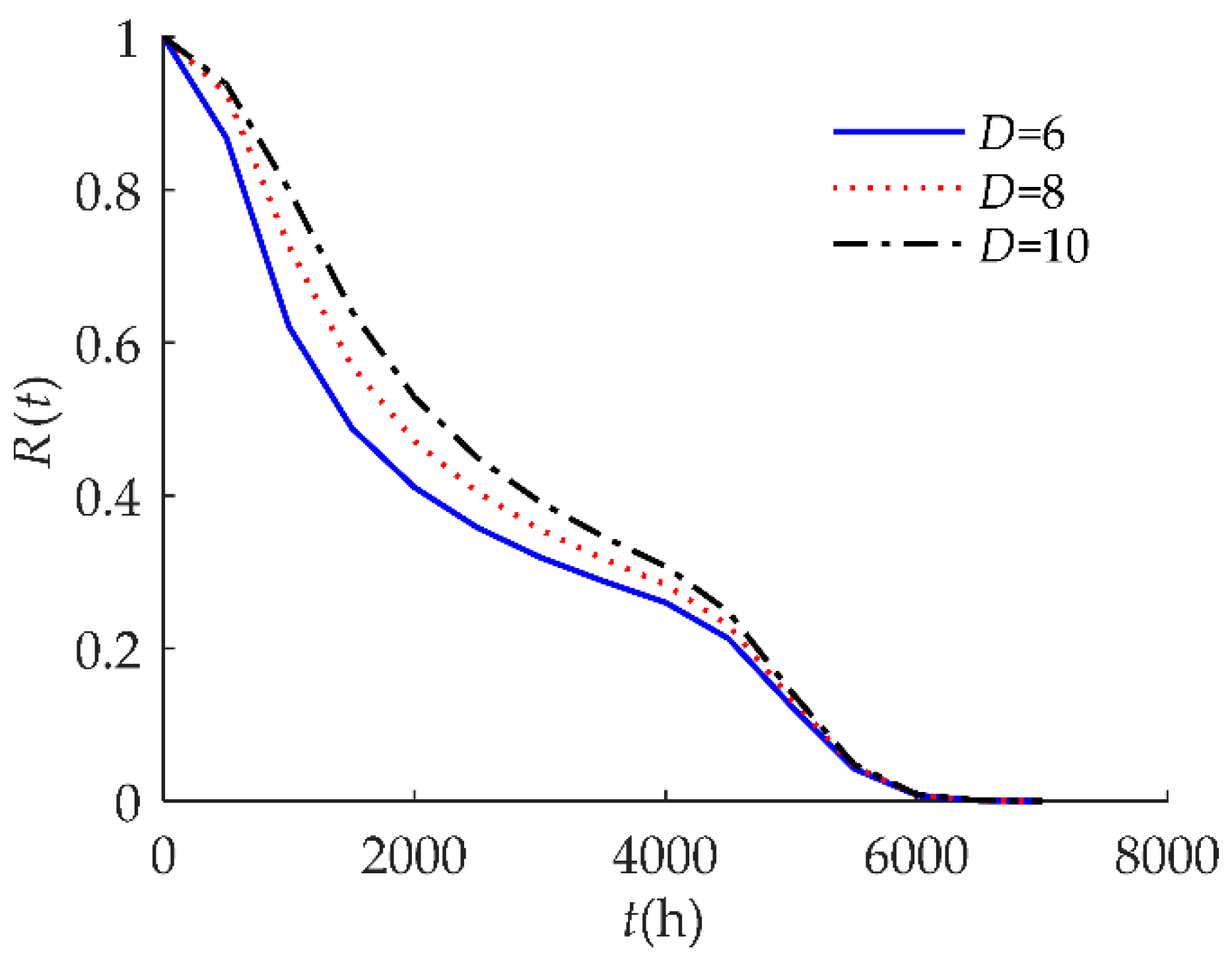
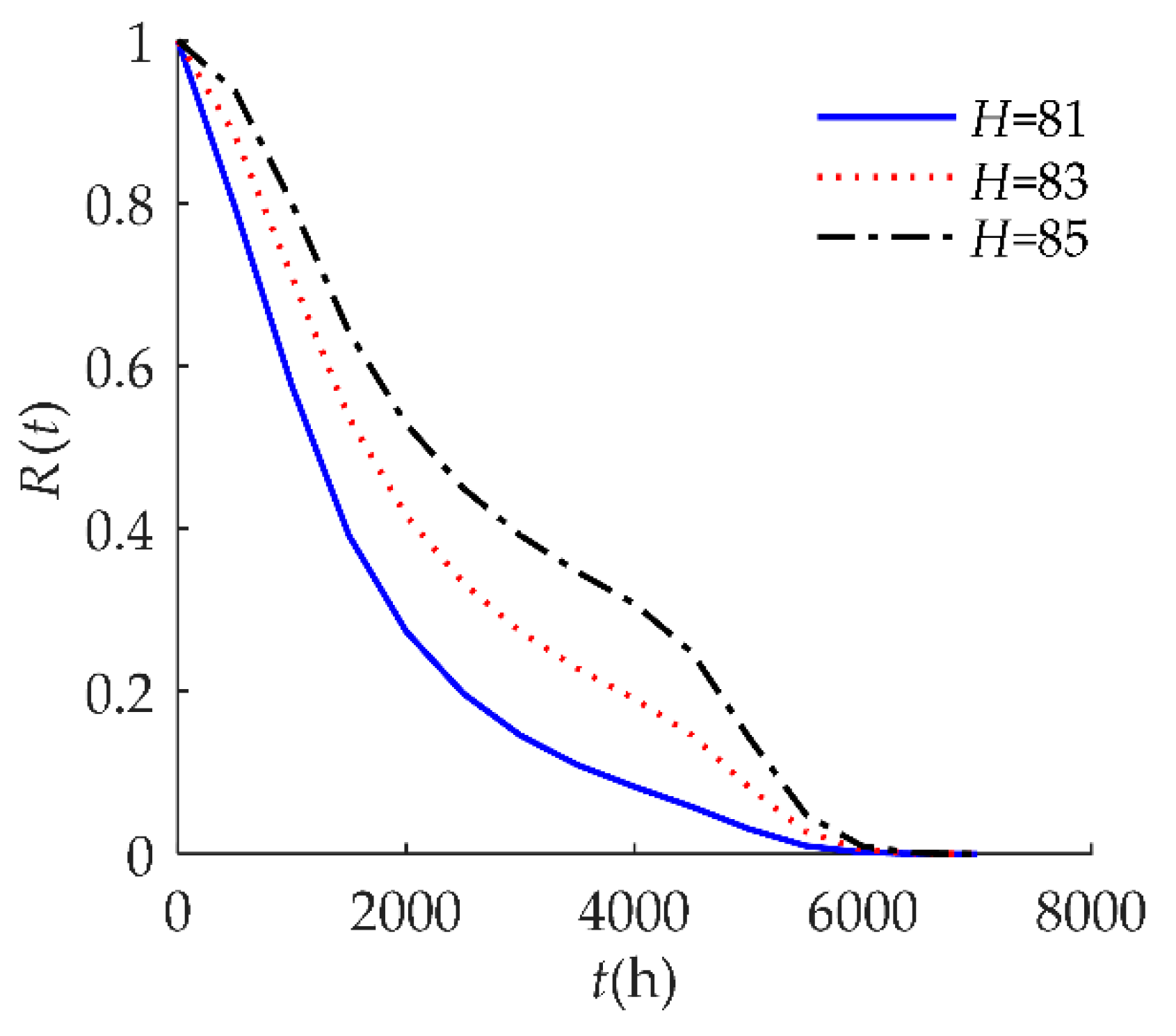
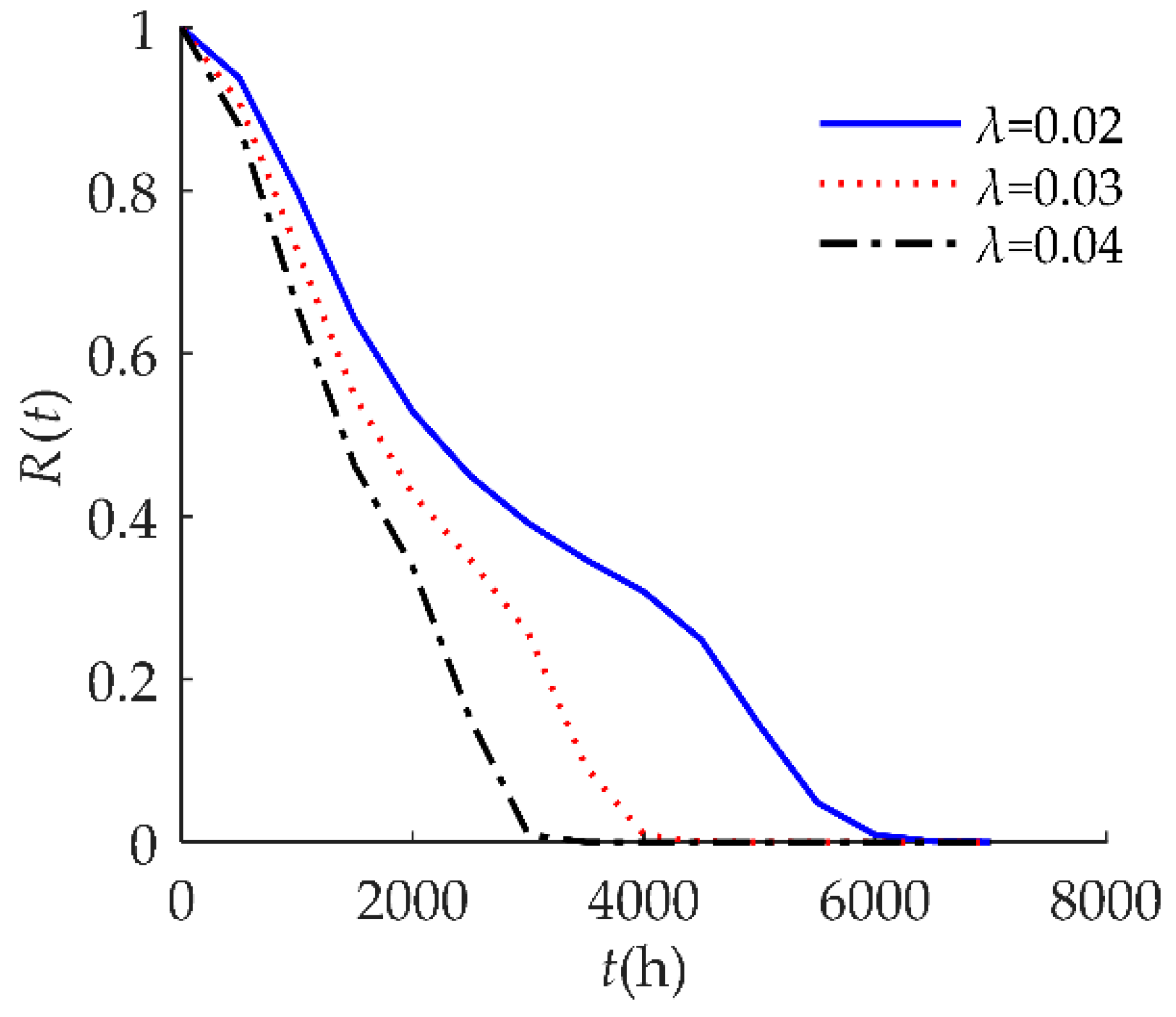
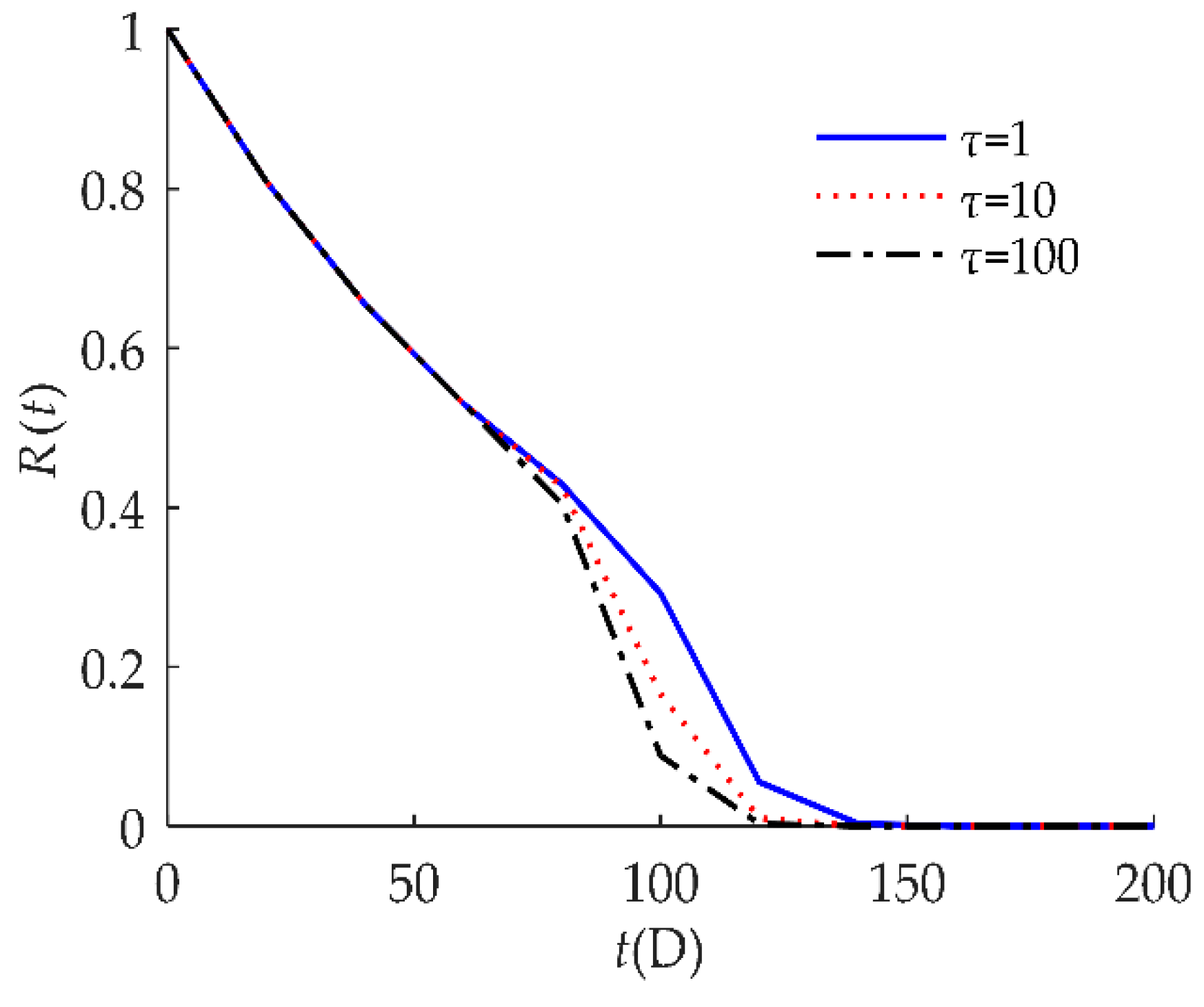
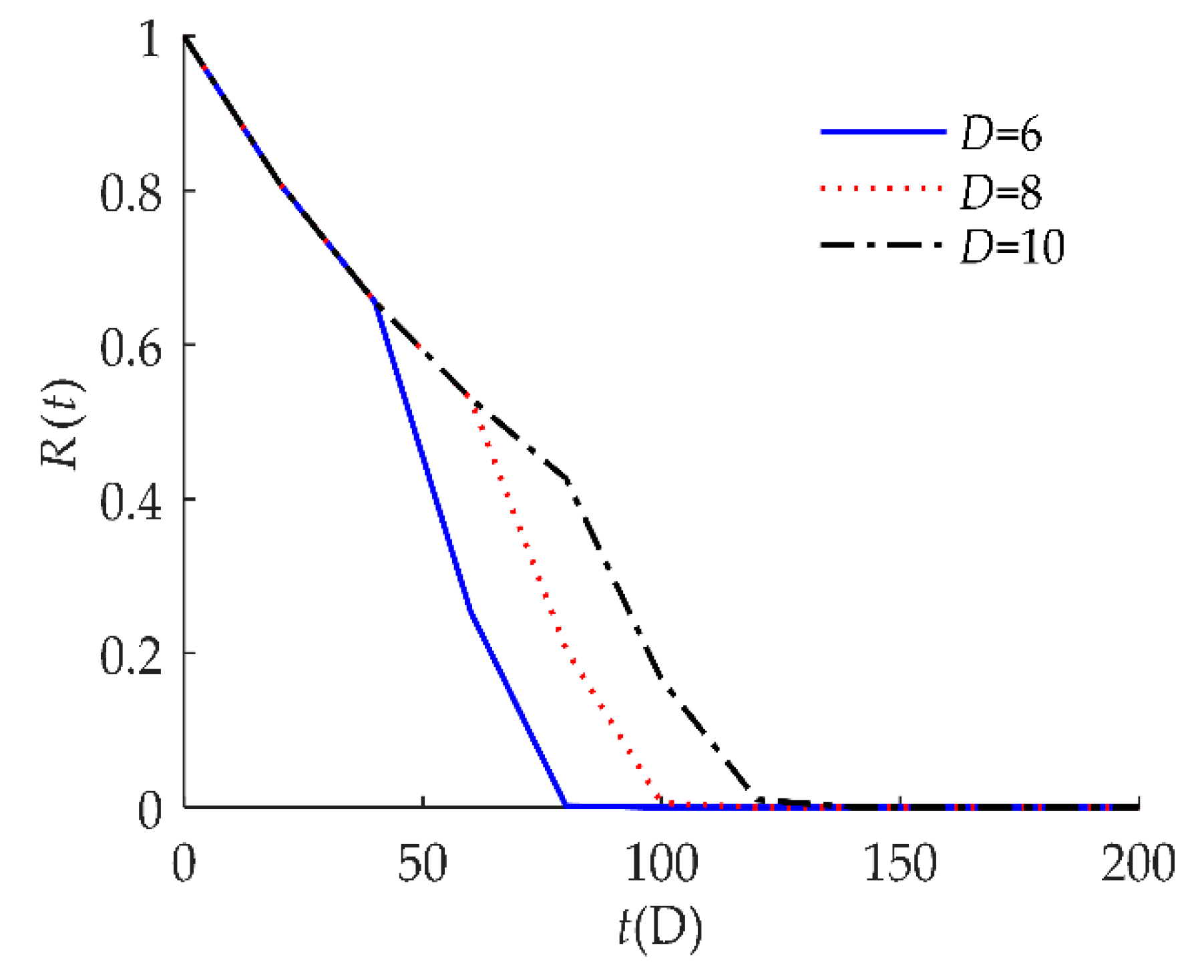
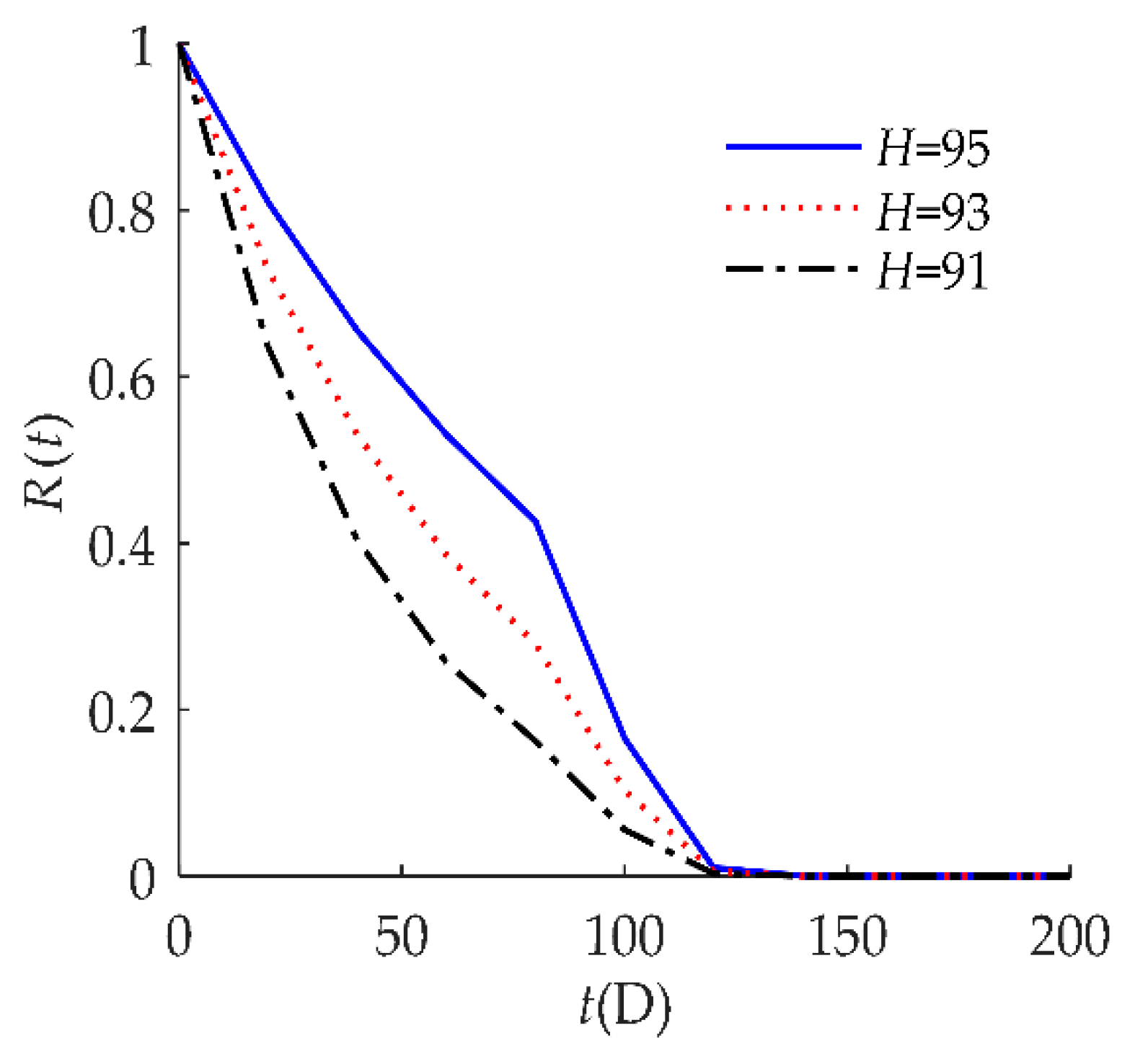
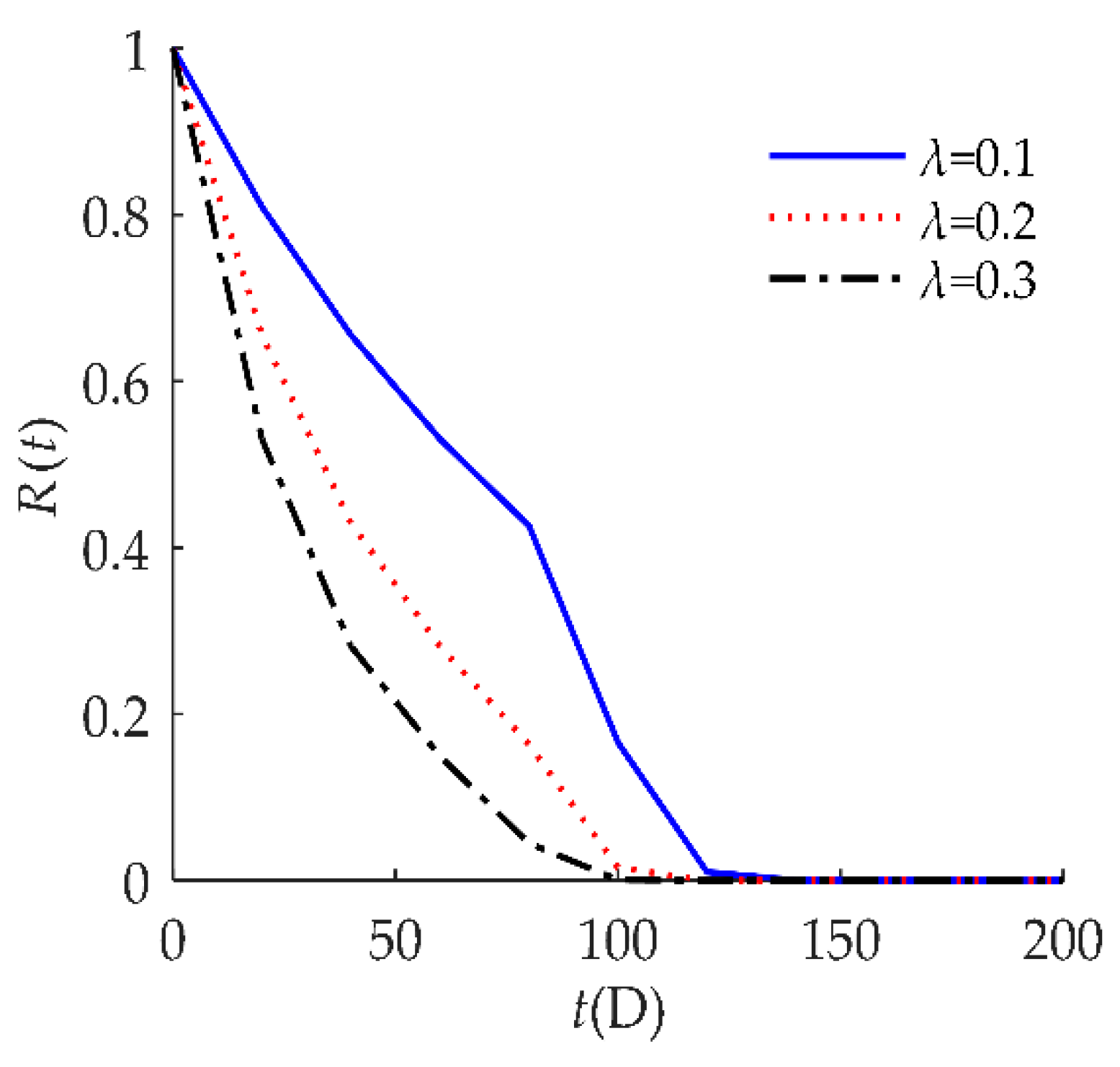
4. Numerical Examples and Results
4.1. Example I
4.2. Example II
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| t | time |
| X(t) | drift of the measured value compared to reference caused by physical ageing at time t |
| N(t) | the number of shocks |
| Yi | a positive offset between the sensor measured value and the actual conditions caused by the i-th shock |
| Wi | the magnitude of the i-th shock |
| D | the threshold of soft failure |
| H | the threshold of hard failure |
| λ | the rate of a homogeneous Poisson random shock process |
| XS(t) | total drift volume at time t composed to long-term continuous drift, positive offsets caused by random shocks, and offset reduction due to self-recovery |
| R(t) | time-dependent reliability |
| Ti | inter-arrival time between the i-th shock and the (i + 1)-th shock |
| τ | the self-recovery threshold |
| S(t) | cumulative positive offset caused by random shocks at time t |
References
- Hernandezrivera, D.; Rodriguezroldan, G.; Moramartinez, R.; Suastegomez, E. A Capacitive Humidity Sensor Based on an Electrospun PVDF/Graphene Membrane. Sensors 2017, 17, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessler, A.E.; Sherwood, S.C. A Matter of Humidity. Science 2009, 323, 1020–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liehr, S.; Breithaupt, M.; Krebber, K. Distributed Humidity Sensing in PMMA Optical Fibers at 500 nm and 650 nm Wavelengths. Sensors 2017, 17, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Previati, M.; Canone, D.; Bevilacqua, I.; Boetto, G.; Pognant, D.; Ferraris, S. Evaluation of wood degradation for timber check dams using time domain reflectometry water content measurements. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 44, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudaden, J.; Steinmabl, M.; Endres, H.E.; Drost, A.; Eisele, I.; Kutter, C.; Muller-Buschbaum, P. Polyimide-Based Capacitive Humidity Sensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Lee, S.; Jeong, S.H.; Jung, U.H.; Park, H.; Lee, M.G.; Kim, S.; Lee, J. Enhanced Moisture-Reactive Hydrophilic-PTFE-Based Flexible Humidity Sensor for Real-Time Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, T.A.; Eksperiandova, L.P.; Belikov, K.N. Recent trends of ceramic humidity sensors development: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 416–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.J.; Jiang, R.; Yam, R.C.M. Approaches for reliability modeling of continuous-state devices. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2002, 48, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.S.; Grady, M.; Purdy, K.; Singh, A.D. Exploiting defect clustering for yield and reliability prediction. IEE Proc.-Comput. Dig. Tech. 2005, 152, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Askin, R.G. A generalized SSI reliability model considering stochastic loading and strength aging degradation. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2004, 53, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallor, F.; Santos, J. Classification of Shock Models in System Reliability; VII Jornadas Zaragoza-Pau de Matemática Aplicada y Estadística: Jaca (Huesca), 17–18 de Septiembre de 2001; Prensas Universitarias de Zaragoza: Zaragoza, Spain, 2003; pp. 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Ghurye, S.G.; Levine, R.A. Multicomponent Lifetime Distributions in the Presence of Ageing. J. Appl. Probab. 2000, 37, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.J.; Meeker, W.Q. Using Degradation Measures to Estimate a Time-to-Failure Distribution. Technometrics 1993, 35, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharoufer, J.P.; Cox, S.M. Stochastic models for degradation-based reliability. IIE Trans. 2005, 37, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Padgett, W.J. Stochastic degradation models with several accelerating variables. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2006, 55, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.H.; Shen, S.H.; Zhang, Z.G.; Love, E. An extended optimal replacement model of systems subject to shocks. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 175, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keedy, E.; Feng, Q. A physics-of-failure-based reliability and maintenance modeling framework for stent deployment and operation. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2012, 103, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pham, H. An inspection-maintenance model for systems with multiple competing processes. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2005, 54, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.H.; Pulcini, G. A Dependent Competing Risks Model for Technological Units Subject to Degradation Phenomena and Catastrophic Failures. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2016, 32, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pham, H. A Multi-Objective Optimization of Imperfect Preventive Maintenance Policy for Dependent Competing Risk Systems with Hidden Failure. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2011, 60, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Feng, Q.; Coit, D.W. Reliability and maintenance modeling for systems subject to multiple dependent competing failure processes. IIE Trans. 2010, 43, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, K.; Feng, Q.; Coit, D.W. Condition-based maintenance for repairable deteriorating systems subject to generalized mixed shock model. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2015, 64, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Sun, D. Reliability modeling for systems subject to multiple dependent competing failure processes with shock loads above a certain level. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 157, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, K.; Feng, Q.; Coit, D.W. Reliability assessment of competing risks with generalized mixed shock models. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 159, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, K.T.; Barros, A.; Berenguer, C.; Castro, I.T. A periodic inspection and replacement policy for systems subject to competing failure modes due to degradation and traumatic events. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2011, 96, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Alkhalifa, K.N.; Hamouda, A.S.; Coit, D.W.; Elsayed, E.A. Condition-based maintenance for continuously monitored degrading systems with multiple failure modes. IIE Trans. 2013, 45, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regina, F.; Richard, M.C.; Benjamin, D.; Alan, P.; Asutosh, T.; Giovanna, D.M.S. Self-healing and self-repairing technologies. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 69, 1033–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Yeh, R.H.; Cai, B. Reliability modeling for dependent competing failure processes of damage self-healing systems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 105, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pham, H. Imperfect preventive maintenance policies for two-process cumulative damage model of degradation and random shocks. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2011, 2, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.J.; Kou, W.; Kvam, P.H. Degradation models and implied lifetime distribution. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2007, 92, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, K.; Feng, Q.; Coit, D.W. Reliability modeling for dependent competing failure processes with changing degradation rate. IIE Trans. 2014, 46, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Xiao, N. An approach to reliability assessment under degradation and shock process. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2011, 60, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Vooge, F.; Schaar, C.V.D.; Nath, S.; Nenadovic, N.; Vanhelmont, F.; Lous, E.J.; Suy, H.; Zandt, M.I.; Sakic, A.; et al. Reliability tests for modeling of relative humidity sensor drifts. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Reliability Physics Symposium, Monterey, CA, USA, 2–6 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Denton, D.D.; Jaafar, M.A.S.; Ralston, A.R.K. The long term reliability of a switched-capacitor relative humidity sensor system. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 10–13 May 1992; Volume 4, pp. 1840–1843. [Google Scholar]
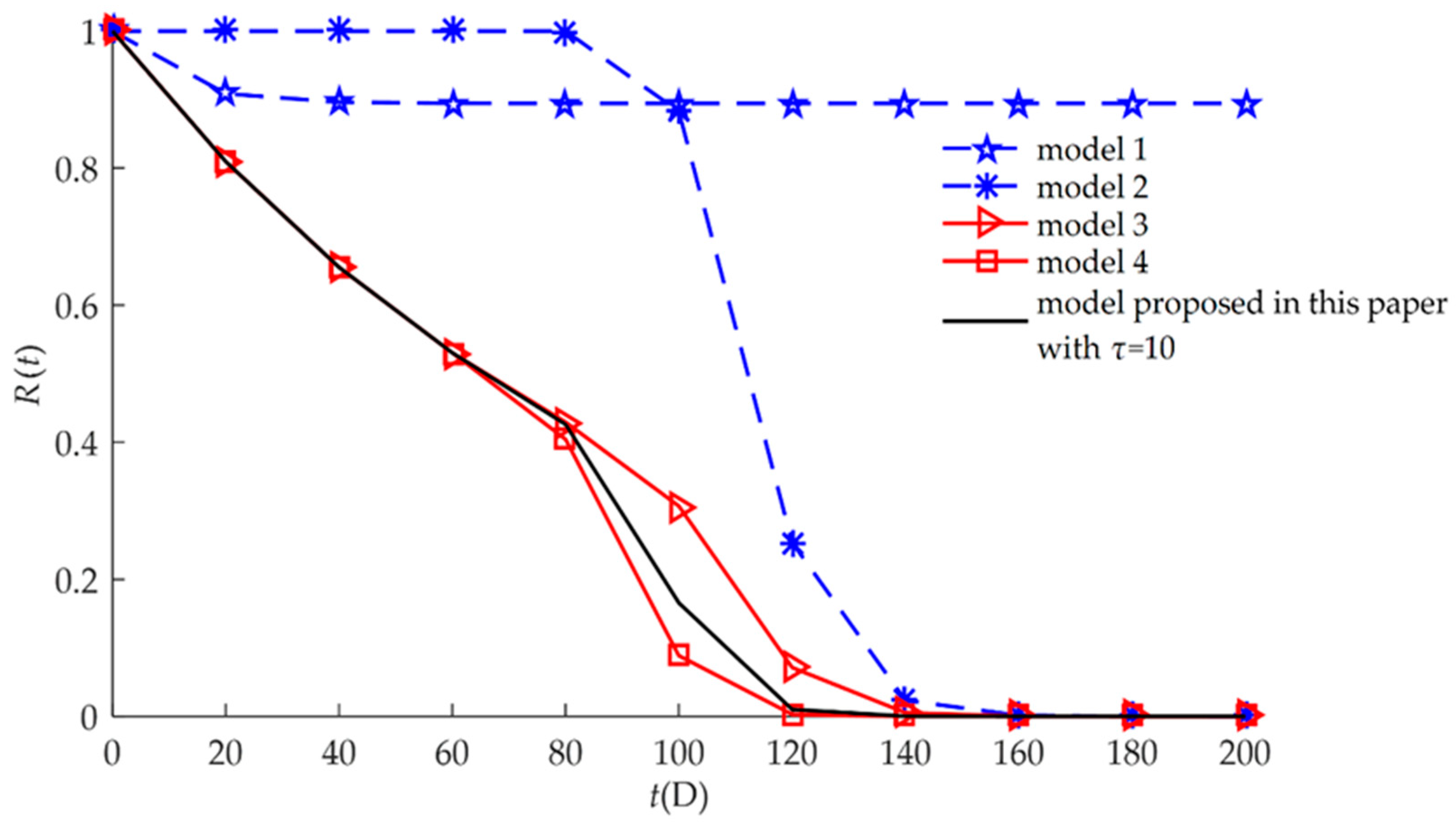
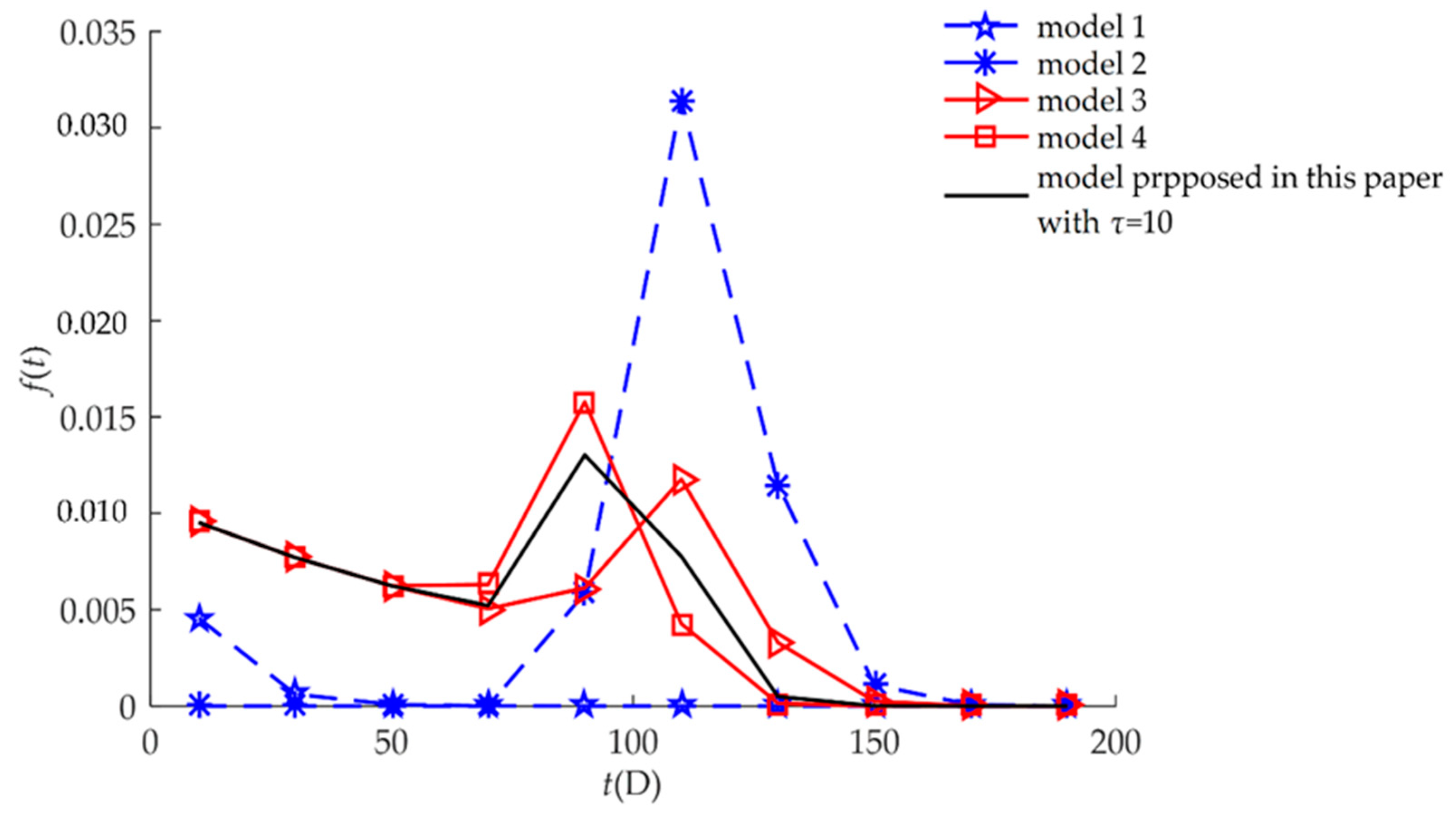
| Model | Description of the Failure Process | Expression |
|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | This model characterizes hard failure which is caused by a stochastic shock process. | Equation (21) |
| Model 2 | This model characterizes soft failure process. Products may not be subject to random shocks. | Equation (19) |
| Model 3 | This model characterizes independent competing failure processes. Soft failure and hard failure are independent. | Equation (17) |
| Model 4 | This model characterizes MDCFPs but ignores self-recovery. All non-fatal shocks can cause sudden increases in degradation. | Equation (15) |
| Model proposed in this paper | This model characterizes MDCFPs by considering self-recovery and can be transformed into four different reliability models (Models 1, 2, 3, and 4) by varying parameters. | Equation (13) |
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| D | 10 | The soft failure threshold is 10: when the drift amount rises by 10%, soft failure occurs. |
| H | 85 | The hard failure threshold is 85: when relative humidity exceeds 85%, hard failure occurs. |
| β | N(0.0005, 0.0052) | The drift rate. |
| α | α = 0 | The drift value at the initial time (t = 0). |
| Wi | N(65, 82) | The i-th shock amplitude. |
| λ | 0.02/h | The rate of a homogeneous Poisson random shock process. |
| Yi | N(0.2, 0.022) | The positive offsets caused by the i-th shock. |
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| D | 10 | The soft failure threshold is 10: when the drift amount rises by 10%, soft failure occurs. |
| H | 95 | The hard failure threshold is 95: when ambient temperature exceeds 95 °C, hard failure occurs. |
| β | N(0.0893, (0.0090)2) | The drift rate of capacitance–RH characteristic at 85 °C/85% RH. |
| α | α = 0 | The drift value at the initial time (t = 0). |
| Wi | N(85, 82) | The i-th shock amplitude. |
| λ | 0.1/Day | The rate of a homogeneous Poisson random shock process. |
| Yi | N(0.2, 0.022) | The positive offsets caused by the i-th shock. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, J.; Zhou, Z.; Niu, C.; Wang, C.; Wu, J. Reliability Modeling for Humidity Sensors Subject to Multiple Dependent Competing Failure Processes with Self-Recovery. Sensors 2018, 18, 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082714
Qi J, Zhou Z, Niu C, Wang C, Wu J. Reliability Modeling for Humidity Sensors Subject to Multiple Dependent Competing Failure Processes with Self-Recovery. Sensors. 2018; 18(8):2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082714
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Jia, Zhen Zhou, Chenchen Niu, Chunyu Wang, and Juan Wu. 2018. "Reliability Modeling for Humidity Sensors Subject to Multiple Dependent Competing Failure Processes with Self-Recovery" Sensors 18, no. 8: 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082714
APA StyleQi, J., Zhou, Z., Niu, C., Wang, C., & Wu, J. (2018). Reliability Modeling for Humidity Sensors Subject to Multiple Dependent Competing Failure Processes with Self-Recovery. Sensors, 18(8), 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082714




