Atmospheric Pollution Monitoring in Urban Area by Employing a 450-nm Lidar System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
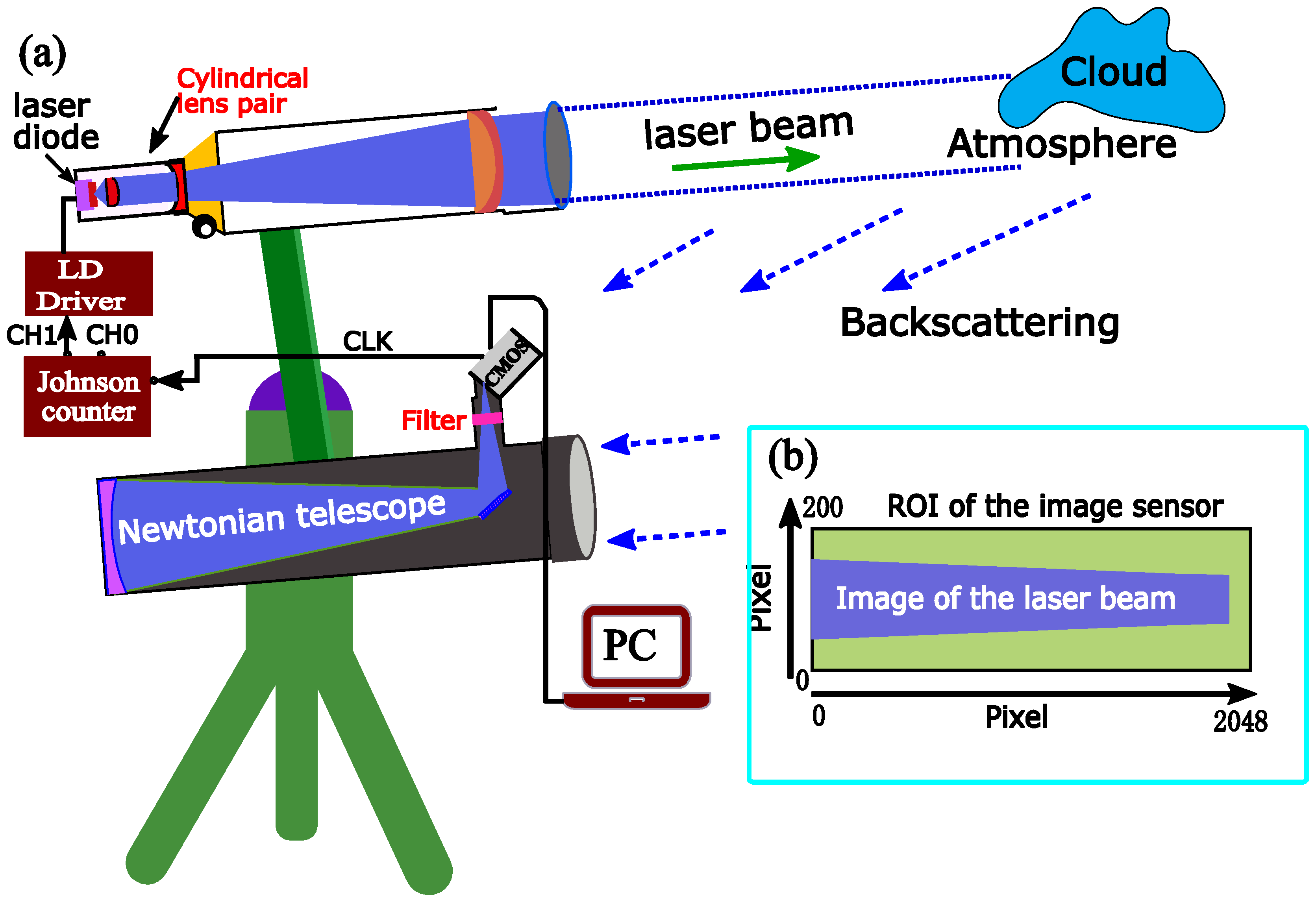
2.1. The 450-nm Scheimpflug Lidar (SLidar) System
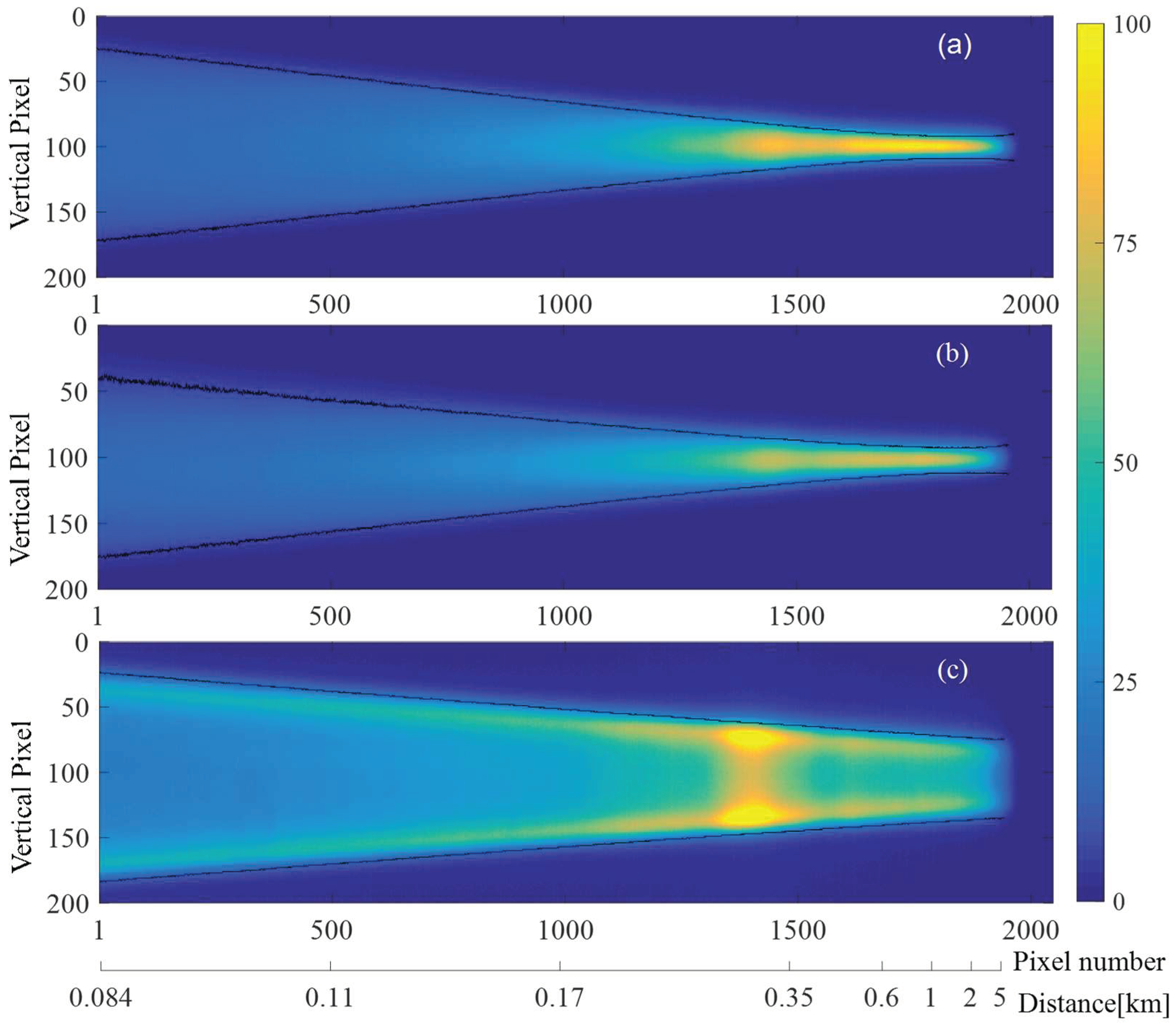
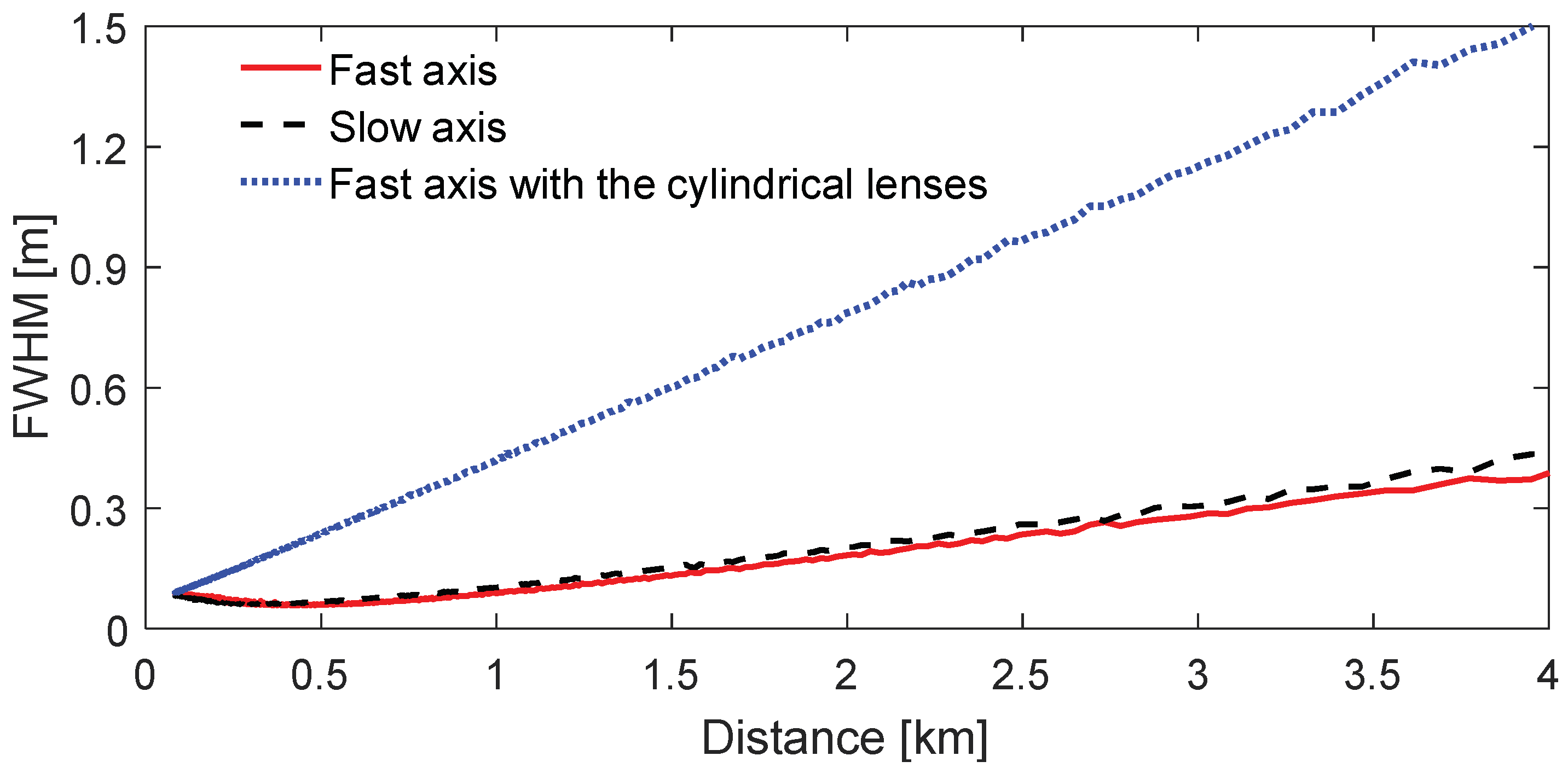
2.2. Divergences of the Laser Beam
3. Measurements
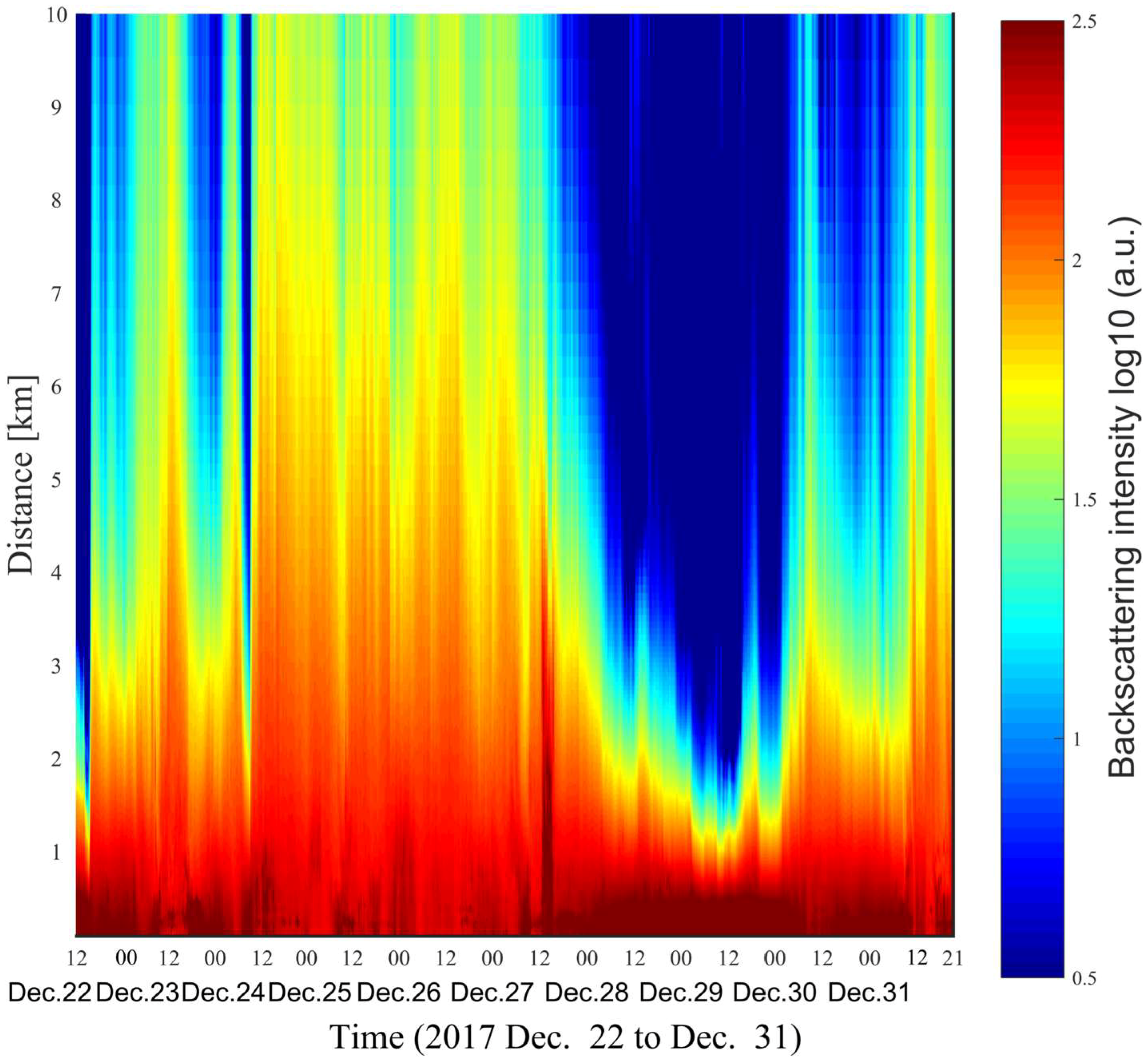
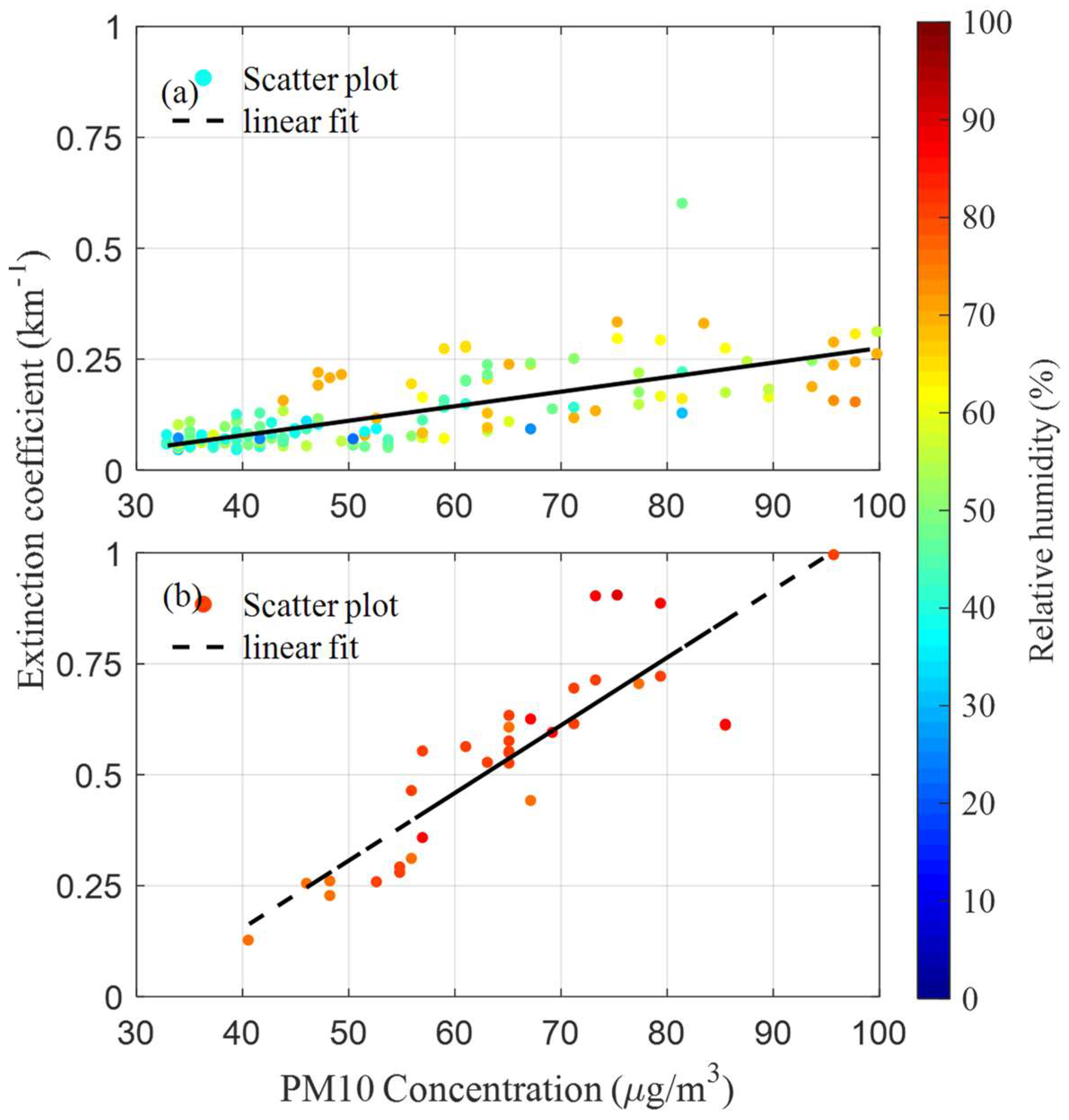
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.Y.; Saravanan, R. Asian pollution climatically modulates mid-latitude cyclones following hierarchical modelling and observational analysis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.N.; Andersson, H.; Zhang, S.Q. Air pollution control policies in China: A retrospective and prospects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pui, D.Y.H.; Chen, S.C.; Zuo, Z.L. PM2.5 in China: Measurements, sources, visibility and health effects, and mitigation. Particuology 2014, 13, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Rosenfeld, D.; Artaxo, P.; Costa, A.A.; Frank, G.P.; Longo, K.M.; Silva-Dias, M.A.F. Smoking rain clouds over the Amazon. Science 2004, 303, 1337–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Q. Influence of absorbing aerosols on the inference of solar surface radiation budget and cloud absorption. J. Clim. 1998, 11, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.Z.; Shi, G.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Arimoto, R.; Zhao, J.Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z.H. Analysis of 40 years of solar radiation data from China, 1961–2000. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L06803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 996. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; da Costa, R.F.; Bedoya, A.E.; Guardani, R.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Bastidas, A.E.; Landulfo, E. Multispectral elastic scanning lidar for industrial flare research: Characterizing the electronic subsystem and application. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 31063–31077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, H.G.; Hou, X.L.; Zhao, H.; Yan, L.J.; Wei, X.; Zhao, H.; Hua, D.X. Detections and analyses of aerosol optical properties under different weather conditions using multi-wavelength Mie lidar. Acta Phys. Sin. 2014, 63, 244206. [Google Scholar]
- Rocadenbosch, F.; Reba, M.N.; Sicard, M.; Comeron, A. Practical analytical backscatter error bars for elastic one-component lidar inversion algorithm. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 3380–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchant, C.C.; Moon, T.K.; Gunther, J.H. An iterative least square approach to elastic-lidar retrievals for well-characterized aerosols. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2430–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthais, V.; Freudenthaler, V.; Amodeo, A.; Balin, I.; Balis, D.; Bosenberg, J.; Chaikovsky, A.; Chourdakis, G.; Comeron, A.; Delaval, A.; et al. Aerosol lidar intercomparison in the framework of the EARLINET project. 1. Instruments. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 961–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, K.; Gong, W.; Temple, D.A.; Omar, A.H.; Mangana, J. Development of a 3-D scanning 1.5 μm portable aerosol lidar. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2002: IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium and 24th Canadian Symposium on Remote Sensing, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; Volumes I–VI, pp. 3595–3598. [Google Scholar]
- Spuler, S.M.; Mayor, S.D. Scanning eye-safe elastic backscatter lidar at 1.54 μm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 22, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.Y.; Stanic, S.; Gao, F.; Bergant, K.; Veberic, D.; Song, X.Q.; Dolzan, A. Tracking of urban aerosols using combined LIDAR-based remote sensing and ground-based measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parracino, S.; Richetta, M.; Gelfusa, M.; Malizia, A.; Bellecci, C.; de Leo, L.; Perrimezzi, C.; Fin, A.; Forin, M.; Giappicucci, F.; et al. Real-time vehicle emissions monitoring using a compact LiDAR system and conventional instruments: First results of an experimental campaign in a suburban area in southern Italy. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 103107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wekker, S.F.J.; Mayor, S.D. Observations of atmospheric structure and dynamics in the Owens valley of California with a ground-based, eye-safe, scanning aerosol lidar. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2009, 48, 1483–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, A.; Pal, S.; Wulfmeyer, V.; Valdebenito, A.M.; Lammel, G. A novel approach for the characterization of transport and optical properties of aerosol particles near sources—Part I: Measurement of particle backscatter coefficient maps with a scanning UV lidar. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2795–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.B.; Zhao, M.; Wang, B.X.; Zhong, Z.Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.J. Study of the scanning lidar on the atmospheric detection. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2015, 150, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.W.; Das, S.K.; Chiang, H.W.; Nee, J.B.; Sun, S.H.; Chen, S.W.; Lin, P.H.; Chu, J.C.; Su, C.S.; Su, L.S. A new mobile and portable scanning lidar for profiling the lower troposphere. Geosci. Instrum. Meth. 2015, 4, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegner, M.; Geiss, A. Aerosol profiling with the Jenoptik ceilometer CHM15kx. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1953–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heese, B.; Flentje, H.; Althausen, D.; Ansmann, A.; Frey, S. Ceilometer lidar comparison: Backscatter coefficient retrieval and signal-to-noise ratio determination. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Brydegaard, M. Continuous-wave differential absorption lidar. Laser Photonic Rev. 2015, 9, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydegaard, M.; Gebru, A.; Svanberg, S. Super resolution laser radar with blinking atmospheric particles—Application to interacting flying insects. PIER 2014, 147, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Brydegaard, M. Atmospheric aerosol monitoring by an elastic Scheimpflug lidar system. Opt. Express 2015, 23, A1613–A1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.Y.; Ljungholm, M.; Malmqvist, E.; Bianco, G.; Hansson, L.A.; Svanberg, S.; Brydegaard, M. Inelastic hyperspectral lidar for profiling aquatic ecosystems. Laser Photonic Rev. 2016, 10, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, J.W.; Lin, H.Z.; He, S.L. Oil pollution discrimination by an inelastic hyperspectral Scheimpflug lidar system. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 25515–25522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volten, H.; Brinksma, E.J.; Berkhout, A.J.C.; Hains, J.; Bergwerff, J.B.; van der Hoff, G.R.; Apituley, A.; Dirksen, R.J.; Calabretta-Jongen, S.; Swart, D.P.J. NO2 lidar profile measurements for satellite interpretation and validation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Fukuchi, T.; Fujii, T.; Collins, R.L.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z. Error analysis for NO2 DIAL measurement in the troposphere. Appl. Phys. B 2006, 82, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yue, G.; Tan, K.; Ji, Y.; Xu, B. A new differential absorption lidar for NO2 measurements using Raman-shifted technique. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2003, 1, 435–437. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, L.; Guan, P.; Kong, Z. Remote sensing of atmospheric NO2 by employing the continuous-wave differential absorption lidar technique. Opt. Express 2017, 25, A953–A962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, L.; Zhang, L.; Kong, Z.; Li, H. Noise modeling, evaluation and reduction for the atmospheric lidar technique employing an image sensor. Opt. Commun. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]



| Model | Specifications | |
|---|---|---|
| Laser source | Nichia, NDB7K75 | Wavelength: 450 nm; Power: 3.5 W; Divergence: 14° ║ × 46° ┴; |
| Collimator | Tianlang, F6 refractor | Focal length: 600 mm, Diameter: 100 mm |
| Cylindrical lens pair: LJ1918L1-A & LK1426L1-A | Convex lens: f = 5.8 mm, height: 4 mm; Concave lens: f = −25 mm, height: 10 mm Laser beam divergence: 0.1 × 0.36 mrad | |
| Receiver | Skywatcher, CFP200 | Focal length: 800 mm; Diameter: 200 mm |
| Detector | CMOS, CMV2000 Lt225NIR | Tilt angle: 45°; Resolution: 2048 × 1024 Pixels; Frame rate:170 fps; Bit depth: 12/8 bit; Pixel size: 5.5 µm × 5.5 µm; Quantum efficiency: 45% @ 450 nm; ROI: 2048 × 200 pixels |
| Filters | 450 nm interference filters | 10 nm FWHM (Edmund optics) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Guan, P.; Li, L.; Mei, L. Atmospheric Pollution Monitoring in Urban Area by Employing a 450-nm Lidar System. Sensors 2018, 18, 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061880
Kong Z, Liu Z, Zhang L, Guan P, Li L, Mei L. Atmospheric Pollution Monitoring in Urban Area by Employing a 450-nm Lidar System. Sensors. 2018; 18(6):1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061880
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Zheng, Zhi Liu, Lishan Zhang, Peng Guan, Limei Li, and Liang Mei. 2018. "Atmospheric Pollution Monitoring in Urban Area by Employing a 450-nm Lidar System" Sensors 18, no. 6: 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061880
APA StyleKong, Z., Liu, Z., Zhang, L., Guan, P., Li, L., & Mei, L. (2018). Atmospheric Pollution Monitoring in Urban Area by Employing a 450-nm Lidar System. Sensors, 18(6), 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061880





