Reproducible Molecularly Imprinted Piezoelectric Sensor for Accurate and Sensitive Detection of Ractopamine in Swine and Feed Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
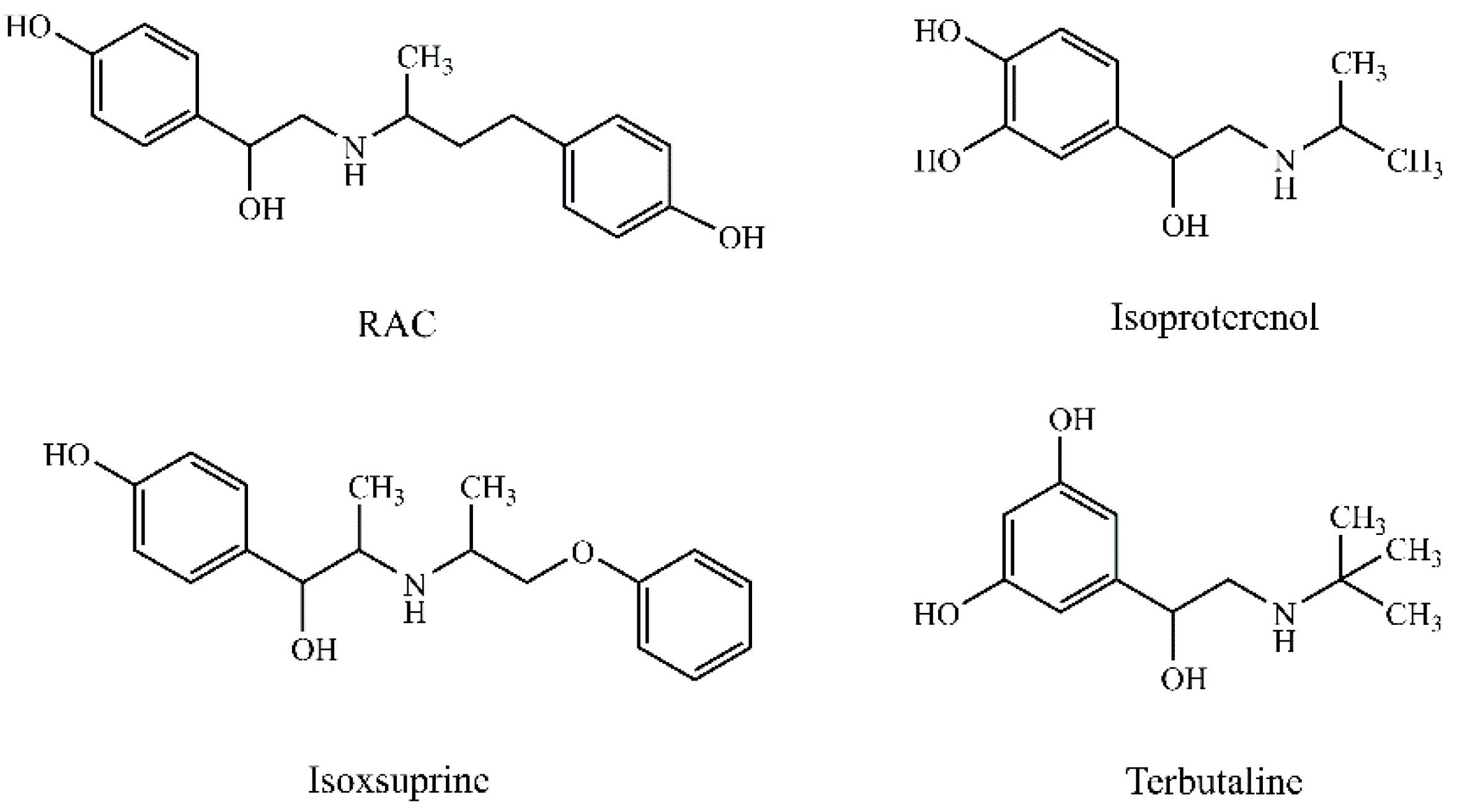
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
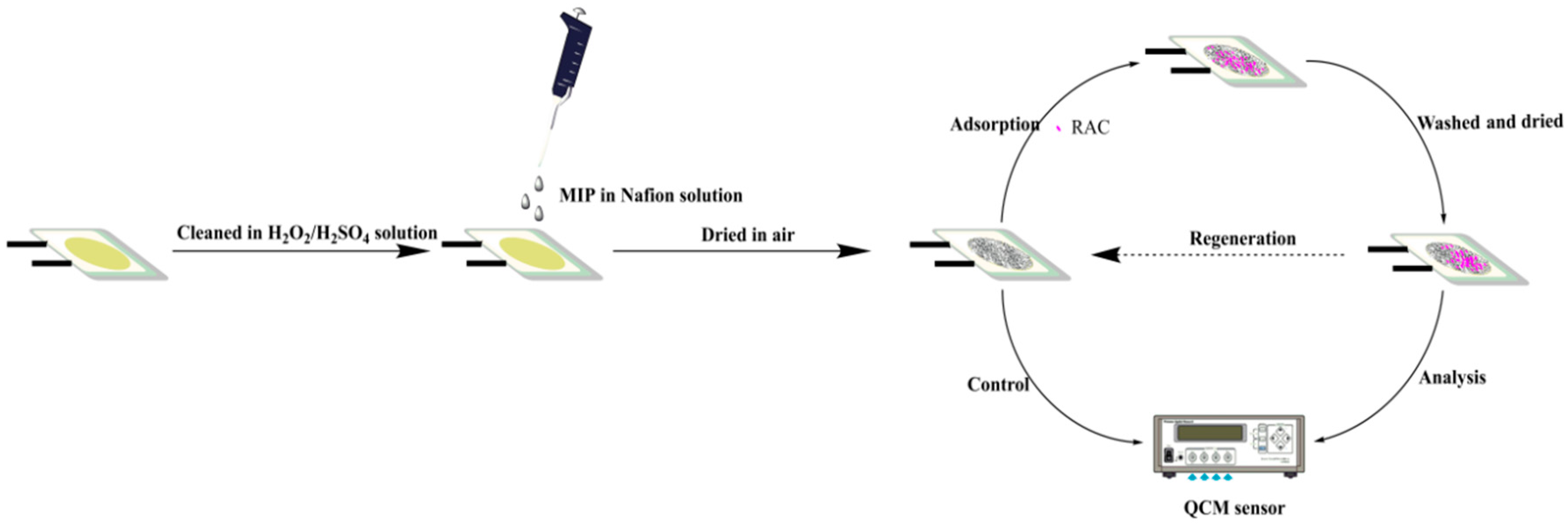
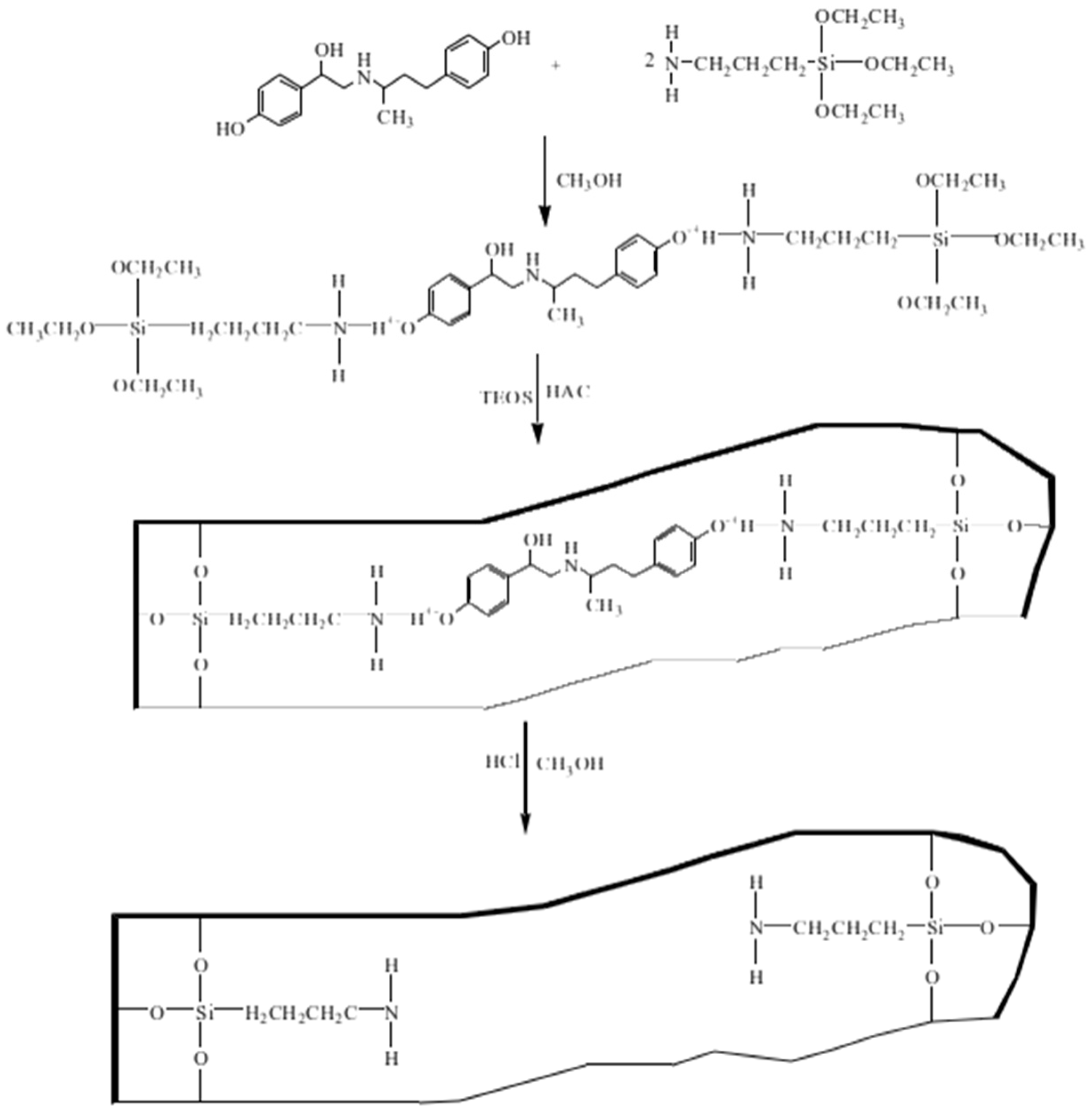
2.3. Synthesis of RAC Imprinted Material
2.4. Modification of the RAC Imprinted Material on the Au Electrode Surface
2.5. Measurement Procedure for RAC
2.6. Sample Pretreatment and Spiking Method
3. Results and Discussion
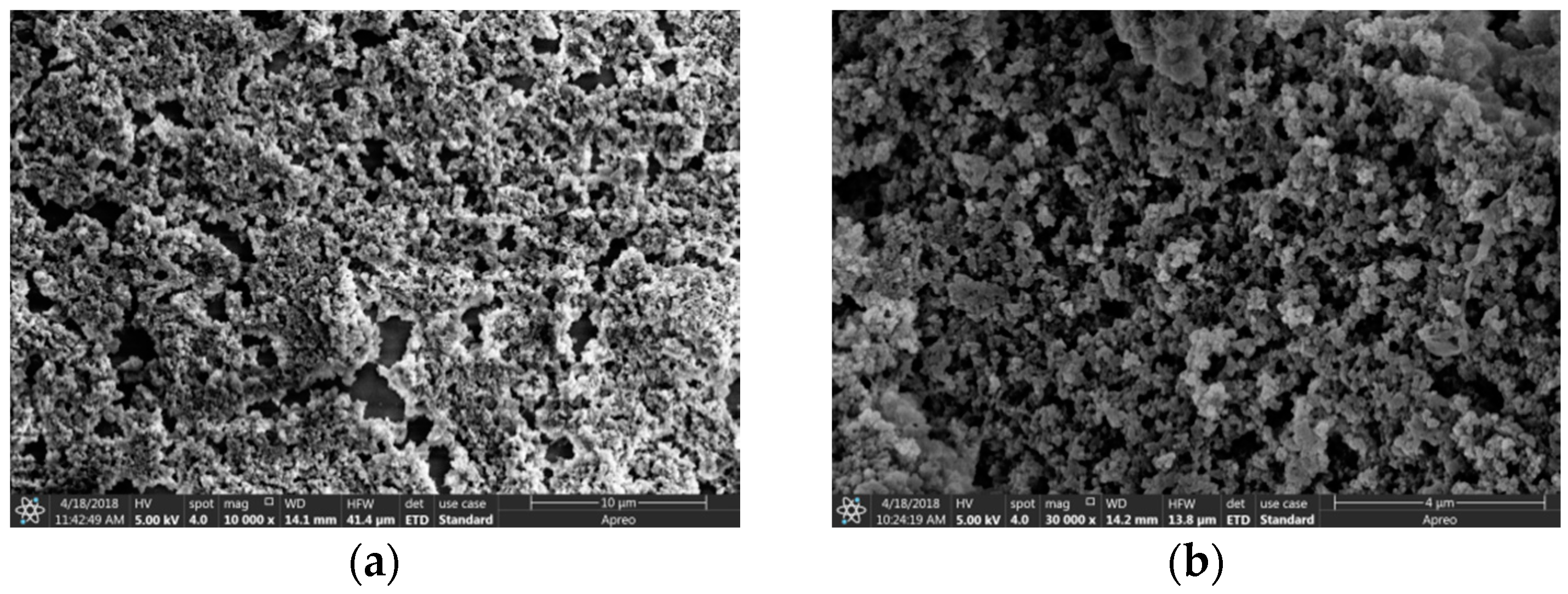
3.1. Surface Morphology of the MIP Piezoelectric Sensor
3.2. Optimization of the Amount of RAC Imprinted Material
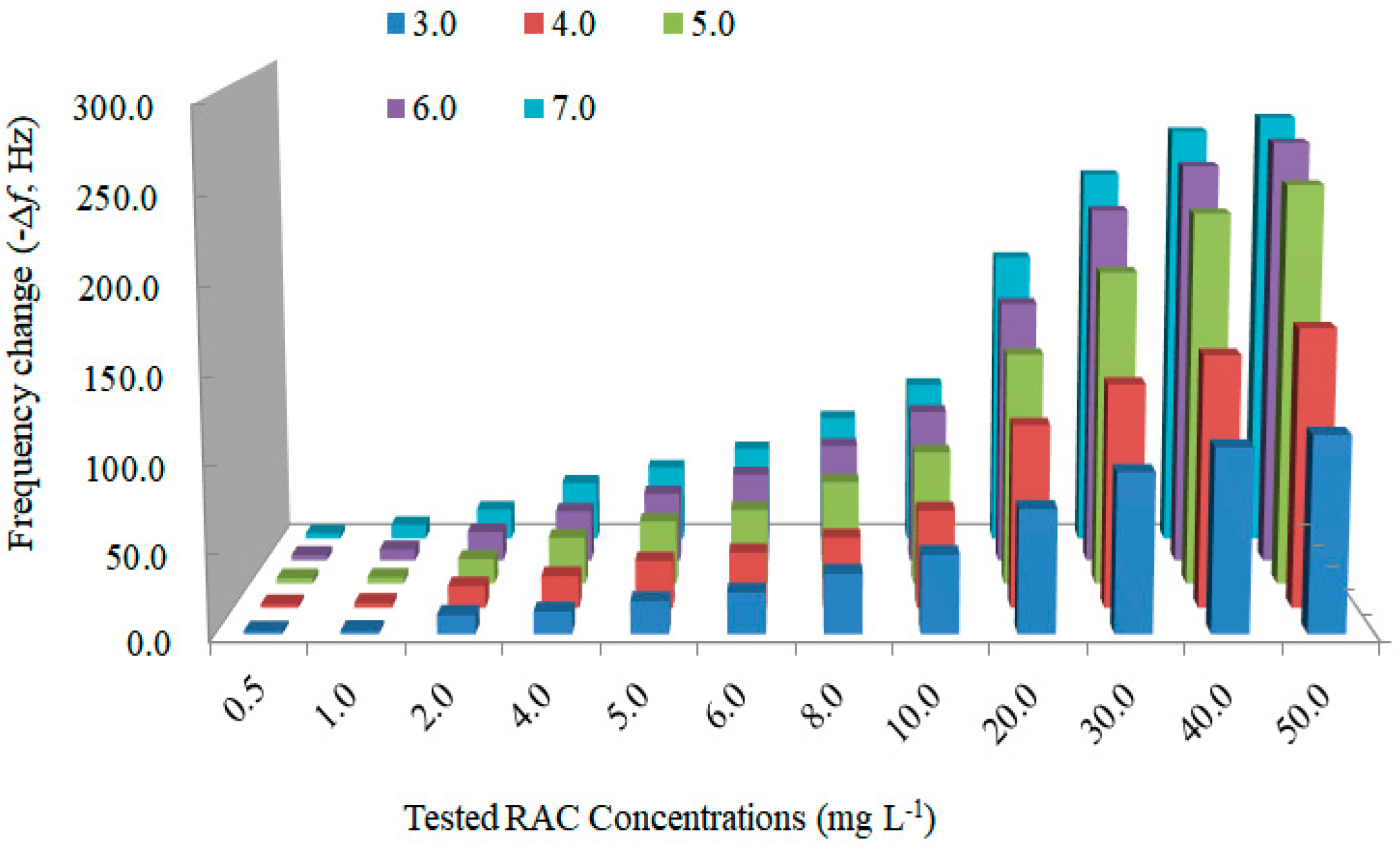
3.3. Response of the Developed Piezoelectric Chip to RAC
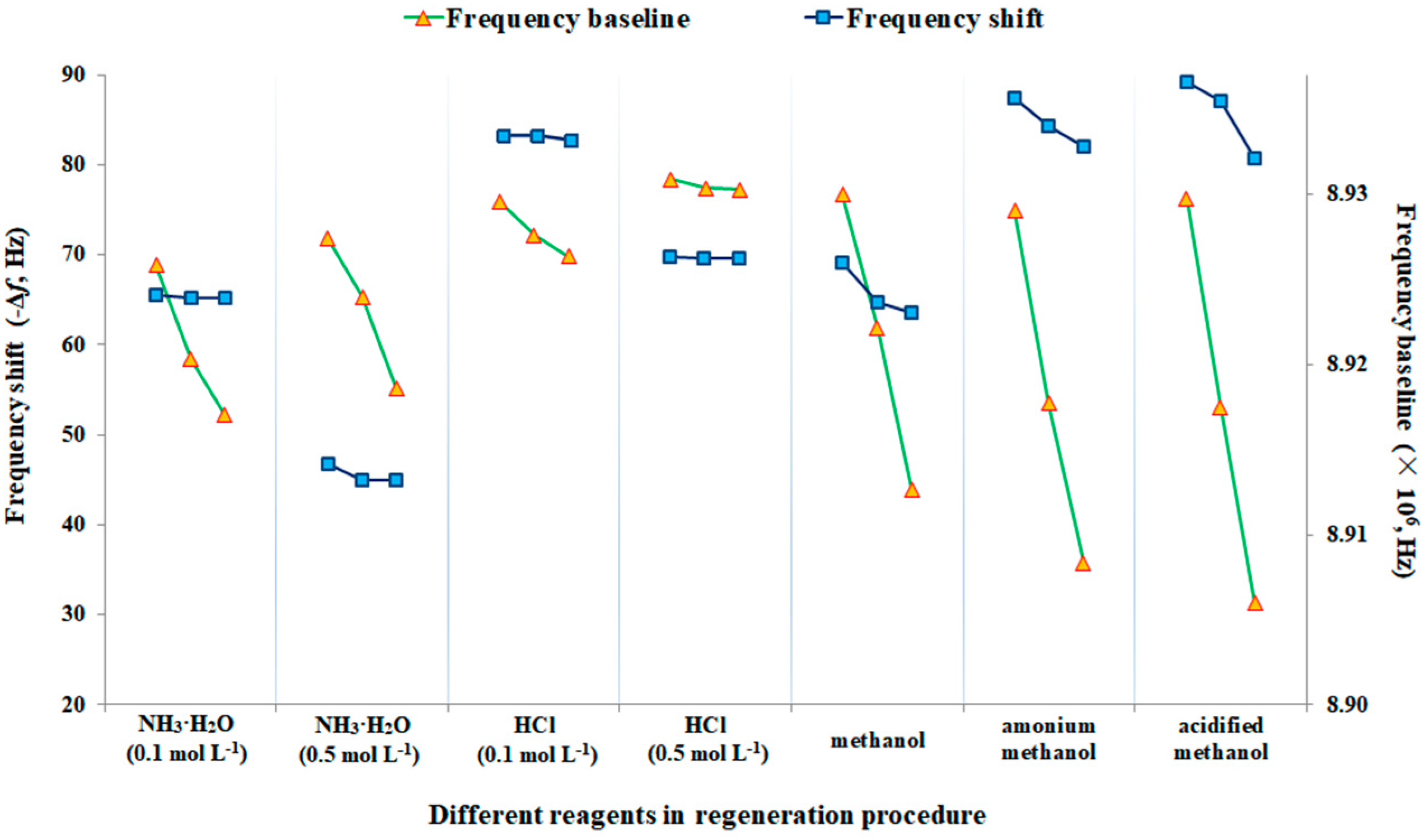
3.4. Regeneration of the Developed Piezoelectric Chip
3.5. Sample Matrix Effect and Recovery Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergen, W.; Johnson, S.; Skjaerlund, D.; Babiker, A.; Ames, N.; Merkel, R.; Anderson, D. Muscle protein metabolism in finishing pigs fed ractopamine. J. Anim. Sci. 1989, 67, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Shelver, W.; Hong, C.; Mccann, S.; Davis, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ambrosone, C.; Smith, D. Urinary excretion of the β-adrenergic feed additives ractopamine and zilpaterol in breast and lung cancer patients. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7632–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wettere, W.; Pain, S.; Hughes, P. Dietary ractopamine supplementation during the first lactation affects milk composition, piglet growth and sow reproductive performance. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2016, 174, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Shi, J.; Pan, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, D.; Xie, S.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, Z. Elimination and concentration correlations between edible tissues and biological fluids and hair of ractopamine in pigs and goats fed with ractopamine-medicated feed. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2012–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcolla, C.; Holanda, D.; Ferreira, S.; Rocha, G.; Nvl, S.; Duarte, M.; Abreu, M.; Saraiva, A. Chromium, CLA, and ractopamine for finishing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 4472–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, E.; Bridi, A.; Novais, A.; Santos, R.; Frederico, G.; Alves, J.; Barata, C.; Santos, E.; Caio, A. Use of ractopamine during compensatory gain of finishing pigs on carcass and meat performance and quality. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2017, 69, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanca, J.; Muñoz, P.; Morgado, M.; Méndez, N.; Aranda, A.; Reuvers, T.; Hooghuis, H. Determination of clenbuterol, ractopamine and zilpaterol in liver and urine by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 529, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, T.; Vers, D.; Wagner, J.; Anderson, D.; Weldon, W.; Berg, E. The effect of dietary ractopamine concentration and duration of feeding on growth performance, carcass characteristics, and meat quality of finishing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 82, 3245–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noel, J.; Barstow, T.; Broxterman, R.; Mccoy, G.; Phelps, K.; Gonzalez, J. Effect of Ractopamine-HCL on muscle fiber types and finishing barrow exhaustion. Meat Sci. 2016, 112, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Ministry of Agriculture. Regulation NO. 193; The Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Niño, A.; Granja, R.; Wanschel, A.; Salerno, A. The challenges of ractopamine use in meat production for export to European Union and Russia. Food Control 2015, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Fang, G.; Zhang, C.; He, J. Molecularly imprinted polymer for the determination of trace ractopamine in pork using SPE followed by HPLC with fluorescence detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, X.; Lan, J.; Gao, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, M.; Li, J. Determination of ractopamine in pork using a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer as adsorbent followed by HPLC. Food Chem. 2016, 201, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koostra, P.; Kuijpers, C.; Wubs, K.; van Doorn, D.; Sterk, S.; van Ginkel, L.; Stephany, R. The analysis of beta-agonists in bovine muscle using molecular imprinted polymers with ion trap LCMS screening. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 529, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Su, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X. Determination of ractopamine and clenbuterol in feeds by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2007, 132, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressler, V.; Franzen, A.; de Lima, G.; Tavernari, F.; Dalla Costa, O.; Feddern, V. Development of a readily applied method to quantify ractopamine residue in meat and bone meal by QuEchERS-LC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1015–1016, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valese, A.; Oliveira, G.; Kleemann, C.; Molognoni, L.; Daguer, H. A QuEChERS/LC–MS method for the analysis of ractopamine in pork. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 47, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvereva, E.; Shpakova, N.; Zherdev, A.; Liu, L.; Xu, C.; Eremin, S.; Dzantiev, B. Fluorescence polarization immunoassay of ractopamine. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2016, 52, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Guo, C.; Song, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Peng, D.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C. Chitosan stabilized gold nanoparticle based electrochemical ractopamine immunoassay. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2919–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, P.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Su, X.; He, Y.; Shi, L.; Yao, D. Label free electrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of ractopamine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Gan, N.; Hu, F.; Li, T.; Cao, Y.; Pan, D. An on-site immunosensor for ractopamine based on a personal glucose meter and using magnetic beta-cyclodextrin-coated nanoparticles for enrichment, and an invertase-labeled nanogold probe for signal amplification. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yang, M.; Zheng, N.; Xie, N.; Liu, D.; Xie, C.; Yao, D. A novel aptasensor for electrochemical detection of ractopamine, clenbuterol, salbutamol, phenylethanolamine and procaterol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirhagl, R. Bioapplications for molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chem. 2004, 86, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachkov, A.; Cheong, S.; El’Skaya, A.; Yano, K.; Karube, I. Molecularly imprinted polymers as artificial steroid receptors. Polym. Adv. Technol. 1998, 9, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, N.; Granja, R.; Reche, K.; Giannotti, F.; de Souza, J.; Ferrari, S.; Dos Santos, A.; Wanschel, A.; Salerno, A. Laboratory validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the detection of ractopamine, clenbuterol and salbutamol in bovine and swine muscle at sub-μg/kg regulatory limits. Food Addit. Contam. A. 2017, 34, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- And, U.; Peppas, N. Structural analysis and diffusional behavior of molecularly imprinted polymer networks for cholesterol recognition. Chem. Mater. 2015, 17, 6719–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G. Enzyme-like catalysis by molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Long, Y.; Pan, J.; Li, K.; Liu, F. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers to solid-phase extraction of analytes from real samples. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, K.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in biomimetic sensors. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piletsky, S.; Turner, A. Electrochemical sensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2004, 23, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerlig, J.; Schirhagl, R. Applications of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles and their advances toward industrial use: A review. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emir, D.; Keçili, R.; Ersöz, A.; Say, R. Molecular imprinting technology in quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lach, P.; Sharma, P.; Golebiewska, K.; Cieplak, M.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer chemosensor for selective determination of an N-Nitroso-l-proline food toxin. Chem.-Eur. J. 2017, 23, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Singh, M. Electrochemical and piezoelectric monitoring of taurine via electropolymerized molecularly imprinted films. J. Mol. Recognit. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayankojo, A.; Reut, J.; Boroznjak, R.; Öpik, A.; Syritski, V. Molecularly imprinted poly(meta-phenylenediamine) based QCM sensor for detecting Amoxicillin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvolini, G.; Marrazza, G. MIP-Based sensors: Promising new tools for cancer biomarker determination. Sensors 2017, 17, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugimiya, A.; Takeuchi, T. Molecularly imprinted polymer-coated quartz crystal microbalance for detection of biological hormone. Electroanalysis 2015, 11, 1158–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battal, D.; Akgönüllü, S.; Yalcin, M.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer based quartz crystal microbalance sensor system for sensitive and label-free detection of synthetic cannabinoids in urine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 111, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, Y.; Pan, M.; Fang, G.; Gu, Y.; Wen, W.; Xue, R.; Wang, S. An electrodeposited molecularly imprinted quartz crystal microbalance sensor sensitized with AuNPs and rGO material for highly selective and sensitive detection of amantadine. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 6600–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Sample | Spiked Levels (ng g−1) | The Developed MIP Piezoelectric Chip | HPLC-MS/MS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery (%) | RSD (%, n = 3) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%, n = 3) | ||
| Swine | 10.0 | 75.9 | 6.4 | 78.9 | 4.2 |
| 20.0 | 85.6 | 4.4 | 84.9 | 2.7 | |
| 40.0 | 92.1 | 2.3 | 93.0 | 2.4 | |
| Feed | 10.0 | 84.3 | 4.1 | 86.7 | 3.7 |
| 20.0 | 88.4 | 3.8 | 89.2 | 2.6 | |
| 40.0 | 93.3 | 3.2 | 92.9 | 1.8 | |
| Methods | Linear Range | LOD | Required Time | Samples | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIP-SPE HPLC | 0.04–18 µg L−1 | 4.6 ng L−1 | >30 min | Swine | [12] |
| Fe3O4@MIP-SPE HPLC | 0.5–100.0 µg kg−1 | 0.05 µg kg−1 | >50 min | Swine | [13] |
| LC-MS/MS | — | 1.0 µg kg−1 | >30 min | Bovine muscle | [14] |
| 0–100.0 µg kg−1 | 1.91 µg kg−1 | >60 min | Meat, bone meal | [16] | |
| 2.5–20 µg kg−1 | 1.5 µg kg−1 | 4.5 min | Swine | [17] | |
| GC/MS | 10.0–500.0 µg L−1 | 4.0 µg kg−1 | >60 min | Feed | [15] |
| Fluorescence immunoassay | 2.3–50 µg L−1 | 1.0 µg L−1 | 10 min | Turkey meat | [18] |
| Electrochemical immunosensor | 0.01–5 µg∙mL−1 | 2.3 ng L−1 | >2 h | Swine urine | [19] |
| 1–40 µg L−1 | 0.34 µg L−1 | — | Swine muscle | [21] | |
| Electrochemical aptasensor | 10−12–10−8 mol L−1 | 5.0 × 10−13 mol L−1 | >35 min | Swine urine | [20] |
| MIP piezoelectric sensor | 2.5–100.0 μg kg−1 | 0.46 and 0.38 ng g−1 | <8 min (reused at least 30 times) | Swine, feeds | This research |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, M.; Li, R.; Xu, L.; Yang, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, S. Reproducible Molecularly Imprinted Piezoelectric Sensor for Accurate and Sensitive Detection of Ractopamine in Swine and Feed Products. Sensors 2018, 18, 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061870
Pan M, Li R, Xu L, Yang J, Cui X, Wang S. Reproducible Molecularly Imprinted Piezoelectric Sensor for Accurate and Sensitive Detection of Ractopamine in Swine and Feed Products. Sensors. 2018; 18(6):1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061870
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Mingfei, Rui Li, Leling Xu, Jingying Yang, Xiaoyuan Cui, and Shuo Wang. 2018. "Reproducible Molecularly Imprinted Piezoelectric Sensor for Accurate and Sensitive Detection of Ractopamine in Swine and Feed Products" Sensors 18, no. 6: 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061870
APA StylePan, M., Li, R., Xu, L., Yang, J., Cui, X., & Wang, S. (2018). Reproducible Molecularly Imprinted Piezoelectric Sensor for Accurate and Sensitive Detection of Ractopamine in Swine and Feed Products. Sensors, 18(6), 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061870





