Etracker: A Mobile Gaze-Tracking System with Near-Eye Display Based on a Combined Gaze-Tracking Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We create a complete prototype of an efficient, easy-to-use, and inexpensive mobile gaze-tracking system, Etracker. Compared to existing gaze-tracking systems [6,7,8,9], Etracker is small, lightweight, unobtrusive, and user-friendly. It records eye movements and computes gaze positions in real time.
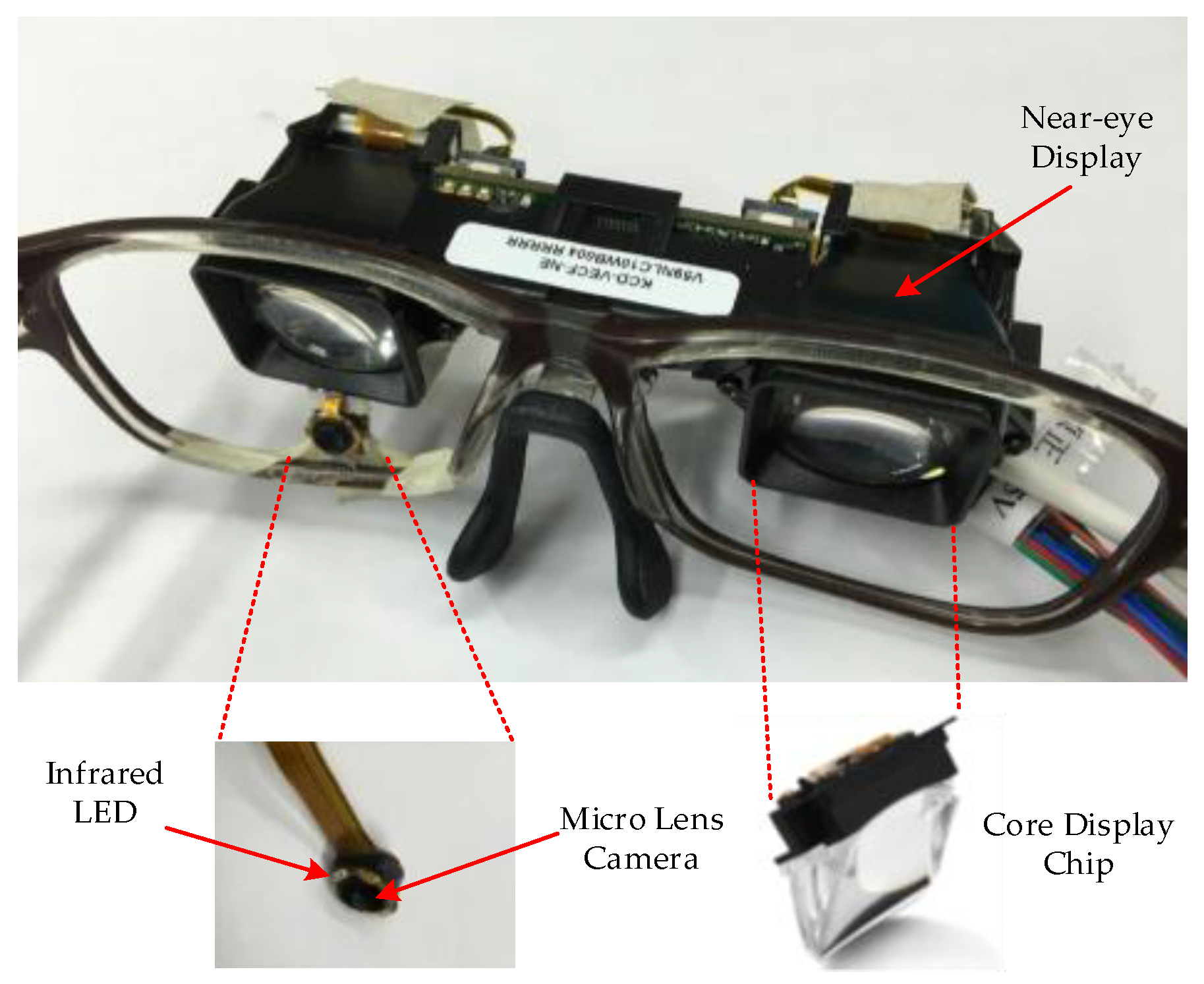
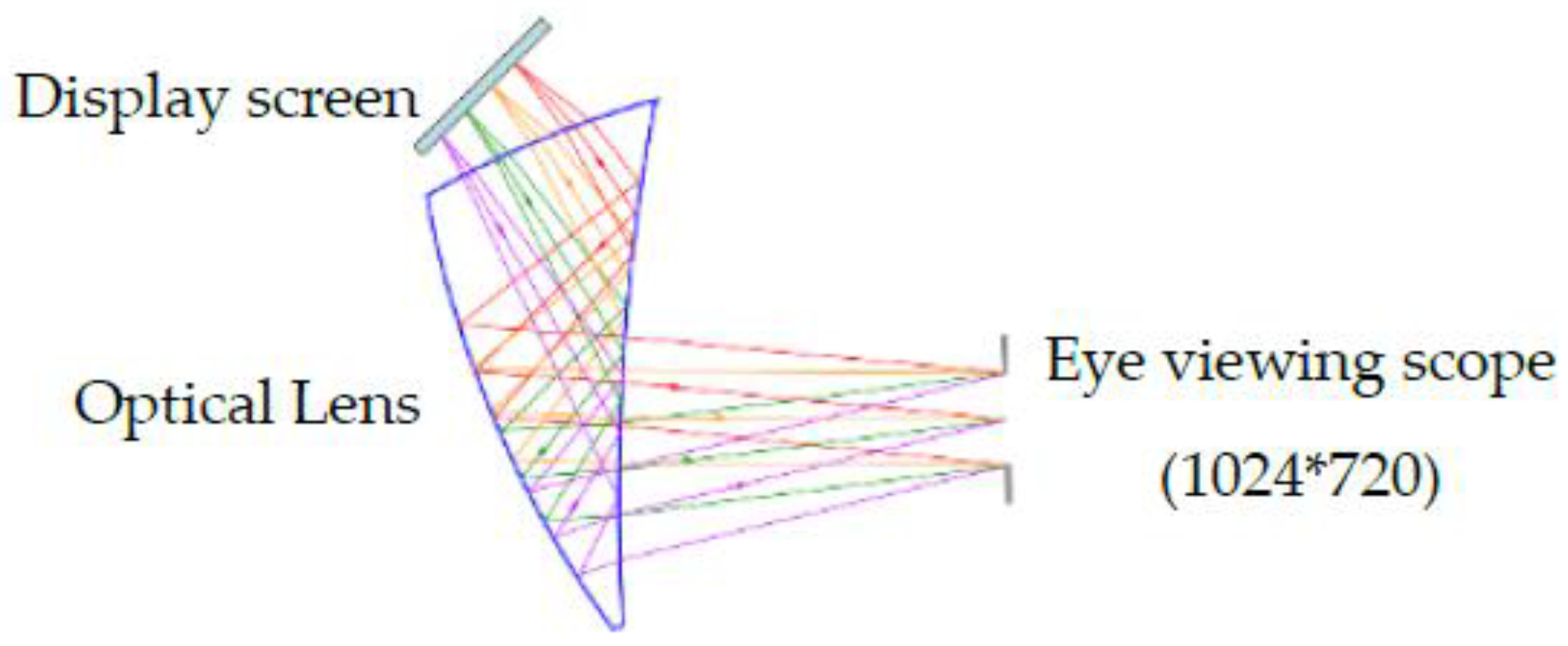
- We use a novel near-eye viewing device in the gaze-tracking system, which replaces the traditional large display devices, e.g., computer monitors, TVs, and projectors. The near-eye viewing device has a millimeter-sized display chip with a resolution of pixels and displays a size of cm2 virtual image at a distance of 0.5 m from the human eyes.
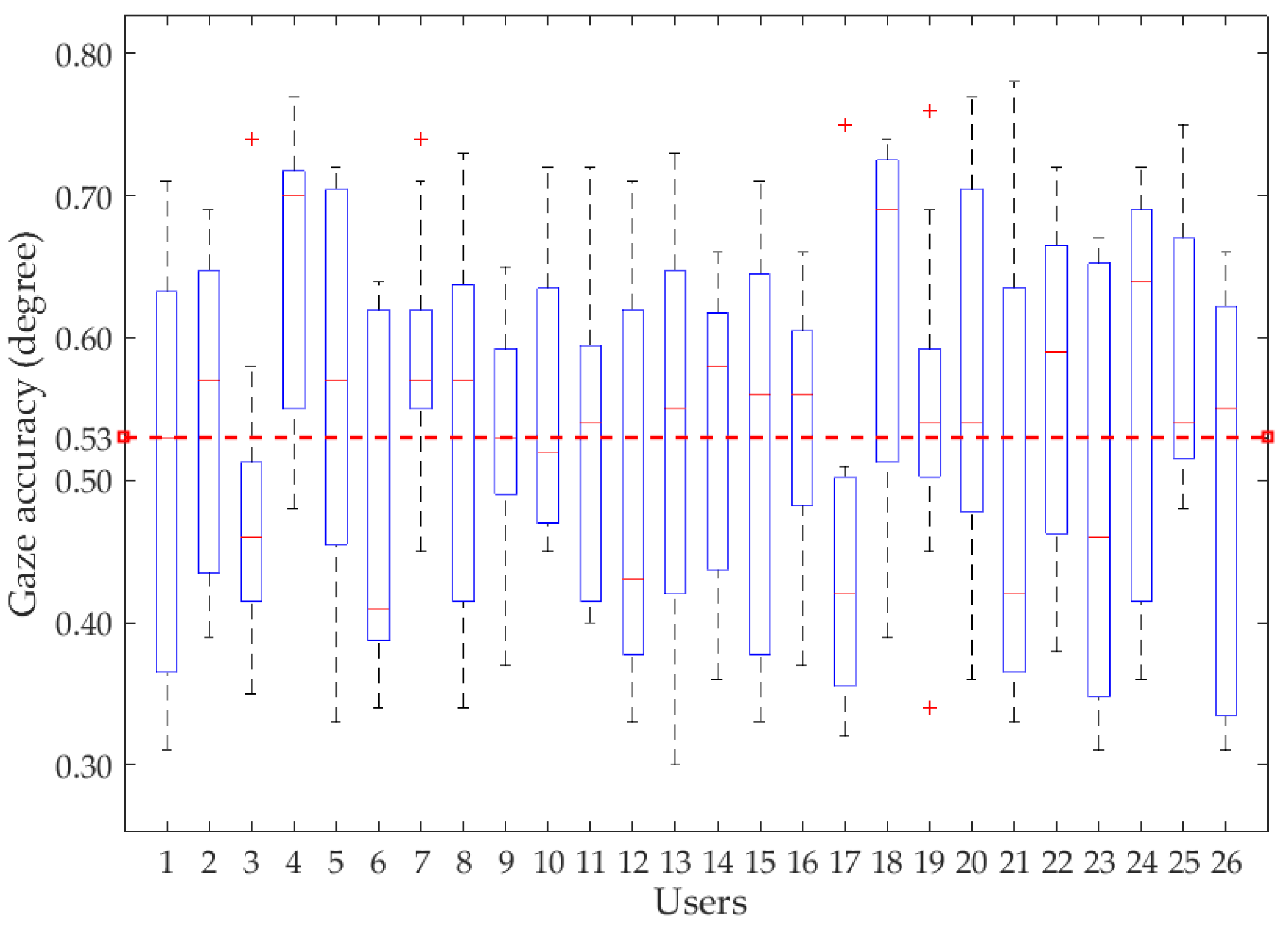
- We propose a combined gaze estimation method based on CNNs (ResNet-101) and a geometric model. The CNN is used to remove the blinking eye images and locate the coarse gaze position, and the accurate gaze positions are detected by a geometric model. The gaze accuracy can reach 0.53°.
- We propose using the mean value of pupil centers to smooth the changes caused by nystagmus in calibration algorithms. Therefore, an individual user only needs to calibrate it the first time.
2. Related Work
2.1. Gaze-Tracking System
2.2. Image-Based Eye Detection Methods
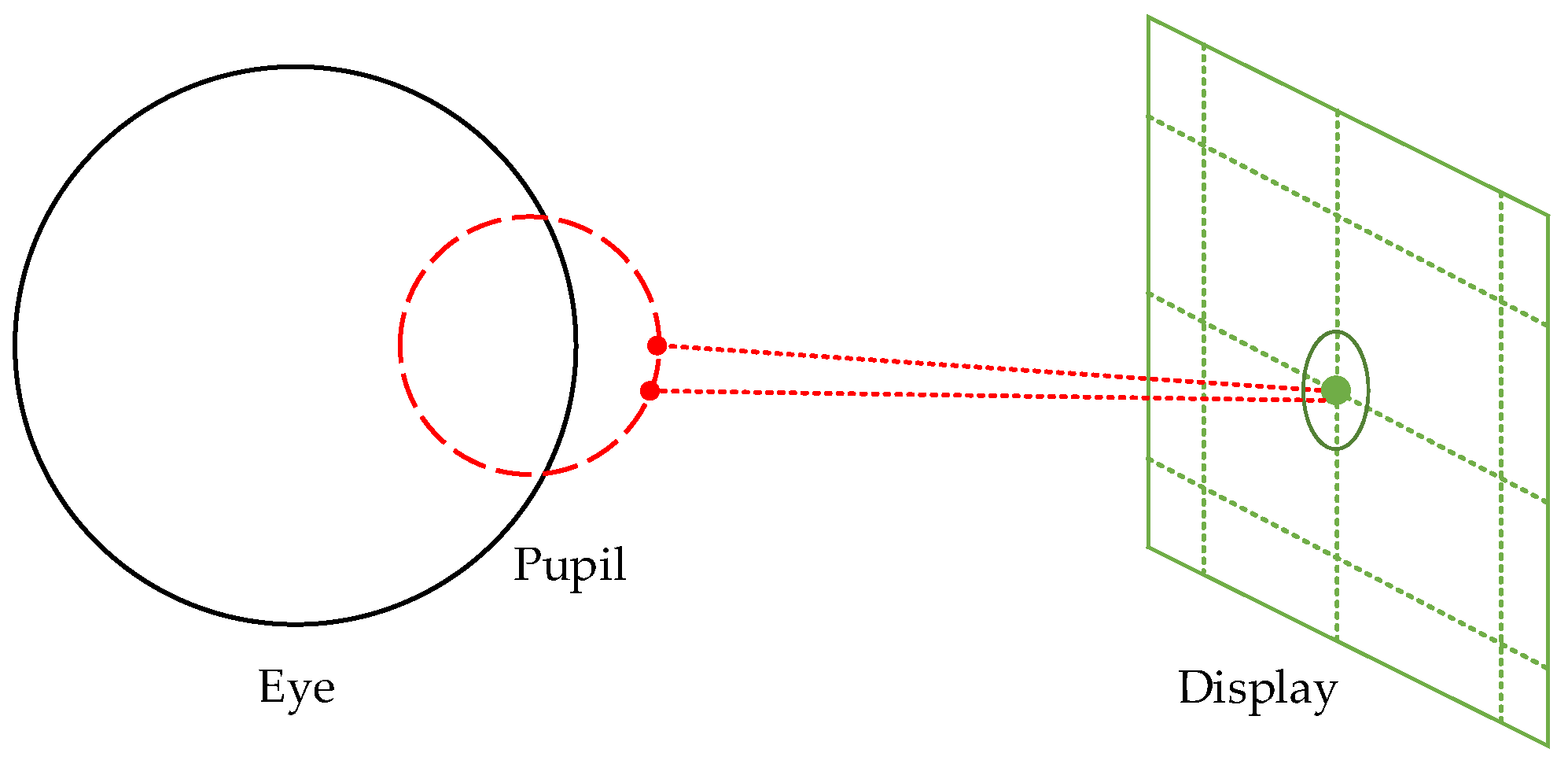
3. The Proposed Method
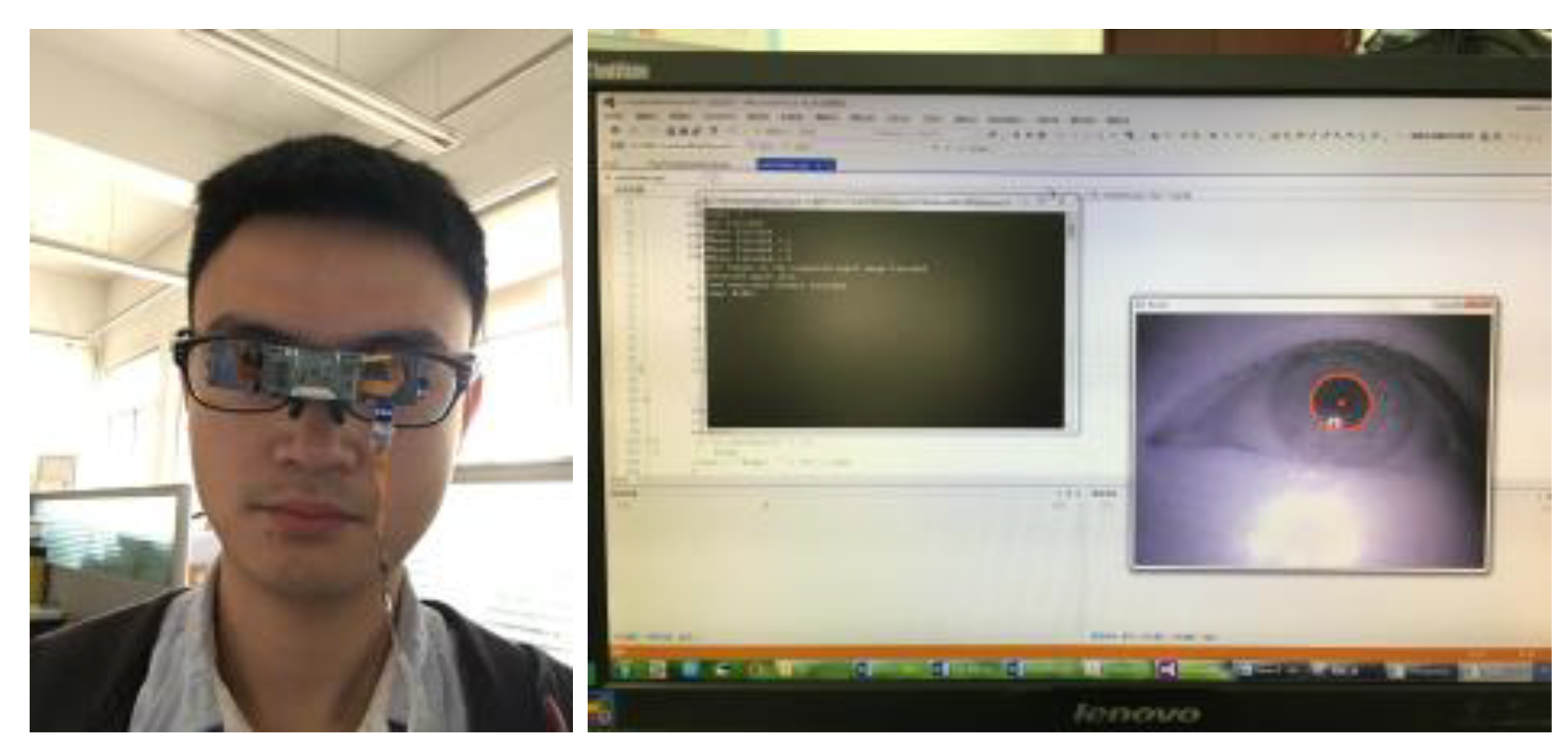
3.1. Etracker Hardware System and Experimental Environment
3.2. Workflow of Proposed Gaze-Tracking Method
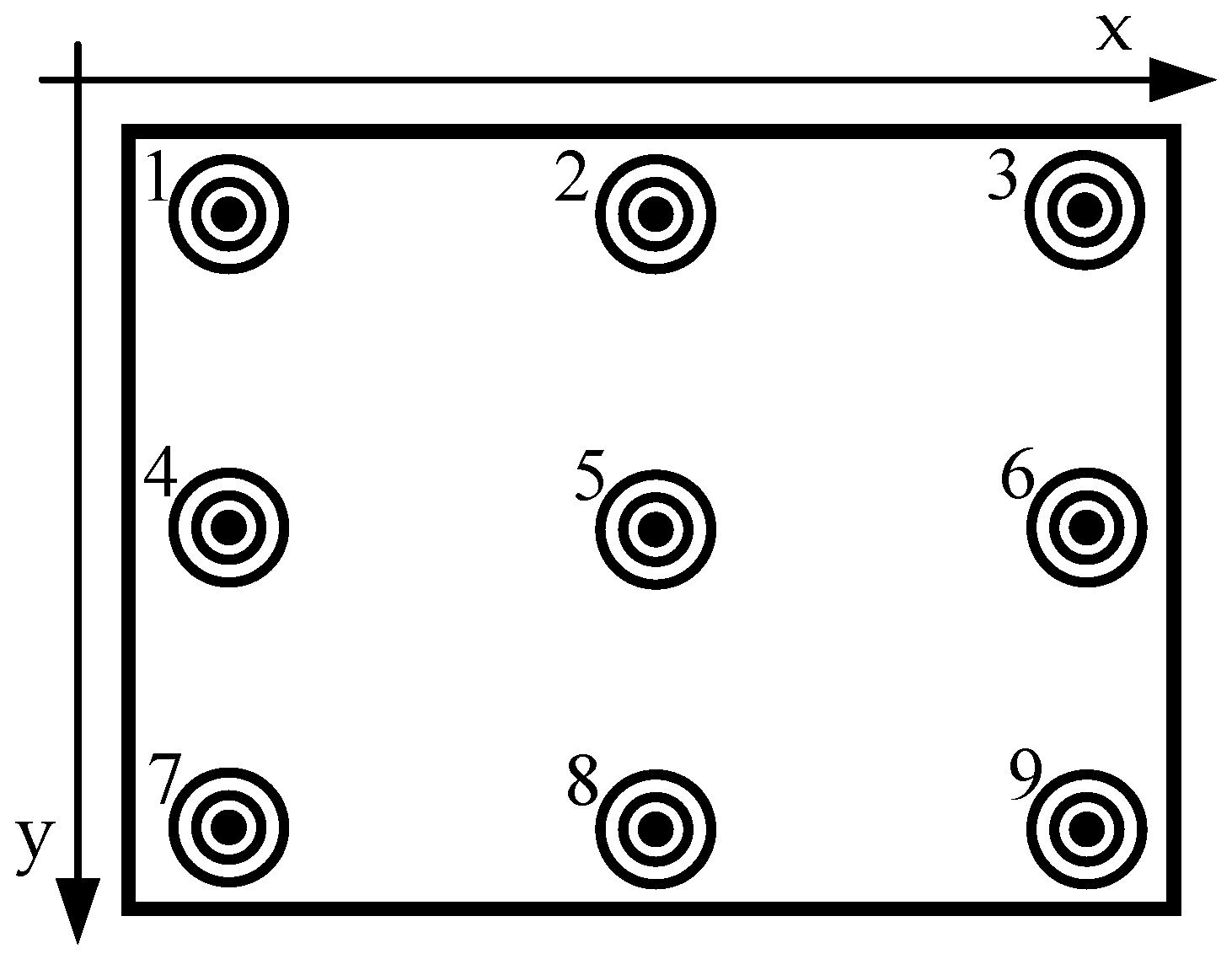
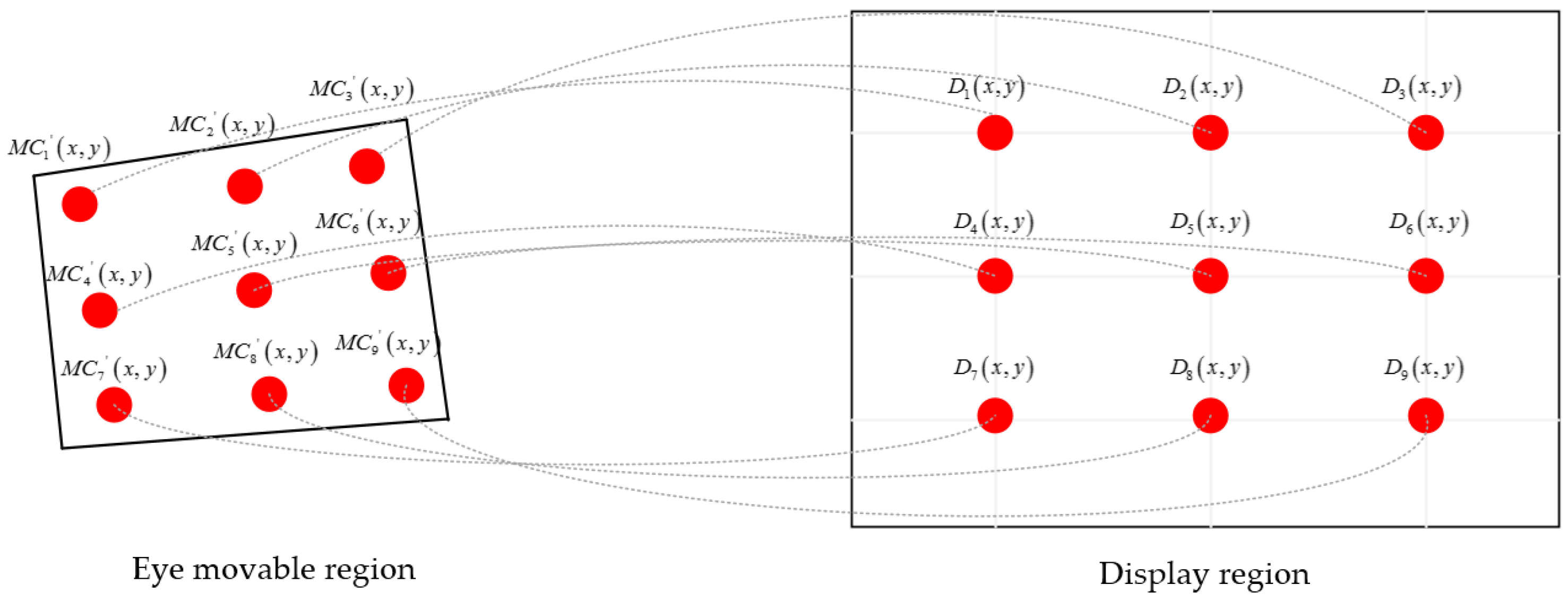
3.3. Initial Calibration
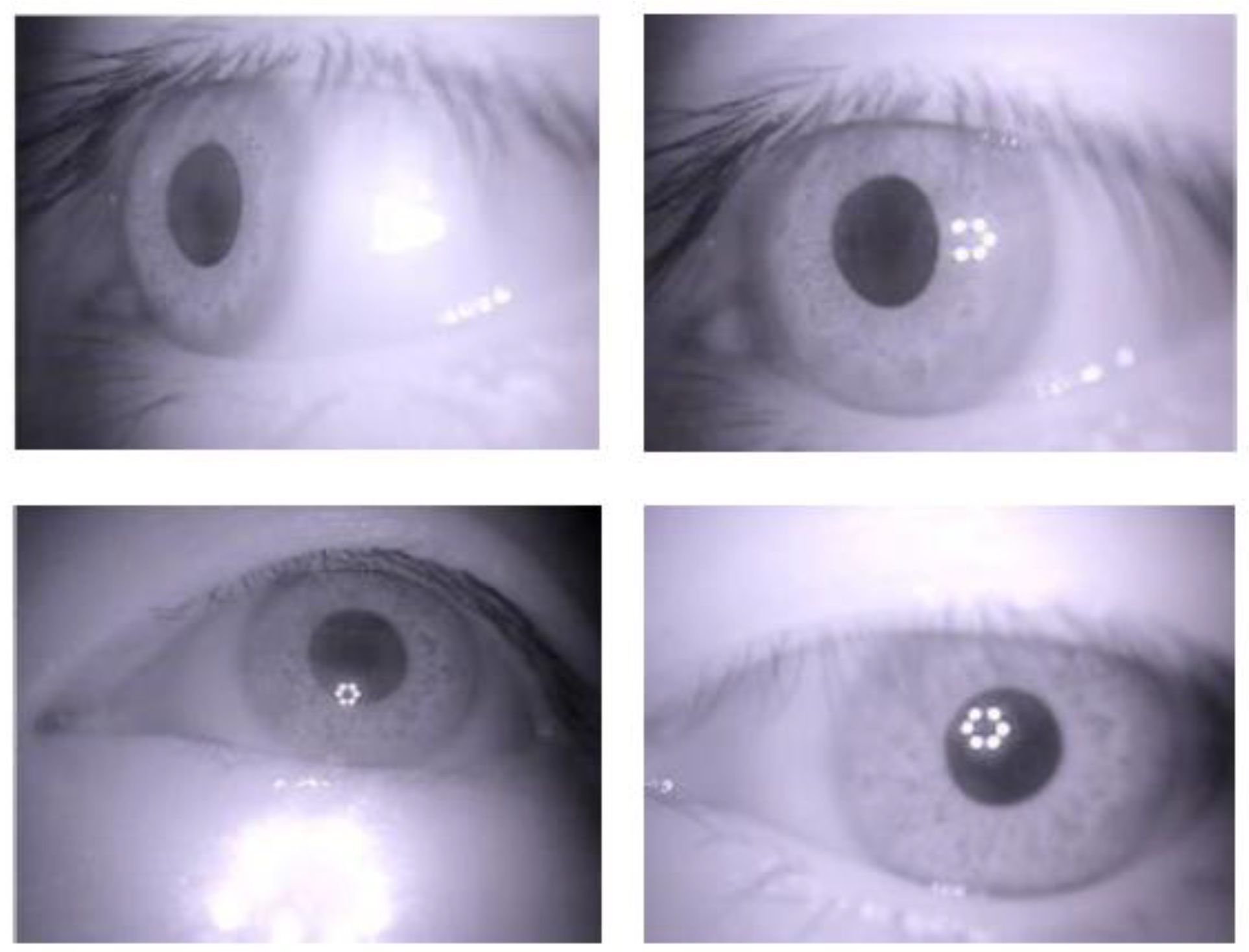
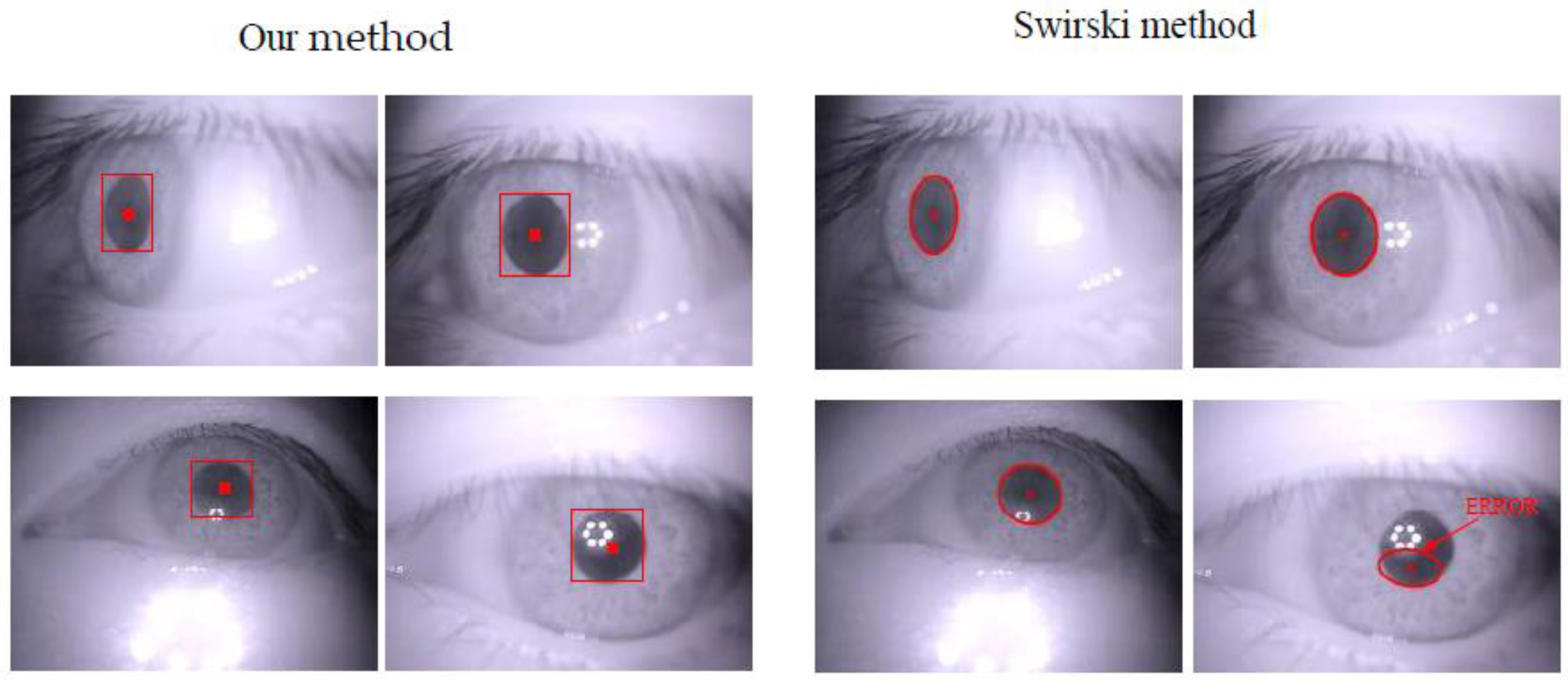
3.4. Coarse Gaze Estimation and Blinking Image Removal by CNNs
3.5. Combined Gaze-Tracking Algorithm
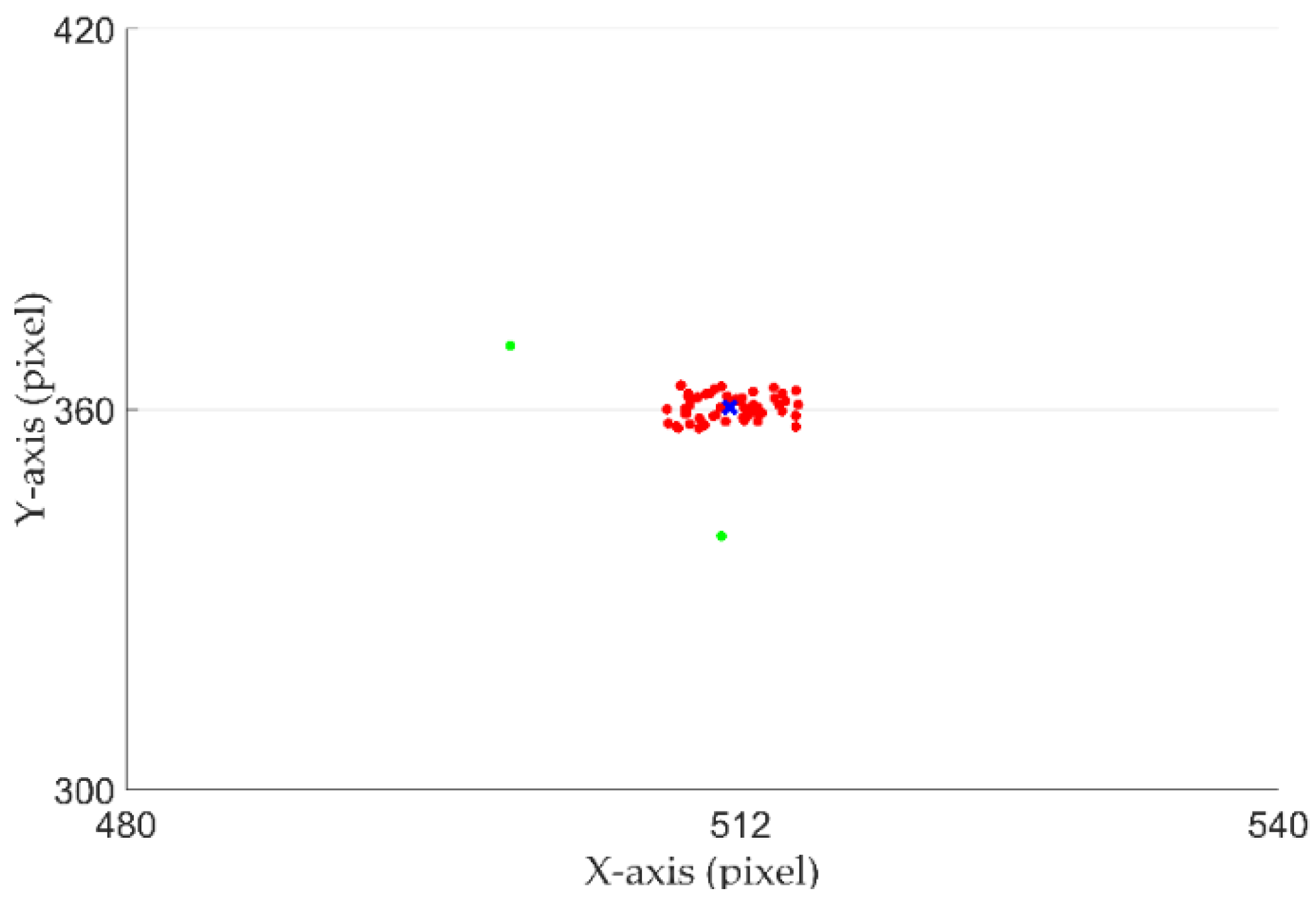
4. Results
4.1. Dataset Collection
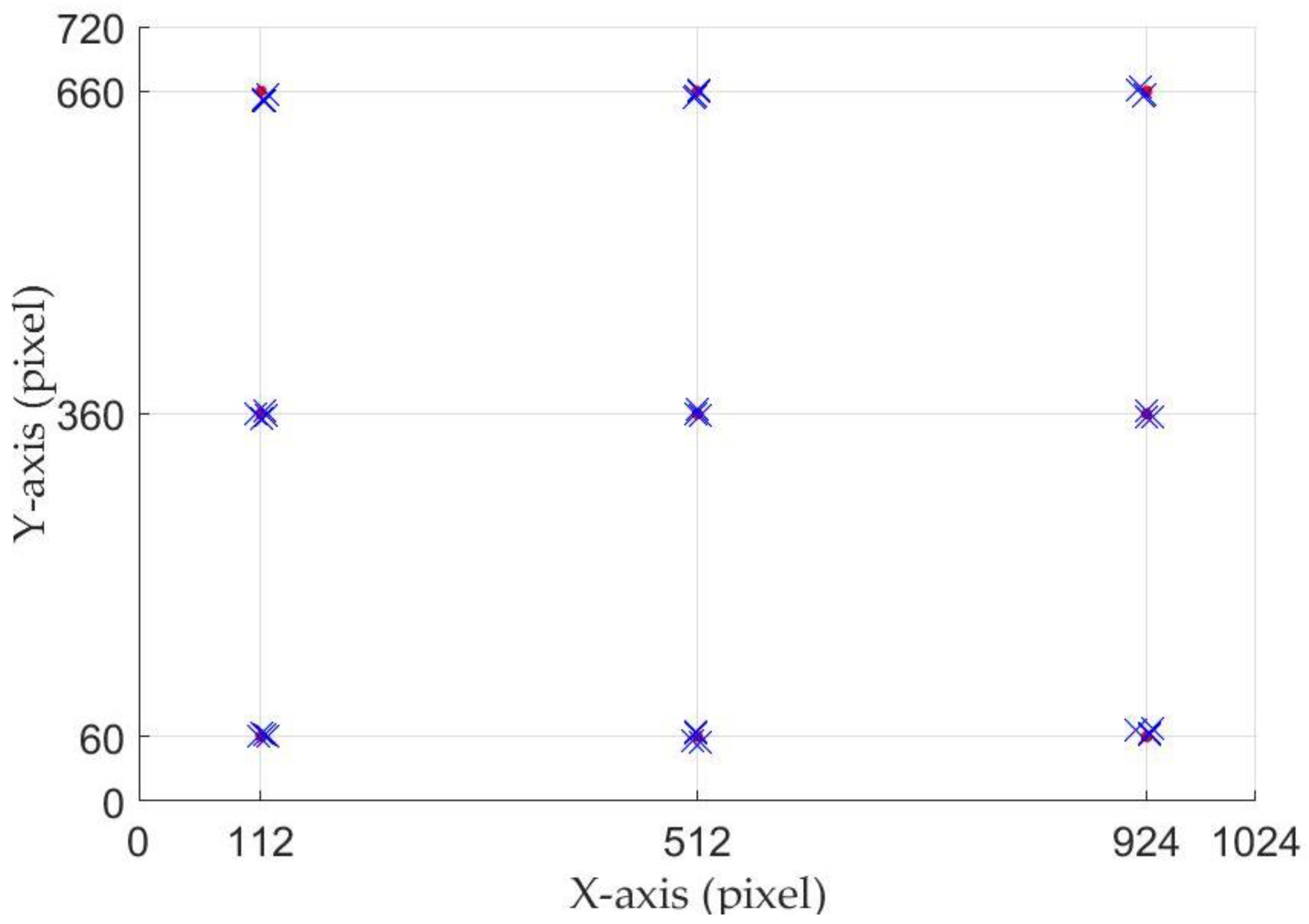
4.2. Gaze Tracking Results
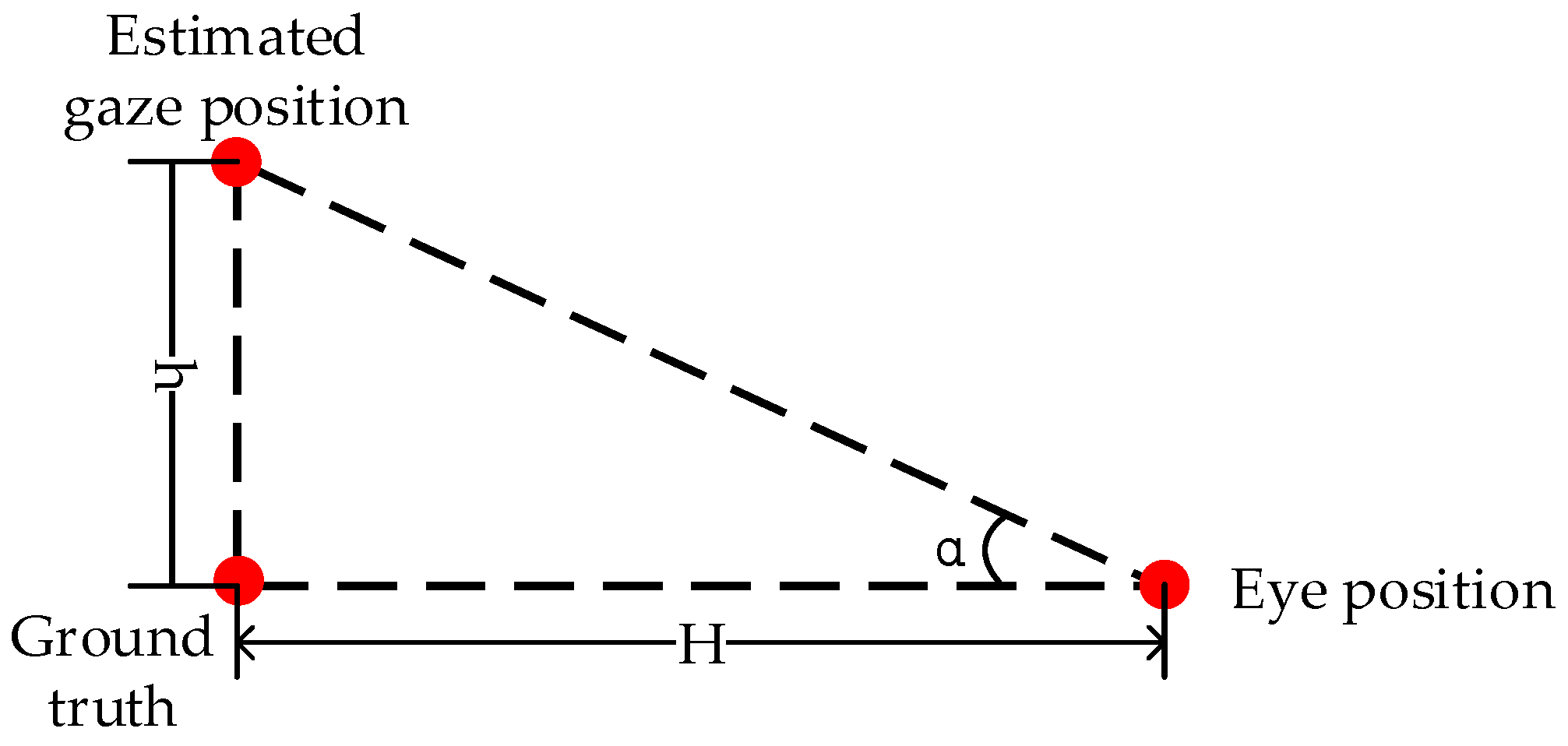
4.3. Further Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopez-Basterretxea, A.; Mendez-Zorrilla, A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. Eye/head tracking technology to improve HCI with iPad applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 2244–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.H.; Chang, P.Y.; Huang, C.Y. Using eye-tracking and support vector machine to measure learning attention in elearning. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 311, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlstrom, C.; Kircher, K.; Kircher, A. A Gaze-Based Driver Distraction Warning System and Its Effect onVisual Behavior. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2013, 14, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Fu, H.; Lo, W.L.; Chi, Z. Strabismus Recognition Using Eye-tracking Data and Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 7692198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Fu, H.; Lo, W.; Yu, J.; Sit, C.H.P.; Wen, D. Evaluation of the fine motor skills of children with DCD using the digitalised visual-motor tracking system. J. Eng. 2018, 2018, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, S.Y.; Cho, C.W.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, W.O.; Park, K.R. Gaze tracking system for user wearing glasses. Sensors 2014, 14, 2110–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, P.; Langdon, P. Multimodal intelligent eye-gaze tracking system. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2015, 31, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocejko, T.; Bujnowski, A.; Wtorek, J. Eye Mouse for Disabled. In Proceedings of the Conference on Human System Interactions, Krakow, Poland, 25–27 May 2008; pp. 199–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kassner, M.; Patera, W.; Bulling, A. Pupil: An open source platform for pervasive eye tracking and mobile gaze-based interaction. In Proceedings of the 2014 ACM international joint conference on pervasive and ubiquitous computing: Adjunct publication, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–17 September 2014; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1151–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Su, M.-C.; Wang, K.-C.; Chen, G.-D. An Eye Tracking System and Its Application in Aids for People with Severe Disabilities. Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun. 2006, 18, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Lee, W.O.; Cho, C.W.; Gwon, S.Y.; Park, K.R.; Lee, H.; Cha, J. Remote Gaze Tracking System on a Large Display. Sensors 2013, 13, 13439–13463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, R.A.; Arsalan, M.; Batchuluun, G.; Yoon, H.S.; Park, K.R. Deep learning-based gaze detection system for automobile drivers using a NIR camera sensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, V.; Josephine, S. One millisecond face alignment with an ensemble of regression trees. In Proceedings of the 27th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2014, Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 1867–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.W.; Hong, H.G.; Nam, G.P.; Park, K.R. A Study of Deep CNN-Based Classification of Open and Closed Eyes Using a Visible Light Camera Sensor. Sensors 2017, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krafka, K.; Khosla, A.; Kellnhofer, P.; Kannan, H.; Bhandarkar, S.; Matusik, W.; Torralba, A. Eye tracking for everyone. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1606.05814. [Google Scholar]
- Cerrolaza, J.J.; Villanueva, A.; Cabeza, R. Taxonomic study of polynomial regressions applied to the calibration of video-oculographic systems. In Proceedings of the 2008 symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications, Savannah, GA, USA, 26–28 March 2008; pp. 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Tawari, A.; Chen, K.H.; Trivedi, M.M. Where is the driver looking: Analysis of head, eye and iris for robust gaze zone estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Qingdao, China, 8–11 October 2014; pp. 988–994. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, D.; Lee, J.M.; Gwon, S.Y.; Pan, W.; Lee, H.C.; Park, K.R.; Kim, H.-C. Compensation method of natural head movement for gaze tracking system using an ultrasonic sensor for distance measurement. Sensors 2016, 16, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Jung, D.; Yoon, H.S.; Lee, D.E.; Naqvi, R.A.; Lee, K.W.; Park, K.R. Empirical study on designing of gaze tracking camera based on the information of user’s head movement. Sensors 2016, 16, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, S.; Rangesh, A.; Trivedi, M.M. On generalizing driver gaze zone estimation using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Redondo Beach, CA, USA, 11–14 June 2017; pp. 849–854. [Google Scholar]
- Galante, A.; Menezes, P. A Gaze-Based Interaction System for People with Cerebral Palsy. Procedia Technol. 2012, 5, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, B.R.; Devyver, M.; Tsukada, A.; Kanade, T. Unwrapping the eye for visible-spectrum gaze tracking on wearable devices. Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision WACV), Tampa, FL, USA, 15–17 January 2013; pp. 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Plopski, A.; Nitschke, C.; Kiyokawa, K.; Schmalstieg, D.; Takemura, H. Hybrid Eye Tracking: Combining Iris Contour and Corneal Imaging. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference onArtificial Reality and Telexistence and Eurographics Symposium on Virtual Environments, Kyoto, Japan, 28–30 October 2015; pp. 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Borsato, F.H.; Morimoto, C.H. Episcleral surface tracking: Challenges and possibilities for using mice sensors for wearable eye tracking. In Proceedings of the Ninth Biennial ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications, Charleston, WV, USA, 14–17 March 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Topal, C.; Gunal, S.; Koçdeviren, O.; Doğan, A.; Gerek, Ö.N. A low-computational approach on gaze estimation with eye touch system. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 44, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonsen, M.; Steil, J.; Sugano, Y.; Bulling, A. InvisibleEye: Mobile Eye Tracking Using Multiple Low-Resolution Cameras and Learning-Based Gaze Estimation. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2017, 1, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocejko, T.; Ruminski, J.; Wtorek, J.; Martin, B. Eye tracking within near-to-eye display. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 8th International Conference on Human System Interaction (HSI), Warsaw, Poland, 25–27 June 2015; pp. 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Shi, J. 2D gaze estimation based on pupil-glint vector using an artificial neural network. Appl. Sci. Basel 2016, 6, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, R.; Gevers, T. Accurate eye center location through invariant isocentric patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1785–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, N.; Frljaka, M.; Pandzia, I.S.; Ahlbergb, J.; Forchheimer, R. Eye pupil localization with an ensemble of randomized trees. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timm, F.; Barth, E. Accurate eye centre localisation by means of gradients. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, Vilamoura, Portugal, 5–7 March 2011; Volume 11, pp. 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Świrski, L.; Bulling, A.; Dodgson, N. Robust real-time pupil tracking in highly off-axis images. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 28–30 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, G.M.; Ribeiro, F.M.L.; Silva, E.A.B.; Goldenstein, S.K. Fast eye localization without a face model using inner product detectors. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 1366–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Borza, D.; Darabant, A.S.; Danescu, R. Real-Time Detection and Measurement of EyeFeatures from Color Images. Sensors 2016, 16, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhl, W.; Kübler, T.; Sippel, K.; Rosenstiel, W.; Kasneci, E. Excuse: Robust pupil detection in real-world scenarios. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns (CAIP), Valletta, Malta, 2–4 September 2015; pp. 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Fuhl, W.; Santini, T.; Kasneci, G.; Kasneci, E. PupilNet: Convolutional neural networks for robust pupil detection. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1601.04902. [Google Scholar]
- Amos, B.; Ludwiczuk, B.; Satyanarayanan, M. Openface: A General-Purpose Face Recognition Library with Mobile Applications; CMU School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, K.; Wang, F.Y.; Ji, Q. A joint cascaded framework for simultaneous eye detection and eye state estimation. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 67, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Savakis, A. Lean histogram of oriented gradients features for effective eye detection. J. Electron. Imaging 2015, 24, 063007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Fu, H. Real time eye detector with cascaded Convolutional Neural Networks. Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput. 2018, 2018, 1439312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayberry, A.; Hu, P.; Marlin, B.; Salthouse, C.; Ganesan, D. iShadow: Design of a wearable, real-time mobile gaze tracker. In Proceedings of the 12th annual international conference on Mobile systems, applications, and services, Bretton Woods, NH, USA, 16–19 June 2014; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 82–94. [Google Scholar]


| Device | Tobii Glasses II | PupilLabs | Tobii X2-30 | Tobii X2-60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Head-mounted | Head-mounted | Table-mounted | Table-mounted |
| Sample rate | 50–100 Hz | 30–200 Hz | 30 Hz | 60 Hz |
| Gaze Accuracy | 0.5° | 0.6° | 0.4° | 0.4° |
| Weight | 45 g | 48 g | 200 g | 200 g |
| Calibration | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| SDK | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Connection | Micro USB | USB Type C | USB2.0 | USB2.0 |
| Price | 30,000 € | 1840 € | >10,000€ | >30,000 € |
| Resolution | pixels |
| Field of View (Horizontal) | 31.6° |
| Field of View (Vertical) | 24.2° |
| Weight | 31 g |
| Device Size | cm3 |
| Core Display Chip size | mm3 |
| Connection | VGA |
| Layer | Kernel Size | Filters Number | Feature Map Size | Stride | Padding | Iterations Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image Layer | |||||||
| Conv-1 | 64 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| Max pool | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | |||
| Conv-2 | Conv-2-1 | 64 | 1 | 0 | 3 | ||
| Conv-2-2 | 64 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Conv-2-3 | 256 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| Conv-3 | Conv-3-1 | 128 | 2 | 0 | 4 | ||
| Conv-3-2 | 128 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Conv-3-3 | 512 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| Conv-4 | Conv-4-1 | 256 | 2 | 0 | 23 | ||
| Conv-4-2 | 256 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Conv-4-3 | 1024 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| Conv-5 | Conv-5-1 | 512 | 2 | 0 | 3 | ||
| Conv-5-2 | 512 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Conv-5-3 | 2048 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| Average pool | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| Full Connect layer | 10 | - | - | - | - | 1 | |
| Softmax | 10 | - | - | - | - | 1 | |
| User | User 1 | User 2 | User 3 | User 4 | User 5 | User 6 | User 7 | User 8 | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaze Point | ||||||||||
| 1 | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.81 | 0.72 | 0.82 | |
| 2 | 0.75 | 0.97 | 0.60 | 0.73 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.70 | |
| 3 | 0.95 | 0.81 | 0.87 | 0.98 | 0.67 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.81 | |
| 4 | 0.53 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.52 | 0.68 | 0.73 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.64 | |
| 5 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.60 | |
| 6 | 0.63 | 0.51 | 0.78 | 0.52 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 0.88 | 0.65 | 0.64 | |
| 7 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 0.84 | 0.87 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 0.74 | 0.93 | 0.84 | |
| 8 | 0.74 | 0.81 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.73 | 0.95 | 0.72 | 0.77 | |
| 9 | 0.68 | 0.94 | 0.69 | 0.97 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 1.01 | 0.97 | 0.88 | |
| Average | 0.72 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.73 | 0.74 * | |
| User | User 1 | User 2 | User 3 | User 4 | User 5 | User 6 | User 7 | User 8 | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaze Point | ||||||||||
| 1 | 0.50 | 0.77 | 0.42 | 0.48 | 0.57 | 0.34 | 0.71 | 0.58 | 0.55 | |
| 2 | 0.34 | 0.55 | 0.50 | 0.71 | 0.45 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.61 | 0.58 | |
| 3 | 0.42 | 0.54 | 0.35 | 0.31 | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.52 | |
| 4 | 0.36 | 0.47 | 0.37 | 0.32 | 0.39 | 0.54 | 0.49 | 0.40 | 0.42 | |
| 5 | 0.39 | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.38 | 0.64 | 0.52 | 0.71 | 0.45 | 0.58 | |
| 6 | 0.42 | 0.48 | 0.78 | 0.62 | 0.39 | 0.52 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.54 | |
| 7 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.59 | 0.67 | 0.48 | 0.45 | 0.48 | 0.42 | 0.50 | |
| 8 | 0.32 | 0.69 | 0.33 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.55 | 0.77 | 0.72 | 0.58 | |
| 9 | 0.75 | 0.49 | 0.42 | 0.53 | 0.69 | 0.56 | 0.74 | 0.40 | 0.57 | |
| Average | 0.45 | 0.57 | 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.64 | 0.52 | 0.54 * | |
| Coordinate Error | H | V | |
|---|---|---|---|
| User | |||
| User 1 | 0.48 | 0.49 | |
| User 2 | 0.52 | 0.54 | |
| User 3 | 0.37 | 0.48 | |
| User 4 | 0.48 | 0.51 | |
| User 5 | 0.49 | 0.58 | |
| User 6 | 0.53 | 0.57 | |
| User 7 | 0.59 | 0.71 | |
| User 8 | 0.49 | 0.53 | |
| Average | 0.49 | 0.55 | |
| Coordinate Error | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User | ||||||
| User 1 | 0.45 | 0.42 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.46 | |
| User 2 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.6 | 0.56 | |
| User 3 | 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.49 | 0.53 | 0.51 | |
| User 4 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.53 | |
| User 5 | 0.55 | 0.49 | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.53 | |
| User 6 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.56 | 0.55 | 0.55 | |
| User 7 | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.67 | 0.58 | 0.62 | |
| User 8 | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.49 | 0.60 | 0.54 | |
| Average | 0.54 | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.54 * | |
| Normalized Error | Gaze Accuracy (°) | Method | Rate (Hz) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | ||||
| Mayberry [42] | 3 | ANN | 30 | |
| Tonsen [26] | 1.79 | ANN | - | |
| Borsato [24] | 2.1 | Optical Flow | 1000 | |
| Kassner [9] | 0.6 | Geometric Model | 24 | |
| Gwon [6] | 0.7 | Corneal Reflection | 15 | |
| Ours | 0.75 | CNNs | 60 | |
| Ours | 0.53 | Combined gaze-tracking algorithm | 30–60 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Fu, H.; Wen, D.; LO, W. Etracker: A Mobile Gaze-Tracking System with Near-Eye Display Based on a Combined Gaze-Tracking Algorithm. Sensors 2018, 18, 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051626
Li B, Fu H, Wen D, LO W. Etracker: A Mobile Gaze-Tracking System with Near-Eye Display Based on a Combined Gaze-Tracking Algorithm. Sensors. 2018; 18(5):1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051626
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bin, Hong Fu, Desheng Wen, and WaiLun LO. 2018. "Etracker: A Mobile Gaze-Tracking System with Near-Eye Display Based on a Combined Gaze-Tracking Algorithm" Sensors 18, no. 5: 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051626
APA StyleLi, B., Fu, H., Wen, D., & LO, W. (2018). Etracker: A Mobile Gaze-Tracking System with Near-Eye Display Based on a Combined Gaze-Tracking Algorithm. Sensors, 18(5), 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051626




