Thermoelectric Array Sensors with Selective Combustion Catalysts for Breath Gas Monitoring
Abstract
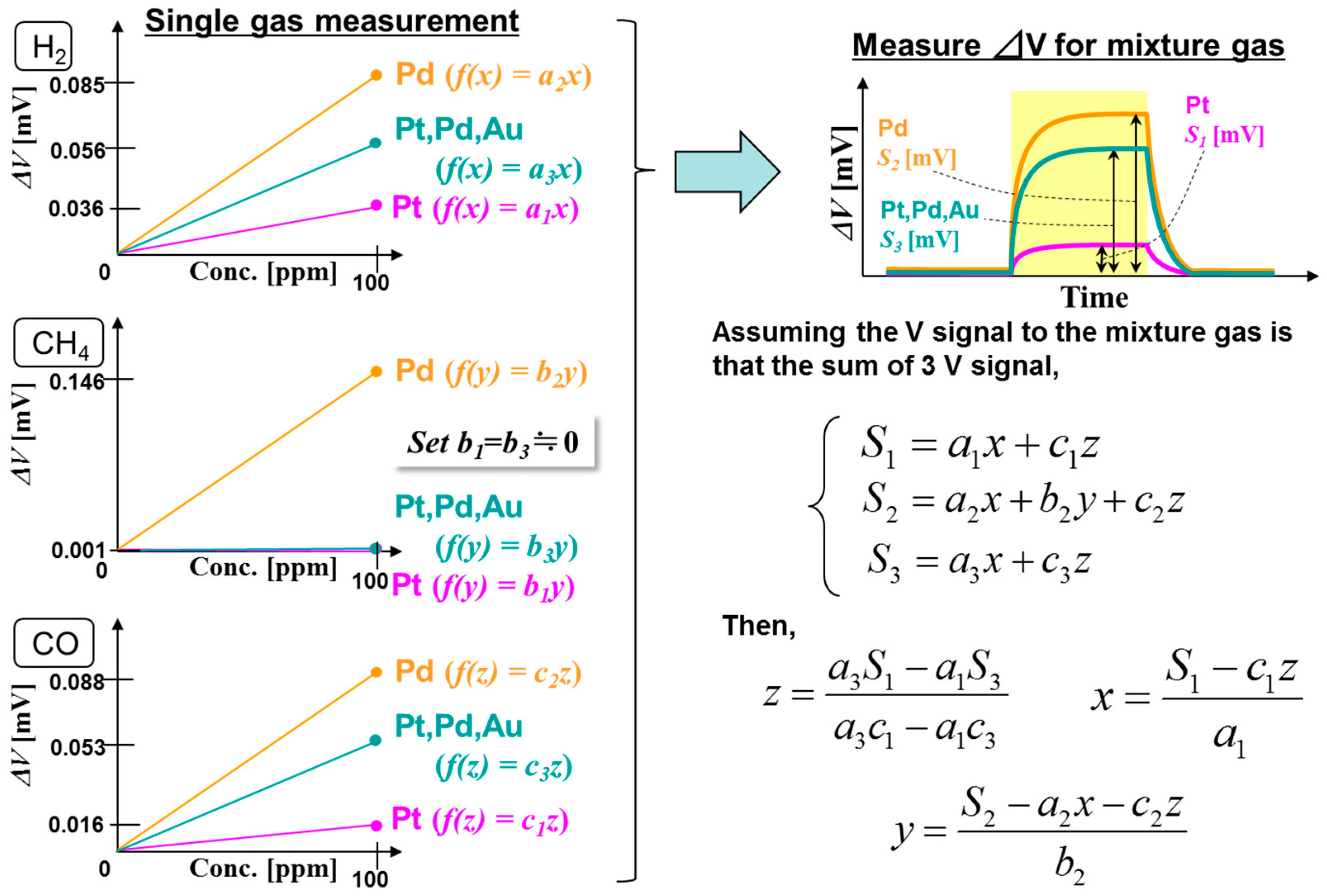
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
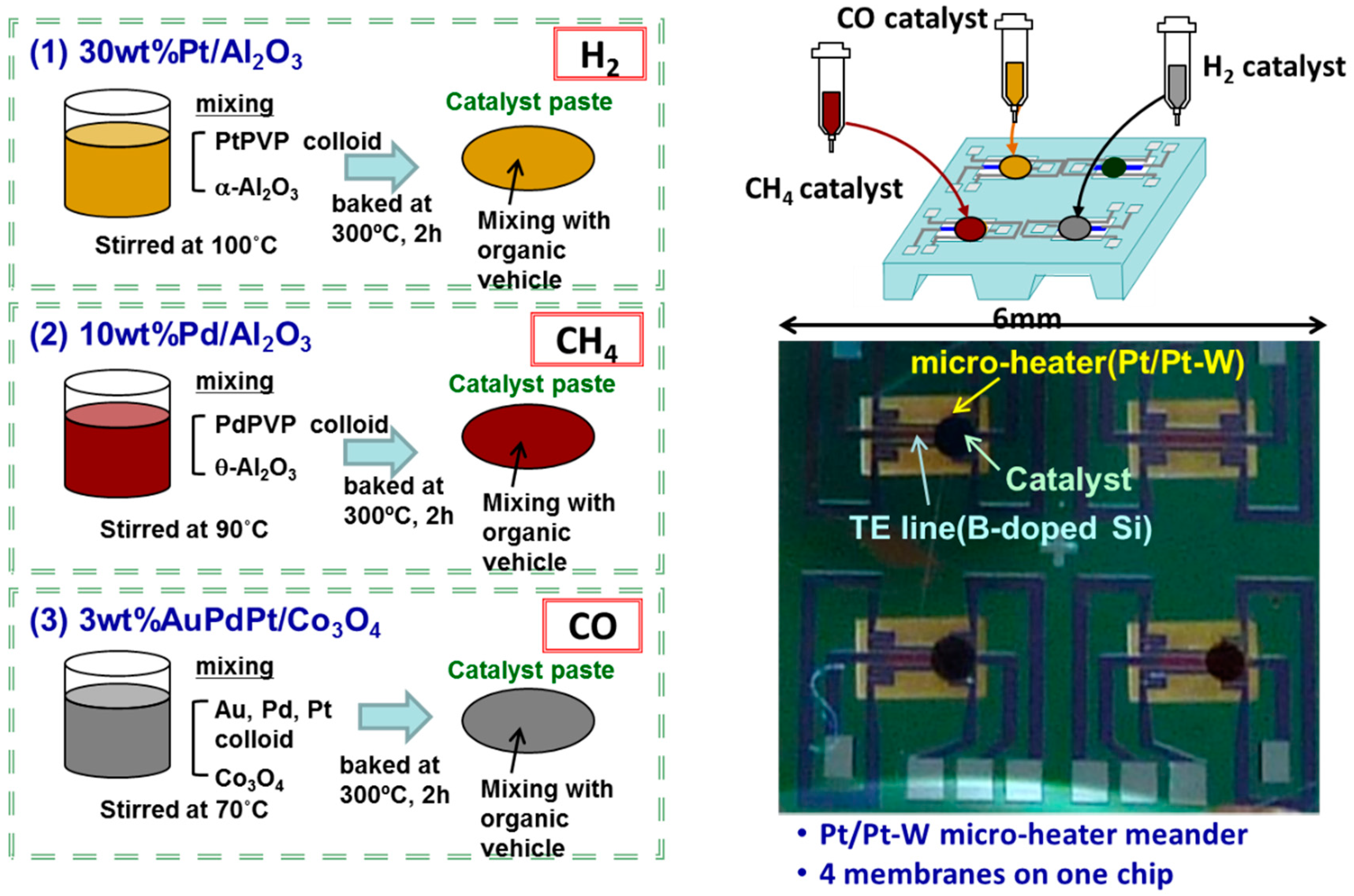
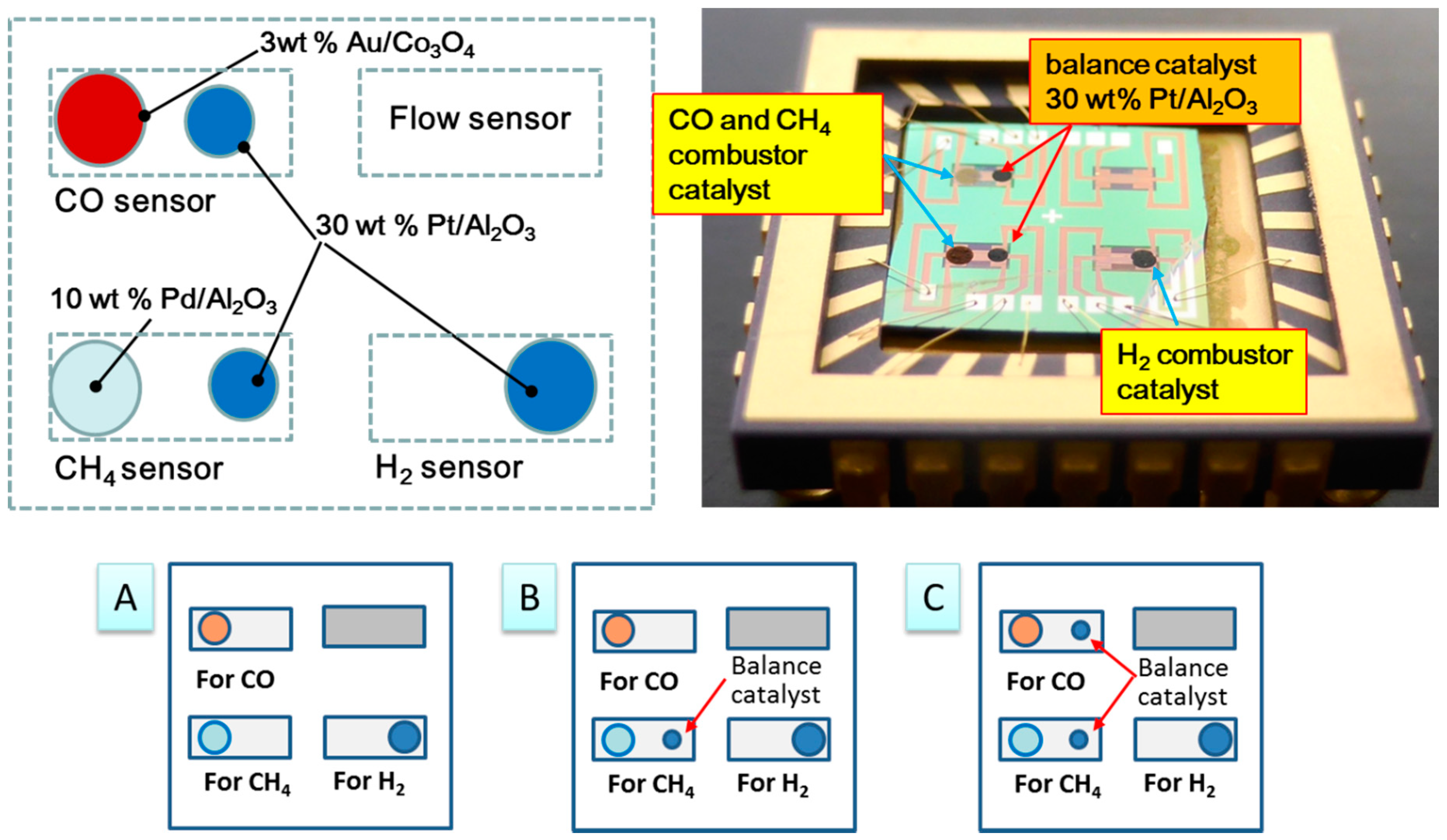
2.1. Integration of Catalyst Combustor onto Array Sensor
2.2. Sensor Response Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Combustion Performance of Pt/Al2O3, Pt,Pd,Au/Co3O4, and Pd/Al2O3 Catalysts
3.2. Double Catalyst to Enhance TAS Gas Selectivity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Philips, M.; Herrera, J.; Krishnan, S.; Zain, M.; Greenberg, J.; Cataneo, R.N. Variation in volatile organic compounds in the breath of normal humans. J. Chromatogr. 1999, 729, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W. Medical applications of breath hydrogen measurements. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3931–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, S.; Toda, K. Micro gas analyzers for environmental and medical applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 619, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Duan, Y. Current status of methods and techniques for breath analysis. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2007, 37, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumbach, J.I.; Eiceman, G.A. Ion Mobility Spectrometry: Arriving On Site and Moving Beyond a Low Profile. Appl. Spectrosc. 1999, 53, 338A–355A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbig, J.; Amann, A. Proton Transfer Reaction-Mass Spectrometry Applications in Medical Research. J Breath Res. 2009, 3, 020201–020202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, M.; Simon, E.; Rumpel, E.; Ulmer, H.; Harbeck, M.; Wandel, M.; Fietzek, C.; Weimar, U.; Meixner, H. Detection of volatile compounds correlated to human diseases through breath analysis with chemical sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 83, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Tisch, U.; Adams, O.; Hakim, M.; Shehada, N.; Broza, Y.Y.; Billan, S.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Haick, H. Diagnosing lung cancer in exhaled breath using gold nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomchenko, A.A.; Harmer, G.P.; Marquis, B.T.; Allen, J.W. Semiconducting metal oxide sensor array for the selective detection of combustion gases. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 93, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.-K.; Shin, H.W.; Park, H.S.; Yun, D.H.; Kwon, C.H.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.-T.; Moriizumi, T. Gas identification using micro gas sensor array and neural-network pattern recognition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1996, 33, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitzner, K.D.; Sternhagen, J.; Galipeau, D.W. Development of a micromachined hazardous gas sensor array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 93, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaowu, M.; Okawa, Y.; Tajima, M.; Nakai, T.; Yoshitake, N.; Natsukawa, K. Micro-machined gas sensor array based on metal film micro-heater. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 79, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Nishibori, M.; Shin, W.; Houlet, L.F.; Tajima, K.; Izu, N.; Itoh, T.; Murayama, N.; Matsubara, I. New structural design of micro-thermoelectric sensor for wide range hydrogen detection. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 114, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Nishibori, M.; Izu, N.; Itoh, T.; Matsubara, I.; Nose, K.; Shimouchi, A. Monitoring Breath Hydrogen using Thermoelectric Sensor. Sens. Lett. 2011, 9, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishibori, M.; Shin, W.; Izu, N.; Itoh, T.; Matsubara, I. Fabrication of micro-multi-gas sensor for the detection of hydrogen, carbon monoxide and methane in breath. Sens. Lett. 2011, 9, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, D.; Nakashima, T.; Nishibori, M.; Itoh, T.; Izu, N.; Shin, W. Thermoelectric gas sensor with CO combustion catalyst for ppm level carbon monoxide Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 182, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, D.; Nishibori, M.; Itoh, T.; Kawabe, T.; Sato, K.; Shin, W. Ppm level methane detection using micro-thermoelectric gas sensors with Pd/Al2O3 combustion catalyst films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Itoh, T.; Akamatsu, T.; Sekino, T.; Shin, W. Relationship between the CO sensing performance of micro-thermoelectric gas sensors and characteristics of PtPd/Co3O4 and PtPd/SnO2 catalysts. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 847–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.L.; Brkljača, R.; Taylor, K.M.; Burgell, R.E.; Yao, C.K.; Ward, S.A.; McSweeney, C.S.; Muir, J.G.; Gibson, P.R. A human pilot trial of ingestible electronic capsules capable of sensing different gases in the gut. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, D.; Hirooka, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Ohno, E.; Ishikawa, T.; Suhara, H.; Takeyama, T.; Koya, T.; Tanaka, H.; Iida, T.; et al. Increase in breath hydrogen concentration was correlated with the main pancreatic duct stenosis. J. Breath Res. 2018, 12, 36004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
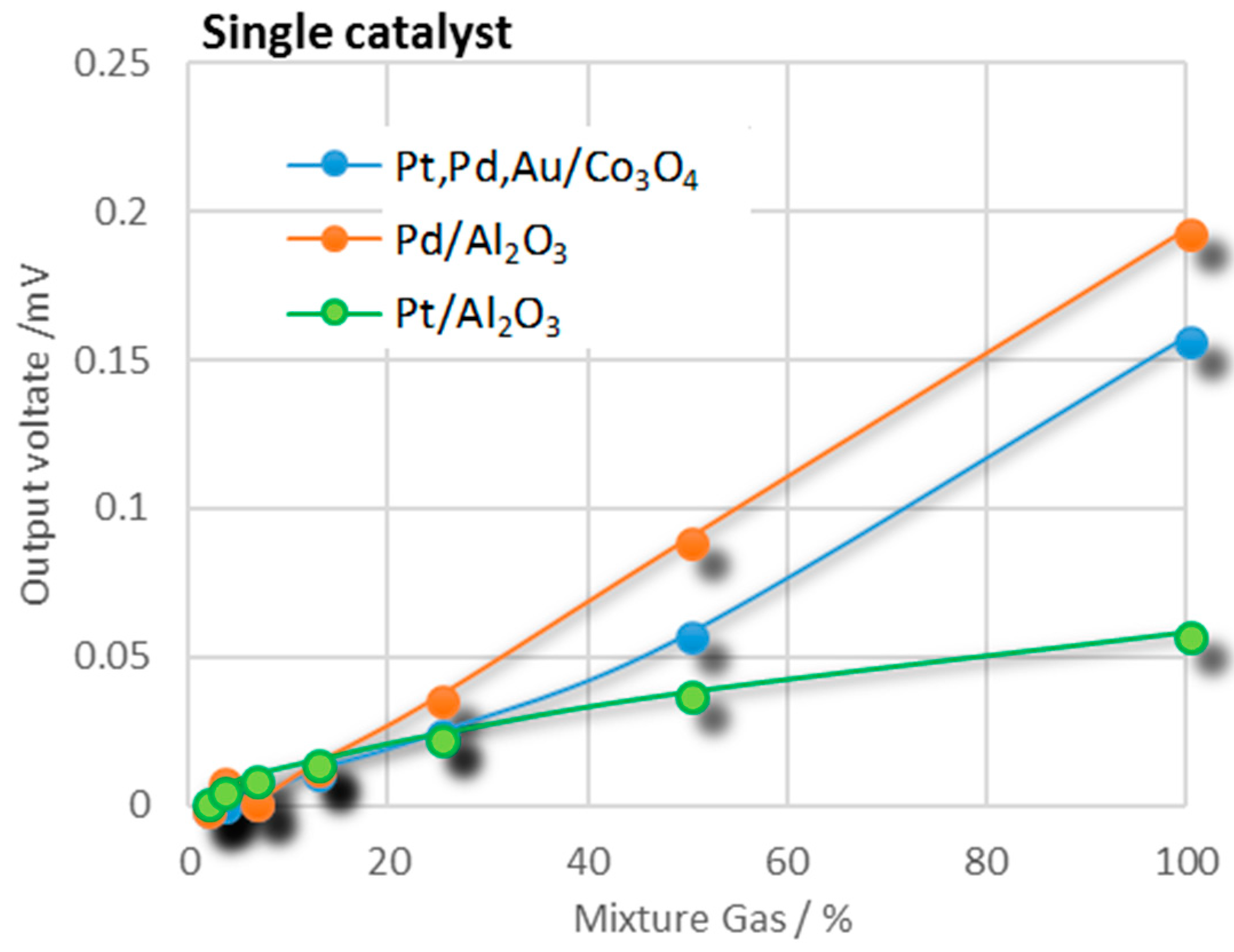
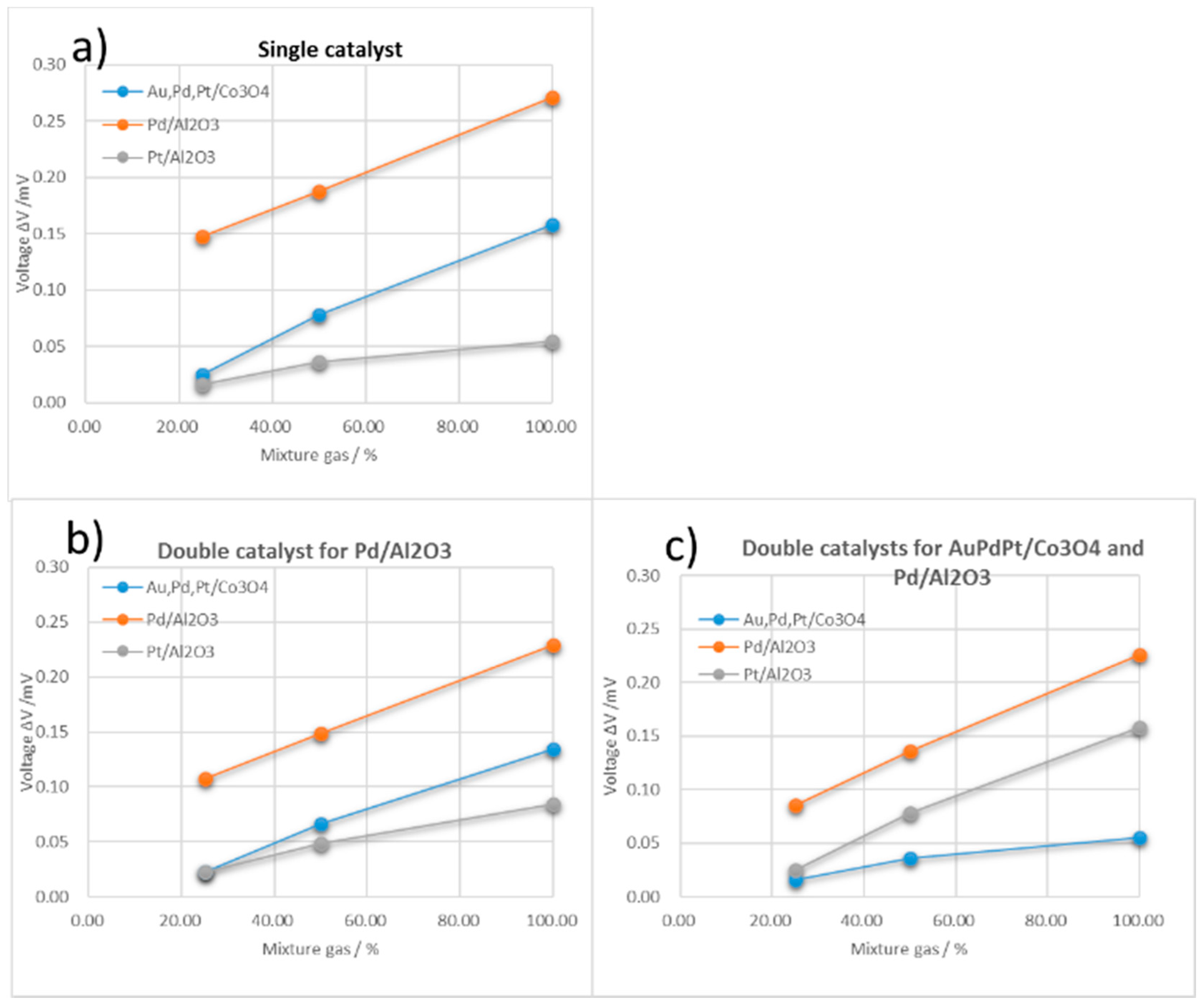
| Catalyst Material | Catalyst | ΔV for Single Gas at 100 ppm (mV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. (°C) | H2 | CH4 | CO | |
| Pt/Al2O3 | 125 | 0.036 | 0.001 | 0.016 |
| Pt,Pd,Au/Co3O4 | 200 | 0.056 | 0.001 | 0.053 |
| Pd/Al2O3 | 320 | 0.085 | 0.146 | 0.088 |
| Single Catalyst Type A | ||||||
| Catalyst | Single Gas 100 ppm | Mix Gas (%) | ||||
| H2 | CH4 | CO | 25 | 50 | 100 | |
| Pt/Al2O3 | 0.0386 | 0.0034 | 0.0256 | 0.016 | 0.036 | 0.055 |
| Pd/Al2O3 | 0.142 | 0.164 | 0.082 | 0.18 | 0.229 | 0.33 |
| Pt,Pd,Au/Co3O4 | 0.0307 | 0.12 | 0.083 | 0.025 | 0.078 | 0.158 |
| One Double Catalyst Type B | ||||||
| Catalyst | Single Gas 100 ppm | Mix Gas (%) | ||||
| H2 | CH4 | CO | 25 | 50 | 100 | |
| Pt/Al2O3 | 0.230 | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.025 | 0.078 | 0.158 |
| Double | 0.125 | 0.176 | 0.027 | 0.086 | 0.136 | 0.226 |
| Pt,Pd,Au/Co3O4 | 0.045 | 0.003 | 0.055 | 0.016 | 0.036 | 0.055 |
| Two Double Catalyst Type C | ||||||
| Catalyst | Single Gas 100 ppm | Mix Gas (%) | ||||
| H2 | CH4 | CO | 25 | 50 | 100 | |
| Pt/Al2O3 | 0.150 | −0.030 | −0.030 | 0.023 | 0.0668 | 0.134 |
| Double | 0.092 | 0.146 | −0.003 | 0.108 | 0.149 | 0.229 |
| Double | 0.110 | 0.120 | 0.260 | 0.0232 | 0.0485 | 0.152 |
| Type A | Type B | Type C | Mixture Gas Composition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2 conc. (x) | 121 | 62 | 108 | 100 ppm |
| CH4 conc. (y) | 86 | 77 | 89 | 50 ppm |
| CO2 conc. (z) | 21 | 46 | −4 | 25 ppm |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, W.; Goto, T.; Nagai, D.; Itoh, T.; Tsuruta, A.; Akamatsu, T.; Sato, K. Thermoelectric Array Sensors with Selective Combustion Catalysts for Breath Gas Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051579
Shin W, Goto T, Nagai D, Itoh T, Tsuruta A, Akamatsu T, Sato K. Thermoelectric Array Sensors with Selective Combustion Catalysts for Breath Gas Monitoring. Sensors. 2018; 18(5):1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051579
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Woosuck, Tomoyo Goto, Daisuke Nagai, Toshio Itoh, Akihiro Tsuruta, Takafumi Akamatsu, and Kazuo Sato. 2018. "Thermoelectric Array Sensors with Selective Combustion Catalysts for Breath Gas Monitoring" Sensors 18, no. 5: 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051579
APA StyleShin, W., Goto, T., Nagai, D., Itoh, T., Tsuruta, A., Akamatsu, T., & Sato, K. (2018). Thermoelectric Array Sensors with Selective Combustion Catalysts for Breath Gas Monitoring. Sensors, 18(5), 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051579






