A Four-Feet Walking-Type Rotary Piezoelectric Actuator with Minute Step Motion
Abstract
1. Introduction
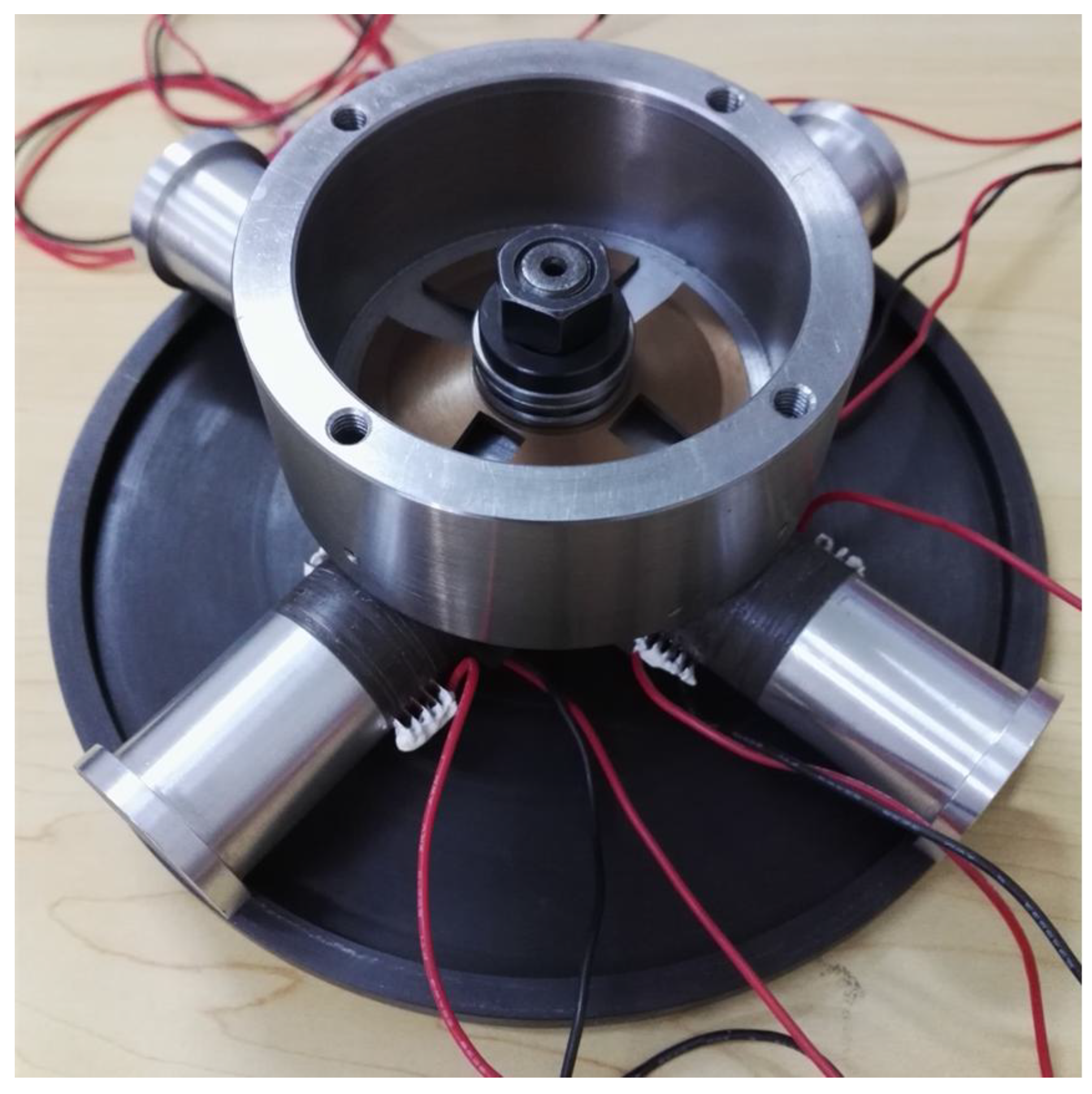
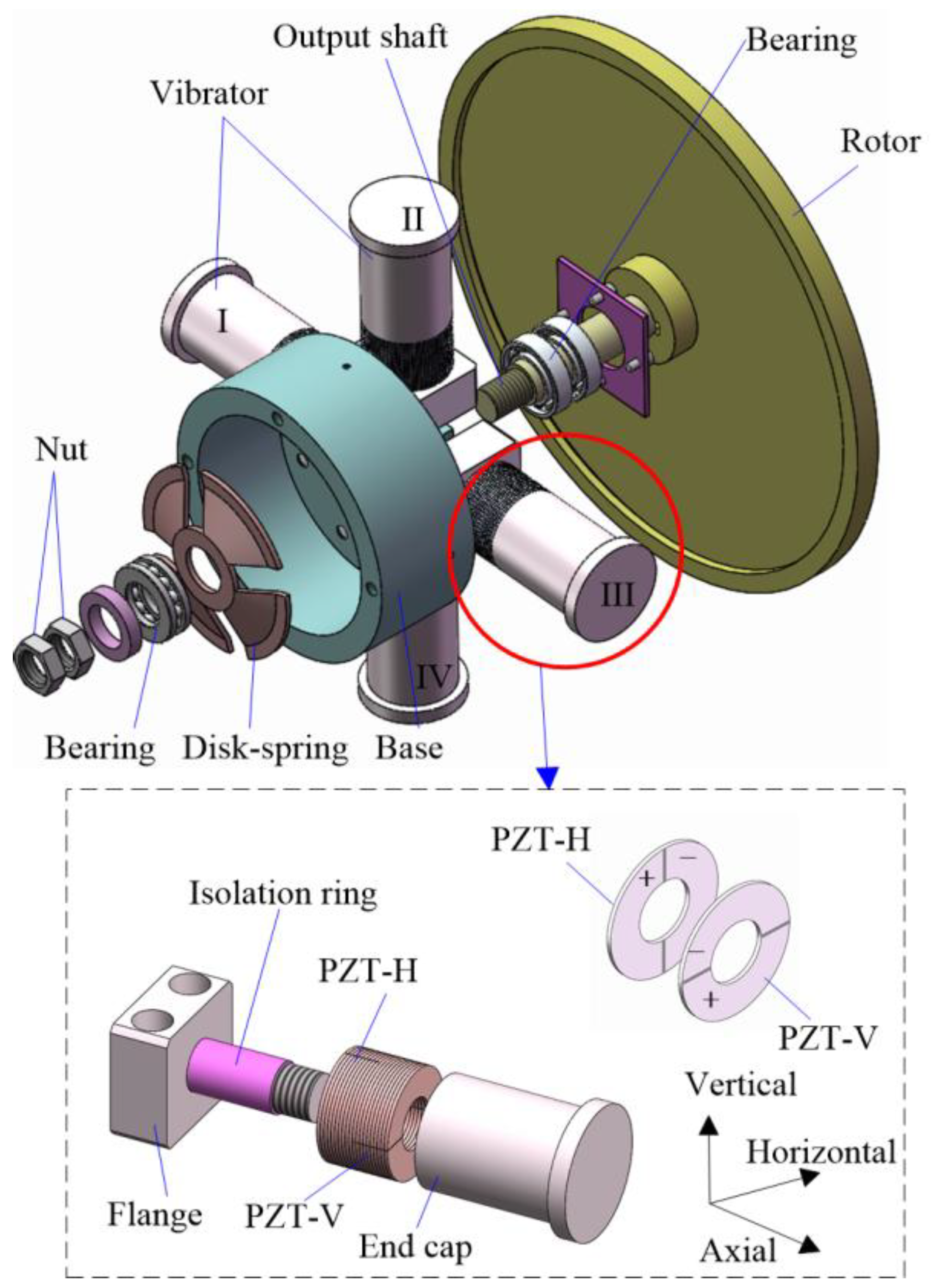
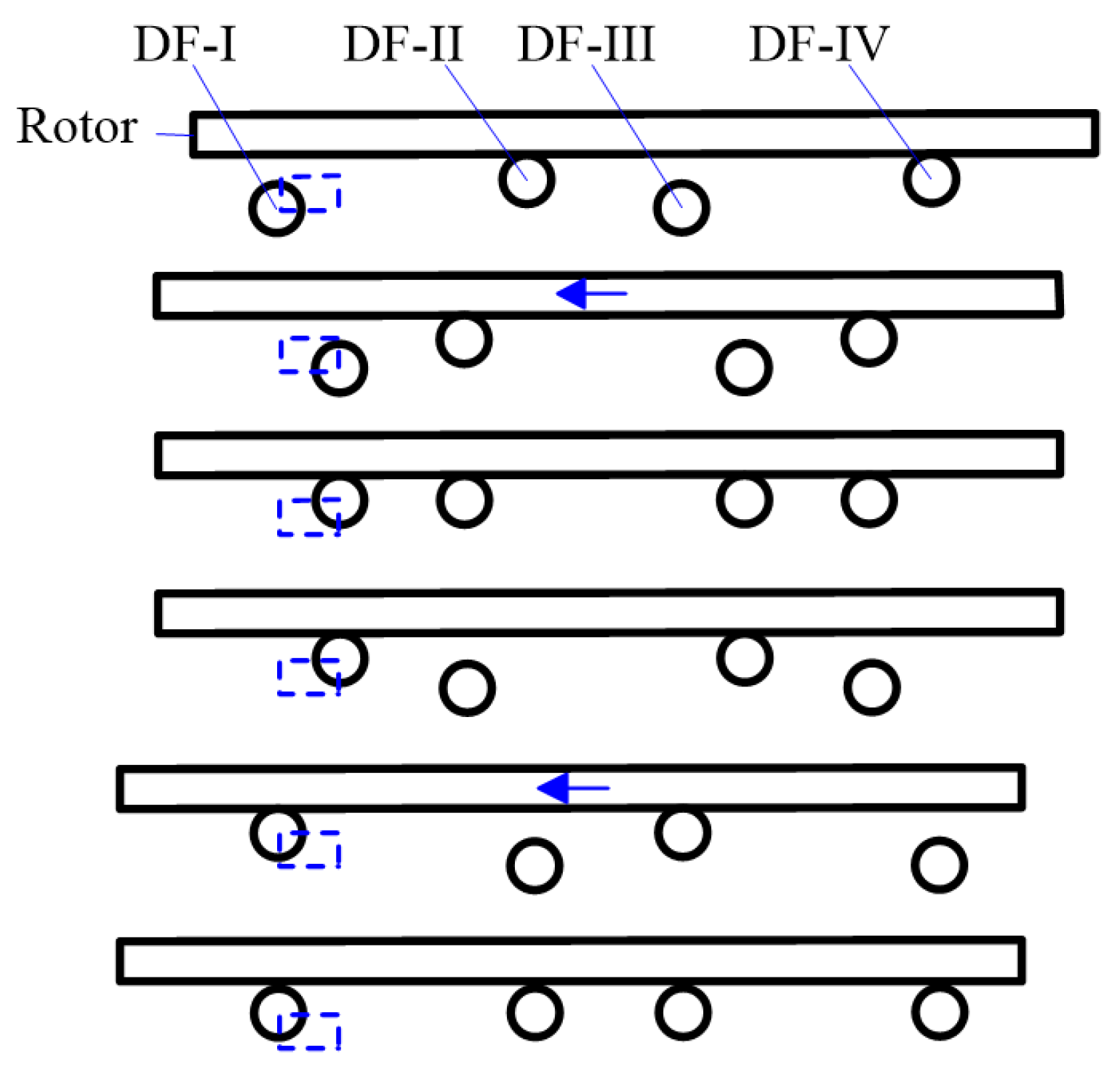
2. Structures and Principles
- (1)
- DF-I and DF-III bend downward and depart from the rotor, DF-II and DF-IV lock the rotor.
- (2)
- DF-I and DF-III bend rightward, DF-II and DF-IV bend leftward synchronously and push the rotor leftward for one step.
- (3)
- DF-I and DF-III bend upward to lock the rotor.
- (4)
- DF-II and DF-IV bend downward and depart from the rotor, DF-I and DF-III remain locking the rotor.
- (5)
- DF-I and DF-III bend leftward and push the rotor leftward for another step, DF-II and DF-IV bend rightward synchronously.
- (6)
- DF-II and DF-IV bend upward to lock the rotor.
- (7)
- Repeat (1)–(2)–(3)–(4)–(5)–(6).
3. Simulation Analyses
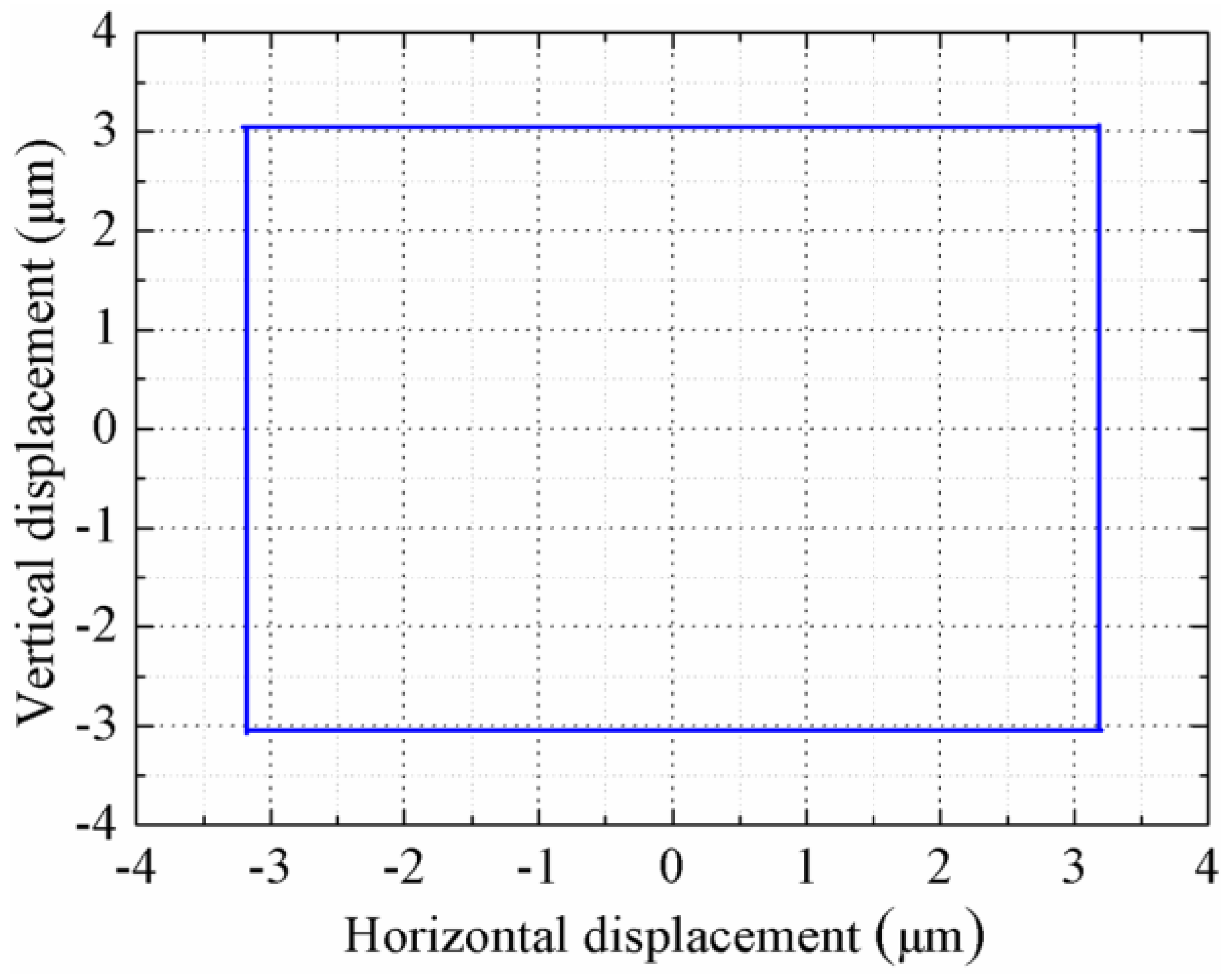
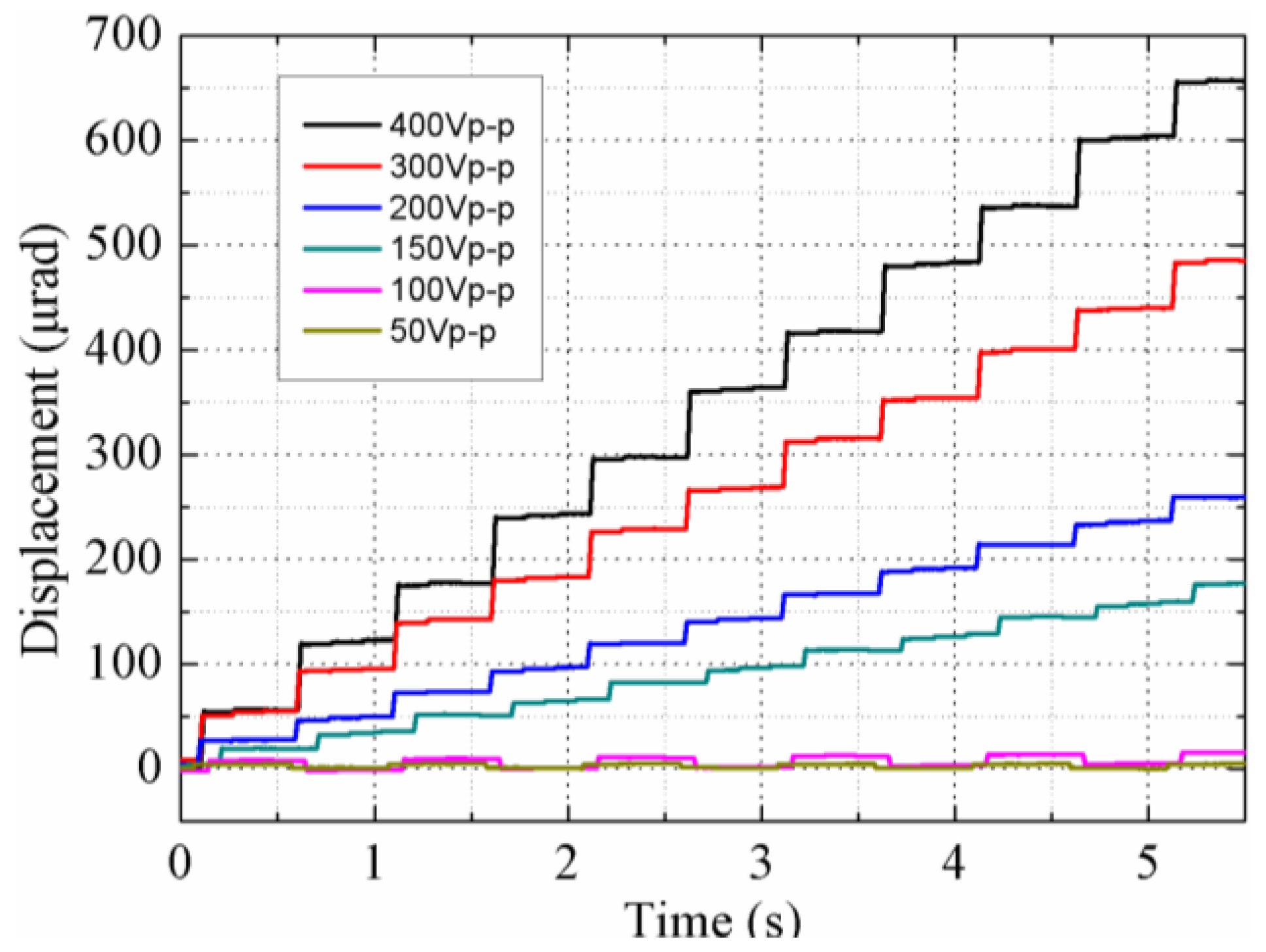
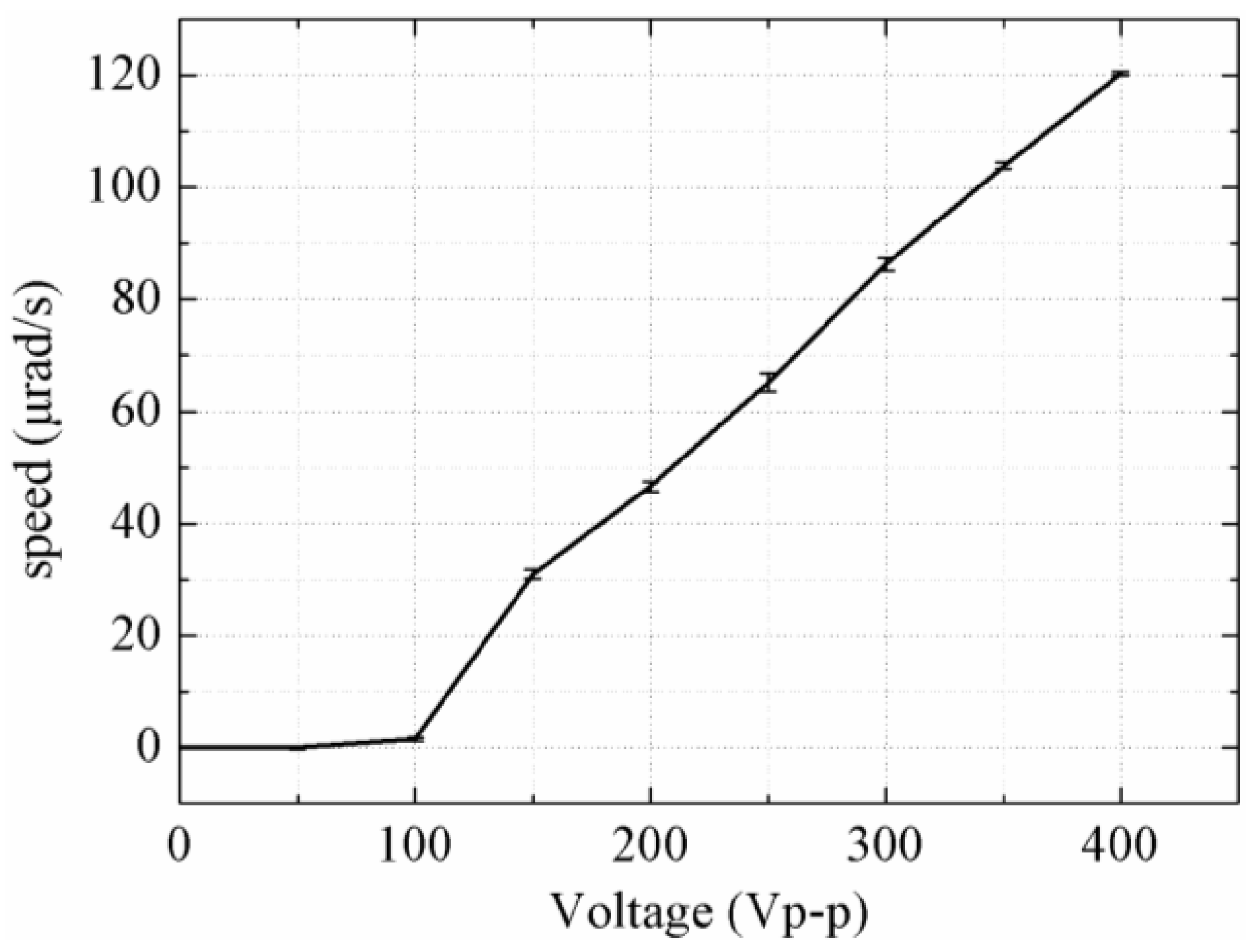
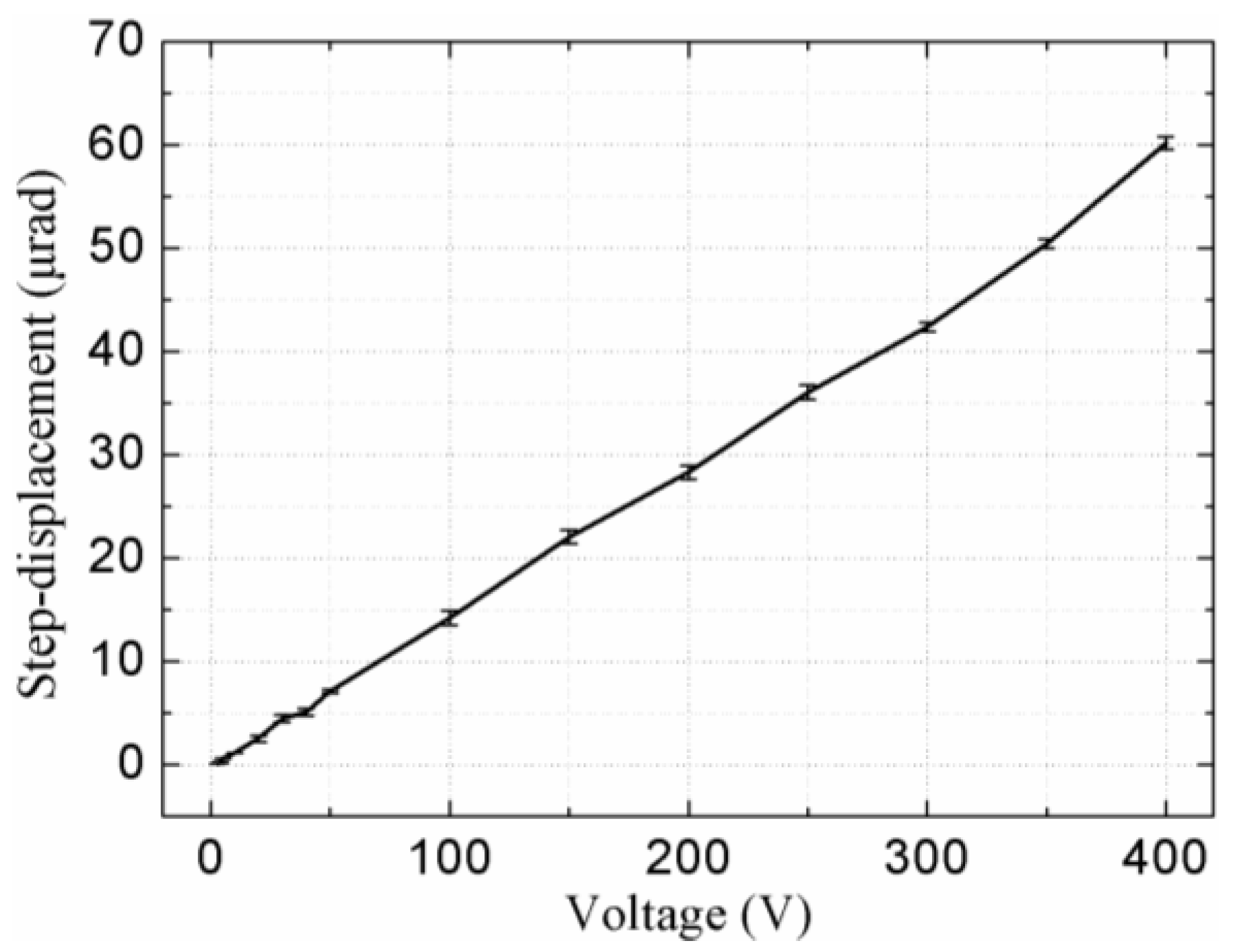
4. Experiments and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uchino, K. Piezoelectric Actuators and Ultrasonic Motors, 1st ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; ISBN 978–0-7923-9811-0. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.X.; Yang, X.H.; Chen, W.S.; Xu, D.M. A bonded-type piezoelectric actuator using the first and second bending vibration modes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.H.; Li, H.Y.; He, M.; Zhao, H.W.; Lu, X.H.; Gao, H.B. Investigation on driving characteristics of a piezoelectric stick–slip actuator based on resonant/off-resonant hybrid excitation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 035042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.Z.; Zhang, F.X.; Qin, Z.; Wen, S.Z. A 3-DOFs mobile robot driven by a piezoelectric actuator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, D.; Cheng, T.H.; He, P.; Lu, X.H.; Zhao, H.W. A friction regulation hybrid driving method for backward motion restraint of the smooth impact drive mechanism. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 085033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherepanov, V.; Coenen, P.; Voigtlander, B. A nanopositioner for scanning probe microscopy: The KoalaDrive. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 023703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.K.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhao, L.L.; Xu, D.M.; Chen, W.S.; Deng, J. Design and experiments of a single-foot linear piezoelectric actuator operated in stepping mode. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Tay, C.J.; Quan, C.G.; Kobayashi, T.; Lee, C. Piezoelectric MEMS energy harvester for low-frequency vibrations with wideband operation range and steadily increased output power. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2011, 20, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.H.; He, M.; Li, H.Y.; Lu, X.H.; Zhao, H.W.; Gao, H.B. A novel trapezoid-type stick-slip piezoelectric linear actuator using right circular flexure hinge mechanism. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 5545–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Chen, W.S.; Yang, X.H.; Liu, J.K. A rotary piezoelectric actuator using the third and fourth bending vibration modes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 4366–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.S.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, J.K.; Jiang, Q. A frog-shaped linear piezoelectric actuator using first-order longitudinal vibration mode. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2188–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; He, S.Y. Standing wave brass-PZT square tubular ultrasonic motor. Ultrasonics 2012, 52, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.X.; Chen, W.S.; Liu, J.K.; Yang, X.H. A high-power linear ultrasonic motor using bending vibration transducer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5160–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.Y.; Chiarot, P.R.; Park, S. A single vibration mode tubular piezoelectric ultrasonic motor. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2011, 58, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.M.; Liu, Y.X.; Shi, S.J.; Liu, J.K.; Chen, W.S.; Wang, L. Development of a non-resonant piezoelectric motor with nanometer resolution driving ability. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.Y.; Li, C.X.; Zhu, L.M.; Su, C.Y. Modeling and identification of Piezoelectric-Actuated stages cascading hysteresis nonlinearity with linear dynamics. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.Y.; Zhu, L.M.; Su, C.Y. Modeling and compensation of asymmetric hysteresis nonlinearity for piezoceramic actuators with a modified Prandtl-Ishlinskii model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.; Shirinzadeh, B.; Bhagat, U.; Smith, J.; Zhong, Y. Development and control of a two DOF linear-angular precision positioning stage. Mechatronics 2015, 32, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.P.; Rong, W.B.; Wang, L.F.; Pei, Z.C.; Sun, L.N. Design, analysis and experimental performance of a piezoelectric rotary actuator based on compliant foot driving. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 3765–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Zhou, X.Q.; Zhao, H.W.; Shao, M.K.; Fan, Z.Q.; Liu, H. Design and experimental tests of a dual-servo piezoelectric nanopositioning stage for rotary motion. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2015, 86, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, G.Y.; Zhu, L.M.; Su, C.Y.; Ding, H.; Fatikow, S. Modeling and control of piezo-actuated nanopositioning stages: A survey. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2016, 13, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Quan, Q.Q.; Deng, J.; Yu, H.P. A Quadruped Micro-Robot Based on Piezoelectric Driving. Sensors 2018, 18, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.P.; Liu, Y.X.; Shi, S.J.; Chen, W.S. A three-DOF ultrasonic motor using four piezoelectric ceramic plates in bonded-type structure. J. Vibroeng. 2018, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.P.; Quan, Q.Q.; Tian, X.Q.; Li, H. Optimization and Analysis of a U-Shaped Linear Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Motor Using Longitudinal Transducers. Sensors 2018, 18, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asumi, K.; Fukunaga, R.; Fujimura, T.; Kurosawa, M.K. Miniaturization of a V-shape transducer ultrasonic motor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48, 07GM02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Zhao, H.W.; Qu, H.; Cui, T.; Fu, L.; Huang, H.; Ren, L.Q.; Fan, Z.Q. A piezoelectric-driven rotary actuator by means of inchworm motion. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 194, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szufnarowski, F. Dynamic Modeling and Bioinspired Control of a Walking Piezoelectric Motor. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bielefeld, Bielefeld, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Juuti, J.; Kordas, K.; Lonnakko, R.; Moilanen, V.P.; Leppavuori, S. Mechanically amplified large displacement piezoelectric actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2005, 120, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Q.S. A novel piezoactuated XY stage with parallel, decoupled, and stacked flexure structure for micro-/nanopositioning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 3601–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergander, A.; Breguet, J.M.; Schmitt, C.; Clavel, R. Micropositioners for microscopy applications based on the stick-slip effect. In Proceedings of the 2000 International Symposium on Micromechatronics and Human Science (MHS 2000), Nagoya, Japan, 22–25 October 2000; pp. 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Peng, Y.X.; Kaneko, J.; Azuma, T.; Ito, S.; Gao, W.; Lu, T.F. Design and construction of the motion mechanism of an XY micro-stage for precision positioning. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 201, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, Y.; Aoyama, H. Development of inertia driven micro robot with nano tilting stage for SEM operation. Microsyst. Technol. 2007, 13, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.D.; Choi, S.B. A hybrid inchworm linear motor. Mechatronics 2002, 12, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.M.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, J.K.; Shi, S.J.; Chen, W.S. Motion planning of a stepping-wriggle type piezoelectric actuator operating in bending modes. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 2371–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, C.W.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, J.K. A new fast inchworm type actuator with the robust I/Q heterodyne interferometer feedback. Mechatronics 2006, 16, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.Y.; Lee, H.P.; Ong, C.J.; Lim, S.P. Design and finite element analysis of a new stack ultrasonic motor based on in-plane mode. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 115002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Unit | Nomenclature | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | kg/m3 | ρ | 7600 |
| Poisson’s ratio | ×1010 N/m2 | σE | 0.32 |
| Elastic modulus | c11 | 14.3 | |
| c12 | 7.85 | ||
| c13 | 7.85 | ||
| c33 | 11.5 | ||
| c44 | 2.6 | ||
| c66 | 2.45 | ||
| Piezoelectric constants | C/m2 | e31 | −2.4 |
| e33 | 17.3 | ||
| e15 | 12.95 | ||
| Relative dielectric constants | 765 | ||
| 640 |
| Time Rise Time of Signal (ms) | a (m/s2) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1555 |
| 0.5 | 123.5 |
| 1 | 68.34 |
| 2 | 30.87 |
| 5 | 12.35 |
| Vibrator No. | Step-Displacement (μm) |
|---|---|
| I | 6.27 |
| II | 6.43 |
| III | 6.68 |
| IV | 6.55 |
| Actuator | Mechanism | Structure | Resolution (μrad) | Stroke (μrad) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The proposed actuator | Walking | Clamped transducer | 0.095 | 2π × 106 |
| The actuator by Clark et al. [18] | Direct driving | Flexure hinge | 0.075 | 535.8 |
| The actuator by Wang et al. [19] | Inertial driving | Flexure hinge | 0.24 | 2π × 106 |
| The actuator by Li et al. [20] | Inertial driving | Flexure hinge | 1.54 | 2π × 106 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, D.; Li, K.; Shan, X.; Deng, J. A Four-Feet Walking-Type Rotary Piezoelectric Actuator with Minute Step Motion. Sensors 2018, 18, 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051471
Liu Y, Wang Y, Liu J, Xu D, Li K, Shan X, Deng J. A Four-Feet Walking-Type Rotary Piezoelectric Actuator with Minute Step Motion. Sensors. 2018; 18(5):1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051471
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yingxiang, Yun Wang, Junkao Liu, Dongmei Xu, Kai Li, Xiaobiao Shan, and Jie Deng. 2018. "A Four-Feet Walking-Type Rotary Piezoelectric Actuator with Minute Step Motion" Sensors 18, no. 5: 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051471
APA StyleLiu, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, J., Xu, D., Li, K., Shan, X., & Deng, J. (2018). A Four-Feet Walking-Type Rotary Piezoelectric Actuator with Minute Step Motion. Sensors, 18(5), 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051471







