Noise Source Visualization Using a Digital Voice Recorder and Low-Cost Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sound Measurement Using a Digital Recorder
3. Visualization of Sound Measurement
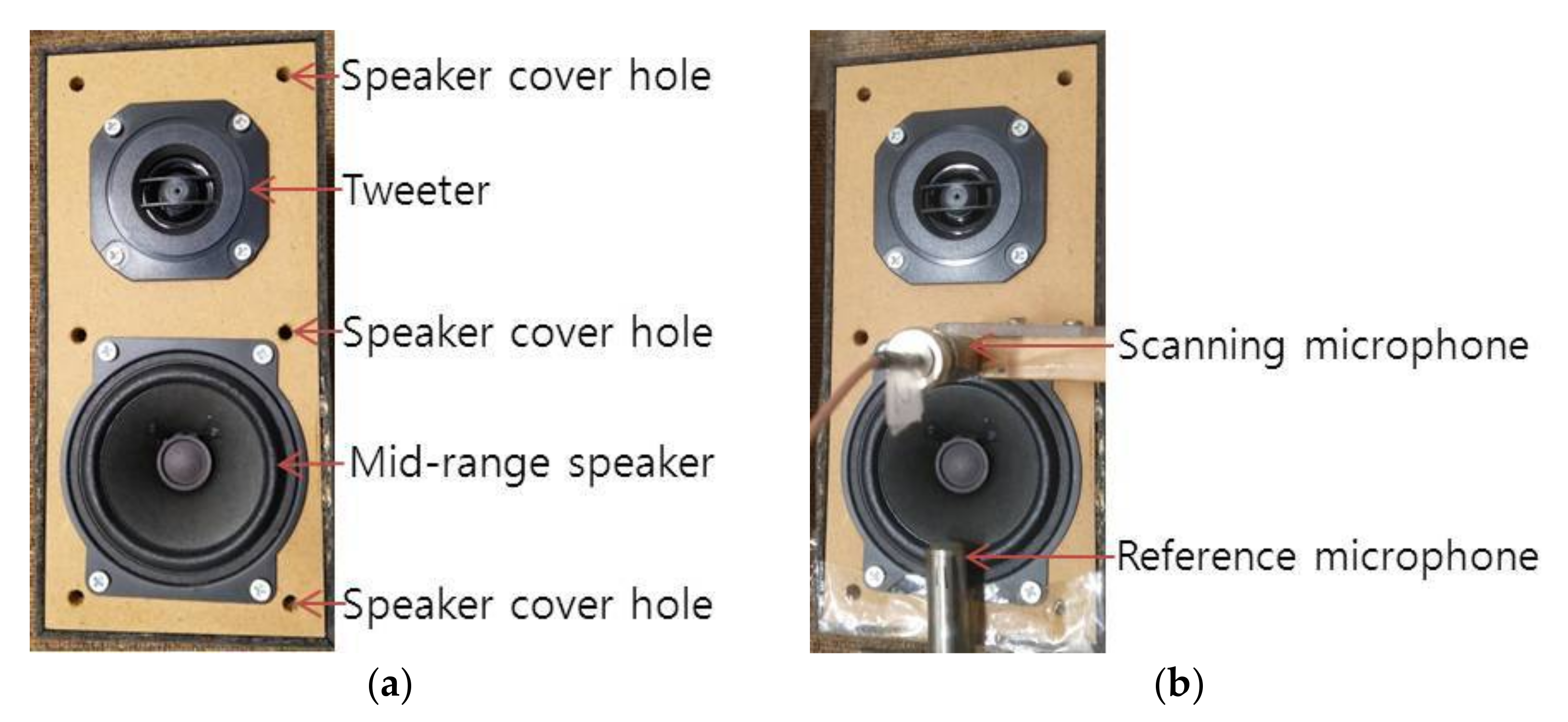
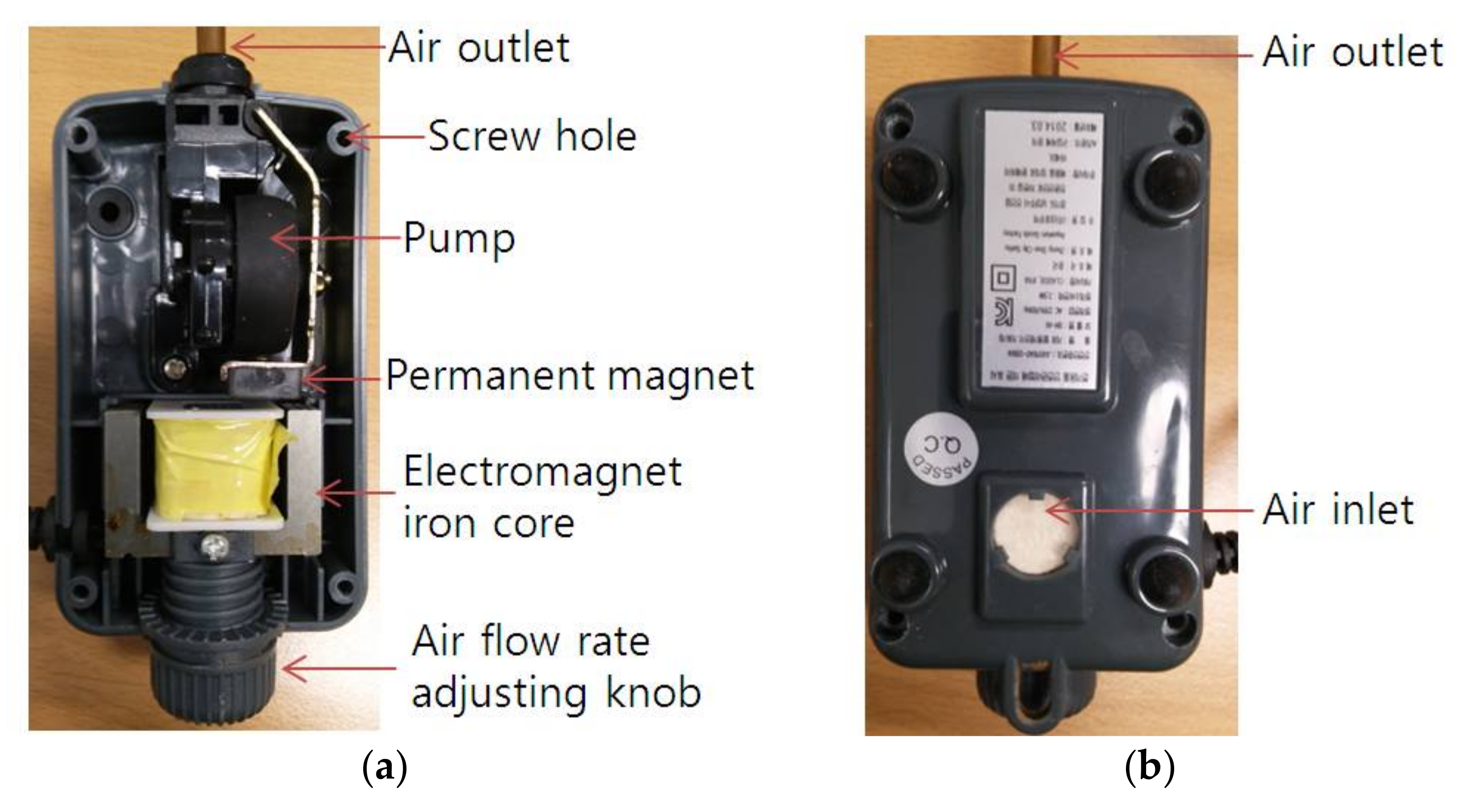
4. Measurement Description
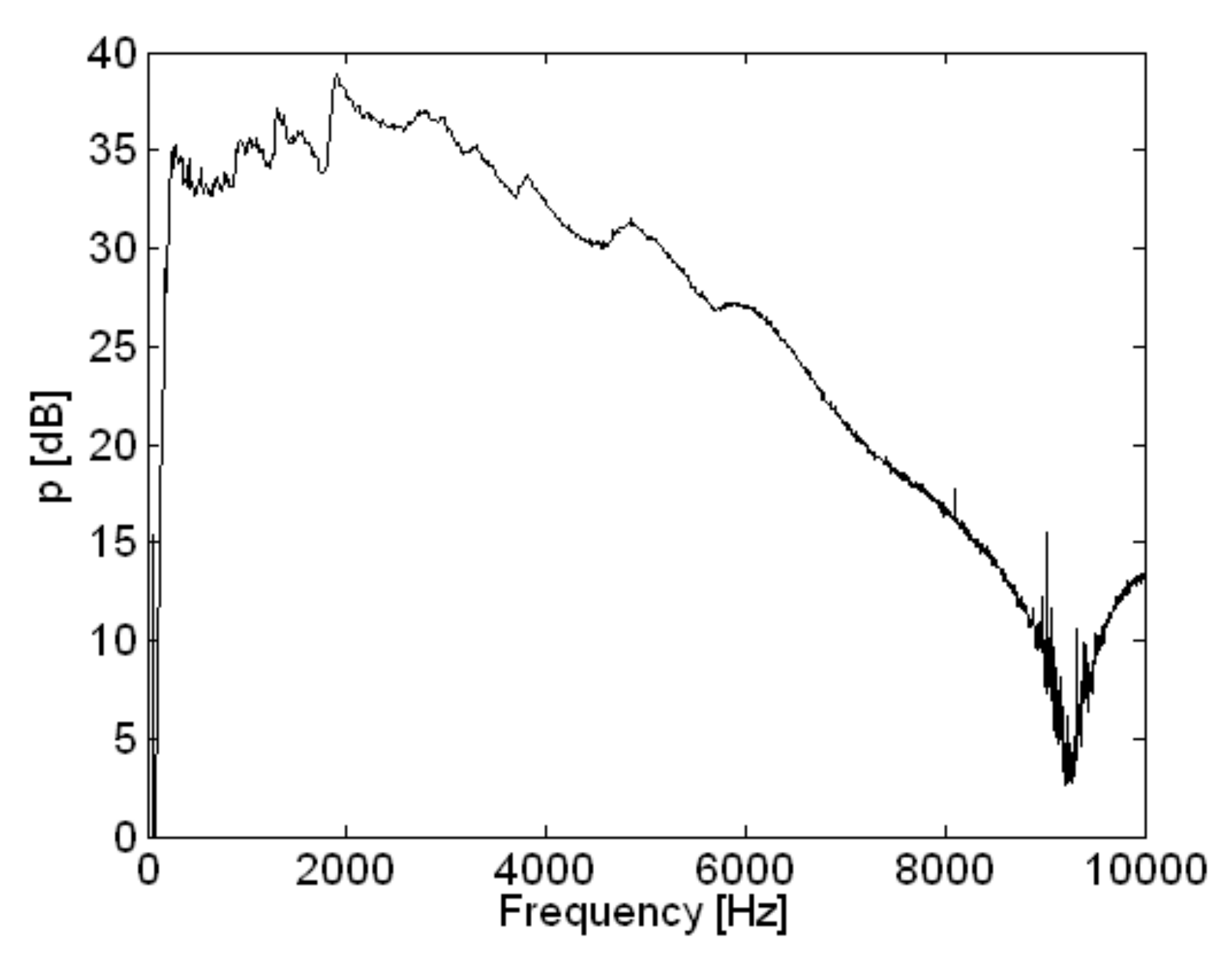
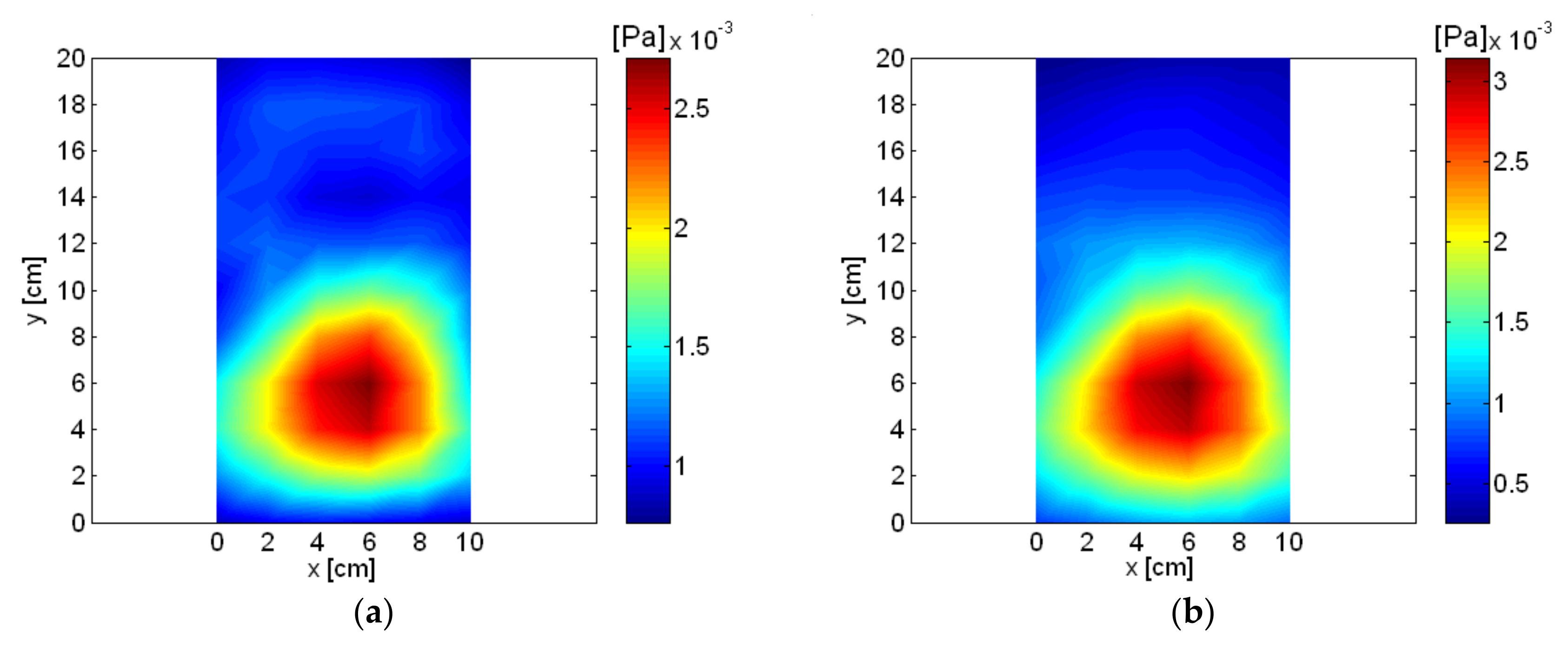
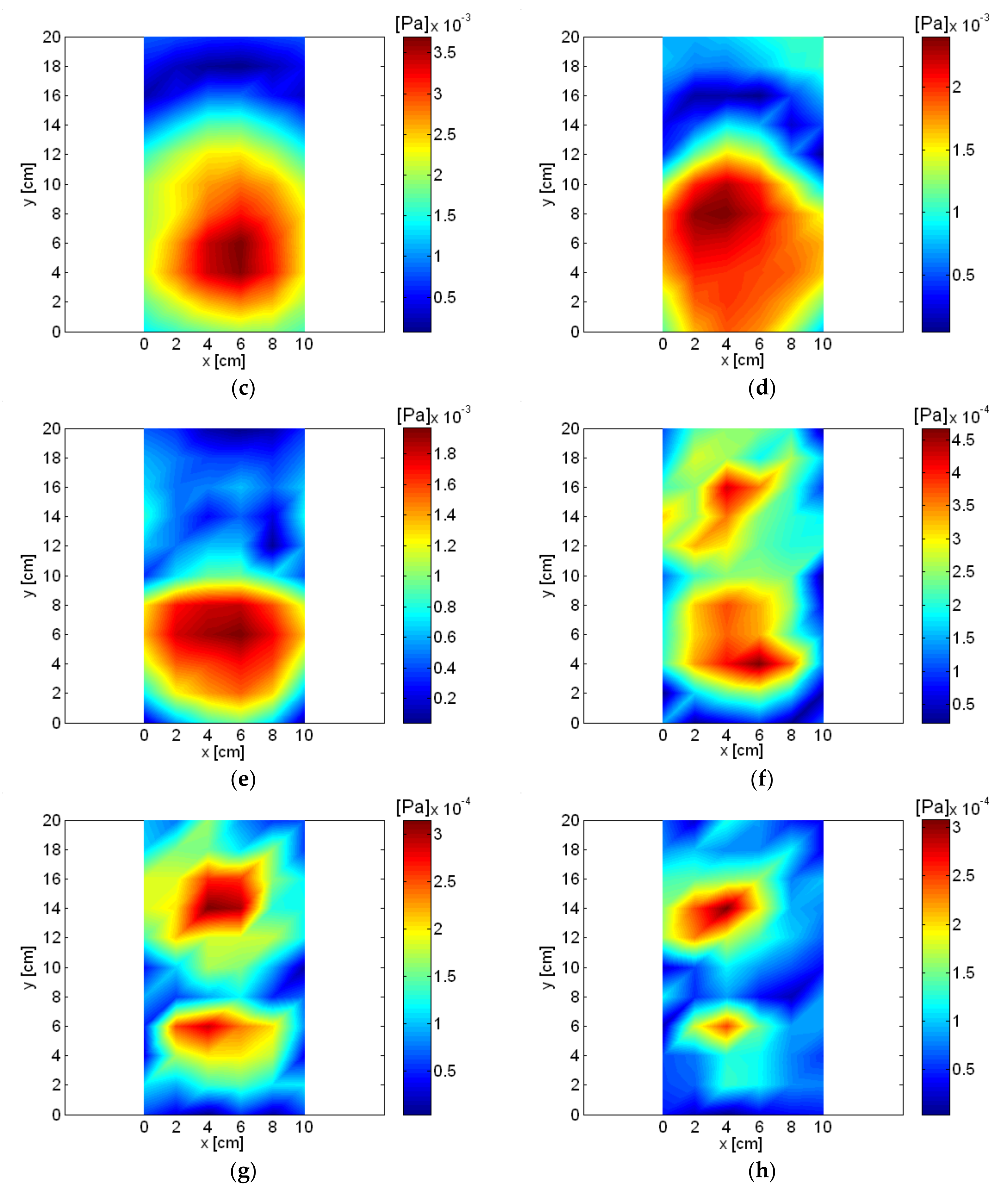
5. Measurement Results
6. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petersen, C.L.; Chen, T.P.; Ansermino, J.M.; Dumont, G.A. Design and evaluation of a low-cost smartphone pulse oximeter. Sensors 2013, 13, 16882–16893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, Y.; Joo, H.S.; Yang, H.; Kang, S.; Hong, S.H.; Woo, J. Smartphone-Based Hearing Screening in Noisy Environments. Sensors 2014, 14, 10346–10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yafia, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Hoorfar, M.; Najjaran, H. Ultra-portable smartphone controlled integrated digital microfluidic system in a 3D-printed modular assembly. Micromachines 2014, 6, 1289–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrio, A.; Sampedro, C.; Sanchez-Lopez, J.K.; Pimienta, M.; Campoy, P. Automated low-cost smartphone-based lateral flow saliva test reader for drugs-of-abuse detection. Sensors 2015, 15, 29569–29593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, S.; El-Sheimy, N. Activity recognition using fusion of low-cost sensors on a smartphone for mobile navigation application. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1100–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, T.C.; Pering, T.D.; McGonigle, A.J.; Tamburello, G.; Willmott, J.R. A low-cost smartphone sensor-based UV camera for volcanic SO2 Emission measurements. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.D.; Koo, Y.; Yun, Y. A smartphone-based automatic measurement method for colorimetric pH detection using a color adaptation algorithm. Sensors 2017, 17, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; El-Sheimy, N.; Lan, H.; Liu, Z. Map-based indoor pedestrian navigation using an auxiliary particle filter. Micromachines 2017, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Lee, C.; Chiang, P. Simple smartphone-based guiding system for visually impaired people. Sensors 2017, 17, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mnati, M.J.; Bossche, A.V.; Chisab, R.F. A smart voltage and current monitoring system for three phase inverters using an android smartphone application. Sensors 2017, 17, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.; Phelps, T.; Yao, C.; Venkatesh, A.G.; Conrad, D.; Hall, D.A. Smartphone-based pH sensor for home monitoring of pulmonary exacerbations in cystic fibrosis. Sensors 2017, 17, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, D.; Takizawa, H.; Aoyagi, M.; Ezaki, N.; Mizuno, S. Smartphone-based escalator recognition for the visually impaired. Sensors 2017, 17, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, D.; Hernández, S.; Fraile-Ardanuy, J.; Serrano, J.; Fernández, R.; Álvarez, F. Modelling the effect of driving events on electrical vehicle energy consumption using inertial sensors in smartphones. Enegies 2018, 11, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco, F.; Jiménez, A.R. Smartphone-based cooperative indoor localization with RFID technology. Sensors 2018, 18, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeuw, T.; Boss, E. The hydrocolor app: Above water measurements of remote sensing reflectance and turbidity using a smartphone camera. Sensors 2018, 18, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardos, C.A.; Shaw, P.B. Evaluation of smartphone sound measurement application. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, EL186–EL192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nast, D.; Speer, W.; Le Prell, C. Sound level measurements using smartphone “apps”: Useful or inaccurate? Noise Health 2014, 16, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thap, T.; Chung, H.; Jeong, C.; Hwang, K.; Kim, H.; Yoon, K.; Lee, J. High-resolution time-frequency spectrum-based lung function test from a smartphone microphone. Sensors 2016, 16, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, J.; Xia, H.; Liu, S.; Qiao, Y. Mapping urban environmental noise using smartphones. Sensors 2016, 16, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.; King, E.A. Testing the accuracy of smartphones and sound level meter applications for measuring environmental noise. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 106, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.; King, E.A. Smartphone-based noise mapping: Integrating sound level meter app data into the strategic noise mapping process. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, W.; Calafate, C.T.; Cano, J.; Manzoni, P. Accurate ambient noise assessment using smartphones. Sensors 2017, 17, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kompella, M.S.; Davies, P.; Bernhard, R.J.; Ufford, D.A. A technique to determine the number of incoherent sources contributing to the response of a system. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 1994, 8, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Bolton, J.S. Compensation for source non-stationarity in multi-reference, scan-based nearfield acoustical holography. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sony Corporation. SONY IC Recorder Operating Instructions ICD-PX312; Sony Corporation: Tokyo, Japan, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, E.G. Fourier Acoustics: Sound Radiation and Nearfield Acoustical Holography; Academic Press: London, UK, 1999; ISBN 0-12-753960-3. [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich, G.; Arnold, E.B. Method for measuring acoustic radiation fields. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1980, 68, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, J.D.; Williams, E.G.; Lee, Y. Nearfield acoustic holography: I. Theory of generalized holography and the development of NAH. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 1395–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.G.; Dardy, H.D.; Washburn, K.B. Generalized nearfield acoustic holography for cylindrical geometry: Theory and experiment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1987, 81, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, R.; Hald, J. Near-field acoustical holography without the errors and limitations caused by the use of spatial DFT. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Sound and Vibration (ICSV6), Copenhagen, Denmark, 5–8 July 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hald, J. Patch near-field acoustical holography using a new statistically optimal method. In Proceedings of the International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering (INTER-NOISE) 2003, Jeju, Korea, 25–28 August 2004; pp. 2203–2210. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.T.; Bolton, J.S.; Hald, J. Source visualization by using statistically optimized near-field acoustical holography in cylindrical coordinates. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 118, 2355–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.T.; Bolton, J.S. Visualization of automotive power seat slide motor noise. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Noise Control Engineering (NOISE-CON 2014), Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 8–10 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.T. Characterizing sources of small DC motor noise and vibration. Micromachines 2018, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.T.; Bolton, J.S. Holographic Visualization of Sound Radiation from Computer Hard Drives. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Noise Control Engineering (NOISE-CON 2013), Denver, CO, USA, 26–28 August 2013. [Google Scholar]






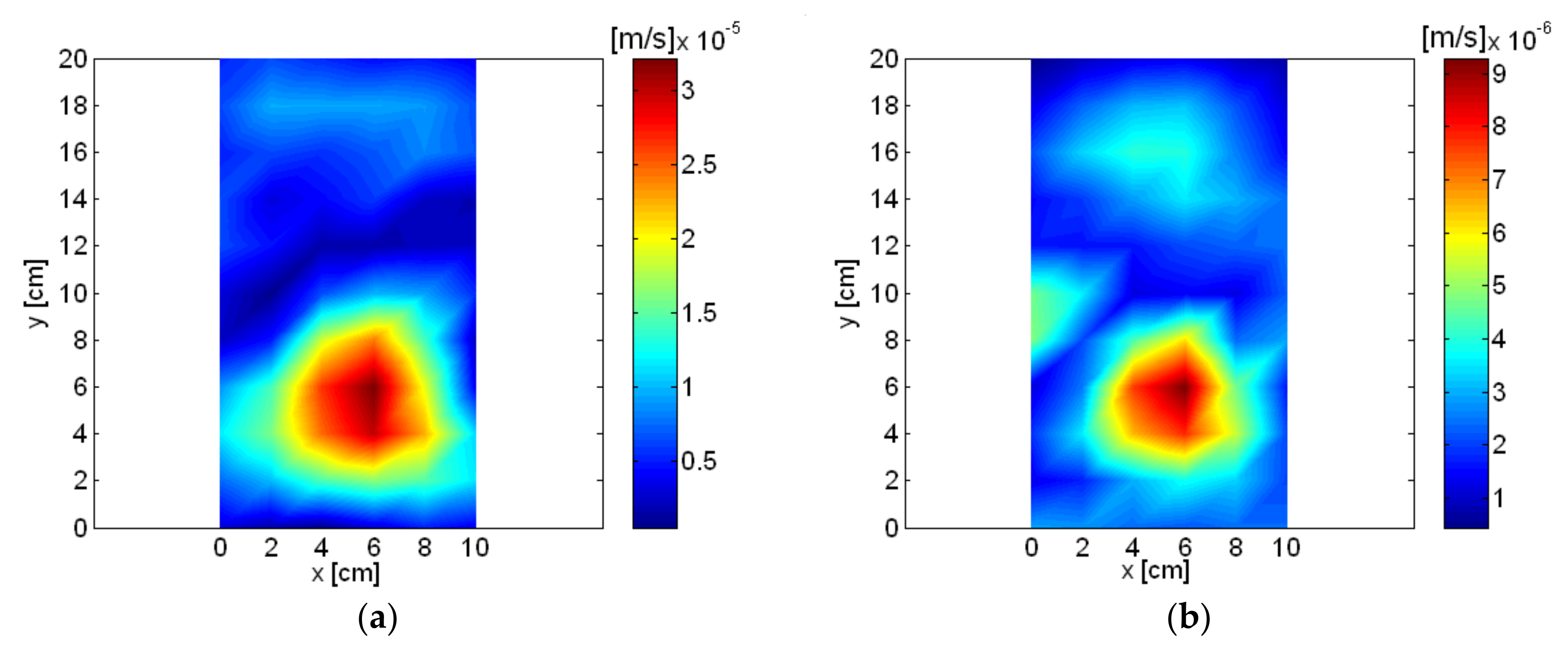
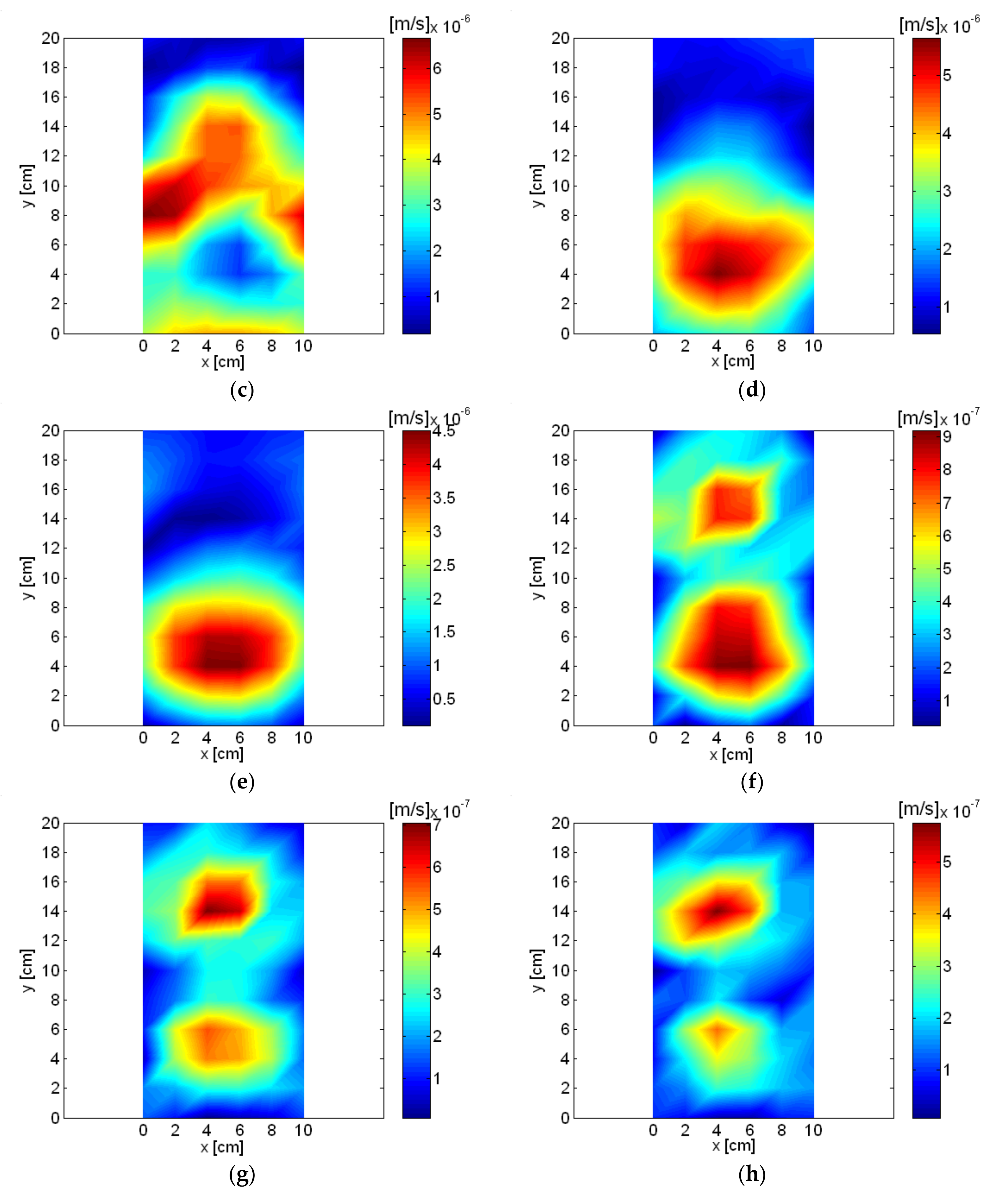
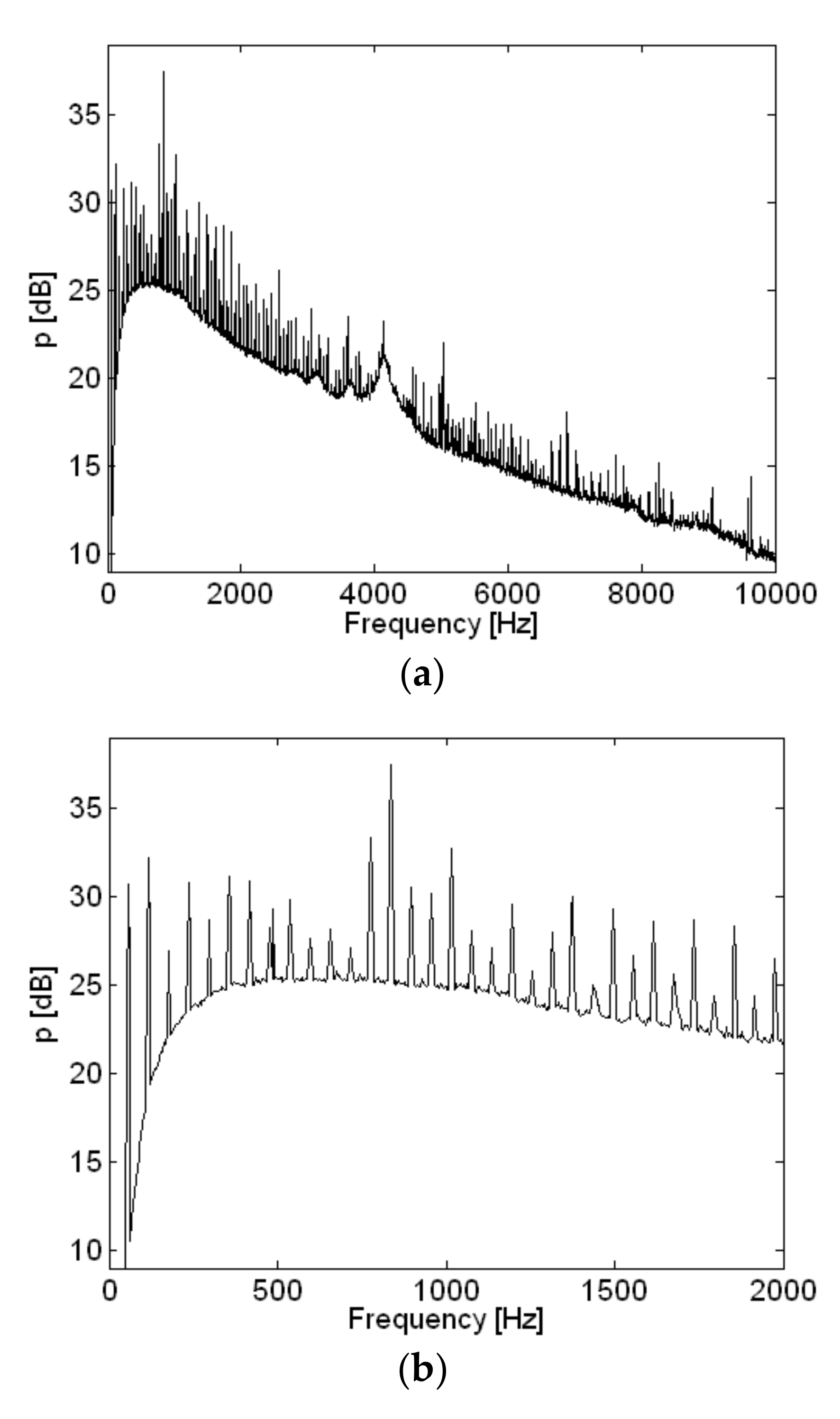
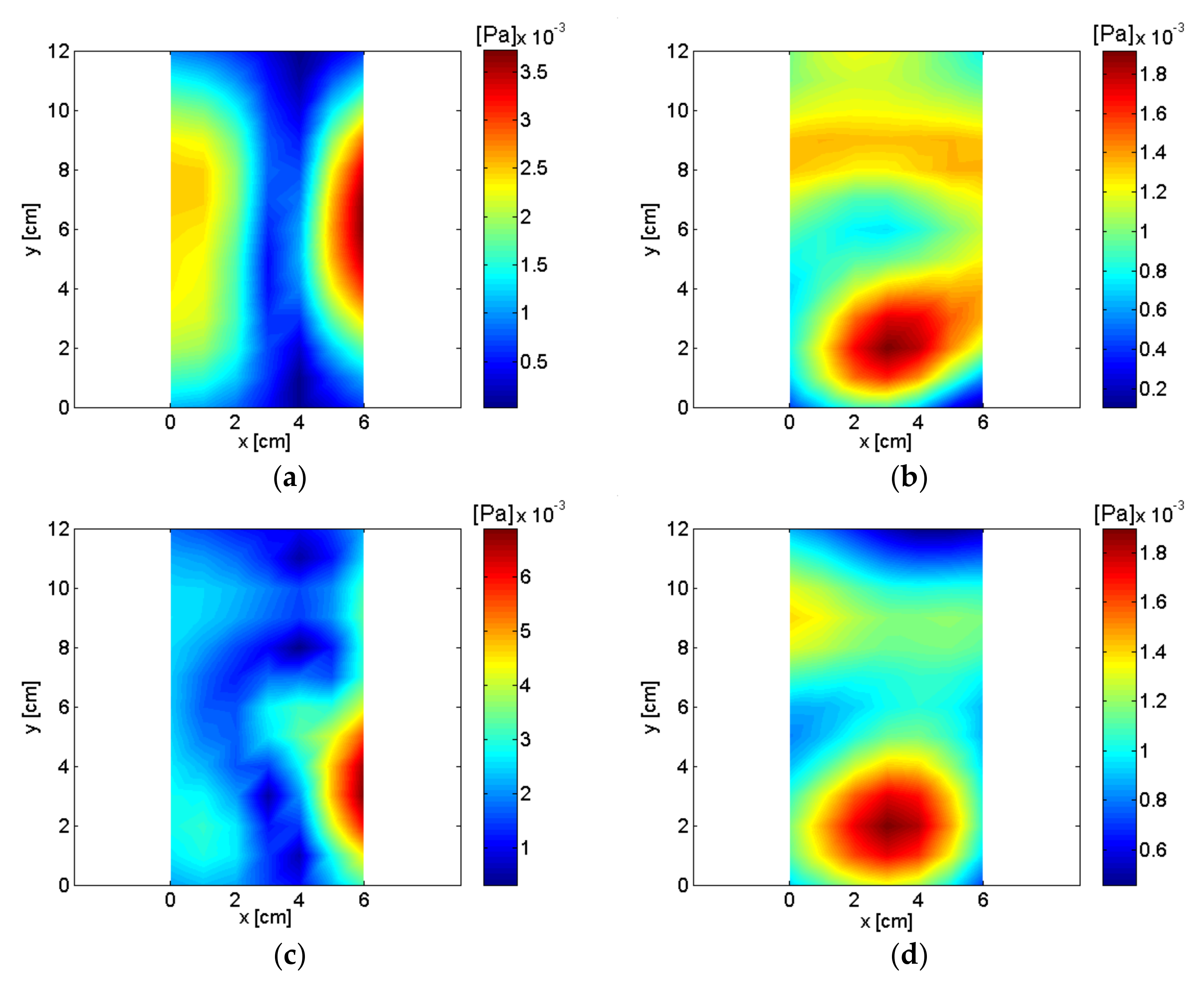
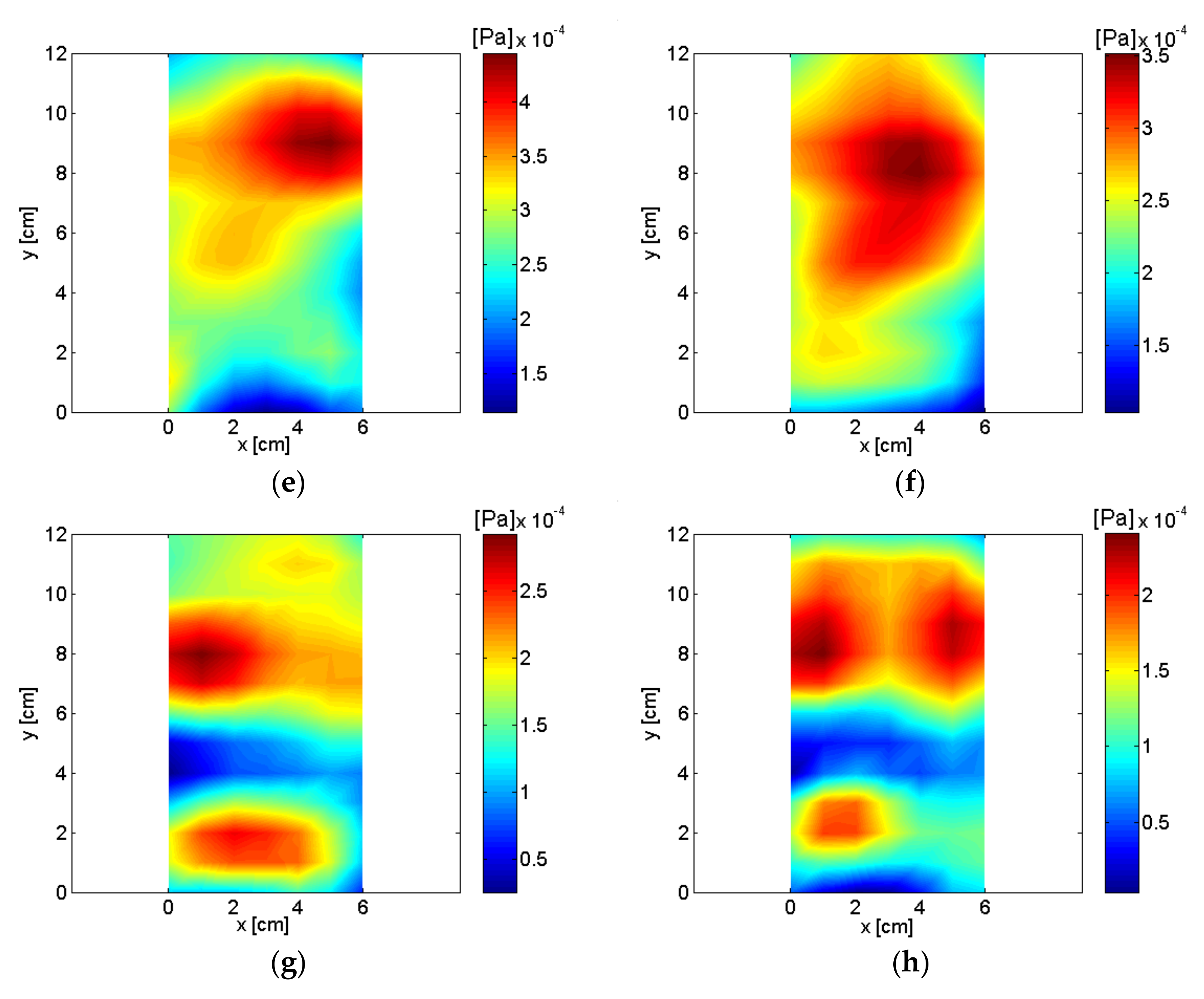

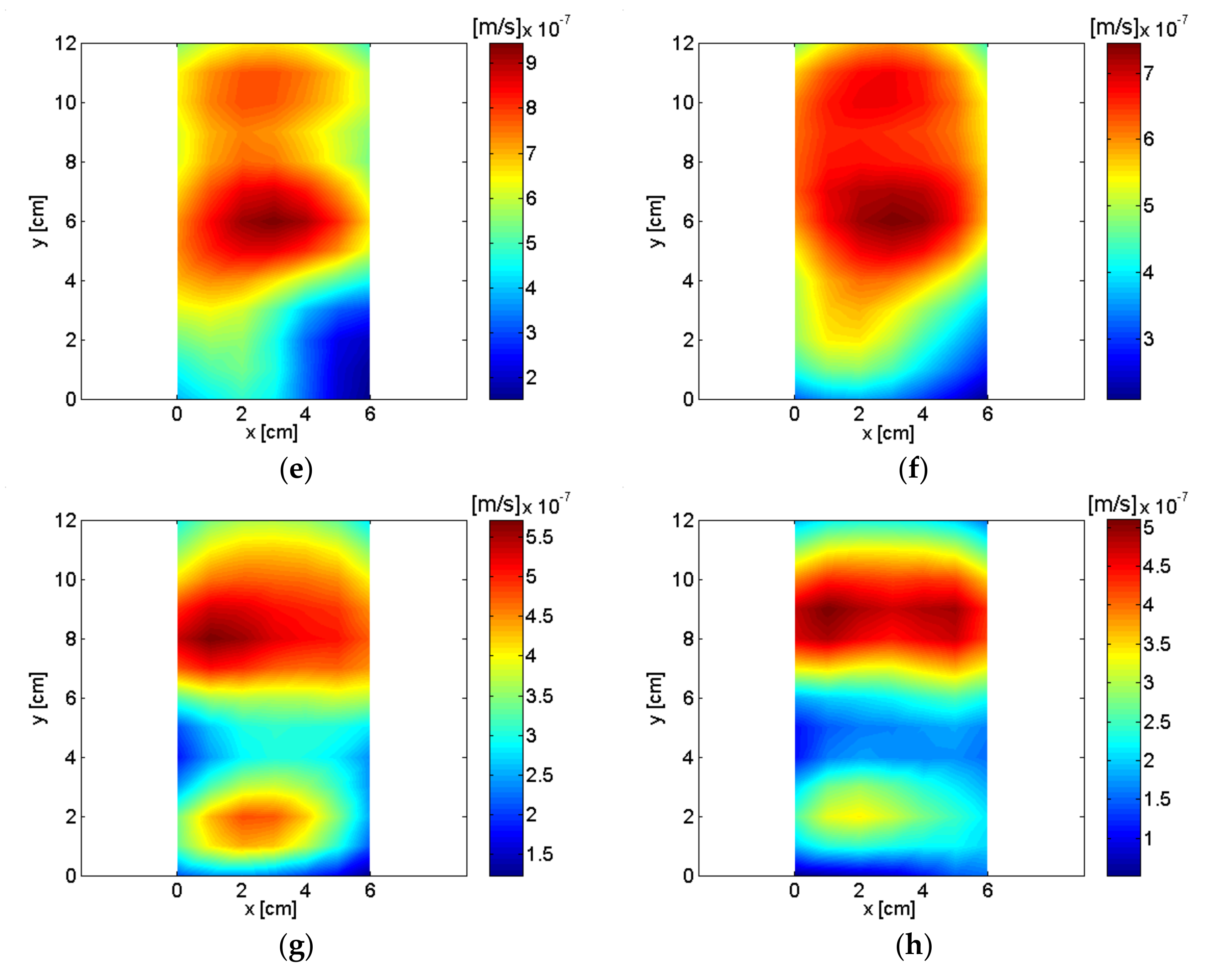
| Frequency | Order | Description of Source |
|---|---|---|
| 56 Hz | 1st | Rotational vibration |
| 356 Hz | 6th | Air inlet |
| 836 Hz | 14th | Permanent magnet oscillator (PMO) |
| 1016 Hz | 17th | Air inlet |
| 4132 Hz | 69th | PMO and air outlet |
| 5036 Hz | 84th | PMO and air outlet |
| 6888 Hz | 115th | Pump and air inlet |
| 8264 Hz | 138th | Pump and air inlet |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, Y.T. Noise Source Visualization Using a Digital Voice Recorder and Low-Cost Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041076
Cho YT. Noise Source Visualization Using a Digital Voice Recorder and Low-Cost Sensors. Sensors. 2018; 18(4):1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041076
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Yong Thung. 2018. "Noise Source Visualization Using a Digital Voice Recorder and Low-Cost Sensors" Sensors 18, no. 4: 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041076
APA StyleCho, Y. T. (2018). Noise Source Visualization Using a Digital Voice Recorder and Low-Cost Sensors. Sensors, 18(4), 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041076




