Research into Kinect/Inertial Measurement Units Based on Indoor Robots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Independent Localization Based on Kinect and INS
2.1. Kinect Method
2.1.1. Kinect Obtaining 3D Point Cloud Data
2.1.2. Absolute Orientation Algorithm
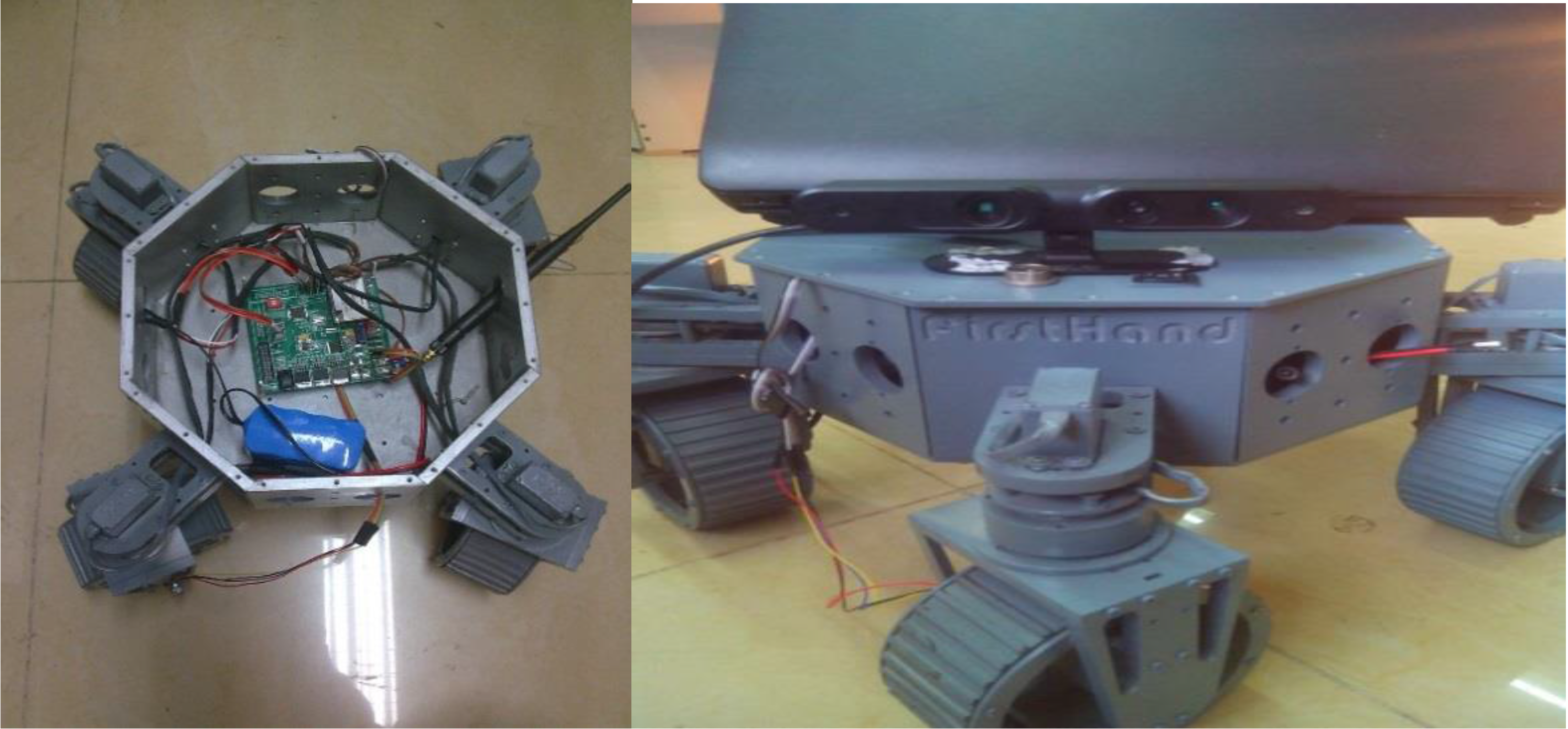
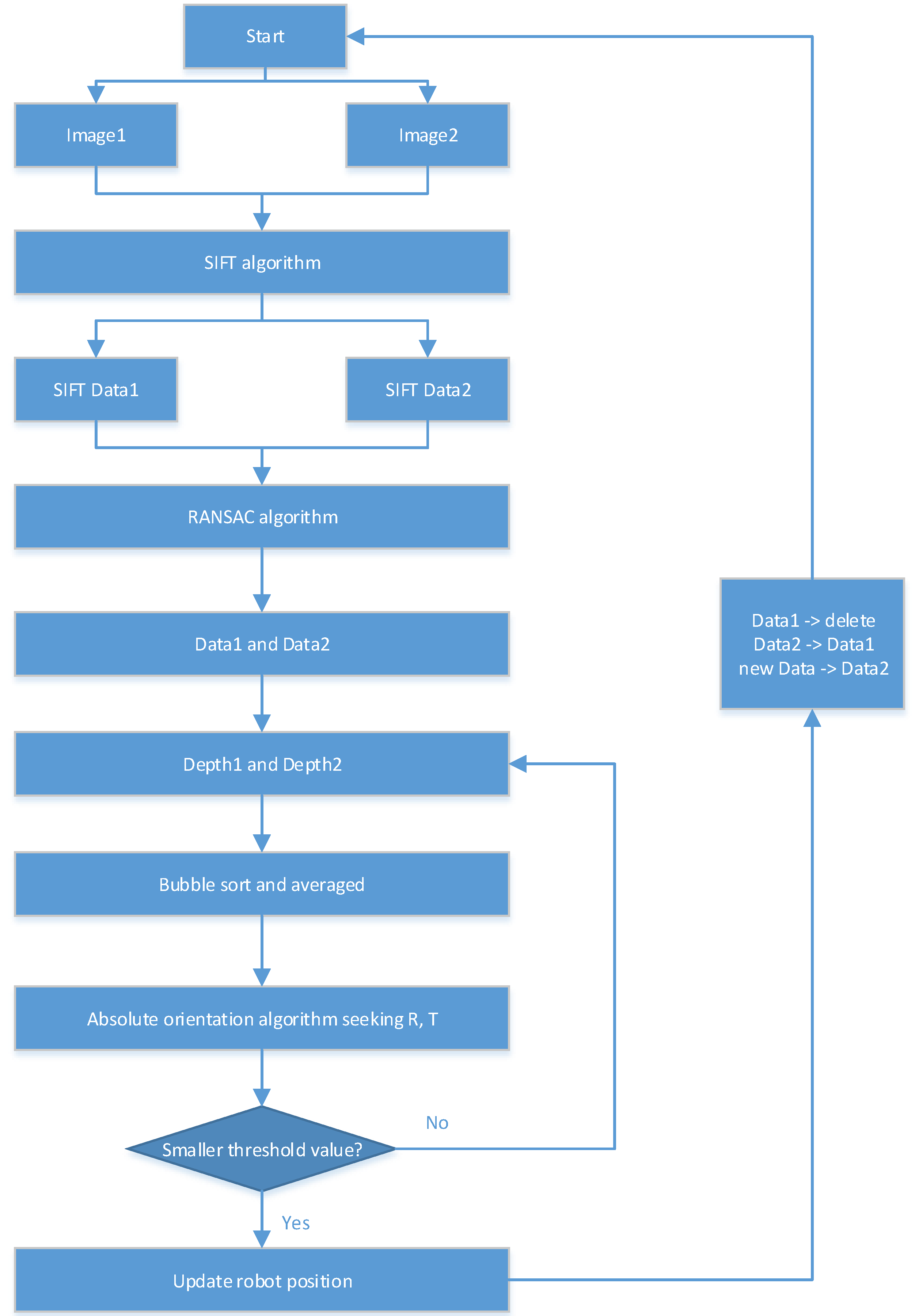
2.1.3. Implementation of Kinect Self-Localization Algorithm
2.2. Principle and Algorithm Design of SINS
3. Integrated Navigation Scheme
4. Indoor Positioning Experiment
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, H.B.; Huang, J.F.; Yang, X.N.; Ye, J.H.; He, S.M. A Robot Collision Avoidance Method Using Kinect and Global Vision. Telkomnika 2017, 15, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cunha, J.; Pedrosa, E.; Cruz, C.; Neves, A.J.; Lau, N. Using a Depth Camera for Indoor Robot Localization and Navigation. Ind. Organ. India 2011, 116, 823–831. [Google Scholar]
- Huai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yilmaz, A. Real-time large scale 3D reconstruction by fusing Kinect and IMU data. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, II-3-W5, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, D.; Ryu, D.; Kal, M. Multiple intensity differentiation for 3-D surface reconstruction with mono-vision infrared proximity array sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 3352–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.W.; Shi, L.W.; Guo, S.X. A Kinect-Based Real-Time Compressive Tracking Prototype System for Amphibious Spherical Robots. Sensors 2015, 15, 8232–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noel, R.R.; Salekin, A.; Islam, R.; Rahaman, S.; Hasan, R.; Ferdous, H.S. A natural user interface classroom based on Kinect. IEEE Learn. Technol. 2011, 13, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.K. A Study of Movement Attitude Capture System Based on Kinect. Rev. Fac. Ing. 2017, 32, 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- Stowers, J.; Hayes, M.; Bainbridge-Smith, A. Altitude control of a quadrotor helicopter using depth map from Microsoft Kinect sensor. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics (ICM), Istanbul, Turkey, 1 August 2011; pp. 358–362. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.C.; Xu, S.M. Research on Vision Location Algorithm Based on Kinect in Complex Condition. Mach. Electron. 2017, 35, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; He, B.W. Study of Self-localization of Indoor Robot Based on Kinect Sensor. Mach. Build. Autom. 2014, 5, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.A.; Bower, K.J.; Mentiplay, B.F.; Paterson, K.; Pua, Y.-H. Concurrent validity of the Microsoft Kinect for assessment of spatiotemporal gait variables. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2722–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidi, O.; Kanade, T.; Fujita, K. A visual odometer for autonomous helicopter flight. Robot. Autonom. Syst. 1999, 28, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Huang, X. Observability analysis of navigation system using point-based visual and inertial sensors. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 2014, 125, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.-S.; Yang, H.-C.; Zhang, S.-B. An Absolute Orientation Method Suitable for Digital Close—Range Image. Surv. Mapp. 2008, 33, 111–112. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguram, R.; Frahm, J.M.; Pollefeys, M. A comparative analysis of RANSAC techniques leading to adaptive real-time random sample consensus. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2008, European Conference on Computer Vision (DBLP), Marseille, France, 12–18 October 2008; pp. 500–513. [Google Scholar]
- Bortz, J.E. A new mathematical formulation for strapdown inertial navigation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, AES-7, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.B. A new strapdown attitude algorithm. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2012, 6, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-Y.; Zeng, Q.-H.; Zhao, W. Navigation System Theory and Application; Northwestern Polytechnical University Press: Xi’an, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.G.; Mark, J.G.; Tazartes, D.A.; Yong, J.Y. Extension of strapdown attitude algorithm for high-frequency base motion. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2012, 13, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Liang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y. Monocular vision and IMU based navigation for a small unmanned helicopter. In Proceedings of the 2012 7th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Singapore, 18–20 July 2012; pp. 1694–1699. [Google Scholar]
- Sirtkaya, S.; Seymen, B.; Alatan, A.A. Loosely coupled Kalman filtering for fusion of Visual Odometry and inertial navigation. In Proceedings of the 2013 16th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Istanbul, Turkey, 9–12 July 2013; pp. 219–226. [Google Scholar]


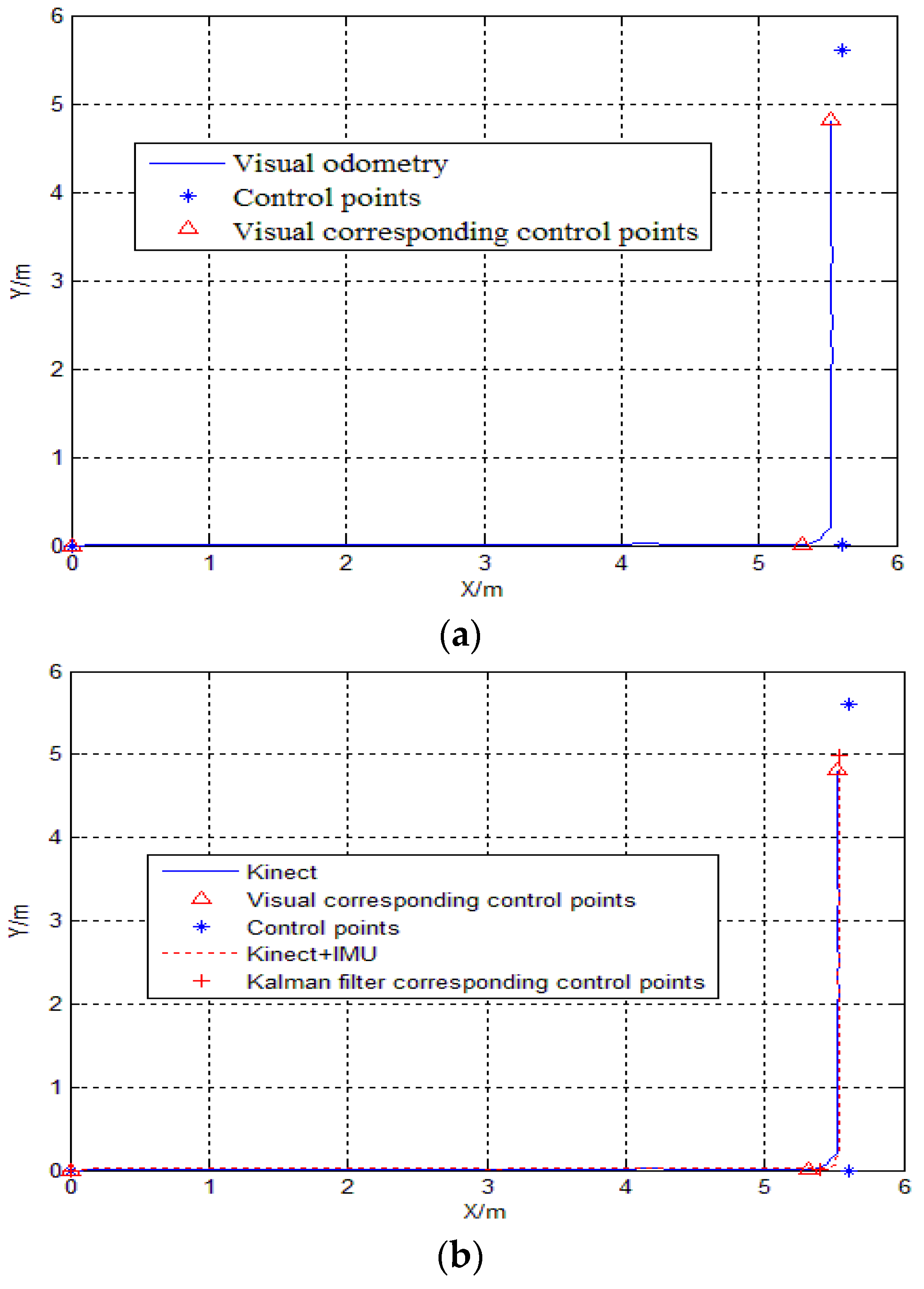
| Number of Control Points | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control Points | (0, 0) | (5.61, 0.01) | (5.60, 5.61) |
| Number of Control Points | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| The position of the control point | (0.00, 0.00) | (5.61, 0.01) | (5.60, 5.61) |
| Visual position | (0.00, 0.00) | (5.321, 0.0062) | (5.5248, 4.8182) |
| Distance errors (Positioning errors) | 0.00 | 0.2890 | 0.7954 |
| Number of Control Points | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual odometry | 0.00 | 0.2890 | 0.7954 |
| Kalman filter of Kinect/IMU | 0.00 | 0.2077 | 0.6078 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Wen, X.; Guo, H.; Yu, M. Research into Kinect/Inertial Measurement Units Based on Indoor Robots. Sensors 2018, 18, 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030839
Li H, Wen X, Guo H, Yu M. Research into Kinect/Inertial Measurement Units Based on Indoor Robots. Sensors. 2018; 18(3):839. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030839
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Huixia, Xi Wen, Hang Guo, and Min Yu. 2018. "Research into Kinect/Inertial Measurement Units Based on Indoor Robots" Sensors 18, no. 3: 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030839
APA StyleLi, H., Wen, X., Guo, H., & Yu, M. (2018). Research into Kinect/Inertial Measurement Units Based on Indoor Robots. Sensors, 18(3), 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030839






